WSR 24-07-009
EMERGENCY RULES
DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
[Filed March 7, 2024, 8:46 a.m., effective March 7, 2024, 8:46 a.m.]
Effective Date of Rule: Immediately upon filing.
Purpose: This rule-making order amends chapter 16-470 WAC, Quarantine—Agricultural pests, to expand the boundaries of the internal quarantine for Japanese beetle within Washington state. The quarantine prohibits the movement of regulated articles located inside the quarantine area from moving outside of it. The quarantine prevents potentially infested host material from being transported to other parts of the state, thereby limiting the spread of Japanese beetle and protecting noninfested areas from infestation.
Additionally, this rule-making order adds soil samples as a regulated article and specifies conditions governing the movement of soil samples from internal quarantined areas. It also adds a requirement that any business located in the internal quarantine area that is selling regulated articles under WAC 16-470-710 (4) or (7) must post signage developed by the department of agriculture (department) clearly stating that regulated articles purchased cannot be transported outside of the quarantine area. The rule amendment clarifies that under WAC 16-470-710(7), "cut flowers for decorative purposes" includes those flowers that are exposed to open air environments during their harvest, transportation, or trade. Lastly, the amendment adds a condition for the transport of cut flowers grown in the quarantined area to areas outside the quarantined area.
Citation of Rules Affected by this Order: New WAC 16-470-711; and amending WAC 16-470-705, 16-470-710, and 16-470-717.
Under RCW
34.05.350 the agency for good cause finds that immediate adoption, amendment, or repeal of a rule is necessary for the preservation of the public health, safety, or general welfare, and that observing the time requirements of notice and opportunity to comment upon adoption of a permanent rule would be contrary to the public interest.
Reasons for this Finding: Immediate amendment of the rule is necessary for the general welfare of the public and is necessary to protect the forest, agricultural, horticultural, floricultural, beekeeping, and environmental interests of this state. Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica Newman) is a highly invasive plant pest native to Japan. It has been known to cause severe damage to more than 300 species of ornamental and agricultural plants, including roses, grapes, and hops. Adult beetles damage plants by skeletonizing foliage and feeding on buds, flowers, and fruit. The larvae also damage the roots of plants, such as turf grass. Although this feeding does not always kill the plant, it weakens it and may reduce the plant's overall yield.
In 2021, the department caught 24,048 Japanese beetles in the current internal quarantine area. Throughout 2021, 2022, and 2023, the department took extensive measures to reduce the spread of the beetle, with an ultimate goal of eradicating it. Measures that have been taken include treating residential and public properties with pesticide, trapping, and establishing an internal quarantine. Despite these efforts, by the end of the 2022 trapping season, numerous Japanese beetles, which indicate a reproducing population, were caught outside of the currently established internal quarantine area. This occurred again in 2023, with beetles being caught even further outside of the internal quarantine area than in 2022. Due to this, immediate action is needed to expand the internal Japanese beetle quarantine to reflect the area of infestation more accurately and strengthen the quarantine's protections. Further, the department believes that adding soil samples as a regulated article, requiring signage be posted for businesses selling certain regulated articles, and clarifying the requirement around cut flowers is necessary to prevent the beetles' further dissemination within this state and to protect the state's forest, agricultural, horticultural, floricultural, beekeeping, and environmental interests.
If Japanese beetle becomes permanently established throughout the state, it could severely threaten several of Washington's agricultural industries. The threat this pest poses is particularly concerning due to the area in which the detections have occurred. There are a number of farms and nurseries in close proximity to the detection sites growing plant species known to be targeted by Japanese beetle. Not only do these beetles pose a threat to the plants themselves but, if established, they have the potential to impact the availability of export markets for agricultural commodities grown in the area. Expanding the Japanese beetle internal quarantine and other proposed quarantine amendments will help prevent the spread of this invasive pest and protect Washington's agricultural industries, as well as maintain access to national and international markets.
Number of Sections Adopted in Order to Comply with Federal Statute: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0; Federal Rules or Standards: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0; or Recently Enacted State Statutes: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0.
Number of Sections Adopted at the Request of a Nongovernmental Entity: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0.
Number of Sections Adopted on the Agency's own Initiative: New 1, Amended 3, Repealed 0.
Number of Sections Adopted in Order to Clarify, Streamline, or Reform Agency Procedures: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0.
Number of Sections Adopted using Negotiated Rule Making: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0; Pilot Rule Making: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0; or Other Alternative Rule Making: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0.
Date Adopted: March 7, 2024.
Derek I. Sandison
Director
OTS-5250.1
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-17-068, filed 8/15/22, effective 9/15/22)
WAC 16-470-705Areas under quarantine.
