WSR 15-17-037
PROPOSED RULES
BUILDING CODE COUNCIL
[Filed August 12, 2015, 10:46 a.m.]
Original Notice.
Preproposal statement of inquiry was filed as WSR 15-10-079.
Title of Rule and Other Identifying Information: Adoption and amendment of the 2015 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC)/Washington State Energy Code (WSEC) (commercial), chapter 51-11C WAC.
Hearing Location(s): DES Presentation Room, 1500 Jefferson S.E., Olympia, WA 98504, on October 16, 2015, at 10 a.m.
Date of Intended Adoption: November 13, 2015.
Submit Written Comments to: Dave Kokot, Chair, State Building Code Council (SBCC), P.O. Box 41449, Olympia, WA 98504-1449, e-mail sbcc@ga.wa.gov, fax (360) 586-9088, by October 23, 2015.
Assistance for Persons with Disabilities: Contact Peggy Bryden by September 24, 2015, (360) 407-9280.
Purpose of the Proposal and Its Anticipated Effects, Including Any Changes in Existing Rules: The proposed rules adopt the 2015 edition of WSEC (commercial) with amendments to incorporate requirements from the 2015 IECC (commercial), and formatted to the 2015 IECC, to provided [provide] increased clarity and energy efficiency as required in RCW 19.27A.160.
Note: Sections that had no changes are not shown in this filing.
The 2015 WSEC contains several extensive reorganizational items:
Existing Buildings (2015 IECC Change). Provisions for existing buildings have been removed from Section C101.4 and elsewhere in the code and relocated to a new Chapter 5 and broken out into additions, alterations, repairs and change of use. (Proposed State Amendment.) An exception is added to Section C503.3 for air leakage testing of alteration, unless the alteration involves a change in space conditioning. Replacement exterior lighting and parking garage lighting is now addressed in the alterations Section C503.6.
Compliance Options (2015 IECC Change). Section C402.1 was extensively rewritten for the 2015 edition. The IECC added a component performance alternative, in Section C402.1.5, based on Washington's method. This new section replaces the old WSEC language. The prescriptive compliance path is now shown as a number list of items. The exception to C402.1 was moved to the list of exempt equipment buildings shown in C402.1.2. Low energy and semi-heated buildings were also moved into this section as subsections.
Refrigerated Spaces (2015 IECC Change/Proposed State Amendment). The 2015 IECC added requirements equivalent to those found in the 2012 WSEC. The 2015 WSEC relocates all of these requirements to a new Section C410. Duplicative language was removed and language was clarified. Federal efficiency tables were added. Use of the component performance method was clarified.
Economizers (2015 IECC Change/Proposed State Amendment). The 2015 IECC was reorganized to remove the division between simple systems and complex systems. All of the economizer requirements (and exceptions) were moved to C403.3. Much of C403.4 was moved into C403.3. Section C403.4.1.3 moved to C403.3.1 and was integrated into the ASHRAE 90.1 economizer control requirements. New requirements for modulating airflow units from ASHRAE are also added. Section C403.4.1.4 became Section C403.3.2. Section C403.3.1.1 became Section C403.3.3. Section C403.4.1.1 became Section C403.3.4.
Economizer Exceptions: Two new economizer exceptions were added for controlled atmosphere agricultural buildings and buildings utilizing waste heat for space heating or water heating. Exceptions for replacement equipment were moved to Chapter 5. The size limitation of the VRF exception was removed.
Lighting Controls (2015 IECC Change). The 2015 IECC reorganizes the lighting controls section significantly. It is broken into five main topics: Occupant sensors, time switches, manual control, daylight responsive controls and additional controls.
Commissioning (Proposed State Amendment). The term "certified commissioning professional" replaced most instances of "registered design professional" throughout this section. All of the documentation requirements were moved to Section C103.6. Commissioning plan was moved from Section C408.1.1 to C408.1.2 and revised to incorporate ASHRAE 202 requirements, as was the final commissioning report language. The checklist was revised to reflect the new section numbers and titles. System specific sections were revised to clarify exemptions and simplify language. The electrical section scope increased to all systems covered under Section C405.
As well as several new requirements:
DOAS (Proposed State Amendment). New Section C403.2.6.1 mandates dedicated outdoor air systems (DOAS) in certain occupancy types (office, retail, education, libraries and fire stations) to separate the ventilation system and heating/cooling system to reduce fan energy use. Section C403.2.6.1.1 allows the code official to waive this requirement if it is shown to be impractical. Section C403.2.6.1.2 sets fan control requirements for DOAS systems.
Section C406: Additional Efficiency Package Options (2015 IECC Change/Proposed State Amendment). The 2015 IECC revised the requirements for additional efficiency options, adding more options and simplifying the others provided. SBCC determined this would be an efficient, tested method of gaining energy efficiency and incorporated it into WSEC. All buildings are now required to achieve two credits from the available options. Based on the changes made to the LPA tables, the C406 LPA was reduced a further fifteen percent over the C405.2 values.
Controlled Receptacles (Proposed State Amendment). A new requirement was added in Section C405.10 for fifty percent of receptacles to be controlled by time switches or occupancy sensors.
Appendix E: Renewable Energy (Proposed State Amendment). A new appendix is included requiring commercial buildings to provide some type of renewable energy generation or energy recovery. This appendix is not adopted as a statewide requirement, but may be adopted by a local jurisdiction.
Other notable changes include:
Ventilation (Proposed State Amendment). Modification of Section C403.2.6 to limit the amount of outdoor air introduced into the building to reduce the amount of energy needed to heat/cool that air. Exceptions are provided for when needed for specific nonventilation functions, residential buildings, alterations and systems with ERV.
Table C402.1.3 (Proposed State Amendments). Two options are presented for this table. They differ only in the mass wall category. Option 1 uses the value from the 2015 IECC (and 2012 IECC) and deletes the footnote allowing uninsulated walls for some building types. Option 2 also deletes the footnote, but increases the R-value to that of the 2012 Seattle Energy Code. The other change, present in both options, is the additional column to the compliance option for continuous insulation fasteners, increasing the allowable penetrations to 0.12 percent.
Lighting Power Allowance (Proposed State Amendment). Both the building area method and space-by-space method were decreased by twenty percent over those proposed in the integrated draft.
A number of changes were made to update to new ASHRAE 90.1 requirements:
Efficiency tables C403.2.3 (1) through (10), C404.2, C405.8 (1) through (4).
C403.2.3.1, Water-cooled centrifugal chilling packages.
C403.2.3.2, Positive displacement (air- and water-cooled) chilling packages.
C403.2.4.1.3, Setpoint overlap restrictions.
C403.2.4.5, Zone isolation.
C403.2.4.6, Freeze protection systems.
C403.2.4.12, Direct digital control systems.
C403.2.7.1, Kitchen exhaust.
C403.2.11.5, Fan airflow control.
C403.4.1.1, Static pressure sensor location.
C403.4.1.2, Set points for DDC.
C403.4.2.5, Boiler turndown.
C403.4.4, Mechanical systems serving multiple zones.
C403.4.4.3, Multiple zone VAV control.
C404.7.3, Controls for hot water storage.
C405.6, Electrical transformers.
Several sections were moved to accommodate the reorganization (and thus shown as underlined text), but were not changed (or had very minor editorial changes):
Area weighted U-factors moved from C402.3.4 to C402.4.3.4.
Doors moved from C402.2.7 to C402.4.4.
Off hour controls moved from C403.2.4.3 to C403.2.4.2.
Group R-2/R-3 dwelling units moved from C403.2.4.8 to C403.2.4.10.
Group R-2 sleeping units moved from C403.2.4.9 to C403.2.4.11.
Occupancy sensors moved from C403.2.5.2 to C403.2.6.3.
Laboratory exhaust moved from C403.2.5.4.2 to C403.2.7.2.
Manual controls moved from C405.2.1 to C405.2.3.
Area controls moved from C405.2.5 to C405.2.8.
Many changes were minor editorial changes to correlate section references or minor language adjustments:
C101.1, C101.2, C101.3, C108, C402.1, C402.2, C402.2.6, C402.4.1.3, Table C402.4, C403.2.1, C403.2.2, C403.2.3.4, C403.2.4, C403.2.4.5, C405.1, C405.5, C409.1, C409.3.
For a more detailed description of all of the changes, please see SBCC's web site at https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/Page.aspx?cid=3119.
A more in-depth analysis can be found on our web site, www.sbcc.wa.gov, or by contacting the office (contact information is noted under the small business/cost-benefit analysis section).
Reasons Supporting Proposal: RCW 19.27.031 and 19.27.074.
Statutory Authority for Adoption: RCW 19.27A.020, 19.27A.025, 19.27A.045, 19.27A.160.
Rule is not necessitated by federal law, federal or state court decision.
Agency Comments or Recommendations, if any, as to Statutory Language, Implementation, Enforcement, and Fiscal Matters: SBCC is seeking comments on the issues proposed in the rules shown below.
Name of Proponent: SBCC, governmental.
Name of Agency Personnel Responsible for Drafting and Implementation: Krista Braaksma, 1500 Jefferson S.E., P.O. Box 41449, Olympia, WA, (360) 407-9278.
A small business economic impact statement has been prepared under chapter 19.85 RCW.
Small Business Economic Impact Statement
Description: SBCC is filing a proposed rule to adopt the updated 2015 edition of IECC with state amendments, known as the 2015 WSEC: Chapters 51-11R and 51-11C WAC. Since 1985 SBCC has been responsible to update new editions of the building code per RCW 19.27.074.
The administrative compliance requirements are under the authority of the local government. RCW 19.27.050. Enforcement activities including permit issuance, plan review and approval, and inspections occur at the local level. Requirements for construction document submittal and other reporting requirements are determined by the local jurisdiction and are consistent with previously established policies. The proposed amendments to chapter 51-51 WAC include specific technical requirements for building construction to be consistent with national standards.
WSEC is updated every three years by SBCC. The code development process conducted by the model code organization is open to all interest groups within the design and construction industry and from governmental organizations. See www.iccsafe.org for more information about the model code development process.
Professional Services: Washington has had a statewide building code in effect since 1974. The local enforcement authority having jurisdiction administers the codes through the building and/or fire departments. Administrative procedures for state building code compliance are established and will not be changed by the adoption of the update to the current building codes. Small businesses will employ the same types of professional services for the design and construction of buildings and systems to comply with the state building code.
The proposed rule updates the state building code and does not require additional equipment, supplies, labor or other services. Services needed to comply with the building code are existing within the construction industry as required by the local authority having jurisdiction.
Costs of Compliance for Businesses: SBCC accepts proposals to amend WSEC to meet the legislative goals. The statewide code amendment proposal process is defined in chapter 51-04 WAC and SBCC bylaws. Proposals must increase the energy efficiency in buildings. Each proponent must identify where a proposed amendment has an economic impact and must quantify costs. SBCC developed a specific set of forms for WSEC, so proponents could identify where a proposed amendment was editorial, technical or a policy change.
SBCC received one hundred fifty-four proposals to improve WSEC. The energy code technical advisory group (TAG) recommended approval of one hundred sixteen amendments as submitted or as modified. Of those, TAG identified twenty-one as editorial corrections, and eighty-seven as technical corrections. The remaining eight proposed amendments were identified by TAG as having a significant cost.
The energy code TAG and the SBCC economic workgroup determined there is a cost for compliance on businesses for the following proposed state amendments. SBCC recommended filing the proposed rule to allow input through the public hearing process. See the preliminary cost-benefit analysis of the 2015 WSEC for a detailed review of each of these amendments.
Proposal Number |
Section/Subject |
Economic Workgroup Comments |
15-E009 |
R403.7.1 Ductless mini-split heat pumps |
Look at costs outside of the Tacoma area. Note that there is a side benefit of cooling being provided without additional cost. |
Link: https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/File.ashx?cid=4888 |
||
15-E012 (Mod 2) |
R406.2 Additional Requirements |
Look at analysis of Option 2 point requirements, small house requirement in particular. |
Link: https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/File.ashx?cid=4892 Mod2: https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/File.ashx?cid=5534 |
||
15-E029 and E036 |
Table C402.1.1 Appendix A Mass Walls |
Requesting more information on the analysis done by the minority report proponents. |
Link E029: https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/File.ashx?cid=4939 Link E036: https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/File.ashx?cid=4941 |
||
15-E070 |
C403.2.6.1 Dedicated Outdoor Air Systems |
Look at a model for east of the Cascades. |
Link: https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/File.ashx?cid=4909 |
||
15-E098 |
C405.14 Controlled Receptacles |
|
Link: https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/File.ashx?cid=4980 |
||
15-E114 |
C405.4.2 Lighting Power Allowance |
|
Link: https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/File.ashx?cid=4992 |
||
15-E121 |
C406 Additional Requirements |
Looking for more cost-benefit data from the proponents, example analyses. |
Link: https://fortress.wa.gov/ga/apps/SBCC/File.ashx?cid=4997 |
||
Loss of Sales or Revenue: The proposed rules make the state code for building construction consistent with national standards. Businesses with new products or updated test or design standards are recognized in the updated building code. For these businesses there will be a gain in sales and revenue.
The results of reduced energy use in buildings include avoiding the need for new power generation, reducing environmental impact, and providing local employment. The legislative findings state that energy efficiency is the cheapest, quickest, and cleanest way to meet rising energy needs, confront climate change, and boost our economy.
Cost of Compliance for Small Businesses: The majority of businesses affected by the updates to the building codes are small businesses; over ninety-five percent of those listed in the construction and related industries have under fifty employees. The costs per employee are comparable between the largest businesses and the majority of small businesses. The cost to comply with the updated codes is not a disproportionate impact on small business. Where SBCC found the cost of compliance for small businesses to be disproportionate, the proposed rule mitigates the cost. The proposed rules include a definition of small business and provide exceptions for compliance with the updated rule.
Small Businesses Involved in the Development of the Rule: SBCC conducted open public meetings of the energy code TAG, available via telephone conference bridge and over the internet, and allowed comment on every item on every agenda. SBCC appointed over one hundred representatives of all segments of the business and construction community to serve on the TAGs.
List of Industries: Below is a list of industries required to comply with the energy code:
NAICS # |
Type of Business |
Businesses with fewer than 50 employees |
Businesses with 50 or more employees |
236115 |
New Single-Family Housing Construction |
2523 |
18 |
236116 |
New Multifamily Housing Construction |
69 |
4 |
236118 |
Residential Remodelers |
4298 |
3 |
236210 |
Industrial Building Construction |
88 |
8 |
236220 |
Commercial and Institutional Building Construction |
1151 |
40 |
238120 |
Structural Steel and Precast Concrete Contractors |
154 |
10 |
238130 |
Framing Contractors |
1866 |
17 |
238140 |
Masonry Contractors |
517 |
1 |
238150 |
Glass and Glazing Contractors |
208 |
6 |
238190 |
Other Foundation, Structure, and Building Exterior Contractors |
145 |
1 |
238220 |
Plumbing, Heating, and Air-Conditioning Contractors |
2245 |
66 |
238290 |
Other Building Equipment Contractors |
315 |
6 |
238310 |
Drywall and Insulation Contractors |
898 |
18 |
321911 |
Wood Window and Door Manufacturing |
31 |
1 |
327331 |
Concrete Block and Brick Manufacturing |
13 |
1 |
332311 |
Prefabricated Metal Building and Component Manufacturing |
16 |
4 |
332312 |
Fabricated Structural Metal Manufacturing |
67 |
8 |
332321 |
Metal Window and Door Manufacturing |
10 |
1 |
332322 |
Sheet Metal Work Manufacturing |
69 |
8 |
333415 |
Air-Conditioning and Warm Air Heating Equipment |
13 |
2 |
335110 |
Electric Lamp Bulb and Part Manufacturing |
3 |
|
335121 |
Residential Electric Lighting Fixture Manufacturing |
14 |
|
335122 |
Commercial, Industrial, and Institutional Electric Light |
2 |
1 |
335129 |
Other Lighting Equipment Manufacturing |
3 |
1 |
423320 |
Brick, Stone, and Related Construction Material Merchant |
68 |
1 |
423330 |
Roofing, Siding, and Insulation Material Merchant Wholesale |
33 |
4 |
423390 |
Other Construction Material Merchant Wholesalers |
78 |
|
423720 |
Plumbing and Heating Equipment and Supplies (Hydronics) |
99 |
6 |
423730 |
Warm Air Heating and Air-Conditioning Equipment and Supplies |
48 |
1 |
531110 |
Lessors Of Residential Buildings and Dwellings |
1525 |
152 |
531120 |
Lessors Of Nonresidential Buildings (Except Mini Warehouse) |
2046 |
7 |
541310 |
Architectural Services |
579 |
19 |
541330 |
Engineering Services |
2351 |
82 |
541340 |
Drafting Services |
69 |
|
541350 |
Building Inspection Services |
168 |
1 |
922160 |
Fire Protection |
246 |
31 |
Estimate of the Number of Jobs That Will Be Created or Lost: The adoption of the latest code edition is not expected to significantly impact the number of jobs in the construction industry. These rules are likely to be job neutral overall, i.e., they will not result in any job gains or losses. The scheduled effective date of the new edition is July 1, 2016. Building permits issued prior to that date will be vested under the 2012 building code. Permits issued for projects under the 2015 code edition will start with the 2017 construction season.
The construction industry has experienced growth over the period June 2014 to June 2015.
(Data from Current Employment Statistics (CES))
Wage and salary workers |
2015 |
2014 |
Residential building construction |
25,600 |
22,400 |
Nonresidential building construction |
18,700 |
16,500 |
Specialty trade contractors |
114,200 |
101,400 |
A copy of the statement may be obtained by contacting Tim Nogler, Washington SBCC, P.O. Box 41449, Olympia, WA 98504-1449, phone (360) 407-9280, fax (360) 586-9088, e-mail sbcc@ga.wa.gov.
A cost-benefit analysis is required under RCW 34.05.328. A preliminary cost-benefit analysis may be obtained by contacting Tim Nogler, Managing Director, Washington SBCC, P.O. Box 41449, Olympia, WA 98504-1449, phone (360) 407-9280, fax (360) 586-9088, e-mail sbcc@ga.wa.gov.
August 12, 2015
David F. Kokot
Council Chair
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-10100 Section C101—Scope and general requirements.
C101.1 Title. This code shall be known as the ((International Energy Conservation Code of [NAME OF JURISDICTION])) Washington State Energy Code, and shall be cited as such. It is referred to herein as "this code."
C101.2 Scope. This code applies to commercial buildings and the buildings sites and associated systems and equipment.
EXCEPTION: | The provisions of this code do not apply to temporary growing structures used solely for the commercial production of horticultural plants including ornamental plants, flowers, vegetables, and fruits. (("Temporary growing structure" means a structure that has the sides and roof covered with polyethylene, polyvinyl, or similar flexible synthetic material and is used to provide plants with either frost protection or increased heat retention.)) A temporary growing structure is not considered a building for the purposes of this code. |
C101.3 Intent. This code shall regulate the design and construction of buildings for the ((effective)) use and conservation of energy over the ((useful)) life of each building. This code is intended to provide flexibility to permit the use of innovative approaches and techniques to achieve this objective. This code is not intended to abridge safety, health or environmental requirements contained in other applicable codes or ordinances.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-122, filed 12/3/14, effective 1/3/15)
WAC 51-11C-10140 Section C101.4—Applicability.
C101.4 Applicability. Where, in any specific case, different sections of this code specify different materials, methods of construction or other requirements, the most restrictive shall govern. Where there is a conflict between a general requirement and a specific requirement, the specific requirement shall govern.
C101.4.1 ((Existing buildings. Except as specified in this chapter, this code shall not be used to require the removal, alteration or abandonment of, nor prevent the continued use and maintenance of, an existing building or building system lawfully in existence at the time of adoption of this code.
C101.4.2 Historic buildings. The building official may modify the specific requirements of this code for historic buildings and require alternate provisions which will result in a reasonable degree of energy efficiency. This modification may be allowed for those buildings or structures that are listed in the state or national register of historic places; designated as a historic property under local or state designation law or survey; certified as a contributing resource with a national register listed or locally designated historic district; or with an opinion or certification that the property is eligible to be listed on the national or state registers of historic places either individually or as a contributing building to a historic district by the state historic preservation officer or the keeper of the national register of historic places.
C101.4.3 Additions, alterations, renovations or repairs. Additions, alterations, renovations or repairs to an existing building, building system or portion thereof shall conform to the provisions of this code as they relate to new construction without requiring the unaltered portion(s) of the existing building or building system to comply with this code. Additions, alterations, renovations or repairs shall not create an unsafe or hazardous condition or overload existing building systems. An addition shall be deemed to comply with this code if the addition alone complies or if the existing building and addition comply with this code as a single building.
EXCEPTION: | The following need not comply provided the energy use of the building is not increased: |
1. Storm windows installed over existing fenestration. | |
2. Glass only replacements in an existing sash and frame. | |
3. Existing ceiling, wall or floor cavities exposed during construction provided that these cavities are insulated to full depth with insulation having a minimum nominal value of R-3.0 per inch installed per Section C402. | |
4. Construction where the existing roof, wall or floor cavity is not exposed. | |
5. Reroofing for roofs where neither the sheathing nor the insulation is exposed. Roofs without insulation in the cavity and where the sheathing or insulation is exposed during reroofing shall be insulated either above or below the sheathing. | |
6. Replacement of existing doors that separate conditioned space from the exterior shall not require the installation of a vestibule or revolving door, provided, however, that an existing vestibule that separates a conditioned space from the exterior shall not be removed. | |
7. Alterations to lighting systems only that replace less than 60 percent of the luminaires in a space, provided that such alterations do not increase the installed interior lighting power. | |
8. Alterations that replace only the bulb and ballast within the existing luminaires in a space provided that the alteration does not increase the installed interior lighting power. |
C101.4.3.1 Lighting and motors. Alterations that replace 60 percent or more of the luminaires in a space enclosed by walls or ceiling-height partitions shall comply with Section C405.5. Where less than 60 percent of the luminaires in a space enclosed by walls or ceiling-height partitions are new, the installed lighting wattage shall be maintained or reduced.
Alterations that replace 60 percent or more of the exterior luminaires shall comply with Section C405.6. Where less than 60 percent of the exterior luminaires are new, the installed lighting wattage shall be maintained or reduced.
Where new wiring is being installed to serve added fixtures and/or fixtures are being relocated to a new circuit, controls shall comply with Sections C405.2.1, C405.2.2.3, C405.2.3, C405.2.4, and as applicable C408.3. In addition, office areas less than 300 ft2 enclosed by walls or ceiling-height partitions, and all meeting and conference rooms, and all school classrooms, shall be equipped with occupancy sensors that comply with Section C405.2.2 and C408.3. Where a new lighting panel (or a moved lighting panel) with all new raceway and conductor wiring from the panel to the fixtures is being installed, controls shall also comply with the other requirements in Sections C405.2.2 and C408.3.
Where new walls or ceiling-height partitions are added to an existing space and create a new enclosed space, but the lighting fixtures are not being changed, other than being relocated, the new enclosed space shall have controls that comply with Sections C405.2.1, C405.2.2, C405.2.3 and C408.3.
Those motors which are altered or replaced shall comply with Section C403.2.13.
C101.4.3.2 Mechanical systems. Those parts of systems which are altered or replaced shall comply with Section C403. Additions or alterations shall not be made to an existing mechanical system that will cause the existing mechanical system to become out of compliance.
All new systems in existing buildings, including packaged unitary equipment and packaged split systems, shall comply with Section C403.
Where mechanical cooling is added to a space that was not previously cooled, the mechanical cooling system shall comply with the economizer requirements in Section C403.3.1 or C403.4.1.
EXCEPTION: | Alternate designs that are not in full compliance with this code may be approved when the building official determines that existing building or occupancy constraints make full compliance impractical or where full compliance would be economically impractical. |
Alterations to existing mechanical cooling systems shall not decrease economizer capacity unless the system complies with Section C403.3.1 or C403.4.1. In addition, for existing mechanical cooling systems that do not comply with Sections C403.3.1 or Section 403.4.1, including both the individual unit size limits and the total building capacity limits on units without economizer, other alterations shall comply with Table C101.4.3.2.
When space cooling equipment is replaced, controls shall be installed to provide for integrated operation with economizer in accordance with Section C403.3.
Existing equipment currently in use may be relocated within the same floor or same tenant space if removed and reinstalled within the same permit.
C101.4.4 Change in occupancy or use. Spaces undergoing a change in occupancy from an F, S or U occupancy to an occupancy other than F, S or U shall comply with this code. Any space that is converted to a Group R dwelling unit or portion thereof, from another use or occupancy shall comply with this code. Where the use in a space changes from one use in Table C405.5.2 (1) or (2) to another use in Table C405.5.2 (1) or (2), the installed lighting wattage shall comply with Section C405.5.
EXCEPTION: | Where the component performance building envelope option in Section C402.1.3 is used to comply with this section, the Proposed UA is allowed to be up to 110 percent of the Target UA. Where the total building performance option in Section C407 is used to comply with this section, the annual energy consumption of the proposed design is allowed to be 110 percent of the annual energy consumption otherwise allowed by Section C407.3 and Section C401.2 (3). |
C101.4.5 Change in space conditioning. Any nonconditioned space that is altered to become conditioned space or semi-heated space shall be required to be brought into full compliance with this code. Any semi-heated space that is altered to become conditioned space shall be required to be brought into full compliance with this code.
EXCEPTION: | Where the component performance building envelope option in Section C402.1.3 is used to comply with this section, the Proposed UA is allowed to be up to 110 percent of the Target UA. Where the total building performance option in Section C407 is used to comply with this section, the annual energy consumption of the proposed design is allowed to be 110 percent of the annual energy consumption otherwise allowed by Section C407.3 and Section C401.2 (3). |
C101.4.6)) Mixed occupancy. Where a building includes both residential and commercial occupancies, each occupancy shall be separately considered and meet the applicable provisions of ((IECC)) WSEC—Commercial Provisions or ((IECC)) WSEC—Residential Provisions.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-20-120, filed 10/1/13, effective 11/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-10143 ((Table C101.4.3.2—Economizer compliance options for mechanical alterations.)) Reserved.
((Table C101.4.3.2
Economizer Compliance Options for Mechanical Alterations
Option A |
Option B (alternate to A) |
Option C (alternate to A) |
Option D (alternate to A) |
|
Unit Type |
Any alteration with new or replacement equipment |
Replacement unit of the same type with the same or smaller output capacity |
Replacement unit of the same type with a larger output capacity |
New equipment added to existing system or replacement unit of a different type |
1. Packaged Units |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 3 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 3 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 4 |
2. Split Systems |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12 |
Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capability |
Only for new units < 54,000 Btu/h replacing unit installed prior to 1991 (one of two): Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Economizer: 50%6 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 4 |
For units ˃ 54,000 Btu/h or any units installed after 1991: Option A |
||||
3. Water Source Heat Pump |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12 |
(two of three): Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Flow control valve7 Economizer: 50%6 |
(three of three): Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Flow control valve7 Economizer: 50%6 (except for certain pre-1991 systems8) |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 4 (except for certain pre-1991 systems8) |
4. Hydronic Economizer using Air-Cooled Heat Rejection Equipment (Dry Cooler) |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: 14332 |
Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Option A |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 4 |
5. Air-Handling Unit (including fan coil units) where the system has an air-cooled chiller |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12 |
Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Option A (except for certain pre-1991 systems8) |
Option A (except for certain pre-1991 systems8) |
6. Air- Handling Unit (including fan coil units) and Water-cooled Process Equipment, where the system has a water-cooled chiller10 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12 |
Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Option A (except for certain pre-1991 systems8 and certain 1991-2004 systems9) |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 4 (except for certain pre-1991 systems8 and certain 1991-2004 systems9) |
7. Cooling Tower |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12 |
No requirements |
Option A |
Option A |
8. Air-Cooled Chiller |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12 |
Efficiency: + 5%11 Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency (two of two): (1) + 10%12 and (2) multistage Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 4 |
9. Water- Cooled Chiller |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12 |
Efficiency (one of two): (1) + 10%13 or (2) plate frame heat exchanger15 Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency (two of two): (1) + 15%14 and (2) plate frame heat exchanger15 Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 4 |
10. Boiler |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12 |
Efficiency: + 8%16 Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency: + 8%16 Economizer: Shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.4.12, 4 |
1 | Minimum equipment efficiency shall comply with Section C403.2.3 and Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(9). | |
2 | System and building shall comply with Section C403.4.1 (including both the individual unit size limits and the total building capacity limits on units without economizer). It is acceptable to comply using one of the exceptions to Section C403.4.1. | |
3 | All equipment replaced in an existing building shall have air economizer complying with Sections C403.3.1 and C403.4.1 unless both the individual unit size and the total capacity of units without air economizer in the building is less than that allowed in Exception 1 to Section C403.3.1. | |
4 | All separate new equipment added to an existing building shall have air economizer complying with Sections C403.3.1 and C403.4.1 unless both the individual unit size and the total capacity of units without air economizer in the building is less than that allowed in Exception 1 to Section C403.4.1. | |
5 | Equipment shall have a capacity-weighted average cooling system efficiency: | |
a. | For units with a cooling capacity below 54,000 Btu/h, a minimum of 10% greater than the requirements in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2) (1.10 x values in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)). | |
b. | For units with a cooling capacity of 54,000 Btu/h and greater, a minimum of 5% greater than the requirements in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2) (1.05 x values in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)). | |
6 | Minimum of 50% air economizer that is ducted in a fully enclosed path directly to every heat pump unit in each zone, except that ducts may terminate within 12 inches of the intake to an HVAC unit provided that they are physically fastened so that the outside air duct is directed into the unit intake. If this is an increase in the amount of outside air supplied to this unit, the outside air supply system shall be capable of providing this additional outside air and equipped with economizer control. | |
7 | Have flow control valve to eliminate flow through the heat pumps that are not in operation with variable speed pumping control complying with Section C403.4.3 for that heat pump. | |
– When the total capacity of all units with flow control valves exceeds 15% of the total system capacity, a variable frequency drive shall be installed on the main loop pump. | ||
– As an alternate to this requirement, have a capacity-weighted average cooling system efficiency that is 5% greater than the requirements in note 5 (i.e., a minimum of 15%/10% greater than the requirements in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2) (1.15/1.10 x values in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)). | ||
8 | Systems installed prior to 1991 without fully utilized capacity are allowed to comply with Option B, provided that the individual unit cooling capacity does not exceed 90,000 Btu/h. | |
9 | Economizer not required for systems installed with water economizer plate and frame heat exchanger complying with previous codes between 1991 and June 2013, provided that the total fan coil load does not exceed the existing or added capacity of the heat exchangers. | |
10 | For water-cooled process equipment where the manufacturers' specifications require colder temperatures than available with waterside economizer, that portion of the load is exempt from the economizer requirements. | |
11 | The air-cooled chiller shall have an IPLV efficiency that is a minimum of 5% greater than the IPLV requirements in Table C403.2.3(7) (1.05 x IPLV values in Table C403.2.3(7)). | |
12 | The air-cooled chiller shall: | |
a. | Have an IPLV efficiency that is a minimum of 10% greater than the IPLV requirements in Table C403.2.3(7) (1.10 x IPLV values in Table C403.2.3(7)); and | |
b. | Be multistage with a minimum of two compressors. | |
13 | The water-cooled chiller shall have an IPLV efficiency that is a minimum of 10% greater than the IPLV requirements in Table C403.2.3(7) (1.10 x IPLV values in Table C403.2.3(7)). | |
14 | The water-cooled chiller shall have an IPLV efficiency that is a minimum of 15% greater than the IPLV requirements in Table C403.2.3(7), (1.15 x IPLV values in Table C403.2.3(7)). | |
15 | Economizer cooling shall be provided by adding a plate-frame heat exchanger on the waterside with a capacity that is a minimum of 20% of the chiller capacity at standard AHRI rating conditions. | |
16 | The replacement boiler shall have an efficiency that is a minimum of 8% higher than the value in Table C403.2.3(5) (1.08 x value in Table C403.2.3(5)), except for electric boilers.)) | |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-10150 Section C101.5—Compliance.
C101.5 Compliance. Residential buildings shall meet the provisions of ((IECC)) WSEC—Residential Provisions. Commercial buildings shall meet the provisions of ((IECC)) WSEC—Commercial Provisions.
C101.5.1 Compliance materials. The code official shall be permitted to approve specific computer software, worksheets, compliance manuals and other similar materials that meet the intent of this code.
((C101.5.2 Low energy buildings. The following buildings, or portions thereof, separated from the remainder of the building by building thermal envelope assemblies complying with this code shall be exempt from all thermal envelope provisions of this code:
1. Those that are heated and/or cooled with a peak design rate of energy usage less than 3.4 Btu/h • ft2 (10.7 W/m2) or 1.0 watt/ft2 (10.7 W/m2) of floor area for space conditioning purposes.
2. Those that do not contain conditioned space.
3. Greenhouses isolated from any conditioned space and not intended for occupancy.
C101.5.2.1 Semi-heated spaces. A semi-heated space shall meet all of the building thermal envelope requirements, except that insulation is not required for opaque wall assemblies. Component performance calculations involving semi-heated spaces shall calculate fully insulated opaque walls for the Target UA calculation, and Total Building Performance calculations involving semi-heated spaces shall calculate fully insulated opaque walls for the Standard Reference Design.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-10300 Section C103—Construction documents.
C103.1 General. Construction documents and other supporting data shall be submitted in one or more sets with each application for a permit. The construction documents shall be prepared by a registered design professional where required by the statutes of the jurisdiction in which the project is to be constructed. Where special conditions exist, the code official is authorized to require necessary construction documents to be prepared by a registered design professional.
EXCEPTION: | The code official is authorized to waive the requirements for construction documents or other supporting data if the code official determines they are not necessary to confirm compliance with this code. |
C103.2 Information on construction documents. Construction documents shall be drawn to scale upon suitable material. Electronic media documents are permitted to be submitted when approved by the code official. Construction documents shall be of sufficient clarity to indicate the location, nature and extent of the work proposed, and show in sufficient detail pertinent data and features of the building, systems and equipment as herein governed. Details shall include, but are not limited to, as applicable((,)):
1. Insulation materials and their R-values((;)).
2. Fenestration U-factors and SHGCs((;)).
3. Area-weighted U-factor and SHGC calculations((;)).
4. Mechanical system design criteria((;)).
5. Mechanical and service water heating system and equipment types, sizes and efficiencies((;)).
6. Economizer description((;)).
7. Equipment and systems controls((;)).
8. Fan motor horsepower (hp) and controls((;)).
9. Duct sealing, duct and pipe insulation and location((;)).
10. Lighting fixture schedule with wattage and control narrative((; and air sealing details)).
11. Location of daylight zones on floor plan.
12. Air barrier details including all air barrier boundaries and associated square foot calculations on all six sides of the air barrier as applicable.
C103.2.1 Building thermal envelope depiction. The building's thermal envelope shall be represented on the construction documents.
C103.3 Examination of documents. The code official shall examine or cause to be examined the accompanying construction documents and shall ascertain whether the construction indicated and described is in accordance with the requirements of this code and other pertinent laws or ordinances.
C103.3.1 Approval of construction documents. When the code official issues a permit where construction documents are required, the construction documents shall be endorsed in writing and stamped "Reviewed for Code Compliance." Such approved construction documents shall not be changed, modified or altered without authorization from the code official. Work shall be done in accordance with the approved construction documents.
One set of construction documents so reviewed shall be retained by the code official. The other set shall be returned to the applicant, kept at the site of work and shall be open to inspection by the code official or a duly authorized representative.
C103.3.2 Previous approvals. This code shall not require changes in the construction documents, construction or designated occupancy of a structure for which a lawful permit has been heretofore issued or otherwise lawfully authorized, and the construction of which has been pursued in good faith within 180 days after the effective date of this code and has not been abandoned.
C103.3.3 Phased approval. The code official shall have the authority to issue a permit for the construction of part of an energy conservation system before the construction documents for the entire system have been submitted or approved, provided adequate information and detailed statements have been filed complying with all pertinent requirements of this code. The holders of such permit shall proceed at their own risk without assurance that the permit for the entire energy conservation system will be granted.
C103.4 Amended construction documents. Changes made during construction that are not in compliance with the approved construction documents shall be resubmitted for approval as an amended set of construction documents.
C103.5 Retention of construction documents. One set of approved construction documents shall be retained by the code official for a period of not less than 180 days from date of completion of the permitted work, or as required by state or local laws.
C103.6 Building documentation and close out submittal requirements. The construction documents shall specify that the documents described in this section be provided to the building owner or owner's authorized agent within 180 days of the date of receipt of the certificate of occupancy.
C103.6.1 Record documents. Construction documents shall be updated to convey a record of the completed work. Such updates shall include mechanical, electrical and control drawings red-lined, or redrawn if specified, that show all changes to size, type and locations of components, equipment and assemblies.
C103.6.2 Manuals. An operating and maintenance manual shall be provided for each component, device, piece of equipment, and system required to be commissioned by this code. The manual shall include all of the following:
1. Submittal data indicating all selected options for each piece of equipment.
2. Manufacturer's operation manuals and maintenance manuals for each device, piece of equipment, and system requiring maintenance, except equipment not furnished as part of the project. Required routine maintenance actions, cleaning and recommended relamping shall be clearly identified.
3. Name and address of at least one service agency.
4. Controls system inspection schedule, maintenance and calibration information, wiring diagrams, schematics, and control sequence descriptions. Desired or field-determined setpoints shall be permanently recorded on control drawings at control devices or, for digital control systems, on the graphic where settings may be changed.
C103.6.3 Compliance documentation. All energy code compliance forms and calculations shall be delivered in one document to the building owner as part of the project record documents, manuals, or as a standalone document. This document shall include the specific energy code year utilized for compliance determination for each system. NFRC certificates for the installed windows, list total area for each NFRC certificate, the interior lighting power compliance path (building area, space-by-space) used to calculate the lighting power allowance.
For projects complying with C401.2, item one the documentation shall include:
1. The envelop insulation compliance path (prescriptive or component performance).
2. All completed code compliance forms, and all compliance calculations including, but not limited to, those required by sections C402.1.5, C403.2.12.1, C405.4, and C405.5.
For projects complying with C407 the documentation shall include:
1. A list of all proposed envelop component types, areas and U-values.
2. A list of all lighting area types with areas, lighting power allowance, and installed lighting power density.
3. A list of each HVAC system modeled with the assigned and proposed system type.
4. Electronic copies of the baseline and proposed model input and output file. The input files shall be in a format suitable for rerunning the model and shall not consist solely of formatted reports of the inputs.
C103.6.4 Systems operation training. Training of the maintenance staff for equipment included in the manuals required by Section C103.6.2 shall include at a minimum:
1. Review of manuals and permanent certificate.
2. Hands-on demonstration of all normal maintenance procedures, normal operating modes, and all emergency shutdown and start-up procedures.
3. Training completion report.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-122, filed 12/3/14, effective 1/3/15)
WAC 51-11C-10400 Section C104—Inspections.
C104.1 General. Construction or work for which a permit is required shall be subject to inspection by the code official or his designated agent, and such construction or work shall remain accessible and exposed for inspection purposes until approved. It shall be the duty of the permit applicant to cause the work to remain accessible and exposed for inspection purposes. Neither the code official nor the jurisdiction shall be liable for expense entailed in the removal or replacement of any material, product, system or building component required to allow inspection to validate compliance with this code.
C104.2 Required ((approvals. Work shall not be done beyond the point indicated in each successive inspection without first obtaining the approval of the code official. The code official, upon notification, shall make the requested inspections and shall either indicate the portion of the construction that is satisfactory as completed, or notify the permit holder or his or her agent wherein the same fails to comply with this code. Any portions that do not comply shall be corrected and such portion shall not be covered or concealed until authorized by the code official. Where applicable, inspections shall include at least the requirements in Sections C104.2.1 through C104.2.3.2.
C104.2.1 Envelope
C104.2.1.1 Wall Insulation Inspection: To be made after all wall insulation and air vapor retarder sheet or film materials are in place, but before any wall covering is placed.
C104.2.1.2 Glazing Inspection: To be made after glazing materials are installed in the building.
C104.2.1.3 Exterior Roofing Insulation: To be made after the installation of the roof insulation, but before concealment.
C104.2.1.4 Slab/Floor Insulation: To be made after the installation of the slab/floor insulation, but before concealment.
C104.2.2 Mechanical
C104.2.2.1 Mechanical Equipment Efficiency and Economizer: To be made after all equipment and controls required by this code are installed and prior to the concealment of such equipment or controls.
C104.2.2.2 Mechanical Pipe and Duct Insulation: To be made after all pipe and duct insulation is in place, but before concealment.
C104.2.3 Lighting and motors
C104.2.3.1 Lighting Equipment and Controls: To be made after the installation of all lighting equipment and controls required by this code, but before concealment of the lighting equipment.
C104.2.3.2 Motor Inspections: To be made after installation of all equipment covered by this code, but before concealment.
C104.3)) inspections. The code official or his designated agent, upon notification, shall make the inspections set forth in Sections C104.2.1 through C104.2.6.
C104.2.1 Footing and foundation inspection. Inspections associated with footings and foundations shall verify compliance with the code as to R-value, location, thickness, depth of burial and protection of insulation as required by the code and approved plans and specifications.
C104.2.2 Insulation and fenestration inspection. Inspections shall be made before application of interior finish and shall verify compliance with the code as to types of insulation and corresponding R-values and their correct location and proper installation; fenestration properties (U-factor, SHGC and VT) and proper installation; and air leakage controls as required by the code and approved plans and specifications.
C104.2.3 Plumbing inspection. Inspections verify compliance as required by the code and approved plans and specifications as to types of insulation and corresponding R-values and protection, required controls and required heat traps.
C104.2.4 Mechanical inspection. Inspections shall verify compliance as required by the code and approved plans and specifications as to installed HVAC equipment type and size, required controls, system insulation and corresponding R-value, system and damper air leakage and required energy recovery and/or economizers.
C104.2.5 Electrical and lighting inspection. Inspections shall verify compliance as required by the code and approved plans and specifications as to installed lighting systems, components and controls; motors and installation of an electric meter for each dwelling unit.
C104.2.6 Final inspection. The building shall have a final inspection and not be occupied until approved.
((C104.4)) C104.3 Reinspection. A building shall be reinspected when determined necessary by the code official.
((C104.5)) C104.4 Approved inspection agencies. The code official is authorized to accept reports of approved inspection agencies, provided such agencies satisfy the requirements as to qualifications and reliability relevant to the building components and systems they are inspecting.
((C104.6)) C104.5 Inspection requests. It shall be the duty of the holder of the permit or their duly authorized agent to notify the code official when work is ready for inspection. It shall be the duty of the permit holder to provide access to and means for inspections of such work that are required by this code.
((C104.7)) C104.6 Reinspection and testing. Where any work or installation does not pass an initial test or inspection, the necessary corrections shall be made so as to achieve compliance with this code. The work or installation shall then be resubmitted to the code official for inspection and testing.
((C104.8)) C104.7 Approval. After the prescribed tests and inspections indicate that the work complies in all respects with this code, a notice of approval shall be issued by the code official.
((C104.8.1)) C104.7.1 Revocation. The code official is authorized to, in writing, suspend or revoke a notice of approval issued under the provisions of this code wherever the certificate is issued in error, or on the basis of incorrect information supplied, or where it is determined that the building or structure, premise, or portion thereof is in violation of any ordinance or regulation or any of the provisions of this code.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-10600 Section C106—Referenced standards.
C106.1 Referenced codes and standards. The codes and standards referenced in this code shall be those listed in Chapter 5, and such codes and standards shall be considered as part of the requirements of this code to the prescribed extent of each such reference and as further regulated in Sections C106.1.1 and C106.1.2.
C106.1.1 Conflicts. Where differences occur between provisions of this code and referenced codes and standards, the provisions of this code shall apply.
C106.1.2 Provisions in referenced codes and standards. Where the extent of the reference to a referenced code or standard includes subject matter that is within the scope of this code, the provisions of this code, as applicable, shall take precedence over the provisions in the referenced code or standard.
C106.2 ((Conflicting requirements. Where the provisions of this code and the referenced standards conflict, the provisions of this code shall take precedence.
C106.3)) Application of references. References to chapter or section numbers, or to provisions not specifically identified by number, shall be construed to refer to such chapter, section or provision of this code.
((C106.4)) C106.3 Other laws. The provisions of this code shall not be deemed to nullify any provisions of local, state or federal law. In addition to the requirements of this code, all occupancies shall conform to the provisions included in the State Building Code (chapter 19.27 RCW). In case of conflicts among the codes enumerated in RCW 19.27.031 (1) through (4) and this code, an earlier named code shall govern over those following. In the case of conflict between the duct sealing and insulation requirements of this code and the duct insulation requirements of Sections 603 and 604 of the International Mechanical Code, the duct insulation requirements of this code, or where applicable, a local jurisdiction's energy code shall govern.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-10800 Section C108—Stop work order.
C108.1 Authority. Whenever the code official finds any work regulated by this code being performed in a manner either contrary to the provisions of this code or dangerous or unsafe, the code official is authorized to issue a stop work order.
C108.2 Issuance. The stop work order shall be in writing and shall be given to the owner of the property involved, or to the owner's agent, or to the person doing the work. Upon issuance of a stop work order, the cited work shall immediately cease. The stop work order shall state the reason for the order, and the conditions under which the cited work will be permitted to resume.
C108.3 Emergencies. Where an emergency exists, the code official shall not be required to give a written notice prior to stopping the work.
C108.4 Failure to comply. Any person who shall continue any work after having been served with a stop work order, except such work as that person is directed to perform to remove a violation or unsafe condition, shall be liable to a fine ((of not less than [AMOUNT] dollars or more than [AMOUNT] dollars)) as set by the applicable governing authority.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20201 Section C202.1—A.
ABOVE-GRADE WALL. A wall enclosing conditioned space that is not a below-grade wall. This includes between-floor spandrels, peripheral edges of floors, roof and basement knee walls, dormer walls, gable end walls, walls enclosing a mansard roof and skylight shafts.
ACCESSIBLE. Admitting close approach as a result of not being guarded by locked doors, elevation or other effective means (see "Readily accessible").
ADDITION. An extension or increase in the conditioned space floor area or height of a building or structure.
AIR BARRIER. Material(s) assembled and joined together to provide a barrier to air leakage through the building envelope. An air barrier may be a single material or a combination of materials.
AIR CURTAIN. A device, installed at the building entrance, that generates and discharges a laminar air stream intended to prevent the infiltration of external, unconditioned air into the conditioned spaces, or the loss of interior, conditioned air to the outside.
ALTERATION. Any construction, retrofit or renovation to an existing structure other than repair or addition that requires a permit. Also, a change in a building, electrical, gas, mechanical or plumbing system that involves an extension, addition or change to the arrangement, type or purpose of the original installation that requires a permit.
APPROVED. Approval by the code official as a result of investigation and tests conducted by him or her, or by reason of accepted principles or tests by nationally recognized organizations.
APPROVED AGENCY. An established and recognized agency regularly engaged in conducting tests or furnishing inspection services, when such agency has been approved by the code official.
ATTIC AND OTHER ROOFS. All other roofs, including roofs with insulation entirely below (inside of) the roof structure (i.e., attics, cathedral ceilings, and single-rafter ceilings), roofs with insulation both above and below the roof structure, and roofs without insulation but excluding roofs with insulation entirely above deck and metal building roofs.
