WSR 16-04-092
PROPOSED RULES
DEPARTMENT OF ECOLOGY
[Order 12-03—Filed February 1, 2016, 9:57 a.m.]
Original Notice.
Preproposal statement of inquiry was filed as WSR 12-19-055 and 12-19-056.
Title of Rule and Other Identifying Information: Water quality standards for surface waters of the state of Washington, chapter 173-201A WAC. Adopt human health toxics criteria into the standards. Adopt clarifying language and new language related to implementation tools for implementing the surface water quality standards. This rule proposal combines rule-making activities announced in two separate preproposal statement of inquiries (CR-101) – WSR 12-19-055 and 12-19-056 and updates rule language previously proposed in January 2015.
Hearing Location(s): The public comment period on the proposed rule is open through April 22, 2016. You may give verbal or written comments at one of the in-person public hearings, or by the end of the comment period. If you attend an online webinar, you may give verbal comments, but written comments need to be submitted through one of the following options: Standard mail: Washington State Department of Ecology, Water Quality Program, Attn: Becca Conklin, Water Quality Standards Coordinator, P.O. Box 47600, Olympia, WA 98504-7600, e-mail swqs@ecy.wa.gov, or fax (360) 407-6426.
All comments are due by 5:00 p.m. on April 22, 2016.
Public Hearing Schedule: We will be holding in-person and online workshops followed by public hearings on this rule proposal. Workshops will consist of a short presentation followed by a question and answer session. The formal public hearing will start after the workshop is over. At that time, we will invite public testimony.
Ecology will provide details about these workshops and public hearings on its web site and through e-mail announcements. For instructions on how to join and participate through the webinar, visit http://www.ecy.wa.gov/programs/wq/ruledev/wac173201A/1203inv.html.
In-Person Hearings |
Western Washington - Evening Date: Tuesday, April 5, 2016 Time: 6:30 p.m. Location: Georgetown Campus South Seattle Community College 6737 Corson Avenue South Building C Seattle, WA 98108 Eastern Washington - Evening Date: Wednesday, April 6, 2016 Time: 6:30 p.m. Location: CenterPlace Regional Events Center 2426 North Discovery Place Spokane Valley, WA 99216 |
Webinar Hearings |
Daytime Webinar Date: Thursday, April 7, 2016 Time: 1:30 p.m. - 4:30 p.m. Evening Webinar Date: Thursday, April 7, 2016 Time: 6:30 p.m. |
Date of Intended Adoption: On or after August 1, 2016.
Submit Written Comments to: Becca Conklin, Water Quality Program, Washington Department of Ecology, P.O. Box 47600, Olympia, WA 98504-7600, e-mail swqs@ecy.wa.gov, fax (360) 407-6426, by April 22, 2016, at 5:00 p.m.
Assistance for Persons with Disabilities: Contact water quality reception at ecology, (360) 407-6600, by April 22, 2016, TTY (877) 833-6341.
Purpose of the Proposal and Its Anticipated Effects, Including Any Changes in Existing Rules: Ecology is proposing amendments to water quality standards for surface waters of the state of Washington, chapter 173-201A WAC. The state's water quality standards guide how the state regulates water pollution.
1. This rule making is to amend the water quality standards and provide new human health criteria. Adoption of new human health criteria into Washington's water quality standards will take into account factors used to calculate each chemical criterion such as the amount of fish and shellfish people eat. The new criteria will be used for all federal clean water actions; including wastewater discharge permits, water pollution identification, and water cleanup plans.
2. This proposal will also propose amendments regarding implementation of the water quality standards. The implementation tools being proposed include language revisions to the compliance schedule and variance sections, and a new section to allow the use of intake credits. Ecology is also proposing to add new language clarifying combined sewer overflow (CSO) treatment facilities.
Reasons Supporting Proposal: Ecology is proposing to adopt new human health criteria to protect public health, safety, and welfare. The current human health criteria applied to Washington waters are outdated federal standards that do not reflect current science on protection from toxic chemicals. With adoption of this amendment, our state will have water quality standards for toxics that more accurately reflect the amount of fish and shellfish people eat in Washington.
Adopting new human health criteria was identified as a high priority when ecology conducted a triennial review of the water quality standards in 2010. The triennial review is required by the federal Clean Water Act to ensure that states update standards as needed to reflect new and emerging science and information.
This rule proposal will also provide more language regarding how to implement the water quality standards. The proposed amendments to the implementation tools section of this rule are meant to provide more predictable regulatory tools to help entities that are subject to national pollutant discharge elimination system (NPDES) permits comply with more protective standards. The rule making to amend implementation tools also directly addresses legislation passed (RCW 90.48.605) that obligates ecology to amend water quality standards to allow compliance schedules in excess of ten years under certain circumstances for permitted discharges.
Statutory Authority for Adoption: RCW 90.48.035 Rule-making authority.
Statute Being Implemented: Chapter 90.48 RCW, Water pollution control.
Rule is necessary because of federal law, Federal Clean Water Act (33 U.S.C. 1251).
Name of Proponent: Washington state department of ecology, governmental.
Name of Agency Personnel Responsible for Drafting: Susan Braley, Washington Department of Ecology, Lacey, Washington, (360) 407-6414; Implementation: Cheryl Niemi, Washington Department of Ecology, Lacey, Washington, (360) 407-6440; and Enforcement: Heather Bartlett, Washington Department of Ecology, Lacey, Washington, (360) 407-6405.
A small business economic impact statement has been prepared under chapter 19.85 RCW.
Small Business Economic Impact Statement
Executive Summary: Based on research and analysis required by the Regulatory Fairness Act (RFA), RCW 19.85.070, ecology has determined that the proposed water quality standards (WQS) for surface waters of the state of Washington (chapter 173-201A WAC) does not have a disproportionate impact on small business. This is because the rule is only likely to impact large businesses. (A small business is defined by RFA as having fifty or fewer employees.) Ecology did not, therefore, include language in the proposed rule to minimize disproportionate impacts.
The proposed rule establishes human health criteria that must be met to comply with Washington's WQS. The proposed rule amendments:
• | Update the scientific values for: |
o | Toxicity factors - reflecting current research. |
o | Body weight representative of current population mean - 80kg, up from 70kg. |
o | Drinking water intake - 2.4 L/day. |
• | Change the level of protectiveness: |
o | Fish consumption rate - 175 g/day, up from 6.5 g/day. |
• | Do not change polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) criteria from current national toxics rule (NTR) levels. |
• | Set the arsenic criteria to the Safe Water Drinking Act regulatory level. |
The proposed rule also updates implementation tools that can be used to meet Washington WQS:
• | Removing the time limit on compliance schedules. |
• | Allowing intake credits where there is no net addition of pollutants. |
• | Establishes a public, technical, and timed process for variances. |
Ecology involved small businesses (or their representatives) and local governments and agencies in the development of this rule during the stakeholder and public processes.
Ecology does not expect the proposed rule to result in significant net loss or gain of any jobs due to quantifiable compliance costs to private industry.
Ecology identified additional possible costs to some private dischargers and potentially in-water construction projects, but was unable to quantify these possible costs due to uncertainty about facility or project attributes and behaviors, water body or site attributes, and the nature of potentially resulting required actions. If additional actions are required, and private businesses incur costs as a result, the impact to net jobs in the state depends on the nature of the actions, and whether on-site, in-state, or out-of-state resources are used to complete them.
If on-site or in-state resources are used, expenditures on them are likely to support offsetting output and jobs in those industries, and ecology does not expect significant reductions in jobs as a result of the proposed rule. If out-of-state resources are used, the model represents this as a loss in output and jobs in industries incurring costs, with no offsetting gains to the suppliers they use to take additional required actions under the proposed rule.
Section 1: Background, Baseline, and Proposed Rule:
1.1 Introduction: Based on research and analysis required by RFA, RCW 19.85.070, ecology has determined that the proposed WQS for surface waters of the state of Washington (chapter 173-201A WAC) does not have a disproportionate impact on small business. This is because the rule is likely to only impact large businesses. (A small business is defined by RFA as having fifty or fewer employees.) Ecology did not, therefore, include language in the proposed rule to minimize disproportionate impacts.
The small business economic impact statement (SBEIS) is intended to be read with the associated cost-benefit analysis (Ecology publication #XX-XX-XXX), which contains more in-depth discussion of the analysis.
1.2 Proposed rule amendments: The proposed rule updates the levels at which toxic pollutants can be present in water and still protect human health. These levels, known as human health criteria (HHC), are determined using the following Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) HHC equations:
• | For carcinogens: |
o | Freshwater criterion = (RL x BW)/(CSF x [DWI + (FCR x BCF)]) |
o | Marine criterion = (RL x BW)/(CSF x FCR x BCF) |
• | For noncarcinogens: |
o | Freshwater criterion = (RfD x RSC x BW)/[DWI + (FCR x BCF)] |
o | Marine criterion = (RfD x RSC x BW)/(FCR x BCF) |
For the above equations:
• | RL: Excess cancer risk level. The maximum allowable level of excess cancer. |
• | BW: Body weight. The representative adult body weight for the population, as based on population attributes. |
• | CSF: Cancer slope factor. A toxic-specific number representing the risk of cancer associated with exposure to a carcinogenic or potentially carcinogenic substance. A slope factor is an upper bound, approximating a ninety-five percent confidence limit, on the increased cancer risk from a lifetime of exposure to an agent by ingestion. |
• | DWI: Drinking water intake. Typical drinking water intake, based on the existing NTR (EPA, 1992). |
• | FCR: Fish consumption rate. |
• | BCF: Bioconcentration factor. A chemical-specific number representing contaminant uptake. |
• | RfD: Reference dose. A toxic-specific number representing a daily oral exposure to the human population (including sensitive subgroups) that is likely to be without an appreciable risk of deleterious effects during a lifetime. |
• | RSC: Relative source contribution. The RSC identifies or estimates the portion of a person's total exposure attributed to water and fish consumption and thereby accounts for potential exposure from other sources such as skin absorption, inhalation, other foods, and occupational exposures. |
This rule making is proposing to change the human health criteria for water quality as follows:
• | Updates to scientific values for: |
o | Toxicity factors - reflecting current research. |
o | Body weight representative of current population mean - 80kg, up from 70kg. |
o | Drinking water intake - 2.4 L/day. |
• | Changes to the level of protectiveness: |
o | Fish consumption rate - 175 g/day, up from 6.5 g/day. |
• | Does not change PCB criteria from current NTR levels. |
• | Sets the arsenic criteria to the Safe Drinking Water Act regulatory level. |
• | Does not set methylmercury criteria or change total mercury criteria established by NTR. |
The proposed rule updates implementation tools that can be used to meet all Washington WQS:
• | Removing time limit on compliance schedules. |
• | Allowing intake credits where there is no net addition of pollutants. |
• | Establishing a public, technical, and timed process for variances. |
It is important to note that the proposed rule changes real cancer risk differently for different people, depending on their real fish consumption. The proposed rule amendments do not assume everyone consumes one hundred seventy-five g/day of fish and shellfish.
1.3 Reasons for the proposed rule amendments: The Federal Clean Water Act (CWA) directs states, with oversight by EPA, to adopt WQS to protect the public health and welfare, enhance the quality of water, and serve the purposes of CWA. Under section 303, states' WQS must include at a minimum:
1. Designated uses for all water bodies within their jurisdictions.
2. Water quality criteria sufficient to protect the most sensitive of the uses.
3. An antidegradation policy consistent with the regulations at 40 C.F.R. 131.12.
States are also required to hold public hearings once every three years for the purpose of reviewing applicable WQS and, as appropriate, modifying and proposing standards. The results of this triennial review must be submitted to EPA, and EPA must approve or disapprove any new or revised standards. Section 303(c) also directs the EPA administrator to promulgate WQS to supersede state standards that have been disapproved, or in cases where the administrator determines that a new or revised standard is needed to meet CWA requirements.
As part of the triennial review, ecology identified a need to adopt new HHC, based on more accurate numbers used in the EPA HHC equations for determining numeric chemical criteria. In this rule making, ecology is proposing the inputs and resultant criteria necessary to protect public health, safety, and welfare. Before the proposal of these new HHC, Washington state continued to use federal standards that do not reflect current science on protection from toxic chemicals, as well as past standards for levels of protectiveness of the population.
Ecology also identified a need to update sections of WQS that direct the implementation of HHC and other WQS. The goal of revising these implementation tools is to provide clear and predictable regulatory requirements to help entities comply with regulatory requirements included in NPDES permits, state waste discharge permits, and CWA section 401 water quality certification. The proposed implementation tools also address legislation (RCW 90.48.605) obligating ecology to amend WQS to allow compliance schedules in excess of ten years under certain circumstances for permitted dischargers.
