(1) Toxic substances shall not be introduced above natural background levels in waters of the state which have the potential either singularly or cumulatively to adversely affect characteristic water uses, cause acute or chronic toxicity to the most sensitive biota dependent upon those waters, or adversely affect public health, as determined by the department.
(2) The department shall employ or require chemical testing, acute and chronic toxicity testing, and biological assessments, as appropriate, to evaluate compliance with subsection (1) of this section and to ensure that aquatic communities and the existing and designated uses of waters are being fully protected.
(3) USEPA Quality Criteria for Water, 1986, as revised, shall be used in the use and interpretation of the values listed in subsection (5) of this section.
(4) Concentrations of toxic, and other substances with toxic propensities not listed in Table 240 of this section shall be determined in consideration of USEPA Quality Criteria for Water, 1986, and as revised, and other relevant information as appropriate.
(5) The following criteria, found in Table 240, shall be applied to all surface waters of the state of Washington. Values are µg/L for all substances except ammonia and chloride which are mg/L, and asbestos which is million fibers/L. The department shall formally adopt any appropriate revised criteria as part of this chapter in accordance with the provisions established in chapter 34.05 RCW, the Administrative Procedure Act. The department shall ensure there are early opportunities for public review and comment on proposals to develop revised criteria.
(a) Aquatic life protection. The department may revise the criteria in Table 240 for aquatic life on a statewide or water body-specific basis as needed to protect aquatic life occurring in waters of the state and to increase the technical accuracy of the criteria being applied. The department shall formally adopt any appropriate revised criteria as part of this chapter in accordance with the provisions established in chapter 34.05 RCW, the Administrative Procedure Act.
(b) Human health protection. The following provisions apply to the human health criteria in Table 240. All waters shall maintain a level of water quality when entering downstream waters that provides for the attainment and maintenance of the water quality standards of those downstream waters, including the waters of another state. The human health criteria in the tables were calculated using a fish consumption rate of 175 g/day. Criteria for carcinogenic substances were calculated using a cancer risk level equal to one-in-one-million, or as otherwise specified in this chapter. The human health criteria calculations and variables include chronic durations of exposure up to seventy years. All human health criteria for metals are for total metal concentrations, unless otherwise noted. Dischargers have the obligation to reduce toxics in discharges through the use of AKART.
Table 240
Toxics Substances Criteria
Compound/Chemical | Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS)# | Category | Aquatic Life Criteria - Freshwater | Aquatic Life Criteria - Marine Water | Human Health Criteria for Consumption of: | |||
Acute | Chronic | Acute | Chronic | Water & Organisms | Organisms Only | |||
Metals: | ||||||||
Antimony | 7440360 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | - | - | - | - | 12 | 180 |
Arsenic | 7440382 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | 360.0 (c,dd) | 190.0 (d,dd) | 69.0 (c,ll,dd) | 36.0 (d,cc,ll,dd) | 10 (A) | 10 (A) |
Asbestos | 1332214 | Toxic pollutants and hazardous substances | - | - | - | - | 7,000,000 fibers/L (C) | - |
Beryllium | 7440417 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Cadmium | 7440439 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | (i,c,dd) | (j,d,dd) | 42.0 (c,dd) | 9.3 (d,dd) | - | - |
Chromium (III) | 16065831 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | (m,c,gg) | (n,d,gg) | - | - | - | - |
Chromium (VI) | 18540299 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | 15.0 (c,l,ii,dd) | 10.0 (d,jj,dd) | 1,100.0 (c,l,ll,dd) | 50.0 (d,ll,dd) | - | - |
Copper | 7440508 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | (o,c,dd) | (p,d,dd) | 4.8 (c,ll,dd) | 3.1 (d,ll,dd) | 1,300 (C) | - |
Lead | 7439921 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | (q,c,dd) | (r,d,dd) | 210.0 (c,ll,dd) | 8.1 (d,ll,dd) | - | - |
Mercury | 7439976 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | 2.1 (c,kk,dd) | 0.012 (d,ff,s) | 1.8 (c,ll,dd) | 0.025 (d,ff,s) | (G) | (G) |
