EXPEDITED RULES
LABOR AND INDUSTRIES
Title of Rule and Other Identifying Information: Chapter 296-874 WAC, Scaffolds.
THIS RULE IS BEING PROPOSED UNDER AN EXPEDITED RULE-MAKING PROCESS THAT WILL ELIMINATE THE NEED FOR THE AGENCY TO HOLD PUBLIC HEARINGS, PREPARE A SMALL BUSINESS ECONOMIC IMPACT STATEMENT, OR PROVIDE RESPONSES TO THE CRITERIA FOR A SIGNIFICANT LEGISLATIVE RULE. IF YOU OBJECT TO THIS USE OF THE EXPEDITED RULE-MAKING PROCESS, YOU MUST EXPRESS YOUR OBJECTIONS IN WRITING AND THEY MUST BE SENT TO Rules Coordinator, Department of Labor and Industries, P.O. Box 4400, Olympia, WA 98504-4001 , AND RECEIVED BY July 2, 2007.
Purpose of the Proposal and Its Anticipated Effects, Including Any Changes in Existing Rules: On January 23, 2007, the department adopted changes to chapter 296-874 WAC, Scaffolds. The purpose of this rule making is to correct errors and to make housekeeping changes to keep this rule as-effective-as the federal equivalent.
For example: In WAC 296-874-20052, the word "arrest" was removed from the existing rule and replaced with the word "restraint." We are correcting that error by adding the word "arrest" back into the rule, which keeps us as-effective-as the federal equivalent.
In addition, we will be repealing the crawling board requirements in WAC 296-874-40016, and one crawling board requirement in WAC 296-874-20056, because they do not meet the requirements for the scaffolds rule, and already exist in the construction rule, chapter 296-155 WAC.
WAC 296-874-100 Scope.
| | Correcting a referenced WAC number. |
| | Correcting a title to: "Working surfaces, guarding floors and wall openings." |
| | Adding the word "arrest" and removing the word "restraint." |
| | Removing a requirement that does not belong in the rule. |
| | Correcting the title of the illustration to match the actual requirement. |
| | Adding a reference. |
| | Removing an illustration that does not belong in this section of the rule. |
| | Removing a definition (crawling board) that does not belong in the rule. |
| | Repealing crawling board requirements from this chapter because they do not meet the requirements for the scaffolds rule, and already exist in the construction rule, chapter 296-155 WAC. |
Reasons Supporting Proposal: The department is expediting the rule making to correct errors and to make housekeeping changes to keep this rule as effective as the federal equivalent.
Statutory Authority for Adoption: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.050, 49.17.060.
Statute Being Implemented: Chapter 49.17 RCW.
Rule is not necessitated by federal law, federal or state court decision.
Name of Proponent: Department of labor and industries, division of occupational safety and health (DOSH), governmental.
Name of Agency Personnel Responsible for Drafting: Tracy Spencer, Tumwater, Washington, (360) 902-5530; Implementation and Enforcement: Stephen M. Cant, Tumwater, Washington, (360) 902-5495.
May 1, 2007
Judy Schurke
Director
OTS-9623.1
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 05-01-054, filed 12/7/04,
effective 3/1/05)
WAC 296-874-100
Scope.
This chapter applies to suspended
and supported scaffolds, including their supporting structure and
anchorage points.
| Exemption: | This chapter does not apply to: |
| Manually propelled elevating work platforms; | |
| Self-propelled elevating work platforms; | |
| Boom-supported elevating work platforms; | |
| Aerial lifts; | |
| Crane or derrick suspended personnel platforms; | |
| Personnel platforms supported by powered industrial trucks (PITs). |
| Reference: | Additional requirements for the following types of platforms are found in the general safety and health standards, chapter 296-24 WAC. Go to the following sections: |
| For elevating work platforms and aerial lifts, go to elevating work platforms, WAC 296-24-875; | |
| For crane or derrick suspended personnel platforms, go to WAC 296-24-23533; | |
| For personnel platforms supported by powered industrial trucks (PITs), go to (( |
A scaffold is a temporary elevated platform, including its supporting structure and anchorage points, used for supporting employees or materials.