AUTOMATIC. Self-acting, operating by its own mechanism when actuated by some impersonal influence, as, for example, a change in current strength, pressure, temperature or mechanical configuration (see "Manual").
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20202 Section C202.2—B.
BELOW-GRADE WALL. That portion of a wall in the building envelope that is entirely below the finish grade and in contact with the ground.
BOILER, MODULATING. A boiler that is capable of more than a single firing rate in response to a varying temperature or heating load.
BOILER SYSTEM. One or more boilers, their piping and controls that work together to supply steam or hot water to heat output devices remote from the boiler.
BUBBLE POINT. The refrigerant liquid saturation temperature at a specified pressure.
BUILDING. Any structure used or intended for supporting or sheltering any use or occupancy, including any mechanical systems, service water heating systems and electric power and lighting systems located on the building site and supporting the building.
BUILDING COMMISSIONING. A process that verifies and documents that the selected building systems have been designed, installed, and function according to the owner's project requirements and construction documents, and to minimum code requirements.
BUILDING ENTRANCE. Any door, set of doors, doorway, or other form of portal that is used to gain access to the building from the outside by the public.
BUILDING SITE. A contiguous area of land that is under the ownership or control of one entity.
BUILDING THERMAL ENVELOPE. The below-grade walls, above-grade walls, floor, roof, and any other building elements that enclose conditioned space or provides a boundary between conditioned space, semiheated space and exempt or unconditioned space.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20203 Section C202.3—C.
-FACTOR (THERMAL CONDUCTANCE).C The coefficient of heat transmission (surface to surface) through a building component or assembly, equal to the time rate of heat flow per unit area and the unit temperature difference between the warm side and cold side surfaces (Btu/h ft2 x °F) [W/(m2 x K)].
CERTIFIED COMMISSIONING PROFESSIONAL. An individual who is certified by an ANSI/ISO/IEC 17024:2012 accredited organization to lead, plan, coordinate and manage commissioning teams and implement commissioning processes. The individual's accredited certification required by the referenced standard provides a measured level of experience and competence with the various whole building commissioning processes and ability to deliver quality service. The engineer of record for the project may be considered the certified commissioning professional if she/he is qualified to perform commissioning services for the entire process.
CIRCULATING HOT WATER SYSTEM. A specifically designed water distribution system where one or more pumps are operated in the service hot water piping to circulate heated water from the water-heating equipment to the fixture supply and back to the water-heating equipment.
CLIMATE ZONE. A geographical region based on climatic criteria as specified in this code.
CODE OFFICIAL. The officer or other designated authority charged with the administration and enforcement of this code, or a duly authorized representative.
COEFFICIENT OF PERFORMANCE (COP) - COOLING. The ratio of the rate of heat removal to the rate of energy input, in consistent units, for a complete refrigerating system or some specific portion of that system under designated operating conditions.
COEFFICIENT OF PERFORMANCE (COP) - HEATING. The ratio of the rate of heat removal to the rate of heat delivered to the rate of energy input, in consistent units, for a complete heat pump system, including the compressor and, if applicable, auxiliary heat, under designated operating conditions.
COMMERCIAL BUILDING. For this code, all buildings that are not included in the definition of "Residential buildings."
COMPUTER ROOM. A room whose primary function is to house equipment for the processing and storage of electronic data and that has a design electronic data equipment power density exceeding 20 watts per square foot of conditioned area.
CONDENSING UNIT. A factory-made assembly of refrigeration components designed to compress and liquefy a specific refrigerant. The unit consists of one or more refrigerant compressors, refrigerant condensers (air-cooled, evaporatively cooled, or water-cooled), condenser fans and motors (where used) and factory-supplied accessories.
CONDITIONED FLOOR AREA. The horizontal projection of the floors associated with the conditioned space.
CONDITIONED SPACE. An area ((or room within a building being heated or cooled, containing uninsulated ducts, or with a fixed opening directly into an adjacent conditioned space)), room or space that is enclosed within the building thermal envelope and that is directly heated or cooled or that is indirectly heated or cooled. Spaces are indirectly heated or cooled where they communicate through openings with conditioned spaces, where they are separated from conditioned spaces by uninsulated walls, floors or ceilings, or where they contain uninsulated ducts, piping or other sources of heating or cooling.
CONTINUOUS AIR BARRIER. A combination of materials and assemblies that restrict or prevent the passage of air through the building thermal envelope.
CONTINUOUS INSULATION (CI). ((Insulation)) Insulating material that is continuous across all structural members without thermal bridges other than ((service openings and penetrations by metal fasteners with a cross-sectional area, as measured in the plane of the surface, of less than 0.04% of the opaque surface area of the assembly)) fasteners and service openings. It is installed on the interior or exterior or is integral to any opaque surface of the building envelope.
CONTROLLED PLANT GROWTH ENVIRONMENT. Group F and U buildings or spaces that are specifically controlled to facilitate and enhance plant growth and production by manipulating various indoor environment conditions. Technologies include indoor agriculture, cannabis growing, hydroponics, aquaculture and aquaponics. Controlled indoor environment variables include, but are not limited to, temperature, air quality, humidity, and carbon dioxide.
CURTAIN WALL. Fenestration products used to create an external nonload-bearing wall that is designed to separate the exterior and interior environments.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20204 Section C202.4—D.
DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEM. An electronic system managed by the building owner to collect, tabulate and display metering information.
DAYLIGHT RESPONSIVE CONTROL. A device or system that provides automatic control of electric light levels based on the amount of daylight in a space.
DAYLIGHT ZONE. (((See also Fig. C202.4)
1. Under skylights. The area under skylights whose horizontal dimension, in each direction, is equal to the skylight dimension in that direction plus either 70 percent of the floor-to-ceiling height or the dimension to a ceiling height opaque partition, or one-half the distance to adjacent skylights or vertical fenestration, whichever is least.
2. Adjacent to vertical fenestration. The area adjacent to vertical fenestration which receives daylight through the fenestration. For purposes of this definition and unless more detailed analysis is provided, the primary daylight zone depth is assumed to extend into the space a distance equal to the window head height and the secondary daylighted zone extends from the edge of the primary zone to a distance equal to two times the window head height or to the nearest ceiling height opaque partition, whichever is less. The daylight zone width is assumed to be the width of the window plus 2 feet (610 mm) on each side, or the window width plus the distance to an opaque partition, or the window width plus one-half the distance to adjacent skylight or vertical fenestration, whichever is least.
3. In parking garages. The area within 20 feet of any portion of a perimeter wall that has a net opening to wall ratio of at least 40 percent and no exterior obstructions within 20 feet.
4. Under atrium glazing. The area at the floor directly beneath the atrium and the top floor under the atrium whose horizontal dimension, in each direction, is equal to the distance between the floor and ceiling height. Levels below the top floor that are not directly beneath the atrium are unaffected.
Figure C202.1
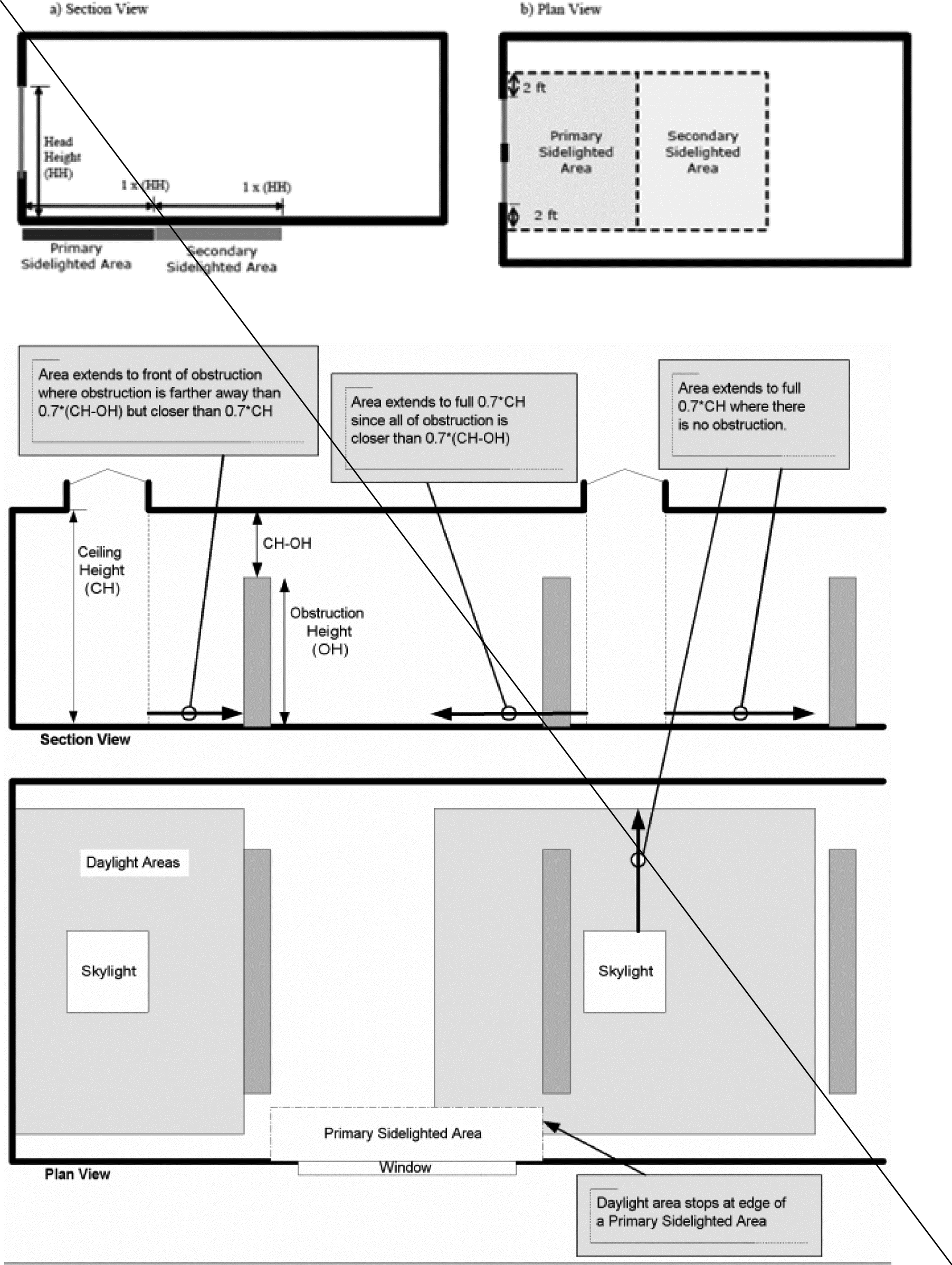 )) |
The portion of the building interior floor area that is illuminated by natural daylight through sidelight and toplight fenestration.
DEMAND CONTROL VENTILATION (DCV). A ventilation system capability that provides for the automatic reduction of outdoor air intake below design rates when the actual occupancy of spaces served by the system is less than design occupancy.
DEMAND RECIRCULATION WATER SYSTEM. A water distribution system where ((pump(s))) pumps prime the service hot water piping with heated water upon demand for hot water.
DUCT. A tube or conduit utilized for conveying air. The air passages of self-contained systems are not to be construed as air ducts.
DUCT SYSTEM. A continuous passageway for the transmission of air that, in addition to ducts, includes duct fittings, dampers, plenums, fans and accessory air-handling equipment and appliances.
DWELLING UNIT. A single unit providing complete independent living facilities for one or more persons, including permanent provisions for living, sleeping, eating, cooking and sanitation.
DYNAMIC GLAZING. Any fenestration product that has the fully reversible ability to change its performance properties, including U-factor, SHGC, or VT.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20206 Section C202.6—F.
FAN BRAKE HORSEPOWER (BHP). The horsepower delivered to the fan's shaft. Brake horsepower does not include the mechanical drive losses (belts, gears, etc.).
FAN EFFICIENCY GRADE (FEG). A numerical rating identifying the fan's aerodynamic ability to convert shaft power, or impeller power in the case of a direct-driven fan, to air power.
FAN SYSTEM BHP. The sum of the fan brake horsepower of all fans that are required to operate at fan system design conditions to supply air from the heating or cooling source to the conditioned space(s) and return it to the source or exhaust it to the outdoors.
FAN SYSTEM DESIGN CONDITIONS. Operating conditions that can be expected to occur during normal system operation that result in the highest supply fan airflow rate to conditioned spaces served by the system.
FAN SYSTEM MOTOR NAMEPLATE HP. The sum of the motor nameplate horsepower of all fans that are required to operate at design conditions to supply air from the heating or cooling source to the conditioned space(s) and return it to the source or exhaust it to the outdoors.
FENESTRATION. ((Skylights, roof windows, vertical windows (fixed or moveable), opaque doors, glazed doors, glazed block and combination opaque/glazed doors. Fenestration includes products with glass and nonglass glazing materials.)) Products classified as either vertical fenestration or skylights.
SKYLIGHT. Glass or other transparent or translucent glazing material installed at a slope of less than 60 degrees (91.05 rad) from horizontal.
VERTICAL FENESTRATION. Windows (fixed or moveable), opaque doors, glazed doors, glazed block and combination opaque/glazed doors composed of glass or other transparent or translucent glazing materials and installed at a slope of at least 60 degrees (91.05 rad) from horizontal.
CLERESTORY FENESTRATION. An upper region of vertical fenestration provided for the purpose of admitting daylight beyond the perimeter of a space. The entire clerestory fenestration assembly is installed at a height greater than 8 feet above the finished floor.
FENESTRATION AREA. Total area of the fenestration measured using the rough opening, and including the glazing, sash and frame.
FENESTRATION PRODUCT, FIELD-FABRICATED. A fenestration product whose frame is made at the construction site of standard dimensional lumber or other materials that were not previously cut, or otherwise formed with the specific intention of being used to fabricate a fenestration product or exterior door. Field fabricated does not include site-built fenestration.
FENESTRATION PRODUCT, SITE-BUILT. A fenestration designed to be made up of field-glazed or field-assembled units using specific factory cut or otherwise factory-formed framing and glazing units. Examples of site-built fenestration include storefront systems, curtain walls, and atrium roof systems.
-FACTOR.F The perimeter heat loss factor for slab-on-grade floors (Btu/h x ft x °F) [W/(m x K)].
FLOOR AREA, NET. The actual occupied area not including unoccupied accessory areas such as corridors, stairways, toilet rooms, mechanical rooms and closets.
FURNACE ELECTRICITY RATIO. The ratio of furnace electricity use to total furnace energy computed as ratio = (3.412 x EAE)/1000 x EF + 3.412 x EAE) where EAE (average annual auxiliary electrical consumption) and EF (average annual fuel energy consumption) are defined in Appendix N to Subpart B of Part 430 of Title 10 of the Code of Federal Regulations and EF is expressed in millions of Btus per year.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20207 Section C202.7—G.
GENERAL LIGHTING. Lighting that provides a substantially uniform level of illumination throughout an area. General lighting shall not include ((decorative lighting or)) lighting that provides a dissimilar level of illumination to serve a ((specialized)) specific application or decorative feature within such area.
GENERAL PURPOSE ELECTRIC MOTOR (SUBTYPE I). A motor that is designed in standard ratings with either of the following:
1. Standard operating characteristics and standard mechanical construction for use under usual service conditions, such as those specified in NEMA MG1, paragraph 14.02, "Usual Service Conditions," and without restriction to a particular application or type of application.
2. Standard operating characteristics or standard mechanical construction for use under unusual service conditions, such as those specified in NEMA MG1, paragraph 14.03, "Unusual Service Conditions," or for a particular type of application, and that can be used in most general purpose applications.
General purpose electric motors (Subtype I) are constructed in NEMA T-frame sizes or IEC metric equivalent, starting at 143T.
GENERAL PURPOSE ELECTRIC MOTOR (SUBTYPE II). A motor incorporating the design elements of a general purpose electric motor (Subtype I) that is configured as one of the following:
1. A U-frame motor.
2. A Design C motor.
3. A close-coupled pump motor.
4. A footless motor.
5. A vertical, solid-shaft, normal-thrust motor (as tested in a horizontal configuration).
6. An 8-pole motor (900 rpm).
7. A polyphase motor with voltage of not more than 600 volts (other than 230 or 460 volts).
GREENHOUSE. A permanent structure or a thermally isolated area of a building that maintains a specialized sunlit environment that is used exclusively for, and is essential to, the cultivation, protection or maintenance of plants. Greenhouses are those that are erected for a period of 180 days or more.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20208 Section C202.8—H.
HEAT TRAP. An arrangement of piping and fittings, such as elbows, or a commercially available heat trap that prevents thermosyphoning of hot water during standby periods.
HEATED SLAB-ON-GRADE FLOOR. Slab-on-grade floor construction in which the heating elements, hydronic tubing, or hot air distribution system is in contact with, or placed within or under, the slab.
((HIGH-EFFICACY LUMINAIRES. Luminaires with compact fluorescent lamps, T-8 or smaller diameter linear fluorescent lamps, or lamps with a minimum efficacy of:
1. 60 Lumens per watt for lamps over 40 watts;
2. 50 Lumens per watt for lamps over 15 watts to 40 watts; and
3. 40 Lumens per watt for lamps 15 watts or less.))
HIGH SPEED DOOR. A nonswinging door used primarily to facilitate vehicular access or material transportation, with a minimum opening rate of 32 inches (813 mm) per second, a minimum closing rate of 24 inches (610 mm) per second and that includes an automatic-closing device.
HISTORIC BUILDINGS. Buildings that are listed in or eligible for listing in the National Register of Historic Places, or designated as historic under an appropriate state or local law.
HUMIDISTAT. A regulatory device, actuated by changes in humidity, used for automatic control of relative humidity.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20209 Section C202.9—I.
INFILTRATION. The uncontrolled inward air leakage into a building caused by the pressure effects of wind or the effect of differences in the indoor and outdoor air density or both.
((INSULATING SHEATHING. An insulating board with a core material having a minimum R-value of R-2.))
INSULATION ENTIRELY ABOVE DECK. A roof with all insulation:
1. Installed above (outside of) the roof structure; and
2. Continuous (i.e., uninterrupted by framing members).
INTEGRATED ENERGY EFFICIENCY RATIO (IEER). A single-number figure of merit expressing cooling part-load EER efficiency for unitary air-conditioning and heat pump equipment on the basis of weighted operation at various load capacities for the equipment.
INTEGRATED PART LOAD VALUE (IPLV). A single number figure of merit based on part-load EER, COP, or kW/ton expressing part-load efficiency for air conditioning and heat pump equipment on the basis of weighted operation at various load capacities for equipment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20212 Section C202.12—L.
LABELED. Equipment, materials or products to which have been affixed a label, seal, symbol or other identifying mark of a nationally recognized testing laboratory, inspection agency or other organization concerned with product evaluation that maintains periodic inspection of the production of the above-labeled items and whose labeling indicates either that the equipment, material or product meets identified standards or has been tested and found suitable for a specified purpose.
LINER SYSTEM (LS). A system that includes the following:
1. A continuous vapor barrier liner membrane that is installed below the purlins and that is uninterrupted by framing members.
2. An uncompressed, unfaced insulation resting on top of the liner membrane and located between the purlins.
For multilayer installations, the last rated R-value of insulation is for unfaced insulation draped over purlins and then compressed when the metal roof panels are attached.
LISTED. Equipment, materials, products or services included in a list published by an organization acceptable to the code official and concerned with evaluation of products or services that maintains periodic inspection of production of listed equipment or materials or periodic evaluation of services and whose listing states either that the equipment, material, product or service meets identified standards or has been tested and found suitable for a specified purpose.
LOW-SLOPED ROOF. A roof having a slope less than 2 units vertical in 12 units horizontal.
LOW-VOLTAGE DRY-TYPE DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORMER. A transformer that is air-cooled, does not use oil as a coolant, has an input voltage less than or equal to 600.
LOW-VOLTAGE LIGHTING. A lighting system consisting of an isolating power supply, the low voltage luminaires, and associated equipment that are all identified for the use. The output circuits of the power supply operate at 30 volts (42.4 volts peak) or less under all load conditions.
LUMINAIRE. A complete lighting unit consisting of a lamp or lamps together with the housing designed to distribute the light, position and protect the lamps, and connect the lamps to the power supply.
LUMINAIRE-LEVEL LIGHTING CONTROL. A lighting system consisting of one or more luminaire(s) with embedded lighting control logic, occupancy and ambient light sensors, wireless networking capabilities, and local override switching capability.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20213 Section C202.13—M.
MANUAL. Capable of being operated by personal intervention (see "Automatic").
MASS TRANSFER DECK SLAB EDGE. That portion of the above-grade wall made up of the concrete slab where it extends past the footprint of the floor above. The area of the slab edge shall be defined as the thickness of the slab multiplied by the perimeter of the edge condition. Examples of this condition include, but are not limited to, the transition from an above-grade structure to a below-grade structure or the transition from a tower to a podium.
METAL BUILDING ROOF. A roof that:
1. Is constructed with a metal, structural, weathering surface;
2. Has no ventilated cavity; and
3. Has the insulation entirely below deck (i.e., does not include composite concrete and metal deck construction nor a roof framing system that is separated from the superstructure by a wood substrate) and whose structure consists of one or more of the following configurations:
a. Metal roofing in direct contact with the steel framing members;
b. Metal roofing separated from the steel framing members by insulation;
c. Insulated metal roofing panels installed as described in a or b.
METAL BUILDING WALL. A wall whose structure consists of metal spanning members supported by steel structural members (i.e., does not include spandrel glass or metal panels in curtain wall systems).
METER. A device that measures the flow of energy.
MICROCELL. A wireless communication facility consisting of an antenna that is either: (a) Four (4) feet in height and with an area of not more than 580 square inches; or (b) if a tubular antenna, no more than four (4) inches in diameter and no more than six (6) feet in length; and the associated equipment cabinet that is six (6) feet or less in height and no more than 48 square feet in floor area.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20215 Section C202.15—O.
OCCUPANT SENSOR CONTROL. An automatic control device or system that detects the presence or absence of people within an area and causes lighting, equipment or appliances to be regulated accordingly.
ON-SITE RENEWABLE ENERGY. Energy derived from solar radiation, wind, waves, tides, landfill gas, biomass, or the internal heat of the earth. The energy system providing on-site renewable energy shall be located on the project site.
OPAQUE DOOR. A door that is not less than 50 percent opaque in surface area.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20216 Section C202.16—P.
PERSONAL WIRELESS SERVICE FACILITY. A wireless communication facility (WCF), including a microcell, which is a facility for the transmission and/or reception of radio frequency signals and which may include antennas, equipment shelter or cabinet, transmission cables, a support structure to achieve the necessary elevation, and reception and/or transmission devices or antennas.
POWERED ROOF/WALL VENTILATORS. A fan consisting of a centrifugal or axial impeller with an integral driver in a weather-resistant housing and with a base designed to fit, usually by means of a curb, over a wall or roof opening.
PROPOSED DESIGN. A description of the proposed building used to estimate annual energy use for determining compliance based on total building performance.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-054, filed 11/25/14, effective 5/1/15)
WAC 51-11C-20218 Section C202.18—R.
RADIANT HEATING SYSTEM. A heating system that transfers heat to objects and surfaces within a conditioned space, primarily by infrared radiation.
READILY ACCESSIBLE. Capable of being reached quickly for operation, renewal or inspection without requiring those to whom ready access is requisite to climb over or remove obstacles or to resort to portable ladders or access equipment (see "Accessible").
REFRIGERANT DEW POINT. The refrigerant vapor saturation temperature at a specified pressure.
REFRIGERATED WAREHOUSE COOLER. An enclosed storage space that has a total chilled storage area of 3,000 ft2 or greater and is designed to maintain a temperature of greater than 32°F but less than 55°F.
REFRIGERATED WAREHOUSE FREEZER. An enclosed storage space that has a total chilled storage area of 3,000 ft2 or greater and is designed to maintain a temperature at or below 32°F.
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM, LOW TEMPERATURE. Systems for maintaining food product in a frozen state in refrigeration applications.
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM, MEDIUM TEMPERATURE. Systems for maintaining food product above freezing in refrigeration applications.
REGISTERED DESIGN PROFESSIONAL. An individual who is registered or licensed to practice their respective design profession as defined by the statutory requirements of the professional registration laws of the state or jurisdiction in which the project is to be constructed.
REPAIR. The reconstruction or renewal of any part of an existing building.
REROOFING. The process of recovering or replacing an existing roof covering. See "Roof Recover" and "Roof Replacement."
RESIDENTIAL BUILDING. For this code, includes detached one- and two-family dwellings and multiple single-family dwellings (townhouses) as well as Group R-2, R-3 and R-4 buildings three stories or less in height above grade plane.
ROOF ASSEMBLY. A system designed to provide weather protection and resistance to design loads. The system consists of a roof covering and roof deck or a single component serving as both the roof covering and the roof deck. A roof assembly includes the roof covering, underlayment, roof deck, insulation, vapor retarder and interior finish.
ROOF RECOVER. The process of installing an additional roof covering over a prepared existing roof covering without removing the existing roof covering.
ROOF REPAIR. Reconstruction or renewal of any part of an existing roof for the purposes of its maintenance.
ROOF REPLACEMENT. The process of removing the existing roof covering, repairing any damaged substrate and installing a new roof covering.
ROOFTOP MONITOR. A raised section of a roof containing vertical fenestration along one or more sides.
-VALUE (THERMAL RESISTANCE).R The inverse of the time rate of heat flow through a body from one of its bounding surfaces to the other surface for a unit temperature difference between the two surfaces, under steady state conditions, per unit area (h • ft2 • °F/Btu) [(m2 • K)/W].
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20219 Section C202.19—S.
SATURATED-CONDENSING TEMPERATURE. The saturation temperature corresponding to the measured refrigerant pressure at the condenser inlet for single component and azeotropic refrigerants, and the arithmetic average of the dew point and bubble point temperatures corresponding to the refrigerant pressure at the condenser entrance for zeotropic refrigerants.
SCREW LAMP HOLDERS. A lamp base that requires a screw-in-type lamp, such as a compact-fluorescent, incandescent, or tungsten-halogen bulb.
SEMI-HEATED SPACE. An enclosed space within a building, including adjacent connected spaces separated by an uninsulated component (e.g., basements, utility rooms, garages, corridors), which:
1. Is heated but not cooled, and has a maximum installed heating system output capacity of 3.4 Btu/(h-ft2) but not greater than 8 Btu/(h-ft2);
2. Is not a ((cold storage space or frozen storage space)) walk-in or warehouse cooler or freezer space.
SERVICE WATER HEATING. Heating water for domestic or commercial purposes other than space heating and process requirements.
SKYLIGHT. Glass or other transparent or translucent glazing material installed at a slope of less than 60 degrees (1.05 rad) from horizontal. Glazing material in skylights, including unit skylights, solariums, sunrooms, roofs and sloped walls is included in this definition.
SLAB BELOW GRADE. Any portion of a slab floor in contact with the ground which is more than 24 inches below the final elevation of the nearest exterior grade.
SLAB-ON-GRADE FLOOR. That portion of a slab floor of the building envelope that is in contact with the ground and that is either above grade or is less than or equal to 24 inches below the final elevation of the nearest exterior grade.
SLEEPING UNIT. A room or space in which people sleep, which can also include permanent provisions for living, eating, and either sanitation or kitchen facilities but not both. Such rooms and spaces that are also part of a dwelling unit are not sleeping units.
SMALL ELECTRIC MOTOR. A general purpose, alternating current, single speed induction motor.
SMALL BUSINESS. Any business entity (including a sole proprietorship, corporation, partnership or other legal entity) which is owned and operated independently from all other businesses, which has the purpose of making a profit, and which has fifty or fewer employees.
SOLAR HEAT GAIN COEFFICIENT (SHGC). The ratio of the solar heat gain entering the space through the fenestration assembly to the incident solar radiation. Solar heat gain includes directly transmitted solar heat and absorbed solar radiation which is then reradiated, conducted or convected into the space.
STANDARD REFERENCE DESIGN. A version of the proposed design that meets the minimum requirements of this code and is used to determine the maximum annual energy use requirement for compliance based on total building performance.
STEEL-FRAMED WALL. A wall with a cavity (insulated or otherwise) whose exterior surfaces are separated by steel framing members (i.e., typical steel stud walls and curtain wall systems).
STOREFRONT. A nonresidential system of doors and windows mulled as a composite fenestration structure that has been designed to resist heavy use. Storefront systems include, but are not limited to, exterior fenestration systems that span from the floor level or above to the ceiling of the same story on commercial buildings, with or without mulled windows and doors.
SUBSYSTEM METER. A meter placed downstream of the energy supply meter that measures the energy delivered to a load or a group of loads.
((SUNROOM. A one-story structure attached to a dwelling with a glazing area in excess of 40 percent of the gross area of the structure's exterior walls and roof.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20220 Section C202.20—T.
((THERMAL ISOLATION. Physical and space conditioning separation from conditioned space(s). The conditioned space(s) shall be controlled as separate zones for heating and cooling or conditioned by separate equipment.)) TEMPORARY GROWING STRUCTURE. A temporary growing structure has sides and roof covered with polyethylene, polyvinyl or similar flexible synthetic material and is used to provide plants with either frost protection or increased heat retention. Temporary structures are those that are erected for a period of less than 180 days.
THERMOSTAT. An automatic control device used to maintain temperature at a fixed or adjustable set point.
TIME SWITCH CONTROL. An automatic control device or system that controls lighting or other loads, including switching off, based on time schedules.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20221 Section C202.21—U.
-FACTOR (THERMAL TRANSMITTANCE).U The coefficient of heat transmission (air to air) through a building component or assembly, equal to the time rate of heat flow per unit area and unit temperature difference between the warm side and cold side air films (Btu/h • ft2 • °F) [W/(m2 • K)].
UNHEATED SLAB-ON-GRADE FLOOR. A slab-on-grade floor that is not a heated slab-on-grade floor.
UNIFORM ILLUMINATION. A quality of illumination delivered by a lighting system typically comprised of similar fixtures mounted at a regular spacing interval. This lighting system provides a uniform contrast ratio of no greater than 5:1 maximum-to-minimum ratio throughout the entire area served, including task areas.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20222 Section C202.22—V.
VARIABLE REFRIGERANT FLOW SYSTEM. An engineered direct-expansion (DX) refrigerant system that incorporates a common condensing unit, at least one variable capacity compressor, a distributed refrigerant piping network to multiple indoor fan heating and cooling units each capable of individual zone temperature control, through integral zone temperature control devices and a common communications network. Variable refrigerant flow utilizes three or more steps of control on common interconnecting piping.
VENTILATION. The natural or mechanical process of supplying conditioned or unconditioned air to, or removing such air from, any space.
VENTILATION AIR. That portion of supply air that comes from outside (outdoors) plus any recirculated air that has been treated to maintain the desired quality of air within a designated space.
VERTICAL FENESTRATION. All fenestration other than skylights.
VISIBLE TRANSMITTANCE [VT]. The ratio of visible light entering the space through the fenestration product assembly to the incident visible light, visible transmittance, includes the effects of glazing material and frame and is expressed as a number between 0 and 1.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-20223 Section C202.23—W.
WALK-IN COOLER. An enclosed storage space capable of being refrigerated to temperatures above 32°F ((that can be walked into and has a total chilled storage area of less than 3,000 ft2)) (0°C) and less than 55°F (12.8°C) that can be walked into, has a ceiling height of not less than 7 feet (2134 mm) and has a total chilled storage area of less than 3,000 square feet (279 m2).
WALK-IN FREEZER. An enclosed storage space capable of being refrigerated to temperatures at or below 32°F ((that can be walked into and has a total chilled storage area of less than 3,000 ft2)) (0°C) that can be walked into, has a ceiling height of not less than 7 feet (2134 mm) and has a total chilled storage area of less than 3,000 square feet (279 m2).
WALL. That portion of the building envelope, including opaque area and fenestration, that is vertical or tilted at an angle of 60 degrees from horizontal or greater. This includes above-grade walls and below-grade walls, between floor spandrels, peripheral edges of floors, and foundation walls.
WATER HEATER. Any heating appliance or equipment that heats potable water and supplies such water to the potable hot water distribution system.
WOOD-FRAMED AND OTHER WALLS. All other wall types, including wood stud walls.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-30310 Section 303.1—Identification.
C303.1 Identification. Materials, systems and equipment shall be identified in a manner that will allow a determination of compliance with the applicable provisions of this code.
C303.1.1 Building thermal envelope insulation. An R-value identification mark shall be applied by the manufacturer to each piece of building thermal envelope insulation 12 inches (305 mm) or greater in width. Alternately, the insulation installers shall provide a certification listing the type, manufacturer and R-value of insulation installed in each element of the building thermal envelope. For blown or sprayed insulation (fiberglass and cellulose), the initial installed thickness, settled thickness, settled R-value, installed density, coverage area and number of bags installed shall be listed on the certification. For sprayed polyurethane foam (SPF) insulation, the installed thickness of the areas covered and R-value of installed thickness shall be listed on the certification. For insulated siding, the R-value shall be labeled on the product's package and shall be listed on the certification. The insulation installer shall sign, date and post the certification in a conspicuous location on the job site.
C303.1.1.1 Blown or sprayed roof/ceiling insulation. The thickness of blown-in or sprayed roof/ceiling insulation (fiberglass or cellulose) shall be written in inches (mm) on markers that are installed at least one for every 300 square feet (28 m2) throughout the attic space. The markers shall be affixed to the trusses or joists and marked with the minimum initial installed thickness with numbers ((a minimum)) of not less than 1 inch (25 mm) in height. Each marker shall face the attic access opening. Spray polyurethane foam thickness and installed R-value shall be listed on certification provided by the insulation installer.
C303.1.2 Insulation mark installation. Insulating materials shall be installed such that the manufacturer's R-value mark is readily observable upon inspection.
C303.1.3 Fenestration product rating. U-factors of fenestration products (windows, doors and skylights) shall be determined in accordance with NFRC 100 by an accredited, independent laboratory, and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
EXCEPTION: | Where required, garage door U-factors shall be determined in accordance with either NFRC 100 or ANSI/DASMA 105. |
U-factors shall be determined by an accredited, independent laboratory, and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
Products lacking such a labeled U-factor shall be assigned a default U-factor from Table C303.1.3(1), C303.1.3(2) or C303.1.3(4). The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) and visible transmittance (VT) of glazed fenestration products (windows, glazed doors and skylights) shall be determined in accordance with NFRC 200 by an accredited, independent laboratory, and labeled and certified by the manufacturer. Products lacking such a labeled SHGC or VT shall be assigned a default SHGC or VT from Table C303.1.3(3).
EXCEPTION: | Units without NFRC ratings produced by a small business may be assigned default U-factors from Table C303.1.3(5) for vertical fenestration. |
C303.1.4 Insulation product rating. The thermal resistance (R-value) of insulation shall be determined in accordance with the U.S. Federal Trade Commission R-value rule (C.F.R. Title 16, Part 460) in units of h x ft2 x °F/Btu at a mean temperature of 75°F (24°C).
C303.1.4.1 Insulated siding. The thermal resistance (R-Value) shall be determined in accordance with ASTM C1363. Installation for testing shall be in accordance with the manufacturer's installation instructions.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-303131 Table C303.1.3(1)—Default glazed fenestration U-factors.
Table C303.1.3(1)
Default Glazed Fenestration U-Factors
FRAME TYPE |
SINGLE PANE |
DOUBLE PANE |
SKY-LIGHT |
Metal |
1.20 |
0.80 |
|
Metal with Thermal Break |
1.10 |
0.65 |
See Table C303.1.3(4) |
Nonmetal or Metal Clad |
0.95 |
0.55 |
|
Glazed Block |
0.60 |
||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-30320 Section C303.2—Installation.
C303.2 Installation. ((All)) Materials, systems and equipment shall be installed in accordance with the manufacturer's ((installation)) instructions and the International Building Code.
C303.2.1 Protection of exposed foundation insulation. Insulation applied to the exterior of basement walls, crawlspace walls and the perimeter of slab-on-grade floors shall have a rigid, opaque and weather-resistant protective covering to prevent the degradation of the insulation's thermal performance. The protective covering shall cover the exposed exterior insulation and extend ((a minimum of)) not less than 6 inches (153 mm) below grade.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40100 Section C401—General.
C401.1 Scope. The ((requirements contained)) provisions in this chapter are applicable to commercial buildings((, or portions of commercial buildings)) and their building sites.
C401.2 Application. Commercial buildings shall comply with one of the following:
1. The requirements of Sections C402, C403, C404, C405, C406, C408 ((and)), C409 and C410.
2. The requirements of Section C407, C408, C409, C410, C402.4, C403.2, C404, C405.2, C405.3, C405.4, C405.6 and C405.7. The building energy consumption shall be equal to or less than ((93)) 87 percent of the standard reference design building.
((C401.2.1 Application to existing buildings. Additions, alterations and repairs to existing buildings shall comply with Sections C402, C403, C404, C405, C408 and C409.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40210 Section C402.1—General (Prescriptive).
C402.1 General (Prescriptive). ((The)) Building thermal envelope ((shall)) assemblies for buildings that are intended to comply with ((Section C402.1.1. Section C402.1.2 or Section C402.1.3 shall be permitted as an alternative to the R-values specified in Section C402.1.1. Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers shall comply with C402.5. Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers shall comply with C402.6.
EXCEPTION: | Unstaffed equipment shelters or cabinets used solely for personal wireless service facilities.)) |
the code on a prescriptive basis, in accordance with the compliance path described in Item 1 of Section C401.2, shall comply with the following:
1. The opaque portions of the building thermal envelope shall comply with the specific insulation requirements of Section C402.2 and the thermal requirements of either the R-value based method of Section C402.1.3, the U-, C- and F-factor based method of Section C402.1.4, or the component performance alternative of Section C402.1.5.
2. Fenestration in building envelope assemblies shall comply with Section C402.5.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40211 Section C402.1.1—((Insulation and fenestration criteria)) Low energy buildings.
C402.1.1 ((Insulation and fenestration criteria. The building thermal envelope shall meet the requirements of Tables C402.2 and C402.3 based on the climate zone specified in Chapter 3. Commercial buildings or portions of commercial buildings enclosing Group R occupancies shall use the R-values from the "Group R" column of Table C402.2. Commercial buildings or portions of commercial buildings enclosing occupancies other than Group R shall use the R-values from the "All other" column of Table C402.2.)) Low energy buildings. The following buildings, or portions thereof, separated from the remainder of the building by building thermal envelope assemblies complying with this code shall be exempt from all thermal envelope provision of this code:
1. Those that are heated and/or cooled with a peak design rate of energy usage less than 3.4 Btu/hx ft2(10.7 W/m2) or 1.0 watt/ft2(10.7 W/m2) of floor area for space conditioning purposes.
2. Those that do not contain conditioned space.
3. Greenhouses where cooling does not include a condensing unit and that are isolated from any other conditioned space.
4. Unstaffed equipment shelters or cabinets used solely for personal wireless service facilities.
C402.1.1.1 Semi-heated buildings and spaces. The building envelope of semi-heated buildings, or portions thereof, shall comply with the same requirements as that for conditioned spaces in Section C402. Building envelope assemblies separating conditioned space from semi-heated space shall comply with exterior envelope insulation requirements. Semi-heated spaces heated by mechanical systems that do not include electric resistance heating equipment are not required to comply with the opaque wall insulation provisions of Section C402.2.3 for walls that separate semi-heated spaces from the exterior or low energy spaces. Semi-heated spaces shall be calculated separately from other conditioned spaces for compliance purposes. Opaque walls in semi-heated spaces shall be calculated as fully code compliant opaque walls for both the target and proposed for the Target UA calculations for Component Performance compliance per Section C402.1.5, and for the Standard Reference Design for Total Building Performance compliance per Section C407.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40212 Section C402.1.2—((U-factor alternative)) Equipment buildings.
C402.1.2 ((U-factor alternative. An assembly with a U-factor, C-factor, or F-factor equal or less than that specified in Table C402.1.2 shall be permitted as an alternative to the R-value in Table C402.2. Commercial buildings or portions of commercial buildings enclosing Group R occupancies shall use the U-factor, C-factor, or F-factor from the "Group R" column of Table C402.1.2. Commercial buildings or portions of commercial buildings enclosing occupancies other than Group R shall use the U-factor, C-factor or F-factor from the "All other" column of Table C402.1.2. The U-factors for typical construction assemblies are included in Appendix A. These values shall be used for all calculations. Where proposed construction assemblies are not represented in Appendix A, values shall be calculated in accordance with the ASHRAE Handbook—Fundamentals using the framing factors listed in Appendix A where applicable and shall include the thermal bridging effects of framing materials.)) Equipment buildings. Buildings that comply with all of the following shall be exempt from the building thermal envelope provisions of this code:
1. Are separate buildings with floor area no more than 500 square feet (50 m2).
2. Are intended to house electronic equipment with installed equipment power totaling at least 7 watts per square foot (75 W/m2) and not intended for human occupancy.
3. Have a heating system capacity not greater than (17,000 Btu/hr) (5 kW) and a heating thermostat set point that is restricted to not more than 50°F (10°C).
4. Have an average wall and roof U-factor less than 0.200.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-402121 Table ((C402.1.2)) C402.1.3—Opaque thermal envelope assembly R-value requirements.
((Table C402.1.2
Opaque Thermal Envelope Assembly Requirementsa
CLIMATE ZONE |
5 AND MARINE 4 |
6 |
||
All Other |
Group R |
All Other |
Group R |
|
Roofs |
||||
Insulation entirely above deck |
U-0.034 |
U-0.031 |
U-0.032 |
U-0.031 |
Metal buildings |
U-0.031 |
U-0.031 |
U-0.029 |
U-0.031 |
Attic and other |
U-0.021 |
U-0.021 |
U-0.021 |
U-0.021 |
Walls, Above Grade |
||||
Mass |
U-0.104d |
U-0.078 |
U-0.078 |
U-0.071 |
Metal building |
U-0.052 |
U-0.052 |
U-0.052 |
U-0.044 |
Steel framed |
U-0.055 |
U-0.055 |
U-0.049 |
U-0.044 |
Wood framed and other |
U-0.054 |
U-0.054 |
U-0.051 |
U-0.044 |
Walls, Below Grade |
||||
Below-grade wallb |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Floors |
||||
Mass |
U-0.031 |
U-0.031 |
U-0.031 |
U-0.031 |
Joist/framing |
U-0.029 |
U-0.029 |
U-0.029 |
U-0.029 |
Slab-on-Grade Floors |
||||
Unheated slabs |
F-0.54 |
F-0.54 |
F-0.54 |
F-0.52 |
Heated slabsc |
F-0.55 |
F-0.55 |
F-0.55 |
F-0.55 |
a | Use of opaque assembly U-factors, C-factors, and F-factors from Appendix A is required unless otherwise allowed by Section C402.1.2. |
b | Where heated slabs are below grade, below-grade walls shall comply with the F-factor requirements for heated slabs. |
c | Heated slab F-factors shall be determined specifically for heated slabs. Unheated slab factors shall not be used. |
d | Exception: Integral insulated concrete block walls complying with ASTM C90 with all cores filled and meeting both of the following: |
1 | At least 50 percent of cores must be filled with vermiculite or equivalent fill insulation; and |
2 | The building thermal envelope encloses one or more of the following uses: Warehouse (storage and retail), gymnasium, auditorium, church chapel, arena, kennel, manufacturing plant, indoor swimming pool, pump station, water and waste water treatment facility, storage facility, storage area, motor vehicle service facility. Where additional uses not listed (such as office, retail, etc.) are contained within the building, the exterior walls that enclose these areas may not utilize this exception and must comply with the appropriate mass wall U-factor from Table C402.1.2.)) |
OPTION 1:
Table C402.1.3
Opaque Thermal Envelope Insulation Component
Minimum Requirements, R-value Methoda,g
CLIMATE ZONE |
5 AND MARINE 4 |
|
All Other |
Group R |
|
Roofs |
||
Insulation entirely above deck |
R-30ci |
R-38ci |
Metal buildingsb |
R-25 + R-11 LS |
R-25 + R-11 LS |
Attic and other |
R-49 |
R-49 |
Walls, Above Grade |
||
Mass |
R-11.4ci |
R-13.3ci |
Metal buildings |
R-19ci |
R-19ci |
Steel framed |
R-13 + R-10ci |
R-19 + R-8.5ci |
Wood framed and other |
R-21 int |
R-21 int |
Walls, Below Grade |
||
Below-grade walld |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Floors |
||
Massf |
R-30ci |
R-30ci |
Joist/framing |
R-30e |
R-30e |
Slab-on-Grade Floors |
||
Unheated slabs |
R-10 for 24" below |
R-10 for 24" below |
Heated slabs |
R-10 perimeter & under entire slab |
R-10 perimeter & under entire slab |
Opaque Doors |
||
Nonswinging |
R-4.75 |
R-4.75 |
For SI: | 1 inch = 25.4 mm. ci = Continuous insulation. NR = No requirement. |
LS = | Liner system—A continuous membrane installed below the purlins and uninterrupted by framing members. Uncompressed, unfaced insulation rests on top of the membrane between the purlins. |
a | Assembly descriptions can be found in Chapter 2 and Appendix A. |
b | Where using R-value compliance method, a thermal spacer block shall be provided, otherwise use the U-factor compliance method in Table C402.1.4. |
c | Reserved. |
d | Where heated slabs are below grade, below-grade walls shall comply with the exterior insulation requirements for heated slabs. |
e | Steel floor joist systems shall be insulated to R-38 + R-10ci. |
f | "Mass floors" shall include floors weighing not less than: 1. 35 pounds per square foot of floor surface area; or 2. 25 pounds per square foot of floor surface area where the material weight is not more than 120 pounds per cubic foot. |
g | For roof, wall or floor assemblies where the proposed assembly would not be continuous insulation, an alternate nominal R-value compliance option for assemblies with isolated metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation is: |
Assemblies with continuous insulation (see definition) |
Alternate option for assemblies with metal penetrations, greater than 0.04% but less than 0.08% |
Alternate option for assemblies with metal penetrations, greater than or equal to 0.08% but less than 0.12% |
R-9.5ci |
R-11.9ci |
R-13ci |
R-11.4ci |
R-14.3ci |
R-15.7ci |
R-13.3ci |
R-16.6ci |
R-18.3ci |
R-15.2ci |
R-19.0ci |
R-21ci |
R-30ci |
R-38ci |
R-42ci |
R-38ci |
R-48ci |
R-53ci |
R-13 + R-7.5ci |
R-13 + R-9.4ci |
R-13 + R-10.3ci |
R-13 + R-10ci |
R-13 + R-12.5ci |
R-13 + R-13.8ci |
R-13 + R-12.5ci |
R-13 + R-15.6ci |
R-13 + R-17.2ci |
R-13 + R-13ci |
R-13 + R-16.3ci |
R-13 + R-17.9ci |
R-19 + R-8.5ci |
R-19 + R-10.6ci |
R-19 + R-11.7ci |
R-19 + R-14ci |
R-19 + R-17.5ci |
R-19 + R-19.2ci |
R-19 + R-16ci |
R-19 + R-20ci |
R-19 + R-22ci |
R-20 + R-3.8ci |
R-20 + R-4.8ci |
R-20 + R-5.3ci |
R-21 + R-5ci |
R-21 + R-6.3ci |
R-21 + R-6.9ci |
This alternate nominal R-value compliance option is allowed for projects complying with all of the following:
1. | The ratio of the cross-sectional area, as measured in the plane of the surface, of metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation to the opaque surface area of the assembly is greater than 0.0004 (0.04%), but less than 0.0012 (0.12%). |
2. | The metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation are isolated or discontinuous (e.g., brick ties or other discontinuous metal attachments, offset brackets supporting shelf angles that allow insulation to go between the shelf angle and the primary portions of the wall structure). No continuous metal elements (e.g., metal studs, z-girts, z-channels, shelf angles) penetrate the otherwise continuous portion of the insulation. |
3. | Building permit drawings shall contain details showing the locations and dimensions of all the metal penetrations (e.g., brick ties or other discontinuous metal attachments, offset brackets, etc.) of otherwise continuous insulation. In addition, calculations shall be provided showing the ratio of the cross-sectional area of metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation to the overall opaque wall area. |
For other cases where the proposed assembly is not continuous insulation, see Section C402.1.2 for determination of U-factors for assemblies that include metal other than screws and nails.