Methylmercury | 22967926 | Nonconventional | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Nickel | 7440020 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | (t,c,dd) | (u,d,dd) | 74.0 (c,ll,dd) | 8.2 (d,ll,dd) | 150 | 190 |
Selenium | 7782492 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | 20.0 (c,ff) | 5.0 (d,ff) | 290 (c,ll,dd) | 71.0 (d,x,ll,dd) | 120 | 480 |
Silver | 7440224 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | (y,a,dd) | - | 1.9 (a,ll,dd) | - | - | - |
Thallium | 7440280 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | - | - | - | - | 0.24 | 0.27 |
Zinc | 7440666 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | (aa,c,dd) | (bb,d,dd) | 90.0 (c,ll,dd) | 81.0 (d,ll,dd) | 2,300 | 2,900 |
Other chemicals: | ||||||||
1,1,1-Trichloroethane | 71556 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 47,000 | 160,000 |
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane | 79345 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.12 (B) | 0.46 (B) |
1,1,2-Trichloroethane | 79005 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.44 (B) | 1.8 (B) |
1,1-Dichloroethane | 75343 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | - | - |
1,1-Dichloroethylene | 75354 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 1200 | 4100 |
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene | 120821 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.12 (B) | 0.14 (B) |
1,2-Dichlorobenzene | 95501 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 2000 | 2500 |
1,2-Dichloroethane | 107062 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 9.3 (B) | 120 (B) |
1,2-Dichloropropane | 78875 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.71 (B) | 3.1 (B) |
1,3-Dichloropropene | 542756 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.24 (B) | 2 (B) |
1,2-Diphenylhydrazine | 122667 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.015 (B) | 0.023 (B) |
1,2-Trans-Dichloroethylene | 156605 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 600 | 5,800 |
1,3-Dichlorobenzene | 541731 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 13 | 16 |
1,4-Dichlorobenzene | 106467 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 460 | 580 |
2,3,7,8-TCDD (Dioxin) | 1746016 | Dioxin | - | - | - | - | 0.000000064 | 0.000000064 |
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol | 88062 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.25 (B) | 0.28 (B) |
2,4-Dichlorophenol | 120832 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | 25 | 34 |
2,4-Dimethylphenol | 105679 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | 85 | 97 |
2,4-Dinitrophenol | 51285 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | 60 | 610 |
2,4-Dinitrotoluene | 121142 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.039 (B) | 0.18 (B) |
2,6-Dinitrotoluene | 606202 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
2-Chloroethyvinyl Ether | 110758 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | - | - |
2-Chloronaphthalene | 91587 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 170 | 180 |
2-Chlorophenol | 95578 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | 15 | 17 |
2-Methyl-4,6-Dinitrophenol (4,6-dinitro-o-cresol) | 534521 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | 7.1 | 25 |
2-Nitrophenol | 88755 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine | 91941 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.0031 (B) | 0.0033 (B) |
3-Methyl-4-Chlorophenol (parachlorometa cresol) | 59507 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | 36 | 36 |
4,4'-DDD | 72548 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 0.000036 (B) | 0.000036 (B) |
4,4'-DDE | 72559 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 0.000051 (B) | 0.000051 (B) |
4,4'-DDT | 50293 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 0.000025 (B) | 0.000025 (B) |
4,4'-DDT(and metabolites) | Pesticides/PCBs | 1.1 (a) | 0.001 (b) | 0.13 (a) | 0.001 (b) | - | - | |
4-Bromophenyl Phenyl Ether | 101553 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
4-Chorophenyl Phenyl Ether | 7005723 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
4-Nitrophenol | 100027 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Acenaphthene | 83329 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 110 | 110 |
Acenaphthylene | 208968 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Acrolein | 107028 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 1.0 | 1.1 |