1.4 Baseline: The baseline generally consists of a collection of existing rules and laws, and their underlying assumptions. For economic analyses, the baseline necessarily also includes the implementation of those regulations, including the guidelines and policies that result in behavior and real impacts. This is what allows us to make a consistent comparison between the state of the world with or without the proposed rule amendments. For this rule making, we discuss the baseline below, grouped into existing:
• | Rules and laws. |
• | NTR criteria assumptions.1 |
• | Permitting guidelines. |
• | 303(d) listing policy. |
• | Compliance behavior. |
• | Growth trajectories. |
• | Allowance for compliance schedules. |
• | Intake credits. |
• | Allowance for variances. |
1The Federal Register (F.R.) citation for the human health criteria are from two sources. 57 F.R. 60848 is NTR which was issued by EPA in 1992. 64 F.R. 61182 is a revision to NTR that changed the PCB criteria from individual aroclors to total PCBs. NTR can be found at 40 C.F.R. 131.36.
1.4.1 Existing rules and laws: The underlying elements of the baseline are existing state and federal laws and rules. Relevant local regulations are included when applicable.
1.4.1.1 Federal requirement: CWA 303 (c)(2)(A) states, about surface WQS:
… Such standards shall be such as to protect the public health or welfare, enhance the quality of the water and serve the purposes of this chapter. Such standards shall be established taking into consideration their use and value for public water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, recreational purposes and agricultural, industrial and other purposes and also taking into consideration their use and value for navigation.
1.4.1.2 State requirements: In addition to the federal requirements the department of ecology is required under state statute to "retain and secure high quality waters," and to "vigorously exercise state power" to do so at the state level. (Author's bolding, below.)
Water Pollution Control Act - RCW 90.48.010 Policy enunciated.
It is declared to be the public policy of the state of Washington to maintain the highest possible standards to insure the purity of all waters of the state consistent with public health and public enjoyment thereof, the propagation and protection of wild life, birds, game, fish and other aquatic life, and the industrial development of the state, and to that end require the use of all known available and reasonable methods by industries and others to prevent and control the pollution of the waters of the state of Washington. Consistent with this policy, the state of Washington will exercise its powers, as fully and as effectively as possible, to retain and secure high quality for all waters of the state. The state of Washington in recognition of the federal government's interest in the quality of the navigable waters of the United States, of which certain portions thereof are within the jurisdictional limits of this state, proclaims a public policy of working cooperatively with the federal government in a joint effort to extinguish the sources of water quality degradation, while at the same time preserving and vigorously exercising state powers to insure that present and future standards of water quality within the state shall be determined by the citizenry, through and by the efforts of state government, of the state of Washington.
Water Pollution Control Act - RCW 90.48.035 Rule-making authority.
The department shall have the authority to, and shall promulgate, amend, or rescind such rules and regulations as it shall deem necessary to carry out the provisions of this chapter, including but not limited to rules and regulations relating to standards of quality for waters of the state and for substances discharged therein in order to maintain the highest possible standards of all waters of the state in accordance with the public policy as declared in RCW 90.48.010.
Water Pollution Control Act - RCW 90.48.260 Federal Clean Water Act - Department designated as state agency, authority - Delegation of authority - Powers, duties and functions.
The department of ecology is hereby designated as the state water pollution control agency for all purposes of the Federal Clean Water Act as it exists on February 4, 1987, and is hereby authorized to participate fully in the programs of the act.
Water Resources Act of 1971 - RCW 90.54.020 General declaration of fundamentals for utilization and management of waters of the state.
(b) Waters of the state shall be of high quality. Regardless of the quality of the waters of the state, all wastes and other materials and substances proposed for entry into said waters shall be provided with all known, available, and reasonable methods of treatment prior to entry. Notwithstanding that standards of quality established for the waters of the state would not be violated, wastes and other materials and substances shall not be allowed to enter such waters which will reduce the existing quality thereof, except in those situations where it is clear that overriding considerations of the public interest will be served.
1.4.2 Previous human health criteria: NTR criteria assumptions: The values for inputs into the equation for NTR (40 C.F.R. 131.36) criteria are listed below. These are inputs into the EPA HHC equations that calculate HHC levels for surface waters, before this proposal of an amended rule.
• | Excess cancer risk level = 10-6 (one in one million; "RL" in EPA HHC equations below). |
• | Relative source contribution = 1.0 ("RSC" in EPA HHC equations below). |
• | Hazard quotient = 1.0 (an underlying factor of "RfD" below). |
• | Body weight = 70 kg ("BW" in EPA HHC equations below). |
• | Drinking water intake = 2 L/day ("DWI" in EPA HHC equations below). |
• | Fish consumption rate = 6.5 g/day for chemicals excluding mercury ("FCR" in EPA HHC equations below). |
• | Fish consumption rate for mercury = 18.7 g/day. |
The EPA HHC equations using these inputs are:
• | For carcinogens: |
o | Freshwater criterion = (RL x BW)/(CSF x [DWI + (FCR x BCF)]) |
o | Marine criterion = (RL x BW)/(CSF x FCR x BCF) |
• | For noncarcinogens: |
o | Freshwater criterion = (RfD x RSC x BW)/[DWI + (FCR x BCF)] |
o | Marine criterion = (RfD x RSC x BW)/(FCR x BCF) |
1.4.3 Existing permitting guidelines: Permitting guidelines help permit writers translate the requirement to meet water quality criteria for protection of human health to permittee-specific requirements. While not a legal requirement, guidance informs how HHC impact permittees who discharge effluent to water bodies. Therefore, in describing the baseline for this analysis of the proposed rule amendments, it is necessary to consider the permitting guidelines in the baseline and proposed scenarios, as they will contribute to the cost and benefit estimates and discussion of impacts.
Ecology uses the Water Quality Program Permit Writer's Manual (Ecology, 2015) for technical guidance when developing wastewater discharge permits. A general overview of the permitting process for all dischargers includes:
• | Ecology receiving the permit application. |
• | Review of the application for completeness and accuracy. |
• | Derivation of applicable technology-based effluent limits. |
• | Determination of whether effluent will cause, or have reasonable potential to cause or contribute to, violation of WQS. |
• | If yes, derivation of human health-based effluent limits necessary to meet WQS. |
• | Derivation of monitoring requirements and other special conditions. |
• | Review process for the draft or proposed permit. |
• | Issuance of the final permit decision. |
For example, within the complex process of NPDES permit-writing (see Ecology, 2011, Figure II-2), a step includes determination of whether toxic pollutants are present in the effluent. Next, the permit writer must determine the best methods of controlling the levels of those toxic chemicals. Using existing technology-based guidelines, or developing them using best professional judgment, a reasonable potential determination is made based on modeling as to whether technology-based controls are sufficient to meet WQS. If not, water quality-based limits are developed.
The basic requirements and process for developing permits will not change under the proposed rule amendments. Extensive discussion of all of the considerations made during the permitting process can be found in Ecology, 2015.
1.4.4 Existing 303(d) impaired water body listing policy: The Federal Clean Water Act's section 303(d) established a process to identify and cleanup polluted waters. Every two years, all states are required to perform a water quality assessment of surface waters in the state, including all the rivers, lakes, and marine waters where data are available. Ecology compiles its own water quality data and federal data, and invites other groups to submit water quality data they have collected. All data submitted must be collected using appropriate scientific methods. The assessed waters are placed in categories that describe the status of water quality. Once the assessment is complete, the public is given a chance to review it and give comments. The final assessment is formally submitted to EPA for approval.
Waters whose beneficial uses - such as for drinking, recreation, aquatic habitat, and industrial use - are impaired by pollutants are placed in the polluted water category in the water quality assessment (303(d) list). These water bodies fall short of state surface WQS and are not expected to improve within the next two years. The 303(d) list, so called because the processes for developing the list and addressing the polluted waters on the list are described in section 303(d) of the Federal Clean Water Act, comprises waters in the polluted water category.
Ecology's assessment of which waters to place on the 303(d) list is guided by:
• | Federal laws, |
• | State WQS, and the |
• | Policy on the Washington state water quality assessment (WQP Policy 1-11; revised July 2012). |
The policy describes how the standards are applied, requirements for the data used, and how to prioritize total maximum daily loads (TMDL), among other issues.2 In addition, even before a TMDL is completed, the inclusion of a water body on the 303(d) list can reduce the amount of pollutants allowed to be released under permits issued by ecology.
2A TMDL is the sum of the load allocations and wasteload allocations, plus reserves for future growth and a margin of safety, which are equal to the Loading Capacity of the water body. This is a requirement of Section 303(d) of the Federal Clean Water Act and is defined in 40 C.F.R. 130.2(i). The term "TMDL" is often also applied to the process to determine a TMDL ("Ecology is doing a TMDL") and to the final documentation of the TMDL ("Ecology has submitted a TMDL").
Waters placed on the 303(d) list require the preparation of a water cleanup plan (TMDL) or other approved water quality improvement project. The improvement plan identifies how much pollution needs to be reduced or eliminated to achieve clean water, and allocates that amount of required pollution reduction among the existing sources.
Ecology periodically revises the water quality assessment policy based on new information and updates to EPA guidance. Each revision includes a public review process. Ecology submitted a revised 303(d) list to EPA in 2015 and we expect approval from EPA in early 2016, therefore ecology used the revised list for the analysis included in this section.
1.4.5 Past or existing compliance behavior: The baseline includes past or existing compliance behavior. This includes behavior undertaken in response to federal and state laws, rules, permits, guidance, and policies. This also includes business decisions in response to regulatory, economic, or environmental changes. Such behavior might include, but is not limited to, existing treatment technologies, production processes, and effluent volumes.
1.4.6 Past or existing growth trajectories: The proposed rules apply to existing and future dischargers, on existing and future impaired water bodies, and water bodies with and without TMDLs, so the baseline must also account for:
• | Attributes and behaviors of future dischargers. |
• | Future TMDLs. |
The regulatory environment that current and future dischargers would encounter under the baseline would include the elements of the baseline described above, as well as any change in TMDLs.
1.4.7 Existing allowance for compliance schedules: The baseline includes existing compliance schedules. A compliance schedule is an enforceable tool used as part of a permit, order, or directive to achieve compliance with applicable effluent standards and limitations, WQS, or other legally applicable requirements. Compliance schedules include a sequence of interim requirements such as actions, operations, or milestone events to achieve the stated goals. Compliance schedules are a broadly used tool for achieving compliance with state and federal regulations; compliance schedules under the Clean Water Act are defined federally at CWA 502(17) and 40 C.F.R. Section 122.2. Under the baseline, compliance schedules may last up to ten years.
1.4.8 Existing intake credits: An intake credit is a procedure that allows permitting authorities to conclude that a permittee does not cause, have the reasonable potential to cause, or contribute to an excursion above WQS when he or she returns an unaltered intake water pollutant to the body of water it was taken from under identified circumstances. In other words, when effluent has the same contaminants and concentrations as water taken in, an intake credit allows authorities to not assign responsibility for those contaminant concentrations to the discharger.
Washington's current WQS do not allow intake credits.
1.4.9 Existing allowance for variances: A variance is a time-limited designated use and criterion for a specific pollutant(s) or water quality parameter(s) for a single discharger, a group of dischargers, or stretch of waters. Variances establish a set of temporary requirements that apply instead of the otherwise applicable WQS and related water quality criteria. A variance may be considered when the standards are expected to be attained by the end of the variance period or the attainable use cannot be reliably determined. Variances can be targeted to specific pollutants, sources, and/or stretches of waters.
The United States EPA has dictated that state variance procedures, as part of state WQS, must be consistent with the substantive requirements of 40 C.F.R. 131.14. EPA has approved state-adopted variances in the past and has indicated that it will continue to do so if:
• | Each variance is adopted into rule as part of WQS. |
• | The state demonstrates that meeting the standard is unattainable based on one or more of the grounds outlined in 40 C.F.R. 131.10(g) for removing a designated use. Note: EPA's new WQS regulation makes this requirement only applicable to Clean Water Act 101 (1)(2) uses (the "fishable/swimmable" uses of the Clean Water Act), which is ecology's intent also. Variances for other uses must include consideration of the "use and value" of the water. (Please see 40 C.F.R. 131.14 for new federal requirements.) |
• | The justification submitted by the state includes documentation that treatment more advanced than that required by sections 303 (c)(2)(A) and (B) has been carefully considered, and that alternative effluent control strategies have been evaluated. |
• | The more stringent state criterion is maintained and is binding upon all other dischargers on the stream or stream segment. |
• | The discharger who is given a variance for one particular constituent is required to meet the applicable criteria for other constituents. |
• | The variance is granted for a specific period of time and can be renewed upon expiration. |
• | The discharger either must meet the standard upon the expiration of this time period or must make a new demonstration of "unattainability." |
• | Reasonable progress is being made toward meeting the standards. |
• | The variance was subjected to public notice, opportunity for comment, and public hearing. The public notice should contain a clear description of the impact of the variance upon achieving WQS in the affected stretch of waters. |
Section 2: Analysis of Compliance Costs: After reviewing, filtering, and assessing real cases of existing effluent data for dischargers using existing analytical methods and permitting practices, we conclude that, based on the reasonable potential analyses using proposed HHC, the majority of facilities will not be impacted. To be impacted, a facility must have the following attributes:
• | Discharge a chemical for which criteria values would change as a result of the proposed rule amendments. |
• | Discharge that chemical in quantities greater than the detection limits for that chemical using required test methods. If a facility uses the required sufficiently sensitive test method, a nondetect in an effluent sample generally means the discharge has no reasonable potential to violate standards. |
• | Currently, or under the baseline, discharge that chemical in quantities such that the concentration at the edge of the chronic mixing zone exceed the relevant proposed criteria value. |
• | Not be in an existing TMDL, as ecology will not be revising TMDLs as a result of this rule making. |
• | Have samples that consistently indicate the presence of the chemical. |
• | Have a continuous discharge (i.e., not be an intermittent discharge, such as stormwater or CSO). |
and potentially:
• | Discharge to sediments of concern for the chemicals of concern in the discharge, at rates in excess of sediment concentrations, as this may violate nondegradation requirements. |
Note that for chemicals with both baseline and proposed HHC below the quantitation limit, the proposed rule will not impose additional costs compared to the baseline.