(1) Exterior: The entire states of Alabama, Arkansas, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Vermont, Virginia, West Virginia, Wisconsin, the District of Columbia, the Provinces of Ontario and Quebec, and any other state, province, parish, or county where infestations of Japanese beetle are detected are declared to be under quarantine for Japanese beetle.
(a) The director may exempt individual counties of the states under quarantine from meeting the conditions in WAC 16-470-715 if the director determines that:
(i) The state has adopted and is enforcing restrictions on the interstate and intrastate movement of regulated articles that are equivalent to or exceed the restrictions placed on the movement of regulated articles as provided in WAC 16-470-715; and
(ii) Annual surveys are conducted in such counties and the results of these surveys are negative for Japanese beetle; and
(iii) One or more neighboring counties are not subject to an unacceptable heavy Japanese beetle infestation.
(b) A plant health official of any state may request exemption of one or more counties under this subsection. The request must be in writing, and it must state the area surveyed, the survey method, personnel conducting the survey, and dates of any previous Japanese beetle infestations in that county.
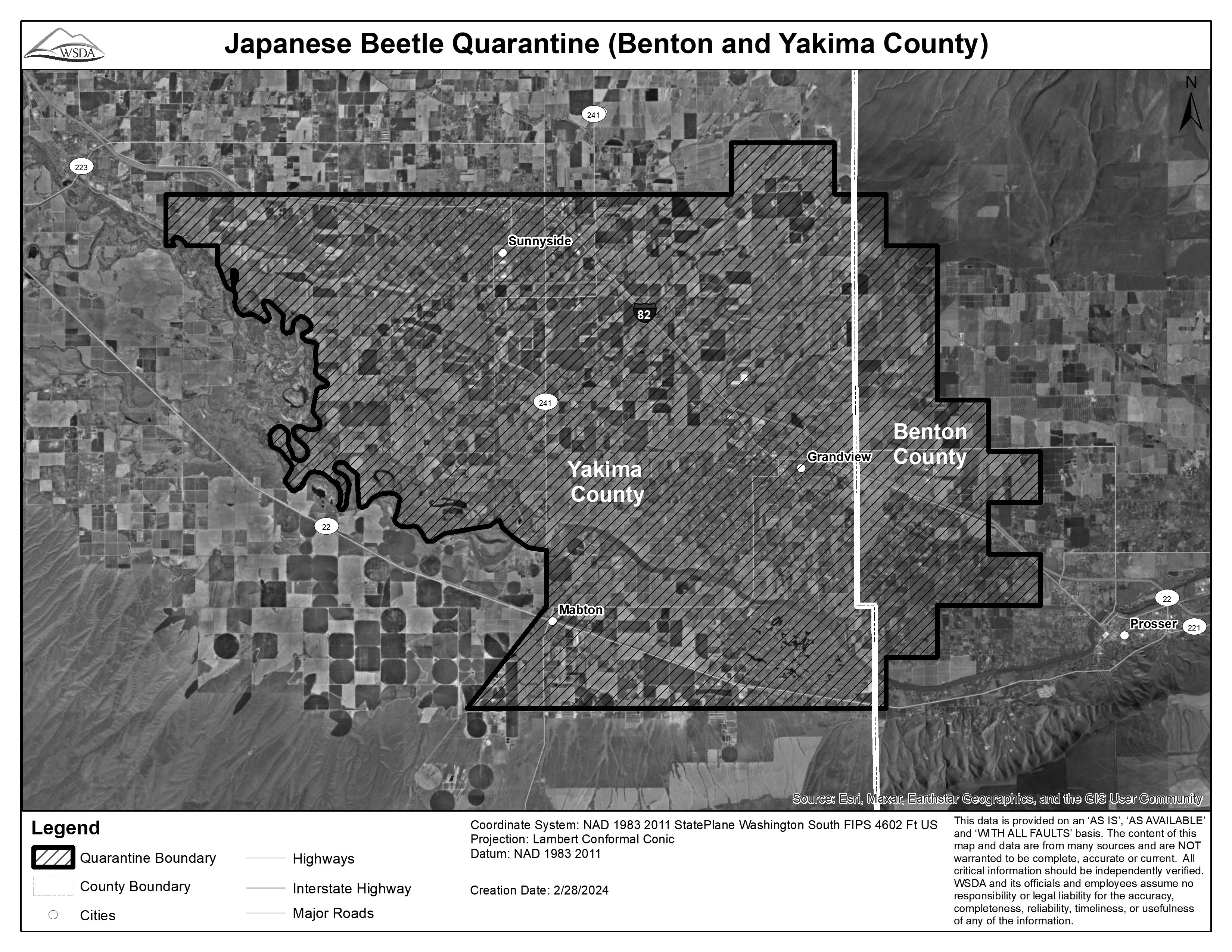
(2) Interior: Within the state of Washington, those areas where infestations of Japanese beetle exist are declared to be under quarantine. These areas include the portion of Yakima and Benton counties designated as follows: Beginning within Yakima County at latitude ((N46°18'8" and longitude W120°0'26"; thence easterly across the Yakima-Benton County line to latitude N46°18'5" and longitude W119°51'39"; thence southerly to latitude N46°16'21" and longitude W119°51'40"; thence easterly to longitude W119°50'25"; thence southerly to latitude N46°13'44" and longitude W119°50'27"; thence westerly to latitude N46°13'44" and longitude W119°51'42"; thence southerly to latitude N46°12'00" and longitude W119°51'42"; thence westerly across the Yakima-Benton County line to latitude N46°12'3" and longitude W119°59'14"; thence northerly to latitude N46°14'39" and longitude W119°59'12"; thence westerly to longitude W120°0'28"))N46°19'54" and longitude W120°09'12"; thence easterly to latitude N46°19'51" and longitude W119°55'24"; thence northerly to latitude N46°20'43" and longitude W119°55'23"; thence easterly to latitude N46°20'42" and longitude W119°52'53"; thence southerly to N46°19'50" and longitude W119°52'53"; thence easterly across the Yakima-Benton County line to latitude N46°19'50"; and longitude W119°51'38" southerly to latitude N46°18'57" and longitude W119°51'39"; thence easterly to latitude N46°18'57" and longitude W119°50'24"; thence southerly to latitude N46°16'21" and longitude W119°50'25"; thence easterly to latitude N46°16'20" and longitude W119°49'10"; thence southerly to latitude N46°15'28" and longitude W119°49'11"; thence