Acrylonitrile | 107131 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.019 (B) | 0.028 (B) |
Aldrin | 309002 | Pesticides/PCBs | 2.5 (a,e) | 0.0019 (b,e) | 0.71 (a,e) | 0.0019 (b,e) | 0.0000057 (B) | 0.0000058 (B) |
alpha-BHC | 319846 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 0.0005 (B) | 0.00056 (B) |
alpha-Endosulfan | 959988 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 9.7 | 10 |
Anthracene | 120127 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 3,100 | 4,600 |
Benzene | 71432 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.44 (B) | 1.6 (B) |
Benzidine | 92875 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.00002 (B) | 0.000023 (B) |
Benzo(a) Anthracene | 56553 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.014 (B) | 0.021 (B) |
Benzo(a) Pyrene | 50328 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.0014 (B) | 0.0021 (B) |
Benzo(b) Fluoranthene | 205992 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.014 (B) | 0.021 (B) |
Benzo(ghi) Perylene | 191242 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Benzo(k) Fluoranthene | 207089 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.014 (B) | 0.21 (B) |
beta-BHC | 319857 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 0.0018 (B) | 0.002 (B) |
beta-Endosulfan | 33213659 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 9.7 | 10 |
Bis(2-Chloroethoxy) Methane | 111911 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Ether | 111444 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.02 (B) | 0.06 (B) |
Bis(2-Chloroisopropyl) Ether | 39638329 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate | 117817 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.23 (B) | 0.25 (B) |
Bromoform | 75252 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 5.8 (B) | 27 (B) |
Butylbenzyl Phthalate | 85687 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.56 (B) | 0.58 (B) |
Carbon Tetrachloride | 56235 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.2 (B) | 0.35 (B) |
Chlordane | 57749 | Pesticides/PCBs | 2.4 (a) | 0.0043 (b) | 0.09 (a) | 0.004 (b) | 0.000093 (B) | 0.000093 (B) |
Chlorobenzene | 108907 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 380 | 890 |
Chlorodibromomethane | 124481 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.65 (B) | 3 (B) |
Chloroethane | 75003 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Chloroform | 67663 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 260 | 1200 |
Chrysene | 218019 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 1.4 (B) | 2.1 (B) |
Cyanide | 57125 | Metals, cyanide, and total phenols | 22.0 (c,ee) | 5.2 (d,ee) | 1.0 (c,mm,ee) | (d,mm,ee) | 19 (D) | 270 (D) |
delta-BHC | 319868 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Dibenzo(a,h) Anthracene | 53703 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.0014 (B) | 0.0021 (B) |
Dichlorobromomethane | 75274 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.77 (B) | 3.6 (B) |
Dieldrin | 60571 | Pesticides/PCBs | 2.5 (a,e) | 0.0019 (b,e) | 0.71 (a,e) | 0.0019 (b,e) | 0.0000061 (B) | 0.0000061 (B) |
Diethyl Phthalate | 84662 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 4,200 | 5,000 |
Dimethyl Phthalate | 131113 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 92,000 | 130,000 |
Di-n-Butyl Phthalate | 84742 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 450 | 510 |
Di-n-Octyl Phthalate | 117840 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Endosulfan | Pesticides/PCBs | 0.22 (a) | 0.056 (b) | 0.034 (a) | 0.0087 (b) | - | - | |
Endosulfan Sulfate | 1031078 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 9.7 | 10 |
Endrin | 72208 | Pesticides/PCBs | 0.18 (a) | 0.0023 (b) | 0.037 (a) | 0.0023 (b) | 0.034 | 0.035 |
Endrin Aldehyde | 7421934 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 0.034 | 0.035 |
Ethylbenzene | 100414 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 200 | 270 |
Fluoranthene | 206440 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 16 | 16 |
Fluorene | 86737 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 420 | 610 |
Hexachlorocyclohexane (gamma-BHC; Lindane) | 58899 | Pesticides/PCBs | 2.0 (a) | 0.08 (b) | 0.16 (a) | - | 15 | 17 |
Heptachlor | 76448 | Pesticides/PCBs | 0.52 (a) | 0.0038 (b) | 0.053 (a) | 0.0036 (b) | 0.0000099 (B) | 0.00001 (B) |
Heptachlor Epoxide | 1024573 | Pesticides/PCBs | - | - | - | - | 0.0000074 (B) | 0.0000074 (B) |
Hexachlorobenzene | 118741 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.000051 (B) | 0.000052 (B) |