Some facilities, however, are likely to incur costs under the proposed rule:
• | Two industrial facilities may incur additional unquantifiable costs: |
• | Costs of compliance actions if action required to comply with hazardous waste regulations was insufficient to also meet the proposed HHC. |
• | Costs of compliance actions if a facility chooses to continue operations rather than curtailing them. |
• | Quantifiable total capital cost to eleven public and two private facilities to comply with proposed standards for phthalates: $10.6 thousand. |
• | Unquantifiable costs of source control plan implementation, and compliance schedule or variance acquisition costs if the proposed HHC cannot be met using the source control plan. |
• | Possible unquantifiable sampling and testing costs, as well as costs of more stringent requirements and best management practices at up to five percent of in-water construction sites seeking Section 401 Certification, if ecology determines turbidity is not a sufficient proxy for the likelihood of contaminating the water column. |
• | Potential compliance costs to a hypothetical unrepresented discharger, cleanup site, or in-water construction project, to control chemicals not currently observed in samples. |
Section 3: Quantification of Cost Ratios: Based on ecology's cost estimate results, we determined that the proposed rule does not impact small businesses (employing fifty or fewer employees, at the highest ownership level).
The smallest business likely to experience identifiable costs due to the proposed rule employs approximately six hundred forty employees.3 It is therefore not possible to compare relative costs to small versus the largest ten percent of businesses.
3Employment data taken from individual company web sites, the Northwest Pulp and Paper Association (available at http://nwpulpandpaper.org/about-us/member-profiles/), and "Find the Company" web site (accessed January 13, 2016, from http://listings.findthecompany.com/).
Section 4: Actions Taken to Reduce Impact of the Rule on Small Businesses: Ecology did not take any action to reduce the impact of the proposed rule on small businesses because the proposed rule does not have a disproportionate impact on small businesses.
Public entities, such as publicly owned treatment works (POTW), are not subject to this analysis under RFA. They were identified by the associated cost-benefit analysis as likely to incur additional costs under the proposed rule. While not required to mitigate costs to small publicly owned entities, ecology notes that small POTWs are not required to test for the chemicals that would cause them to incur costs, and their costs under the proposed rule are mitigated by this exemption.
Section 5: The Involvement of Small Businesses and Local Government in the Development of the Proposed Rule: To support the rule-making effort, in September 2012, ecology established an extensive public process to engage stakeholders and key parties. Ecology held a series of water quality policy forums to engage and educate the public on the complex technical and policy issues involved in adopting HHC. Ecology also convened a delegates' table consisting of delegates from key stakeholder groups to discuss concerns and gain an increased understanding of the broad range of issues associated with this rule making.
As ecology moves forward with rule making, we will continue to use our existing e-mail listserv and web pages to communicate to our stakeholders and interest groups along with continuing to make ourselves available to meet with people as requested.
5.1 Delegates' table business and local government representatives:
• | Chandler, Gary - Association of Washington Business (Alternate: Brandon Housekeeper) |
• | Hope, Bruce - Western States Petroleum Association (Alternate: Courtney Barnes) |
• | Johnson, Ken - Weyerhaeuser |
• | Judd, Nancy - Association of Washington Business |
• | Kibbey, Heather - City of Everett |
• | Kilroy, Sandra - King County (Alternate: Josh Weiss) |
• | Myrum, Tom - Washington State Water Resources Association |
• | O'Keefe, Gerry - Washington Public Ports Association |
• | Rawls, Bruce - Spokane County (Alternate: Josh Weiss) |
• | Schroeder, Carl - Association of Washington Cities |
• | Steele, David - Pacific Coast Shellfish Growers (Alternate: Margaret Barrette) |
• | Stuhlmiller, John - Washington Farm Bureau (Alternate: Evan Sheffels) |
5.2 Water quality policy forums & informational meetings business and local government representatives:
• | Aldrich, Nancy (City of Richland) |
• | Archer Parsons, Andrea (City of Port Orchard) |
• | Baca, Matthew (Earthjustice) |
• | Balliet, Jamie (East Columbia Basin Irrigation District) |
• | Barrette, Margaret (Pacific Coast Shellfish Growers Association) |
• | Bierlink, Henry (Whatcom Farm Friends) |
• | Blair, Lori (The Boeing Company) |
• | Boehme, Jonathan (City of Port Angeles) |
• | Booth, Kevin (Avista Corp) |
• | Borden, Bruce (Lowes) |
• | Brazil, Brian (TansAlta) |
• | Bridges, Thomas (Mukilteo Water & Wastewater Disrict) |
• | Brouillard, Elaine (Roza Sunnyside Board of Joint Control) |
• | Budworth, Chad (The Boeing Company) |
• | Butkus, Paul (PCA /Boise Paper) |
• | Castle, Art (Building Industry Association of Washington) |
• | Cave, Scott (City of Quincy) |
• | Chisolm, B (WAPG) |
• | Crowley, Allison (Seattle City Light) |
• | Cummings, Dano (City of Spokane) |
• | Daly, Brad (City of Walla Walla) |
• | Davis, Marcia (City of Spokane) |
• | Dayao, Donnelle (City of Sumner) |
• | Deardorff, Gary (City of Kennewick) |
• | Defoe, Seth (Kennewick Irrigation District) |
• | DeVaney, Jon (Yakima Valley Growers-Shippers Association) |
• | Finley, Ande (Fisherman Bay Sewer District) |
• | Fleming, Josh (Boise Paper) |
• | Gallardo, Angela (City of Burien) |
• | Gatchalian, Don (Yakima County) |
• | Gaub, Ty (U.S. Oil & Refining Co.) |
• | Graham, Jeremy (City of Olympia) |
• | Gyselinck, Craig (Quincy-Columbia Basin Irrigation District) |
• | Halstrom, Jim (Washington State Horticultural Association/WA Water Policy Alliance) |
• | Haslip, Heather (Port of Skagit) |
• | Hegel, Kevin (City of Montesano) |
• | Hermanson, Mike (Spokane County Water Resources) |
• | Hildebrandt, Pete (Alcoa & Western States Petroleum Association) |
• | Himebaugh, Jan (Building Industry Association of Washington) |
• | Houskeeper, Brandon (Association of Washington Business) |
• | Hutton-Tine, Alex (Recology) |
• | Iams, Karl (U.S. Oil & Refining Co.) |
• | Jack, Richard (King County Dept Natural Resources and Parks) |
• | Jarnot, Brittany (Everett, Fife, Issaquah, Kent, Lake Stevens, Puyallup, Redmond, Renton) |
• | Johnson, Ken (Weyerhaeuser) |
• | Johnson Arledge, Rebecca (City of Seattle) |
• | Judd, Nancy (Windward Environmental for AWB) |
• | Kibbey, Heather (City of Everett) |
• | Kilroy, Sandra (King County) |
• | Kook, Shirley (Lewis County) |
• | Kounts, John (Washington PUD Association) |
• | Krider, Leah (The Boeing Company) |
• | Loehr, Lincoln (City of Everett) |
• | Mauren, Lorna (City of Tacoma) |
• | Meehan, Maureen (City of Seattle, Department of Transportation) |
• | Merrill, Laura (Washington State Association of Counties) |
• | Morgan, Matt (Roza Sunnyside Board of Joint Control) |
• | Norcross, Neil (Tesoro Refining & Marketing Co. LLC) |
• | O'Keefe, Gerry (WPPA) |
• | Percynski, Beth (Procter & Gamble) |
• | Peterson, John (Clark Regional Wastewater District) |
• | Phillips, Sandra (Spokane Regional Health District) |
• | Plusquellec, Scott (City of Seattle, Office of Intergovernmental Relations) |
• | Rae, Alyson (Snohomish County) |
• | Ramos, C (Boise Paper) |
• | Ransavage, Ryan (Miles Sand & Gravel Company) |
• | Rhoads, Kate (Seattle Public Utilities) |
• | Rhodes, Brian (Western States Petroleum Association and Shell) |
• | Riggs, Michele (Cedar Grove Composting) |
• | Sackellares, Robert (Georgia Pacific) |
• | Saffery, Susan (City of Seattle, Seattle Public Utilities) |
• | Schmidt, Lynn (City of Spokane) |
• | Schmidtz, David (Phillips 66 Ferndale Refinery) |
• | Schroeder, Carl (Association of Washington Cities) |
• | Shopbell, Stephanie (South Columbia Basin Irrigation District) |
• | Sklare, Julie (City of Everett) |
• | Skrinde, Rolf (Twin City Foods) |
• | Spain, Glen (Pacific Coast Federation of Fishermen's Associations (PCFFA)) |
• | Steinmetz, Marcie (Chelan PUD) |
• | Taylor, Calvin (City of Tacoma) |
• | Taylor, Toni (Spokane County Water Resources Division) |
• | Thorpe, Ed (Coalition for Clean Water) |
• | Turner, Doris (The Boeing Company) |
• | VanderWood, Jerry (Associated General Contractors of Washington) |
• | VanNatta, Kathryn (Northwest Public Power Association) |
• | Varner, Phyllis (City of Bellevue) |
• | Verity, Laura (Ponderay Newsprint Co.) |
• | Vincent, Carla (Pierce County SWM) |
• | Wagner, Theresa (City of Seattle) |
• | Waldron, Chris (PIONEER Technologies Corporation) |
• | Webber, Terry (American Forest & Paper Association) |
• | Wendling, Peg (City of Bellingham) |
• | Wertz, Ingrid (Seattle Public Utilities) |
• | Whitaker, Brandon (Port of Everett) |
• | Wood, Jill (Island County Public Health) |
• | Wright, Jeff (City of Everett) |
• | Zlateff, Dana (City of Issaquah) |
• | Zorza, Dubber (Hood River Sand & Gravel) |
5.3 Water quality partnership business and local government representatives:
• | Archer-Parsons, Andrea (City of Port Orchard) |
• | Blair, Lori (Boeing, Environment - Stormwater) |
• | Burroughs, Blair (Washington Association of Sewer & Water Districts) |
• | Callahan, Jason (Washington State House of Representatives) |
• | Carstens, Steve (City of Puyallup) |
• | Clark, Mark (WA State Conservation Commission) |
• | Coburn, Gail (Seattle Public Utilities) |
• | Cooper, Betsy (Department of Natural Resources and Parks) |
• | Erwin, Tanyalee (WSU Puyallup Research and Extension Center) |
• | Fohn, Mindy (Kitsap County Public Works) |
• | Gordon, Jay (Washington State Dairy Federation) |
• | Harbison, Patrick (Cowlitz County Public Works) |
• | Hildebrandt, Pete (Western States Petroleum Association) |
• | Johnson, Ken (Weyerhaeuser Company) |
• | Griffin, Heather (City of Everett Public Works) |
• | Leif, Bill (Snohomish County Department of Public Works) |
• | Lewis, Teresa (Pierce County Public Works and Utilities) |
• | Mayhew, Miles (Seattle Public Utilities) |
• | McCabe, Christian (Northwest Pulp & Paper) |
• | McCart, Wes (Stevens County Commissioner, District 1) |
• | Meehan, Maureen (City of Seattle Department of Transportation) |
• | Meyer, Andy (Association of Washington Cities) |
• | Michael, Hal (Sustainable Fisheries Foundation) |
• | Navetski, Doug (King County) |
5.4 E-mail listserv: Ecology also communicated with interested parties using the water quality information (WQInfo) mailing list (listserv). This list includes over one thousand one hundred recipients at public, businesses, local governments, education, military, and other interests.
Section 6: The SIC Codes of Impacted Industries: RFA requires ecology to list the SIC (standard industry classification) codes of impacted industries. The SIC system has long been replaced by the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS).
Based on our analysis of costs, the only likely impacted NAICS code is 3221 (Pulp, Paper, and Paperboard Mills), exclusively through cleanup sites that treat groundwater and are permitted dischargers of treated groundwater to surface waters. Additional possibly impacted NAICS codes include 3221, 3313, and 4247. There are also potential costs to entities seeking Section 401 Certification, if ecology determines that turbidity is no longer an appropriate measure of the likelihood of in-water construction impacting surface water quality with toxic chemicals in sediments.