A suspended scaffold is one or more platforms suspended from an overhead structure by ropes or other nonrigid means.
A supported scaffold is one or more platforms supported by rigid means such as outrigger beams, brackets, poles, legs, uprights, posts, or frames.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. 05-01-054, § 296-874-100, filed 12/7/04, effective 3/1/05.]
You must:
Make sure ramps and walkways are not inclined at a slope steeper than one vertical in three horizontal (1:3 or twenty degrees from the horizontal).
Make sure ramps and walkways that are inclined at a slope steeper than one vertical in eight horizontal (1:8) have cleats to provide footing which are:
Securely fastened to the planks;
AND
Spaced not more than fourteen inches (35 cm) apart.
| Reference: | Ramps and walkways that are four feet (1.2 m) or more above a lower level need to have a guardrail system. Those requirements are found in other chapters. |
| For general industry activities, go to: | |
| ▪ Working surfaces, guarding floors and wall openings, (( |
|
| For construction activities, go to: | |
| ▪ Floor openings, wall openings, and stairways, Part K, in the safety standards for construction work, chapter 296-155 WAC. |
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. 05-01-054, § 296-874-20030, filed 12/7/04, effective 3/1/05.]
You must:
Protect each employee on a scaffold more than ten feet (3.1 m) above a lower level, from falling to the lower level, by providing either:
A personal fall ((restraint)) arrest system;
OR
Guardrails.
| REFERENCE | ||
| Fall protection requirements for employees: | Are located in the following chapters: | In the following sections: |
| On walkways within scaffolds | Chapter 296-874 WAC, Scaffolds | WAC 296-874-20056 |
| Erecting or dismantling supported scaffolds | Chapter 296-874 WAC, Scaffolds | WAC 296-874-40010 |
| Erecting or dismantling suspended scaffolds in general industry | Chapter 296-24 WAC, General safety and health standards | Part J-1 Working surfaces, guarding floors and wall openings, ladders AND Part J-3 Powered platforms |
| Erecting or dismantling suspended scaffolds in construction work | Chapter 296-155 WAC, Safety standards for construction work | Part C-1 Fall restraint and fall arrest AND Part K Floor openings, wall openings, and stairways |
Make sure employees erecting the scaffold install the guardrail system, if required, before the scaffold is used by any other employees.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. 07-03-163, § 296-874-20052, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07; 05-01-054, § 296-874-20052, filed 12/7/04, effective 3/1/05.]
You must:
Use a personal fall arrest system to protect employees on the following scaffolds:
Boatswain's chair;
Catenary scaffold;
Float scaffold;
Ladder jack scaffold;
Needle beam scaffold.
Use a personal fall arrest system and a guardrail system to protect employees on:
Single-point adjustable suspension scaffolds;
AND
Two-point adjustable suspension scaffolds.
(( Protect employees working on a crawling board (chicken
ladder) by using at least one of the following:
A personal fall arrest system;
A guardrail system with a minimum two hundred pound toprail capacity;
A three-quarter inch (1.9 cm) diameter grabline or equivalent handhold securely fastened beside each crawling board.))
Protect employees working on a self-contained adjustable scaffold that has the platform:
Supported by the frame structure, using a guardrail system with a minimum two hundred pound toprail capacity.
Suspended by ropes, using:
▪ A guardrail system with a minimum two hundred pound toprail capacity;
AND
▪ A personal fall arrest system.
Protect employees on walkways located within a scaffold by using a guardrail system that meets all of the following:
Has a minimum two hundred pound toprail capacity;
Is installed within nine and one-half inches (24.1 cm) of the walkway;
Is installed along at least one side of the walkway.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. 05-01-054, § 296-874-20056, filed 12/7/04, effective 3/1/05.]