Hexachlorobutadiene | 87683 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.69 (B) | 4.1 (B) |
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | 77474 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 150 | 630 |
Hexachloroethane | 67721 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.11 (B) | 0.13 (B) |
Indeno(1,2,3-cd) Pyrene | 193395 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.014 (B) | 0.021 (B) |
Isophorone | 78591 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 27 (B) | 110 (B) |
Methyl Bromide | 74839 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 520 | 2,400 |
Methyl Chloride | 74873 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Methylene Chloride | 75092 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 16 (B) | 250 (B) |
Napthalene | 91203 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Nitrobenzene | 98953 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 55 | 320 |
N-Nitrosodimethylamine | 62759 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.00065 (B) | 0.34 (B) |
N-Nitrosodi-n-Propylamine | 621647 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.0044 (B) | 0.058 (B) |
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine | 86306 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 0.62 (B) | 0.69 (B) |
Pentachlorophenol (PCP) | 87865 | Acid compounds | (w,c) | (v,d) | 13.0 (c) | 7.9 (d) | 0.046 (B) | 0.1 (B) |
Phenanthrene | 85018 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Phenol | 108952 | Acid compounds | - | - | - | - | 18,000 | 200,000 |
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) | Pesticides/PCBs | 2.0 (b) | 0.014 (b) | 10.0 (b) | 0.030 (b) | 0.00017 (E) | 0.00017 (E) | |
Pyrene | 129000 | Base/neutral compounds | - | - | - | - | 310 | 460 |
Tetrachloroethylene | 127184 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 4.9 (B) | 7.1 (B) |
Toluene | 108883 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 180 | 410 |
Toxaphene | 8001352 | Pesticides/PCBs | 0.73 (c,z) | 0.0002 (d) | 0.21 (c,z) | 0.0002 (d) | 0.000032 (B) | 0.000032 (B) |
Trichloroethylene | 79016 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.38 (B) | 0.86 (B) |
Vinyl Chloride | 75014 | Volatile | - | - | - | - | 0.02 (B, F) | 0.26 (B, F) |
Ammonia (hh) | Nonconventional | (f,c) | (g,d) | 0.233 (h,c) | 0.035 (h,d) | - | - | |
Chloride (dissolved) (k) | Nonconventional | 860.0 (h,c) | 230.0 (h,d) | - | - | - | - | |
Chlorine (total residual) | Nonconventional | 19.0 (c) | 11.0 (d) | 13.0 (c) | 7.5 (d) | - | - | |
Chlorpyrifos | Toxic pollutants and hazardous substances | 0.083 (c) | 0.041 (d) | 0.011 (c) | 0.0056 (d) | - | - | |
Parathion | Toxic pollutants and hazardous substances | 0.065 (c) | 0.013 (d) | - | - | - | - | |
Footnotes for aquatic life criteria in Table 240: | |
a. | An instantaneous concentration not to be exceeded at any time. |
b. | A 24-hour average not to be exceeded. |
c. | A 1-hour average concentration not to be exceeded more than once every three years on the average. |
d. | A 4-day average concentration not to be exceeded more than once every three years on the average. |
e. | Aldrin is metabolically converted to Dieldrin. Therefore, the sum of the Aldrin and Dieldrin concentrations are compared with the Dieldrin criteria. |
f. | Shall not exceed the numerical value in total ammonia nitrogen (mg N/L) given by: |
For salmonids present: | 0.275 | + | 39.0 |
1 + 107.204-pH | 1 + 10pH-7.204 | ||
For salmonids absent: | 0.411 | + | 58.4 |
1 + 107.204-pH | 1 + 10pH-7.204 |
g. | Shall not exceed the numerical concentration calculated as follows: |
Unionized ammonia concentration for waters where salmonid habitat is an existing or designated use: |
0.80 ÷ (FT)(FPH)(RATIO) | ||||
where: | RATIO | = | 13.5; 7.7 ≤ pH ≤ 9 | |
RATIO | = | (20.25 x 10(7.7-pH)) ÷ (1 + 10(7.4-pH)); 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 7.7 | ||
FT | = | 1.4; 15 ≤ T ≤ 30 | ||
FT | = | 10[0.03(20-T)]; 0 ≤ T ≤ 15 | ||
FPH | = | 1; 8 ≤ pH ≤ 9 | ||
FPH | = | (1 + 10(7.4-pH)) ÷ 1.25; 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 8.0 | ||
Total ammonia concentrations for waters where salmonid habitat is not an existing or designated use and other fish early life stages are absent:
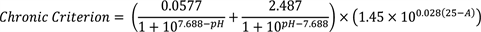 |
where: A | = | the greater of either T (temperature in degrees Celsius) or 7. |
Applied as a thirty-day average concentration of total ammonia nitrogen (in mg N/L) not to be exceeded more than once every three years on average. The highest four-day average within the thirty-day period should not exceed 2.5 times the chronic criterion.