Section 7: Impact on Jobs: We used the Washington state office of financial management's Washington input-output model (OFM-IO) to assess the proposed rule's impact on jobs across the state. This methodology estimates the impact as reductions or increases in spending in certain sectors of the state economy flow through to purchases, suppliers, and demand for other goods. Compliance costs incurred by an industry are entered in the OFM-IO model as a decrease in spending and investment.4
4For more information, see http://www.ofm.wa.gov/economy/io/2007/default.asp.
The OFM-IO model addresses only private sector industries, as does the SBEIS. As such, only a subset of total costs estimated and quantified by the cost-benefit analysis are addressed in the jobs impact analysis. Approximately $1.5 thousand in quantifiable costs are likely for private industry. Using the OFM-IO model, this is not likely to result in a net loss or gain of jobs in Washington.
Ecology identified additional possible costs to some private dischargers and potentially in-water construction projects, but was unable to quantify these possible costs due to uncertainty about facility or project attributes and behaviors, water body or site attributes, and the nature of potentially resulting required actions. If additional actions are required, and private businesses incur costs as a result, the impact to net jobs in the state depends on the nature of the actions, and whether on-site, in-state, or out-of-state resources are used to complete them.
If on-site or in-state resources are used, expenditures on them are likely to support offsetting output and jobs in those industries, and ecology does not expect significant reductions in jobs as a result of the proposed rule. If out-of-state resources are used, the model represents this as a loss in output and jobs in industries incurring costs, with no offsetting gains to the suppliers they use to take additional required actions under the proposed rule.
A copy of the statement may be obtained by contacting Becca Conklin, Washington Department of Ecology, P.O. Box 47600, Olympia, WA 98504-7600, phone (360) 407-6413, fax (360) 407-6426, e-mail swqs@ecy.wa.gov.
A cost-benefit analysis is required under RCW 34.05.328. A preliminary cost-benefit analysis may be obtained by contacting Becca Conklin, Washington Department of Ecology, P.O. Box 47600, Olympia, WA 98504-7600, phone (360) 407-6413, fax (360) 407-6426, e-mail swqs@ecy.wa.gov.
January 29, 2016
Maia D. Bellon
Director
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text above occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 11-09-090, filed 4/20/11, effective 5/21/11)
WAC 173-201A-020 Definitions.
The following definitions are intended to facilitate the use of chapter 173-201A WAC:
"1-DMax" or "1-day maximum temperature" is the highest water temperature reached on any given day. This measure can be obtained using calibrated maximum/minimum thermometers or continuous monitoring probes having sampling intervals of thirty minutes or less.
"7-DADMax" or "7-day average of the daily maximum temperatures" is the arithmetic average of seven consecutive measures of daily maximum temperatures. The 7-DADMax for any individual day is calculated by averaging that day's daily maximum temperature with the daily maximum temperatures of the three days prior and the three days after that date.
"Action value" means a total phosphorus (TP) value established at the upper limit of the trophic states in each ecoregion (see Table 230(1)). Exceedance of an action value indicates that a problem is suspected. A lake-specific study may be needed to confirm if a nutrient problem exists.
"Actions" refers broadly to any human projects or activities.
"Acute conditions" are changes in the physical, chemical, or biologic environment which are expected or demonstrated to result in injury or death to an organism as a result of short-term exposure to the substance or detrimental environmental condition.
"AKART" is an acronym for "all known, available, and reasonable methods of prevention, control, and treatment." AKART shall represent the most current methodology that can be reasonably required for preventing, controlling, or abating the pollutants associated with a discharge. The concept of AKART applies to both point and nonpoint sources of pollution. The term "best management practices," typically applied to nonpoint source pollution controls is considered a subset of the AKART requirement.
"Background" means the biological, chemical, and physical conditions of a water body, outside the area of influence of the discharge under consideration. Background sampling locations in an enforcement action would be up-gradient or outside the area of influence of the discharge. If several discharges to any water body exist, and enforcement action is being taken for possible violations to the standards, background sampling would be undertaken immediately up-gradient from each discharge.
"Best management practices (BMP)" means physical, structural, and/or managerial practices approved by the department that, when used singularly or in combination, prevent or reduce pollutant discharges.
"Biological assessment" is an evaluation of the biological condition of a water body using surveys of aquatic community structure and function and other direct measurements of resident biota in surface waters.
"Bog" means those wetlands that are acidic, peat forming, and whose primary water source is precipitation, with little, if any, outflow.
"Carcinogen" means any substance or agent that produces or tends to produce cancer in humans. For implementation of this chapter, the term carcinogen will apply to substances on the United States Environmental Protection Agency lists of A (known human) and B (probable human) carcinogens, and any substance which causes a significant increased incidence of benign or malignant tumors in a single, well conducted animal bioassay, consistent with the weight of evidence approach specified in the United States Environmental Protection Agency's Guidelines for Carcinogenic Risk Assessment as set forth in 51 FR 33992 et seq. as presently published or as subsequently amended or republished.
"Chronic conditions" are changes in the physical, chemical, or biologic environment which are expected or demonstrated to result in injury or death to an organism as a result of repeated or constant exposure over an extended period of time to a substance or detrimental environmental condition.
"Combined sewer overflow (CSO) treatment plant" is a facility that provides at-site treatment as provided for in chapter 173-245 WAC. A CSO treatment plant is a specific facility identified in a department-approved CSO reduction plan (long-term control plan) that is designed, operated and controlled by a municipal utility to capture and treat excess combined sanitary sewage and storm water from a combined sewer system.
"Compliance schedule" or "schedule of compliance" is a schedule of remedial measures included in a permit or an order, including an enforceable sequence of interim requirements (for example, actions, operations, or milestone events) leading to compliance with an effluent limit, other prohibition, or standard.
"Created wetlands" means those wetlands intentionally created from nonwetland sites to produce or replace natural wetland habitat.
"Critical condition" is when the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the receiving water environment interact with the effluent to produce the greatest potential adverse impact on aquatic biota and existing or designated water uses. For steady-state discharges to riverine systems the critical condition may be assumed to be equal to the 7Q10 flow event unless determined otherwise by the department.
"Damage to the ecosystem" means any demonstrated or predicted stress to aquatic or terrestrial organisms or communities of organisms which the department reasonably concludes may interfere in the health or survival success or natural structure of such populations. This stress may be due to, but is not limited to, alteration in habitat or changes in water temperature, chemistry, or turbidity, and shall consider the potential build up of discharge constituents or temporal increases in habitat alteration which may create such stress in the long term.
"Department" means the state of Washington department of ecology.
"Designated uses" are those uses specified in this chapter for each water body or segment, regardless of whether or not the uses are currently attained.
"Director" means the director of the state of Washington department of ecology.
"Drainage ditch" means that portion of a designed and constructed conveyance system that serves the purpose of transporting surplus water; this may include natural water courses or channels incorporated in the system design, but does not include the area adjacent to the water course or channel.
"Ecoregions" are defined using EPAs Ecoregions of the Pacific Northwest Document No. 600/3-86/033 July 1986 by Omernik and Gallant.
"Enterococci" refers to a subgroup of fecal streptococci that includes S. faecalis, S. faecium, S. gallinarum, and S. avium. The enterococci are differentiated from other streptococci by their ability to grow in 6.5% sodium chloride, at pH 9.6, and at 10°C and 45°C.
"E. coli" or "Escherichia coli" is an aerobic and facultative gram negative nonspore forming rod shaped bacterium that can grow at 44.5 degrees Celsius that is ortho-nitrophenyl-B-D-galactopyranoside (ONPG) positive and Methylumbelliferyl glucuronide (MUG) positive.
"Existing uses" means those uses actually attained in fresh or marine waters on or after November 28, 1975, whether or not they are designated uses. Introduced species that are not native to Washington, and put-and-take fisheries comprised of nonself-replicating introduced native species, do not need to receive full support as an existing use.
"Extraordinary primary contact" means waters providing extraordinary protection against waterborne disease or that serve as tributaries to extraordinary quality shellfish harvesting areas.
"Fecal coliform" means that portion of the coliform group which is present in the intestinal tracts and feces of warm-blooded animals as detected by the product of acid or gas from lactose in a suitable culture medium within twenty-four hours at 44.5 plus or minus 0.2 degrees Celsius.
"Geometric mean" means either the nth root of a product of n factors, or the antilogarithm of the arithmetic mean of the logarithms of the individual sample values.
"Ground water exchange" means the discharge and recharge of ground water to a surface water. Discharge is inflow from an aquifer, seeps or springs that increases the available supply of surface water. Recharge is outflow downgradient to an aquifer or downstream to surface water for base flow maintenance. Exchange may include ground water discharge in one season followed by recharge later in the year.
"Hardness" means a measure of the calcium and magnesium salts present in water. For purposes of this chapter, hardness is measured in milligrams per liter and expressed as calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
"Intake credit" is a procedure for establishing effluent limits that take into account the amount of a pollutant that is present in waters of the state, at the time water is removed from the body of water by the discharger or other facility supplying the discharger with intake water.
"Irrigation ditch" means that portion of a designed and constructed conveyance system that serves the purpose of transporting irrigation water from its supply source to its place of use; this may include natural water courses or channels incorporated in the system design, but does not include the area adjacent to the water course or channel.
"Lakes" shall be distinguished from riverine systems as being water bodies, including reservoirs, with a mean detention time of greater than fifteen days.
"Lake-specific study" means a study intended to quantify existing nutrient concentrations, determine existing characteristic uses for lake class waters, and potential lake uses. The study determines how to protect these uses and if any uses are lost or impaired because of nutrients, algae, or aquatic plants. An appropriate study must recommend a criterion for total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN) in µg/l, or other nutrient that impairs characteristic uses by causing excessive algae blooms or aquatic plant growth.
"Mean detention time" means the time obtained by dividing a reservoir's mean annual minimum total storage by the thirty-day ten-year low-flow from the reservoir.
"Migration or translocation" means any natural movement of an organism or community of organisms from one locality to another locality.
"Mixing zone" means that portion of a water body adjacent to an effluent outfall where mixing results in the dilution of the effluent with the receiving water. Water quality criteria may be exceeded in a mixing zone as conditioned and provided for in WAC 173-201A-400.
"Natural conditions" or "natural background levels" means surface water quality that was present before any human-caused pollution. When estimating natural conditions in the headwaters of a disturbed watershed it may be necessary to use the less disturbed conditions of a neighboring or similar watershed as a reference condition. (See also WAC 173-201A-260(1).)
"New or expanded actions" mean human actions that occur or are regulated for the first time, or human actions expanded such that they result in an increase in pollution, after July 1, 2003, for the purpose of applying this chapter only.
"Nonpoint source" means pollution that enters any waters of the state from any dispersed land-based or water-based activities including, but not limited to, atmospheric deposition; surface water runoff from agricultural lands, urban areas, or forest lands; subsurface or underground sources; or discharges from boats or marine vessels not otherwise regulated under the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System program.
"Permit" means a document issued pursuant to chapter 90.48 RCW specifying the waste treatment and control requirements and waste discharge conditions.
"pH" means the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration.
"Pollution" means such contamination, or other alteration of the physical, chemical, or biological properties, of any waters of the state, including change in temperature, taste, color, turbidity, or odor of the waters, or such discharge of any liquid, gaseous, solid, radioactive, or other substance into any waters of the state as will or is likely to create a nuisance or render such waters harmful, detrimental, or injurious to the public health, safety, or welfare, or to domestic, commercial, industrial, agricultural, recreational, or other legitimate beneficial uses, or to livestock, wild animals, birds, fish, or other aquatic life.
"Primary contact recreation" means activities where a person would have direct contact with water to the point of complete submergence including, but not limited to, skin diving, swimming, and water skiing.
"Secondary contact recreation" means activities where a person's water contact would be limited (e.g., wading or fishing) to the extent that bacterial infections of eyes, ears, respiratory or digestive systems, or urogenital areas would normally be avoided.
"Shoreline stabilization" means the anchoring of soil at the water's edge, or in shallow water, by fibrous plant root complexes; this may include long-term accretion of sediment or peat, along with shoreline progradation in such areas.
"Storm water" means that portion of precipitation that does not naturally percolate into the ground or evaporate, but flows via overland flow, interflow, pipes, and other features of a storm water drainage system into a defined surface water body, or a constructed infiltration facility.
"Storm water attenuation" means the process by which peak flows from precipitation are reduced and runoff velocities are slowed as a result of passing through a surface water body.
"Surface waters of the state" includes lakes, rivers, ponds, streams, inland waters, saltwaters, wetlands and all other surface waters and water courses within the jurisdiction of the state of Washington.
"Temperature" means water temperature expressed in degrees Celsius (°C).