easterly to latitude N46°15'28" and longitude W119°47'56"; thence southerly to latitude N46°14'35" and longitude W119°47'56"; thence westerly to latitude N46°14'36" and longitude W119°49'12"; thence southerly to latitude N46°13'44" and longitude W119°49'12"; thence easterly to N46°13'43" and longitude W119°47'57"; thence southerly to latitude N46°12'51" and longitude W119°47'58"; thence westerly to latitude N46°12'52" and longitude W119°50'28"; thence southerly to latitude N46°11'60" and longitude W119°50'29"; thence westerly to latitude N46°12'00" and longitude W119°51'44"; thence southerly to latitude N46°11'08" and longitude W119°51'44"; thence westerly to latitude N46°11'11" and longitude W120°01'55"; thence northerly and easterly along the Yakama Nation Reservation boundary line; thence northerly and turning westerly along the Yakama Nation Reservation boundary to latitude N46°18'42" and longitude W120°07'57"; then northerly to latitude N46°19'02" and longitude W120°07'57"; then westerly to latitude N46°19'02" and longitude W120°08'42"; thence northerly and westerly and turning southerly along the Yakama Nation Reservation boundary to latitude N46°19'02" and longitude W120°09'00"; thence westerly to latitude N46°19'02" and longitude W120°09'12"; thence northerly to the point of beginning.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-17-068, filed 8/15/22, effective 9/15/22)
WAC 16-470-710Regulated articles.
The following are declared to be hosts or possible carriers of Japanese beetle and are regulated articles under the Japanese beetle quarantine:
(1) The upper eight inches of topsoil containing vegetative material from all properties including, but not limited to, residential, agricultural, and commercial properties (including construction sites);
(2) Humus and compost (except when produced commercially), ((and)) growing media (except when commercially packaged), and soil samples;
(3) Yard debris, meaning plant material commonly created in the course of maintaining yards and gardens and through horticulture, gardening, landscaping, or similar activities. Yard debris includes, but is not limited to, grass clippings, leaves, branches, brush, weeds, flowers, roots, windfall fruit, and vegetable garden debris;
(4) Plants for planting and propagation, except when dormant and bareroot and free from soil or growing media, including:
(a) All plants with roots;
(b) Plant crowns or roots;
(c) Bulbs;
(d) Corms;
(e) Tubers; and
(f) Rhizomes;
(5) Turfgrass (sod);
(6) Hop bines and unshucked corn ears harvested during the Japanese beetle adult flight season (May 15th through October 15th);
(7) Cut flowers for decorative purposes, including those exposed to open air environments during their harvest, transportation, or trade; and
(8) Any other plant, plant part, article, or means of conveyance when it is determined by the director to present a hazard of spreading live Japanese beetle due to either infestation, or exposure to infestation.