OPTION 2:
Table C402.1.3
Opaque Thermal Envelope Insulation Component
Minimum Requirements, R-value Methoda,g
CLIMATE ZONE |
5 AND MARINE 4 |
|
All Other |
Group R |
|
Roofs |
||
Insulation entirely above deck |
R-30ci |
R-38ci |
Metal buildingsb |
R-25 + R-11 LS |
R-25 + R-11 LS |
Attic and other |
R-49 |
R-49 |
Walls, Above Grade |
||
Mass |
R-13.3ci |
R-13.3ci |
Metal buildings |
R-19ci |
R-19ci |
Steel framed |
R-13 + R-10ci |
R-19 + R-8.5ci |
Wood framed and other |
R-21 int |
R-21 int |
Walls, Below Grade |
||
Below-grade walld |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Floors |
||
Massf |
R-30ci |
R-30ci |
Joist/framing |
R-30e |
R-30e |
Slab-on-Grade Floors |
||
Unheated slabs |
R-10 for 24" below |
R-10 for 24" below |
Heated slabsd |
R-10 perimeter & under entire slab |
R-10 perimeter & under entire slab |
Opaque Doors |
||
Nonswinging |
R-4.75 |
R-4.75 |
For SI: | 1 inch = 25.4 mm. ci = Continuous insulation. NR = No requirement. |
LS = | Liner system—A continuous membrane installed below the purlins and uninterrupted by framing members. Uncompressed, unfaced insulation rests on top of the membrane between the purlins. |
a | Assembly descriptions can be found in Chapter 2 and Appendix A. |
b | Where using R-value compliance method, a thermal spacer block shall be provided, otherwise use the U-factor compliance method in Table C402.1.4. |
c | Reserved. |
d | Where heated slabs are below grade, below-grade walls shall comply with the exterior insulation requirements for heated slabs. |
e | Steel floor joist systems shall be insulated to R-38 + R-10ci. |
f | "Mass floors" shall include floors weighing not less than: 1. 35 pounds per square foot of floor surface area; or 2. 25 pounds per square foot of floor surface area where the material weight is not more than 120 pounds per cubic foot. |
g | For roof, wall or floor assemblies where the proposed assembly would not be continuous insulation, an alternate nominal R-value compliance option for assemblies with isolated metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation is: |
Assemblies with continuous insulation (see definition) |
Alternate option for assemblies with metal penetrations, greater than 0.04% but less than 0.08% |
Alternate option for assemblies with metal penetrations, greater than or equal to 0.08% but less than 0.12% |
R-11.4ci |
R-14.3ci |
R-13ci |
R-13.3ci |
R-16.6ci |
R-15.7ci |
R-15.2ci |
R-19.0ci |
R-18.3ci |
R-30ci |
R-38ci |
R-21ci |
R-38ci |
R-48ci |
R-42ci |
R-13 + R-7.5ci |
R-13 + R-9.4ci |
R-53ci |
R-13 + R-10ci |
R-13 + R-12.5ci |
R-13 + R-10.3ci |
R-13 + R-12.5ci |
R-13 + R-15.6ci |
R-13 + R-13.8ci |
R-13 + R-13ci |
R-13 + R-16.3ci |
R-13 + R-17.2ci |
R-19 + R-8.5ci |
R-19 + R-10.6ci |
R-13 + R-17.9ci |
R-19 + R-14ci |
R-19 + R-17.5ci |
R-19 + R-11.7ci |
R-19 + R-16ci |
R-19 + R-20ci |
R-19 + R-19.2ci |
R-20 + R-3.8ci |
R-20 + R-4.8ci |
R-19 + R-22ci |
R-21 + R-5ci |
R-21 + R-6.3ci |
R-20 + R-5.3ci |
This alternate nominal R-value compliance option is allowed for projects complying with all of the following:
1. | The ratio of the cross-sectional area, as measured in the plane of the surface, of metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation to the opaque surface area of the assembly is greater than 0.0004 (0.04%), but less than 0.0012 (0.12%). |
2. | The metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation are isolated or discontinuous (e.g., brick ties or other discontinuous metal attachments, offset brackets supporting shelf angles that allow insulation to go between the shelf angle and the primary portions of the wall structure). No continuous metal elements (e.g., metal studs, z-girts, z-channels, shelf angles) penetrate the otherwise continuous portion of the insulation. |
3. | Building permit drawings shall contain details showing the locations and dimensions of all the metal penetrations (e.g., brick ties or other discontinuous metal attachments, offset brackets, etc.) of otherwise continuous insulation. In addition, calculations shall be provided showing the ratio of the cross-sectional area of metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation to the overall opaque wall area. |
For other cases where the proposed assembly is not continuous insulation, see Section C402.1.2 for determination of U-factors for assemblies that include metal other than screws and nails.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-122, filed 12/3/14, effective 1/3/15)
WAC 51-11C-40213 Section C402.1.3—((Component performance option)) Insulation component R-value method.
((C402.1.3 Component performance building envelope option.
C402.1.3.1 General. Buildings or structures whose design heat loss rate (UAp) and solar heat gain coefficient rate (SHGC * Ap) are less than or equal to the target heat loss rate (UAt) and solar heat gain coefficient rate (SHGC * At) shall be considered in compliance with this section. The stated U-factor, F-factor or allowable area of any component assembly, listed in Table C402.1.2 and Table C402.3, such as roof/ceiling, opaque wall, opaque door, fenestration, floor over conditioned space, slab-on-grade floor, radiant floor or opaque floor may be increased and the U-factor or F-factor for other components decreased, provided that the total heat gain or loss for the entire building envelope does not exceed the total resulting from compliance to the U-factors, F-factors or allowable areas specified in this section. Compliance shall be calculated in total for the building envelope for other than Group R spaces and for Group R spaces.
C402.1.3.2 Component U-factors. The U-factors for typical construction assemblies are included in Chapter 3 and Appendix A. These values shall be used for all calculations. Where proposed construction assemblies are not represented in Chapter 3 or Appendix A, values shall be calculated in accordance with the ASHRAE Handbook—Fundamentals, using the framing factors listed in Appendix A.
For envelope assemblies containing metal framing, the U-factor shall be determined by one of the following methods:
1. Results of laboratory measurements according to acceptable methods of test.
2. ASHRAE Handbook—Fundamentals where the metal framing is bonded on one or both sides to a metal skin or covering.
3. The zone method as provided in ASHRAE Handbook—Fundamentals.
4. Effective framing/cavity R-values as provided in Appendix A.
When return air ceiling plenums are employed, the roof/ceiling assembly shall:
a. For thermal transmittance purposes, not include the ceiling proper nor the plenum space as part of the assembly; and
b. For gross area purposes, be based upon the interior face of the upper plenum surface.
5. Tables in ASHRAE 90.1-2010 Normative Appendix A.
C402.1.3.3 UA calculations. The target UAt and the proposed UAp shall be calculated using Equations C402-1 and C402-2 and the corresponding areas and U-factors from Table C402.1.2 and Table C402.3. For the target UAt calculation, the skylights shall be located in roof/ceiling area up to the maximum skylight area per Section C402.3.1 and the remainder of the fenestration allowed per Section C402.3.1 shall be located in the wall area.
C402.1.3.4 SHGC rate calculations. Solar heat gain coefficient shall comply with Table C402.3. The target SHGCAt and the proposed SHGCAp shall be calculated using Equations C402-3 and C402-4 and the corresponding areas and SHGCs from Table C402.3.)) C402.1.3 Insulation component R-value-based method. Building thermal envelope opaque assemblies shall meet the requirements of Section C402.2 and C402.4 based on the climate zone specified in Chapter 3. For opaque portions of the building thermal envelope intended to comply on an insulation component R-value basis, the R-values for insulation in framing areas, where required, and for continuous insulation, where required, shall not be less than that specified in Table C402.1.3. Commercial buildings or portions of commercial buildings enclosing Group R occupancies shall use the R-values from the "Group R" column of Table C402.1.3. Commercial buildings or portions of commercial buildings enclosing occupancies other than Group R shall use the R-values from the "All other" column of Table C402.1.3. The thermal resistance or R-value of the insulating material installed in, or continuously on, below grade exterior walls of the building envelope required in accordance with Table C402.1.3 shall extend to the lowest floor of the conditioned space enclosed by the below grade wall. Doors having less than 50 percent opaque glass area shall be considered opaque doors. Opaque swinging doors shall comply with the Table C402.1.4 and opaque nonswinging doors shall comply with Table C402.1.3 or C402.1.4.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-122, filed 12/3/14, effective 1/3/15)
WAC 51-11C-402131 ((Equation C402-1—Target UAt.)) Reserved.
((Equation C402-1
Target UAt
UAt |
= |
UradtAradt + UmrtAmrt + UratArat + Umwt(Amwt + Amwbgt) + Umbwt(Ambwt + Ambwbgt) + Usfwt(Asfwt + Asfwbgt) + Uwfwt(Awfwt + Awfwbgt) + UfmtAfmt + UfjtAfjt + FstPst + FsrtPsrt + UdstAdst + UdrtAdrt + UvgtAvgt + UvgmtAvgmt + UvgmotAvgmot + UvgdtAvgdt + UogtAogt |
||
UAt |
= |
The target combined specific heat transfer of the gross roof/ceiling assembly, exterior wall and floor area. |
||
Where: |
||||
Uradt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for roofs with the insulation entirely above deck found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Umrt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for metal building roofs found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Urat |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for attic and other roofs found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Umwt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for opaque mass walls found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Umbwt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for opaque metal building walls found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Usfwt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for opaque steel-framed walls found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Uwfwt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for opaque wood framed and other walls found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Ufmt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for mass floors over unconditioned space found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Ufjt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for joist floors over unconditioned space found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Fst |
= |
The F-factor for slab-on-grade floors found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Fsrt |
= |
The F-factor for radiant slab floors found in Table C402.1.2. |
||
Udst |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for opaque swinging doors found in Table C402.2. |
||
Udrt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for opaque roll-up or sliding doors found in Table C402.2. |
||
Uvgt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for vertical fenestration with nonmetal framing found in Table C402.3 which corresponds to the proposed vertical fenestration area as a percent of gross exterior wall area. *Buildings utilizing Section C402.3.1.3 shall use the thermal transmittance value specified there. |
||
Uvgmt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for vertical fenestration with fixed metal framing found in Table C402.3 which corresponds to the proposed vertical fenestration area as a percent of gross exterior wall area. *Buildings utilizing Section C402.3.1.3 shall use the thermal transmittance value specified there. |
||
Uvgmot |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for vertical fenestration with operable metal framing found in Table C402.3 which corresponds to the proposed vertical fenestration area as a percent of gross exterior wall area. *Buildings utilizing Section C402.3.1.3 shall use the thermal transmittance value specified there. |
||
Uvgdt |
= |
The thermal transmittance value for entrance doors found in Table C402.3 which corresponds to the proposed vertical fenestration area as a percent of gross exterior wall area. Buildings utilizing Section C402.3.1.3 shall use the thermal transmittance value specified there. |
||
Uogt |
= |
The thermal transmittance for skylights found in Table C402.3 which corresponds to the proposed skylight area as a percent of gross exterior roof area. |
||
Afmt |
= |
The proposed mass floor over unconditioned space area, Afm. |
||
Afjt |
= |
The proposed joist floor over unconditioned space area, Afj. |
||
Pst |
= |
The proposed linear feet of slab-on-grade floor perimeter, Ps. |
||
Psrt |
= |
The proposed linear feet of radiant slab floor perimeter, Prs. |
||
Adst |
= |
The proposed opaque swinging door area, Ads. |
||
Adrt |
= |
The proposed opaque roll-up or sliding door area, Adr. |
||
and |
||||
If the vertical fenestration area as a percent of gross above-grade exterior wall area does not exceed the maximum allowed in Section C402.3.1.3: |
||||
Amwt |
= |
The proposed opaque above grade mass wall area, Amw. |
||
Amwbgt |
= |
The proposed opaque below grade mass wall area, Amw. |
||
Ambwt |
= |
The proposed opaque above grade metal building wall area, Ambw. |
||
Ambwbgt |
= |
The proposed opaque below grade metal building wall area, Ambwbg. |
||
Asfwt |
= |
The proposed opaque above grade steel framed wall area, Amfw. |
||
Asfwbgt |
= |
The proposed opaque below grade steel framed wall area, Amfwbg. |
||
Awfwt |
= |
The proposed opaque above grade wall wood framed and other area, Awfwbg. |
||
Awfwbgt |
= |
The proposed opaque below grade wall wood framed and other area, Awfwbg. |
||
Avgt |
= |
The proposed vertical fenestration area with nonmetal framing, Avg. |
||
Avgmt |
= |
The proposed vertical fenestration area with fixed metal framing, Avgm. |
||
Avgmot |
= |
The proposed vertical fenestration area with operable metal framing, Avgmo. |
||
Avgdt |
= |
The proposed entrance door area, Avgd. |
||
or |
||||
If the vertical fenestration area as a percent of gross above-grade exterior wall area exceeds the maximum allowed in Section C402.3.1, the area of each vertical fenestration element shall be reduced in the base envelope design by the same percentage and the net area of each above-grade wall type increased proportionately by the same percentage so that the total vertical fenestration area is exactly equal to the allowed percentage per Section C402.3.1 of the gross above-grade wall area. The target wall area of a given wall type shall be the sum of the proposed below grade area and the increased above-grade area. |
||||
and |
||||
If the skylight area as a percent of gross exterior roof area does not exceed the maximum allowed in Section C402.3.1: |
||||
Aradt |
= |
The proposed roof area with insulation entirely above the deck, Arad. |
||
Amrt |
= |
The proposed roof area for metal buildings, Amr. |
||
Arat |
= |
The proposed attic and other roof area, Aor. |
||
Aogat |
= |
The proposed skylight area, Aogor. |
||
or |
||||
If the skylight area as a percent of gross exterior roof area exceeds the maximum allowed in Section C402.3.1, the area of each skylight element shall be reduced in the base envelope design by the same percentage and the net area of each roof type increased proportionately by the same percentage so that the total skylight area is exactly equal to the allowed percentage per Section C402.3.1 of the gross roof area. |
||||
*Note: |
The vertical fenestration area does not include opaque doors and opaque spandrel panels.)) |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-23-096, filed 11/20/13, effective 4/1/14)
WAC 51-11C-402132 ((Equation C402-2—Proposed UAp.)) Reserved.
((Equation C402-2
Proposed UAp
UAp |
= |
UradArad + UmrAmr + UraAra + UmwAmw + UmbwAmbw + UsfwAsfw + UwfowAwfow + UfmAfm + UfjAfj + FsPs + FsrPsr + UdsAds + UdrAdr + UvgAvg + UvgmfAvgmf + UvgmoAvgmo + UvgdAvgd + UogAog |
||
Where: |
||||
UAp |
= |
The combined proposed specific heat transfer of the gross exterior wall, floor and roof/ceiling assembly area. |
||
Urad |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the roof area where the insulation is entirely above the roof deck. |
||
Arad |
= |
Opaque roof area where the insulation is entirely above the roof deck. |
||
Umr |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the metal building roof area. |
||
Amr |
= |
Opaque metal building roof area. |
||
Ura |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the roof over attic and other roof area. |
||
Ara |
= |
Opaque roof over attic and other roof area. |
||
Umw |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the opaque mass wall area. |
||
Amw |
= |
Opaque mass wall area (not including opaque doors). |
||
Umbw |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the opaque metal building wall area. |
||
Ambw |
= |
Opaque metal building wall area (not including opaque doors). |
||
Usfw |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the opaque steel framed wall area. |
||
Asfw |
= |
Opaque steel framed wall area (not including opaque doors). |
||
Uwfw |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the opaque wood framed and other wall area. |
||
Awfw |
= |
Opaque wood framed and other wall area (not including opaque doors). |
||
Ufm |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the mass floor over unconditioned space area. |
||
Afm |
= |
Mass floor area over unconditioned space. |
||
Ufj |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the joist floor over unconditioned space area. |
||
Afj |
= |
Joist floor area over unconditioned space. |
||
Fs |
= |
Slab-on-grade floor component F-factor. |
||
Ps |
= |
Linear feet of slab-on-grade floor perimeter. |
||
Fsr |
= |
Radiant floor component F-factor. |
||
Psr |
= |
Lineal feet of radiant floor perimeter. |
||
Uds |
= |
The thermal transmittance value of the opaque swinging door area. |
||
Ads |
= |
Opaque swinging door area. |
||
Udr |
= |
The thermal transmittance value of the opaque roll-up or sliding door area. |
||
Adr |
= |
Opaque roll-up or sliding door area. |
||
Uvg |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the vertical fenestration area with nonmetal framing.* |
||
Avg |
= |
Vertical fenestration area with nonmetal framing.* |
||
Uvgmf |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the vertical fenestration area with fixed metal framing. |
||
Avgmf |
= |
Vertical fenestration area with fixed metal framing.* |
||
Uvgmo |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the vertical fenestration area with operable metal framing.* |
||
Avgmo |
= |
Vertical fenestration area with operable metal framing.* |
||
Uvgd |
= |
The thermal transmittance of the vertical fenestration area for entrance doors. |
||
Avgd |
= |
Vertical fenestration area for entrance doors. |
||
Uog |
= |
The thermal transmittance for the skylights. |
||
Aog |
= |
Skylight area. |
||
NOTE: |
Where more than one type of wall, window, roof/ceiling, door and skylight is used, the U and A terms for those items shall be expanded into subelements as: |
Umw1Amw1 + Umw2Amw2 + Usfw1Asfw1 + ...etc. |
|
*NOTE: |
The vertical fenestration area does not include opaque doors and opaque spandrel panels.)) |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-23-096, filed 11/20/13, effective 4/1/14)
WAC 51-11C-402133 ((Equation C402-3—Target SHGCAt.)) Reserved.
((Equation C402-3
Target SHGCAt
SHGCAt |
= |
SHGCogt(Aogort + SHGCvgt (Aogt + Avgt + Avgmt + Avgmot + Avgdt) |
Where: |
||
SHGCAt |
= |
The target combined solar heat gain of the target fenestration area. |
SHGCogt |
= |
The solar heat gain coefficient for skylight fenestration found in Table C402.3, and Aogt, as defined in Equation C402-1. |
SHGCvgt |
= |
The solar heat gain coefficient for vertical fenestration found in Table C402.3 which corresponds to the proposed total fenestration area as a percent of gross exterior wall area, and Avgt, Avgmt, Avgmot and Avgdt are defined under Equation C402-1. Buildings utilizing Section C402.3.1.3 shall use the SHGC value specified there. The SHGC may be adjusted for projection factors per the requirements of Section C402.3.3. |
NOTE: |
The vertical fenestration area does not include opaque doors and opaque spandrel panels.)) |
|
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-23-096, filed 11/20/13, effective 4/1/14)
WAC 51-11C-402134 ((Equation C402-4—Proposed SHGCAp.)) Reserved.
((Equation C402-4
Proposed SHGCAp
SHGCAp |
= |
SHGCogAog + SHGCvgAvg |
Where: |
||
SHGCAt |
= |
The combined proposed solar heat gain of the proposed fenestration area. |
SHGCog |
= |
The solar heat gain coefficient of the skylights. |
Aog |
= |
The skylight area. |
SHGCvg |
= |
The solar heat gain coefficient of the vertical fenestration. |
Avg |
= |
The vertical fenestration area. |
NOTE: |
The vertical fenestration area does not include opaque doors and opaque spandrel panels.)) |
|
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40214 Section C402.1.4—((Semi-heated spaces)) Assembly U-factor, C-factor, or F-factor-based method.
C402.1.4 ((Semi-heated spaces. All spaces shall comply with the requirements in Section C402 unless they meet the definition for semi-heated spaces. For semi-heated spaces, the building envelope shall comply with the same requirements as that for conditioned spaces in Section C402; however, for semi-heated spaces heated by other than electric resistance heating equipment, wall insulation is not required for those walls that separate semi-heated spaces from the exterior provided that the space meets all the requirements of semi-heated space. Semi-heated spaces shall be calculated separately from other conditioned spaces for compliance purposes. Building envelope assemblies separating conditioned space from semi-heated space shall comply with exterior envelope insulation requirements. When choosing the uninsulated wall option, the wall shall not be included in Component Performance Building Envelope Option calculation.)) Assembly U-factor, C-factor, or F-factor-based method. Building thermal envelope opaque assemblies intended to comply on an assembly U-, C-, or F-factor basis shall have a U-, C-, or F-factor not greater than that specified in Table C402.1.4. Commercial buildings or portions of commercial buildings enclosing Group R occupancies shall use the U-, C-, or F-factor from the "Group R" column of Table C402.1.4. Commercial buildings or portions of commercial buildings enclosing occupancies other than Group R shall use the U-, C-, or F-factor from the "All other" column of Table C402.1.4. The C-factor for the below-grade exterior walls of the building envelope, as required in accordance with Table C402.1.4, shall extend to the level of the lowest conditioned floor. Opaque swinging doors shall comply with Table C402.1.4 and opaque nonswinging doors shall comply with Table C402.1.3 or C402.1.4. The U-factors for typical construction assemblies are included in Appendix A. These values shall be used for all calculations. Where proposed construction assemblies are not represented in Appendix A, values shall be calculated in accordance with the ASHRAE Handbook—Fundamentals using the framing factors listed in Appendix A where applicable and shall include the thermal bridging effects of framing materials.
C402.1.4.1 Thermal resistance of cold-formed steel walls. U-factors of walls with cold-formed steel studs shall be permitted to be determined in accordance with Equation 4-1:
Equation 4-1:
U = 1/[Rs + (ER)] |
||
Where: |
||
Rs |
= |
The cumulative R-value of the wall components along the path of heat transfer, excluding the cavity insulation and steel studs. |
ER |
= |
The effective R-value of the cavity insulation with steel studs. |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-402141 Table C402.1.4—Opaque thermal envelope requirements, U-factor method.
OPTION 1:
Table C402.1.4
Opaque Thermal Envelope Requirementsa,f
CLIMATE ZONE |
5 AND MARINE 4 |
|
All Other |
Group R |
|
Roofs |
||
Insulation entirely above deck |
U-0.027 |
U-0.027 |
Metal buildings |
U-0.031 |
U-0.031 |
Attic and other |
U-0.021 |
U-0.021 |
Joist or single rafter |
U-0.027 |
U-0.027 |
Walls, Above Grade |
||
Mass |
U-0.090 |
U-0.080 |
Mass transfer deck slab edge |
U-0.20 |
U-0.20 |
Metal building |
U-0.052 |
U-0.052 |
Steel framed |
U-0.055 |
U-0.055 |
Wood framed and other |
U-0.054 |
U-0.054 |
Walls, Below Grade |
||
Below-grade wallb |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Floors |
||
Masse |
U-0.031 |
U-0.031 |
Joist/framing |
U-0.029 |
U-0.029 |
Slab-on-Grade Floors |
||
Unheated slabs |
F-0.54 |
F-0.54 |
Heated slabsc |
F-0.55 |
F-0.55 |
Opaque Doors |
||
Swinging |
U-0.37 |
U-0.37 |
Nonswinging |
U-0.34 |
U-0.34 |
a | Use of opaque assembly U-factors, C-factors, and F-factors from Appendix A is required unless otherwise allowed by Section C402.1.2. |
b | Where heated slabs are below grade, below-grade walls shall comply with the F-factor requirements for heated slabs. |
c | Heated slab F-factors shall be determined specifically for heated slabs. Unheated slab factors shall not be used. |
d | Reserved. |
e | "Mass floors" shall include floors weighing not less than: 1. 35 pounds per square foot of floor surface area; or 2. 25 pounds per square foot of floor surface area where the material weight is not more than 120 pounds per cubic foot. |
f | Opaque assembly U-factors based on designs tested in accordance with ASTM C1363 shall be permitted. The R-value of continuous insulation shall be permitted to be added or substracted from the original test design. |
OPTION 2:
Table C402.1.4
Opaque Thermal Envelope Requirementsa,f
CLIMATE ZONE |
5 AND MARINE 4 |
|
All Other |
Group R |
|
Roofs |
||
Insulation entirely above deck |
U-0.027 |
U-0.027 |
Metal buildings |
U-0.031 |
U-0.031 |
Attic and other |
U-0.021 |
U-0.021 |
Joist and single rafter |
U-0.027 |
U-0.027 |
Walls, Above Grade |
||
Mass |
U-0.078 |
U-0.078 |
Mass transfer deck slab edge |
U-0.20 |
U-0.20 |
Metal building |
U-0.052 |
U-0.052 |
Steel framed |
U-0.055 |
U-0.055 |
Wood framed and other |
U-0.054 |
U-0.054 |
Walls, Below Grade |
||
Below-grade wallb |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Floors |
||
Masse |
U-0.031 |
U-0.031 |
Joist/framing |
U-0.029 |
U-0.029 |
Slab-on-Grade Floors |
||
Unheated slabs |
F-0.54 |
F-0.54 |
Heated slabsc |
F-0.55 |
F-0.55 |
Opaque Doors |
||
Swinging |
U-0.37 |
U-0.37 |
Nonswinging |
U-0.34 |
U-0.34 |
a | Use of opaque assembly U-factors, C-factors, and F-factors from Appendix A is required unless otherwise allowed by Section C402.1.2. |
b | Where heated slabs are below grade, below-grade walls shall comply with the F-factor requirements for heated slabs. |
c | Heated slab F-factors shall be determined specifically for heated slabs. Unheated slab factors shall not be used. |
d | Reserved. |
e | "Mass floors" shall include floors weighing not less than: 1. 35 pounds per square foot of floor surface area; or 2. 25 pounds per square foot of floor surface area where the material weight is not more than 120 pounds per cubic foot. |
f | Opaque assembly U-factors based on designs tested in accordance with ASTM C1363 shall be permitted. The R-value of continuous insulation shall be permitted to be added or substracted from the original test design. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-402142 Table C402.1.4.1—Effective R-values for steel stud wall assemblies.
Table C402.1.4.1
Effective R-values For Steel Stud Wall Assemblies
NOMINAL STUD DEPTH (inches) |
SPACING OF FRAMING (inches) |
CAVITY R-VALUE (insulation) |
CORRECTION FACTOR (Fc) |
EFFECTIVE R-VALUE (ER) (Cavity R-Value x Fc) |
|
3 1/2 |
16 |
13 |
0.46 |
5.98 |
|
15 |
0.43 |
6.45 |
|||
3 1/2 |
24 |
13 |
0.55 |
7.15 |
|
15 |
0.52 |
7.80 |
|||
6 |
16 |
19 |
0.37 |
7.03 |
|
21 |
0.35 |
7.35 |
|||
6 |
24 |
19 |
0.45 |
8.55 |
|
21 |
0.43 |
9.03 |
|||
8 |
16 |
25 |
0.31 |
7.75 |
|
24 |
25 |
0.38 |
9.50 |
||
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40215 Section C402.1.5—Component performance alternative.
C402.1.5 Component performance alternative. Building envelope values and fenestration areas determined in accordance with Equation 4-2 shall be permitted in lieu of compliance with the U-factors and F-factors in Table C402.1.4 and C402.4 and the maximum allowable fenestration areas in Section C402.4.1.
Equation 4-2
A + B + C + D = ≤ Zero |
||||
Where: |
||||
A = |
Sum of the (UA Dif) values for each distinct assembly type of the building thermal envelope, other than slabs on grade and below-grade walls |
|||
UA Dif |
= |
UA Dif = UA Proposed – UA Table |
||
UA Proposed |
= |
UA Proposed = Proposed U-value x Area |
||
UA Table |
= |
(U-factor from Table C402.1.4 or C402.4 or Section C402.1.3) x Area |
||
B = |
Sum of the (FL Dif) values for each distinct slab on grade perimeter condition of the building thermal envelope |
|||
FL Dif |
= |
FL Dif = FL Proposed – FL Table |
||
FL Proposed |
= |
FL Proposed = Proposed F-value x Perimeter length |
||
FL Table |
= |
(F-factor specified in Table C402.1.4) x Perimeter length |
||
The maximum allowed prescriptive vertical fenestration area as a percent of the gross above-grade wall area ratio is either: |
||
1. |
30% |
|
2. |
40% if the building complies with Section C402.4.1.1; or |
|
3. |
40% if the U-values used in calculating A for vertical fenestration are taken from Section C402.4.1.3 rather than Table C402.4 |
|
Where the proposed vertical fenestration area is less than or equal to the maximum allowed prescriptive vertical fenestration area, the value of D (Excess Vertical Glazing Value) shall be zero. Otherwise: |
|||
C = |
(CA x UV) – (CA x UWall), but not less than zero |
||
CA |
= |
(Proposed Vertical Fenestration Area) – (Vertical Fenestration Area allowed) |
|
UA Wall |
= |
Sum of the (UA Proposed) values for each opaque assembly of the exterior wall |
|
UAW |
= |
Sum of the (UA proposed) values for each above-grade wall assembly |
|
UWall |
= |
UAW/sum of wall area (excludes vertical fenestration area) |
|
UAV |
= |
Sum of the (UA Proposed) values for each vertical fenestration assembly |
|
UV |
= |
UAV/total vertical fenestration area |
|
Where the proposed skylight area is less than or equal to the skylight area allowed by Section C402.4.1, the value of E (Excess Skylight Value) shall be zero. Otherwise: |
|||
D = |
(DA x US) – (DA x URoof), but not less than zero |
||
DA |
= |
(Proposed Skylight Area) – (Allowable Skylight Area from Section C402.4.1) |
|
UAR |
= |
Sum of the (UA Proposed) values for each roof assembly |
|
URoof |
= |
UAR/sum of roof area (excludes skylight area) |
|
UAS |
= |
Sum of the (UA Proposed) values for each skylight assembly |
|
US |
= |
UAS/total skylight area |
|
C402.1.5.1 Component U-factors. The U-factors for typical construction assemblies are included in Chapter 3 and Appendix A. These values shall be used for all calculations. Where proposed construction assemblies are not represented in Chapter 3 or Appendix A, values shall be calculated in accordance with the ASHRAE Handbook—Fundamentals, using the framing factors listed in Appendix A.
For envelope assemblies containing metal framing, the U-factor shall be determined by one of the following methods:
1. Results of laboratory measurements according to acceptable methods of test.
2. ASHRAE Handbook—Fundamentals where the metal framing is bonded on one or both sides to a metal skin or covering.
3. The zone method as provided in ASHRAE Handbook—Fundamentals.
4. Effective framing/cavity R-values as provided in Appendix A.
When return air ceiling plenums are employed, the roof/ceiling assembly shall:
a. For thermal transmittance purposes, not include the ceiling proper nor the plenum space as part of the assembly; and
b. For gross area purposes, be based upon the interior face of the upper plenum surface.
5. Tables in ASHRAE 90.1-2010 Normative Appendix A.
C402.1.5.2 SHGC rate calculations. Solar heat gain coefficient shall comply with Table C402.4. The target SHGCAt and the proposed SHGCAp shall be calculated using Equations 4-3 and 4-4 and the corresponding areas and SHGCs from Table C402.4.
Equation 4-3—Target SHGCAt
Equation C402-3
Target SHGCAt
SHGCAt |
= |
SHGCogt(Aogort + SHGCvgt (Aogt + Avgt + Avgmt + Avgmot + Avgdt) |
Where: |
||
SHGCAt |
= |
The target combined solar heat gain of the target fenestration area. |
SHGCogt |
= |
The solar heat gain coefficient for skylight fenestration found in Table C402.3, and Aogt, as defined in Equation C402-1. |
SHGCvgt |
= |
The solar heat gain coefficient for vertical fenestration found in Table C402.3 which corresponds to the proposed total fenestration area as a percent of gross exterior wall area, and Avgt, Avgmt, Avgmot and Avgdt are defined under Equation C402-1. Buildings utilizing Section C402.3.1.3 shall use the SHGC value specified there. The SHGC may be adjusted for projection factors per the requirements of Section C402.3.3. |
NOTE: |
The vertical fenestration area does not include opaque doors and opaque spandrel panels. |
|
Equation 4-4
Proposed SHGCAp
SHGCAp |
= |
SHGCogAog + SHGCvgAvg |
Where: |
||
SHGCAt |
= |
The combined proposed solar heat gain of the proposed fenestration area. |
SHGCog |
= |
The solar heat gain coefficient of the skylights. |
Aog |
= |
The skylight area. |
SHGCvg |
= |
The solar heat gain coefficient of the vertical fenestration. |
Avg |
= |
The vertical fenestration area. |
NOTE: |
The vertical fenestration area does not include opaque doors and opaque spandrel panels. |
|
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40220 Section C402.2—Specific insulation requirements.
C402.2 Specific building thermal envelope insulation requirements (Prescriptive). ((Opaque assemblies shall comply with Table C402.2. Where two or more layers of continuous insulation board are used in a construction assembly, the continuous insulation boards shall be installed in accordance with Section C303.2. If the continuous insulation board manufacturer's installation instructions do not address installation of two or more layers, the edge joints between each layer of continuous insulation boards shall be staggered.)) Insulation in building thermal envelope opaque assemblies shall comply with Sections C402.2.1 through C402.2.6 and Table C402.1.3.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-23-096, filed 11/20/13, effective 4/1/14)
WAC 51-11C-402200 ((Table C402.2—Opaque thermal envelope requirements.)) Reserved.
((Table C402.2
Opaque Thermal Envelope Requirementsa, f
CLIMATE ZONE |
5 AND MARINE 4 |
6 |
||
All Other |
Group R |
All Other |
Group R |
|
Roofs |
||||
Insulation entirely above deck |
R-30ci |
R-38ci |
R-30ci |
R-38ci |
Metal buildings (with R-3.5 thermal blocks)a, b |
R-25 + R-11 LS |
R-25 + R-11 LS |
R-25 + R-11 LS |
R-30 + R-11 LS |
Attic and other |
R-49 |
R-49 |
R-49 |
R-49 |
Walls, Above Grade |
||||
Massc |
R-9.5ci |
R-13.3ci |
R-11.4ci |
R-15.2ci |
Metal building |
R-13 + R-13ci |
R-13 + R-13ci |
R-13 + R-13ci |
R-19 + R-16ci |
Steel framed |
R-13 + R-10ci |
R-19 + R-8.5ci |
R-13 + R-12.5ci |
R-19 + R-14ci |
Wood framed and other |
R-21 int |
R-21 int |
R-13 + R-7.5ci or R-20 + R-3.8ci |
R-21 + R-5ci |
Walls, Below Grade |
||||
Below-grade walld |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Same as above grade |
Floors |
||||
Mass |
R-30ci |
R-30ci |
R-30ci |
R-30ci |
Joist/framing |
R-30e |
R-30e |
R-38e |
R-38e |
Slab-on-Grade Floors |
||||
Unheated slabs |
R-10 for 24" below |
R-10 for 24" below |
R-10 for 48" below |
R-15 for 48" below |
Heated slabsd |
R-10 perimeter & under entire slab |
R-10 perimeter & under entire slab |
R-10 perimeter & under entire slab |
R-10 perimeter & under entire slab |
Opaque Doors |
||||
Swinging |
U-0.37 |
U-0.37 |
U-0.37 |
U-0.37 |
Roll-up or sliding |
R-4.75 |
R-4.75 |
R-4.75 |
R-4.75 |
For SI: | 1 inch = 25.4 mm. ci = Continuous insulation. NR = No requirement. |
LS = | Liner system—A continuous membrane installed below the purlins and uninterrupted by framing members. Uncompressed, unfaced insulation rests on top of the membrane between the purlins. |
a | Assembly descriptions can be found in Chapter 2 and Appendix A. |
b | Where using R-value compliance method, a thermal spacer block shall be provided, otherwise use the U-factor compliance method in Table C402.1.2. |
c | Exception: Integral insulated concrete block walls complying with ASTM C90 with all cores filled and meeting both of the following: |
1 At least 50 percent of cores must be filled with vermiculite or equivalent fill insulation; and | |
2 The building thermal envelope encloses one or more of the following uses: Warehouse (storage and retail), gymnasium, auditorium, church chapel, arena, kennel, manufacturing plant, indoor swimming pool, pump station, water and waste water treatment facility, storage facility, storage area, motor vehicle service facility. Where additional uses not listed (such as office, retail, etc.) are contained within the building, the exterior walls that enclose these areas may not utilize this exception and must comply with the appropriate mass wall R-factor from Table C402.2 or U-factor from Table C402.1.2. | |
d | Where heated slabs are below grade, below-grade walls shall comply with the exterior insulation requirements for heated slabs. |
e | Steel floor joist systems shall be insulated to R-38 + R-10ci. |
f | For roof, wall or floor assemblies where the proposed assembly would not be continuous insulation, an alternate nominal R-value compliance options for assemblies with isolated metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation is: |
Assemblies with continuous insulation (see definition) |
Alternate option for assemblies with metal penetrations, greater than 0.04% but less than 0.08% |
R-11.4ci |
R-14.3ci |
R-13.3ci |
R-16.6ci |
R-15.2ci |
R-19.0ci |
R-30ci |
R-38ci |
R-38ci |
R-48ci |
R-13 + R-7.5ci |
R-13 + R-9.4ci |
R-13 + R-10ci |
R-13 + R-12.5ci |
R-13 + R-12.5ci |
R-13 + R-15.6ci |
R-13 + R-13ci |
R-13 + R-16.3ci |
R-19 + R-8.5ci |
R-19 + R-10.6ci |
R-19 + R-14ci |
R-19 + R-17.5ci |
R-19 + R-16ci |
R-19 + R-20ci |
R-20 + R-3.8ci |
R-20 + R-4.8ci |
R-21 + R-5ci |
R-21 + R-6.3ci |
This alternate nominal R-value compliance option is allowed for projects complying with all of the following:
1. | The ratio of the cross-sectional area, as measured in the plane of the surface, of metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation to the opaque surface area of the assembly is greater than 0.0004 (0.04%), but less than 0.0008 (0.08%). |
2. | The metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation are isolated or discontinuous (e.g., brick ties or other discontinuous metal attachments, offset brackets supporting shelf angles that allow insulation to go between the shelf angle and the primary portions of the wall structure). No continuous metal elements (e.g., metal studs, z-girts, z-channels, shelf angles) penetrate the otherwise continuous portion of the insulation. |
3. | Building permit drawings shall contain details showing the locations and dimensions of all the metal penetrations (e.g., brick ties or other discontinuous metal attachments, offset brackets, etc.) of otherwise continuous insulation. In addition, calculations shall be provided showing the ratio of the cross-sectional area of metal penetrations of otherwise continuous insulation to the overall opaque wall area. |
For other cases where the proposed assembly is not continuous insulation, see Section C402.1.2 for determination of U-factors for assemblies that include metal other than screws and nails.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40221 Section C402.2.1—((Roof assembly)) Multiple layers of continuous insulation.
((C402.2.1 Roof assembly. The minimum thermal resistance (R-value) of the insulating material installed either between the roof framing or continuously on the roof assembly shall be as specified in Table C402.2, based on construction materials used in the roof assembly. Skylight curbs shall be insulated to the level of roofs with insulation entirely above deck or R-5, whichever is less.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Continuously insulated roof assemblies where the thickness of insulation varies 1 inch (25 mm) or less and where the area-weighted U-factor is equivalent to the same assembly with the R-value specified in Table C402.2. |
2. Unit skylight curbs included as a component of an NFRC 100 rated assembly shall not be required to be insulated. |
Insulation installed on a suspended ceiling with removable ceiling tiles shall not be considered part of the minimum thermal resistance of the roof insulation.
C402.2.1.1 Roof solar reflectance and thermal emittance. Low-sloped roofs, with a slope less than 2 units vertical in 12 horizontal, directly above cooled conditioned spaces in Climate Zones 1, 2, and 3 shall comply with one or more of the options in Table C402.2.1.1.
EXCEPTIONS: | The following roofs and portions of roofs are exempt from the requirements in Table C402.2.1.1: |
1. Portions of roofs that include or are covered by: | |
1.1. Photovoltaic systems or components. | |
1.2. Solar air or water heating systems or components. | |
1.3. Roof gardens or landscaped roofs. | |
1.4. Above-roof decks or walkways. | |
1.5. Skylights. | |
1.6. HVAC systems, components, and other opaque objects mounted above the roof. | |
2. Portions of roofs shaded during the peak sun angle on the summer solstice by permanent features of the building, or by permanent features of adjacent buildings. | |
3. Portions of roofs that are ballasted with a minimum stone ballast of 17 pounds per square foot (psf) (74 kg/m2) or 23 psf (117 kg/m2) pavers. | |
4. Roofs where a minimum of 75 percent of the roof area meets a minimum of one of the exceptions above.)) |
C402.2.1 Multiple layers of continuous insulation. Where two or more layers of continuous insulation board are used in a construction assembly, the continuous insulation boards shall be installed in accordance with Section C303.2. If the continuous insulation board manufacturer's installation instructions do not address installation of two or more layers, the edge joints between each layer of continuous insulation boards shall be staggered.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-402211 ((Table C402.2.1.1—Reflectance and emittance options.)) Reserved.
((Table C402.2.1.1
Reflectance and Emittance Optionsa
Three-year aged solar reflectanceb of 0.55 and three-year aged thermal emittancec of 0.75 |
Initial solar reflectanceb of 0.70 and initial thermal emittancec of 0.75 |
Three-year-aged solar reflectance indexd of 64 initial solar reflectance indexd of 82 |
a | The use of area-weighted averages to meet these requirements shall be permitted. Materials lacking initial tested values for either solar reflectance or thermal emittance, shall be assigned both an initial solar reflectance of 0.10 and an initial thermal emittance of 0.90. Materials lacking three-year aged tested values for either solar reflectance or thermal emittance shall be assigned both a three-year aged solar reflectance of 0.10 and a three-year aged thermal emittance of 0.90. |
b | Solar reflectance tested in accordance with ASTM C 1549, ASTM E 903 or ASTM E 1918. |
c | Thermal emittance tested in accordance with ASTM C 1371 or ASTM E 408. |
d | Solar reflectance index (SRI) shall be determined in accordance with ASTM E 1980 using a convection coefficient of 2.1 Btu/h x ft2 x °F (12W/m2 x K). Calculation of aged SRI shall be based on aged tested values of solar reflectance and thermal emittance. Calculation of initial SRI shall be based on initial tested values of solar reflectance and thermal emittance.)) |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40222 Section C402.2.2—((Classification of walls)) Roof assembly.
C402.2.2 ((Classification of walls. Walls associated with the building envelope shall be classified in accordance with Section C202.)) Roof assembly. The minimum thermal resistance (R-value) of the insulating material installed either between the roof framing or continuously on the roof assembly shall be as specified in Table C402.1.3, based on construction materials used in the roof assembly. Skylight curbs shall be insulated to the level of roofs with insulation entirely above deck or R-5, whichever is less.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Continuously insulated roof assemblies where the thickness of insulation varies 1 inch (25 mm) or less and where the area-weighted U-factor is equivalent to the same assembly with the R-value specified in Table C402.1.3. |
2. Where tapered insulation is used with insulation entirely above deck, those roof assemblies shall show compliance on a U-factor basis per Section C402.1.4. The effective U-factor shall be determined through the use of Tables A102.2.6(1), A102.2.6(2) and A102.2.6(3). | |
3. Unit skylight curbs included as a component of a skylight listed and labeled in accordance with NFRC 100 shall not be required to be insulated. |
Insulation installed on a suspended ceiling with removable ceiling tiles shall not be considered part of the minimum thermal resistance of the roof insulation.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40223 Section C402.2.3—Above-grade walls.
C402.2.3 Thermal resistance of above-grade walls. The minimum thermal resistance (R-value) of ((the insulating)) materials installed in the wall cavity between the framing members and continuously on the walls shall be as specified in Table ((C402.2)) C402.1.3, based on framing type and construction materials used in the wall assembly. The R-value of integral insulation installed in concrete masonry units (CMU) shall not be used in determining compliance with Table ((C402.2)) C402.1.3.
"Mass walls" shall include walls ((weighing not less than)):
1. Weighing not less than 35 psf (170 kg/m2) of wall surface area((; or)).
2. Weighing not less than 25 psf (120 kg/m2) of wall surface area ((if)) where the material weight is not more than 120 pounds per cubic foot (pcf) (1,900 kg/m3).
3. Having a heat capacity exceeding 7 Btu/ft2 x °F (144 kJ/m2 x K).
4. Having a heat capacity exceeding 5 Btu/ft2 x °F (103 kJ/m2 x K) where the material weight is not more than 120 pcf (1900 kg/m3).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40224 Section C402.2.4—Below-grade walls.
C402.2.4 Thermal resistance of below-grade walls. The minimum thermal resistance (R-value) of the insulating material installed in, or continuously on, the below-grade walls shall be as specified in Table ((C402.2)) C402.1.3.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40225 Section C402.2.5—Floors ((over unconditioned space)).
((C402.2.5 Floors over outdoor air or unconditioned space. The minimum thermal resistance (R-value) of the insulating material installed either between the floor framing or continuously on the floor assembly shall be as specified in Table C402.2, based on construction materials used in the floor assembly.
"Mass floors" shall include floors weighing not less than:
1. 35 psf (170 kg/m2) of floor surface area; or
2. 25 psf (120 kg/m2) of floor surface area if the material weight is not more than 120 pcf (1,900 kg/m3).)) C402.2.5 Floors. The thermal properties (component R-values or assembly U- or F-factors) of floor assemblies over outdoor air or unconditioned space shall be as specified in Table C402.1.3 or C402.1.4 based on the construction materials used in the floor assembly. Floor framing cavity insulation or structural slab insulation shall be installed to maintain permanent contact with the underside of the subfloor decking or structural slabs.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. The floor framing cavity insulation or structural slab insulation shall be permitted to be in contact with the top side of sheathing or continuous insulation installed on the bottom side of floor assemblies framing where combined with insulation that meets or exceeds the minimum R-value in Table C401.1.4 for "Metal framed" or "Wood framed and other" values for "Walls, Above Grade" and extends from the bottom to the top of all perimeter floor framing or floor assembly members. |
2. Insulation applied to the underside of concrete floor slabs shall be permitted an air space of not more than 1 inch where it turns up and is in contact with the underside of the floor under walls associated with the building thermal envelope. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40226 Section C402.2.6—Slab-on-grade perimeter insulation.