Total ammonia concentration for waters where salmonid habitat is not an existing or designated use and other fish early life stages are present:
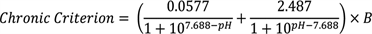 |
where: B | = | the lower of either 2.85, or 1.45 x 100.028 x (25-T). T = temperature in degrees Celsius. |
Applied as a thirty-day average concentration of total ammonia nitrogen (in mg N/L) not to be exceeded more than once every three years on the average. The highest four-day average within the thirty-day period should not exceed 2.5 times the chronic criterion. | |
h. | Measured in milligrams per liter rather than micrograms per liter. |
i. | ≤ (0.944)(e(1.128[ln(hardness)]-3.828)) at hardness = 100. Conversion factor (CF) of 0.944 is hardness dependent. CF is calculated for other hardnesses as follows: CF = 1.136672 - [(ln hardness)(0.041838)]. |
j. | ≤ (0.909)(e(0.7852[ln(hardness)]-3.490)) at hardness = 100. Conversions factor (CF) of 0.909 is hardness dependent. CF is calculated for other hardnesses as follows: CF = 1.101672 - [(ln hardness)(0.041838)]. |
k. | Criterion based on dissolved chloride in association with sodium. This criterion probably will not be adequately protective when the chloride is associated with potassium, calcium, or magnesium, rather than sodium. |
l. | Salinity dependent effects. At low salinity the 1-hour average may not be sufficiently protective. |
m. | ≤ (0.316)(e(0.8190[ ln(hardness)] + 3.688)) |
n. | ≤ (0.860)(e(0.8190[ ln(hardness)] + 1.561)) |
o. | ≤ (0.960)(e(0.9422[ ln(hardness)] - 1.464)) |
p. | ≤ (0.960)(e(0.8545[ ln(hardness)] - 1.465)) |
q. | ≤ (0.791)(e(1.273[ ln(hardness)] - 1.460)) at hardness = 100. Conversion factor (CF) of 0.791 is hardness dependent. CF is calculated for other hardnesses as follows: CF = 1.46203 - [(ln hardness)(0.145712)]. |
r. | ≤ (0.791)(e(1.273[ ln(hardness)] - 4.705)) at hardness = 100. Conversion factor (CF) of 0.791 is hardness dependent. CF is calculated for other hardnesses as follows: CF = 1.46203 - [(ln hardness)(0.145712)]. |
s. | If the four-day average chronic concentration is exceeded more than once in a three-year period, the edible portion of the consumed species should be analyzed. Said edible tissue concentrations shall not be allowed to exceed 1.0 mg/kg of methylmercury. |
t. | ≤ (0.998)(e(0.8460[ ln(hardness)] + 3.3612)) |
u. | ≤ (0.997)(e(0.8460[ ln(hardness)] + 1.1645)) |
v. | ≤ e[1.005(pH) - 5.290] |
w. | ≤ e[1.005(pH) - 4.830] |
x. | The status of the fish community should be monitored whenever the concentration of selenium exceeds 5.0 ug/ l in salt water. |
y. | ≤ (0.85)(e(1.72[ln(hardness)] - 6.52)) |
z. | Channel Catfish may be more acutely sensitive. |
aa. | ≤ (0.978)(e(0.8473[ln(hardness)] + 0.8604)) |
bb. | ≤ (0.986)(e(0.8473[ln(hardness)] + 0.7614)) |
cc. | Nonlethal effects (growth, C-14 uptake, and chlorophyll production) to diatoms (Thalassiosira aestivalis and Skeletonema costatum) which are common to Washington's waters have been noted at levels below the established criteria. The importance of these effects to the diatom populations and the aquatic system is sufficiently in question to persuade the state to adopt the USEPA National Criteria value (36 µg/L) as the state threshold criteria, however, wherever practical the ambient concentrations should not be allowed to exceed a chronic marine concentration of 21 µg/L. |
dd. | These ambient criteria in the table are for the dissolved fraction. The cyanide criteria are based on the weak acid dissociable method. The metals criteria may not be used to calculate total recoverable effluent limits unless the seasonal partitioning of the dissolved to total metals in the ambient water are known. When this information is absent, these metals criteria shall be applied as total recoverable values, determined by back-calculation, using the conversion factors incorporated in the criterion equations. Metals criteria may be adjusted on a site-specific basis when data are made available to the department clearly demonstrating the effective use of the water effects ratio approach established by USEPA, as generally guided by the procedures in USEPA Water Quality Standards Handbook, December 1983, as supplemented or replaced by USEPA or ecology. The adjusted site specific criteria are not in effect until they have been incorporated into this chapter and approved by EPA. Information which is used to develop effluent limits based on applying metals partitioning studies or the water effects ratio approach shall be identified in the permit fact sheet developed pursuant to WAC 173-220-060 or 173-226-110, as appropriate, and shall be made available for the public comment period required pursuant to WAC 173-220-050 or 173-226-130(3), as appropriate. Ecology has developed supplemental guidance for conducting water effect ratio studies. |