"Treatment wetlands" means those wetlands intentionally constructed on nonwetland sites and managed for the primary purpose of wastewater or storm water treatment. Treatment wetlands are considered part of a collection and treatment system, and generally are not subject to the criteria of this chapter.
"Trophic state" means a classification of the productivity of a lake ecosystem. Lake productivity depends on the amount of biologically available nutrients in water and sediments and may be based on total phosphorus (TP). Secchi depth and chlorophyll-a measurements may be used to improve the trophic state classification of a lake. Trophic states used in this rule include, from least to most nutrient rich, ultra-oligotrophic, oligotrophic, lower mesotrophic, upper mesotrophic, and eutrophic.
"Turbidity" means the clarity of water expressed as nephelometric turbidity units (NTU) and measured with a calibrated turbidimeter.
"Upwelling" means the natural process along Washington's Pacific Coast where the summer prevailing northerly winds produce a seaward transport of surface water. Cold, deeper more saline waters rich in nutrients and low in dissolved oxygen, rise to replace the surface water. The cold oxygen deficient water enters Puget Sound and other coastal estuaries at depth where it displaces the existing deep water and eventually rises to replace the surface water. Such surface water replacement results in an overall increase in salinity and nutrients accompanied by a depression in dissolved oxygen. Localized upwelling of the deeper water of Puget Sound can occur year-round under influence of tidal currents, winds, and geomorphic features.
"USEPA" means the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
"Variance" is a time-limited designated use and criterion as defined in 40 C.F.R. 131.3, and must be adopted by rule.
"Wetlands" means areas that are inundated or saturated by surface water or ground water at a frequency and duration sufficient to support, and that under normal circumstances do support, a prevalence of vegetation typically adapted for life in saturated soil conditions. Wetlands generally include swamps, marshes, bogs, and similar areas. Wetlands do not include those artificial wetlands intentionally created from nonwetland sites((,)) including, but not limited to, irrigation and drainage ditches, grass-lined swales, canals, detention facilities, wastewater treatment facilities, farm ponds, and landscape amenities, or those wetlands created after July 1, 1990, that were unintentionally created as a result of the construction of a road, street, or highway. Wetlands may include those artificial wetlands intentionally created from nonwetland areas to mitigate the conversion of wetlands. (Water bodies not included in the definition of wetlands as well as those mentioned in the definition are still waters of the state.)
"Wildlife habitat" means waters of the state used by, or that directly or indirectly provide food support to, fish, other aquatic life, and wildlife for any life history stage or activity.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 11-09-090, filed 4/20/11, effective 5/21/11)
WAC 173-201A-240 Toxic substances.
(1) Toxic substances shall not be introduced above natural background levels in waters of the state which have the potential either singularly or cumulatively to adversely affect characteristic water uses, cause acute or chronic toxicity to the most sensitive biota dependent upon those waters, or adversely affect public health, as determined by the department.
(2) The department shall employ or require chemical testing, acute and chronic toxicity testing, and biological assessments, as appropriate, to evaluate compliance with subsection (1) of this section and to ensure that aquatic communities and the existing and designated uses of waters are being fully protected.
(3) USEPA Quality Criteria for Water, 1986, as revised, shall be used in the use and interpretation of the values listed in subsection (5) of this section.
(4) Concentrations of toxic, and other substances with toxic propensities not listed in Table 240 of this section shall be determined in consideration of USEPA Quality Criteria for Water, 1986, and as revised, and other relevant information as appropriate.
(5) The following criteria, found in Table 240(((3))), shall be applied to all surface waters of the state of Washington ((for the protection of aquatic life)). Values are µg/L for all substances except ammonia and chloride which are mg/L, and asbestos which is million fibers/L.
(a) Aquatic life protection. The department may revise the ((following)) criteria in Table 240 for aquatic life on a statewide or water body-specific basis as needed to protect aquatic life occurring in waters of the state and to increase the technical accuracy of the criteria being applied. The department shall formally adopt any appropriate revised criteria as part of this chapter in accordance with the provisions established in chapter 34.05 RCW, the Administrative Procedure Act. The department shall ensure there are early opportunities for public review and comment on proposals to develop revised criteria. ((Values are µg/L for all substances except Ammonia and Chloride which are mg/L:))
(b) Human health protection. The following provisions apply to the human health criteria in Table 240. All waters shall maintain a level of water quality when entering downstream waters that provides for the attainment and maintenance of the water quality standards of those downstream waters, including the waters of another state. The human health criteria in the tables were calculated using a fish consumption rate of 175 g/day. Criteria for carcinogenic substances were calculated using a cancer risk level equal to one-in-one-million, or as otherwise specified in this chapter. The human health criteria calculations and variables include chronic durations of exposure up to seventy years. All human health criteria for metals are for total metal concentrations, unless otherwise noted. Dischargers have the obligation to reduce toxics in discharges through the use of AKART.
Table 240(((3)))
Toxics Substances Criteria
((Substance |
Freshwater |
Marine Water |
||||
Acute |
Chronic |
Acute |
Chronic |
|||
Aldrin/Dieldrin e |
2.5a |
0.0019b |
0.71a |
0.0019b |
||
Ammonia (un-ionized NH3) hh |
f,c |
g,d |
0.233h,c |
0.035h,d |
||
Arsenic dd |
360.0c |
190.0d |
69.0c,ll |
36.0d,cc,ll |
||
Cadmium dd |
i,c |
j,d |
42.0c |
9.3d |
||
Chlordane |
2.4a |
0.0043b |
0.09a |
0.004b |
||
Chloride (Dissolved) k |
860.0h,c |
230.0h,d |
- |
- |
||
Chlorine (Total Residual) |
19.0c |
11.0d |
13.0c |
7.5d |
||
Chlorpyrifos |
0.083c |
0.041d |
0.011c |
0.0056d |
||
Chromium (Hex) dd |
15.0c,l,ii |
10.0d,jj |
1,100.0c,l,ll |
50.0d,ll |
||
Chromium (Tri) gg |
m,c |
n,d |
- |
- |
||
Copper dd |
o,c |
p,d |
4.8c,ll |
3.1d,ll |
||
Cyanide ee |
22.0c |
5.2d |
1.0c,mm |
d,mm |
||
DDT (and metabolites) |
1.1a |
0.001b |
0.13a |
0.001b |
||
Dieldrin/Aldrin e |
2.5a |
0.0019b |
0.71a |
0.0019b |
||
Endosulfan |
0.22a |
0.056b |
0.034a |
0.0087b |
||
Endrin |
0.18a |
0.0023b |
0.037a |
0.0023b |
||
Heptachlor |
0.52a |
0.0038b |
0.053a |
0.0036b |
||
Hexachlorocyclohexane (Lindane) |
2.0a |
0.08b |
0.16a |
- |
||
Lead dd |
q,c |
r,d |
210.0c,ll |
8.1d,ll |
||
Mercury s |
2.1c,kk,dd |
0.012d,ff |
1.8c,ll,dd |
0.025d,ff |
||
Nickel dd |
t,c |
u,d |
74.0c,ll |
8.2d,ll |
||
Parathion |
0.065c |
0.013d |
- |
- |
||
Pentachlorophenol (PCP) |
w,c |
v,d |
13.0c |
7.9d |
||
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) |
2.0b |
0.014b |
10.0b |
0.030b |
||
Selenium |
20.0c,ff |
5.0d,ff |
290c,ll,dd |
71.0d, x,ll,dd |
||
Silver dd |
y,a |
- |
1.9a,ll |
- |
||
Toxaphene |
0.73c,z |
0.0002d |
0.21c,z |
0.0002d |
||
Zinc dd |
aa,c |
bb,d |
90.0c,ll |
81.0d,ll |
||
Notes to Table 240(3):))
Compound/Chemical |
Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS)# |
Category |
Aquatic Life Criteria - Freshwater |
Aquatic Life Criteria - Marine Water |
Human Health Criteria for Consumption of: |
|||
Acute |
Chronic |
Acute |
Chronic |
Water & Organisms |
Organisms Only |
|||
Metals: |
||||||||
Antimony |
7440360 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
12 |
180 |
||||
Arsenic |
7440382 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
360.0 (c,dd) |
190.0 (d,dd) |
69.0 (c,ll,dd) |
36.0 (d,cc,ll,dd) |
10 (A) |
10 (A) |
Asbestos |
1332214 |
Toxic pollutants and hazardous substances |
7,000,000 fibers/L (C) |
|||||
Beryllium |
7440417 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
||||||
Cadmium |
7440439 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
(I,c,dd) |
(I,c,dd) |
42.0 (c,dd) |
9.3 (d,dd) |
||
Chromium (III) |
16065831 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
(m,c,gg) |
(n,d,gg) |
||||
Chromium (VI) |
18540299 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
15.0 (c,l,ii,dd) |
10.0 (d,jj,dd) |
1,100.0 (c,l,ll,dd) |
50.0 (d,ll,dd) |
||
Copper |
7440508 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
(o,c,dd) |
(p,d,dd) |
4.8 (c,ll,dd) |
3.1 (d,ll,dd) |
1,300 (C) |
|
Lead |
7439921 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
(q,c,dd) |
(r,d,dd) |
210.0 (c,ll,dd) |
8.1 (d,ll,dd) |
||
Mercury |
7439976 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
2.1 (c,kk,dd) |
0.012 (d,ff,s) |
1.8 (c,ll,dd) |
0.025 (d,ff,s) |
(G) |
(G) |
Methylmercury |
22967926 |
Nonconventional |
||||||
Nickel |
7440020 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
(t,c,dd) |
(u,d,dd) |
74.0 (c,ll,dd) |
8.2 (d,ll,dd) |
150 |
190 |
Selenium |
7782492 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
20.0 (c,ff) |
5.0 (d,ff) |
290 (c,ll,dd) |
71.0 (d,x,ll,dd) |
120 |
480 |
Silver |
7440224 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
(y,a,dd) |
1.9 (a,ll,dd) |
||||
Thallium |
7440280 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
0.24 |
0.27 |
||||
Zinc |
7440666 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
(aa,c,dd) |
(bb,d,dd) |
90.0 (c,ll,dd) |
81.0 (d,ll,dd) |
2,300 |
2,900 |
Other chemicals: |
||||||||
1,1,1-Trichloroethane |
71556 |
Volatile |
47,000 |
160,000 |
||||
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane |
79345 |
Volatile |
0.12 (B) |
0.46 (B) |
||||
1,1,2-Trichloroethane |
79005 |
Volatile |
0.44 (B) |
1.8 (B) |
||||
1,1-Dichloroethane |
75343 |
Volatile |
||||||
1,1-Dichloroethylene |
75354 |
Volatile |
1200 |
4100 |
||||
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene |
120821 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.12 (B) |
0.14 (B) |
||||
1,2-Dichlorobenzene |
95501 |
Volatile |
2000 |
2500 |
||||
1,2-Dichloroethane |
107062 |
Volatile |
9.3 (B) |
120 (B) |
||||
1,2-Dichloropropane |
78875 |
Volatile |
0.71 (B) |
3.1 (B) |
||||
1,3-Dichloropropene |
542756 |
Volatile |
0.24 (B) |
2 (B) |
||||