C402.2.6 Slabs-on-grade perimeter insulation. Where the slab-on-grade is in contact with the ground, the minimum thermal resistance (R-value) of the insulation around the perimeter of unheated or heated slab-on-grade floors designed in accordance with the R-value method of Section C402.1.3 shall be as specified in Table ((C402.2)) C402.1.3. The insulation shall be placed on the outside of the foundation or on the inside of the foundation wall. The insulation shall extend downward from the top of the slab for a minimum distance as shown in the table or to the top of the footing, whichever is less, or downward to at least the bottom of the slab and then horizontally to the interior or exterior for the total distance shown in the table. Insulation extending away from the building shall be protected by pavement or by a minimum of 10 inches (254 mm) of soil. Insulation complying with Table C402.1.3 shall be provided under the entire area of heated slabs on grade.
EXCEPTION: | Where the slab-on-grade floor is greater than 24 inches (61 mm) below the finished exterior grade, perimeter insulation is not required. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40227 ((Section C402.2.7—Opaque doors.)) Reserved.
((C402.2.7 Opaque doors. Opaque doors (doors having less than 50 percent glass area) shall meet the applicable requirements for doors as specified in Table C402.2 and be considered as part of the gross area of above-grade walls that are part of the building envelope.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40228 Section C402.2.8—Insulation of radiant heating systems.
C402.2.8 Insulation of radiant heating systems. Radiant heating system panels, and their associated ((U-bends and headers, designed for sensible heating of an indoor space through heat transfer from the thermally effective panel surfaces to the occupants or indoor space by thermal radiation and natural convection and the bottom surfaces of floor structures incorporating radiant heating shall be insulated with a minimum of R-3.5 (0.62 m2/K × W))) components that are installed in interior or exterior assemblies shall be insulated with a minimum of R-3.5 (0.62 m2/K × W) on all surfaces not facing the space being heated. Radiant heating systems panels that are installed in the building thermal envelope shall be separated from the exterior of the building or unconditioned or exempt spaces by not less than the R-value of insulation installed in the opaque assembly in which they are installed or the assembly shall comply with Section C402.1.4.
EXCEPTION: | Heated slabs on grade insulated in accordance with Section C402.2.5. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40230 Section ((C402.3)) C402.4—Fenestration (Prescriptive).
C402.3 Reserved.
C402.4 Fenestration (Prescriptive). Fenestration shall comply with ((Table C402.3. Automatic daylighting controls specified by this section shall comply with Section C405.2.2.3.2)) Sections C402.4 through C402.4.4 and Table C402.4, Daylight responsive controls shall comply with this section and Section C405.2.4.1.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-402300 Table ((C402.3)) C402.4—Building envelope requirements—Fenestration.
Table ((C402.3)) C402.4
Building Envelope ((Requirements—))Fenestration Maximum U-factor and SHGC Requirements
CLIMATE ZONE |
5 AND MARINE 4 |
((6)) |
Vertical Fenestration |
||
U-factor |
||
Nonmetal framing (all)a |
0.30 |
((0.30)) |
Metal framing (fixed)b |
0.38 |
((0.36)) |
Metal framing (operable)c |
0.40 |
((0.40)) |
Metal framing (entrance doors)d |
0.60 |
((0.60)) |
SHGC |
||
((SHGC |
0.40 |
0.40)) |
Orientation |
SEW |
N |
PF < 0.2 |
0.40 |
0.53 |
0.2 < PF < 0.5 |
0.48 |
0.58 |
PF ˃ 0.5 |
0.64 |
0.64 |
Skylights |
||
U-factor |
0.50 |
((0.50)) |
SHGC |
0.35 |
((0.35)) |
NR = | No requirement. |
a "Nonmetal framing" includes framing materials other than metal, with or without metal reinforcing or cladding. | |
b "Metal framing" includes metal framing, with or without thermal break. "Fixed" includes curtain wall, storefront, picture windows, and other fixed windows. | |
c "Metal framing" includes metal framing, with or without thermal break. "Operable" includes openable fenestration products other than "entrance doors." | |
d "Metal framing" includes metal framing, with or without thermal break. "Entrance door" includes glazed swinging entrance doors. Other doors which are not entrance doors, including sliding glass doors, are considered "operable." |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-23-096, filed 11/20/13, effective 4/1/14)
WAC 51-11C-40231 Section ((C402.3.1)) C402.4.1—Maximum area.
((C402.3.1)) C402.4.1 Maximum area. The vertical fenestration area (not including opaque doors and opaque spandrel panels) shall not exceed 30 percent of the gross above-grade wall area. The skylight area shall not exceed ((3)) 5 percent of the gross roof area.
((C402.3.1.1)) C402.4.1.1 Increased vertical fenestration area with ((daylighting)) daylight responsive controls. ((In Climate Zones 1 through 6,)) A maximum of 40 percent of the gross above-grade wall area shall be permitted to be vertical fenestration for the purpose of prescriptive compliance with Section C402.1.4 or for the component performance alternative in Section C402.1.5, provided all of the following requirements are met:
1. In buildings not greater than two stories above grade, no less than 50 percent of the conditioned floor area is within a daylight zone((;)).
2. ((Automatic daylighting)) In buildings three or more stories above grade, not less than 25 percent of the net floor area is within a daylight zone.
3. Daylight responsive controls complying with Section C402.2.3.1 are installed in daylight zones((; and
3)).
4. Visible transmittance (VT) of vertical fenestration is greater than or equal to 1.1 times solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC).
EXCEPTION: | Fenestration that is outside the scope of NFRC 200 is not required to comply with Item ((3)) 4. |
((C402.3.1.2 Increased skylight area with daylighting controls. The skylight area shall be permitted to be a maximum of 5 percent of the roof area provided automatic daylighting controls are installed in daylight zones under skylights.
C402.3.1.3)) C402.4.1.2 Reserved.
C402.4.1.3 Increased vertical fenestration area with high-performance fenestration. The vertical fenestration area (not including opaque doors and opaque spandrel panels) is permitted to exceed 30 percent but shall not exceed 40 percent of the gross above grade wall area, for the purpose of prescriptive compliance with Section ((C402.1.2 or for the target UA calculation in Equation C402-1,)) C402.1.3 provided that each of the following conditions are met:
1. The vertical fenestration shall have the following U-factors:
a. Nonmetal framing (all) = 0.28
b. Metal framing (fixed) = 0.34
c. Metal framing (operable) = 0.36
d. Metal framing (entrance doors) = 0.60
2. The SHGC of the vertical fenestration shall be less than or equal to 0.35, adjusted for projection factor in compliance with ((C402.3.3.1)) C402.4.3.1.
An area-weighted average shall be permitted to satisfy the U-factor requirement for each fenestration product category listed in Item 1 of this section. Individual fenestration products from different fenestration product categories shall not be combined in calculating the area-weighted average U-factor.
The compliance path described in this section is not permitted to be used for the total building performance compliance path in Section C407. The compliance path described in this section is permitted to be used for the component performance alternative in Section C402.1.5, provided that the requirements of Section C402.1.5 are met.
C402.4.1.4 Increased vertical fenestration area with high-performance mechanical systems. The vertical fenestration area (not including opaque doors and opaque spandrel panels) is permitted to exceed 30 percent but shall not exceed 40 percent of the gross above-grade wall area, for the purpose of prescriptive compliance with Section C402.1.4 or for the component performance alternative in Section C402.1.5, provided that the mechanical system complies with all requirements of Section C403.2.6.1 Dedicated outdoor air systems (DOAS). This increased glazing fraction is not permitted to be used to establish the reference case for the Total Building Performance compliance path in Section C407.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40232 Section ((C402.3.2)) C402.4.2—Minimum skylight fenestration area.
((C402.3.2)) C402.4.2 Minimum skylight fenestration area. For single story buildings only, in an enclosed space greater than ((10,000)) 2,500 square feet (((929)) 232 m2) in floor area, directly under a roof with not less than 75 percent of the ceiling area with a ceiling height((s)) greater than 15 feet (4572 mm), and used as an office, lobby, atrium, concourse, corridor, gymnasium/exercise center, convention center, automotive service, manufacturing, nonrefrigerated warehouse, retail store, distribution/sorting area, transportation, or workshop, the total daylight zone under skylights shall be not less than half the floor area and shall provide ((a minimum skylight area to daylight zone under skylights of either)) one of the following:
1. A minimum skylight area to daylight zone under skylights of not less than 3 percent ((with a)) where all skylights have a VT of at least 0.40((; or)) as determined in accordance with Section C303.1.3.
2. ((Provide)) A minimum skylight effective aperture of at least 1 percent determined in accordance with Equation ((C4-1)) 4-5.
Skylight Effective Aperture |
= |
(085 x Skylight Area x Skylight VT x WF)/Daylight zone under skylight |
(Equation ((C4-1)) 4-5)
Where: |
||
Skylight area |
= |
Total fenestration area of skylights. |
Skylight VT |
= |
Area weighted average visible transmittance of skylights. |
WF |
= |
Area weighted average well factor, where well factor is 0.9 if light well depth is less than 2 feet (610 mm), or 0.7 if light well depth is 2 feet (610 mm) or greater. |
Light well depth |
= |
Measure vertically from the underside of the lowest point of the skylight glazing to the ceiling plane under the skylight. |
EXCEPTION: | Skylights above daylight zones of enclosed spaces are not required in: |
1. ((Buildings in Climate Zones 6 through 8.)) Reserved. | |
2. Spaces where the designed general lighting power densities are less than 0.5 W/ft2 (5.4 W/m2). | |
3. Areas where it is documented that existing structures or natural objects block direct beam sunlight on at least half of the roof over the enclosed area for more than 1,500 daytime hours per year between 8 a.m. and 4 p.m. | |
4. Spaces where the daylight zone under rooftop monitors is greater than 50 percent of the enclosed space floor area. | |
5. Spaces where the total floor area minus the area of daylight zones adjacent to vertical fenestration is less than 2,500 square feet (232 m2), and where the lighting is controlled according to Section C405.2.5. |
((C402.3.2.1)) C402.4.2.1 Lighting controls in daylight zones under skylights. ((All lighting in the daylight zone shall be controlled by automatic daylighting controls that comply with Section C405.2.2.3.2.
EXCEPTION: | Skylights above daylight zones of enclosed spaces are not required in: |
1. Buildings in Climate Zones 6 through 8. | |
2. Spaces where the designed general lighting power densities are less than 0.5 W/ft2 (5.4 W/m2). | |
3. Areas where it is documented that existing structures or natural objects block direct beam sunlight on at least half of the roof over the enclosed area for more than 1,500 daytime hours per year between 8 a.m. and 4 p.m. | |
4. Spaces where the daylight zone under rooftop monitors is greater than 50 percent of the enclosed space floor area. |
C402.3.2.2)) Daylight responsive controls complying with Section C405.2.4.1 shall be provided to control all electric lights within daylight zones.
C402.4.2.2 Haze factor. Skylights in office, storage, automotive service, manufacturing, nonrefrigerated warehouse, retail store, and distribution/sorting area spaces shall have a glazing material or diffuser with a ((measured)) haze factor greater than 90 percent when tested in accordance with ASTM D 1003.
EXCEPTION: | Skylights designed and installed to exclude direct sunlight entering the occupied space by the use of fixed or automated baffles, or the geometry of skylight and light well ((need not comply with Section C402.3.2.2)). |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40233 Section ((C402.3.3)) C402.4.3—Maximum U-factor and SHGC.
((C402.3.3)) C402.4.3 Maximum U-factor and SHGC. ((For vertical fenestration,)) The maximum U-factor and solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) for fenestration shall be as specified in Table ((C402.3, based on the window projection factor. For skylights, the maximum U-factor and solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) shall be as specified in Table C402.3)) C402.4.
The window projection factor shall be determined in accordance with Equation ((C4-2)) 4-6.
PF = A/B
(Equation ((C4-2)) 4-6)
Where: |
||
PF |
= |
Projection factor (decimal). |
A |
= |
Distance measured horizontally from the furthest continuous extremity of any overhang, eave, or permanently attached shading device to the vertical surface of the glazing. |
B |
= |
Distance measured vertically from the bottom of the glazing to the underside of the overhang, eave, or permanently attached shading device. |
Where different windows or glass doors have different PF values, they shall each be evaluated separately.
((C402.3.3.1 SHGC adjustment. Where the fenestration projection factor for a specific vertical fenestration product is greater than or equal to 0.2, the required maximum SHGC from Table C402.3 shall be adjusted by multiplying the required maximum SHGC by the multiplier specified in Table C402.3.3.1 corresponding with the orientation of the fenestration product and the projection factor.
Table C402.3.3.1
SHGC Adjustment Multipliers
PROJECTION FACTOR |
ORIENTED WITHIN 45 DEGREES OF TRUE NORTH |
ALL OTHER ORIENTATION |
0.2 ≤ PF < 0.5 |
1.1 |
1.2 |
PF ≥ 0.5 |
1.2 |
1.6 |
C402.3.3.2 Increased vertical fenestration SHGC. In Climate Zones 1, 2 and 3, vertical fenestration entirely located not less than 6 feet (1729 mm) above the finished floor shall be permitted a maximum SHGC of 0.40.
C402.3.3.3 Reserved.
C402.3.3.4 Reserved.
C402.3.3.5 Dynamic glazing. For compliance with Section C402.3.3, the SHGC for dynamic glazing shall be determined using the manufacturer's lowest-rated SHGC, and the VT/SHGC ratio shall be determined using the maximum VT and maximum SHGC. Dynamic glazing shall be considered separately from other fenestration, and area-weighted averaging with other fenestration that is not dynamic glazing shall not be permitted.)) C402.4.3.1 Reserved.
C402.4.3.2 Reserved.
C402.4.3.3 Dynamic glazing. Where dynamic glazing is intended to satisfy the SHGC and VT requirements of Table C402.4, the ratio of the higher to lower labeled SHGC shall be greater than or equal to 2.4, and the dynamic glazing shall be automatically controlled to modulate the amount of solar gain into the space in multiple steps. Dynamic glazing shall be considered separately from other fenestration, and area-weighted averaging with other fenestration that is not dynamic glazing shall not be permitted.
EXCEPTION: | Dynamic glazing is not required to comply with this section where both the lower and higher labeled SHGC already comply with the requirements of Table C402.4. |
C402.4.3.4 Area-weighted U-factor. An area-weighted average shall be permitted to satisfy the U-factor requirements for each fenestration product category listed in Table C402.4. Individual fenestration products from different fenestration product categories listed in Table C402.4 shall not be combined in calculating area-weighted average U-factor.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40234 Section ((C402.3.4—Area-weighted U-factor)) C402.4.4—Doors.
((C402.3.4 Area-weighted U-factor. An area-weighted average shall be permitted to satisfy the U-factor requirements for each fenestration product category listed in Table C402.3. Individual fenestration products from different fenestration product categories listed in Table C402.3 shall not be combined in calculating area-weighted average U-factor.)) C402.4.4 Doors. Opaque doors shall comply with the applicable requirements for doors as specified in Tables C402.1.3 and C402.1.4 and be considered part of the gross area of above grade walls that are part of the building thermal envelope. Other doors shall comply with the provisions of Section C402.4.3 for vertical fenestration.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40240 Section ((C402.4)) C402.5—Air leakage-thermal envelope.
((C402.4)) C402.5 Air leakage-thermal envelope (Mandatory). The thermal envelope of buildings shall comply with Sections ((C402.4.1 through C402.4.8)) C402.5.1 through C402.5.8.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40241 Section ((C402.4.1)) C402.5.1—Air barriers.
((C402.4.1)) C402.5.1 Air barriers. A continuous air barrier shall be provided throughout the building thermal envelope. The air barriers shall be permitted to be located on the inside or outside of the building envelope, located within the assemblies composing the envelope, or any combination thereof. The air barrier shall comply with Sections ((C402.4.1.1 and C402.4.1.2)) C402.5.1.1 and C402.5.1.2.
((EXCEPTION: | Air barriers are not required in buildings located in Climate Zones 1, 2 and 3. |
C402.4.1.1)) C402.5.1.1 Air barrier construction. The continuous air barrier shall be constructed to comply with the following:
1. The air barrier shall be continuous for all assemblies that are the thermal envelope of the building and across the joints and assemblies.
2. Air barrier joints and seams shall be sealed, including sealing transitions in places and changes in materials. ((Air barrier penetrations shall be sealed in accordance with Section C402.4.2.)) The joints and seals shall be securely installed in or on the joint for its entire length so as not to dislodge, loosen or otherwise impair its ability to resist positive and negative pressure from wind, stack effect and mechanical ventilation.
3. Penetrations of the air barrier shall be caulked, gasketed or otherwise sealed in a manner compatible with the construction materials and location. Joints and seals associated with penetrations shall be sealed in the same manner or taped or covered with moisture vapor-permeable wrapping material. Sealing materials shall be appropriate to the construction materials being sealed and shall be securely installed around the penetration so as not to dislodge, loosen or otherwise impair the penetrations' ability to resist positive and negative pressure from wind, stack effect, and mechanical ventilation. Sealing of concealed fire sprinklers, where required, shall be in a manner that is recommended by the manufacturer. Caulking or other adhesive sealants shall not be used to fill voids between fire sprinkler cover plates and walls or ceilings.
4. Recessed lighting fixtures shall comply with Section ((C404.2.8)) C402.5.8. Where similar objects are installed which penetrate the air barrier, provisions shall be made to maintain the integrity of the air barrier.
((EXCEPTION: | Buildings that comply with Section C402.4.1.2.3 are not required to comply with Items 1 and 3. |
C402.4.1.2 Air barrier compliance options. A continuous air barrier for the opaque building envelope shall comply with Section C402.4.1.2.3.
C402.4.1.2.1 Materials. Materials with an air permeability no greater than 0.004 cfm/ft2 (0.02 L/s • m2) under a pressure differential of 0.3 inches water gauge (w.g.) (75 Pa) when tested in accordance with ASTM E 2178 shall comply with this section. Materials in Items 1 through 15 shall be deemed to comply with this section provided joints are sealed and materials are installed as air barriers in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
1. Plywood with a thickness of not less than 3/8 inch (10 mm).
2. Oriented strand board having a thickness of not less than 3/8 inch (10 mm).
3. Extruded polystyrene insulation board having a thickness of not less than 1/2 inch (12 mm).
4. Foil-back polyisocyanurate insulation board having a thickness of not less than 1/2 inch (12 mm).
5. Closed cell spray foam a minimum density of 1.5 pcf (2.4 kg/m3) having a thickness of not less than 1 1/2 inches (36 mm).
6. Open cell spray foam with a density between 0.4 and 1.5 pcf (0.6 and 2.4 kg/m3) and having a thickness of not less than 4.5 inches (113 mm).
7. Exterior or interior gypsum board having a thickness of not less than 1/2 inch (12 mm).
8. Cement board having a thickness of not less than 1/2 inch (12 mm).
9. Built up roofing membrane.
10. Modified bituminous roof membrane.
11. Fully adhered single-ply roof membrane.
12. A Portland cement/sand parge, or gypsum plaster having a thickness of not less than 5/8 inch (16 mm).
13. Cast-in-place and precast concrete.
14. Fully grouted concrete block masonry.
15. Sheet steel or aluminum.
C402.4.1.2.2 Assemblies. Assemblies of materials and components with an average air leakage not to exceed 0.04 cfm/ft2 (0.2 L/s • m2) under a pressure differential of 0.3 inches of water gauge (w.g.)(75 Pa) when tested in accordance with ASTM E 2357, ASTM E 1677 or ASTM E 283 shall comply with this section. Assemblies listed in Items 1 and 2 shall be deemed to comply provided joints are sealed and requirements of Section C402.4.1.1 are met.
1. Concrete masonry walls coated with one application either of block filler and two applications of a paint or sealer coating;
2. A Portland cement/sand parge, stucco or plaster minimum 1/2 inch (12 mm) in thickness.
C402.4.1.2.3)) 5. Construction documents shall contain a diagram showing the building's pressure boundary in plan(s) and section(s) and a calculation of the area of the pressure boundary to be considered in the test.
C402.5.1.2 Building test. The completed building shall be tested and the air leakage rate of the building envelope shall not exceed 0.40 cfm/ft2 at a pressure differential of 0.3 inches water gauge (2.0 L/s • m2 at 75 Pa) at the upper 95 percent confidence interval in accordance with ASTM E 779 or an equivalent method approved by the code official. A report that includes the tested surface area, floor area, air by volume, stories above grade, and leakage rates shall be submitted to the building owner and the Code Official. If the tested rate exceeds that defined here, a visual inspection of the air barrier shall be conducted and any leaks noted shall be sealed to the extent practicable. An additional report identifying the corrective actions taken to seal air leaks shall be submitted to the building owner and the Code Official and any further requirement to meet the leakage air rate will be waived.
1. Test shall be accomplished using either (1) both pressurization and depressurization or (2) pressurization alone, but not depressurization alone. If both pressurization and depressurization are not tested, the air leakage shall be plotted against the corrected P for pressurization in accordance with Section 9.4.
2. The test pressure range shall be from 25 Pa to 80 Pa per Section 8.10, but the upper limit shall not be less than 50 Pa, and the difference between the upper and lower limit shall not be less than 25 Pa.
3. If the pressure exponent n is less than 0.45 or greater than 0.85 per Section 9.6.4, the test shall be rerun with additional readings over a longer time interval.
C402.5.1.2.1 Building test for mixed-use buildings. Where a building is three or fewer stories above grade plane and contains both commercial and residential uses, the air barrier of the R-2 and R-3 occupancy areas of the building is permitted to be separately tested according to Section R402.X. Alternatively, it is permissible to test the air barrier of the entire building according to Section C402.5.1.2, provided that the tested air leakage rate does not exceed the rate specified in Section C402.5.1.2.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40242 ((Section C402.4.2—Air barrier penetrations.)) Reserved.
((C402.4.2 Air barrier penetrations. Penetrations of the air barrier and paths of air leakage shall be caulked, gasketed or otherwise sealed in a manner compatible with the construction materials and location. Joints and seals shall be sealed in the same manner or taped or covered with a moisture vapor-permeable wrapping material. Sealing materials shall be appropriate to the construction materials being sealed. The joints and seals shall be securely installed in or on the joint for its entire length so as not to dislodge, loosen or otherwise impair its ability to resist positive and negative pressure from wind, stack effect and mechanical ventilation.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40243 Section ((C402.4.3—Air leakage of fenestration)) C402.5.3—Rooms containing fuel-burning appliances.
((C402.4.3 Air leakage of fenestration. The air leakage of fenestration assemblies shall meet the provisions of Table C402.4.3. Testing shall be in accordance with the applicable reference test standard in Table C402.4.3 by an accredited, independent testing laboratory and labeled by the manufacturer.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Field-fabricated fenestration assemblies that are sealed in accordance with Section C402.4.1. |
2. Fenestration in buildings that comply with Section C402.4.1.2.3 are not required to meet the air leakage requirements in Table C402.4.3. | |
3. Custom exterior windows and doors manufactured by a small business provided they meet the applicable provisions of Chapter 24 of the International Building Code. Once visual inspection has confirmed the presence of a gasket, operable windows and doors manufactured by small business shall be permitted to be sealed off at the frame prior to the test. |
Table C402.4.3
Maximum Air Infiltration Rate
for Fenestration Assemblies
FENESTRATION ASSEMBLY |
MAXIMUM RATE (CFM/FT2) |
TEST PROCEDURE |
Windows |
0.20a |
AAMA/WDMA/CSA101/I.S.2/A440 or NFRC 400 |
Sliding doors |
0.20a |
|
Swinging doors |
0.20a |
|
Skylights - With condensation weepage openings |
0.30 |
|
Skylights - All other |
0.20a |
|
Curtain walls |
0.06 |
NFRC 400 or |
Storefront glazing |
0.06 |
ASTM E 283 at |
Commercial glazed swinging entrance doors |
1.00 |
1.57 psf (75 Pa) |
Revolving doors |
1.00 |
|
Garage doors |
0.40 |
ANSI/DASMA 105, NFRC 400, or |
Rolling doors |
1.00 |
ASTM E 283 at 1.57 psf (75 Pa) |
For SI: | 1 cubic foot per minute = 0.47 L/s, 1 square foot = 0.093 m2. |
a | The maximum rate for windows, sliding and swinging doors, and skylights is permitted to be 0.3 cfm per square foot of fenestration or door area when tested in accordance with AAMA/WDMA/CSA101/I.S.2/A440 at 6.24 psf (300 Pa).)) |
C402.5.3 Rooms containing fuel-burning appliances. Where open combustion air ducts provide combustion air to open combustion space conditioning fuel-burning appliances, the appliances and combustion air openings shall be located outside of the building thermal envelope or enclosed in a room isolated from inside the thermal envelope. Such rooms shall be sealed and insulated in accordance with the envelope requirements of Table C402.1.3 or C402.1.4, where the walls, floors and ceilings shall meet the minimum of the below-grade wall R-value requirement. The door into the room shall be fully gasketed, and any water lines and ducts in the room insulated in accordance with Section C403. The combustion air duct shall be insulated, where it passes through conditioned space, to a minimum of R-8.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Direct vent appliances with both intake and exhaust pipes installed continuous to the outside. |
2. Fireplaces and stoves complying with Sections 901 through 905 of the International Mechanical Code, and Section 2111.13 of the International Building Code. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40244 Section ((C402.4.4)) C402.5.4—Doors and access openings.
((C402.4.4)) C402.5.4 Doors and access openings to shafts, chutes, stairways, and elevator lobbies. Doors and access openings from conditioned space to shafts, chutes, stairways and elevator lobbies ((shall either meet the requirements of)) not within the scope of the fenestration assemblies covered by Section ((C402.4.3 or)) C402.5.2 shall be gasketed, weatherstripped or sealed.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Door openings required to comply with Section 715 or 715.4 of the International Building Code((; or doors and door openings required by the International Building Code to comply with UL 1784 shall not be required to comply with Section C402.4.4)). |
2. Doors and door openings required to comply with UL 1784 by the International Building Code. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-054, filed 11/25/14, effective 5/1/15)
WAC 51-11C-40245 Section ((C402.4.5)) C402.5.5—Air intakes, exhaust openings, stairways and shafts.
((C402.4.5)) C402.5.5 Air intakes, exhaust openings, stairways and shafts. Stairway enclosures ((and)), elevator shaft vents and other outdoor air intakes and exhaust openings integral to the building envelope shall be provided with dampers in accordance with Section((s C402.4.5.1 and C402.4.5.2.
C402.4.5.1 Stairway and shaft vents. Stairway and shaft vents shall be provided with Class I motorized dampers with a maximum leakage rate of 4 cfm/ft2 (20.3 L/s • m2) at 1.0 inch water gauge (w.g.) (249 Pa) when tested in accordance with AMCA 500D.
Stairway and shaft vent dampers shall be installed with controls so that they are capable of automatically opening upon:
1. The activation of any fire alarm initiating device of the building's fire alarm system; or
2. The interruption of power to the damper.
C402.4.5.2 Outdoor air intakes, exhaust outlets, relief outlets, and return openings. Outdoor air supply, exhaust openings and relief outlets shall be provided with Class I motorized dampers which close automatically when the system is off. Dampers shall have a maximum leakage rate of 4 cfm/ft2 (20.3 L/s • m2) at 1.0 inch water gauge (w.g.) (249 Pa) when tested in accordance with AMCA 500D.
Return air openings used for airside economizer operation shall be equipped with Class I motorized dampers. Dampers shall have a maximum leakage rate of 4 cfm/ft2 (20.3 L/s • m2) at 1.0 inch water gauge (w.g.) (249 Pa) when tested in accordance with AMCA 500D.
See also section C403.2.4.4 for additional requirements from damper shut-off controls.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Gravity (nonmotorized) dampers having a maximum leakage rate of 20 cfm/ft2 (101.6 L/s • m2) at 1.0 inch water gauge (w.g.) (249 Pa) when tested in accordance with AMCA 500D are permitted to be used for relief openings in buildings less than three stories in height above grade if equipment has less than 5,000 cfm total supply flow. Gravity (nonmotorized) dampers for ventilation air intakes shall be protected from direct exposure to wind. |
2. Gravity dampers smaller than 24 inches (610 mm) in either dimension shall be permitted to have a leakage of 40 cfm/ft2 (203.2 L/s • m2) at 1.0 inch water gauge (w.g.) (249 Pa) when tested in accordance with AMCA 500D. | |
3. Gravity (nonmotorized) dampers in Group R occupancies where the design outdoor air intake or exhaust capacity does not exceed 400 cfm (189 L/s). | |
4. Motorized dampers on return air openings in unitary packaged equipment that have the minimum leakage rate available from the manufacturer shall be deemed to comply.)) |
C403.2.4.3.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40246 Section ((C402.4.6)) C402.5.6—Loading dock weatherseals.
((C402.4.6)) C402.5.6 Loading dock weatherseals. Cargo doors and loading dock doors shall be equipped with weatherseals to restrict infiltration when vehicles are parked in the doorway.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40247 Section ((C402.4.7)) C402.5.7—Vestibules.
((C402.4.7)) C402.5.7 Vestibules. All building entrances shall be protected with an enclosed vestibule, with all doors opening into and out of the vestibule equipped with self-closing devices. Vestibules shall be designed so that in passing through the vestibule it is not necessary for the interior and exterior doors to open at the same time. The installation of one or more revolving doors in the building entrance shall not eliminate the requirement that a vestibule be provided on any doors adjacent to revolving doors. For the purposes of this section, "building entrances" shall include exit-only doors in buildings where separate doors for entering and exiting are provided.
Interior and exterior doors shall have a minimum distance between them of not less than 7 feet. The exterior envelope of conditioned vestibules shall comply with the requirements for a conditioned space. Either the interior or exterior envelope of unconditioned vestibules shall comply with the requirements for a conditioned space. The building lobby is not considered a vestibule.
((EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Buildings in Climate Zones 1 and 2. |
2. Doors not intended to be used by the public, such as doors to mechanical or electrical equipment rooms, or intended solely for employee use. | |
3. Doors opening directly from a sleeping unit or dwelling unit. | |
4. Doors that open directly from a space less than 3,000 square feet (298 m2) in area and are separate from the building entrance. | |
5. Revolving doors. | |
6. Doors used primarily to facilitate vehicular movement or material handling and adjacent personnel doors. | |
7. Building entrances in buildings that are less than four stories above grade and less than 10,000 ft2 in area. | |
8. Elevator doors in parking garages provided that the elevators have an enclosed lobby at each level of the garage.)) | |
EXCEPTION: | Vestibules are not required for the following: |
1. Doors not intended to be used as building entrances. | |
2. Unfinished ground-level space greater than 3,000 square feet (298 m2) if a note is included on the permit documents at each exterior entrance to the space stating "Vestibule required at time of tenant build-out if entrance serves a space greater than 3,000 square feet in area." | |
3. Doors opening directly from a sleeping unit or dwelling unit. | |
4. Doors between a space smaller than 3,000 square feet (298 m2) in area and the exterior of the building or the building entrance lobby, where those doors do not comprise one of the primary entrance paths to the remainder of the building. | |
5. Revolving doors. | |
6. In buildings less than 3 stories above grade or in spaces that do not directly connect with the building elevator lobby, doors that have an air curtain with a velocity of not less than 6.56 feet per second (2 m/s) at the floor that have been tested in accordance with ANSI/AMCA 220 and installed in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Manual or automatic controls shall be provided that will operate the air curtain with the opening and closing of the door. Air curtains and their controls shall comply with Section C408.2.3. | |
7. Building entrances in buildings that are less than four stories above grade and less than 10,000 ft2 in area. | |
8. Elevator doors in parking garages provided that the elevators have an enclosed lobby at each level of the garage. | |
9. Entrances to semi-heated spaces. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40248 Section ((C402.4.8)) C402.5.8—Recessed lighting.
((C402.4.8)) C402.5.8 Recessed lighting. Recessed luminaires installed in the building thermal envelope shall be ((sealed to limit air leakage between conditioned and unconditioned spaces. All recessed luminaires shall be IC-rated and)) all of the following:
1. IC rated.
2. Labeled as having an air leakage rate of not more than 2.0 cfm (0.944 L/s) when tested in accordance with ASTM E 283 at a 1.57 psf (75 Pa) pressure differential.
((All recessed luminaires shall be)) 3. Sealed with a gasket or caulk between the housing and interior wall or ceiling covering.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40250 ((Section C402.5—Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers.)) Reserved.
((C402.5 Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers. Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers shall comply with all of the following:
1. Shall be equipped with automatic door closers that firmly close walk-in doors that have been closed to within 1 inch of full closure.
EXCEPTION: | Doors wider than 3 feet 9 inches or taller than 7 feet. |
2. Doorways shall have strip doors (curtains), spring-hinged doors, or other method of minimizing infiltration when doors are open.
3. Walk-in coolers shall contain wall, ceiling, and door insulation of at least R-25 and walk-in freezers at least R-32.
EXCEPTION: | Glazed portions of doors or structural members. |
4. Walk-in freezers shall contain floor insulation of at least R-28.
5. Transparent reach-in doors for walk-in freezers and windows in walk-in freezer doors shall be of triple-pane glass, either filled with inert gas or with heat-reflective treated glass.
6. Transparent reach-in doors for walk-in coolers and windows in walk-in cooler doors shall be double-pane glass with heat-reflective treated glass and gas filled; or triple-pane glass, either filled with inert gas or with heat-reflective treated glass.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40260 ((Section C402.6—Refrigerated warehouse coolers and freezers.)) Reserved.
((C402.6 Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers. Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers shall comply with all of the following:
1. Shall be equipped with automatic door closers that firmly close walk-in doors that have been closed to within 1 inch of full closure.
EXCEPTION: | Doors wider than 3 feet 9 inches or taller than 7 feet. |
2. Doorways shall have strip doors (curtains), spring-hinged doors, or other method of minimizing infiltration when doors are open.
3. Refrigerated warehouse coolers shall contain wall, ceiling, and door insulation of at least R-25 and refrigerated warehouse freezers at least R-32.
EXCEPTION: | Glazed portions of doors or structural members. |
4. Refrigerated warehouse freezers shall contain floor insulation of at least R-28.
5. Transparent reach-in doors for refrigerated warehouse freezers and windows in refrigerated warehouse freezer doors shall be of triple-pane glass, either filled with inert gas or with heat-reflective treated glass.
6. Transparent reach-in doors for refrigerated warehouse coolers and windows in refrigerated warehouse cooler doors shall be double-pane glass with heat-reflective treated glass and gas filled; or triple-pane glass, either filled with inert gas or with heat-reflective treated glass.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40310 Section C403.1—General.
C403.1 General. Mechanical systems and equipment serving heating, cooling, ventilating, and other needs shall comply with Section C403.2 (((referred to as the mandatory provisions) and either:
1. Section C403.3 (Simple systems); or
2. Section C403.4 (Complex systems).)) and shall comply with Sections C403.3 and C403.4 based on the equipment and systems provided.
EXCEPTION: | Energy using equipment used by a manufacturing, industrial or commercial process other than for conditioning spaces or maintaining comfort and amenities for the occupants and not otherwise regulated by C403.2.3, Tables(( C403.2.1)) C403.2.3 (1) through (((9))) (10) inclusive, C403.2.4.5, ((C403.2.5.4, C403.2.8, C403.2.13, C403.4.6, C403.5, C403.6, C404.2, or Table C404.2)) C403.2.4.6, C403.2.7, C403.2.9, C403.5.4, C404.2, Table C404.2, C405.8 and C410. Data center HVAC equipment is not covered by this exception. |
((Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers shall comply with Section C403.5. Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers shall comply with Section C403.6.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40320 Section C403.2—Provisions applicable to all mechanical systems.
C403.2 Provisions applicable to all mechanical systems (Mandatory). Mechanical systems and equipment serving the building heating, cooling or ventilating needs shall comply with Sections C403.2.1 through ((C403.2.11)) C403.2.13.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40321 Section C403.2.1—Calculation of heating and cooling loads.
C403.2.1 Calculation of heating and cooling loads. Design loads associated with heating, ventilating and air conditioning of the building shall be determined in accordance with the procedures described in ANSI/ASHRAE/ACCA Standard 183((. The design loads shall account for the building envelope, lighting, ventilation and occupancy loads based on the project design)) or by an approved equivalent computational procedure, using the design parameters specified in Chapter 3. Heating and cooling loads shall be adjusted to account for load reductions that are achieved where energy recovery systems are utilized in the HVAC system in accordance with the ASHRAE HVAC Systems and Equipment Handbook((. Alternatively, design loads shall be determined by an approved equivalent computation procedure, using the design parameters specified in Chapter 3)) by an approved equivalent computational procedure.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40322 Section C403.2.2—Equipment and systems sizing.
C403.2.2 Equipment and system sizing. The output capacity of heating and cooling equipment ((and systems shall not)) shall be no greater than that of the smallest available equipment size that exceeds the loads calculated in accordance with Section C403.2.1. A single piece of equipment providing both heating and cooling shall satisfy this provision for one function with the capacity for the other function as small as possible, within available equipment options.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Required standby equipment and systems provided with controls and devices that allow such systems or equipment to operate automatically only when the primary equipment is not operating. |
2. Multiple units of the same equipment type with combined capacities exceeding the design load and provided with controls that ((have the capability)) are configured to sequence the operation of each unit based on load. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40323 Section C403.2.3—HVAC equipment performance requirements.
C403.2.3 HVAC equipment performance requirements. Equipment shall meet the minimum efficiency requirements of Tables C403.2.3(1), C403.2.3(2), C403.2.3(3), C403.2.3(4), C403.2.3(5), C403.2.3(6), C403.2.3(7) ((and)), C403.2.3(8) and C403.2.3(9) when tested and rated in accordance with the applicable test procedure. Plate-type liquid-to-liquid heat exchangers shall meet the minimum requirements of Table C403.2.3(((9))) (10). The efficiency shall be verified through certification and listed under an approved certification program or, if no certification program exists, the equipment efficiency ratings shall be supported by data furnished by the manufacturer. Where multiple rating conditions or performance requirements are provided, the equipment shall satisfy all stated requirements. Where components, such as indoor or outdoor coils, from different manufacturers are used, calculations and supporting data shall be furnished by the designer that demonstrates that the combined efficiency of the specified components meets the requirements herein.
Gas-fired and oil-fired forced air furnaces with input ratings ≥ 225,000 Btu/h (65 kW) and all unit heaters shall also have an intermittent ignition or interrupted device (IID), and have either mechanical draft (including power venting) or a flue damper. A vent damper is an acceptable alternative to a flue damper for furnaces where combustion air is drawn from the conditioned space. All furnaces with input ratings ≥ 225,000 Btu/h (65 kW), including electric furnaces, that are not located within the conditioned space shall have jacket losses not exceeding 0.75 percent of the input rating.
Chilled water plants and buildings with more than 500 tons total capacity shall not have more than 100 tons provided by air-cooled chillers.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Where the designer demonstrates that the water quality at the building site fails to meet manufacturer's specifications for the use of water-cooled equipment. |
2. Air-cooled chillers with minimum efficiencies at least 10 percent higher than those listed in Table C403.2.3(7). | |
3. Replacement of existing equipment. |
C403.2.3.1 Water-cooled centrifugal chilling packages. Equipment not designed for operation at AHRI Standard 550/590 test conditions of 44°F (7°C) leaving chilled-water temperature and 2.4 gmp/ton evaporator fluid flow and 85°F (29°C) entering condenser water temperature with 3 gpm/ton (0.054 I/s • kW) condenser water flow shall have maximum full-load kW/ton (FL) and ((NPLV)) part-load ratings adjusted using Equations ((C4-3 and C4-4)) 4-7 and 4-8.
((Adjusted minimum full-load COP ratings |
= |
(Full-load COP from Table 6.8.1C of AHRI Standard 550/590) |
× |
Kadj |
(Equation C4-3)
Adjusted minimum NPLV rating |
= |
(IPLV from Table 6.8.1C of AHRI Standard 550/590) |
× |
Kadj |
(Equation C4-4)))
FL adj |
= |
FL/Kadj |
(Equation 4-7)
PLVadj |
= |
IPLV/Kadj |
(Equation 4-8)
Where: |
|||
Kadj |
= |
A × B |
|
FL |
= |
Full-load kW/ton values as specified in Table C403.2.3(7) |
|
FLadj |
= |
Maximum full-load kW/ton rating, adjusted for nonstandard conditions |
|
IPLV |
= |
Value as specified in Table C403.2.3(7) |
|
PLVadj |
= |
Maximum NPLV rating, adjusted for nonstandard conditions |
|
A |
= |
((0.0000015318)) 0.00000014592 × (LIFT)4 - ((0.000202076)) 0.0000346496 × (LIFT)3 + ((0.0101800)) 0.00314196 × (LIFT)2 - ((0.264958)) 0.147199 × LIFT + ((3.930196)) 3.9302 |
|
B |
= |
((0.0027)) 0.0015 × Lvg Evap (°C) + ((0.982)) 0.934 |
|
LIFT |
= |
LvgCond - LvgEvap |
|
LvgCond |
= |
Full-load condenser leaving ((water)) fluid temperature (((°C))) (°F) |
|
LvgEvap |
= |
Full-load ((leaving)) evaporator leaving temperature (((°C))) (°F) |
|
((SI units shall be used in the Kadj equation.)) |
|||
The ((adjusted full-load and NPLV values shall only be)) FLadj and PLVadj values are only applicable for centrifugal chillers meeting all of the following full-load design ranges:
1. ((The leaving evaporator fluid temperature is not less than 36°F (2.2°C).
2. The leaving condenser fluid temperature is not greater than 115°F (46.1°C).)) Minimum evaporator leaving temperature: 36°F.
2. Maximum condenser leaving temperature: 115°F.
3. LIFT is not less than 20°F (11.1°C) and not greater than 80°F (44.4°C).
((EXCEPTION: | Centrifugal chillers designed to operate outside of these ranges need not comply with this code.)) |
C403.2.3.2 Positive displacement (air- and water-cooled) chilling packages. Equipment with a leaving fluid temperature higher than 32°F (0°C)((,)) and water-cooled positive displacement chilling packages with a condenser leaving fluid temperature below 115°F (46°C) shall meet the requirements of Table C403.2.3(7) when tested or certified with water at standard rating conditions, in accordance with the referenced test procedure.
C403.2.3.3 Packaged electric heating and cooling equipment. Packaged electric equipment providing both heating and cooling with a total cooling capacity greater than ((20,000)) 6,000 Btu/h shall be a heat pump.
EXCEPTION: | Unstaffed equipment shelters or cabinets used solely for personal wireless service facilities. |
C403.2.3.4 Humidification. If an air economizer is required on a cooling system for which humidification equipment is to be provided to maintain minimum indoor humidity levels, then the humidifier shall be of the adiabatic type (direct evaporative media or fog atomization type).
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Health care facilities licensed by the state where ((WAC 246-320-525 allows only)) chapter 246-320 or 246-330 WAC requires steam injection humidifiers in duct work downstream of final filters. |
2. Systems with water economizer. | |
3. 100% outside air systems with no provisions for air recirculation to the central supply fan. | |
4. Nonadiabatic humidifiers cumulatively serving no more than 10% of a building's air economizer capacity as measured in cfm. This refers to the system cfm serving rooms with stand alone or duct mounted humidifiers. |
Reviser's note: The typographical error in the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appears in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403231 Table C403.2.3(1)—Minimum efficiency requirements—Electrically operated unitary air conditioners and condensing units.