ee. | The criteria for cyanide is based on the weak acid dissociable method in the 19th Ed. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 4500-CN I, and as revised (see footnote dd, above). |
ff. | These criteria are based on the total-recoverable fraction of the metal. |
gg. | Where methods to measure trivalent chromium are unavailable, these criteria are to be represented by total-recoverable chromium. |
hh. | The listed fresh water criteria are based on un-ionized or total ammonia concentrations, while those for marine water are based on un-ionized ammonia concentrations. Tables for the conversion of total ammonia to un-ionized ammonia for freshwater can be found in the USEPA's Quality Criteria for Water, 1986. Criteria concentrations based on total ammonia for marine water can be found in USEPA Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Ammonia (Saltwater)-1989, EPA440/ 5-88-004, April 1989. |
ii. | The conversion factor used to calculate the dissolved metal concentration was 0.982. |
jj. | The conversion factor used to calculate the dissolved metal concentration was 0.962. |
kk. | The conversion factor used to calculate the dissolved metal concentration was 0.85. |
ll. | Marine conversion factors (CF) which were used for calculating dissolved metals concentrations are given below. Conversion factors are applicable to both acute and chronic criteria for all metals except mercury. The CF for mercury was applied to the acute criterion only and is not applicable to the chronic criterion. Conversion factors are already incorporated into the criteria in the table. Dissolved criterion = criterion x CF |
Metal | CF | ||
Arsenic | 1.000 | ||
Cadmium | 0.994 | ||
Chromium (VI) | 0.993 | ||
Copper | 0.83 | ||
Lead | 0.951 | ||
Mercury | 0.85 | ||
Nickel | 0.990 | ||
Selenium | 0.998 | ||
Silver | 0.85 | ||
Zinc | 0.946 | ||
mm. | The cyanide criteria are: 2.8µg/l chronic and 9.1µg/l acute and are applicable only to waters which are east of a line from Point Roberts to Lawrence Point, to Green Point to Deception Pass; and south from Deception Pass and of a line from Partridge Point to Point Wilson. The chronic criterion applicable to the remainder of the marine waters is l µg/L. |
Footnotes for human health criteria in Table 240: | |
A. | This criterion for total arsenic is the maximum contaminant level (MCL) developed under the Safe Drinking Water Act. The MCL for total arsenic is applied to surface waters where consumption of organisms-only and where consumption of water + organisms reflect the designated uses. When the department determines that a direct or indirect industrial discharge to surface waters designated for domestic water supply may be adding arsenic to its wastewater, the department will require the discharger to develop and implement a pollution prevention plan to reduce arsenic through the use of AKART. Industrial wastewater discharges to a privately or publicly owned wastewater treatment facility are considered indirect discharges. |
B. | This criterion was calculated based on an additional lifetime cancer risk of one-in-one-million (1 x 10-6 risk level). |
C. | This criterion is based on a regulatory level developed under the Safe Drinking Water Act. |
D. | This recommended water quality criterion is expressed as total cyanide, even though the integrated risk information system RfD used to derive the criterion is based on free cyanide. The multiple forms of cyanide that are present in ambient water have significant differences in toxicity due to their differing abilities to liberate the CN-moiety. Some complex cyanides require even more extreme conditions than refluxing with sulfuric acid to liberate the CN-moiety. Thus, these complex cyanides are expected to have little or no "bioavailability" to humans. If a substantial fraction of the cyanide present in a water body is present in a complexed form (e.g., Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3), this criterion may be overly conservative. |
E. | This criterion applies to total PCBs, (e.g., the sum of all congener or all isomer or homolog or Aroclor analyses). The PCBs criteria were calculated using a chemical-specific risk level of 4 x 10-5. Because that calculation resulted in a higher (less protective) concentration than the current criterion concentration (40 C.F.R. 131.36) the state made a chemical-specific decision to stay at the current criterion concentration. |
F. | This criterion was derived using the cancer slope factor of 1.4 (linearized multistage model with a twofold increase to 1.4 per mg/kg-day to account for continuous lifetime exposure from birth). |
G. | The human health criteria for mercury are contained in 40 C.F.R. 131.36. |