(Effective until October 29, 2023)
Section C202.13—M.
MANUAL. Capable of being operated by personal intervention (see "Automatic").
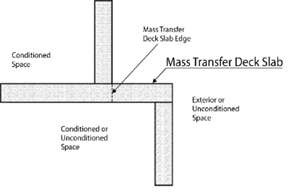
MASS TRANSFER DECK SLAB EDGE. That portion of the above-grade wall made up of the concrete slab where it extends past the footprint of the floor above, and there is space (conditioned or unconditioned) below the slab. The area of the slab edge shall be defined as the thickness of the slab multiplied by the perimeter of the edge condition. Examples of this condition include, but are not limited to, the transition from an above-grade structure to a below-grade structure or the transition from a tower to a podium. Cantilevered balconies do not meet this definition.
MECHANICAL COOLING. Reducing the temperature of a gas or liquid by using vapor compression, absorption, desiccant dehumidification combined with evaporative cooling, or another energy-driven thermodynamic cycle. Indirect or direct evaporative cooling alone is not considered mechanical cooling.
MECHANICAL HEATING. Raising the temperature of a gas or liquid by use of fossil fuel burners, electric resistance heaters, heat pumps, or other systems that require energy to operate.
MECHANICAL LOAD COEFFICIENT (MLC). In a data center, the ratio of the cooling system's net use of energy to that of the ITE. The design MLC is calculated for a local peak weather condition (stipulated in ASHRAE Standard 90.4) and equals the sum of all active cooling equipment input power, divided by total power into the ITE. The annual MLC is calculated using hourly TMY3 weather data for the data center's location and equals the sum of all energy flowing into the cooling system to respond to that weather, minus any energy successfully recovered to avoid any new energy use, all divided by the energy flowing into the ITE during the same period.
METAL BUILDING ROOF. A roof that:
1. Is constructed with a metal, structural, weathering surface;
2. Has no ventilated cavity; and
3. Has the insulation entirely below deck (i.e., does not include composite concrete and metal deck construction nor a roof framing system that is separated from the superstructure by a wood substrate) and whose structure consists of one or more of the following configurations:
a. Metal roofing in direct contact with the steel framing members;
b. Metal roofing separated from the steel framing members by insulation;
c. Insulated metal roofing panels installed as described in a or b.
METAL BUILDING WALL. A wall whose structure consists of metal spanning members supported by steel structural members (i.e., does not include spandrel glass or metal panels in curtain wall systems).
METER. A device that measures the flow of energy.
MICROCELL. A wireless communication facility consisting of an antenna that is either: (a) Four (4) feet in height and with an area of not more than 580 square inches; or (b) if a tubular antenna, no more than four (4) inches in diameter and no more than six (6) feet in length; and the associated equipment cabinet that is six (6) feet or less in height and no more than 48 square feet in floor area.
[Statutory Authority: RCW
19.27A.020,
19.27A.025,
19.27A.160 and chapter
19.27 RCW. WSR 19-24-040, § 51-11C-20213, filed 11/26/19, effective 7/1/20. Statutory Authority: RCW
19.27A.025,
19.27A.160, and
19.27.074. WSR 16-03-072, § 51-11C-20213, filed 1/19/16, effective 7/1/16. Statutory Authority: RCW
19.27A.020,
19.27A.025 and chapters
19.27 and
34.05 RCW. WSR 13-04-056, § 51-11C-20213, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13.]
(Effective October 29, 2023)
Section C202.13—M.
MANUAL. Capable of being operated by personal intervention (see "Automatic").
MASS TRANSFER DECK SLAB. A concrete slab designed to transfer structural load from the building perimeter wall or column line above, laterally to an offset wall or column line below, and which has conditioned or semiheated space on the inside of the upper wall and exterior or unconditioned space on the outside of the upper wall. The area of the slab edge shall be defined as the thickness of the slab multiplied by the length of the edge condition. Examples of this condition include, but are not limited to, the transition from an above-grade structure to a below-grade structure or the transition from a tower to a podium. A cantilevered concrete balcony does not constitute a mass transfer deck slab.
MECHANICAL COOLING. Reducing the temperature of a gas or liquid by using vapor compression, absorption, desiccant dehumidification combined with evaporative cooling, or another energy-driven thermodynamic cycle. Indirect or direct evaporative cooling alone is not considered mechanical cooling.
MECHANICAL HEATING. Raising the temperature of a gas or liquid by use of fossil fuel burners, electric resistance heaters, heat pumps, or other systems that require energy to operate.
MECHANICAL LOAD COEFFICIENT (MLC). In a data center, the ratio of the cooling system's net use of energy to that of the ITE. The annual MLC is calculated using hourly weather data for the data center's location and equals the sum of all energy flowing into the cooling system to respond to that weather, minus any energy successfully recovered to avoid any new energy use, all divided by the energy flowing into the ITE during the same period.
MECHANICAL ROOM. A room or space in which mechanical equipment and appliances are located that has sufficient room for access and maintenance of the equipment or appliances with room energy doors closed.
METAL BUILDING ROOF. A roof that:
1. Is constructed with a metal, structural, weathering surface;
2. Has no ventilated cavity; and
3. Has the insulation entirely below deck (i.e., does not include composite concrete and metal deck construction nor a roof framing system that is separated from the superstructure by a wood substrate) and whose structure consists of one or more of the following configurations:
a. Metal roofing in direct contact with the steel framing members;
b. Metal roofing separated from the steel framing members by insulation;
c. Insulated metal roofing panels installed as described in a or b.
METAL BUILDING WALL. A wall whose structure consists of metal spanning members supported by steel structural members (i.e., does not include spandrel glass or metal panels in curtain wall systems).
METER. A device that measures the flow of energy.
MICROCELL. A wireless communication facility consisting of an antenna that is either: (a) Four (4) feet in height and with an area of not more than 580 square inches; or (b) if a tubular antenna, no more than four (4) inches in diameter and no more than six (6) feet in length; and the associated equipment cabinet that is six (6) feet or less in height and no more than 48 square feet in floor area.
MULTI-PASS HEAT PUMP WATER HEATER. A heat pump water heater control strategy requiring multiple passes of water through the heat pump to reach the final target storage water temperature.
[Statutory Authority: RCW
19.27A.020,
19.27A.025,
19.27A.160 and chapters
19.27A and
19.27 RCW. WSR 22-14-091 and 23-12-101, § 51-11C-20213, filed 7/1/22 and 6/7/23, effective 10/29/23. Statutory Authority: RCW
19.27A.020,
19.27A.025,
19.27A.160 and chapter
19.27 RCW. WSR 19-24-040, § 51-11C-20213, filed 11/26/19, effective 7/1/20. Statutory Authority: RCW
19.27A.025,
19.27A.160, and
19.27.074. WSR 16-03-072, § 51-11C-20213, filed 1/19/16, effective 7/1/16. Statutory Authority: RCW
19.27A.020,
19.27A.025 and chapters
19.27 and
34.05 RCW. WSR 13-04-056, § 51-11C-20213, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13.]