Table C403.2.3(1)A
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Electrically Operated Unitary Air Conditioners and Condensing Units
((Minimum Efficiency |
||||||
Equipment Type |
Size Category |
Heating Section Type |
Subcategory or Rating Condition |
Before 6/1/2011 |
As of 6/1/2011 |
Test Procedurea |
Air conditioners, air cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System |
13.0 SEER |
13.0 SEER |
AHRI 210/240 |
Single Package |
13.0 SEER |
13.0 SEER |
||||
Through-the-wall (air cooled) |
≤ 30,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System |
12.0 SEER |
12.0 SEER |
|
Single Package |
12.0 SEER |
12.0 SEER |
||||
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.2 EER 11.4 IEER |
11.2 EER 11.4 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 11.2 IEER |
11.0 EER 11.2 IEER |
|||
Air conditioners, air cooled |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 11.2 IEER |
11.0 EER 11.2 IEER |
AHRI 340/360 |
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.8 EER 11.0 IEER |
10.8 EER 11.0 IEER |
|||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h and < 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
10.0 EER 10.1 IEER |
10.0 EER 10.1 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
9.8 EER 9.9 IEER |
9.8 EER 9.9 IEER |
|||
≥760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
9.7 EER 9.8 IEER |
9.7 EER 9.8 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
9.5 EER 9.6 IEER |
9.5 EER 9.6 IEER |
|||
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System and Single Package |
12.1 EER 12.3 IEER |
12.1 EER 12.3 IEER |
AHRI 210/240 |
|
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.5 EER 11.7 IEER |
12.1 EER 12.3 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
11.3 EER 11.5 IEER |
11.9 EER 12.1 IEER |
|||
Air conditioners, water cooled |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 11.2 IEER |
12.5 EER 12.7 IEER |
AHRI 340/360 |
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.8 EER 11.0 IEER |
12.3 EER 12.5 IEER |
|||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h and < 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 11.1 IEER |
12.4 EER 12.6 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.8 EER 10.9 IEER |
12.2 EER 12.4 IEER |
|||
≥ 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 11.1 IEER |
12.2 EER 12.4 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.8 EER 10.9 IEER |
12.0 EER 12.2 IEER |
|||
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System and Single Package |
12.1 EER 12.3 IEER |
12.1 EER 12.3 IEER |
AHRI 210/240 |
|
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.5 EER 11.7 IEER |
12.1 EER 12.3 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
11.3 EER 11.5 IEER |
11.9 EER 12.1 IEER |
|||
Air conditioners, evaporatively cooled |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 11.2 IEER |
12.0 EER 12.2 IEER |
AHRI 340/360 |
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.8 EER 11.0 IEER |
11.8 EER 12.0 IEER |
|||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h and < 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 11.1 IEER |
11.9 EER 12.1 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.8 EER 10.9 IEER |
12.2 EER 11.9 IEER |
|||
≥ 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 11.1 EER |
11.7 EER 11.9 EER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.8 EER 10.9 EER |
11.5 EER 11.7 EER |
|||
Condensing units, air cooled |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
10.1 EER 11.4 IEER |
10.5 EER 11.8 IEER |
|||
Condensing units, water cooled |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
13.1 EER 13.6 IEER |
13.5 EER 14.0 IEER |
AHRI 365 |
||
Condensing units, evaporatively cooled |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
13.1 EER 13.6 IEER |
13.5 EER 14.0 IEER)) |
|||
Equipment Type |
Size Category |
Heating Section Type |
Subcategory or Rating Condition |
Minimum Efficiency |
Test ProcedureA |
Air conditioners, air cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System |
13.0 SEER |
|
Single Package |
14.0 SEER |
||||
Through-the-wall (air cooled) |
≤ 30,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split system |
12.0 SEER |
|
Single Package |
12.0 SEER |
||||
Small duct high velocity, air cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split system |
11.0 SEER |
|
Air conditioners, air cooled |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.2 EER 12.9 IEER |
|
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 12.7 IEER |
|||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER 12.4 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.8 EER 12.2 IEER |
|||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h and < 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
10.0 EER 11.6 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
9.8 EER 11.4 IEER |
|||
≥ 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
9.7 EER 11.2 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
9.5 EER 11.6 IEER |
|||
Air conditioners, water cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System and Single Package |
12.1 EER 12.3 IEER |
|
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
12.1 EER 13.9 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
11.9 EER 13.7 IEER |
|||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
12.5 EER 13.9 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
12.3 EER 13.7 IEER |
|||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h and < 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
12.4 EER 13.6 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
12.2 EER 13.4 IEER |
|||
≥ 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
12.2 EER 13.5 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
12.0 EER 13.3 IEER |
|||
Air conditioners, evaporatively cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System and Single Package |
12.1 EER 12.3 IEER |
AHRI 210/240 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
12.1 EER 12.3 IEER |
AHRI 340/360 |
|
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
11.9 EER 12.1 IEER |
|||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
12.0 EER 12.2 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
11.8 EER 12.0 IEER |
|||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h and < 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.9 EER 12.1 IEER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
11.7 EER 11.9 IEER |
|||
≥ 760,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.7 EER 11.9 EER |
||
All other |
Split System and Single Package |
11.5 EER 11.7 EER |
|||
Condensing units, air cooled |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
10.5 EER 11.8 IEER |
AHRI 365 |
||
Condensing units, water cooled |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
13.5 EER 14.0 IEER |
|||
Condensing units, evaporatively cooled |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
13.5 EER 14.0 IEER |
For SI: | 1 British thermal unit per hour = 0.2931 W. |
a | Chapter 6 of the referenced standard contains a complete specification of the referenced test procedure, including the reference year version of the test procedure. |
b | Single-phase, air-cooled air conditioners less than 65,000 Btu/h are regulated by NAECA. SEER values are those set by NAECA. |
Table C403.2.3(1)B
((Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Air Conditioners and Condensing Units Serving Computer Rooms
Equipment Type |
Net Sensible Cooling Capacitya |
Minimum Scop-127b Efficiency Downflow Units/upflow Units |
Test Procedure |
Air conditioners, air cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.20/2.09 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 19 kW and < 70 kW) |
2.10/1.99 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
1.90/1.79 |
||
Air conditioners, water cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.60/2.49 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 19 kW and < 70 kW) |
2.50/2.39 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
2.40/2.29 |
||
Air conditioners, water cooled with fluid economizer |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.55/2.44 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 19 kW and < 70 kW) |
2.45/2.34 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
2.35/2.24 |
||
Air conditioners, glycol cooled (rated at 40% propylene glycol) |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.50/2.39 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 19 kW and < 70 kW) |
2.15/2.04 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
2.10/1.99 |
||
Air conditioners, glycol cooled (rated at 40% propylene glycol) with fluid economizer |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.45/2.34 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 19 kW and < 70 kW) |
2.10/1.99 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
2.05/1.94 |
a | Net sensible cooling capacity: The total gross cooling capacity less the latent cooling less the energy to the air movement system (Total Gross - Latent - Fan Power). |
b | Sensible coefficient of performance (SCOP-127): A ratio calculated by dividing the net sensible cooling capacity in watts by the total power input in watts (excluding reheaters and humidifiers) at conditions defined in ASHRAE Standard 127. The net sensible cooling capacity is the gross sensible capacity minus the energy dissipated into the cooled space by the fan system. |
Table C403.2.3(1)C))
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Electrically Operated Variable Refrigerant Flow Air Conditioners
Equipment Type |
Size Category |
Heating Section Type |
Subcategory or Rating Condition |
Minimum Efficiency |
Test Procedure |
VRF Air Conditioners, Air Cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System |
13.0 SEER |
AHRI 1230 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or none) |
VRF Multi-Split System |
11.2 EER 13.1 IEER (before 1/1/2017) 15.5 IEER (as of 1/1/2017) |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or none) |
VRF Multi-Split System |
11.0 EER 12.9 IEER (before 1/1/2017) 14.9 IEER (as of 1/1/2017) |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or none) |
VRF Multi-split System |
10.0 EER 11.6 IEER (before 1/1/2017) 13.9 IEER (as of 1/1/2017) |
Table ((C403.2.3(1)D)) C403.2.3(1)C
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Electrically Operated Variable Refrigerant Flow Air-to-Air and Applied Heat Pumps
Equipment Type |
Size Category |
Heating Section Type |
Subcategory or Rating Condition |
Minimum Efficiency |
Test Procedure |
VRF Air Cooled (cooling mode) |
< 65,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System |
13.0 SEER |
AHRI 1230 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or none) |
VRF Multi-Split System |
11.0 EER 12.9 IEER (before 1/1/2017) 14.6 IEER (as of 1/1/2017) |
||
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or none) |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery |
10.8 EER 12.7 IEER (before 1/1/2017) 14.4 IEER (as of 1/1/2017) |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or none) |
VRF Multi-Split System |
10.6 EER 12.3 IEER (before 1/1/2017) 13.9 IEER (as of 1/1/2017) |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or none) |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery |
10.4 EER 12.1 IEER (before 1/1/2017) 13.7 IEER (as of 1/1/2017) |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or none) |
VRF Multi-Split System |
9.5 EER 11.0 IEER (before 1/1/2017) 12.7 IEER (as of 1/1/2017) |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or none) |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery |
9.3 EER 10.8 IEER (before 1/1/2017) 12.5 IEER (as of 1/1/2017) |
||
VRF Water Source (cooling mode) |
< 65,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System 86ºF entering water |
12.0 EER |
AHRI 1230 |
< 65,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery 86ºF entering water |
11.8 EER |
||
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System 86ºF entering water |
12.0 EER |
||
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery 86ºF entering water |
11.8 EER |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System 86ºF entering water |
10.0 EER |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery 86ºF entering water |
9.8 EER |
||
VRF Groundwater Source (cooling mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System 59ºF entering water |
16.2 EER |
AHRI 1230 |
< 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery 59ºF entering water |
16.0 EER |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System 59ºF entering water |
13.8 EER |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery 59ºF entering water |
13.6 EER |
||
VRF Ground Source (cooling mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System 77ºF entering water |
13.4 EER |
AHRI 1230 |
< 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery 77ºF entering water |
13.2 EER |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System 77ºF entering water |
11.0 EER |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
VRF Multi-Split System with Heat Recovery 77ºF entering water |
10.8 EER |
||
VRF Air Cooled (heating mode) |
< 65,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
VRF Multi-Split System |
7.7 HSPF |
AHRI 1230 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
VRF Multi-Split System 47ºF db/43ºF wb outdoor air 17ºF db/15ºF wb outdoor air |
3.3 COP 2.25 COP |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
VRF Multi-Split System 47ºF db/43ºF wb outdoor air 17ºF db/15ºF wb outdoor air |
3.2 COP 2.05 COP |
||
VRF Water Source (heating mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
VRF Multi-Split System 68ºF entering water |
4.2 COP |
AHRI 1230 |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
VRF Multi-Split System 68ºF entering water |
3.9 COP |
||
VRF Groundwater Source (heating mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
VRF Multi-Split System 50ºF entering water |
3.6 COP |
AHRI 1230 |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
VRF Multi-Split System 50ºF entering water |
3.3 COP |
||
VRF Ground Source (heating mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
VRF Multi-Split System 32ºF entering water |
3.1 COP |
AHRI 1230 |
≥ 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
VRF Multi-Split System 32ºF entering water |
2.8 COP |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403232 Table C403.2.3(2)—Minimum efficiency requirements—Electrically operated unitary and applied heat pumps.
Table C403.2.3(2)
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Electrically Operated Unitary and Applied Heat Pumps
Equipment Type |
Size Category |
Heating Section Type |
Subcategory or Rating Condition |
Minimum Efficiency |
Test Procedurea |
Air cooled (cooling mode) |
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System |
((13.0)) 14.0 SEER |
AHRI 210/240 |
Single Packaged |
((13.0)) 14.0 SEER |
||||
Through-the-wall, air cooled (cooling mode) |
≤ 30,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System |
12.0 SEER |
|
Single Packaged |
12.0 SEER |
||||
Small duct high velocity, air cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
All |
Split System |
11.0 SEER |
|
Air cooled (cooling mode) |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
11.0 EER ((11.2)) 12.2 IEER |
AHRI 340/360 |
All Other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.8 EER ((11.0)) 12.0 IEER |
|||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
10.6 EER ((10.7)) 11.6 IEER |
||
All Other |
Split System and Single Package |
10.4 EER ((10.5)) 11.4 IEER |
|||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h |
Electric Resistance (or None) |
Split System and Single Package |
9.5 EER ((9.6)) 10.6 IEER |
||
All Other |
Split System and Single Package |
9.3 EER ((9.4)) 10.4 IEER |
|||
Water source (cooling mode) |
< 17,000 Btu/h |
All |
86°F entering water |
((11.2)) 12.2 EER |
ISO 13256-1 |
≥ 17,000 Btu/h and < 65,000 Btu/h |
All |
86°F entering water |
((12.0)) 13.0 EER |
||
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
86°F entering water |
((12.0)) 13.0 EER |
||
Ground water source (cooling mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
59°F entering water |
((16.2)) 18.0 EER |
|
Ground water source (cooling mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
77°F entering water |
((13.4)) 14.1 EER |
|
Water-source water to water (cooling mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
86°F entering water |
10.6 EER |
ISO 13256-2 |
59°F entering water |
16.3 EER |
||||
Ground water source brine to water (cooling mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h |
All |
77°F entering fluid |
12.1 EER |
|
Air cooled (heating mode) |
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
— |
Split System |
((7.7)) 8.2 HSPF |
AHRI 210/240 |
— |
Single Package |
((7.7)) 8.0 HSPF |
|||
Through-the-wall, (air cooled, heating mode) |
≤ 30,000 Btu/hb (cooling capacity) |
— |
Split System |
7.4 HSPF |
|
— |
Single Package |
7.4 HSPF |
|||
Small-duct high velocity (air cooled, heating mode) |
< 65,000 Btu/hb |
— |
Split System |
6.8 HSPF |
|
Air cooled (heating mode) |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
47°F db/43ºF wb Outdoor Air |
3.3 COP |
AHRI 340/360 |
17ºF db/15ºF wb Outdoor Air |
2.25 COP |
||||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
47°F db/43ºF wb Outdoor Air |
3.2 COP |
||
17ºF db/15ºF wb Outdoor Air |
2.05 COP |
||||
Water source (heating mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
68°F entering water |
((4.2)) 4.3 COP |
ISO 13256-1 |
Ground water source (heating mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
50°F entering water |
((3.6)) 3.7 COP |
|
Ground source (heating mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
32°F entering fluid |
((3.1)) 3.2 COP |
|
Water-source water to water (heating mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
68°F entering water |
3.7 COP |
ISO 13256-2 |
— |
50°F entering water |
3.1 COP |
|||
Ground source brine to water (heating mode) |
< 135,000 Btu/h (cooling capacity) |
— |
32°F entering fluid |
2.5 COP |
For SI: | 1 British thermal unit per hour = 0.2931 W, °C = [(°F) - 32]/1.8. |
a | Chapter 6 of the referenced standard contains a complete specification of the referenced test procedure, including the reference year version of the test procedure. |
b | Single-phase, air-cooled air conditioners less than 65,000 Btu/h are regulated by NAECA. SEER values are those set by NAECA. |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403233 Table C403.2.3(3)—Minimum efficiency requirements—Electrically operated PTAC, PTHP, SPVAC, SPVHP, room air conditioners.
Table C403.2.3(3)
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Electrically Operated Packaged Terminal Air Conditioners, Packaged Terminal Heat Pumps, Single-Package Vertical Air Conditioners, Single-Package Vertical Heat Pumps, Room Air Conditioners and Room Air-Conditioner Heat Pumps
Minimum Efficiency |
|||||
Equipment Type |
Size Category (Input) |
Subcategory or Rating Condition |
((Before 10/08/2012 |
As of 10/08/2012)) |
Test Procedurea |
PTAC (cooling mode) new construction |
All Capacities |
95°F db outdoor air |
((12.5 - (0.213 × Cap/1000) EER)) |
((13.8)) 14.0 - (0.300 × Cap/1000) EER |
AHRI 310/380 |
PTAC (cooling mode) replacementsb |
All Capacities |
95°F db outdoor air |
((10.9 - (0.213 × Cap/1000) EER)) |
10.9 - (0.213 × Cap/1000) EER |
|
PTHP (cooling mode) new construction |
All Capacities |
95°F db outdoor air |
((12.3 - (0.213 × Cap/1000) EER)) |
14.0 - (0.300 × Cap/1000) EER |
|
PTHP (cooling mode) replacementsb |
All Capacities |
95°F db outdoor air |
((10.8 - (0.213 × Cap/1000) EER)) |
10.8 - (0.213 × Cap/1000) EER |
|
PTHP (heating mode) new construction |
All Capacities |
— |
((3.2 - (0.026 × Cap/1000) COP)) |
3.7 - (0.052 × Cap/1000) COP |
|
PTHP (heating mode) replacementsb |
All Capacities |
— |
((2.9 - (0.026 × Cap/1000) COP)) |
2.9 - (0.026 × Cap/1000) COP |
|
SPVAC (cooling mode) |
< 65,000 Btu/h |
95°F db/75°F wb outdoor air |
((9.0 EER |
9.0)) 10.0 EER |
AHRI 390 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
95°F db/75°F wb outdoor air |
((8.9 EER |
8.9)) 10.0 EER |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
95°F db/75°F wb outdoor air |
((8.6 EER |
8.6)) 10.0 EER |
||
SPVHP (cooling mode) |
< 65,000 Btu/h |
95°F db/75°F wb outdoor air |
((9.0 EER |
9.0)) 10.0 EER |
|
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
95°F db/75°F wb outdoor air |
((8.9 EER |
8.9)) 10.0 EER |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
95°F db/75°F wb outdoor air |
((8.6 EER |
8.6)) 10.0 EER |
||
SPVHP (heating mode) |
<65,000 Btu/h |
47°F db/43°F wb outdoor air |
((3.0 COP)) |
3.0 COP |
AHRI 390 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 135,000 Btu/h |
47°F db/43°F wb outdoor air |
((3.0 COP)) |
3.0 COP |
||
≥ 135,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
47°F db/43°F wb outdoor air |
((2.9 COP |
2.9)) 3.0 COP |
||
Room air conditioners, with louvered sides |
< 6,000 Btu/h |
— |
((9.7 SEER)) |
9.7 SEER |
ANSI/AHA-MRAC-1 |
≥ 6,000 Btu/h and < 8,000 Btu/h |
— |
((9.7 EER)) |
9.7 ((EER)) SEER |
||
≥ 8,000 Btu/h and < 14,000 Btu/h |
— |
((9.8 EER)) |
9.8 EER |
||
≥ 14,000 Btu/h and < 20,000 Btu/h |
— |
((9.7 SEER)) |
9.7 SEER |
||
≥ 20,000 Btu/h |
— |
((8.5 EER)) |
8.5 EER |
||
Room air conditioners, without louvered sides |
< 8,000 Btu/h |
— |
((9.0 EER)) |
9.0 EER |
|
≥ 8,000 Btu/h and < 20,000 Btu/h |
— |
((8.5 EER)) |
8.5 EER |
||
≥ 20,000 Btu/h |
— |
((8.5 EER)) |
8.5 EER |
||
Room air-conditioner heat pumps with louvered sides |
< 20,000 Btu/h |
— |
((9.0 EER)) |
9.0 EER |
|
≥ 20,000 Btu/h |
— |
((8.5 EER)) |
8.5 EER |
||
Room air-conditioner heat pumps without louvered sides |
< 14,000 Btu/h |
— |
((8.5 EER)) |
8.5 EER |
|
≥ 14,000 Btu/h |
— |
((8.0 EER)) |
8.0 EER |
||
Room air conditioner casement only |
All capacities |
— |
((8.7 EER)) |
8.7 EER |
|
Room air conditioner casement-slider |
All capacities |
— |
((9.5 EER)) |
9.5 EER |
|
For SI: | 1 British thermal unit per hour = 0.2931 W, °C = [(°F) - 32]/1.8. |
"Cap" = The rated cooling capacity of the product in Btu/h. If the unit's capacity is less than 7000 Btu/h, use 7000 Btu/h in the calculation. If the unit's capacity is greater than 15,000 Btu/h, use 15,000 Btu/h in the calculations. | |
a | Chapter 6 of the referenced standard contains a complete specification of the referenced test procedure, including the referenced year version of the test procedure. |
b | Replacement unit shall be factory labeled as follows: "MANUFACTURED FOR NONSTANDARD SIZE APPLICATIONS ONLY; NOT TO BE INSTALLED IN NEW STANDARD PROJECTS" or "MANUFACTURED FOR REPLACEMENT APPLICATIONS ONLY: NOT TO BE INSTALLED IN NEW CONSTRUCTION PROJECTS." Replacement efficiencies apply only to units with existing sleeves less than 16 inches (406 mm) in height and less than 42 inches (1067 mm) in width. |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403235 Table C403.2.3(5)—Minimum efficiency requirements—Gas- and oil-fired boilers.
Table C403.2.3(5)
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Gas- and Oil-Fired Boilers
Equipment Typea |
Subcategory or Rating Condition |
Size Category (Input) |
Minimum Efficiency |
Test Procedure |
Boilers, hot water |
Gas-fired |
< 300,000 Btu/h |
((80)) 82% AFUE |
10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
≥ 300,000 Btu/h and ≤ 2,500,000 Btu/hb |
80% Et |
10 C.F.R. Part 431 |
||
˃ 2,500,000 Btu/ha |
82% Ec |
|||
Oil-firedc |
< 300,000 Btu/h |
((80)) 84% AFUE |
10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
|
≥ 300,000 Btu/h and ≤ 2,500,000 Btu/hb |
82% Et |
10 C.F.R. Part 431 |
||
˃ 2,500,000 Btu/ha |
84% Ec |
|||
Boilers, steam |
Gas-fired |
< 300,000 Btu/h |
((75)) 80% AFUE |
10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
Gas-fired - All, except natural draft |
≥ 300,000 Btu/h and ≤ 2,500,000 Btu/hb |
79% Et |
10 C.F.R. Part 431 |
|
˃ 2,500,000 Btu/ha |
79% Et |
|||
Gas-fired-natural draft |
≥ 300,000 Btu/h and ≤ 2,500,000 Btu/hb |
77% Et |
||
˃ 2,500,000 Btu/ha |
77% Et |
|||
Oil-firedc |
< 300,000 Btu/h |
((80)) 82% AFUE |
10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
|
≥ 300,000 Btu/h and ≤ 2,500,000 Btu/hb |
81% Et |
10 C.F.R. Part 431 |
||
˃ 2,500,000 Btu/ha |
81% Et |
For SI: | 1 British thermal unit per hour = 0.2931 W. | ||
Ec | = | Combustion efficiency (100 percent less flue losses). | |
Et | = | Thermal efficiency. See referenced standard document for detailed information. | |
a | These requirements apply to boilers with rated input of 8,000,000 Btu/h or less that are not packaged boilers and to all packaged boilers. Minimum efficiency requirements for boilers cover all capacities of packaged boilers. | ||
b | Maximum capacity minimum and maximum ratings as provided for and allowed by the unit's controls. | ||
c | Includes oil-fired (residual). | ||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403237 Table C403.2.3(7)—Minimum efficiency requirements—Water chilling packages.
Table C403.2.3(7)
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Water Chilling Packagesa
((As of 1/1/2010b |
|||||||||
Before 1/1/2010 |
Path A |
Path B |
|||||||
Equipment Type |
Size Category |
Units |
Full Load |
IPLV |
Full Load |
IPLV |
Full Load |
IPLV |
Test Procedurec |
Air cooled chillers |
< 150 tons |
EER |
≥ 9.562 |
≥10.416 |
≥ 9.562 |
≥ 12.500 |
NA |
NA |
AHRI 550/590 |
≥ 150 tons |
EER |
≥ 9.562 |
≥ 12.750 |
NA |
NA |
||||
Air cooled without condenser, electrical operated |
All capacities |
EER |
≥ 10.586 |
≥ 11.782 |
Air cooled chillers without condensers shall be rated with matching condensers and comply with the air cooled chiller efficiency requirements |
||||
Water cooled, electrically operated, reciprocating |
All capacities |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.837 |
≤ 0.696 |
Reciprocating units shall comply with water cooled positive displacement efficiency requirements |
||||
Water cooled, electrically operated, positive displacement |
< 75 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.790 |
≤ 0.676 |
≤ 0.780 |
≤ 0.630 |
≤ 0.800 |
≤ 0.600 |
|
≥75 tons and < 150 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.775 |
≤ 0.615 |
≤ 0.790 |
≤ 0.586 |
||||
≥ 150 tons and < 300 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.717 |
≤ 0.627 |
≤ 0.680 |
≤ 0.580 |
≤ 0.718 |
≤ 0.540 |
||
≥ 300 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.639 |
≤ 0.571 |
≤ 0.620 |
≤ 0.540 |
≤ 0.639 |
≤ 0.490 |
||
Water cooled, electrically operated, centrifugal |
< 150 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.703 |
≤ 0.669 |
≤ 0.634 |
≤ 0.596 |
≤ 0.639 |
≤ 0.450 |
|
≥ 150 tons and < 300 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.634 |
≤ 0.596 |
||||||
≥ 300 tons and < 600 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.576 |
≤ 0.549 |
≤ 0.576 |
≤ 0.549 |
≤ 0.600 |
≤ 0.400 |
||
≥600 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.576 |
≤ 0.549 |
≤ 0.570 |
≤ 0.539 |
≤ 0.590 |
≤ 0.400 |
||
Air cooled, absorption single effect |
All capacities |
COP |
≥ 0.600 |
NR |
≥ 0.600 |
NR |
NA |
NA |
AHRI 560 |
Water cooled, absorption single effect |
All capacities |
COP |
≥ 0.700 |
NR |
≥ 0.700 |
NR |
NA |
NA |
|
Absorption double effect, indirect fired |
All capacities |
COP |
≥ 1.000 |
≥ 1.050 |
≥1.000 |
≥ 1.050 |
NA |
NA |
|
Absorption double effect, direct fired |
All capacities |
COP |
≥ 1.000 |
≥ 1.000 |
≥ 1.000 |
≥ 1.000 |
NA |
NA)) |
|
Equipment Type |
Size Category |
Units |
As of 1/1/2015b |
Test Procedurec |
|||
Path A |
Path B |
||||||
Full Load |
IPLV |
Full Load |
IPLV |
||||
Air-cooled chillers |
< 150 tons |
EER |
≥ 10.100 |
≥ 13.700 |
≥ 9.700 |
≥ 15.800 |
|
≥ 150 tons |
EER |
≥ 10.100 |
≥ 14.000 |
≥ 9.700 |
≥ 16.100 |
||
Air cooled without condenser, electrically operated |
All capacities |
EER |
Air-cooled chillers without condensers shall be rated with matching condensers and comply with the air-cooled chiller efficiency requirements |
||||
Water cooled, electrically operated, reciprocating |
All capacities |
kW/ton |
Reciprocating units shall comply with water cooled positive displacement efficiency requirements |
||||
Water cooled, electrically operated, positive displacement |
< 75 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.750 |
≤ 0.600 |
≤ 0.780 |
≤ 0.500 |
|
≥ 75 tons and < 150 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.720 |
≤ 0.560 |
≤ 0.750 |
≤ 0.490 |
AHRI 550/590 |
|
≥ 150 tons and < 300 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.660 |
≤ 0.540 |
≤ 0.680 |
≤ 0.440 |
||
≥ 300 tons and < 600 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.610 |
≤ 0.520 |
≤ 0.625 |
≤ 0.410 |
||
≥ 600 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.560 |
≤ 0.500 |
≤ 0.585 |
≤ 0.380 |
||
Water cooled, electrically operated, centrifugal |
< 150 tons |
kW/ton |
0.610 |
≤ 0.550 |
≤ 0.695 |
≤ 0.440 |
|
≥ 150 tons and < 300 tons |
kW/ton |
||||||
≥ 300 tons and < 400 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.560 |
≤ 0.520 |
≤ 0.595 |
≤ 0.390 |
||
≥ 400 tons |
kW/ton |
≤ 0.560 |
≤ 0.500 |
≤ 0.585 |
≤ 0.380 |
||
Air cooled, absorption single effect |
All capacities |
COP |
≥ 0.600 |
NR |
NA |
NA |
|
Water cooled, absorption single effect |
All capacities |
COP |
≥ 0.700 |
NR |
NA |
NA |
AHRI 560 |
Absorption double effect, indirect fired |
All capacities |
COP |
≥ 1.000 |
≥ 1.050 |
NA |
NA |
|
Absorption double effect, direct fired |
All capacities |
COP |
≥ 1.000 |
≥ 1.000 |
NA |
NA |
|
For SI: | 1 ton = 3517 W, 1 British thermal unit per hour = 0.2931 W, °C = [(°F) - 32]/1.8. |
NA = Not applicable, not to be used for compliance; |
NR = No requirement. |
a | The centrifugal chiller equipment requirements, after adjustment in accordance with Section C403.2.3.1 or Section C403.2.3.2, do not apply to chillers used in low-temperature applications where the design leaving fluid temperature is less than 36ºF. The requirements do not apply to positive displacement chillers with leaving fluid temperatures less than or equal to 32ºF. The requirements do not apply to absorption chillers with design leaving fluid temperatures less than 40ºF. |
b | Compliance with this standard can be obtained by meeting the minimum requirements of Path A or B. However, both the full load and IPLV shall be met to fulfill the requirements of Path A or B. |
c | Chapter 6 of the referenced standard contains a complete specification of the referenced test procedure, including the referenced year version of the test procedure. |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403238 Table C403.2.3(8)—Minimum efficiency requirements—Heat rejection equipment.
Table C403.2.3(8)
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Heat Rejection Equipment
Equipment Typea |
Total System Heat Rejection Capacity at Rated Conditions |
Subcategory or Rating Condition |
Performance Requiredb,c,d,g,h |
Test Proceduree,f |
Propeller or axial fan open circuit cooling towers |
All |
95°F Entering Water 85°F Leaving Water 75°F Entering wb |
≥ 38.2 gpm/hp |
CTI ATC-105 and CTI STD-201 |
Centrifugal fan open circuit cooling towers |
All |
95°F Entering Water 85°F Leaving Water 75°F Entering wb |
≥ 20.0 gpm/hp |
CTI ATC-105 and CTI STD-201 |
Propeller or axial fan closed circuit cooling towers |
All |
102°F Entering Water 90°F Leaving Water 75°F Entering wb |
≥ 14.0 gpm/hp |
CTI ATC-105S and CTI STD-201 |
Centrifugal closed circuit cooling towers |
All |
102°F Entering Water 90°F Leaving Water 75°F Entering wb |
≥ 7.0 gpm/hp |
CTI ATC-105S and CTI STD-201 |
Propeller or axial fan evaporative condensers |
All |
R-507A Test Fluid 165°F Entering Gas Temperature 105°F Condensing Temperature 75°F Entering wb |
≥□b5°F Enterin□□□□ |
CTI ATC-160 |
Propeller or axial fan evaporative condensers |
All |
Ammonia Test Fluid 140°F Entering Gas Temperature 96.3°F Condensing Temperature 75°F Entering wb |
≥□b5°F Enterin□□□□ |
CTI ATC-160 |
Centrifugal fan evaporative condensers |
All |
R-507A Test Fluid 165°F Entering Gas Temperature 105°F Condensing Temperature 75°F Entering wb |
≥□b5°F Enterin□□□□ |
CTI ATC-160 |
Centrifugal fan evaporative condensers |
All |
Ammonia Test Fluid 140°F Entering Gas Temperature 96.3°F Condensing Temperature 75°F Entering wb |
≥□b5°F Enterin□□□□ |
CTI ATC-160 |
Air cooled condensers |
All |
125°F Condensing Temperature R-22 Test Fluid 190°F Entering Gas Temperature 15°F Subcooling 95°F Entering db |
≥ 176,000 Btu/h • hp |
AHRI 460 |
For SI: | °C = [(°F) - 32]/1.8, L/s • kW = (gpm/hp)/(11.83), COP = (Btu/h • hp)/(2550.7). |
db = dry bulb temperature, °F; | |
wb = wet bulb temperature, °F. |
a | The efficiencies and test procedures for both open and closed circuit cooling towers are not applicable to hybrid cooling towers that contain a combination of wet and dry heat exchange sections. |
a | For purposes of this table, open circuit cooling tower performance is defined as the water flow rating of the tower at the thermal rating condition listed in Table 403.2.3(8) divided by the fan nameplate rated motor power. |
c | For purposes of this table, closed circuit cooling tower performance is defined as the water flow rating of the tower at the thermal rating condition listed in Table 403.2.3(8) divided by the sum of the fan nameplate rated motor power and the spray pump nameplate rated motor power. |
d | For purposes of this table, air cooled condenser performance is defined as the heat rejected from the refrigerant divided by the fan nameplate rated motor power. |
e | Chapter 6 of the referenced standard contains a complete specification of the referenced test procedure, including the referenced year version of the test procedure. |
f | ((If)) Where a certification program exists for a covered product, and it includes provisions for verification and challenge of equipment efficiency ratings, then the product shall be listed in the certification program, or, ((if)) where a certification program exists for a covered product, and it includes provisions for verification and challenge of equipment efficiency ratings, but the product is not listed in the existing certification program, the ratings shall be verified by an independent laboratory test report. |
g | Cooling towers shall comply with the minimum efficiency listed in the table for that specific type of tower with the capacity effect of any project-specific accessories and/or options included in the capacity of the cooling tower. |
h | For purposes of this table, evaporative condenser performance is defined as the heat rejected at the specified rating condition in the table, divided by the sum of the fan motor nameplate power and the integral spray pump nameplate power. |
i | Requirements for evaporative condensers are listed with ammonia (R-717) and R-507A as test fluids in this table. Evaporative condensers intended for use with halocarbon refrigerants other than R-507A must meet the minimum efficiency requirements listed above with R-507A as the test fluid. |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403239 Table C403.2.3(9) and Table C403.2.3(10)—Minimum efficiency requirements((—Heat transfer equipment)).
Table C403.2.3(9)
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Air Conditioners and Condensing Units Serving Computer Rooms
Equipment Type |
Net Sensible Cooling Capacitya |
Minimum SCOP-127b Efficiency Downflow units/Upflow units |
Test Procedure |
Air conditioners, air cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.20/2.09 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h ( 19 kW and < 70 kW) |
2.10/1.99 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
1.90/1.79 |
||
Air conditioners, water cooled |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.60/2.49 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 19 kW and < 70 kW) |
2.50/2.39 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
2.40/2.29 |
||
Air conditioners, water cooled with fluid economizer |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.55/2.44 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 19kW and < 70 kW) |
2.45/2.34 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
2.35/2.24 |
||
Air conditioners, glycol cooled (rated at 40% propylene glycol) |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.50/2.39 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 19 kW and < 70 kW) |
2.15/2.04 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
2.10/1.99 |
||
Air conditioners, glycol cooled (rated at 40% propylene glycol) with fluid economizer |
< 65,000 Btu/h (< 19 kW) |
2.45/2.34 |
ANSI/ASHRAE 127 |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 19 kW and < 70 kW) |
2.10/1.99 |
||
≥ 240,000 Btu/h (≥ 70 kW) |
2.05/1.94 |
a | Net sensible cooling capacity: The total gross cooling capacity less the latent cooling less the energy to the air movement system. (Total Gross – Latent – Fan Power.) |
b | Sensible coefficient of performance (SCOP-127): A ratio calculated by dividing the net sensible cooling capacity in watts by the total power input in watts (excluding reheaters and humidifiers) at conditions defined in ASHRAE Standard 127. The net sensible cooling capacity is the gross sensible capacity minus the energy dissipated into the cooled space by the fan system. |
Table C403.2.3(((9))) (10)
Minimum Efficiency Requirements—Heat Transfer Equipment
Equipment Type |
Subcategory |
Minimum Efficiency |
Test Procedurea |
Liquid-to-liquid heat exchangers |
Plate type |
NR |
AHRI 400 |
NR = No requirement. | |
a | Chapter 6 of the referenced standard contains a complete specification of the referenced test procedure, including the referenced year version of the test procedure. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40324 Section C403.2.4—HVAC system controls.
C403.2.4 HVAC system controls. Each heating and cooling system shall be provided with thermostatic controls as specified in Section C403.2.4.1, C403.2.4.1.3, C403.2.4.2, C403.2.4.3, ((C403.2.4.4)) C403.2.4.5, C403.3.1, C403.4, C403.4.1, C403.4.2, C403.4.3, or C403.4.4((, C403.4.5, C403.4.6, C403.4.7, C403.4.8, C403.4.9, or C403.4.10)).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403241 Section C403.2.4.1—Thermostatic controls.
C403.2.4.1 Thermostatic controls. The supply of heating and cooling energy to each zone shall be controlled by individual thermostatic controls capable of responding to temperature within the zone. Controls in the same zone or in neighboring zones connected by openings larger than 10 percent of the floor area of either zone shall not allow for simultaneous heating and cooling. At a minimum, each floor of a building shall be considered as a separate zone. Controls on systems required to have economizers and serving single zones shall have multiple cooling stage capability and activate the economizer when appropriate as the first stage of cooling. See Section C403.3.1 ((or C403.4.1)) for further economizer requirements. Where humidification or dehumidification or both is provided, at least one humidity control device shall be provided for each humidity control system.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Independent perimeter systems that are designed to offset only building envelope heat losses or gains or both serving one or more perimeter zones also served by an interior system provided: |
((1.)) 1.1. The perimeter system includes at least one thermostatic control zone for each building exposure having exterior walls facing only one orientation (within +/-45 degrees) (0.8 rad) for more than 50 contiguous feet (15,240 mm); ((and)) | |
((2.)) 1.2. The perimeter system heating and cooling supply is controlled by a thermostat located within the zones served by the system((.)); and | |
1.3. Controls are configured to prevent the perimeter system from operating in a different heating or cooling mode from the other equipment within the zones or from neighboring zones connected by openings larger than 10 percent of the floor area of either zone. | |
2. Controls capable of and configured to prevent simultaneous heating and cooling for all zones with area within 15 feet of the perimeter unless separated by an interior wall. | |
3. Any nonperimeter zones not separated from perimeter zones by an interior wall with openings no larger than 10 percent of the perimeter floor zone area shall have setpoints and deadbands coordinated so that cooling in adjacent zones shall not operate until the adjacent zone temperature is 5°F (2.8°C) higher than the perimeter zone temperature. |
C403.2.4.1.1 Heat pump supplementary heat. Unitary air cooled heat pumps shall include microprocessor controls that minimize supplemental heat usage during start-up, set-up, and defrost conditions. These controls shall anticipate need for heat and use compression heating as the first stage of heat. Controls shall indicate when supplemental heating is being used through visual means (e.g., LED indicators). Heat pumps equipped with supplementary heaters shall be installed with controls that prevent supplemental heater operation above 40°F.
EXCEPTION: | Packaged terminal heat pumps (PTHPs) of less than 2 tons (24,000 Btu/hr) cooling capacity provided with controls that prevent supplementary heater operation above 40°F. |
C403.2.4.1.2 Deadband. Where used to control both heating and cooling, zone thermostatic controls shall be configured to provide a temperature range or deadband of at least 5°F (2.8°C) within which the supply of heating and cooling energy to the zone is shut off or reduced to a minimum.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Thermostats requiring manual changeover between heating and cooling modes. |
2. Occupancies or applications requiring precision in indoor temperature control as approved by the code official. |
C403.2.4.1.3 Setpoint overlap restriction. Where a zone has a separate heating and a separate cooling thermostatic control located within the zone, a limit switch, mechanical stop or direct digital control system with software programming shall be configured to prevent the heating set point from exceeding the cooling setpoint and to maintain a deadband in accordance with Section C403.2.4.1.2.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403242 Section C403.2.4.2—((Setpoint overlap restriction)) Off-hour controls.
((C403.2.4.2 Setpoint overlap restriction. Where used to control both heating and cooling, zone thermostatic controls shall provide a temperature range or deadband of at least 5°F (2.8°C) within which the supply of heating and cooling energy to the zone is capable of being shut off or reduced to a minimum.
EXCEPTION: | Thermostats requiring manual changeover between heating and cooling modes.)) |
C403.2.4.2 Off-hour controls. For all occupancies other than Group R, each zone shall be provided with thermostatic setback controls that are controlled by either an automatic time clock or programmable control system.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Zones that will be operated continuously. |
2. Zones with a full HVAC load demand not exceeding 6,800 Btu/h (2 kW) and having a readily accessible manual shutoff switch. |
C403.2.4.2.1 Thermostatic setback. Thermostatic setback controls shall be configured to set back or temporarily operate the system to maintain zone temperatures down to 55°F (13°C) or up to 85°F (29°C).
C403.2.4.2.2 Automatic setback and shutdown. Automatic time clock or programmable controls shall be capable of starting and stopping the system for seven different daily schedules per week and retaining their programming and time setting during a loss of power for at least 10 hours. Additionally, the controls shall have a manual override that allows temporary operation of the system for up to 2 hours; a manually operated timer configured to operate the system for up to 2 hours; or an occupancy sensor.
C403.2.4.2.3 Automatic start capabilities. Automatic start controls shall be provided for each HVAC system. The controls shall be capable of automatically adjusting the daily start time of the HVAC system in order to bring each space to the desired occupied temperature immediately prior to scheduled occupancy.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403243 Section C403.2.4.3—((Off-hour controls)) Shutoff dampers.
((C403.2.4.3 Off-hour controls. For all occupancies other than Group R, each zone shall be provided with thermostatic setback controls that are controlled by either an automatic time clock or programmable control system.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Zones that will be operated continuously. |
2. Zones with a full HVAC load demand not exceeding 6,800 Btu/h (2 kW) and having a readily accessible manual shutoff switch. |
C403.2.4.3.1 Thermostatic setback capabilities. Thermostatic setback controls shall have the capability to set back or temporarily operate the system to maintain zone temperatures down to 55°F (13°C) or up to 85°F (29°C).
C403.2.4.3.2 Automatic setback and shutdown capabilities. Automatic time clock or programmable controls shall be capable of starting and stopping the system for seven different daily schedules per week and retaining their programming and time setting during a loss of power for at least 10 hours. Additionally, the controls shall have a manual override that allows temporary operation of the system for up to 2 hours; a manually operated timer capable of being adjusted to operate the system for up to 2 hours; or an occupancy sensor.
C403.2.4.3.3 Automatic start capabilities. Automatic start controls shall be provided for each HVAC system. The controls shall be capable of automatically adjusting the daily start time of the HVAC system in order to bring each space to the desired occupied temperature immediately prior to scheduled occupancy.)) C403.2.4.3 Shutoff dampers. Outdoor air supply, exhaust openings and relief outlets and stairway and shaft vents shall be provided with Class I motorized dampers.
Return air openings used for airside economizer operation shall be equipped with Class I motorized dampers.
Class 1 dampers shall have a maximum leakage rate of 4 cfm/ft2(20.3 L/s x m2) at 1.0 inch water gauge (w.g.) (249 Pa) when tested in accordance with AMCA 500D and shall be labeled by an approved agency such purpose.
EXCEPTION: | Motorized dampers on return air openings in unitary packaged equipment that have the minimum leakage rate available from the manufacturer shall be deemed to comply. |
Outdoor air intake and exhaust dampers shall be installed with automatic controls configured to close when the systems or spaces served are not in use or during unoccupied period warm-up and setback operation, unless the systems served require outdoor or exhaust air in accordance with the International Mechanical Code or the dampers are opened to provide intentional economizer cooling.
Stairway and shaft vent dampers shall be installed with automatic controls configured to open upon the activation of any fire alarm initiating device of the building's fire alarm system or the interruption of power to the damper.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Gravity (nonmotorized) dampers shall be permitted to be used as follows: |
1.1. Relief dampers serving systems less than 5,000 cfm total supply shall be permitted in buildings less than three stories in height. | |
1.2. Gravity (nonmotorized) dampers in Group R occupancies where the design outdoor air intake or exhaust capacity does not exceed 400 cfm (189 L/s). | |
2. Combustion air intakes. |
Gravity (nonmotorized) dampers shall have an air leakage rate not greater than 20 cfm/ft2 (101.6 L/s x m2) where not less than 24 inches (610 mm) in either dimension and 40 cfm/ft2 (203.2 L/s x m2) where less than 24 inches (610 mm) in either dimension. The rate of air leakage shall be determined at 1.0 inch water gauge (249 Pa) when tested in accordance with AMCA 500D for such purpose. The dampers shall be labeled by an approved agency. Gravity dampers for ventilation air intakes shall be protected from direct exposure to wind.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-054, filed 11/25/14, effective 5/1/15)
WAC 51-11C-403244 Section C403.2.4.4—((Shutoff damper controls)) Zone isolation.
((C403.2.4.4 Shutoff damper controls. Both outdoor air supply and exhaust ducts shall be equipped with motorized dampers that will automatically shut when the systems or spaces served are not in use or during building warm-up, cooldown, and setback.
See also section C402.4.5 for additional damper requirements and maximum leakage rates.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Gravity relief dampers serving systems less than 5,000 cfm total supply shall be permitted in buildings less than three stories in height. |
2. Gravity dampers shall be permitted for buildings of any height located in Climate Zones 1, 2 and 3. | |
3. Gravity (nonmotorized) dampers in Group R occupancies where the design outdoor air intake or exhaust capacity does not exceed 400 cfm (189 L/s). | |
4. Systems serving areas which require continuous operation. | |
5. Combustion air intakes. | |
6. Operation of dampers shall be allowed during ventilation prepurge one hour before expected occupancy and for unoccupied period precooling during the cooling season. | |
7. Dampers are not required in systems where specifically prohibited by the International Mechanical Code.)) |
C403.2.4.4 Zone isolation. HVAC systems serving zones that are over 25,000 square feet (2323 m2) in floor area or that span more than one floor and are designed to operate or be occupied nonsimultaneously shall be divided into isolation areas. Each isolation area shall be equipped with isolation devices and controls configured to automatically shut off the supply of conditioned air and outdoor air to and exhaust air from the isolation area. Each isolation area shall be controlled independently by a device meeting the requirements of Section C403.2.4.2.2. Central systems and plants shall be provided with controls and devices that will allow system and equipment operation for any length of time while serving only the smallest isolation area served by the system or plant.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Exhaust air and outdoor air connections to isolation areas where the fan system to which they connect is not greater than 5,000 cfm (2360 L/s). |
2. Exhaust airflow from a single isolation area of less than 10 percent of the design airflow of the exhaust system to which it connects. | |
3. Isolation areas intended to operate continuously or intended to be inoperative only when all other isolation areas in a zone are inoperative. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403245 Section C403.2.4.5—Snowmelt ((system)) and freeze protection controls.
C403.2.4.5 Snow- and ice-melt system controls. Snow- and ice-melting systems, supplied through energy service to the building, shall include automatic controls ((capable of shutting)) configured to shut off the system when the pavement temperature is above 50°F (10°C) and no precipitation is falling and an automatic or manual control that ((will allow)) is configured to shutoff when the outdoor temperature is above 40°F (4°C) so that the potential for snow or ice accumulation is negligible.
C403.2.4.6 Freeze protection system controls. Freeze protection systems, such as heat tracing of outdoor piping and heat exchangers, including self-regulating heat tracing, shall include automatic controls configured to shut off the systems when outdoor air temperatures are above 40°F (4°C) or when the conditions of the protected fluid will prevent freezing.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403246 Section ((C403.2.4.6)) C403.2.4.7—Economizer fault detection and Section C403.2.4.8—Combustion heating equipment controls.
((C403.2.4.6)) C403.2.4.7 Economizer fault detection and diagnostics (FDD). Air-cooled unitary direct-expansion units with a cooling capacity of 54,000 Btu/h or greater listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(3) that are equipped with an economizer in accordance with Section C403.3 shall include a fault detection and diagnostics (FDD) system complying with the following:
1. The following temperature sensors shall be permanently installed to monitor system operation:
1.1. Outside air.
1.2. Supply air.
1.3. Return air.
2. Temperature sensors shall have an accuracy of ±2°F (1.1°C) over the range of 40°F to 80°F (4°C to 26.7°C).
3. Refrigerant pressure sensors, where used, shall have an accuracy of ±3 percent of full scale.
4. The unit controller shall be configured to provide system status by indicating the following:
4.1. Free cooling available.
4.2. Economizer enabled.
4.3. Compressor enabled.
4.4. Heating enabled.
4.5. Mixed air low limit cycle active.
4.6. The current value of each sensor.
5. The unit controller shall be capable of manually initiating each operating mode so that the operation of compressors, economizers, fans and the heating system can be independently tested and verified.
6. The unit shall be configured to report faults to a fault management application accessible by day-to-day operating or service personnel or annunciated locally on zone thermostats.
7. The FDD system shall be configured to detect the following faults:
7.1. Air temperature sensor failure/fault.
7.2. Not economizing when the unit should be economizing.
7.3. Economizing when the unit should not be economizing.
7.4. Damper not modulating.
7.5. Excess outdoor air.
C403.2.4.8 Combustion heating equipment controls. Combustion heating equipment with a capacity over 225,000 Btu/h shall have modulating or staged combustion control.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Boilers. |
2. Radiant heaters. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-20-120, filed 10/1/13, effective 11/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403247 Sections ((C403.2.4.7—Hotel/motel)) C403.2.4.9 through C403.2.4.11—Group R controls.
((C403.2.4.7)) C403.2.4.9 Group R-1 hotel/motel guest rooms. For hotel and motel guest rooms, a minimum of one of the following control technologies shall be required in hotels/motels with over 50 guest rooms such that the space temperature would automatically setback (winter) or set up (summer) by no less than 5°F (3°C) when the occupant is not in the room:
1. Controls that are activated by the room occupant via the primary room access method - Key, card, deadbolt, etc.
2. Occupancy sensor controls that are activated by the occupant's presence in the room.
C403.2.4.10 Group R-2 and R-3 dwelling units. The primary space conditioning system within each dwelling unit shall be provided with at least one programmable thermostat for the regulation of space temperature. The thermostat shall allow for, at a minimum, a 5-2 programmable schedule (weekdays/weekends) and be capable of providing at least two programmable setback periods per day.
Each additional system provided within the dwelling unit shall be provided with at least one adjustable thermostat for the regulation of temperature.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Systems controlled by an occupant sensor that is configured to shut the system off when no occupant is sensed for a period of up to 30 minutes. |
2. Systems controlled solely by a manually operated timer configured to operate the system for no more than two hours. | |
3. Ductless heat pumps. |
Each thermostat shall be capable of being set by adjustment or selection of sensors and configured as follows: When used to control heating only: 55°F to 75°F; when used to control cooling only: 70°F to 85°F; all other: 55°F to 85°F with an adjustable deadband of not less than 10°F.
C403.2.4.11 Group R-2 sleeping units. The primary space conditioning system within each sleeping unit shall be provided with at least one programmable thermostat for the regulation of space temperature. The thermostat shall allow for, at a minimum, a 5-2 programmable schedule (weekdays/weekends) and be capable of providing at least two programmable setback periods per day.
Each additional system provided within the sleeping unit shall be provided with at least one adjustable thermostat for the regulation of temperature.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Systems controlled by an occupant sensor that is configured to shut the system off when no occupant is sensed for a period of up to 30 minutes. |
2. Systems controlled solely by a manually operated timer configured to operate the system for no more than two hours. | |
3. Zones with a full HVAC load demand not exceeding 3,400 Btu/h (1 kW) and having a readily accessible manual shutoff switch. | |
4. Ductless heat pumps. |
Each thermostat shall be capable of being set by adjustment or selection of sensors and configured as follows: When used to control heating only: 55°F to 75°F; when used to control cooling only: 70°F to 85°F; all other: 55°F to 85°F with an adjustable deadband of not less than 10°F.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-20-120, filed 10/1/13, effective 11/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403248 Section ((C403.2.4.8—Residential occupancy)) C403.2.4.12—Direct digital control((s)) systems.