You must:
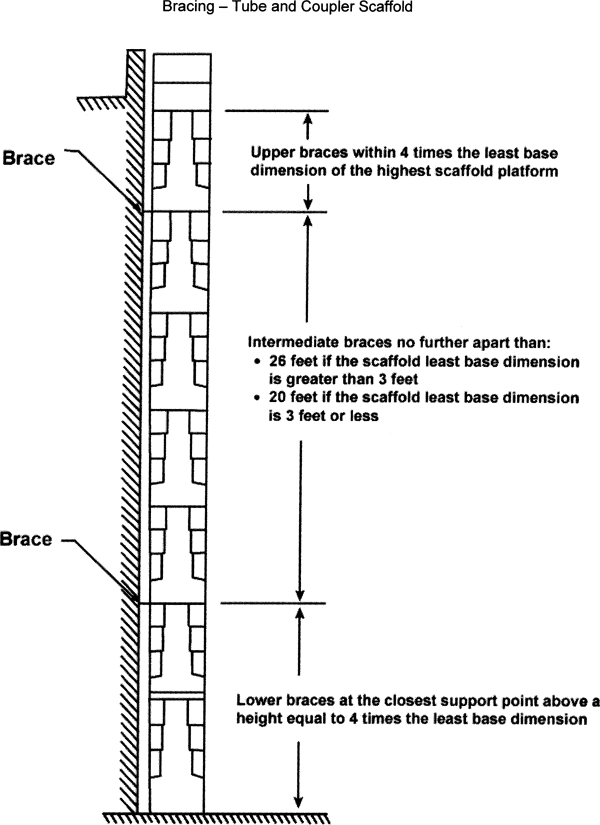
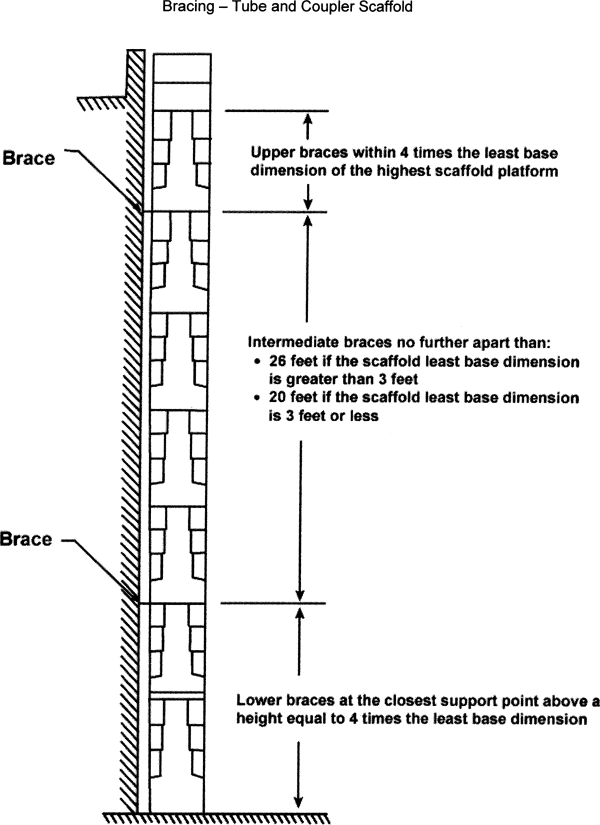
Make sure supported scaffolds with a height to least base dimension ratio of greater than four to one are prevented from tipping by one or more of the following:
Guying;
Tying;
Bracing;
Other equivalent means.
| Note: | The least base dimension includes outriggers, if used. |
Install guys, ties, and braces where horizontal members support both the inner and outer legs of the scaffold.
Install guys, ties, and braces:
According to the scaffold manufacturer's recommendations;
OR
At all points where the following horizontal and vertical planes meet:
▪ First vertical level at a height equal to four times the least base dimension;
▪ Subsequent vertical levels every:
♦ Twenty feet (6.1 m) or less for scaffolds having a width of three feet (0.91 m) or less;
♦ Twenty six feet (7.9 m) or less for scaffolds more than three feet (0.91 m) wide;
▪ Horizontally at:
♦ Each end of the scaffold;
AND
♦ Intervals of thirty feet (9.1 m) or less.
| Note: | The thirty-foot horizontal intervals are measured from one end of the scaffold to the other. |
Make sure the highest level of guys, ties, or braces is no further from the top of the scaffold than a distance equal to four times the least base dimension.