1,2-Diphenylhydrazine |
122667 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.015 (B) |
0.023 (B) |
||||
1,2-Trans-Dichloroethylene |
156605 |
Volatile |
600 |
5,800 |
||||
1,3-Dichlorobenzene |
541731 |
Volatile |
13 |
16 |
||||
1,4-Dichlorobenzene |
106467 |
Volatile |
460 |
580 |
||||
2,3,7,8-TCDD (Dioxin) |
1746016 |
Dioxin |
0.000000064 |
0.000000064 |
||||
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol |
88062 |
Acid compounds |
0.25 (B) |
0.28 (B) |
||||
2,4-Dichlorophenol |
120832 |
Acid compounds |
25 |
34 |
||||
2,4-Dimethylphenol |
105679 |
Acid compounds |
85 |
97 |
||||
2,4-Dinitrophenol |
51285 |
Acid compounds |
60 |
610 |
||||
2,4-Dinitrotoluene |
121142 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.039 (B) |
0.18 (B) |
||||
2,6-Dinitrotoluene |
606202 |
Base/neutral compounds |
||||||
2-Chloroethyvinyl Ether |
110758 |
Volatile |
||||||
2-Chloronaphthalene |
91587 |
Base/neutral compounds |
170 |
180 |
||||
2-Chlorophenol |
95578 |
Acid compounds |
15 |
17 |
||||
2-Methyl-4,6-Dinitrophenol (4,6-dinitro-o-cresol) |
534521 |
Acid compounds |
7.1 |
25 |
||||
2-Nitrophenol |
88755 |
Acid compounds |
||||||
3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine |
91941 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.0031 (B) |
0.0033 (B) |
||||
3-Methyl-4-Chlorophenol (parachlorometa cresol) |
59507 |
Acid compounds |
36 |
36 |
||||
4,4'-DDD |
72548 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.000036 (B) |
0.000036 (B) |
||||
4,4'-DDE |
72559 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.000051 (B) |
0.000051 (B) |
||||
4,4'-DDT |
50293 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.000025 (B) |
0.000025 (B) |
||||
4,4'-DDT(and metabolites) |
Pesticides/PCBs |
1.1 (a) |
0.001 (b) |
0.13 (a) |
0.001 (b) |
|||
4-Bromophenyl Phenyl Ether |
101553 |
Base/neutral compounds |
||||||
4-Chorophenyl Phenyl Ether |
7005723 |
Base/neutral compounds |
||||||
4-Nitrophenol |
100027 |
Acid compounds |
||||||
Acenaphthene |
83329 |
Base/neutral compounds |
110 |
110 |
||||
Acenaphthylene |
208968 |
Base/neutral compounds |
||||||
Acrolein |
107028 |
Volatile |
1.0 |
1.1 |
||||
Acrylonitrile |
107131 |
Volatile |
0.019 (B) |
0.028 (B) |
||||
Aldrin |
309002 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
2.5 (a,e) |
0.0019 (b,e) |
0.71 (a,e) |
0.0019 (b,e) |
0.0000057 (B) |
0.0000058 (B) |
alpha-BHC |
319846 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.0005 (B) |
0.00056 (B) |
||||
alpha-Endosulfan |
959988 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
9.7 |
10 |
||||
Anthracene |
120127 |
Base/neutral compounds |
3,100 |
4,600 |
||||
Benzene |
71432 |
Volatile |
0.44 (B) |
1.6 (B) |
||||
Benzidine |
92875 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.00002 (B) |
0.000023 (B) |
||||
Benzo(a) Anthracene |
56553 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.014 (B) |
0.021 (B) |
||||
Benzo(a) Pyrene |
50328 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.0014 (B) |
0.0021 (B) |
||||
Benzo(b) Fluoranthene |
205992 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.014 (B) |
0.021 (B) |
||||
Benzo(ghi) Perylene |
191242 |
Base/neutral compounds |
||||||
Benzo(k) Fluoranthene |
207089 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.014 (B) |
0.21 (B) |
||||
beta-BHC |
319857 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.0018 (B) |
0.002 (B) |
||||
beta-Endosulfan |
33213659 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
9.7 |
10 |
||||
Bis(2-Chloroethoxy) Methane |
111911 |
Base/neutral compounds |
||||||
Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Ether |
111444 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.02 (B) |
0.06 (B) |
||||
Bis(2-Chloroisopropyl) Ether |
108601 |
Base/neutral compounds |
1,100 |
7,400 |
||||
Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate |
117817 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.23 (B) |
0.25 (B) |
||||
Bromoform |
75252 |
Volatile |
5.8 (B) |
27 (B) |
||||
Butylbenzyl Phthalate |
85687 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.56 (B) |
0.58 (B) |
||||
Carbon Tetrachloride |
56235 |
Volatile |
0.2 (B) |
0.35 (B) |
||||
Chlordane |
57749 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
2.4 (a) |
0.0043 (b) |
0.09 (a) |
0.004 (b) |
0.000093 (B) |
0.000093 (B) |
Chlorobenzene |
108907 |
Volatile |
380 |
890 |
||||
Chlorodibromomethane |
124481 |
Volatile |
0.65 (B) |
3 (B) |
||||
Chloroethane |
75003 |
Volatile |
||||||
Chloroform |
67663 |
Volatile |
260 |
1200 |
||||
Chrysene |
218019 |
Base/neutral compounds |
1.4 (B) |
2.1 (B) |
||||
Cyanide |
57125 |
Metals, cyanide, and total phenols |
22.0 (c,ee) |
5.2 (d,ee) |
1.0 (c,mm,ee) |
(d,mm,ee) |
19 (D) |
270 (D) |
delta-BHC |
319868 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
||||||
Dibenzo(a,h) Anthracene |
53703 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.0014 (B) |
0.0021 (B) |
||||
Dichlorobromomethane |
75274 |
Volatile |
0.77 (B) |
3.6 (B) |
||||
Dieldrin |
60571 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
2.5 (a,e) |
0.0019 (b,e) |
0.71 (a,e) |
0.0019 (b,e) |
0.0000061 (B) |
0.0000061 (B) |
Diethyl Phthalate |
84662 |
Base/neutral compounds |
4,200 |
5,000 |
||||
Dimethyl Phthalate |
131113 |
Base/neutral compounds |
92,000 |
130,000 |
||||
Di-n-Butyl Phthalate |
84742 |
Base/neutral compounds |
450 |
510 |
||||
Di-n-Octyl Phthalate |
117840 |
Base/neutral compounds |
||||||
Endosulfan |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.22 (a) |
0.056 (b) |
0.034 (a) |
0.0087 (b) |
|||
Endosulfan Sulfate |
1031078 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
9.7 |
10 |
||||
Endrin |
72208 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.18 (a) |
0.0023 (b) |
0.037 (a) |
0.0023 (b) |
0.034 |
0.035 |
Endrin Aldehyde |
7421934 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.034 |
0.035 |
||||
Ethylbenzene |
100414 |
Volatile |
200 |
270 |
||||
Fluoranthene |
206440 |
Base/neutral compounds |
16 |
16 |
||||
Fluorene |
86737 |
Base/neutral compounds |
420 |
610 |
||||
Hexachlorocyclohexane (gamma-BHC; Lindane) |
58899 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
2.0 (a) |
0.08 (b) |
0.16 (a) |
15 |
17 |
|
Heptachlor |
76448 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.52 (a) |
0.0038 (b) |
0.053 (a) |
0.0036 (b) |
0.0000099 (B) |
0.00001 (B) |
Heptachlor Epoxide |
1024573 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.0000074 (B) |
0.0000074 (B) |
||||
Hexachlorobenzene |
118741 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.000051 (B) |
0.000052 (B) |
||||
Hexachlorobutadiene |
87683 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.69 (B) |
4.1 (B) |
||||
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene |
77474 |
Base/neutral compounds |
150 |
630 |
||||
Hexachloroethane |
67721 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.11 (B) |
0.13 (B) |
||||
Indeno(1,2,3-cd) Pyrene |
193395 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.014 (B) |
0.021 (B) |
||||
Isophorone |
78591 |
Base/neutral compounds |
27 (B) |
110 (B) |
||||
Methyl Bromide |
74839 |
Volatile |
520 |
2,400 |
||||
Methyl Chloride |
74873 |
Volatile |
||||||
Methylene Chloride |
75092 |
Volatile |
16 (B) |
250 (B) |
||||
Napthalene |
91203 |
Base/neutral compounds |
||||||
Nitrobenzene |
98953 |
Base/neutral compounds |
55 |
320 |
||||
N-Nitrosodimethylamine |
62759 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.00065 (B) |
0.34 (B) |
||||
N-Nitrosodi-n-Propylamine |
621647 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.0044 (B) |
0.058 (B) |
||||
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine |
86306 |
Base/neutral compounds |
0.62 (B) |
0.69 (B) |
||||
Pentachlorophenol (PCP) |
87865 |
Acid compounds |
(w,c) |
(v,d) |
13.0 (c) |
7.9 (d) |
0.046 (B) |
0.1 (B) |
Phenanthrene |
85018 |
Base/neutral compounds |
||||||
Phenol |
108952 |
Acid compounds |
18,000 |
200,000 |
||||
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) |
Pesticides/PCBs |
2.0 (b) |
0.014 (b) |
10.0 (b) |
0.030 (b) |
0.00017 (E) |
0.00017 (E) |
|
Pyrene |
129000 |
Base/neutral compounds |
310 |
460 |
||||
Tetrachloroethylene |
127184 |
Volatile |
4.9 (B) |
7.1 (B) |
||||
Toluene |
108883 |
Volatile |
180 |
410 |
||||
Toxaphene |
8001352 |
Pesticides/PCBs |
0.73 (c,z) |
0.0002 (d) |
0.21 (c,z) |
0.0002 (d) |
0.000032 (B) |
0.000032 (B) |
Trichloroethylene |
79016 |
Volatile |
0.38 (B) |
0.86 (B) |
||||
Vinyl Chloride |
75014 |
Volatile |
0.02 (B, F) |
0.26 (B, F) |
||||
Ammonia (hh) |
Nonconventional |
(f,c) |
(g,d) |
0.233 (h,c) |
0.035 (h,d) |
|||
Chloride (dissolved) (k) |
Nonconventional |
860.0 (h,c) |
230.0 (h,d) |
|||||
Chlorine (total residual) |
Nonconventional |
19.0 (c) |
11.0 (d) |
13.0 (c) |
7.5 (d) |
|||
Chlorpyrifos |
Toxic pollutants and hazardous substances |
0.083 (c) |
0.041 (d) |
0.011 (c) |
0.0056 (d) |
|||
Parathion |
Toxic pollutants and hazardous substances |
0.065 (c) |
0.013 (d) |
|||||
Footnotes for aquatic life criteria in Table 240: | |
a. | An instantaneous concentration not to be exceeded at any time. |
b. | A 24-hour average not to be exceeded. |
c. | A 1-hour average concentration not to be exceeded more than once every three years on the average. |
d. | A 4-day average concentration not to be exceeded more than once every three years on the average. |
e. | Aldrin is metabolically converted to Dieldrin. Therefore, the sum of the Aldrin and Dieldrin concentrations are compared with the Dieldrin criteria. |
f. | Shall not exceed the numerical value in total ammonia nitrogen (mg N/L) given by: |
For salmonids present: |
0.275 |
+ |
39.0 |
1 + 107.204-pH |
1 + 10pH-7.204 |
||
For salmonids absent: |
0.411 |
+ |
58.4 |
1 + 107.204-pH |
1 + 10pH-7.204 |
g. | Shall not exceed the numerical concentration calculated as follows: |
Unionized ammonia concentration for waters where salmonid habitat is an existing or designated use: |
0.80 ÷ (FT)(FPH)(RATIO) |
||||
where: |
RATIO |
= |
13.5; 7.7 ≤ pH ≤ 9 |
|
RATIO |
= |
(20.25 x 10(7.7-pH)) ÷ (1 + 10(7.4-pH)); 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 7.7 |
||
FT |
= |
1.4; 15 ≤ T ≤ 30 |
||
FT |
= |
10[0.03(20-T)]; 0 ≤ T ≤ 15 |
||
FPH |
= |
1; 8 ≤ pH ≤ 9 |
||
FPH |
= |
(1 + 10(7.4-pH)) ÷ 1.25; 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 8.0 |
||
Total ammonia concentrations for waters where salmonid habitat is not an existing or designated use and other fish early life stages are absent:
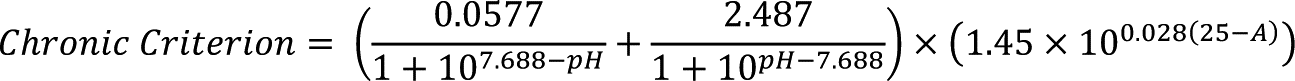 |
where: A |
= |
the greater of either T (temperature in degrees Celsius) or 7. |
Applied as a thirty-day average concentration of total ammonia nitrogen (in mg N/L) not to be exceeded more than once every three years on average. The highest four-day average within the thirty-day period should not exceed 2.5 times the chronic criterion.