((C403.2.4.8 Group R-2 and R-3 dwelling units. The primary space conditioning system within each dwelling unit shall be provided with at least one programmable thermostat for the regulation of space temperature. The thermostat shall allow for, at a minimum, a 5-2 programmable schedule (weekdays/weekends) and be capable of providing at least two programmable setback periods per day.
Each additional system provided within the dwelling unit shall be provided with at least one adjustable thermostat for the regulation of temperature.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Systems controlled by an occupant sensor that is capable of shutting the system off when no occupant is sensed for a period of up to 30 minutes. |
2. Systems controlled solely by a manually operated timer capable of operating the system for no more than two hours. | |
3. Ductless heat pumps. |
Each thermostat shall be capable of being set by adjustment or selection of sensors as follows: When used to control heating only: 55°F to 75°F; when used to control cooling only: 70°F to 85°F; all other: 55°F to 85°F with an adjustable deadband of not less than 10°F.
C403.2.4.9 Group R-2 sleeping units. The primary space conditioning system within each sleeping unit shall be provided with at least one programmable thermostat for the regulation of space temperature. The thermostat shall allow for, at a minimum, a 5-2 programmable schedule (weekdays/weekends) and be capable of providing at least two programmable setback periods per day.
Each additional system provided within the sleeping unit shall be provided with at least one adjustable thermostat for the regulation of temperature.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Systems controlled by an occupant sensor that is capable of shutting the system off when no occupant is sensed for a period of up to 30 minutes. |
2. Systems controlled solely by a manually operated timer capable of operating the system for no more than two hours. | |
3. Zones with a full HVAC load demand not exceeding 3,400 Btu/h (1 kW) and having a readily accessible manual shutoff switch. | |
4. Ductless heat pumps. |
Each thermostat shall be capable of being set by adjustment or selection of sensors as follows: When used to control heating only: 55°F to 75°F; when used to control cooling only: 70°F to 85°F; all other: 55°F to 85°F with an adjustable deadband of not less than 10°F.)) C403.2.4.12 Direct digital control systems. Direct digital control (DDC) shall be required as specified in Sections C403.2.4.12.1 through C403.2.4.12.3.
C403.2.4.12.1 DDC applications. DDC shall be provided in the applications and qualifications listed in Table C403.2.4.12.1.
C403.2.4.12.2 DDC controls. Where DDC is required by Section C403.2.4.12.1, the DDC system shall be capable of all of the following, as required to provide the system and zone control logic required in Sections C403.2, C403.3, and C403.4:
1. Monitoring zone and system demand for fan pressure, pump pressure, heating and cooling.
2. Transferring zone and system demand information from zones to air distribution system controllers and from air distribution systems to heating and cooling plant controllers.
C403.2.4.12.3 DDC display. Where DDC is required by Section C403.2.12.1 for new buildings, the DDC system shall be capable of trending and graphically displaying input and output points.
Table C403.2.4.12.1
DDC Applications and Qualifications
Building Status |
Application |
Qualifications |
New building |
Air-handling system and all zones served by the system |
All air-handling systems in buildings with building cooling capacity greater than 780,000 Btu/h |
Air-handling system and all zones served by the system |
Individual systems supplying more than three zones and with fan system bhp of 10 hp and larger |
|
Chilled-water plant and all coils and terminal units served by the system |
Individual plants supplying more than three zones and with design cooling capacity of 300,000 Btu/h and larger |
|
Hot-water plant and all coils and terminal units served by the system |
Individual plants supplying more than three zones and with design heating capacity of 300,000 Btu/h and larger |
|
Alteration or addition |
Zone terminal unit such as VAV box |
Where existing zones served by the same air-handling, chilled-water, or hot-water system have DDC |
Air-handling system or fan coil |
Where existing air-handling system(s) and fan coil(s) served by the same chilled- or hot-water plant have DDC |
|
New air-handling system and all new zones served by the system |
Individual systems with fan system bhp of 10 hp and larger and supplying more than three zones and more than 75% of zones are new |
|
New or upgraded chilled-water plant |
Where all chillers are new and plant design cooling capacity is 300,000 Btu/h and larger |
|
New or upgraded hot-water plant |
Where all boilers are new and plant design heating capacity is 300,000 Btu/h and larger |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403249 Section ((C403.2.4.9—Direct digital control system capabilities)) C403.2.5—Hot water boiler controls.
((C403.2.4.10 Direct digital control system capabilities. All complex systems equipped with direct digital control (DDC) systems and all buildings with total cooling capacity exceeding 780,000 Btu/h (2,662 kW) shall have the following capability:
1. Trending: All control system input and output points shall be accessible and programmed for trending, and a graphic trending package shall be provided with the control system.
2. Demand Response Setpoint Adjustment: Control logic shall increase the cooling zone set points by at least 2°F (1°C) and reduce the heating zone set points by at least 2°F (1°C) when activated by a demand response signal. The demand response signal shall be a binary input to the control system or other interface approved by the serving electric utility.)) C403.2.5 Hot water boiler outdoor temperature setback control. Hot water boilers that supply heat to the building through one- or two-pipe heating systems shall have an outdoor setback control that lowers the boiler water temperature based on the outdoor temperature.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40325 Section ((C403.2.5)) C403.2.6—Ventilation.
((C403.2.5)) C403.2.6 Ventilation. Ventilation, either natural or mechanical, shall be provided in accordance with Chapter 4 of the International Mechanical Code. Where mechanical ventilation is provided, the system shall ((provide the capability to reduce the outdoor air supply to)) be configured to provide no greater than 150 percent of the minimum outdoor air required by Chapter 4 of the International Mechanical Code or other applicable code or standard, whichever is greater.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. The mechanical system may supply outdoor air at rates higher than the limit above when it is used for economizer, night flushing, dehumidification, pressurization, exhaust make-up, or other process air delivery. Outdoor air shall be reduced to the minimum ventilation rates when not required for the preceding uses. |
2. Air systems supplying Group R-1, R-2 or I-2 occupancies. | |
3. Alterations that replace less than half of the total heating and cooling capacity of the system. | |
4. Systems with energy recovery complying with the requirements of Section C403.5.1. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403251 Section ((C403.2.5.1—Demand control ventilation)) C403.2.6.1—Dedicated outdoor air systems (DOAS).
((C403.2.5.1 Demand controlled ventilation. Demand control ventilation (DCV) shall be provided for spaces larger than 500 square feet (50 m2) and with an occupant load greater than 25 people per 1000 square feet (93 m2) of floor area (as established in Table 403.3 of the International Mechanical Code) and served by systems with one or more of the following:
1. An air-side economizer;
2. Automatic modulating control of the outdoor air damper; or
3. A design outdoor airflow greater than 3,000 cfm (1400 L/s).
EXCEPTION: | Demand control ventilation is not required for systems and spaces as follows: |
1. Systems with energy recovery complying with Section C403.2.6. | |
2. Multiple-zone systems without direct digital control of individual zones communicating with a central control panel. | |
3. System with a design outdoor airflow less than 1,000 cfm (472 L/s). | |
4. Spaces where the supply airflow rate minus any makeup or outgoing transfer air requirement is less than 1,200 cfm (600 L/s). | |
5. Ventilation provided for process loads only.)) |
C403.2.6.1 Dedicated outdoor air systems (DOAS). For office, retail, education, libraries and fire stations, outdoor air shall be provided to each zone by a dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS) which delivers 100 percent outside air without requiring operation of the heating and cooling system fans for ventilation air delivery. The DOAS shall include either energy recovery ventilation and/or demand control ventilation. If the DOAS includes heating or cooling coils, the system shall be configured to deliver supply air within 5°F (3°C) of the space conditioning setpoint, except that DOAS greater than 500 cfm shall not use heating or heat recovery to warm supply air above 60ºF (16ºC) when representative building loads or outdoor air temperature indicate the majority of zones require cooling.
C403.2.6.1.1 Impracticality. In cases where full compliance with all the requirements of Section C403.2.6.1 is impractical, the applicant is permitted to arrange a predesign conference with the design team and the code official to seek modifications. The applicant shall identify specific requirements that are impractical, and shall identify design solutions and modifications that achieve a comparable level of energy efficiency. The code official is authorized to waive specific requirements in this code to the extent that the code official determines those requirements to be impractical.
C403.2.6.1.2 Heating/cooling system fan controls. For systems meeting the requirements of Section C403.2.6.1 dedicated outdoor air systems, equipment and controls shall be configured to cycle off zone heating and cooling equipment fans and/or pumps, primary cooling air, heating and cooling coils, and parallel heating fans when there is no call for heating or cooling in the zone.
EXCEPTION: | Fans used for heating and cooling using less than 0.1 watts per cfm may operate when space temperatures are within the setpoint deadband (Section 403.2.4.1.2) to provide destratification and air mixing in the space. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403252 Section ((C403.2.5.2—Occupancy sensors)) C403.2.6.2—Demand control ventilation.
((C403.2.5.2 Occupancy sensors. Classrooms, gyms, auditoriums and conference rooms larger than 500 square feet of floor area shall have occupancy sensor control that will either close outside air dampers or turn off serving equipment when the space is unoccupied except where equipped with another means to automatically reduce outside air intake below design rates when spaces are partially occupied.)) C403.2.6.2 Demand controlled ventilation. Demand control ventilation (DCV) shall be provided for spaces larger than 500 square feet (50 m2) and with an occupant load greater than or equal to 25 people per 1000 square feet (93 m2) of floor area (as established in Table 403.3 of the International Mechanical Code) and served by systems with one or more of the following:
1. An air-side economizer;
2. Automatic modulating control of the outdoor air damper; or
3. A design outdoor airflow greater than 3,000 cfm (1400 L/s).
EXCEPTION: | Demand control ventilation is not required for systems and spaces as follows: |
1. Systems with energy recovery complying with Section C403.5.1. | |
2. Multiple-zone systems without direct digital control of individual zones communicating with a central control panel. | |
3. System with a design outdoor airflow less than 750 cfm (472 L/s). | |
4. Spaces where the supply airflow rate minus any makeup or outgoing transfer air requirement is less than 1,200 cfm (600 L/s). | |
5. Ventilation provided for process loads only. | |
6. Spaces with one of the following occupancy categories (as defined by the International Mechanical Code): Correctional cells, daycare sickrooms, science labs, barbers, beauty and nail salons, and bowling alley seating. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403253 Section ((C403.2.5.3—Loading dock and parking garage ventilation system controls)) C403.2.6.3—Occupancy sensors.
((C403.2.5.3 Enclosed loading dock and parking garage exhaust ventilation system control. Mechanical ventilation systems for enclosed loading docks and parking garages shall be designed to exhaust the airflow rates (maximum and minimum) determined in accordance with the International Mechanical Code.
Ventilation systems shall be equipped with a control device that operates the system automatically upon detection of vehicle operation or the presence of occupants by approved automatic detection devices. Each of the following types of controllers shall be capable of shutting off fans or modulating fan speed. Control devices shall not reduce airflow rates below the minimum requirement in accordance with the International Mechanical Code during scheduled periods of occupied operation.
1. Gas sensor controllers used to activate the exhaust ventilation system shall stage or modulate fan speed upon detection of specified gas levels. All equipment used in sensor controlled systems shall be designed for the specific use and installed in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. The system shall be arranged to operate automatically by means of carbon monoxide detectors applied in conjunction with nitrogen dioxide detectors. Garages and loading docks shall be equipped with a controller and a full array of carbon monoxide (CO) sensors set to maintain levels of carbon monoxide below 35 parts per million (ppm). Additionally, a full array of nitrogen dioxide detectors shall be connected to the controller set to maintain the nitrogen dioxide level below the OSHA standard for eight hour exposure. Spacing and location of the sensors shall be installed in accordance with manufacturer recommendations.
2. Occupant detection sensors used to activate the system shall detect entry into the parking garage along both the vehicle and pedestrian pathways.
C403.2.5.3.1 System activation devices for enclosed loading docks. Ventilation systems for enclosed loading docks shall be activated by one of the following:
1. Gas sensors installed in accordance with the International Mechanical Code; or
2. Occupant detection sensors used to activate the system that detects entry into the loading area along both the vehicle and pedestrian pathways.
C403.2.5.3.2 System activation devices for enclosed parking garages. Ventilation systems for enclosed parking garages shall be activated by gas sensors.
EXCEPTION: | A parking garage ventilation system having a total design capacity under 8,000 cfm may use occupant sensors.)) |
C403.2.6.3 Occupancy sensors. Classrooms, gyms, auditoriums and conference rooms larger than 500 square feet of floor area shall have occupancy sensor control that will either close outside air dampers or turn off serving equipment when the space is unoccupied except where equipped with another means to automatically reduce outside air intake below design rates when spaces are partially occupied.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-20-120, filed 10/1/13, effective 11/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403254 Section ((C403.2.5.4—Exhaust systems)) C403.2.6.4—Loading dock and parking garage ventilation system controls.
((C403.2.5.4 Exhaust systems.
C403.2.5.4.1 Kitchen hoods. Each kitchen area with total exhaust capacity larger than 2,000 cfm shall be provided with make-up air sized so that at least 50% of exhaust air volume be (a) unheated or heated to no more than 60°F and (b) uncooled or cooled without the use of mechanical cooling.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Where hoods are used to exhaust ventilation air which would otherwise exfiltrate or be exhausted by other fan systems. A detailed accounting of exhaust airflows shall be provided on the plans that accounts for the impact of any required demand controlled ventilation. |
2. Certified grease extractor hoods that require a face velocity no greater than 60 fpm. |
C403.2.5.4.2 Laboratory exhaust systems. Buildings with laboratory exhaust systems having a total exhaust rate greater than 5,000 cfm (2,360 L/s) shall include heat recovery systems to precondition makeup air from laboratory exhaust. The heat recovery system shall be capable of increasing the outside air supply temperature at design heating conditions by 25°F (13.9°C) in Climate Zones 4C/5B and 35°F (19.4°C) in Climate Zone 6B. A provision shall be made to bypass or control the heat recovery system to permit air economizer operation as required by Section C403.4.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Variable air volume laboratory exhaust and room supply systems capable of reducing exhaust and make-up air volume to 50% or less of design values; or |
2. Direct make-up (auxiliary) air supply equal to at least 75% of the exhaust rate, heated no warmer than 2°F (1.1°C) below room set point, cooled to no cooler than 3°F (1.7°C) above room set point, no humidification added, and no simultaneous heating and cooling used for dehumidification control; or | |
3. Combined Energy Reduction Method: VAV exhaust and room supply system capable of reducing exhaust and makeup air volumes and a heat recovery system to precondition makeup air from laboratory exhaust that when combined will produce the same energy reduction as achieved by a heat recovery system with a 50% sensible recovery effectiveness as required above. For calculation purposes, the heat recovery component can be assumed to include the maximum design supply airflow rate at design conditions. The combined energy reduction (QER) shall meet the following: |
QER |
≥ |
QMIN |
|
QMIN |
= |
CFMS • (TR - TO) • 1.1 • 0.6 |
|
QER |
= |
CFMS • (TR - TO) • 1.1(A + B)/100 |
|
Where: |
|||
QMIN |
= |
Energy recovery at 60% sensible effectiveness (Btu/h) |
|
QER |
= |
Combined energy reduction (Btu/h) |
|
CFMS |
= |
The maximum design supply airflow rate to conditioned spaces served by the system in cubic feet per minute |
|
TR |
= |
Space return air dry bulb at winter design conditions |
|
TO |
= |
Outdoor air dry bulb at winter design conditions |
|
A |
= |
Percentage that the exhaust and makeup air volumes can be reduced from design conditions |
|
B |
= |
Percentage sensible heat recovery effectiveness)) |
|
C403.2.6.4 Enclosed loading dock and parking garage exhaust ventilation system control. Mechanical ventilation systems for enclosed loading docks and parking garages shall be designed to exhaust the airflow rates (maximum and minimum) determined in accordance with the International Mechanical Code.
Ventilation systems shall be equipped with a control device that operates the system automatically by means of carbon monoxide detectors applied in conjunction with nitrogen dioxide detectors. Controllers shall be configured to shut off fans or modulate fan speed to 50 percent or less of design capacity, or intermittently operate fans less than 20 percent of the occupied time or as required to maintain acceptable contaminant levels in accordance with the International Mechanical Code provisions.
Gas sensor controllers used to activate the exhaust ventilation system shall stage or modulate fan speed upon detection of specified gas levels. All equipment used in sensor controlled systems shall be designed for the specific use and installed in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. The system shall be arranged to operate automatically by means of carbon monoxide detectors applied in conjunction with nitrogen dioxide detectors. Garages and loading docks shall be equipped with a controller and a full array of carbon monoxide (CO) sensors set to maintain levels of carbon monoxide below 35 parts per million (ppm). Additionally, a full array of nitrogen dioxide detectors shall be connected to the controller set to maintain the nitrogen dioxide level below the OSHA standard for eight hour exposure. Spacing and location of the sensors shall be installed in accordance with manufacturer recommendations.
C403.2.6.4.1 System activation devices for enclosed loading docks. Ventilation systems for enclosed loading docks shall be activated by one of the following:
1. Gas sensors installed in accordance with the International Mechanical Code; or
2. Occupant detection sensors used to activate the system that detects entry into the loading area along both the vehicle and pedestrian pathways.
C403.2.6.4.2 System activation devices for enclosed parking garages. Ventilation systems for enclosed parking garages shall be activated by gas sensors.
EXCEPTION: | A parking garage ventilation system having a total design capacity under 8,000 cfm may use occupant sensors. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-122, filed 12/3/14, effective 1/3/15)
WAC 51-11C-40326 Section ((C403.2.6—Energy recovery)) C403.2.7—Exhaust systems.
((C403.2.6 Energy recovery.
C403.2.6.1 Energy recovery ventilation systems. Any system with minimum outside air requirements at design conditions greater than 5,000 CFM or any system required by Table C403.2.6 shall include an energy recovery system. The energy recovery system shall have the capability to provide a change in the enthalpy of the outdoor air supply of not less than 50 percent of the difference between the outdoor air and return air enthalpies, at design conditions. Where an air economizer is required, the energy recovery system shall include a bypass or controls which permit operation of the economizer as required by Section C403.4. Where a single room or space is supplied by multiple units, the aggregate ventilation (cfm) of those units shall be used in applying this requirement.
EXCEPTION: | An energy recovery ventilation system shall not be required in any of the following conditions: |
1. Where energy recovery systems are prohibited by the International Mechanical Code. | |
2. Laboratory fume hood systems that include at least one of the following features: | |
2.1. Variable-air-volume hood exhaust and room supply systems capable of reducing exhaust and makeup air volume to 50 percent or less of design values. | |
2.2. Direct makeup (auxiliary) air supply equal to at least 75 percent of the exhaust rate, heated no warmer than 2°F (1.1°C) above room setpoint, cooled to no cooler than 3°F (1.7°C) below room setpoint, no humidification added, and no simultaneous heating and cooling used for dehumidification control. | |
3. Systems serving spaces that are heated to less than 60°F (15.5°C) and are not cooled. | |
4. Where more than 60 percent of the outdoor heating energy is provided from site-recovered or site solar energy. | |
5. Heating energy recovery in Climate Zones 1 and 2. | |
6. Cooling energy recovery in Climate Zones 3C, 4C, 5B, 5C, 6B, 7 and 8. | |
7. Systems requiring dehumidification that employ energy recovery in series with the cooling coil. | |
8. Multi-zone systems with cold deck supply air and zone reheat where the minimum outdoor air is less than 70 percent of total supply air. | |
9. Systems serving Group R dwelling or sleeping units where the largest source of air exhausted at a single location at the building exterior is less than 25 percent of the design outdoor air flow rate. |
C403.2.6.2 Condensate systems. On-site steam heating systems shall have condensate water heat recovery. On-site includes a system that is located within or adjacent to one or more buildings within the boundary of a contiguous area or campus under one ownership and which serves one or more of those buildings.
Buildings using steam generated off-site with steam heating systems which do not have condensate water recovery shall have condensate water heat recovery.
C403.2.6.3 Condenser heat recovery. Facilities having food service, meat or deli departments and having 500,000 Btu/h or greater of remote refrigeration condensers shall have condenser waste heat recovery from freezers and coolers and shall use the waste heat for service water heating, space heating or for dehumidification reheat. Facilities having a gross conditioned floor area of 40,000 ft2 or greater and 1,000,000 Btu/h or greater of remote refrigeration shall have condenser waste heat recovery from freezers and coolers and shall use the waste heat for service water heating, and either for space heating or for dehumidification reheat for maintaining low space humidity.)) C403.2.7 Exhaust systems.
C403.2.7.1 Kitchen exhaust systems. Replacement air introduced directly into the exhaust hood cavity shall not be greater than 10 percent of the hood exhaust airflow rate. Conditioned supply air delivered to any space shall not exceed the greater of the following:
1. The ventilation rate required to meet the space heating or cooling load.
2. The hood exhaust flow minus the available transfer air from adjacent space where available transfer air is considered that portion of outdoor ventilation air not required to satisfy other exhaust needs, such as restrooms, and not required to maintain pressurization of adjacent spaces.
Where total kitchen hood exhaust airflow rate is greater than 2,000 cfm each hood shall be a factory built commercial exhaust hood listed by a nationally recognized testing laboratory in compliance with UL 710. Each hood shall have a maximum exhaust rate as specified in Table C403.2.7.1 and shall comply with one of the following:
1. Not less than 50 percent of all replacement air shall be transfer air that would otherwise be exhausted.
2. Demand ventilation systems on not less than 75 percent of the exhaust air that are configured to provide not less than a 50-percent reduction in exhaust and replacement air system airflow rates, including controls necessary to modulate airflow in response to appliance operation and to maintain full capture and containment of smoke, effluent and combustion products during cooking and idle.
3. Listed energy recovery devices with a sensible heat recovery effectiveness of not less than 40 percent on not less than 50 percent of the total exhaust airflow.
Where a single hood, or hood section, is installed over appliances with different duty ratings, the maximum allowable flow rate for the hood or hood section shall be based on the requirements for the highest appliance duty rating under the hood or hood section.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Where not less than 75 percent of all the replacement air is transfer air that would otherwise be exhausted. |
2. Certified grease extractor hoods that require a face velocity no greater than 60 fpm. |
Table C403.2.7.1
Maximum Net Exhaust Flow Rate,
CFM Per Linear Foot of Hood Length
TYPE OF HOOD |
LIGHT-DUTY EQUIPMENT |
MEDIUM-DUTY EQUIPMENT |
HEAVY-DUTY EQUIPMENT |
EXTRA-HEAVY-DUTY EQUIPMENT |
Wall-mounted canopy |
140 |
210 |
280 |
385 |
Single island |
280 |
350 |
420 |
490 |
Double island (per side) |
175 |
210 |
280 |
385 |
Eyebrow |
175 |
175 |
NA |
NA |
Backshelf/pass-over |
210 |
210 |
280 |
NA |
For SI: | 1 cfm = 0.4719 L/s; 1 foot = 305 mm |
NA = Not allowed | |
C403.2.7.2 Laboratory exhaust systems. Buildings with laboratory exhaust systems having a total exhaust rate greater than 5,000 cfm (2360 L/s) shall include heat recovery systems to precondition makeup air from laboratory exhaust. The heat recovery system shall be capable of increasing the outside air supply temperature at design heating conditions by 25°F (13.9°C). A provision shall be made to bypass or control the heat recovery system to permit air economizer operation as required by Section C403.3.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Variable air volume laboratory exhaust and room supply systems configured to reduce exhaust and make-up air volume to 50 percent or less of design values; or |
2. Direct make-up (auxiliary) air supply equal to at least 75 percent of the exhaust rate, heated no warmer than 2°F (1.1°C) below room set point, cooled to no cooler than 3°F (1.7°C) above room set point, no humidification added, and no simultaneous heating and cooling used for dehumidification control; or | |
3. Combined energy reduction method: VAV exhaust and room supply system configured to reduce exhaust and makeup air volumes and a heat recovery system to precondition makeup air from laboratory exhaust that when combined will produce the same energy reduction as achieved by a heat recovery system with a 50 percent sensible recovery effectiveness as required above. For calculation purposes, the heat recovery component can be assumed to include the maximum design supply airflow rate at design conditions. The combined energy reduction (QER) shall meet the following: |
QER |
≥ |
QMIN |
|
QMIN |
= |
CFMS • (TR - TO) • 1.1 • 0.6 |
|
QER |
= |
CFMS • (TR - TO) • 1.1(A + B)/100 |
|
Where: |
|||
QMIN |
= |
Energy recovery at 60 percent sensible effectiveness (Btu/h) |
|
QER |
= |
Combined energy reduction (Btu/h) |
|
CFMS |
= |
The maximum design supply airflow rate to conditioned spaces served by the system in cubic feet per minute |
|
TR |
= |
Space return air dry bulb at winter design conditions |
|
TO |
= |
Outdoor air dry bulb at winter design conditions |
|
A |
= |
Percentage that the exhaust and makeup air volumes can be reduced from design conditions |
|
B |
= |
Percentage sensible heat recovery effectiveness |
|
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403261 ((Table C403.2.6—Energy recovery requirement.)) Reserved.
((Table C403.2.6
Energy Recovery Requirement
Percent (%) Outdoor Air at Full Design Airflow Rate |
||||||
Climate Zone |
≥ 30% and < 40% |
≥ 40% and < 50% |
≥ 50% and < 60% |
≥ 60% and < 70% |
≥ 70% and < 80% |
≥ 80% |
Design Supply Fan Airflow Rate (cfm) |
||||||
3B, 3C, 4B, 4C, 5B |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
≥5000 |
≥ 5000 |
1B, 2B, 5C |
NR |
NR |
≥ 26000 |
≥ 12000 |
≥ 5000 |
≥ 4000 |
6B |
≥ 11000 |
≥ 5500 |
≥ 4500 |
≥ 3500 |
≥ 2500 |
≥ 1500 |
1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A |
≥ 5500 |
≥ 4500 |
≥ 3500 |
≥ 2000 |
≥ 1000 |
˃ 0 |
7, 8 |
≥ 2500 |
≥ 1000 |
˃ 0 |
˃ 0 |
˃ 0 |
˃ 0 |
NR = Not required.)) |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40327 Section ((C403.2.7)) C403.2.8—Duct and plenum insulation and sealing.
((C403.2.7)) C403.2.8 Duct and plenum insulation and sealing.
((C403.2.7.1)) C403.2.8.1 Ducts, shafts and plenums conveying ((outside)) outdoor air from the exterior of the building to the mechanical system shall meet all air leakage and building envelope insulation requirements of Section C402, plus building envelope vapor control requirements from the International Building Code, extending continuously from the building exterior to an automatic shutoff damper or heating or cooling equipment. For the purposes of building envelope insulation requirements, duct surfaces shall meet the requirements for metal framed walls per Table ((C402.1.2)) C402.1.4. Duct surfaces included as part of the building envelope shall not be used in the calculation of maximum glazing area as described in Section ((402.3.1)) C402.4.1.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Outside air ducts serving individual supply air units with less than 2,800 cfm of total supply air capacity, provided these are insulated to R-7. |
2. Unheated equipment rooms with combustion air louvers, provided they are isolated from conditioned space at sides, top and bottom of the room with R-11 nominal insulation. |
((C403.2.7.2)) C403.2.8.2 All other supply and return air ducts and plenums shall be insulated with a minimum of R-6 insulation where located in unconditioned spaces and where located outside the building with a minimum of R-8 insulation ((where located outside the building)) in Climate Zone 4 and R-12 insulation in Climate Zone 5. Where located within a building envelope assembly, the duct or plenum shall be separated from the building exterior or unconditioned or exempt spaces by minimum insulation value as required for exterior walls by Section ((C402.2.3)) C402.1.3.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Where located within equipment. |
2. Where the design temperature difference between the interior and exterior of the duct or plenum does not exceed 15°F (8°C). |
Where located within conditioned space, supply ducts which convey supply air at temperatures less than 55°F or greater than 105°F shall be insulated with a minimum of R-3.3 insulation ((where located within conditioned space)).
EXCEPTION: | Ductwork exposed to view within a zone that serves that zone is not required to be insulated. |
All ducts, air handlers, and filter boxes shall be sealed. Joints and seams shall comply with Section 603.9 of the International Mechanical Code.
((C403.2.7.3)) C403.2.8.3 Duct construction. Ductwork shall be constructed and erected in accordance with the International Mechanical Code.
((C403.2.7.3.1)) C403.2.8.3.1 Low-pressure duct systems. All longitudinal and transverse joints, seams and connections of supply and return ducts operating at a static pressure less than or equal to 2 inches water gauge (w.g.) (500 Pa) shall be securely fastened and sealed with welds, gaskets, mastics (adhesives), mastic-plus embedded-fabric systems or tapes installed in accordance with the manufacturer's installation instructions. Pressure classifications specific to the duct system shall be clearly indicated on the construction documents in accordance with the International Mechanical Code.
EXCEPTION: | Continuously welded and locking-type longitudinal joints and seams on ducts operating at static pressures less than 2 inches water gauge (w.g.) (500 Pa) pressure classification. |
((C403.2.7.3.2)) C403.2.8.3.2 Medium-pressure duct systems. All ducts and plenums designed to operate at a static pressure greater than 2 inches water gauge (w.g.) (500 Pa) but less than 3 inches w.g. (750 Pa) shall be insulated and sealed in accordance with Section C403.2.7. Pressure classifications specific to the duct system shall be clearly indicated on the construction documents in accordance with the International Mechanical Code.
((C403.2.7.3.3)) C403.2.8.3.3 High-pressure duct systems. Ducts designed to operate at static pressures in excess of 3 inches water gauge (w.g.) (750 Pa) shall be insulated and sealed in accordance with Section ((C403.2.7)) C403.2.8. In addition, ducts and plenums shall be leak-tested in accordance with the SMACNA HVAC Air Duct Leakage Test Manual ((with the)) and shown to have a rate of air leakage (CL) less than or equal to ((6.0)) 4.0 as determined in accordance with Equation ((C4-5)) 4-9.
(Equation ((C4-5)) 4-9)
CL |
= |
F/P0.65 |
Where: |
||
F |
= |
The measured leakage rate in cfm per 100 square feet of duct surface. |
P |
= |
The static pressure of the test. |
Documentation shall be furnished by the designer demonstrating that representative sections totaling at least 25 percent of the duct area have been tested and that all tested sections meet the requirements of this section.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40328 Section ((C403.2.8)) C403.2.9—Piping insulation.
((C403.2.8)) C403.2.9 Piping insulation. All piping serving as part of a heating or cooling system shall be thermally insulated in accordance with Table ((C403.2.8)) C403.2.9.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Factory-installed piping within HVAC equipment tested and rated in accordance with a test procedure referenced by this code. |
2. Factory-installed piping within room fan-coils and unit ventilators tested and rated according to AHRI 440 (except that the sampling and variation provisions of Section 6.5 shall not apply) and 840, respectively. | |
3. Piping that conveys fluids that have a design operating temperature range between 60°F (15°C) and 105°F (41°C). | |
4. Piping that conveys fluids that have not been heated or cooled through the use of fossil fuels or electric power. | |
5. Strainers, control valves, and balancing valves associated with piping 1 inch (25 mm) or less in diameter. | |
6. Direct buried piping that conveys fluids at or below 60°F (15°C). |
((C403.2.8.1)) C403.2.9.1 Protection of piping insulation. Piping insulation exposed to weather shall be protected from damage, including that due to sunlight, moisture, equipment maintenance and wind, and shall provide shielding from solar radiation that can cause degradation of the material. Adhesives tape shall not be permitted.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403281 Table ((C403.2.8)) C403.2.9—Minimum pipe insulation thickness.
Table ((C403.2.8)) C403.2.9
Minimum Pipe Insulation Thickness (thickness in inches)a
Fluid Operating Temperature Range and Usage (°F) |
Insulation Conductivity |
Nominal Pipe or Tube Size (inches) |
|||||
Conductivity Btu • in. /(h • ft2 • °F)b |
Mean Rating Temperature, °F |
< 1 |
1 to < 1-1/2 |
1-1/2 to < 4 |
4 to < 8 |
≥ 8 |
|
˃ 350 |
0.32 - 0.34 |
250 |
4.5 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
251 - 350 |
0.29 - 0.32 |
200 |
3.0 |
4.0 |
4.5 |
4.5 |
4.5 |
201 - 250 |
0.27 - 0.30 |
150 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
3.0 |
3.0 |
141 - 200 |
0.25 - 0.29 |
125 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
105 - 140 |
0.21 - 0.28 |
100 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
40 - 60 |
0.21 - 0.27 |
75 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
< 40 |
0.20 - 0.26 |
75 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
a | For piping smaller than 1-1/2 inch (38 mm) and located in partitions within conditioned spaces, reduction of these thicknesses by 1 inch (25 mm) shall be permitted (before thickness adjustment required in footnote b) but not to a thickness less than 1 inch (25 mm). |
b | For insulation outside the stated conductivity range, the minimum thickness (T) shall be determined as follows: |
T |
= |
r{(1 + t/r)K/k - 1} |
||
Where: |
||||
T |
= |
Minimum insulation thickness, |
||
r |
= |
Actual outside radius of pipe, |
||
t |
= |
Insulation thickness listed in the table for applicable fluid temperature and pipe size, |
||
K |
= |
Conductivity of alternate material at mean rating temperature indicated for the applicable fluid temperature (Btu × in/h × ft2 × °F) and |
||
k |
= |
The upper value of the conductivity range listed in the table for the applicable fluid temperature. |
||
c | For direct-buried heating and hot water system piping, reduction of these thicknesses by 1-1/2 inches (38 mm) shall be permitted (before thickness adjustment required in footnote b but not to thicknesses less than 1 inch (25 mm). |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40329 Section ((C403.2.9)) C403.2.10—Mechanical system commissioning and completion requirements.
((C403.2.9)) C403.2.10 Mechanical systems commissioning and completion requirements. Mechanical systems shall be commissioned and completed in accordance with Section ((C408.2)) C408.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-20-120, filed 10/1/13, effective 11/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403291 Section ((C403.2.10)) C403.2.11—Air system design and control.
((C403.2.10)) C403.2.11 Air system design and control. Each HVAC system having a total fan system motor nameplate horsepower (hp) exceeding 5 horsepower (hp) (3.7 kW) shall ((meet)) comply with the provisions of Sections ((C403.2.10.1 through C403.2.10.3)) C403.2.11.1 through C403.2.11.3.
The air flow requirements of Section C403.2.11.5 shall apply to all fan motors. Group R occupancy exhaust fans shall also comply with Section C403.2.11.4.
((C403.2.10.1)) C403.2.11.1 Allowable fan ((floor)) motor horsepower. Each HVAC system at fan system design conditions shall not exceed the allowable fan system motor nameplate hp (Option 1) or fan system bhp (Option 2) as shown in Table ((C403.2.10.1(1))) C403.2.11.1(1). This includes supply fans, exhaust fans, return/relief fans, and fan-powered terminal units associated with systems providing heating or cooling capability. Single zone variable-air-volume systems shall comply with the constant volume fan power limitation.
EXCEPTIONS: | ((The following fan systems are exempt from allowable fan floor horsepower requirement.)) |
1. Hospital, vivarium and laboratory systems that utilize flow control devices on exhaust ((and/))or return to maintain space pressure relationships necessary for occupant health and safety or environmental control shall be permitted to use variable volume fan power limitation. | |
2. Individual exhaust fans with motor nameplate horsepower of 1 hp or less are exempt from allowable fan motor horsepower requirements. |
((C403.2.10.2)) C403.2.11.2 Motor nameplate horsepower. For each fan, the selected fan motor shall be no larger than the first available motor size greater than the brake horsepower (bhp). The fan brake horsepower (bhp) shall be indicated on the design documents to allow for compliance verification by the code official.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. For fans less than 6 bhp (4413 W), where the first available motor larger than the brake horsepower has a nameplate rating within 50 percent of the bhp, selection of the next larger nameplate motor size is allowed. |
2. For fans 6 bhp (4413 W) and larger, where the first available motor larger than the bhp has a nameplate rating within 30 percent of the bhp, selection of the next larger nameplate motor size is allowed. | |
3. For fans used only in approved life safety applications such as smoke evacuation. |
((C403.2.10.3 Fractional hp fan motors. Motors for fans that are 1/12 hp or greater and less than 1 hp shall be electronically commutated motors or shall have a minimum motor efficiency of 70 percent when rated in accordance with DOE 10 C.F.R. 431. These motors shall also have the means to adjust motor speed for either balancing or remote control. Belt-driven fans may use sheave adjustments for airflow balancing in lieu of a varying motor speed.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Motors in the airstream within fan-coils and terminal units that operate only when providing heating to the space served. |
2. Motors installed in space conditioning equipment certified under Section C403.2.3.)) |
C403.2.11.3 Fan efficiency. Fans shall have a fan efficiency grade (FEG) of not less than 67 when determined in accordance with AMCA 205 by an approved, independent testing laboratory and labeled by the manufacturer. The total efficiency of the fan at the design point of operation shall be within 15 percentage points of the maximum total efficiency of the fan.
EXCEPTION: | The following fans are not required to have a fan efficiency grade: |
1. Fans of 5 hp (3.7 kW) or less as follows: | |
1.1. Single fan with a motor nameplate horsepower of 5 hp (3.7 kW) or less, unless Exception 1.2. applies. | |
1.2. Multiple fans in series or parallel that have a combined motor nameplate horsepower of 5 hp (3.7 kW) or less and are operated as the functional equivalent of a single fan. | |
2. Fans that are part of equipment covered under Section C403.2.3. | |
3. Fans included in an equipment package certified by an approved agency for air or energy performance. | |
4. Powered wall/roof ventilators. | |
5. Fans outside the scope of AMCA 205. | |
6. Fans that are intended to operate only during emergency conditions. |
C403.2.11.4 Group R occupancy exhaust fan efficacy. The Group R occupancies of the building shall be provided with ventilation that meets the requirements of the International Mechanical Code, as applicable, or with other approved means of ventilation. Mechanical ventilation system fans with 400 cfm or less in capacity shall meet the efficacy requirements of Table C403.2.11.4.
EXCEPTION: | Where mechanical ventilation fans are integral to tested and listed HVAC equipment, they shall be powered by an electronically commutated motor where required by Section C405.8. |
C403.2.11.5 Fan airflow control. Each cooling system listed in Table C403.2.11.5 shall be designed to vary the indoor fan airflow as a function of load and shall comply with the following requirements:
1. Direct expansion (DX) and chilled water cooling units that control the capacity of the mechanical cooling directly based on space temperature shall have not fewer than two stages of fan control. Low or minimum speed shall not be greater than 66 percent of full speed. At low or minimum speed, the fan system shall draw not more than 40 percent of the fan power at full fan speed. Low or minimum speed shall be used during periods of low cooling load and ventilation-only operation.
2. Other units including DX cooling units and chilled water units that control the space temperature by modulating the airflow to the space shall have modulating fan control. Minimum speed shall be not greater than 50 percent of full speed. At minimum speed, the fan system shall draw more than 30 percent of the power at full fan speed. Low or minimum speed shall be used during periods of low cooling load and ventilation-only operation.
3. Units that include an airside economizer in accordance with Section C403.3 shall have not fewer than two speeds of fan control during economizer operation.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Modulating fan control is not required for chilled water and evaporative cooling units with fan motors of less than 1 hp (0.746 kW) where the units are not used to provide ventilation air and the indoor fan cycles with the load. |
2. Where the volume of outdoor air required to comply with the ventilation requirements of the International Mechanical Code at low speed exceeds the air that would be delivered at the speed defined in Section C403.4.1, the minimum speed shall be selected to provide the required ventilation air. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403292 ((Table C403.2.10.1—Fan power limitation.)) Tables for Section C403.2.11
Table ((C403.2.10.1(1))) C403.2.11.1(1)
Fan Power Limitation
Limit |
Constant Volume |
Variable Volume |
|
Option 1: Fan system motor nameplate hp |
Allowable nameplate motor hp |
hp ≤ CFMS × 0.0011 |
hp ≤ CFMS × 0.0015 |
Option 2: Fan system bhp |
Allowable fan system bhp |
bhp ≤ CFMS × 0.00094 + A |
bhp ≤ CFMS× 0.0013 + A |
Where: |
||
CFMS |
= |
The maximum design supply airflow rate to conditioned spaces served by the system in cubic feet per minute. |
hp |
= |
The maximum combined motor nameplate horsepower. |
bhp |
= |
The maximum combined fan brake horsepower. |
A |
= |
Sum of [PD × CFMD/4131] |
For SI: |
1 cfm = 0.471 L/s. |
|
Where: |
||
PD |
= |
Each applicable pressure drop adjustment from Table C403.2.10.1(2) in. w.c. |
CFMD |
= |
The design airflow through each applicable device from Table C403.2.10.1(2) in cubic feet per minute. |
For SI: |
1 bhp = 735.5 W, 1 hp = 745.5 W. |
Table ((C403.2.10.1(2))) C403.2.11.1(2)
Fan Power Limitation Pressure Drop Adjustment
Device |
Adjustment |
Credits |
|
Fully ducted return and/or exhaust air systems |
0.5 inch w.c. (2.15 inches w.c. for laboratory and vivarium systems) |
Return and/or exhaust air flow control devices |
0.5 inch w.c. |
Exhaust filters, scrubbers, or other exhaust treatment |
The pressure drop of device calculated at fan system design condition |
Particulate filtration credit: MERV 9 - 12 |
0.5 inch w.c. |
Particulate filtration credit: MERV 13 - 15 |
0.9 inch w.c. |
Particulate filtration credit: MERV 16 and greater and electronically enhanced filters |
Pressure drop calculated at 2x clean filter pressure drop at fan system design condition |
Carbon and other gas-phase air cleaners |
Clean filter pressure drop at fan system design condition |
Biosafety cabinet |
Pressure drop of device at fan system design condition |
Energy recovery device, other than coil runaround loop |
(2.2 × energy recovery effectiveness) – 0.5 inch w.c. for each airstream |
Coil runaround loop |
0.6 inch w.c. for each airstream |
Evaporative humidifier/cooler in series with another cooling coil |
Pressure drop of device at fan system design conditions |
Sound attenuation section (fans serving spaces with design background noise goals below NC35) |
0.15 inch w.c. |
Exhaust system serving fume hoods |
0.35 inch w.c. |
Laboratory and vivarium exhaust systems in high-rise buildings |
0.25 inch w.c./100 feet of vertical duct exceeding 75 feet |
Deductions |
|
Systems without central cooling device |
-0.6 inch w.c |
Systems without central heating device |
-0.3 inch w.c. |
Systems with central electric resistance heat |
-0.2 inch w.c. |
w.c. = water column. | |
For SI: 1 inch w.c.= 249 Pa, 1 inch= 25.4 mm. |
Table C403.2.11.4
Mechanical Ventilation System Fan Efficacy
Fan Location |
Air Flow Rate Minimum (cfm) |
Minimum Efficacy (cfm/watt) |
Air Flow Rate Maximum (cfm) |
Exhaust fan: Bathroom, utility room, whole house |
10 |
1.4 cfm/watt |
< 90 |
Exhaust fan: Bathroom, utility room, whole house |
90 |
2.8 cfm/watt |
Any |
Table C403.2.11.5
Fan Control
Cooling System Type |
Fan Motor Size |
Mechanical Cooling Capacity |
DX cooling |
Any |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h |
Chilled water and evaporative cooling |
≥ 5 hp |
Any |
≥ 1/4 hp |
Any |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403293 Section ((C403.2.11)) C403.2.12—Heating outside a building.
((C403.2.11)) C403.2.12 Heating outside a building. Systems installed to provide heat outside a building shall be radiant systems.
Such heating systems shall be controlled by an occupancy sensing device or a timer switch, so that the system is automatically deenergized when no occupants are present.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403294 Section ((C403.2.12)) C403.2.13—System criteria.
((C403.2.12 System criteria.)) C403.2.13 Variable flow capability. For fan and pump motors 7.5 hp and greater including motors in or serving custom and packaged air handlers serving variable air volume fan systems, constant volume fans, heating and cooling hydronic pumping systems, pool and service water pumping systems, domestic water pressure boosting systems, cooling tower fan, and other pump or fan motors where variable flows are required, there shall be:
1. Variable speed drives; or
2. Other controls and devices that will result in fan and pump motor demand of no more than 30 percent of design wattage at 50 percent of design air volume for fans when static pressure set point equals 1/3 the total design static pressure, and 50 percent of design water flow for pumps, based on manufacturer's certified test data. Variable inlet vanes, throttling valves (dampers), scroll dampers or bypass circuits shall not be allowed.
EXCEPTION: | Variable speed devices are not required for motors that serve: |
1. Fans or pumps in packaged equipment where variable speed drives are not available as a factory option from the equipment manufacturer. | |
2. Fans or pumps that are required to operate only for emergency fire-life-safety events (e.g., stairwell pressurization fans, elevator pressurization fans, fire pumps, etc.). |
((C403.2.12.1)) C403.2.13.1 Heat rejection equipment. The requirements of this section apply to heat rejection equipment used in comfort cooling systems such as air-cooled condensers, open cooling towers, closed-circuit cooling towers, and evaporative condensers.
EXCEPTION: | Heat rejection devices included as an integral part of equipment listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(3). |
Heat rejection equipment shall have a minimum efficiency performance not less than values specified in Table C403.2.3(8). These requirements apply to all propeller, axial fan and centrifugal fan cooling towers. Table C403.2.3(8) specifies requirements for air-cooled condensers that are within rating conditions specified within the table.
((C403.2.12.1.1)) C403.2.13.1.1 Variable flow controls. Cooling tower fans 7.5 hp and greater shall have control devices that vary flow by controlling the leaving fluid temperature or condenser temperature/pressure of the heat rejection device.
((C403.2.12.1.2)) C403.2.13.1.2 Limitation on centrifugal fan cooling towers. Open cooling towers with a combined rated capacity of 1,100 gpm and greater at 95°F condenser water return, 85°F condenser water supply and 75°F outdoor wet-bulb temperature shall meet the energy efficiency requirement for axial fan open circuit cooling towers.
EXCEPTION: | Open circuit cooling towers that are ducted (inlet or discharge) or have external sound attenuation that requires external static pressure capability. |
((C403.2.12.2 Large volume fan systems. Single or multiple fan systems serving a zone or adjacent zones without separating walls with total air flow over 10,000 cfm (3,540 L/s) are required to reduce airflow based on space thermostat heating and cooling demand. A variable speed drive shall reduce airflow to a maximum 75 percent of peak airflow or minimum ventilation air requirement as required by Section 403 of the International Mechanical Code, whichever is greater.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Systems where the function of the supply air is for purposes other than temperature control, such as maintaining specific humidity levels or supplying an exhaust system. |
2. Dedicated outdoor air supply unit(s) with heat recovery where airflow is equal to the minimum ventilation requirements and other fans cycle off unless heating or cooling is required. | |
3. An area served by multiple units where designated ventilation units have 50 percent or less of total area airflow and nonventilation unit fans cycle off when heating or cooling is not required. |
All air-conditioning equipment and air-handling units with direct expansion cooling and a cooling capacity at AHRI conditions greater than or equal to 110,000 Btu/h that serve single zones shall have their supply fans controlled by two-speed motors or variable speed drives. At cooling demands less than or equal to 50 percent, the supply fan controls shall be able to reduce the airflow to no greater than the larger of the following:
1. Two-thirds of the full fan speed; or
2. The volume of outdoor air required to meet the ventilation requirements of Section 403 of the International Mechanical Code.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403295 Section ((C403.2.13)) C403.2.14—Electric motor efficiency.