Make sure scaffolds that have an eccentric load applied or transmitted to them, such as a cantilevered work platform, are prevented from tipping by one or more of the following:
Guying;
Tying;
Bracing;
Outriggers;
Other equivalent means.
| (( |
 |
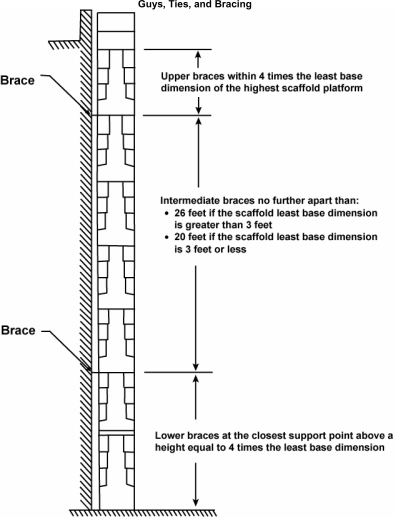
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. 07-03-163, § 296-874-40004, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07; 05-01-054, § 296-874-40004, filed 12/7/04, effective 3/1/05.]
You must:
Make sure supported scaffold poles, legs, posts, frames, and uprights are:
Plumb;
AND
Braced to prevent swaying or displacement.
Make sure supported scaffold poles, legs, posts, frames, and uprights, bear on base plates that rest on:
Mudsills;
OR
Other firm foundations such as concrete or dry, compacted soil.
Make sure foundations are all of the following:
Level;
Sound;
Rigid;
Capable of supporting the loaded scaffold without settling or displacement.
| Note: | The condition of the foundation may change due to weather or other factors. If changes occur, the foundation needs to be evaluated by a competent person to make sure it will safely support the scaffold. |
To support scaffolds or platform units;
OR
As working platforms.
Make sure mobile scaffolds meet these additional requirements:
Wheel and caster stems are pinned or otherwise secured in the scaffold legs or adjustment screws;
Wheels and casters are locked, or equivalent means are used, to prevent movement when the scaffold is being used;
Screw jacks or other equivalent means are used if it's necessary to level the work platform.
Make sure front-end loaders and similar equipment used to support scaffold platforms have been specifically designed for such use by the manufacturer.
| Reference: | When forklifts or other powered industrial trucks are used for personnel lifting on support scaffold platforms, follow the requirements found in Forklifts and other powered industrial trucks, chapter 296-868 WAC. |
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. 07-03-163, § 296-874-40006, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07; 05-01-054, § 296-874-40006, filed 12/7/04, effective 3/1/05.]
You must:
Make sure tube and coupler scaffolds over one hundred twenty-five feet high are:
Designed by a registered professional engineer;
AND
Constructed and loaded as specified in the design.
Leave existing platforms undisturbed until new bearers have been set in place and braced before moving the platforms to the new level.
Install crossbracing across the width of the scaffold that meets all of the following:
Bracing is installed at:
▪ Each end of the scaffold;
AND
▪ At least at every third set of posts horizontally and every fourth runner vertically.
Bracing extends diagonally from the:
▪ Outer posts or runners upwards to the next inner posts or runners;
AND
▪ Inner posts or runners upwards to the next outer posts or runners.
Install building ties:
At the bearer levels between the crossbracing;
AND
At locations specified in WAC 296-874-40004.
Install longitudinal bracing on straight run scaffolds as follows:
Diagonally in both directions across the inner and outer rows of posts;
From the base of the end posts upward to the top of the scaffold at approximately a forty-five degree angle;
As close as possible to the intersection of the bearer and post or runner and post;
If the scaffold is longer than it is tall, repeat the bracing beginning at every fifth post;
If the scaffold is taller than its length, install the bracing:
▪ From the base of the end posts upward to the opposite end posts;
AND
▪ In alternating directions until reaching the top of the scaffold.