Total ammonia concentration for waters where salmonid habitat is not an existing or designated use and other fish early life stages are present:
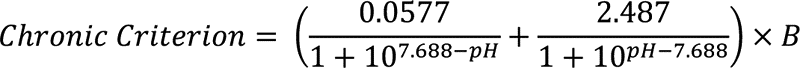 |
where: B |
= |
the lower of either 2.85, or 1.45 x 100.028 x (25-T). T = temperature in degrees Celsius. |
Applied as a thirty-day average concentration of total ammonia nitrogen (in mg N/L) not to be exceeded more than once every three years on the average. The highest four-day average within the thirty-day period should not exceed 2.5 times the chronic criterion. | |
h. | Measured in milligrams per liter rather than micrograms per liter. |
i. | ≤ (0.944)(e(1.128[ln(hardness)]-3.828)) at hardness = 100. Conversion factor (CF) of 0.944 is hardness dependent. CF is calculated for other hardnesses as follows: CF = 1.136672 - [(ln hardness)(0.041838)]. |
j. | ≤ (0.909)(e(0.7852[ln(hardness)]-3.490)) at hardness = 100. Conversions factor (CF) of 0.909 is hardness dependent. CF is calculated for other hardnesses as follows: CF = 1.101672 - [(ln hardness)(0.041838)]. |
k. | Criterion based on dissolved chloride in association with sodium. This criterion probably will not be adequately protective when the chloride is associated with potassium, calcium, or magnesium, rather than sodium. |
l. | Salinity dependent effects. At low salinity the 1-hour average may not be sufficiently protective. |
m. | ≤ (0.316)(e(0.8190[ ln(hardness)] + 3.688)) |
n. | ≤ (0.860)(e(0.8190[ ln(hardness)] + 1.561)) |
o. | ≤ (0.960)(e(0.9422[ ln(hardness)] - 1.464)) |
p. | ≤ (0.960)(e(0.8545[ ln(hardness)] - 1.465)) |
q. | ≤ (0.791)(e(1.273[ ln(hardness)] - 1.460)) at hardness = 100. Conversion factor (CF) of 0.791 is hardness dependent. CF is calculated for other hardnesses as follows: CF = 1.46203 - [(ln hardness)(0.145712)]. |
r. | ≤ (0.791)(e(1.273[ ln(hardness)] - 4.705)) at hardness = 100. Conversion factor (CF) of 0.791 is hardness dependent. CF is calculated for other hardnesses as follows: CF = 1.46203 - [(ln hardness)(0.145712)]. |
s. | If the four-day average chronic concentration is exceeded more than once in a three-year period, the edible portion of the consumed species should be analyzed. Said edible tissue concentrations shall not be allowed to exceed 1.0 mg/kg of methylmercury. |
t. | ≤ (0.998)(e(0.8460[ ln(hardness)] + 3.3612)) |
u. | ≤ (0.997)(e(0.8460[ ln(hardness)] + 1.1645)) |
v. | ≤ e[1.005(pH) - 5.290] |
w. | ≤ e[1.005(pH) - 4.830] |
x. | The status of the fish community should be monitored whenever the concentration of selenium exceeds 5.0 ug/ l in salt water. |
y. | ≤ (0.85)(e(1.72[ln(hardness)] - 6.52)) |
z. | Channel Catfish may be more acutely sensitive. |
aa. | ≤ (0.978)(e(0.8473[ln(hardness)] + 0.8604)) |
bb. | ≤ (0.986)(e(0.8473[ln(hardness)] + 0.7614)) |
cc. | Nonlethal effects (growth, C-14 uptake, and chlorophyll production) to diatoms (Thalassiosira aestivalis and Skeletonema costatum) which are common to Washington's waters have been noted at levels below the established criteria. The importance of these effects to the diatom populations and the aquatic system is sufficiently in question to persuade the state to adopt the USEPA National Criteria value (36 µg/L) as the state threshold criteria, however, wherever practical the ambient concentrations should not be allowed to exceed a chronic marine concentration of 21 µg/L. |
dd. | These ambient criteria in the table are for the dissolved fraction. The cyanide criteria are based on the weak acid dissociable method. The metals criteria may not be used to calculate total recoverable effluent limits unless the seasonal partitioning of the dissolved to total metals in the ambient water are known. When this information is absent, these metals criteria shall be applied as total recoverable values, determined by back-calculation, using the conversion factors incorporated in the criterion equations. Metals criteria may be adjusted on a site-specific basis when data are made available to the department clearly demonstrating the effective use of the water effects ratio approach established by USEPA, as generally guided by the procedures in USEPA Water Quality Standards Handbook, December 1983, as supplemented or replaced by USEPA or ecology. Information which is used to develop effluent limits based on applying metals partitioning studies or the water effects ratio approach shall be identified in the permit fact sheet developed pursuant to WAC 173-220-060 or 173-226-110, as appropriate, and shall be made available for the public comment period required pursuant to WAC 173-220-050 or 173-226-130(3), as appropriate. Ecology has developed supplemental guidance for conducting water effect ratio studies. |
ee. | The criteria for cyanide is based on the weak acid dissociable method in the 19th Ed. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 4500-CN I, and as revised (see footnote dd, above). |
ff. | These criteria are based on the total-recoverable fraction of the metal. |
gg. | Where methods to measure trivalent chromium are unavailable, these criteria are to be represented by total-recoverable chromium. |
hh. | The listed fresh water criteria are based on un-ionized or total ammonia concentrations, while those for marine water are based on un-ionized ammonia concentrations. Tables for the conversion of total ammonia to un-ionized ammonia for freshwater can be found in the USEPA's Quality Criteria for Water, 1986. Criteria concentrations based on total ammonia for marine water can be found in USEPA Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Ammonia (Saltwater)-1989, EPA440/5-88-004, April 1989. |
ii. | The conversion factor used to calculate the dissolved metal concentration was 0.982. |
jj. | The conversion factor used to calculate the dissolved metal concentration was 0.962. |
kk. | The conversion factor used to calculate the dissolved metal concentration was 0.85. |
ll. | Marine conversion factors (CF) which were used for calculating dissolved metals concentrations are given below. Conversion factors are applicable to both acute and chronic criteria for all metals except mercury. The CF for mercury was applied to the acute criterion only and is not applicable to the chronic criterion. Conversion factors are already incorporated into the criteria in the table. Dissolved criterion = criterion x CF |
Metal |
CF |
||
Arsenic |
1.000 |
||
Cadmium |
0.994 |
||
Chromium (VI) |
0.993 |
||
Copper |
0.83 |
||
Lead |
0.951 |
||
Mercury |
0.85 |
||
Nickel |
0.990 |
||
Selenium |
0.998 |
||
Silver |
0.85 |
||
Zinc |
0.946 |
||
mm. | The cyanide criteria are: 2.8µg/l chronic and 9.1µg/l acute and are applicable only to waters which are east of a line from Point Roberts to Lawrence Point, to Green Point to Deception Pass; and south from Deception Pass and of a line from Partridge Point to Point Wilson. The chronic criterion applicable to the remainder of the marine waters is l µg/L. |
(((4) USEPA Quality Criteria for Water, 1986, as revised, shall be used in the use and interpretation of the values listed in subsection (3) of this section.
(5) Concentrations of toxic, and other substances with toxic propensities not listed in subsection (3) of this section shall be determined in consideration of USEPA Quality Criteria for Water, 1986, and as revised, and other relevant information as appropriate. Human health-based water quality criteria used by the state are contained in 40 C.F.R. 131.36 (known as the National Toxics Rule).
(6) Risk-based criteria for carcinogenic substances shall be selected such that the upper-bound excess cancer risk is less than or equal to one in one million.))
Footnotes for human health criteria in Table 240: | |
A. | This criterion for total arsenic is the maximum contaminant level (MCL) developed under the Safe Drinking Water Act. The MCL for total arsenic is applied to surface waters where consumption of organisms-only and where consumption of water + organisms reflect the designated uses. When the department determines that a direct or indirect industrial discharge to surface waters designated for domestic water supply may be adding arsenic to its wastewater, the department will require the discharger to develop and implement a pollution prevention plan to reduce arsenic through the use of AKART. Industrial wastewater discharges to a privately or publicly owned wastewater treatment facility are considered indirect discharges. |
B. | This criterion was calculated based on an additional lifetime cancer risk of one-in-one-million (1 x 10-6 risk level). |
C. | This criterion is based on a regulatory level developed under the Safe Drinking Water Act. |
D. | This recommended water quality criterion is expressed as total cyanide, even though the integrated risk information system RfD used to derive the criterion is based on free cyanide. The multiple forms of cyanide that are present in ambient water have significant differences in toxicity due to their differing abilities to liberate the CN-moiety. Some complex cyanides require even more extreme conditions than refluxing with sulfuric acid to liberate the CN-moiety. Thus, these complex cyanides are expected to have little or no "bioavailability" to humans. If a substantial fraction of the cyanide present in a water body is present in a complexed form (e.g., Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3), this criterion may be overly conservative. |
E. | This criterion applies to total PCBs, (e.g., the sum of all congener or all isomer or homolog or Aroclor analyses). The PCBs criteria were calculated using a chemical-specific risk level of 4 x 10-5. Because that calculation resulted in a higher (less protective) concentration than the current criterion concentration (40 C.F.R. 131.36) the state made a chemical-specific decision to stay at the current criterion concentration. |
F. | This criterion was derived using the cancer slope factor of 1.4 (linearized multistage model with a twofold increase to 1.4 per mg/kg-day to account for continuous lifetime exposure from birth). |
G. | The human health criteria for mercury are contained in 40 C.F.R. 131.36. |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 11-09-090, filed 4/20/11, effective 5/21/11)
WAC 173-201A-420 Variance.
(((1) The criteria established in WAC 173-201A-200 through 173-201A-260 and 173-201A-600 through 173-201A-612 may be modified for individual facilities, or stretches of waters, through the use of a variance. Variances may be approved by the department when:
(a) The modification is consistent with the requirements of federal law (currently 40 C.F.R. 131.10(g) and 131.10(h));
(b) The water body is assigned variances for specific criteria and all other applicable criteria must be met; and
(c) Reasonable progress is being made toward meeting the original criteria.
(2) The decision to approve a variance is subject to a public and intergovernmental involvement process.
(3) The department may issue a variance for up to five years, and may renew the variance after providing for another opportunity for public and intergovernmental involvement and review.
(4) Variances are not in effect until they have been incorporated into this chapter and approved by the USEPA.)) (1) General provisions. Variances for individual facilities, a group of facilities, or stretches of waters may be issued for the criteria and designated uses established in WAC 173-201A-200 through 173-201A-260 and 173-201A-600 through 173-201A-612. The following conditions apply when considering issuance of a variance:
(a) A variance may be considered when the standards are expected to be attained by the end of the variance period or the attainable use cannot be reliably determined.
(b) The variance applies to specific parameters and all other applicable standards remain in effect for the water body.
(c) The modification must be consistent with the requirements of federal regulations (currently 40 C.F.R. 131.14).
(d) Reasonable progress must be made toward meeting the underlying standards during the variance period.
(e) A variance renewal may be considered if the renewal request meets the above conditions.
(2) Types of variances. Upon request or on its own initiative, the department will consider granting the following types of variances to existing water quality standards:
(a) An individual variance is a time-limited designated use and parameter-specific change to the standard(s) of the receiving water body for a specific discharger. The temporary standard(s) only apply at the point(s) of compliance for the individual facility.
(b) A multidischarger variance is a time-limited designated use and parameter-specific change to the standard(s) of any water body that receives discharges from a permitted facility defined within the scope of the multidischarger variance. Any permitted discharger that is defined within the scope of the variance may be covered under the variance that is granted by the department, provided all requirements of the variance for that discharger are met.
(c) A water body variance is a time-limited designated use and parameter-specific change to the standard(s) for a stretch of waters. Any discharger of the specific parameter that is defined within the geographic scope of the water body variance may be covered under the variance that is granted by the department, provided all requirements of the variance for that discharger are met.
(3) Requirements. Any entity initiating a variance request or applying for coverage for an individual, multidischarger, or water body variance must submit the following information to the department:
(a) The pollutant-specific criteria and designated use(s) proposed to be modified by the variance, and the proposed duration of the variance.
(b) A demonstration that attaining the water quality standard for a specific pollutant is not feasible for the requested duration of the variance based on 40 C.F.R. 131.14.
(c) An evaluation of treatment or alternative actions that were considered to meet effluent limits based on the underlying water quality criteria, and a description of why these options are not technically, economically, or otherwise feasible.
(d) Sufficient water quality data and analyses to characterize receiving and discharge water pollutant concentrations.
(e) A description and schedule of actions that the discharger(s) proposes to ensure the underlying water quality standard(s) are met or the highest attainable use is attained within the variance period. Dischargers are also required to submit a schedule for development and implementation of a pollutant minimization plan for the subject pollutant(s).
(f) If the variance is for a water body or stretch of water, the following information must also be provided to the department:
(i) The results from a pollutant source assessment that quantifies the contribution of pollution from permitted sources and nonpermitted sources;
(ii) All cost-effective and reasonable best management practices for permitted sources that address the pollutant the variance is based upon; and
(iii) Best management practices for nonpermitted sources that meet the requirements of chapter 90.48 RCW.
(g) Any additional information the department deems necessary to evaluate the application.
(4) Public review and notification. The decision to grant a variance is a formal rule making subject to a public and intergovernmental involvement process.
(a) The department will provide notice of the proposed variance and consult with Indian tribes or other states that have jurisdiction over adjacent and downstream waters of the proposed variance.
(b) The department shall maintain and make publicly available a list of dischargers that are covered under the variances that are in effect.
(5) Period during which the variance is in effect. A variance is a time-limited designated use and criterion.
(a) Each variance will be granted for the minimum time estimated to meet the underlying standard(s) or, if during the period of the variance it is determined that a designated use cannot be attained, then a use attainability analysis (WAC 173-201A-440) will be initiated.
(b) The ability to apply a variance in permits or other actions may be terminated by the department as a result of a mandatory interim review.
(c) Variances are in effect after they have been incorporated into this chapter and approved by the USEPA.
(6) Contents of a variance. At a minimum a variance adopted into rule will include the following:
(a) The time period for which the variance is applicable.
(b) The geographic area or specific waters in which the variance is applicable.
(c) A description of the permitted and unpermitted dischargers covered by the variance.
(d) Identification of required actions and a schedule, including any measurable milestones, for all pollution sources (permitted and unpermitted) subject to the variance. Dischargers are required to use adaptive management to fine-tune and update actions, schedules, and milestones in order to achieve the goals of the variance.
(e) A provision allowing the department to reopen and modify any permits and to revise BMP requirements for unpermitted dischargers as a result of the mandatory interim review of the variance (see subsection (8) of this section).