((C403.2.13)) C403.2.14 Electric motor efficiency. ((Design A and B squirrel-cage, T-frame induction permanently wired polyphase motors of 1 hp or more having synchronous speeds of 3,600, 1,800 and 1,200 rpm shall have a nominal full-load motor efficiency no less than the corresponding values for energy efficient motors provided in NEMA Standard MG-1.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Motors used in systems designed to use more than one speed of a multi-speed motor. |
2. Motors used as a component of the equipment meeting the minimum equipment efficiency requirements of Section C403.2.3 and Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(9) provided that the motor input is included when determining the equipment efficiency. | |
3. Motors that are an integral part of specialized process equipment. | |
4. Where the motor is integral to a listed piece of equipment for which no complying motor has been approved. |
Fan motors less than 1 hp in series terminal units shall be electronically commutated motors, or shall have a minimum motor efficiency of 65 percent when rated in accordance with NEMA Standard MG-1 at full load rating conditions.)) Electric motors, including fractional hp motors, shall comply with the provisions of Section C405.8.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40330 Section C403.3—((Simple HVAC systems and equipment)) Economizers.
C403.3 ((Simple HVAC systems and equipment (Prescriptive). This section applies to unitary or packaged HVAC systems listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(8), each serving one zone and controlled by a single thermostat in the zone served. It also applies to two-pipe heating systems serving one or more zones, where no cooling system is installed.
To qualify as a simple system, systems shall have no active humidification or simultaneous heating and cooling and shall be one of the following:
1. Air cooled, constant volume packaged equipment, which provide heating, cooling or both, and require only external connection to duct work and energy services with cooling capacity of 135,000 Btu/h or less.
2. Air cooled, constant volume split systems, which provide heating, cooling or both, with cooling capacity of 84,000 Btu/h or less.
3. Heating only systems which have a capacity of less than 1,000 cfm or which have a minimum outside air supply of less than 30 percent of the total air circulation.
The combined airflow rate of all simple systems serving single rooms must be less than 10,000 cfm or they do not qualify as simple systems.)) Economizers. Air economizers shall be provided on all new systems including those serving computer server rooms, electronic equipment, radio equipment, and telephone switchgear. Economizers shall comply with Sections C403.3.1.1 through C403.3.1.4.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Systems complying with Section C403.2.6.1 Dedicated outdoor air systems (DOAS) with year-round cooling loads from lights and equipment of less than 5 watts per square foot. |
2. Unitary or packaged systems serving one zone with dehumidification that affect other systems so as to increase the overall building energy consumption. New humidification equipment shall comply with Section C403.2.3.4. | |
3. Unitary or packaged systems serving one zone where the cooling efficiency meets or exceeds the efficiency requirements in Table C403.3.1(2). | |
4. Water-cooled refrigeration equipment serving chilled beams and chilled ceiling space cooling systems only which are provided with a water economizer meeting the requirements of Section C403.3.4. | |
5. Systems complying with all of the following criteria: | |
5.1. Consist of multiple water source heat pumps connected to a common water loop; | |
5.2. Have a minimum of 60 percent air economizer; | |
5.3. Have water source heat pumps with an EER at least 15 percent higher for cooling and a COP at least 15 percent higher for heating than that specified in Section C403.2.3; | |
5.4. Where provided, have a central boiler or furnace efficiency of 90 percent minimum for units up to 199,000 Btu/h; and | |
5.5. Provide heat recovery with a minimum 50 percent heat recovery effectiveness as defined in Section C403.5 to preheat the outside air supply. | |
6. For Group R occupancies, cooling units installed outdoors or in a mechanical room adjacent to outdoors with a total cooling capacity less than 20,000 Btu/h and other cooling units with a total cooling capacity less than 54,000 Btu/h provided that these are high-efficiency cooling equipment with IEER, SEER, and EER values more than 15 percent higher than minimum efficiencies listed in Tables C403.2.3 (1) through (3), in the appropriate size category, using the same test procedures. Equipment shall be listed in the appropriate certification program to qualify for this exception. For split systems, compliance is based on the cooling capacity of individual fan coil units. | |
7. Variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems, multiple-zone split-system heat pumps, consisting of multiple, individually metered indoor units with multi-speed fan motors, served on a single common refrigeration circuit with an exterior reverse-cycle heat pump with variable speed compressor(s) and variable speed condenser fan(s). These systems shall also be capable of providing simultaneous heating and cooling operation, where recovered energy from the indoor units operating in one mode can be transferred to one or more indoor units operating in the other mode, and shall serve at least 20 percent internal (no perimeter wall within 12') and 20 percent perimeter zones (as determined by conditioned floor area) and the outdoor unit shall be at least 65,000 Btu/h in total capacity. Systems utilizing this exception shall have 50 percent heat recovery effectiveness as defined by Section C403.2.6 on the outside air. For the purposes of this exception, dedicated server rooms, electronic equipment rooms or telecom switch rooms are not considered perimeter zones. | |
8. Equipment used to cool Controlled Plant Growth Environments provided these are high-efficiency cooling equipment with SEER, EER and IEER values a minimum of 20 percent greater than the values listed in Tables C403.2.3 (1), (3) and (7). | |
9. Equipment used to cool any spaces with year-round cooling loads from lights and equipment of greater than 5 watts per square foot, where it can be demonstrated through calculations, to the satisfaction of the code official, that the heat rejection load of the equipment will be recovered and used for on-site space heating or service water heating demands such that the energy use of the building is decreased in comparison to a baseline of the same equipment provided with an air economizer complying with Section C403.3. | |
10. Equipment used to cool any dedicated server room, electronic equipment room or telecom switch room provided the system complies with Option a, b or c in the table below. The total capacity of all systems without economizers shall not exceed 240,000 Btu/h per building or 10 percent of its air economizer capacity, whichever is greater. This exception shall not be used for Total Building Performance. |
Equipment Type |
Higher Equipment Efficiency |
Part-Load Control |
Economizer |
|
Option a |
Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)a |
+15%b |
Required over 85,000 Btu/hc |
None Required |
Option b |
Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)a |
+5%d |
Required over 85,000 Btu/hc |
Waterside Economizere |
Option c |
ASHRAE Standard 127f |
+0%g |
Required over 85,000 Btu/hc |
Waterside Economizere |
Notes for Exception 10: | |
a | For a system where all of the cooling equipment is subject to the AHRI standards listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2), the system shall comply with all of the following (note that if the system contains any cooling equipment that exceeds the capacity limits in Table C403.2.3(1) or C403.2.3(2), or if the system contains any cooling equipment that is not included in Table C403.2.3(1) or C403.2.3(2), then the system is not allowed to use this option). |
b | The cooling equipment shall have an EER value and an IPLV value that is a minimum of 15 percent greater than the value listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2). |
c | For units with a total cooling capacity over 85,000 Btu/h, the system shall utilize part-load capacity control schemes that are able to modulate to a part-load capacity of 50 percent of the load or less that results in the compressor operating at the same or higher EER at part loads than at full load (e.g., minimum of two-stages of compressor unloading such as cylinder unloading, two-stage scrolls, dual tandem scrolls, but hot gas bypass is not credited as a compressor unloading system). |
d | The cooling equipment shall have an EER value and an IPLV value that is a minimum of 5 percent greater than the value listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2). |
e | The system shall include a water economizer in lieu of air economizer. Water economizers shall meet the requirements of C403.4.1.2 through C403.4.1.4 and be capable of providing the total concurrent cooling load served by the connected terminal equipment lacking airside economizer, at outside air temperatures of 50°F dry-bulb/45°F wet-bulb and below. For this calculation, all factors including solar and internal load shall be the same as those used for peak load calculations, except for the outside temperatures. The equipment shall be served by a dedicated condenser water system unless a nondedicated condenser water system exists that can provide appropriate water temperatures during hours when waterside economizer cooling is available. |
f | For a system where all cooling equipment is subject to ASHRAE Standard 127. |
g | The cooling equipment subject to the ASHRAE Standard 127 shall have an EER value and an IPLV value that is equal or greater than the value listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2) when determined in accordance with the rating conditions ASHRAE Standard 127 (i.e., not the rating conditions in AHRI Standard 210/240 or 340/360). This information shall be provided by an independent third party. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-122, filed 12/3/14, effective 1/3/15)
WAC 51-11C-40331 Section C403.3.1—((Economizers)) Integrated economizer control.
((C403.3.1 Economizers. Each cooling system that has a fan shall include an air economizer meeting the requirements of Sections C403.3.1.1 through C403.3.1.1.4.
EXCEPTION: | Economizers are not required for the systems listed below: |
1. Qualifying small equipment: This exception shall not be used for unitary cooling equipment installed outdoors or in a mechanical room adjacent to the outdoors. This exception is allowed to be used for other cooling units and split systems with a total cooling capacity rated in accordance with Section C403.2.3 of less than 33,000 Btu/h (hereafter referred to as qualifying small systems) provided that these are high-efficiency cooling equipment with SEER and EER values more than 15 percent higher than minimum efficiencies listed in Tables C403.2.3 (1) through (3), in the appropriate size category, using the same test procedures. Equipment shall be listed in the appropriate certification program to qualify for this exception. The total capacity of all qualifying small equipment without economizers shall not exceed 72,000 Btu/h per building, or 5 percent of its air economizer capacity, whichever is greater. That portion of the equipment serving Group R occupancies is not included in determining the total capacity of all units without economizers in a building. Redundant units are not counted in the capacity limitations. This exception shall not be used for the shell-and-core permit or for the initial tenant improvement or for Total Building Performance. | |
2. Systems with dehumidification that affect other systems so as to increase the overall building energy consumption. New humidification equipment shall comply with Section C403.2.3.4. | |
3. For Group R occupancies, cooling units installed outdoors or in a mechanical room adjacent to outdoors with a total cooling capacity less than 20,000 Btu/h and other cooling units with a total cooling capacity less than 54,000 Btu/h provided that these are high-efficiency cooling equipment with IEER, SEER, and EER values more than 15 percent higher than minimum efficiencies listed in Tables C403.2.3 (1) through (10), in the appropriate size category, using the same test procedures. Equipment shall be listed in the appropriate certification program to qualify for this exception. For split systems, compliance is based on the cooling capacity of individual fan coil units. | |
4. Where the cooling efficiency meets or exceeds the efficiency requirements in Table C403.3.1(2). | |
5. Equipment used to cool any dedicated server room, electronic equipment room or telecom switch room provided the system complies with Exception 5 of Section C403.4.1. The total allowance for equipment utilizing Exception 5 of Section C403.4.1 includes the sum of both simple and complex systems. |
Table C403.3.1(2)
Equipment Efficiency Performance
Exception for Economizers
Climate Zones |
Cooling Equipment Performance Improvement (EER OR IPLV) |
2B |
10% Efficiency Improvement |
3B |
15% Efficiency Improvement |
4B |
20% Efficiency Improvement |
C403.3.1.1 Air economizers. Air economizers shall comply with Sections C403.3.1.1.1 through C403.3.1.1.4.
C403.3.1.1.1 Design capacity. Air economizer systems shall be capable of modulating outdoor air and return air dampers to provide up to 100 percent of the design supply air quantity as outdoor air for cooling.
C403.3.1.1.2 Control signal. Economizer dampers shall be capable of being sequenced with the mechanical cooling equipment and shall not be controlled by only mixed air temperature. Air economizers on systems with cooling capacity greater than 65,000 Btu/h shall be capable of providing partial cooling even when additional mechanical cooling is required to meet the remainder of the cooling load.
EXCEPTION: | The use of mixed air temperature limit control shall be permitted for systems that are both controlled from space temperature (such as single zone systems) and having cooling capacity less than 65,000 Btu/h. |
C403.3.1.1.3 High-limit shutoff. Air economizers shall be capable of automatically reducing outdoor air intake to the design minimum outdoor air quantity when outdoor air intake will no longer reduce cooling energy usage. High-limit shutoff control types for specific climates shall be chosen from Table C403.3.1.1.3(1). High-limit shutoff control settings for these control types shall be those specified in Table C403.3.1.1.3(2).
C403.3.1.1.4 Relief of excess outdoor air. Systems shall be capable of relieving excess outdoor air during air economizer operation to prevent over-pressurizing the building. The relief air outlet shall be located to avoid recirculation into the building.)) C403.3.1 Integrated economizer control. Economizer systems shall be integrated with the mechanical cooling system and be configured to provide partial cooling even where additional mechanical cooling is required to provide the remainder of the cooling load. Controls shall not be capable of creating a false load in the mechanical cooling system by limiting or disabling the economizer or any other means, such as hot gas bypass, except at the lowest stage of mechanical cooling.
Units that include an air economizer shall comply with the following:
1. Unit controls shall have the mechanical cooling capacity control interlocked with the air economizer controls such that the outdoor air damper is at the 100 percent open position when mechanical cooling is on and the outdoor air damper does not begin to close to prevent coil freezing due to minimum compressor run time until the leaving air temperature is less than 45°F (7°C).
2. Direct expansion (DX) units with cooling capacity 65,000 Btu/h (19 kW) or greater of rated capacity shall comply with the following:
2.1. DX units that control the capacity of the mechanical cooling directly based on occupied space temperature shall have not fewer than two stages of mechanical cooling capacity.
2.2. Other DX units, including those that control space temperature by modulating the airflow to the space, shall be in accordance with Table C403.3.1.
Table C403.3.1
DX Cooling Stage Requirements for Modulating Airflow Units
RATING CAPACITY |
MINIMUM NUMBER OF MECHANICAL COOLING STAGES |
MINIMUM COMPRESSOR DISPLACEMENTa |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h |
3 stages |
≤ 35% of full load |
≥ 240,000 Btu/h |
4 stages |
≤ 25% full load |
For SI: | 1 British thermal unit per hour = 0.2931 W. |
a For mechanical cooling stage control that does not use variable compressor displacement, the percent displacement shall be equivalent to the mechanical cooling capacity reduction evaluated at the full load rating conditions for the compressor. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-20-120, filed 10/1/13, effective 11/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40332 Section C403.3.2—((Hydronic system controls)) Economizer heating system impact.
((C403.3.2 Hydronic system controls. Hydronic systems of at least 300,000 Btu/h (87,930 W) design output capacity supplying heated to comfort conditioning systems shall include controls that meet the requirements of Section C403.4.3.)) C403.3.2 Economizer heating system impact. HVAC system design and economizer controls shall be such that economizer operation does not increase building heating energy use during normal operation.
EXCEPTION: | Economizers on VAV systems that cause zone level heating to increase due to a reduction in supply air temperature. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40333 Section C403.3.3—Air economizers.
C403.3.3 Air economizers. Air economizers shall comply with Sections C403.3.3.1 through C403.3.3.5.
C403.3.3.1 Design capacity. Air economizer systems shall be configured to modulate outdoor air and return air dampers to provide up to 100 percent of the design supply air quantity as outdoor air for cooling.
C403.3.3.2 Control signal. Economizer controls and dampers shall be configured to sequence the dampers with the mechanical cooling equipment and shall not be controlled by only mixed air temperature. Air economizers on systems with cooling capacity greater than 65,000 Btu/h shall be configured to provide partial cooling even when additional mechanical cooling is required to meet the remainder of the cooling load.
EXCEPTION: | The use of mixed air temperature limit control shall be permitted for systems that are both controlled from space temperature (such as single zone systems) and having cooling capacity less than 65,000 Btu/h. |
C403.3.3.3 High-limit shutoff. Air economizers shall be configured to automatically reduce outdoor air intake to the design minimum outdoor air quantity when outdoor air intake will no longer reduce cooling energy usage. High-limit shutoff control types for specific climates shall be chosen from Table C403.3.3.3. High-limit shutoff control settings for these control types shall be those specified in Table C403.3.3.3.
Table C403.3.3.3
High-limit Shutoff Control Setting for Air Economizersb
Device Type |
Climate Zone |
Required High Limit (economizer off when): |
|
Equation |
Description |
||
Fixed dry-bulb |
4C, 5B |
TOA ˃ 75°F |
Outdoor air temperature exceeds 75°F |
Differential dry-bulb |
4C, 5B |
TOA ˃ TRA |
Outdoor air temperature exceeds return air temperature |
Fixed enthalpy with fixed dry-bulb temperatures |
All |
hOA ˃ 28 Btu/lba or TOA ˃ 75°F |
Outdoor air enthalpy exceeds 28 Btu/lb of dry aira or outdoor air temperature exceeds 75°F |
Differential enthalpy with fixed dry-bulb temperature |
All |
hOA ˃ hRA or TOA ˃ 75°F |
Outdoor air enthalpy exceeds return air enthalpy or outdoor air temperature exceeds 75°F |
For SI: | °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9, 1 Btu/lb = 2.33 kJ/kg. |
a | At altitudes substantially different than sea level, the fixed enthalpy limit shall be set to the enthalpy value at 75°F and 50 percent relative humidity. As an example, at approximately 6,000 feet elevation the fixed enthalpy limit is approximately 30.7 Btu/lb. |
b | Devices with selectable setpoints shall be capable of being set to within 2°F and 2 Btu/lb of the setpoint listed. |
C403.3.3.4 Relief of excess outdoor air. Systems shall be capable of relieving excess outdoor air during air economizer operation to prevent over-pressurizing the building. The relief air outlet shall be located to avoid recirculation into the building.
C403.3.3.5 Economizer dampers. Return, exhaust/relief and outdoor air dampers used in economizers shall comply with Section C403.2.4.3.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40334 Section C403.3.4—Water-side economizers.
C403.3.4 Water-side economizers. Water-side economizers shall comply with Sections C403.3.4.1 and C403.3.4.2.
C403.3.4.1 Design capacity. Water economizer systems shall be capable of cooling supply air by indirect evaporation and providing up to 100 percent of the expected system cooling load at outdoor air temperatures of 50°F dry-bulb (10°C dry-bulb)/45°F wet-bulb (7.2°C wet-bulb) and below.
EXCEPTION: | Systems where dehumidification requirements cannot be met using outdoor air temperatures of 50°F dry-bulb (10°C dry-bulb)/45°F wet-bulb (7.2°C wet-bulb) and where 100 percent of the expected system cooling load at 45°F dry-bulb (7.2°C dry-bulb)/40°F wet-bulb (4.5°C wet-bulb) is met with evaporative water economizers. |
C403.3.4.2 Maximum pressure drop. Precooling coils and water-to-water heat exchangers used as part of a water economizer system shall either have a waterside pressure drop of less than 15 feet (4572 mm) of water or a secondary loop shall be created so that the coil or heat exchanger pressure drop is not seen by the circulating pumps when the system is in the normal cooling (noneconomizer) mode.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40340 Section C403.4—((Complex HVAC systems and equipment)) Hydronic and multiple-zone HVAC systems.
C403.4 ((Complex HVAC systems and equipment (prescriptive). This section applies to HVAC equipment and systems not covered in Section C403.3)) Hydronic and multiple-zone HVAC system controls and equipment (prescriptive). Hydronic and multiple zone HVAC system controls and equipment shall comply with this section.
For buildings with a total equipment cooling capacity of 300 tons and above, the equipment shall comply with one of the following:
1. No one unit shall have a cooling capacity of more than 2/3 of the total installed cooling equipment capacity;
2. The equipment shall have a variable speed drive; or
3. The equipment shall have multiple compressors.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-122, filed 12/3/14, effective 1/3/15)
WAC 51-11C-40341 ((Section C403.4.1—Economizers.)) Reserved.
((C403.4.1 Economizers. Air economizers shall be provided on all new systems including those serving computer server rooms, electronic equipment, radio equipment, and telephone switchgear. Economizers shall comply with Sections C403.4.1.1 through C403.4.1.4.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Water-cooled refrigeration equipment serving chilled beams and chilled ceiling space cooling systems only which are provided with a water economizer meeting the requirements of Section C403.4.1.1 through C403.4.1.4. Water economizer capacity per building shall not exceed 500 tons. This exception shall not be used for Total Building Performance. |
2. Systems complying with all of the following criteria: | |
2.1. Consist of multiple water source heat pumps connected to a common water loop; | |
2.2. Have a minimum of 60 percent air economizer; | |
2.3. Have water source heat pumps with an EER at least 15 percent higher for cooling and a COP at least 15 percent higher for heating than that specified in Section C403.2.3; | |
2.4. Where provided, have a central boiler or furnace efficiency of 90 percent minimum for units up to 199,000 Btu/h; and | |
2.5. Provide heat recovery with a minimum 50 percent heat recovery effectiveness as defined in Section C403.2.6 to preheat the outside air supply. | |
3. Chilled water terminal units connected to systems with chilled water generation equipment with IPLV values more than 25 percent higher than minimum part load efficiencies listed in Table C403.2.3(7), in the appropriate size category, using the same test procedures. Equipment shall be listed in the appropriate certification program to qualify for this exception. The total capacity of all systems without economizers shall not exceed 480,000 Btu/h per building, or 20 percent of its air economizer capacity, whichever is greater. That portion of the equipment serving Group R Occupancy is not included in determining the total capacity of all units without economizers in a building. This exception shall not be used for the initial permit (this includes any initial permit for the space including, but not limited to, the shell-and-core permit, built-to-suit permit, and tenant improvement permit) or for Total Building Performance Method. | |
4. For Group R occupancies, cooling units installed outdoors or in a mechanical room adjacent to outdoors with a total cooling capacity less than 20,000 Btu/h and other cooling units with a total cooling capacity less than 54,000 Btu/h provided that these are high-efficiency cooling equipment with SEER and EER values more than 15 percent higher than minimum efficiencies listed in Tables C403.2.3 (1) through (3), in the appropriate size category, using the same test procedures. Equipment shall be listed in the appropriate certification program to qualify for this exception. For split systems and VRF systems, compliance is based on the cooling capacity of individual fan coil units. | |
5. Equipment used to cool any dedicated server room, electronic equipment room or telecom switch room provided that they completely comply with Option a, b, or c in the table below. The total capacity of all systems without economizers shall not exceed 240,000 Btu/h per building or 10 percent of its air economizer capacity, whichever is greater. This exception shall not be used for Total Building Performance. |
Equipment Type |
Higher Equipment Efficiency |
Part-Load Control |
Economizer |
|
Option a |
Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)a |
+15%b |
Required over 85,000 Btu/hc |
None Required |
Option b |
Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)a |
+5%d |
Required over 85,000 Btu/hc |
Waterside Economizere |
Option c |
ASHRAE Standard 127f |
+0%g |
Required over 85,000 Btu/hc |
Waterside Economizere |
Notes for Exception 5: | ||
a | For a system where all of the cooling equipment is subject to the AHRI standards listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2), the system shall comply with all of the following (note that if the system contains any cooling equipment that exceeds the capacity limits in Table C403.2.3(1) or C403.2.3(2), or if the system contains any cooling equipment that is not included in Table C403.2.3(1) or C403.2.3(2), then the system is not allowed to use this option). | |
b | The cooling equipment shall have an EER value and an IPLV value that is a minimum of 15 percent greater than the value listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2) (1.15 x values in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)). | |
c | For units with a total cooling capacity over 85,000 Btu/h, the system shall utilize part-load capacity control schemes that are able to modulate to a part-load capacity of 50 percent of the load or less that results in the compressor operating at the same or higher EER at part loads than at full load (e.g., minimum of two-stages of compressor unloading such as cylinder unloading, two-stage scrolls, dual tandem scrolls, but hot gas bypass is not credited as a compressor unloading system). | |
d | The cooling equipment shall have an EER value and an IPLV value that is a minimum of 5 percent greater than the value listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2) (1.05 x values in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)). | |
e | The system shall include a water economizer in lieu of air economizer. Water economizers shall meet the requirements of C403.4.1.2 through C403.4.1.4 and be capable of providing the total concurrent cooling load served by the connected terminal equipment lacking airside economizer, at outside air temperatures of 50°F dry-bulb/45°F wet-bulb and below. For this calculation, all factors including solar and internal load shall be the same as those used for peak load calculations, except for the outside temperatures. The equipment shall be served by a dedicated condenser water system unless a nondedicated condenser water system exists that can provide appropriate water temperatures during hours when waterside economizer cooling is available. | |
f | For a system where all cooling equipment is subject to ASHRAE Standard 127. | |
g | The cooling equipment subject to the ASHRAE Standard 127 shall have an EER value and an IPLV value that is equal or greater than the value listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2) when determined in accordance with the rating conditions ASHRAE Standard 127 (i.e., not the rating conditions in AHRI Standard 210/240 or 340/360). This information shall be provided by an independent third party. | |
6. Variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems, multiple-zone split-system heat pumps, consisting of multiple, individually metered indoor units with multi-speed fan motors, served on a single common refrigeration circuit with an exterior reverse-cycle heat pump with variable speed compressor(s) and variable speed condenser fan(s). These systems shall also be capable of providing simultaneous heating and cooling operation, where recovered energy from the indoor units operating in one mode can be transferred to one or more indoor units operating in the other mode, and shall serve at least 20 percent internal (no perimeter wall within 12') and 20 percent perimeter zones (as determined by conditioned floor area) and the outdoor unit shall be at least 65,000 Btu/h in total capacity. Systems utilizing this exception shall have 50 percent heat recovery effectiveness as defined by Section C403.2.6 on the outside air. For the purposes of this exception, dedicated server rooms, electronic equipment rooms or telecom switch rooms are not considered perimeter zones. This exception shall be limited to buildings of 60,000 square feet and less. |
C403.4.1.1 Design capacity. Water economizer systems shall be capable of cooling supply air by indirect evaporation and providing up to 100 percent of the expected system cooling load at outdoor air temperatures of 50°F dry-bulb (10°C dry-bulb)/45°F wet-bulb (7.2°C wet-bulb) and below.
EXCEPTION: | Systems in which a water economizer is used and where dehumidification requirements cannot be met using outdoor air temperatures of 50°F dry-bulb (10°C dry-bulb)/45°F wet-bulb (7.2°C wet-bulb) shall satisfy 100 percent of the expected system cooling load at 45°F dry-bulb (7.2°C dry-bulb)/40°F wet-bulb (4.5°C wet-bulb). |
C403.4.1.2 Maximum pressure drop. Precooling coils and water-to-water heat exchangers used as part of a water economizer system shall either have a waterside pressure drop of less than 15 feet (4572 mm) of water or a secondary loop shall be created so that the coil or heat exchanger pressure drop is not seen by the circulating pumps when the system is in the normal cooling (noneconomizer) mode.
C403.4.1.3 Integrated economizer control. Economizer systems shall be integrated with the mechanical cooling system and be capable of providing partial cooling even where additional mechanical cooling is required to meet the remainder of the cooling load.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Direct expansion systems that include controls that reduce the quantity of outdoor air required to prevent coil frosting at the lowest step of compressor unloading, provided this lowest step is no greater than 25 percent of the total system capacity. |
2. Individual direct expansion units that have a rated cooling capacity less than 54,000 Btu/h (15,827 W) and use nonintegrated economizer controls that preclude simultaneous operation of the economizer and mechanical cooling. |
C403.4.1.4 Economizer heating system impact. HVAC system design and economizer controls shall be such that economizer operation does not increase the building heating energy use during normal operation.
EXCEPTION: | Economizers on VAV systems that cause zone level heating to increase due to a reduction in supply air temperature.)) |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40342 Section ((C403.4.2—VAV)) C403.4.1—Fan control.
((C403.4.2 Variable air volume (VAV) fan control. Individual VAV fans with motors of 7.5 horsepower (5.6 kW) or greater shall be:
1. Driven by a mechanical or electrical variable speed drive;
2. Driven by a vane-axial fan with variable-pitch blades; or
3. The fan shall have controls or devices that will result in fan motor demand of no more than 30 percent of their design wattage at 50 percent of design airflow when static pressure set point equals one-third of the total design static pressure, based on manufacturer's certified fan data.
C403.4.2.1)) C403.4.1 Multi-zone system fan control. Controls shall be provided for fans in accordance with Section C403.4.1.1 through C403.4.1.2.
C403.4.1.1 Static pressure sensor location. Static pressure sensors used to control VAV fans shall be ((placed in a position)) located such that the controller setpoint is no greater than ((one-third the total design fan static pressure, except for systems with zone reset control complying with Section C403.4.2.2. For sensors installed)) 1.2 inches w.c. (2099 Pa). Where this results in one or more sensors being located downstream of major duct splits, ((at least)) not less than one sensor shall be located on each major branch to ensure that static pressure can be maintained in each branch.
((C403.4.2.2))
EXCEPTION: | Systems complying with Section C403.4.1.2. |
C403.4.1.2 Set points for direct digital control. For systems with direct digital control of individual zones ((boxes)) reporting to the central control panel, the static pressure setpoint shall be reset based on the zone requiring the most pressure((, i.e., the setpoint is reset lower until one zone damper is nearly wide open)). In such cases, the set point is reset lower until one zone damper is nearly wide open. The direct digital controls shall be capable of monitoring zone damper positions or shall have an alternative method of indicating the need for static pressure that is configured to provide all of the following:
1. Automatically detecting any zone that excessively drives the reset logic.
2. Generating an alarm to the system operational location.
3. Allowing an operator to readily remove one or more zones from the reset algorithm.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-20-120, filed 10/1/13, effective 11/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40343 Section ((C403.4.3)) C403.4.2—Hydronic systems controls.
((C403.4.3)) C403.4.2 Hydronic systems controls. The heating of fluids that have been previously mechanically cooled and the cooling of fluids that have been previously mechanically heated shall be limited in accordance with Sections ((C403.4.3.1 through C403.4.3.3)) C403.4.2.1 through C403.4.2.3. Hydronic heating systems comprised of multiple-packaged boilers and designed to deliver conditioned water or steam into a common distribution system shall include automatic controls ((capable of sequencing)) configured to sequence operation of the boilers. Hydronic heating systems comprised of a single boiler and greater than 500,000 Btu/h (146,550 W) input design capacity shall include either a multi-staged or modulating burner.
((C403.4.3.1)) C403.4.2.1 Three-pipe system. Hydronic systems that use a common return system for both hot water and chilled water are prohibited.
((C403.4.3.2)) C403.4.2.2 Two-pipe changeover system. Systems that use a common distribution system to supply both heated and chilled water shall be designed to allow a dead band between changeover from one mode to the other of at least 15°F (8.3°C) outside air temperatures; be designed to and provided with controls that will allow operation in one mode for at least 4 hours before changing over to the other mode; and be provided with controls that allow heating and cooling supply temperatures at the changeover point to be no more than 30°F (16.7°C) apart.
((C403.4.3.3)) C403.4.2.3 Hydronic (water loop) heat pump systems. Hydronic heat pump systems shall comply with Sections ((C403.4.3.3.1 through C403.4.3.3.3)) C403.4.2.3.1 through C403.4.2.3.3.
((C403.4.3.3.1)) C403.4.2.3.1 Temperature dead band. Hydronic heat pumps connected to a common heat pump water loop with central devices for heat rejection and heat addition shall have controls that are ((capable of providing)) configured to provide a heat pump water supply temperature dead band of at least 20°F (11.1°C) between initiation of heat rejection and heat addition by the central devices.
EXCEPTION: | Where a system loop temperature optimization controller is installed and can determine the most efficient operating temperature based on real time conditions of demand and capacity, dead bands of less than 20°F (11°C) shall be permitted. |
((C403.4.3.3.2)) C403.4.2.3.2 Heat rejection. Heat rejection equipment shall comply with Sections ((C403.4.3.3.2.1 and C403.4.3.3.2.2)) C403.4.2.3.2.1 and C403.4.2.3.2.2.
EXCEPTION: | Where it can be demonstrated that a heat pump system will be required to reject heat throughout the year. |
((C403.4.3.3.2.1)) C403.4.2.3.2.1 Climate Zones 3 and 4. For Climate Zones 3 and 4:
1. If a closed-circuit cooling tower is used directly in the heat pump loop, either an automatic valve shall be installed to bypass all but a minimal flow of water around the tower, or lower leakage positive closure dampers shall be provided.
2. If an open-circuit tower is used directly in the heat pump loop, an automatic valve shall be installed to bypass all heat pump water flow around the tower.
3. If an open- or closed-circuit cooling tower is used in conjunction with a separate heat exchanger to isolate the cooling tower from the heat pump loop, then heat loss shall be controlled by shutting down the circulation pump on the cooling tower loop.
((C403.4.3.3.2.2)) C403.4.2.3.2.2 Climate Zones 5 through 8. For Climate Zones 5 through 8, if an open- or closed-circuit cooling tower is used, then a separate heat exchanger shall be provided to isolate the cooling tower from the heat pump loop, and heat loss shall be controlled by shutting down the circulation pump on the cooling tower loop and providing an automatic valve to stop the flow of fluid.
((C403.4.3.3.3)) C403.4.2.3.3 Isolation valve. Each hydronic heat pump on the hydronic system having a total pump system power exceeding 10 horsepower (hp) (7.5 kW) shall have a two-way (but not three-way) valve. For the purposes of this section, pump system power is the sum of the nominal power demand (i.e., nameplate horsepower at nominal motor efficiency) of motors of all pumps that are required to operate at design conditions to supply fluid from the heating or cooling source to all heat transfer devices (e.g., coils, heat exchanger) and return it to the source. This converts the system into a variable flow system and, as such, the primary circulation pumps shall comply with the variable flow requirements in Section ((C403.4.3.6)) C403.4.2.6.
((C403.4.3.4)) C403.4.2.4 Part load controls. Hydronic systems greater than or equal to 300,000 Btu/h (((87,930 W))) (88 kW) in design output capacity supplying heated or chilled water to comfort conditioning systems shall include controls that ((have the capability)) are configured to:
1. Automatically reset the supply-water temperatures ((using zone-return water temperature, building-return water temperature, or outside air temperature as an indicator of building heating or cooling demand)) in response to varying building heating and cooling demand using coil valve position, zone-return water temperature or outdoor air temperature. The temperature shall be ((capable of being)) reset by ((at least)) not less than 25 percent of the design supply-to-return water temperature difference((; and
2. Reduce system pump flow by at least 50 percent of design flow rate utilizing adjustable speed drive(s) on pump(s), or multiple-staged pumps where at least one-half of the total pump horsepower is capable of being automatically turned off or control valves designed to modulate or step down, and close, as a function of load, or other approved means.
Hydronic systems serving hydronic heat pumps are exempt from item 1, and only those hydronic systems with a total pump system power greater than 3 hp (2.2 kw) shall have controls meeting the requirements of item 2, above.
C403.4.3.5)).
EXCEPTION: | Hydronic systems serving hydronic heat pumps. |
2. Automatically vary fluid flow for hydronic systems with a combined motor capacity of 3 hp or larger with three or more control valves or other devices by reducing the system design flow rate by not less than 50 percent by designed valves that modulate or step open and close, or pumps that modulate or turn on and off as a function of load.
3. Automatically vary pump flow or chilled-water systems and heat rejection loops serving water-cooled unitary air conditioners with a combined motor capacity of 3 hp or larger by reducing pump design flow by not less than 50 percent utilizing adjustable speed drives or pumps, or multiple-staged pumps where not less than one-half of the total pump horsepower is capable of being automatically turned off. Pump flow shall be controlled to maintain one control valve nearly wide open or to satisfy the minimum differential pressure.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Supply-water temperature reset for chilled-water systems supplied by off-site district chilled water or chilled water from ice storage systems. |
2. Minimum flow rates other than 50 percent as required by the equipment manufacturer for proper operation of equipment where using flow bypass or end-of-line 3-way valves. | |
3. Variable pump flow on dedicated equipment circulation pumps where configured in primary/secondary design to provide the minimum flow requirements of the equipment manufacturer for proper operation of equipment. |
C403.4.2.5 Boiler turndown. Boiler systems with design input of greater than 1,000,000 Btu/h (293 kW) shall comply with the turndown ratio specified in Table C403.4.2.5.
The system turndown requirement shall be met through the use of multiple single input boilers, one or more modulating boilers or a combination of single input and modulating boilers.
Table C403.4.2.5
Boiler Turndown
Boiler System Design Input (Btu/h) |
Minimum Turndown Ratio |
≥ 1,000,000 and less than or equal to 5,000,000 |
3 to 1 |
> 5,000,000 and less than or equal to 10,000,000 |
4 to 1 |
> 10,000,000 |
5 to 1 |
C403.4.2.6 Pump isolation. Chilled water plants including more than one chiller shall ((have the capability)) be capable of and configured to reduce flow automatically through the chiller plant when a chiller is shut down and automatically shut off flow to chillers that are shut down. Chillers piped in series for the purpose of increased temperature differential shall be considered as one chiller.
EXCEPTION: | Chillers that are piped in series for the purpose of increased temperature differential. |
Boiler plants including more than one boiler shall ((have the capability)) be capable of and configured to reduce flow automatically through the boiler plant when a boiler is shut down ((and automatically shut off flow to boilers that are shut down)).
((C403.4.3.6)) C403.4.2.7 Variable flow controls. Individual pumps ((requiring variable speed control per Section C403.4.9)) required by this code to have variable speed control shall be controlled in one of the following manners:
1. For systems having a combined pump motor horsepower less than or equal to 20 hp (15 kW) and without direct digital control of individual coils, pump speed shall be a function of either:
1.1. Required differential pressure; or
1.2. Reset directly based on zone hydronic demand, or other zone load indicators; or
1.3. Reset directly based on pump power and pump differential pressure.
2. For systems having a combined pump motor horsepower that exceeds 20 hp (15 kW) or smaller systems with direct digital control, pump speed shall be a function of either:
2.1. The static pressure set point as reset based on the valve requiring the most pressure; or
2.2. Directly controlled based on zone hydronic demand.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-403431 ((Table C403.4.3.1.1.3—High limit shutoff controls.)) Reserved.
((Table C403.3.1.1.3(1)
High-limit Shutoff Control Options for Air Economizers
Climate Zones |
Allowed Control Types |
Prohibited Control Types |
1B, 2B, 3B, 3C, 4B, 4C, 5B, 5C, 6B, 7, 8 |
Fixed dry-bulb Differential dry-bulb Electronic enthalpya Differential enthalpy Dew-point and dry-bulb temperatures |
Fixed enthalpy |
1A, 2A, 3A, 4A |
Fixed dry-bulb Fixed enthalpy Electronic enthalpya Differential enthalpy Dew-point and dry-bulb temperatures |
Differential dry-bulb |
All other climates |
Fixed dry-bulb Differential dry-bulb Fixed enthalpy Electronic enthalpya Differential enthalpy Dew-point and dry-bulb temperatures |
— |
a |
Electronic enthalpy controllers are devices that use a combination of humidity and dry-bulb temperature in their switching algorithm. |
Table C403.3.1.1.3(2)
High-limit Shutoff Control Setting for Air Economizers
Required High Limit (Economizer off When): |
|||
Device Type |
Climate Zone |
Equation |
Description |
Fixed dry-bulb |
1B, 2B, 3B, 3C, 4B, 4C, 5B, 5C, 6B, 7, 8 |
TOA ˃ 75°F |
Outdoor air temperature exceeds 75°F |
5A, 6A, 7A |
TOA ˃ 70°F |
Outdoor air temperature exceeds 70°F |
|
All other zones |
TOA ˃ 65°F |
Outdoor air temperature exceeds 65°F |
|
Differential dry-bulb |
1B, 2B, 3B, 3C, 4B, 4C, 5A, 5B, 5C, 6A, 6B, 7, 8 |
TOA ˃ TRA |
Outdoor air temperature exceeds return air temperature |
Fixed enthalpy |
All |
hOA ˃ 28 Btu/lba |
Outdoor air enthalpy exceeds 28 Btu/lb of dry aira |
Electronic enthalpy |
All |
(TOA, RHOA) ˃ A |
Outdoor air temperature/RH exceeds the "A" setpoint curveb |
Differential enthalpy |
All |
hOA ˃ Hra |
Outdoor air enthalpy exceeds return air enthalpy |
Dew-point and dry-bulb temperatures |
All |
DPOA ˃ 55°F or TOA ˃ 75°F |
Outdoor air dry-bulb exceeds 75°F or outside dew-point exceeds 55°F (65 gr/lb) |
For SI: | °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9, 1 Btu/lb = 2.33 kJ/kg. |
a | At altitudes substantially different than sea level, the fixed enthalpy limit shall be set to the enthalpy value at 75°F and 50 percent relative humidity. As an example, at approximately 6,000 feet elevation the fixed enthalpy limit is approximately 30.7 Btu/lb. |
b | Setpoint "A" corresponds to a curve on the psychometric chart that goes through a point at approximately 75°F and 40 percent relative humidity and is nearly parallel to dry-bulb lines at low humidity levels and nearly parallel to enthalpy lines at high humidity levels.)) |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40344 Section ((C403.4.4)) C403.4.3—Heat rejection equipment ((fan speed control)).
((C403.4.4)) C403.4.3 Heat rejection equipment ((fan speed control. Each fan powered by a motor of 7.5 hp (5.6 kW) or larger shall have controls that automatically change the fan speed to control the leaving fluid temperature or condensing temperature/pressure of the heat rejection device)). Heat rejection equipment such as air-cooled condensers, dry coolers, open-circuit cooling towers, closed-circuit cooling towers and evaporative condensers used for comfort cooling applications shall comply with this section.
EXCEPTION: | Heat rejection devices where energy usage is included in the equipment efficiency ratings listed in Tables C403.2.3(1)A, C403.2.3(1)B, C403.2.3(1)C, C403.2.3(2), C403.2.3(3), C403.2.3(7) and C403.2.3(9). |
C403.4.3.1 Fan speed control.The fan speed shall be controlled as provided in Sections C403.4.3.2.1 and C403.4.3.2.2.
C403.4.3.1.1 Fan motors not less than 7.5 hp. Each fan powered by a motor of 7.5 hp (5.6 kW) or larger shall have controls that automatically change the fan speed to control the leaving fluid temperature or condensing temperature/pressure of the heat rejection device.
C403.4.3.1.2 Multiple-cell heat rejection equipment. Multiple-cell heat rejection equipment with variable speed fan drives shall be controlled in both of the following manners:
1. To operate the maximum number of fans allowed that comply with the manufacturer's requirements for all system components.
2. So all fans can operate at the same fan speed required for the instantaneous cooling duty, as opposed to staged (on/off) operation. Minimum fan speed shall be the minimum allowable speed of the fan drive system in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations.
C403.4.3.2 Limitation on centrifugal fan open-circuit cooling towers. Centrifugal fan open-circuit cooling towers with a combined rated capacity of 1,100 gpm (4164 L/m) or greater at 95°F (35°C) condenser water return, 85°F (29°C) condenser water supply, and 75°F (24°C) outdoor air wet-bulb temperature shall meet the energy efficiency requirement for axial fan open-circuit cooling towers listed in Table C403.2.3(8).
EXCEPTION: | Centrifugal open-circuit cooling towers that are designed with inlet or discharge ducts or require external sound attenuation. |
C403.4.3.3 Tower flow turndown. Open-circuit cooling towers used on water-cooled chiller systems that are configured with multiple- or variable-speed condenser water pumps shall be designed so that all open circuit cooling tower cells can be run in parallel with the larger of the flow that is produced by the smallest pump at its minimum expected flow rate or at 50 percent of the design flow for the cell.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40345 Section ((C403.4.5)) C403.4.4—Requirements for ((complex)) mechanical systems serving multiple zones.
((C403.4.5)) C403.4.4 Requirements for ((complex)) mechanical systems serving multiple zones. Sections ((C403.4.5.1 through C403.4.5.4)) C403.4.4.1 through C403.4.4.4 shall apply to complex mechanical systems serving multiple zones. Supply air systems serving multiple zones shall be VAV systems which, during periods of occupancy, are designed and ((capable of being controlled)) configured to reduce primary air supply to each zone to one of the following before reheating, recooling or mixing takes place:
1. Thirty percent of the maximum supply air to each zone.
2. Three hundred cfm (142 L/s) or less where the maximum flow rate is less than 10 percent of the total fan system supply airflow rate.
3. The minimum ventilation requirements of Chapter 4 of the International Mechanical Code.
4. ((Minimum flow rates required by applicable codes or standards for occupant health and safety.)) Any higher rate that can be demonstrated to reduce overall system annual energy use by offsetting reheat/recool energy losses through a reduction in outdoor air intake for the system, as approved by the code official.
5. The airflow rates to comply with applicable codes or accreditation standards such as pressure relationships or minimum air change rates.
EXCEPTION: | The following define where individual zones or where entire air distribution systems are exempted from the requirement for VAV control: |
((1. Reserved.)) | |
((2.)) 1. Zones or supply air systems where at least 75 percent of the energy for reheating or for providing warm air in mixing systems is provided from a site-recovered or site-solar energy source. | |
((3.)) 2. Zones where special humidity levels are required to satisfy process needs. | |
((4.)) 3. Zones with a peak supply air quantity of 300 cfm (142 L/s) or less and where the flow rate is less than 10 percent of the total fan system supply airflow rate. | |
((5. Zones where the volume of air to be reheated, recooled or mixed is no greater than the volume of outside air required to meet the minimum ventilation requirements of Chapter 4 of the International Mechanical Code.)) | |
4. Zones without DDC for which the volume of air that is reheated, recooled or remixed is less than the larger of the following: | |
4.1. 30 percent of the zone design peak supply rate. | |
4.2. The outdoor airflow rate required to meet the ventilation requirements of Chapter 4 of the International Mechanical Code for the zone. | |
4.3. Any higher rate that can be demonstrated, to the satisfaction of the code official, to reduce overall system annual energy usage by offsetting reheat/recool energy losses through a reduction in outdoor air intake for the system. | |
4.4. The airflow rate required to comply with applicable codes or accreditation standards, such as pressure relationships or minimum air change rates. | |
5. Zones with DDC that comply with all of the following: | |
5.1. The airflow rate in dead band between heating and cooling does not exceed the larger of the following: | |
5.1.1. 20 percent of the zone design peak supply rate. | |
5.1.2. The outdoor airflow rate required to meet the ventilation requirements of Chapter 4 of the International Mechanical Code for the zone. | |
5.1.3. Any higher rate that can be demonstrated, to the satisfaction of the code official, to reduce overall system annual energy usage by offsetting reheat/recool energy losses through a reduction in outdoor air intake for the system. | |
5.1.4. The airflow rate required to comply with applicable codes or accreditation standards, such as pressure relationships or minimum air change rates. | |
5.2. The airflow rate that is reheated, recooled, or mixed shall be less than 50 percent of the zone design peak supply rate. | |
5.3. The first stage of heating consists of modulating the zone supply air temperature setpoint up to a maximum setpoint while the airflow is maintained at the dead band flow rate. | |
5.4. The second stage of heating consists of modulating the airflow rate from the dead band flow rate up to the heating maximum flow rate. | |
6. Zones or supply air systems with thermostatic and humidistatic controls capable of operating in sequence the supply of heating and cooling energy to the zones and which are ((capable of preventing)) configured to prevent reheating, recooling, mixing or simultaneous supply of air that has been previously cooled, either mechanically or through the use of economizer systems, and air that has been previously mechanically heated. |
((C403.4.5.1)) C403.4.4.1 Single duct variable air volume (VAV) systems, terminal devices. Single duct VAV systems shall use terminal devices capable of ((reducing)) and configured to reduce the supply of primary supply air before reheating or recooling takes place.
