(1) Identification. Verify all slings have legible identification information attached to the sling which includes the following information:
(a) Name or trademark of the manufacturer;
(b) Manufacturer's code or stock number;
(c) Type of fiber material;
(d) Rated loads for the types of hitches used, and the angle that the load is based on;
(e) Number of legs, if more than one;
(f) Repairing agency, if the sling has ever been repaired.
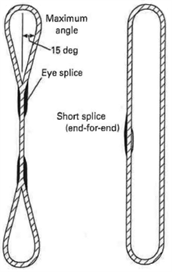 |
Figure 23 Synthetic Fiber Rope Slings |
(2) Inspection.
(a) A qualified person must inspect synthetic fiber rope slings before their initial use, according to Table 23, both:
(i) When the sling is new; and
(ii) Whenever a repair, alteration, or modification has been done.
(b) A qualified person must perform a visual inspection for damage, each day or shift the synthetic fiber rope sling is used. Immediately remove any sling from service that is damaged beyond the criteria listed in Table 23.
(c) A qualified person must perform periodic inspections on synthetic fiber rope slings, according to Table 23.
(i) Examine each sling and component individually, taking care to expose and examine all surfaces.
(ii) Inspect the entire length including splices, end attachments, and fittings.
(iii) Remove slings from use if any of the conditions in Table 23 are found.
(iv) Keep a record of the most recent periodic inspection available, including the condition of the sling.
Note: | An external code mark on the sling is an acceptable means of recording the inspection as long as the code can be traced back to a record. |
Table 23
Synthetic Rope Sling Inspection and Removal Criteria
Inspect synthetic rope slings for the following conditions: | Perform inspections: | |||
• | Missing or illegible sling identification; | |||
• | Cuts, gouges, or areas of extensive fiber breakage along the length; | |||
• | Abraded areas on the rope; | • | At least once a year for slings in normal service; | |
• | Damage that is estimated to have reduced the effective diameter of the rope by more than 10%; | • | At least once a quarter for slings in severe service; | |
• | Uniform fiber breakage along the major part of the length of the rope in the sling such that the entire rope appears covered with fuzz or whiskers; | • | As recommended by a qualified person for slings in special service. | |
• | Inside the rope, fiber breakage, fused or melted fiber (observed by prying or twisting to open the strands) involving damage estimated at 10% of the fiber in any strand or the rope as a whole; | |||
• | Discoloration, brittle fibers, and hard or stiff areas that may indicate chemical, ultraviolet or heat damage; | |||
• | Dirt and grit in the interior of the rope structure that is deemed excessive; | |||
• | Foreign matter that has permeated the rope, making it difficult to handle and attracting and holding grit; | |||
• | Kinks or distortion in the rope structure, particularly if caused by forcibly pulling on loops (known as hockles); | |||
• | Melted, hard, or charred areas that affect more than 10% of the diameter of the rope or affect several adjacent strands along the length that affect more than 10% of strand diameters; | |||
• | Poor condition of thimbles or other components manifested by corrosion, cracks, distortion, sharp edges, or localized wear; | |||
• | Hooks that have any of the following conditions: | |||
– | Any visibly apparent bend or twist from the plane of the unbent hook; | |||
– | Any distortion causing an increase in throat opening 5%, not to exceed one-quarter inch, or as recommended by the manufacturer; | |||
– | Wear exceeding 10%, of the original section dimension of the hook or its load pin, or as recommended by the manufacturer; | |||
– | Self-locking mechanism that does not lock. | |||
• | Other visible damage that raises doubt about the safety of the sling. | |||
(3) Repair, alteration, or modifications. Meet the following requirements when repairing synthetic rope slings:
(a) Synthetic rope slings must only be repaired by the manufacturer or a qualified person;
(b) Mark the sling to show the repairing agency;
(c) Use components that meet the requirements of this part for sling repair;
(d) Do not repair slings by knotting or resplicing existing sling ropes;
(e) Proof load test repaired slings according to the requirements in subsection (4) of this section.