(7) Variance permit conditions. The department must establish and incorporate into NPDES permits all conditions necessary to implement and enforce an approved variance, including:
(a) Effluent limits that represent currently achieved or achievable effluent conditions, or effluent limits that are sufficient to meet the underlying water quality standard upon expiration of the variance;
(b) Monitoring and reporting requirements; and
(c) A provision allowing the department to reopen and modify the permits based on the mandatory interim review of the variance.
(8) Mandatory interim review. The department will conduct an interim review of each variance at least once every five years after the variance is adopted and approved to determine that conditions of the variance are being met and to evaluate whether the variance is still necessary.
(a) Review process for individual discharger and multidischarger variances:
(i) The review shall be coordinated with the public review process of the permit renewal if the variance is being implemented in a permit.
(ii) The review will be focused on the discharger's compliance with permit conditions that are required by the variance as well as an evaluation of whether the variance is still necessary.
(b) Review process for water body variances:
(i) Variances for stretches of waters will be reviewed in a public process conducted by the department every five years after the variance is adopted into this chapter and approved by the USEPA.
(ii) The review will evaluate whether the variance is still necessary, any new information on sources of the pollutant that indicates that reductions could be made that would allow water quality standards to be met in a shorter time frame, as well as any new information that indicates water quality improvements may require more time.
(c) A variance that applies to a permit will be shortened or terminated if the review determines that:
(i) The conditions and requirements of the variance and associated permit requirements have not been complied with unless reasons outside the control of the discharger prevented meeting any condition or requirement; or
(ii) Water quality standards could be met in a shorter time frame, based on new information submitted to the department.
NEW SECTION
WAC 173-201A-460 Intake credits.
(1) General provisions. The following provisions apply to the consideration of intake credits in determining reasonable potential and establishing water quality based effluent limits (WQBELs).
(a) An "intake pollutant" is the amount of a pollutant that is present in waters of the state (including groundwater except as provided in (c) of this subsection) at the time water is removed from the same body of water by the discharger or other facility supplying the discharger with intake water.
(b) An intake pollutant must be from the "same body of water" as the discharge in order to be eligible for an intake credit. An intake pollutant is considered to be from the "same body of water" as the discharge if the department finds that the intake pollutant would have reached the vicinity of the outfall point in the receiving water within a reasonable period had it not been removed by the permittee. This finding will be established if a discharger demonstrates:
(i) The background concentration of the pollutant in the receiving water (excluding any amount of the pollutant in the facility's discharge) is similar to that in the intake water; and
(ii) There is a direct hydrological connection between the intake and discharge points.
(c) An intake pollutant in groundwater partially or entirely due to human activity is not eligible for use of an intake credit.
(d) Where intake water for a facility is provided by a municipal water supply system and the supplier provides treatment of the raw water that removes an intake water pollutant, the concentration of the intake water pollutant will be determined at the point where the water enters the water supplier's distribution system.
(e) Where a facility discharges intake pollutants from multiple sources that originate from the receiving water body and from other water bodies, the department may derive an effluent limit reflecting the flow-weighted amount of each source of the pollutant provided that conditions in subsection (3) of this section are met and adequate monitoring to determine compliance can be established and is included in the permit.
(f) The department may also consider other site-specific factors relevant to the transport and fate of the pollutant to make the finding in a particular case that a pollutant would or would not have reached the vicinity of the outfall point in the receiving water within a reasonable period had it not been removed by the permittee.
(2) Consideration of intake pollutants in reasonable potential determination.
(a) The department may determine there is no reasonable potential for the discharge of an identified intake pollutant to cause or contribute to an exceedance of a narrative or numeric water quality criterion where a discharger demonstrates that all the following conditions are met:
(i) The facility removes the intake water containing the pollutant from the same body of water into which the discharge is made;
(ii) The facility does not alter the identified intake pollutant chemically or physically in a manner that would cause adverse water quality impacts to occur that would not occur if the pollutant had not been removed from the body of water;
(iii) The timing and location of the discharge would not cause adverse water quality impacts to occur that would not occur if the identified intake pollutant had not been removed from the body of water;
(iv) The facility does not increase the identified intake pollutant concentration at the edge of the mixing zone, or at the point of discharge if a mixing zone is not allowed, as compared to the pollutant concentration in the intake water, unless the increased concentration does not cause or contribute to an excursion above an applicable water quality standard; and
(v) The facility does not contribute any additional mass of the identified intake pollutant to its wastewater.
(b) Upon a finding under (a) of this subsection that an intake pollutant in the discharge does not cause, have the reasonable potential to cause, or contribute to an exceedance of an applicable water quality standard, the department is not required to include a water quality-based effluent limit for the identified intake pollutant in the facility's permit.
(3) Consideration of intake pollutants in establishing water quality based effluent limits.
(a) This subsection applies only when the ambient background concentration of the intake pollutant does not meet the most stringent applicable water quality criterion for that pollutant;
(b) The requirements of subsection (2)(a)(i) and (iv) also apply to this subsection.
(c) A discharger may add mass of the pollutant to its waste stream if an equal or greater mass is removed prior to discharge, so there is no net addition of the pollutant in the discharge compared to the intake water.
(d) Where the conditions of this subsection are met, the department may establish effluent limits using an intake credit. The facility's permit must specify how compliance with the limits will be assessed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-14-129, filed 7/1/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 173-201A-510 Means of implementation.
(1) Permitting. The primary means to be used for controlling municipal, commercial, and industrial waste discharges shall be through the issuance of waste discharge permits, as provided for in RCW 90.48.160, 90.48.162, and 90.48.260. Waste discharge permits, whether issued pursuant to the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System or otherwise, must be conditioned so the discharges authorized will meet the water quality standards. No waste discharge permit can be issued that causes or contributes to a violation of water quality criteria, except as provided for in this chapter.
(a) Persons discharging wastes in compliance with the terms and conditions of permits are not subject to civil and criminal penalties on the basis that the discharge violates water quality standards.
(b) Permits must be modified by the department when it is determined that the discharge causes or contributes to a violation of water quality standards. Major modification of permits is subject to review in the same manner as the originally issued permits.
(2) Miscellaneous waste discharge or water quality effect sources. The director shall, through the issuance of regulatory permits, directives, and orders, as are appropriate, control miscellaneous waste discharges and water quality effect sources not covered by subsection (1) of this section.
(3) Nonpoint source and storm water pollution.
(a) Activities which generate nonpoint source pollution shall be conducted so as to comply with the water quality standards. The primary means to be used for requiring compliance with the standards shall be through best management practices required in waste discharge permits, rules, orders, and directives issued by the department for activities which generate nonpoint source pollution.
(b) Best management practices shall be applied so that when all appropriate combinations of individual best management practices are utilized, violation of water quality criteria shall be prevented. If a discharger is applying all best management practices appropriate or required by the department and a violation of water quality criteria occurs, the discharger shall modify existing practices or apply further water pollution control measures, selected or approved by the department, to achieve compliance with water quality criteria. Best management practices established in permits, orders, rules, or directives of the department shall be reviewed and modified, as appropriate, so as to achieve compliance with water quality criteria.
(c) Activities which contribute to nonpoint source pollution shall be conducted utilizing best management practices to prevent violation of water quality criteria. When applicable best management practices are not being implemented, the department may conclude individual activities are causing pollution in violation of RCW 90.48.080. In these situations, the department may pursue orders, directives, permits, or civil or criminal sanctions to gain compliance with the standards.
(d) Activities which cause pollution of storm water shall be conducted so as to comply with the water quality standards. The primary means to be used for requiring compliance with the standards shall be through best management practices required in waste discharge permits, rules, orders, and directives issued by the department for activities which generate storm water pollution. The consideration and control procedures in (b) and (c) of this subsection apply to the control of pollutants in storm water.
(4) General allowance for compliance schedules.
(a) Permits((,)) and orders((, and directives of)) issued by the department for existing discharges may include a schedule for achieving compliance with effluent limits and water quality ((criteria contained in this chapter)) standards that apply to:
(i) Aquatic life uses; and
(ii) Uses other than aquatic life.
((Such)) (b) Schedules of compliance shall be developed to ensure final compliance with all water quality-based effluent limits and the water quality standards in the shortest practicable time. ((Decisions regarding)) The department will decide whether to issue schedules of compliance ((will be made)) on a case-by-case basis ((by the department)). Schedules of compliance may not be issued for new discharges. Examples of schedules of compliance that may be issued ((to allow for)) include:
(i) Construction of necessary treatment capability;
(ii) Implementation of necessary best management practices;
(iii) Implementation of additional storm water best management practices for discharges determined not to meet water quality ((criteria)) standards following implementation of an initial set of best management practices; and
(iv) Completion of necessary water quality studies((; or (v) resolution of a pending water quality standards' issue through rule-making action)) related to implementation of permit requirements to meet effluent limits.
(((b))) (c) For the period of time during which compliance with water quality ((criteria)) standards is deferred, interim effluent ((limitations)) limits shall be formally established, based on the best professional judgment of the department. Interim effluent ((limitations)) limits may be numeric or nonnumeric (e.g., construction of necessary facilities by a specified date as contained in an ((ecology)) order or permit), or both.
(((c))) (d) Prior to establishing a schedule of compliance, the department shall require the discharger to evaluate the possibility of achieving water quality ((criteria)) standards via nonconstruction changes (e.g., facility operation, pollution prevention). Schedules of compliance ((may in no case exceed ten years, and)) shall meet requirements in WAC 173-220-140 and shall require compliance with the specified requirements as soon as practicable. Compliance schedules shall generally not exceed the term of any permit unless the department determines that a longer time period is needed to come into compliance with the applicable water quality standards.
(e) When an approved total maximum daily load, or TMDL, has established waste load allocations for permitted dischargers, a longer period of time for a compliance schedule may be authorized if the department has determined that:
(i) The permittee is not able to meet its waste load allocation in the TMDL solely by controlling and treating its own effluent;
(ii) The permittee has made significant progress to reduce pollutant loading during the term of the permit;
(iii) The permittee is meeting all of its requirements under the TMDL as soon as possible; and
(iv) Actions specified in the compliance schedule are sufficient to achieve water quality standards as soon as possible.
(5) Compliance schedules for dams:
(a) All dams in the state of Washington must comply with the provisions of this chapter.
(b) For dams that cause or contribute to a violation of the water quality standards, the dam owner must develop a water quality attainment plan that provides a detailed strategy for achieving compliance. The plan must include:
(i) A compliance schedule that does not exceed ten years;
(ii) Identification of all reasonable and feasible improvements that could be used to meet standards, or if meeting the standards is not attainable, then to achieve the highest attainable level of improvement;
(iii) Any department-approved gas abatement plan as described in WAC 173-201A-200 (1)(f)(ii);
(iv) Analytical methods that will be used to evaluate all reasonable and feasible improvements;
(v) Water quality monitoring, which will be used by the department to track the progress in achieving compliance with the state water quality standards; and
(vi) Benchmarks and reporting sufficient for the department to track the applicant's progress toward implementing the plan within the designated time period.
(c) The plan must ensure compliance with all applicable water quality criteria, as well as any other requirements established by the department (such as through a total maximum daily load, or TMDL, analysis).
(d) If the department is acting on an application for a water quality certification, the approved water quality attainment plan may be used by the department in its determination that there is reasonable assurance that the dam will not cause or contribute to a violation of the water quality standards.
(e) When evaluating compliance with the plan, the department will allow the use of models and engineering estimates to approximate design success in meeting the standards.
(f) If reasonable progress toward implementing the plan is not occurring in accordance with the designated time frame, the department may declare the project in violation of the water quality standards and any associated water quality certification.
(g) If an applicable water quality standard is not met by the end of the time provided in the attainment plan, or after completion of all reasonable and feasible improvements, the owner must take the following steps:
(i) Evaluate any new reasonable and feasible technologies that have been developed (such as new operational or structural modifications) to achieve compliance with the standards, and develop a new compliance schedule to evaluate and incorporate the new technology;
(ii) After this evaluation, if no new reasonable and feasible improvements have been identified, then propose an alternative to achieve compliance with the standards, such as site specific criteria (WAC 173-201A-430), a use attainability analysis (WAC 173-201A-440), or a water quality offset (WAC 173-201A-450).
(h) New dams, and any modifications to existing facilities that do not comply with a gas abatement or other pollution control plan established to meet criteria for the water body, must comply with the water quality standards at the time of project completion.
(i) Structural changes made as a part of a department approved gas abatement plan to aid fish passage, described in WAC 173-201A-200 (1)(f)(ii), may result in system performance limitations in meeting water quality criteria for that parameter at other times of the year.
(6) Combined sewer overflow treatment plant. The influent to these facilities is highly variable in frequency, volume, duration, and pollutant concentration. The primary means to be used for requiring compliance with the human health criteria shall be through the application of narrative limitations which include, but are not limited to, best management practices required in waste discharge permits, rules, orders and directives issued by the department.