Attach bracing to the runners as close to the post as possible, if bracing can't be attached to the post.
Make sure bearers meet all of the following:
Are installed transversely between posts;
If the bearer is coupled to the post, have the inboard coupler bear directly on the runner coupler;
If the bearer is coupled to the runners, have the couplers as close to the posts as possible;
Extend bearers beyond the posts and runners;
Provide full contact with the coupler;
The bottom bearers are located as close to the base as possible.
Make sure runners meet all of the following:
Are installed along the length of the scaffold;
Are located on both the inside and outside posts at the same height;
Are interlocked on straight runs to form continuous lengths and are coupled to each post;
The bottom runners are located as close to the base as
possible.
| Note: | Tube and coupler guardrails and midrails installed on outside posts can be used in lieu of outside runners. |
Make sure couplers are made of a structural metal, such as drop-forged steel, malleable iron, or structural grade aluminum.
Prohibit using couplers made of gray cast iron.
| (( |
 |
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. 05-01-054, § 296-874-40040, filed 12/7/04, effective 3/1/05.]
Adjustable suspension scaffold a suspended scaffold equipped with one or more hoists that can be operated by employees on the scaffold.
Bearer a horizontal scaffold member (which may be supported by ledgers or runners) upon which the scaffold platform rests and which joins scaffold uprights, posts, poles, and similar members.
Boatswain's chair a single-point adjustable suspended scaffold consisting of a seat or sling designed to support one employee in a sitting position.
Brace a rigid connection that holds one scaffold member in a fixed position with respect to another member, or to a building or structure.
Bricklayers' square scaffold a supported scaffold composed of framed squares which support a platform.
Carpenters' bracket scaffold a supported scaffold consisting of a platform supported by brackets attached to building or structural walls.
Catenary scaffold a suspended scaffold consisting of a platform supported by two essentially horizontal and parallel ropes attached to structural members of a building or other structure. Additional support may be provided by vertical pickups.
Cleat a structural block used at the end of a platform to prevent the platform from slipping off its supports. Cleats are also used to provide footing on sloped surfaces such as access ramps.
Competent person someone who:
Is capable of identifying existing and predictable hazards in the surroundings or working conditions which are unsanitary, hazardous, or dangerous to employees;
AND
Has the authority to take prompt corrective measures to eliminate them.
Coupler a device for locking together the tubes of a tube and coupler scaffold.
((Crawling board (chicken ladder) a supported scaffold
consisting of a plank with cleats spaced and secured to provide
footing, for use on sloped surfaces such as roofs.))
Double-pole (independent pole) scaffold a supported scaffold consisting of one or more platforms resting on cross beams (bearers) supported by ledgers and a double row of uprights independent of support (except ties, guys, braces) from any structure.
Equivalent alternative design, material or method to protect against a hazard. You have to demonstrate it provides an equal or greater degree of safety for employees than the method, material or design specified in the rule.
Exposed power lines electrical power lines which are accessible to and may be contacted by employees. Such lines do not include extension cords or power tool cords.
Eye or eye splice a loop at the end of a wire rope.
Fabricated frame scaffold (tubular welded frame scaffold) a scaffold consisting of platforms supported on fabricated frames with integral posts, horizontal bearers, and intermediate members.
Failure load refusal, breaking, or separation of component parts. Load refusal is the point where the ultimate strength is exceeded.
Float (ship) scaffold a suspended scaffold consisting of a braced platform resting on two parallel bearers and hung from overhead supports by ropes of fixed length.
Form scaffold a supported scaffold consisting of a platform supported by brackets attached to formwork.
Guardrail system a vertical barrier, consisting of, but not limited to, toprails, midrails, and posts, erected to prevent employees from falling off a scaffold platform or walkway.
Handrails (ladder stands) a rail connected to a ladder stand running parallel to the slope and/or top step.
Hoist a manual or power-operated mechanical device to raise or lower a suspended scaffold.
Horse scaffold a supported scaffold consisting of a platform supported by construction horses (saw horses). Horse scaffolds constructed of metal are sometimes known as trestle scaffolds.