NEW SECTION
WAC 16-470-711Signage requirements.
Any business selling regulated articles under WAC 16-470-710 (4) or (7) which is located within the interior quarantine area (see WAC 16-470-705(2)) must post signage which is clearly visible at all business entrances, as well as points of sale and aisles in areas where these regulated articles are being sold. Businesses must use signage developed by or approved by the department, which must clearly state that regulated articles purchased cannot be transported outside of the quarantine area. Signs may be found on the department's website at http://agr.wa.gov/beetles and must be a minimum of 8.5" x 11" in size.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-17-068, filed 8/15/22, effective 9/15/22)
WAC 16-470-717Conditions governing the movement of regulated articles from internal quarantined areas.
Regulated articles within the state of Washington quarantined areas are prohibited from moving outside the quarantined area (from all properties, including commercial and private properties), except as provided for below:
(1) The upper eight inches of topsoil containing vegetative material from all properties; humus and compost (except when produced commercially), ((and)) growing media (except when commercially packaged), and soil samples, may be allowed to move from the quarantine area if they are first treated by one of the following methods. Treatments must be monitored by the department for compliance.
(a) Steam heated to a temperature of 140 degrees Fahrenheit for one hour, to kill all life stages of Japanese beetle;
(b) Soil samples may be transported to a laboratory for testing outside of the quarantine area if they are securely double bagged and clearly labeled with the following statement, "This soil sample originates from a Japanese beetle quarantine area. Sample must either be securely double bagged prior to disposal or incinerated." Laboratories located within Washington state that are receiving soil samples originating from the quarantine area must either securely double bag the samples prior to disposal or incinerate the samples.
(c) Other treatments determined to be effective at eradicating Japanese beetle and approved in writing by the director.
(2) Yard debris may be allowed to move from the quarantine area if it is first treated by one of the following methods. Treatments must be monitored by the department for compliance.
(a) Steam heated to a temperature of 140 degrees Fahrenheit for one hour, to kill all life stages of Japanese beetle;
(b) When consisting solely of woody materials containing no soil, yard debris may be chipped to a screen size of one inch in two dimensions or smaller during the Japanese beetle adult flight season (May 15th through October 15th). Woody material containing no soil can be moved outside of the Japanese beetle adult flight season without chipping;
(c) Another treatment determined to be effective at eradicating Japanese beetle and approved in writing by the director.
(3) Plants for planting and propagation (except when dormant and bareroot and free from soil or growing media), all plants with roots, plant crowns or roots, bulbs, corms, tubers and rhizomes, and turfgrass (sod) may be allowed to move from the quarantine area if each shipment complies with one of the treatment or inspection requirements detailed under (a) through (f) of this subsection. Before the shipment moves outside the quarantined area, the shipment must be approved by the department. Approval will be documented by the issuance of a certificate of treatment or inspection when the department determines that the shipment is in compliance with the treatment or inspection requirements. The certificate must accompany the shipment while the shipment is in transit. Treated plants must be safeguarded from reinfestation prior to shipping. Plants shipped dormant and bareroot with no soil or growing media attached are exempt from these requirements, and should be identified as bareroot on shipping documents.
(a) Production in an approved Japanese beetle free greenhouse/screenhouse. All the following criteria apply to be approved as a Japanese beetle free greenhouse/screenhouse. All media must be sterilized and free of soil. All planting stock must be free of soil (bareroot) before planting into the approved medium. The potted plants must be maintained within the greenhouse/screenhouse during the entire adult flight period (May 15th through October 15th). During the adult flight period, the greenhouse/screenhouse must be made secure so that adult Japanese beetles cannot enter. Such security measures must be approved by the department. No Japanese beetle contaminated material shall be allowed into the secured area at any time. The greenhouse/screenhouse will be officially inspected by the department for the presence of all life stages of Japanese beetle and must be specifically approved as a secure area. The plants and their growing medium must be appropriately protected from subsequent infestation while being stored, packed, and shipped. Certified greenhouse/screenhouse nursery stock may not be transported into or through any infested areas unless identity is preserved and adequate safeguards are applied to prevent possible infestation. Each greenhouse/screenhouse operation must be approved by the department as having met and maintained the above criteria. The certificate accompanying the plants shall bear the following additional declaration: "The rooted plants (or crowns) were produced in an approved Japanese beetle free greenhouse or screenhouse and were grown in sterile, soilless media."