(4) Proof load test. The sling manufacturer or a qualified person must proof load test repaired slings and slings incorporating previously used or welded fittings before initial use, according to Table 24:
Table 24
Synthetic Rope Sling Proof Load Requirements
Type of equipment: | Proof load test: | |
• | Single leg slings; | To a minimum of two times the single leg vertical hitch rated load. |
• | Multiple leg slings; | |
• | Endless slings; | |
• | Fittings attached to single legs. | |
Master links for two-leg bridle slings. | To a minimum of 4 times the single leg vertical hitch rated load. | |
Master links for 3-leg bridle slings. | To a minimum of 6 times the single leg vertical hitch rated load. | |
Master links for 4-leg bridle slings. | To a minimum of 8 times the single leg vertical hitch rated load. | |
(5) Rated load.
Note: | Rated loads are based on the following factors: |
• Strength of the sling material; | |
• Design factor; | |
• Type of hitch (see Figure 24, Hitch Types for Synthetic Rope Slings); | |
• Angle of loading (see Figure 18, Angle of Loading); | |
• Diameter of curvature over which the sling is used (see Figure 19, D/d Ratio). |
(a) You must use synthetic rope slings within the rated loads shown in Tables 18 and 19 in ASME B30.9-2010. For angles that are not shown in these tables, either use the rated load for the next lower angle or one calculated by a qualified person.
(b) Rate slings with the load capacity of the lowest rated component of the sling. For example, if you use fittings that are rated lower than the sling material itself, identify the sling with the lower-rated capacity.
(c) The use of horizontal sling angles less than 30 degrees is prohibited, unless recommended by the sling manufacturer or a qualified person. (See Figure 18.)
(d) Rated loads for slings used in a choker hitch must conform to the values shown in the above referenced tables, provided that the angle of choke is 120 degrees or greater.
(e) Use Figure 20, the manufacturer, or a qualified person to determine the rated load if the angle of choke in a choker hitch is less than 120 degrees.
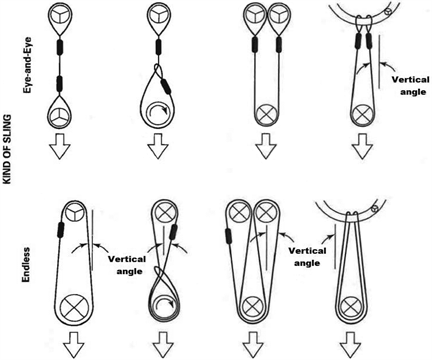 |
Figure 24 Hitch Types for Synthetic Rope Slings |
The symbols below represent load or support in contact with the rope sling. The contact surface diameter divided by the rope diameter is designated D/d ratio as described in Figure 19. | |
 | Represents a contact surface which must have a diameter of curvature at least double the diameter of the rope from which the sling is made. |
 | Represents a contact surface which must have a diameter of curvature at least 8 times the diameter of the rope. |
 | Represents a load in choker hitch and illustrates the rotary force on the load and/or the slippage of the rope in contact with the load. Diameter of curvature of load surface must be at least double the diameter of the rope. |
Note: | Legs 5 degrees or less from vertical may be considered vertical. For slings more than 5 degrees vertical, the actual angle must be used. |
(6) Use of synthetic ropes.
(a) Use synthetic rope slings safely by doing all of the following:
(i) Shorten or adjust slings only with methods approved by the manufacturer or qualified person;
(ii) You must not shorten or lengthen slings by knotting or twisting;
(iii) Hitch slings in a way that provides control of the load;
(iv) You must protect slings in contact with edges, corners, protrusions, or abrasive surfaces with a material of sufficient strength, thickness, and construction to prevent damage, see Figure 14;
(v) Do not allow the sling or load to rotate when hand-tucked slings are used in a single-leg vertical lift application; and
(vi) Keep all parts of the human body from between the sling and the load, crane, or hoist hook.
(b) All of the following is prohibited:
(i) Intentional shock loading; and
(ii) Twisting or kinking.