Independent pole scaffold (see double pole scaffold).
Interior hung scaffold a suspended scaffold consisting of a platform suspended from the ceiling or roof structure by fixed length supports.
Ladder jack scaffold a supported scaffold consisting of a platform resting on brackets attached to ladders.
Ladder stand a mobile, fixed-size, self-supporting ladder consisting of a wide flat tread ladder in the form of stairs.
Landing a platform at the end of a flight of stairs.
Large area scaffold a pole scaffold, tube and coupler scaffold, system scaffold, or fabricated frame scaffold erected over substantially the entire work area. For example: A scaffold erected over the entire floor area of a room.
Lean-to scaffold a supported scaffold which is kept erect by tilting it toward and resting it against a building or structure.
Ledger (see runner).
Lifeline a component consisting of a flexible line that connects to an anchorage at one end to hang vertically (vertical lifeline), or that connects to anchorages at both ends to stretch horizontally (horizontal lifeline). It serves as a means for connecting other components of a personal fall arrest system to the anchorage.
Lower levels areas below the level where the employee is located and to which an employee can fall. Such areas include, but are not limited to, ground levels, floors, roofs, ramps, runways, excavations, pits, tanks, materials, water, and equipment.
Masons' adjustable supported scaffold (see self-contained adjustable scaffold).
Masons' multipoint adjustable suspension scaffold a continuous run suspended scaffold designed and used for masonry operations.
Maximum intended load the total load of all persons, equipment, tools, materials, transmitted loads, and other loads reasonably anticipated to be applied to a scaffold or scaffold component at any one time.
Midrail a rail, approximately midway between the toprail of a guardrail system and the platform, and secured to the uprights erected along the exposed sides and ends of a platform.
Mobile scaffold supported scaffold mounted on casters or wheels.
Multilevel suspended scaffold a two-point or multipoint adjustable suspension scaffold with a series of platforms at various levels resting on common stirrups.
Multipoint adjustable suspension scaffold a suspended scaffold consisting of a platform(s) which is suspended by more than two ropes from overhead supports and equipped with means to raise and lower the platform to desired work levels.
Needle beam scaffold a suspended scaffold which has a platform supported by two bearers (needle beams) suspended from overhead supports.
Outrigger a structural member of a supported scaffold which increases the base width of a scaffold. This provides support for and increases the stability of the scaffold.
Outrigger beam (suspended and supported) the structural member of a suspended scaffold or outrigger scaffold which provides support for the scaffold by extending the scaffold point of attachment to a point out and away from the structure or building.
Outrigger scaffold a supported scaffold consisting of a platform resting on outrigger beams which projects beyond the wall or face of the building or structure. The inboard ends of the outrigger beams are secured inside the building or structure.
Overhand bricklaying the process of laying bricks and masonry so that the surface of the wall is on the opposite side of the wall from the mason, requiring the mason to lean over the wall to complete the work. It includes mason tending and electrical installation incorporated into the brick wall during the overhand bricklaying process.
Personal fall arrest system a system used to arrest an employee's fall. It consists of an anchorage, connectors, and body harness and may also include a lanyard, deceleration device, lifeline, or combinations of these.
Platform a work surface used in scaffolds, elevated above lower levels. Platforms can be constructed using individual wood planks, fabricated planks, fabricated decks, and fabricated platforms.
Pole scaffold (see single-pole scaffold and double (independent) pole scaffold).
Pump jack scaffold a supported scaffold consisting of a platform supported by vertical poles and movable support brackets.
Qualified person a person who has successfully demonstrated the ability to solve problems relating to the subject matter, work, or project, either by:
Possession of a recognized degree, certificate, or professional standing;
OR
Extensive knowledge, training and experience.
Rated load the manufacturer's specified maximum load to be lifted by a hoist or to be applied to a scaffold or scaffold component.
Repair bracket scaffold a supported scaffold consisting of a platform supported by brackets. The brackets are secured in place around the circumference or perimeter of a chimney, stack, tank or other supporting structure by one or more wire ropes placed around the supporting structure.