(b) Production during a pest free window. The entire rooted plant production cycle (planting, growth, harvest, and shipping) will be completed within a pest free window (October 16th through May 14th), in clean containers with sterilized and soilless growing medium, and shipment will occur outside the adult Japanese beetle flight period (May 15th through October 15th). The accompanying phytosanitary certificate shall bear the following additional declaration: "These plants were produced outside the Japanese beetle flight season and were grown in sterile, soilless media."
(c) Application of approved regulatory treatments. All treatments will be performed under direct supervision of the department or under a compliance agreement. Treatments and procedures under a compliance agreement will be monitored throughout the season. State phytosanitary certificates listing and verifying the treatment used must accompany the shipment. Note that not all treatments or methods approved in the U.S. Domestic Japanese Beetle Harmonization Plan are acceptable for use within Washington state. The phytosanitary certificate shall bear the following additional declaration: "The rooted plants are in soilless media and were treated to control Popillia japonica according to the criteria for shipment to Category 1 states as provided in the U.S. Domestic Japanese Beetle Harmonization Plan and Washington state's Japanese beetle quarantine."
(d) Dip treatment - Not an approved treatment.
(e) Drench treatments - Container plants only. Not approved for ornamental grasses or sedges. Not approved for field potted plants. Potting media used must be sterile and soilless, containers must be clean. Only containerized nursery stock with rootballs 12 inches in diameter or smaller and free from field soil are eligible. This is a prophylactic treatment protocol targeting eggs and early first instar larvae. If the containers are exposed to a second flight season, they must be retreated with an approved insecticide. Chemicals approved for drench treatments of container plants under this protocol can be found in the Japanese Beetle National Harmonization Plan for shipping to a Category 1 state, and must be labeled for use in Washington state.
(f) Media (granule) incorporation - Container plants only. Not approved for ornamental grasses or sedges. Only containerized nursery stock with rootballs 12 inches in diameter or smaller, planted in approved growing media, and free from field soil are eligible. Plants grown in field soil and then potted into soilless container substrates are not eligible for certification using this protocol, unless all field soil is removed from the roots so plants are bareroot at the time of potting. All pesticides used for media incorporation must be mixed thoroughly into the media before potting and plants should be watered at least two times following media incorporation before shipment can begin. Approved growing media used must be free from soil and consist of synthetic or other substances (other than soil) used singly or in combinations. Examples of approved growing media include conifer bark, hardwood bark, expanded or baked clay pellets, expanded polystyrene beads, floral foam, ground coconut husk, ground cocoa pods, ground coffee hulls, ground rice husk, peat, perlite, pumice, recycled paper, rock wool, sawdust, sphagnum, styrofoam, synthetic sponge, vermiculite, and volcanic ash or cinder. The media shall contain only substances that were not used previously for growing plants or other agricultural purposes. It must be free of plant pests, sand, and related matter, and safeguarded in such a manner as to prevent the introduction of all life stages of Japanese beetle to the media. The granules must be incorporated into the media before potting. Plants being stepped up into treated potting media must first have undergone an approved drench treatment to eliminate any untreated volume of potting medium. This treatment protocol targets eggs and early first instar larvae and allows for certification of plants that have been exposed to only one flight season after application. If the containers are to be exposed to a second flight season, they must be repotted with a granular incorporated mix or retreated using one of the approved drench treatments. Chemicals approved for media (granule) incorporation for container plants under this protocol can be found in the Japanese Beetle National Harmonization Plan for shipping to a Category 1 state, and must be labeled for use in Washington state.
(4) Hop bines and unshucked corn ears: Fields where hops or corn (intended to be shipped unshucked) are planted must be trapped and monitored by the department and found free of Japanese beetle for the entire adult flight period (May 15th through October 15th), or from the date of planting up to the date of harvest if both dates are within the flight period. Fields that are not sufficiently trapped will not be considered free from Japanese beetle. If the field is found free of Japanese beetle by the department, bines and unshucked corn ears may be moved outside the quarantined area. If the department determines there is evidence of Japanese beetle presence, bines and unshucked corn ears must be treated prior to harvest or movement by a method approved by the director in advance. All shipments of hop bines and unshucked corn ears to areas outside the quarantined area must be accompanied by a compliance document issued by the department stating the field of origin and destination addresses. If a shipment is found to contain Japanese beetles, any further shipments from that field must be in vehicles sufficiently closed/covered to prevent reinfestation after treatment.
(5) Cut flowers for decorative purposes: All shipments of cut flowers grown in the quarantined area, to areas outside the quarantined area must be accompanied by a compliance document issued by the department stating the field of origin and destination address. If a shipment is found to contain Japanese beetles, any further shipments from that field must be in vehicles sufficiently closed/covered to prevent reinfestation after treatment.