Roof bracket scaffold a supported scaffold used on a sloped roof. It consists of a platform resting on angular-shaped supports so that the scaffold platform is level.
Runner (ledger) the lengthwise horizontal spacing or bracing member which may support the bearers.
Scaffold a temporary elevated platform, including its supporting structure and anchorage points, used for supporting employees or materials.
Self-contained adjustable scaffold a combination supported and suspended scaffold consisting of an adjustable platform mounted on an independent supporting frame, not a part of the object being worked on, which is equipped with a means to raise and lower the platform. Such systems include rolling roof rigs, rolling outrigger systems, and some masons' adjustable supported scaffolds.
Shore scaffold a supported scaffold which is placed against a building or structure and held in place with props.
Single-point adjustable suspension scaffold a suspended scaffold consisting of a platform suspended by one rope from an overhead support and equipped with means to permit the movement of the platform to desired work levels.
Single-pole scaffold a supported scaffold consisting of platforms resting on bearers, the outside ends of which are supported on runners secured to a single row of posts or uprights, and the inner ends of which are supported on or in a structure or building wall.
Stair tower (scaffold stairway/tower) a tower comprised of scaffold components which contains internal stairway units and rest platforms. These towers are used to provide access to scaffold platforms and other elevated points such as floors and roofs.
Stall load the load at which the prime mover of a power-operated hoist stalls or the power to the prime mover is automatically disconnected.
Step, platform, and trestle ladder scaffold a platform resting directly on the rungs of a step, platform, or trestle ladder.
Stilts a pair of poles or similar supports with raised footrests, used to permit walking above the ground or working surface.
Stonesetters' multipoint adjustable suspension scaffold a continuous run suspended scaffold designed and used for stonesetters' operations.
Supported scaffold one or more platforms supported by rigid means such as outrigger beams, brackets, poles, legs, uprights, posts, or frames.
Suspended scaffold one or more platforms suspended from an overhead structure by ropes or other nonrigid means.
System scaffold a scaffold consisting of posts with fixed connection points that accept runners, bearers, and diagonals that can be interconnected at predetermined levels.
Toeboard (scaffold) a barrier erected along the exposed sides and ends of a scaffold platform at platform level to prevent material, tools, and other loose objects from falling from the platform.
Top plate bracket scaffold a scaffold supported by brackets that hook over or are attached to the top of a wall. This type of scaffold is similar to carpenters' bracket scaffolds and form scaffolds.
Tube and coupler scaffold a scaffold consisting of platforms supported by tubing, erected with coupling devices connecting uprights, braces, bearers, and runners.
Tubular welded frame scaffold (see fabricated frame scaffold).
Tubular welded sectional folding scaffold a sectional, folding metal scaffold either of ladder frame or inside stairway design. It is substantially built of prefabricated welded sections, which consist of end frames, platform frame, inside inclined stairway frame and braces, or hinged connected diagonal and horizontal braces. It can be folded into a flat package when the scaffold is not in use.
Two-point suspension scaffold (swing stage) a suspended scaffold consisting of a platform supported by hangers (stirrups), suspended by two ropes from overhead supports, and equipped with a means to permit the raising and lowering of the platform to desired work levels.
Unstable objects items whose strength, configuration, or lack of stability may allow them to become dislocated and shift and therefore may not properly support the loads imposed on them. Unstable objects do not constitute a safe base support for scaffolds, platforms, or employees. Examples include, but are not limited to, barrels, boxes, loose brick, and concrete blocks.
Vertical pickup a rope used to support the horizontal rope in a catenary scaffold.
Walkway (scaffold) part of a scaffold used only for access and not as a working level.
Window jack scaffold a platform resting on a bracket or jack that projects through a window opening.
Work level the elevated platform, used for supporting workers and their materials.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. 05-01-054, § 296-874-500, filed 12/7/04, effective 3/1/05.]
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
| WAC 296-874-40016 | Meet these requirements when using crawling boards (chicken ladders). |