((C403.4.5.2)) C403.4.4.2 Dual duct and mixing VAV systems, terminal devices. Systems that have one warm air duct and one cool air duct shall use terminal devices which are capable of ((reducing)) and configured to reduce the flow from one duct to a minimum before mixing of air from the other duct takes place.
((C403.4.5.3 Reserved.
C403.4.5.4)) C403.4.4.3 Multiple-zone VAV system ventilation optimization control. Multiple-zone VAV systems with direct digital control of individual zone boxed reporting to a central control panel shall have automatic controls configured to reduce outdoor air intake flow below design rates in response to changes in system ventilation efficiency (Ev) as defined by the International Mechanical Code.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. VAV systems with zonal transfer fans that recirculate air from other zones without directly mixing it with outdoor air, dual-duct dual-fan VAV systems, and VAV systems with fan-powered terminal units. |
2. Systems having exhaust air energy recovery complying with Section C403.5. | |
3. Systems where total design exhaust airflow is more than 70 percent of total design outdoor air intake flow requirements. |
C403.4.4.4 Supply-air temperature reset controls. Multiple zone HVAC systems shall include controls that automatically reset the supply-air temperature in response to representative building loads, or to outdoor air temperature. The controls shall be capable of resetting the supply air temperature at least 25 percent of the difference between the design supply-air temperature and the design room air temperature.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Systems that prevent reheating, recooling or mixing of heated and cooled supply air. |
2. Seventy-five percent of the energy for reheating is from site-recovered or site solar energy sources. | |
3. Zones with peak supply air quantities of 300 cfm (142 L/s) or less. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40346 ((Section C403.4.6—Heat recovery for service water heating.)) Reserved.
((C403.4.6 Heat recovery for service water heating. Condenser heat recovery shall be installed for heating or reheating of service hot water provided the facility operates 24 hours a day, the total installed heat capacity of water cooled systems exceeds 1,500,000 Btu/hr of heat rejection, and the design service water heating load exceeds 250,000 Btu/hr.
The required heat recovery system shall have the capacity to provide the smaller of:
1. Sixty percent of the peak heat rejection load at design conditions; or
2. The preheating required to raise the peak service hot water draw to 85°F (29°C).
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Facilities that employ condenser heat recovery for space heating or reheat purposes with a heat recovery design exceeding 30 percent of the peak water-cooled condenser load at design conditions. |
2. Facilities that provide 60 percent of their service water heating from site solar or site recovered energy or from other sources.)) |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40350 Section C403.5—((Walk-in coolers and freezers)) Energy recovery.
((C403.5 Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers. Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers shall comply with all of the following:
1. Anti-sweat heaters without anti-sweat heater controls shall have a total door rail, glass, and frame heater power draw of less than or equal to 7.1 watts per square foot of door opening for walk-in freezers, and 3.0 watts per square foot of door opening for walk-in coolers.
2. Anti-sweat heater controls shall reduce the energy use of the anti-sweat heater as a function of the relative humidity in the air outside the door or to the condensation on the inner glass pane.
3. Evaporator fan motors that are less than 1 horsepower and less than 460 volts shall use electronically commutated motors (brushless direct current motors) or 3-phase motors.
4. Condenser fan motors that are less than 1 horsepower shall use electronically commutated motors, permanent split capacitor-type motors or 3-phase motors.)) C403.5 Energy recovery.
C403.5.1 Energy recovery ventilation systems. Any system with minimum outside air requirements at design conditions greater than 5,000 cfm or any system where the system's supply airflow rate exceeds the value listed in Tables C403.5.1(1) and C403.5.1(2), based on the climate zone and percentage of outdoor airflow rate at design conditions, shall include an energy recovery system. Table C403.5.1(1) shall be used for all ventilation systems that operate less than 8,000 hours per year, and Table C403.5.1(2) shall be used for all ventilation systems that operate 8,000 hours or more per year. The energy recovery system shall have the capability to provide a change in the enthalpy of the outdoor air supply of not less than 50 percent of the difference between the outdoor air and return air enthalpies, at design conditions. Where an air economizer is required, the energy recovery system shall include a bypass or controls which permit operation of the economizer as required by Section C403.3. Where a single room or space is supplied by multiple units, the aggregate ventilation (cfm) of those units shall be used in applying this requirement. The return/exhaust air stream temperature for heat recovery device selection shall be 70°F (21°C) at 30 percent relative humidity, or as calculated by the registered design professional.
EXCEPTION: | An energy recovery ventilation system shall not be required in any of the following conditions: |
1. Where energy recovery systems are restricted per Section 514 of the International Mechanical Code to sensible energy, recovery shall comply with one of the following: | |
1.1. Kitchen exhaust systems where they comply with Section C403.2.7.1. | |
1.2. Laboratory fume hood systems where they comply with Exception 2 of Section C403.5.1. | |
1.3. Other sensible energy recovery systems with the capability to provide a change in dry bulb temperature of the outdoor air supply of not less than 50 percent of the difference between the outdoor air and the return air dry bulb temperatures, at design conditions. | |
2. Laboratory fume hood systems that include at least one of the following features and also comply with Section C403.2.7.2: | |
2.1. Variable-air-volume hood exhaust and room supply systems configured to reduce exhaust and makeup air volume to 50 percent or less of design values. | |
2.2. Direct makeup (auxiliary) air supply equal to at least 75 percent of the exhaust rate, heated no warmer than 2°F (1.1°C) above room setpoint, cooled to no cooler than 3°F (1.7°C) below room setpoint, no humidification added, and no simultaneous heating and cooling used for dehumidification control. | |
3. Systems serving spaces that are heated to less than 60°F (15.5°C) and are not cooled. | |
4. Where more than 60 percent of the outdoor air heating energy is provided from site-recovered or site solar energy. | |
5. Systems exhausting toxic, flammable, paint or corrosive fumes or dust. | |
6. Cooling energy recovery in Climate Zones 3C, 4C, 5B, 5C, 6B, 7 and 8. | |
7. Systems requiring dehumidification that employ energy recovery in series with the cooling coil. | |
8. Multiple-zone systems where the supply airflow rate exceeds the values specified in Tables C403.5.1 (1) and (2) minimum outdoor air is less than 70 percent of total supply air. | |
9. Systems serving Group R dwelling or sleeping units where the largest source of air exhausted at a single location at the building exterior is less than 25 percent of the design outdoor air flow rate. |
Table C403.5.1(1)
Energy Recovery Requirement
(Ventilation systems operating less than 8,000 hours per year)
Percent (%) Outdoor Air at Full Design Airflow Rate |
||||||||
Climate zone |
≥ 10% and < 20% |
≥ 20% and < 30% |
≥ 30% and < 40% |
≥ 40% and < 50% |
≥ 50% and < 60% |
≥ 60% and < 70% |
≥ 70% and < 80% |
≥ 80% |
Design Supply Fan Airflow Rate (cfm) |
||||||||
4C, 5B |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
≥ 5000 |
≥ 5000 |
NR = Not required. |
||||||||
Table C403.5.1(2)
Energy Recovery Requirement
(Ventilation systems operating not less than 8,000 hours per year)
Percent (%) Outdoor Air at Full Design Airflow Rate |
||||||||
Climate zone |
≥ 10% and < 20% |
≥ 20% and < 30% |
≥ 30% and < 40% |
≥ 40% and < 50% |
≥ 50% and < 60% |
≥ 60% and < 70% |
≥ 70% and < 80% |
≥ 80% |
Design Supply Fan Airflow Rate (cfm) |
||||||||
4C |
NR |
≥ 19500 |
≥ 9000 |
≥ 5000 |
≥ 4000 |
≥ 3000 |
≥ 1500 |
≥ 0 |
5B |
≥ 2500 |
≥ 2000 |
≥ 1000 |
≥ 500 |
≥ 0 |
≥ 0 |
≥ 0 |
≥ 0 |
NR = Not required. |
||||||||
C403.5.2 Condensate systems. On-site steam heating systems shall have condensate water heat recovery. On-site includes a system that is located within or adjacent to one or more buildings within the boundary of a contiguous area or campus under one ownership and which serves one or more of those buildings.
Buildings using steam generated off-site with steam heating systems which do not have condensate water recovery shall have condensate water heat recovery.
C403.5.3 Condenser heat recovery. Facilities having food service, meat or deli departments and having 500,000 Btu/h or greater of remote refrigeration condensers shall have condenser waste heat recovery from freezers and coolers and shall use the waste heat for service water heating, space heating or for dehumidification reheat. Facilities having a gross conditioned floor area of 40,000 ft2 or greater and 1,000,000 Btu/h or greater of remote refrigeration shall have condenser waste heat recovery from freezers and coolers and shall use the waste heat for service water heating, and either for space heating or for dehumidification reheat for maintaining low space humidity.
C403.5.4 Heat recovery for service water heating. Condenser heat recovery shall be installed for heating or reheating of service hot water provided the facility operates 24 hours a day, the total installed heat capacity of water cooled systems exceeds 1,500,000 Btu/hr of heat rejection, and the design service water heating load exceeds 250,000 Btu/hr.
The required heat recovery system shall have the capacity to provide the smaller of:
1. Sixty percent of the peak heat rejection load at design conditions; or
2. The preheating required to raise the peak service hot water draw to 85°F (29°C).
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Facilities that employ condenser heat recovery for space heating or reheat purposes with a heat recovery design exceeding 30 percent of the peak water-cooled condenser load at design conditions. |
2. Facilities that provide 60 percent of their service water heating from site solar or site recovered energy or from other sources. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40360 ((Section C403.6—Refrigerated warehouse coolers and freezers.)) Reserved.
((C403.6 Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers. Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers shall comply with all of the following:
1. Evaporator fan motors that are less than 1 horsepower and less than 460 volts shall use electronically commutated motors (brushless direct current motors) or 3-phase motors.
2. Condenser fan motors that are less than 1 horsepower shall use electronically commutated motors, permanent split capacitor-type motors or 3-phase motors.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40402 Section C404.2—Service water-heating equipment performance efficiency.
C404.2 Service water-heating equipment performance efficiency. Water-heating equipment and hot water storage tanks shall meet the requirements of Table C404.2. The efficiency shall be verified through certification and listed under an approved certification program, or if no certification program exists, the equipment efficiency ratings shall be supported by data furnished by the manufacturer. Water-heating equipment also intended to be used to provide space heating shall meet the applicable provisions of Table C404.2.
C404.2.1 High input-rated service water heating systems. Gas-fired water-heating equipment installed in new buildings shall be in compliance with this section. Where a singular piece of water-heating equipment serves the entire building and the input rating of the equipment is 1,000,000 Btu/h (293 kW) or greater, such equipment shall have a thermal efficiency, Et, of not less than 90 percent. Where multiple pieces of water-heating equipment serve the building and the combined input rating of the water-heating equipment is 1,000,000 Btu/h (293 kW) or greater, the combined input-capacity-weighted-average thermal efficiency, Et, shall not be less than 90 percent.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Where 25 percent of the annual service water-heating requirement is provided by site-solar or site-recovered energy, the minimum thermal efficiency requirements of this section shall not apply. |
2. The input rating of water heaters installed in individual dwelling units shall not be required to be included in the total input rating of service water-heating equipment for a building. | |
3. The input rating of water heaters with an input rating of not greater than 100,000 Btu/h (29.3 kW) shall not be required to be included in the total input rating of service water-heating equipment for a building. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-404021 Table C404.2—Minimum performance of water-heating equipment.
Table C404.2
Minimum Performance of Water-Heating Equipment
Equipment Type |
Size Category (input) |
Subcategory or Rating Condition |
Performance Requireda, b |
Test Procedure |
Storage water heaters, electric |
≤ 12 kWd |
Resistance ≥ 20 gal and ≥ 55 gal |
((0.97 - 0.00 132V, EF)) 0.96 - 0.000V, EF |
DOE 10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
≤ 12 kWd |
Heat pump ˃ 55 gal and ≥ 120 gal |
2.057 - 0.00113V, EF |
DOE 10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
|
˃ 12 kW |
Resistance |
((1.73V +155 SL, Btu/h)) (0.3 + 27/Vm,%/h |
ANSI Z21.10.3 |
|
((≤ 24 amps and ≤ 250 volts |
Heat pump |
0.93 - 0.00 132V, EF |
DOE 10 C.F.R. Part 430)) |
|
Instantaneous water heaters, electric |
All |
Resistance |
0.93 - 0.00132V, EF |
DOE 10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
Storage water heaters, gas |
≤ 75,000 Btu/h |
≥ 20 gal and ≥ 55 gal |
((0.67 - 0.0019V, EF)) 0.675 - 0.0012V, EF |
DOE 10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
≤ 75,000 Btu/h |
˃ 55 gal and ≥ 100 gal |
0.8012 - 0.00078V, EF |
||
˃ 75,000 Btu/h and ≤ 155,000 Btu/h |
< 4,000 Btu/h/gal |
80% Et (Q/((800)) 799 + ((110)) 16.6√V) SL, Btu/h |
ANSI Z21.10.3 |
|
˃ 155,000 Btu/h |
< 4,000 Btu/h/gal |
80% Et (Q/((800)) 799 + ((110)) 16.6√V) SL, Btu/h |
||
˃ 50,000 Btu/h and < 200,000 Btu/h |
≥ 4,000 (Btu/h)/gal and < 2 gal |
((0.62 - 0.00 19V, EF)) 0.82 - 0.0019V, EF |
DOE 10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
|
Instantaneous water heaters, gas |
≥ 200,000 Btu/hc |
≥ 4,000 Btu/h/gal and < 10 gal |
80% Et |
ANSI Z21.10.3 |
≥ 200,000 Btu/h |
≥ 4,000 Btu/h/gal and ≥ 10 gal |
80% Et (Q/((800)) 799 + ((110)) 16.6√V) SL, Btu/h |
||
Storage water heaters, oil |
≤ 105,000 Btu/h |
((≥ 20 gal)) ≤ 50 gal |
((0.59 - 0.0019V, EF)) 0.68 - 0.0016V, EF |
DOE 10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
˃ 105,000 Btu/h |
< 4,000 Btu/h/gal |
78% Et (Q/((800)) 799 + ((110)) 16.6√V) SL, Btu/h |
ANSI Z21.10.3 |
|
≤ 210,000 Btu/h |
≥ 4,000 Btu/h/gal and < 2 gal |
0.59 - ((0.0019)) 0.0005V, EF |
DOE 10 C.F.R. Part 430 |
|
Instantaneous water heaters, oil |
˃ 210,000 Btu/h |
≥ 4,000 Btu/h/gal and < 10 gal |
80% Et |
ANSI Z21.10.3 |
˃ 210,000 Btu/h |
≥ 4,000 Btu/h/gal and ≥ 10 gal |
78% Et (Q/((800)) 799 + ((110)) 16.6√V) SL, Btu/h |
||
Hot water supply boilers, gas and oil |
≥ 300,000 Btu/h and < 12,500,000 Btu/h |
≥ 4,000 Btu/h/gal and < 10 gal |
80% Et |
ANSI Z21.10.3 |
Hot water supply boilers, gas |
≥ 300,000 Btu/h and < 12,500,000 Btu/h |
≥ 4,000 Btu/h/gal and ≥ 10 gal |
80% Et (Q/((800)) 799 + ((110)) 16.6√V) SL, Btu/h |
|
Hot water supply boilers, oil |
≥ 300,000 Btu/h and < 12,500,000 Btu/h |
≥ 4,000 Btu/h/gal and ˃ 10 gal |
78% Et (Q/((800)) 799 + ((110)) 16.6√V) SL, Btu/h |
|
Pool heaters, gas and oil |
All |
— |
78% Et |
ASHRAE 146 |
Heat pump pool heaters |
All |
— |
4.0 COP |
AHRI 1160 |
Unfired storage tanks |
All |
— |
Minimum insulation requirement R-12.5 (h • ft2 • °F)/Btu |
(none) |
For SI: | °C = [(°F) - 32]/1.8, 1 British thermal unit per hour = 0.2931 W, 1 gallon = 3.785 L, 1 British thermal unit per hour per gallon = 0.078 W/L. |
a | Energy factor (EF) and thermal efficiency (Et) are minimum requirements. In the EF equation, V is the rated volume in gallons. |
b | Standby loss (SL) is the maximum Btu/h based on a nominal 70°F temperature difference between stored water and ambient requirements. In the SL equation, Q is the nameplate input rate in Btu/h. In the SL equation for electric water heaters, V is the rated volume in gallons and Vm is the measured volume in gallons. In the SL equation for oil and gas water heaters and boilers, V is the rated volume in gallons. |
c | Instantaneous water heaters with input rates below 200,000 Btu/h ((must)) shall comply with these requirements if the water heater is designed to heat water to temperatures 180°F or higher. |
d | Electric water heaters with an input rating of 12 kW (40,950 Btu/h) or less that are designed to heat water to temperatures of 180°F or greater shall comply with the requirements for electric water heaters that have an input rating greater than 12 kW (40,950 Btu/h). |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40403 Section C404.3—((Temperature controls)) Efficient heated water supply piping.
((C404.3 Temperature controls. Service water-heating equipment shall be provided with controls to allow a setpoint of 110°F (43°C) for equipment serving dwelling units and 90°F (32°C) for equipment serving other occupancies. The outlet temperature of lavatories in public facility rest rooms shall be limited to 110°F (43°C).)) C404.3 Efficient heated water supply piping. Heated water supply piping shall be in accordance with Section C404.3.1 or C404.3.2. The flow rate through 1/4-inch (6.4 mm) piping shall be not greater than 0.5 gpm (1.9 L/m). The flow rate through 5/16-inch (7.9 mm) piping shall be not greater than 1 gpm (3.8 L/m). The flow rate through 3/8-inch (9.5 mm) piping shall be not greater than 1.5 gpm (5.7 L/m). Water heaters, circulating water systems and heat trace temperature maintenance systems shall be considered sources of heated water.
C404.3.1 Maximum allowable pipe length method. The maximum allowable piping length from the nearest source of heater water to the termination of the fixture supply pipe shall be in accordance with the following. Where the piping contains more than one size of pipe, the largest size of pipe within the piping shall be used for determining the maximum allowable length of the piping in Table C404.3.1.
1. For a public lavatory faucet, use the "Public lavatory faucets" column in Table C404.3.1.
2. For all other plumbing fixtures and plumbing appliances, use the "Other fixtures and appliances" column in Table C404.6.1.
Table C404.6.1
Piping Volume and Maximum Piping Lengths
Nominal Pipe Size (inches) |
Volume (liquid ounces per foot length) |
Maximum Piping Length (feet) |
|
Public lavatory faucets |
Other fixtures and appliances |
||
1/4 |
0.33 |
6 |
50 |
5/16 |
0.5 |
4 |
50 |
3/8 |
0.75 |
3 |
50 |
1/2 |
1.5 |
2 |
43 |
5/8 |
2 |
1 |
32 |
3/4 |
3 |
0.5 |
21 |
7/8 |
4 |
0.5 |
16 |
1 |
5 |
0.5 |
13 |
1 1/4 |
8 |
0.5 |
8 |
1 1/2 |
11 |
0.5 |
6 |
2 or larger |
18 |
0.5 |
4 |
C404.3.2 Maximum allowable pipe volume method. The water volume in the piping shall be calculated in accordance with Section C404.3.2.1.
The volume from the nearest source of heated water to the termination of the fixture supply pipe shall be as follows:
1. For a public lavatory faucet: Not more than 2 ounces (0.06 L).
2. For other plumbing fixtures or plumbing appliances; not more than 0.5 gallon (1.89 L).
C404.3.2.1 Water volume determination. The volume shall be the sum of the internal volumes of pipe, fittings, valves, meters and manifolds between the nearest source of heated water and the termination of the fixture supply pipe. The volume in the piping shall be determined from the "Volume" column in Table C404.3.1. The volume contained within fixture shutoff valves, within flexible water supply connectors to a fixture fitting and within a fixture fitting shall not be included in the water volume determination. Where heated water is supplied by a recirculating system or heat-traced piping, the volume shall include the portion of the fitting on the branch pipe that supplies water to the fixture.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40406 Section C404.6—Pipe insulation.
((C404.6 Pipe insulation. For automatic-circulating hot water and heat-traced systems, piping shall be insulated with not less than 1 inch (25 mm) of insulation having a conductivity not exceeding 0.27 Btu per inch/h × ft2 × °F (1.53 W per 25 mm/m2 × K). The first 8 feet (2438 mm) of piping in nonhot-water-supply temperature maintenance systems served by equipment without integral heat traps shall be insulated with 0.5 inch (12.7 mm) of material having a conductivity not exceeding 0.27 Btu per inch/h × ft2 × °F (1.53 W per 25 mm/m2 × K).
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Heat-traced piping systems shall meet the insulation thickness requirements per the manufacturer's installation instructions. Untraced piping within a heat traced system shall be insulated with not less than 1 inch (25 mm) of insulation having a conductivity not exceeding 0.27 Btu per inch/h × ft2 × °F (1.53 W per 25 mm/m2 × K). |
2. Hot water piping that is part of the final pipe run to the plumbing fixture and is not part of the automatic-circulating hot water recirculation path is not required to meet the minimum insulation requirements of C404.6.)) |
C404.6 Insulation of piping. Piping from a water heater to the termination of the heated water fixture supply pipe shall be insulated in accordance with Table C403.2.9. On both the inlet and outlet piping of a storage water heater or heated water storage tank, the piping to a heat trap or the first 8 feet (2438 mm) of piping, whichever is less, shall be insulated. Piping that is heat traced shall be insulated in accordance with Table C403.2.9 or the heat trace manufacturer's instructions. Tubular pipe insulation shall be installed in accordance with the insulation manufacturer's instructions. Pipe insulation shall be continuous except where the piping passes through a framing member. The minimum insulation thickness requirements of this section shall not supersede any greater insulation thickness requirements necessary for the protection of piping from freezing temperatures or the protection of personnel against external surface temperatures on the insulation.
EXCEPTION: | Tubular pipe insulation shall not be required on the following: |
1. The tubing from the connection at the termination of the fixture supply piping to a plumbing fixture or plumbing appliance. | |
2. Valves, pumps, strainers and threaded unions in piping that is 1 inch (25 mm) or less in nominal diameter. | |
3. Piping from user-controlled shower and bath mixing valves to the water outlets. | |
4. Cold-water piping of a demand recirculation water system. | |
5. Tubing from a hot drinking-water heating unit to the water outlet. | |
6. Piping at locations where a vertical support of the piping is installed. | |
7. Piping surrounded by building insulation with a thermal resistance (R-value) of not less than R-3. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40407 Section C404.7—((Hot water system controls)) Heated-water circulating and temperature maintenance systems.
((C404.7 Hot water system controls. Circulating hot water system pumps or heat trace shall be arranged to be turned off either automatically or manually when there is limited hot water demand. Ready access shall be provided to the operating controls.)) C404.7 Heated-water circulating and temperature maintenance systems. Heated-water circulation systems shall be in accordance with Section C404.7.1. Heat trace temperature maintenance systems shall be in accordance with Section C404.7.2. Controls for hot water storage shall be in accordance with Section C404.7.3. Automatic controls, temperature sensors and pumps shall be accessible. Manual controls shall be readily accessible.
C404.7.1 Circulation systems. Heated-water circulation systems shall be provided with a circulation pump. The system return pipe shall be a dedicated return pipe or a cold water supply pipe. Gravity and thermo-syphon circulation systems shall be prohibited. Controls for circulating hot water system pumps shall start the pump based on the identification of a demand for hot water within the occupancy. The controls shall automatically turn off the pump when the water in the circulation loop is at the desired temperature and when there is no demand for hot water.
C404.7.2 Heat trace systems. Electric heat trace systems shall comply with IEEE 515.1. Controls for such systems shall be able to automatically adjust the energy input to the heat tracing to maintain the desired water temperature in the piping in accordance with the times when heated water is used in the occupancy. Heat trace shall be arranged to be turned off automatically when there is no hot water demand.
C404.7.3 Controls for hot water storage. The controls on pumps that circulate water between a water heater and a heated-water storage tank shall limit operation of the pump from heating cycle startup to not greater than 5 minutes after the end of the cycle.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40408 Section C404.8—((Shut-off controls)) Demand recirculation controls.
((C404.8 Shut-off controls. Systems designed to maintain usage temperatures in hot water pipes, such as circulating hot water systems or heat traced pipes, shall be equipped with automatic time switches or other controls to turn off the system during periods of nonuse.)) C404.8 Demand recirculation controls. A water distribution system having one or more recirculation pumps that pump water from a heated-water supply pipe back to the heated-water source through a cold-water supply pipe shall be a demand recirculation water system. Pumps shall have controls that comply with both of the following:
1. The control shall start the pump upon receiving a signal from the action of a user of a fixture or appliance, sensing the presence of a user of a fixture or sensing the flow of hot or tempered water to a fixture fitting or appliance.
2. The control shall limit the temperature of the water entering the cold-water piping to 104°F (40°C).
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-404091 Section C404.10—Drain water heat recovery units.
C404.10 Drain water heat recovery units. Drain water heat recovery units shall comply with CSA B55.2. Potable waterside pressure loss shall be less than 10 psi (69 kPa) at maximum design flow. For Group R occupancies, the efficiency of drain water heat recovery unit efficiency shall be in accordance with CSA B55.1.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40410 Section ((C404.10)) C404.11—Pools and ((in-ground)) spas.
((C404.10 Pools and in-ground permanently installed spas)) C404.11 Energy consumption of pools and permanent spas (mandatory). ((Pools and in-ground permanently installed spas shall comply with Sections C404.10.1 through C404.10.4)) The energy consumption of pools and permanent spas shall be controlled by the requirements in Sections C404.11.1 through C404.11.4.
((C404.10.1)) C404.11.1 Heaters. Heat pump pool heaters shall have a minimum COP of 4.0 determined in accordance with ASHRAE Standard 146. Other pool heating equipment shall comply with the applicable efficiencies in Section ((C404.2.3)) C404.2.
((All heaters shall be equipped with a readily accessible on-off switch that is mounted outside of the heater to allow shutting off the heater without adjusting the thermostat setting.)) The electric power to all heaters shall be controlled by a readily accessible on-off switch that is an integral part of the heater, mounted on the exterior of the heater, or external to and within 3 feet of the heater. Operation of such switch shall not change the setting of the heater thermostat. Such switches shall be in addition to a circuit breaker for the power to the heater. Gas-fired heaters shall not be equipped with constant burning pilot lights.
((C404.10.2)) C404.11.2 Time switches. Time switches or other control method that can automatically turn off and on heaters and pump((s)) motors according to a preset schedule shall be installed ((on all)) for heaters and pump((s)) motors. Heaters((, pumps)) and pump motors that have built-in ((timers)) time switches shall be ((deemed)) in compliance with this ((requirement)) section.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Where public health standards require 24-hour pump operation. |
2. ((Where pumps are required to)) Pumps that operate solar- and waste-heat-recovery pool heating systems. |
((C404.10.3)) C404.11.3 Covers. Heated pools and ((in-ground permanently installed)) permanent spas shall be provided with a vapor-retardant cover on or at the water surface. Pools heated to more than 90°F shall have a pool cover with a minimum insulation value of R-12, and the sides and bottom of the pool shall also have a minimum insulation value of R-12.
((C404.10.4)) C404.11.4 Heat recovery. Heated indoor swimming pools, spas or hot tubs with water surface area greater than 200 square feet shall provide for energy conservation by an exhaust air heat recovery system that heats ventilation air, pool water or domestic hot water. The heat recovery system shall be ((capable of decreasing)) configured to decrease the exhaust air temperature at design heating conditions (80°F indoor) by 36°F (10°C) ((in Climate Zones 4C and 5B and 48°F (26.7°C) in Climate Zone 6B)).
EXCEPTION: | Pools, spas or hot tubs that include system(s) that provide equivalent recovered energy on an annual basis through one of the following methods: |
1. Renewable energy; | |
2. Dehumidification heat recovery; | |
3. Waste heat recovery; or | |
4. A combination of these system sources capable of ((providing)) and configured to provided at least 70 percent of the heating energy required over an operating season. |
C404.12 Energy consumption of portable spas (mandatory). The energy consumption of electric-powered portable spas shall be controlled by the requirements of APSP 14.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40413 Section C404.13—Service water-heating system commissioning and completion requirements.
C404.13 Service water-heating system commissioning and completion requirements. Service water-heating systems, swimming pool water-heating systems, spa water-heating systems and the controls for those systems shall be commissioned and completed in accordance with Section C408.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40501 Section C405.1—General.
C405.1 General (mandatory). This section covers lighting system controls, ((the connection of ballasts,)) the maximum lighting power for interior applications, electrical energy consumption, ((minimum acceptable lighting equipment for exterior applications)) vertical and horizontal transportation systems, and minimum efficiencies for motors and transformers.
EXCEPTION: | Dwelling units within commercial buildings shall not be required to comply with Sections C405.2 through ((C405.5)) C405.6 provided that ((a minimum of 75 percent of the lamps in permanently installed light fixtures shall be high efficacy lamps)) they comply with Section R404.1. |
((Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers shall comply with C405.10. Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers shall comply with C405.11.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40502 Section C405.2—Electrical power and lighting systems.
C405.2 Lighting controls (mandatory). Lighting systems shall be provided with controls as specified in Sections C405.2.1((, C405.2.2, C405.2.3, C405.2.4 and C405.2.5)) through C405.2.8.
EXCEPTION: | ((Industrial or manufacturing process areas, as may be required for production and safety.)) Except for specific application controls required by Section C405.2.5: |
1. Areas designated as security or emergency areas that are required to be continuously lighted. | |
2. Interior exit stairways, interior exit ramps, and exit passageways. | |
3. Emergency egress lighting that is normally off. | |
4. Industrial or manufacturing process areas, as may be required for production and safety. | |
5. Luminaire-level lighting controls that control interior lighting. The LLLC luminaire shall be independently configured to: | |
5.1. Monitor occupant activity to brighten or dim its lighting when occupied or unoccupied, respectively. | |
5.2. Monitor ambient light (both electric light and daylight) and brighten or dim electric light to maintain desired light level. | |
5.3. Configuration and reconfiguration of performance parameters, including bright and dim setpoints, time-outs, dimming fade rates, sensor sensitivity adjustments, and wireless zoning configurations, for each control strategy. | |
5.4. Meet the operational and commissioning requirements of Sections C405.2.1, C405.2.2, C405.2.3, C405.2.4 and C408. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405021 Section C405.2.1—((Manual lighting)) Occupant sensor controls.
((C405.2.1 Manual lighting controls. All buildings shall include manual lighting controls that meet the requirements of Sections C405.2.1.1 and C405.2.1.2.
C405.2.1.1 Interior lighting controls. Each area enclosed by walls or floor-to-ceiling partitions shall have at least one manual control for the lighting serving that area. The required controls shall be located within the area served by the controls or be a remote switch that identifies the lights served and indicates their status.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Areas designated as security or emergency areas that need to be continuously lighted. |
2. Lighting in stairways or corridors that are elements of the means of egress. |
C405.2.1.2 Light reduction controls. Each area that is required to have a manual control shall also allow the occupant to reduce the connected lighting load in a reasonably uniform illumination pattern by at least 50 percent. Lighting reduction shall be achieved by one of the following or other approved method:
1. Controlling all lamps or luminaires;
2. Dual switching of alternate rows of luminaires, alternate luminaires or alternate lamps;
3. Switching the middle lamp luminaires independently of the outer lamps; or
4. Switching each luminaire or each lamp.
EXCEPTION: | Light reduction controls need not be provided in the following areas and spaces: |
1. Areas that have only one luminaire, with rated power less than 100 watts. | |
2. Areas that are controlled by an occupant-sensing device. | |
3. Corridors, equipment rooms, storerooms, restrooms, public lobbies, electrical or mechanical rooms. | |
4. Sleeping unit (see Section C405.2.3). | |
5. Spaces that use less than 0.6 watts per square foot (6.5 W/m2). | |
6. Daylight spaces complying with Section C405.2.2.3.2.)) |
C405.2.1 Occupant sensor controls. Occupant sensor controls shall be installed to control lights in the following space types:
1. Classrooms/lecture/training rooms.
2. Conference/meeting/multipurpose rooms.
3. Copy/print rooms.
4. Lounges.
5. Employee lunch and break rooms.
6. Private offices.
7. Restrooms.
8. Storage rooms.
9. Janitorial closets.
10. Locker rooms.
11. Other spaces 300 square feet (28 m2) or less that are enclosed by floor-to-ceiling height partitions.
12. Warehouses.
C405.2.1.1 Occupant sensor control function. Occupant sensor controls shall comply with the following:
1. Automatically turn off lights within 30 minutes of all occupants leaving the space.
2. Be manual on or controlled to automatically turn the lighting on to not more than 50 percent power.
EXCEPTION: | Full automatic-on controls shall be permitted to control lighting in public corridors, stairways, restrooms, primary building entrances areas and lobbies, and areas where manual-on operation would endanger the safety or security of the room or building occupants. |
3. Shall incorporate a manual control to allow occupants to turn lights off.
C405.2.1.2 Occupant sensor control function in warehouses. In warehouses, the lighting in aisleways and open areas shall be controlled with occupancy sensors that automatically reduce lighting power by not less than 50 percent when the areas are unoccupied. The occupancy sensor shall control lighting in each aisleway independently, and shall not control lighting beyond the aisleway being controlled by the sensor.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405022 Section C405.2.2—((Additional lighting)) Time switch controls.
C405.2.2 ((Additional lighting)) Time switch controls. Each area of the building that is ((required to have a manual control shall also have controls that meet the requirements of Sections C405.2.2.1, C405.2.2.2 and C405.2.2.3)) not provided with occupant sensor controls complying with Section C405.2.1.1 shall be provided with time switch controls complying with Section C405.2.2.1.
EXCEPTION: | ((Additional lighting controls need not be provided in the following spaces:)) Where a manual control provides light reduction in accordance with Section C405.2.2.2, automatic controls shall not be required for the following: |
1. Sleeping units. | |
2. Spaces where patient care is directly provided. | |
3. Spaces where an automatic shutoff would endanger occupant safety or security. | |
4. Lighting intended for continuous operation. | |
5. Shop and laboratory classrooms. |
C405.2.2.1 ((Automatic)) Time switch control ((devices)) function. ((Automatic time switch controls shall be installed to control lighting in all areas of the building. Automatic time switches shall have a minimum 7 day clock and be capable of being set for 7 different day types per week and incorporate an automatic holiday "shut-off" feature, which turns off all loads for at least 24 hours and then resumes normally scheduled operations. Automatic time switches shall also have program back-up capabilities, which prevent the loss of program and time settings for at least 10 hours, if power is interrupted.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Emergency egress lighting does not need to be controlled by an automatic time switch. |
2. Lighting in spaces controlled by occupancy sensors does not need to be controlled by automatic time switch controls. |
The automatic time switch control device shall include an override switching device that complies with the following:
1. The override switch shall be in a readily accessible location;
2. The override switch shall be located where the lights controlled by the switch are visible; or the switch shall provide a mechanism which announces the area controlled by the switch;
3. The override switch shall permit manual operation;
4. The override switch, when initiated, shall permit the controlled lighting to remain on for a maximum of 2 hours; and
5. Any individual override switch shall control the lighting for a maximum area of 5,000 square feet (465 m2).
EXCEPTION: | Within malls, arcades, auditoriums, single tenant retail spaces, industrial facilities and arenas: |
1. The time limit shall be permitted to exceed 2 hours provided the override switch is a captive key device; and | |
2. The area controlled by the override switch is permitted to exceed 5,000 square feet (465 m2), but shall not exceed 20,000 square feet (1860 m2). |
C405.2.2.2 Occupancy sensors. Occupancy sensors shall be installed in all classrooms, conference/meeting rooms, employee lunch and break rooms, private offices, restrooms, warehouse spaces, storage rooms and janitorial closets, and other spaces 300 square feet (28 m2) or less enclosed by floor-to-ceiling height partitions. These automatic control devices shall be installed to automatically turn off lights within 30 minutes of all occupants leaving the space, and shall either be manual on or shall be controlled to automatically turn the lighting on to not more than 50 percent power.
EXCEPTION: | Full automatic-on controls shall be permitted to control lighting in public corridors, stairways, restrooms, primary building entrance areas and lobbies, and areas where manual-on operation would endanger the safety or security of the room or building occupants. |
C405.2.2.3 Daylight zone control. Daylight zones shall be designed such that lights in the daylight zone are controlled independently of general area lighting and are controlled in accordance with Section C405.2.2.3.2. Each daylight control zone shall not exceed 2,500 square feet (232 m2). Contiguous daylight zones adjacent to vertical fenestration are allowed to be controlled by a single controlling device provided that they do not include zones facing more than two adjacent cardinal orientations (i.e., north, east, south, west). The primary daylight zone shall be controlled separately from the secondary daylight zone. Daylight zones under skylights more than 15 feet (4572 mm) from the perimeter shall be controlled separately from daylight zones adjacent to vertical fenestration. Controls shall:
1. Control only luminaires within the daylit area.
2. Incorporate time-delay circuits to prevent cycling of light level changes of less than three minutes.
EXCEPTION: | Daylight zones enclosed by walls or ceiling height partitions and containing two or fewer light fixtures are not required to have a separate switch for general area lighting. |
C405.2.2.3.1 Reserved.
C405.2.2.3.2 Automatic daylighting controls. Setpoint and other controls for calibrating the lighting control device shall be readily accessible.
Daylighting controls device shall be capable of automatically reducing the lighting power in response to available daylight by either one of the following methods:
1. Continuous dimming using dimming ballasts and daylight-sensing automatic controls that are capable of reducing the power of general lighting in the daylit zone continuously to less than 20 percent of rated power at maximum light output.
2. Stepped dimming using multi-level switching and daylight-sensing controls that are capable of reducing lighting power automatically. The system shall provide a minimum of two control channels per zone and be installed in a manner such that at least one control step is between 50 percent and 70 percent of design lighting power and another control step is no greater than 35 percent of design power, and the system is capable of automatically turning the system off.
C405.2.2.3.3 Reserved.)) Each space provided with time switch controls shall also be provided with a manual control for light reduction in accordance with Section C405.2.2.2. Time switch controls shall comply with the following:
1. Have a minimum 7 day clock.
2. Be capable of being set for 7 different day types per week.
3. Incorporate an automatic holiday "shut-off" feature, which turns off all controlled lighting loads for at least 24 hours and then resumes normally scheduled operations.
4. Have program back-up capabilities, which prevent the loss of program and time settings for at least 10 hours, if power is interrupted.
5. Include an override switching device that complies with the following:
5.1. A manual control.
5.2. The override switch, when initiated, shall permit the controlled lighting to remain on for not more than 2 hours.
5.3. Any individual override switch shall control the lighting for an area not larger than 5,000 square feet (465 m2).
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Within malls, arcades, auditoriums, single tenant retail spaces, industrial facilities and arenas: |
1.1. The time limit shall be permitted to be greater than 2 hours provided the override switch is a captive key device. | |
1.2. The area controlled by the override switch is permitted to be greater than 5,000 square feet (465 m2), but shall not exceed 20,000 square feet (1860 m2). | |
2. Where provided with manual control, the following areas are not required to have light reduction control: | |
2.1. Spaces that have only one luminaire with a rated power of less than 100 watts. | |
2.2. Spaces that use less than 0.6 watts per square foot (6.5 W/m2). | |
2.3. Corridors, equipment rooms, public lobbies, electrical or mechanical rooms. |
C405.2.2.2 Light reduction controls. Spaces required to have light-reduction controls shall have a manual control that allows the occupant to reduce the connected lighting load in a reasonably uniform illumination pattern by at least 50 percent. Lighting reductions shall be achieved by one of the following approved methods:
1. Controlling all lamps or luminaires.
2. Dual switching of alternate rows of luminaires, alternate luminaires or alternate lamps.
3. Switching the middle lamp luminaires independently of the outer lamps.
4. Switching each luminaire or each lamp.
EXCEPTION: | Light reduction controls are not required in daylight zones with daylight responsive controls complying with Section C405.2.4. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405023 Section C405.2.3—((Specific application)) Manual controls.
C405.2.3 ((Specific application)) Manual controls. ((Specific application controls shall be provided for the following:
1. Display and accent light shall be controlled by a dedicated control which is independent of the controls for other lighting within the room or space.
2. Lighting in cases used for display case purposes shall be controlled by a dedicated control which is independent of the controls for other lighting within the room or space.
3. Hotel and motel sleeping units and guest suites shall have a master control device at the main room entry that controls all permanently installed luminaires and switched receptacles. Where a hotel/motel includes more than 50 rooms, controls shall be automatic to ensure all power to the lights and switched outlets are turned off when the occupant is not in the room.
4. Supplemental task lighting, including permanently installed under-shelf or under-cabinet lighting, shall be automatically shut off whenever that space is unoccupied and shall have a control device integral to the luminaires or be controlled by a wall-mounted control device provided the control device is readily accessible.
5. Lighting for nonvisual applications, such as plant growth and food warming, shall be controlled by a dedicated control which is independent of the controls for other lighting within the room or space.
6. Lighting equipment that is for sale or for demonstrations in lighting education shall be controlled by a dedicated control which is independent of the controls for other lighting within the room or space.
7. Luminaires serving the exit access and providing means of egress illumination required by Section 1006.1 of the International Building Code, including luminaires that function as both normal and emergency means of egress illumination shall be controlled by a combination of listed emergency relay and occupancy sensors, or signal from another building control system, that automatically shuts off the lighting when the areas served by that illumination are unoccupied.
EXCEPTION: | Means of egress illumination serving the exit access that does not exceed 0.05 watts per square foot of building area is exempt from this requirement.)) |
Manual controls for lights shall comply with the following:
1. Shall be readily accessible to occupants.
2. Shall be located where the controlled lights are visible, or shall identify the area served by the lights and indicate their status.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405024 Section C405.2.4—((Exterior lighting)) Daylight responsive controls.
C405.2.4 ((Exterior lighting)) Daylight responsive controls. ((Lighting not designated for dusk-to-dawn operation shall be controlled by either a combination of a photosensor and a time switch, or an astronomical time switch. Lighting designated for dusk-to-dawn operation shall be controlled by an astronomical time switch or photosensor. All time switches shall be capable of retaining programming and the time setting during loss of power for a period of at least 10 hours.)) Daylight responsive controls complying with Section C405.2.3.1 shall be provided to control the lighting within daylight zones in the following spaces:
1. Sidelight daylight zones as defined in Section C405.2.4.2 with more than two general lighting fixtures within the primary and secondary sidelight daylight zones.
2. Toplight daylight zones as defined in Section C405.2.4.3 with more than two general lighting fixtures within the daylight zone.
EXCEPTION: | Daylight responsive controls are not required for the following: |
1. Spaces in health care facilities where patient care is directly provided. | |
2. Dwelling units and sleeping units. | |
3. Lighting that is required to have specific application control in accordance with Section C405.2.4. | |
4. Sidelight daylight zones on the first floor above grade in Group A-2 and Group M occupancies. | |
5. Daylight zones where the total proposed lighting power density is less than 35 percent of the lighting power allowance per Section C405.4.2. |
C405.2.4.1 Daylight responsive controls function. Where required, daylight responsive controls shall be provided within each space for control of lights in that space and shall comply with all of the following:
1. Lights in primary sidelight daylight zones shall be controlled independently of lights in secondary sidelight daylight zones in accordance with Section C405.2.4.2.
EXCEPTION: | Spaces enclosed by walls or ceiling height partitions with no more than three general lighting fixtures may have combined daylight zone control of primary and secondary daylight zones provided uniform illumination can be achieved. |
2. Lights in toplight daylight zones in accordance with Section C405.2.4.3 shall be controlled independently of lights in sidelight daylight zones in accordance with Section C405.2.4.2.
3. Daylight responsive controls within each space shall be configured so that they can be calibrated from within that space by authorized personnel.
4. Calibration mechanisms shall be readily accessible.
5. Daylight responsive controls shall be configured to completely shut off all controlled lights in that zone.
6. Lights in sidelight daylight zones in accordance with Section C405.2.4.2 facing different cardinal orientations (i.e., within 45 degrees of due north, east, south, west) shall be controlled independently of each other.
EXCEPTION: | Up to 150 watts of lighting in each space is permitted to be controlled together with lighting in a daylight zone facing a different cardinal orientation. |
7. Incorporate time-delay circuits to prevent cycling of light level changes of less than three minutes.
8. The maximum area a single daylight responsive control device serves shall not exceed 2,500 square feet (232 m2).
C405.2.4.1.1 Dimming. Daylight responsive controls shall be capable of automatically reducing the power of general lighting in the daylight zone in response to available daylight, while maintaining uniform illumination in the space through one of the following methods:
1. Continuous dimming using dimming ballasts/dimming drivers and daylight-sensing controls. The system shall reduce lighting power continuously to less than 15 percent of rated power at maximum light output.
2. Stepped dimming using multi-level switching and daylight-sensing controls. The system shall provide a minimum of two steps of uniform illumination between 0 percent and 100 percent of rated power at maximum light output. Each step shall be in equal increments of power, plus or minus 10 percent.
General lighting within daylight zones in offices, classrooms, laboratories and library reading rooms shall use the continuous dimming method. Stepped dimming is not allowed as a method of daylight zone control in these spaces.
C405.2.4.2 Sidelight daylight zone. The sidelight daylight zone is the floor area adjacent to vertical fenestration which complies with the following:
1. Where the fenestration is located in a wall, the sidelight daylight zone includes the primary and secondary daylight zones. The primary daylight zone shall extend laterally to the nearest full height wall, or up to 1.0 times the height from the floor to the top of the fenestration, and longitudinally from the edge of the fenestration to the nearest full height wall, or up to 2 feet (610 mm), whichever is less, as indicated in Figure C405.2.4.2(1). The secondary daylight zone begins at the edge of the primary daylight zone and extends laterally to the nearest full height wall, or up to 2.0 times the height from the floor to the top of the fenestration, whichever is less, as indicated in Figure C405.2.4.2(1).
2. Where the fenestration is located in a rooftop monitor, the sidelight daylight zone shall extend laterally to the nearest obstruction that is taller than 0.7 times the ceiling height, or up to 1.0 times the height from the floor to the bottom of the fenestration, whichever is less, and longitudinally from the edge of the fenestration to the nearest obstruction that is taller than 0.7 times the ceiling height, or up to 0.25 times the height from the floor to the bottom of the fenestration, whichever is less, as indicated in Figures C405.2.4.2(2) and C405.2.4.2(3).
3. Where clerestory fenestration is located in a wall, the sidelight daylight zone includes a lateral area twice the depth of the clerestory fenestration height, projected upon the floor at a 45 degree angle from the center of the clerestory fenestration. The longitudinal width of the daylight zone is calculated the same as for fenestration located in a wall. Where the 45 degree angle is interrupted by an obstruction greater than 0.7 times the ceiling height, the daylight zone shall remain the same lateral area but be located between the clerestory and the obstruction, as indicated in Figure C405.2.4.2(4).
4. If the rough opening area of a vertical fenestration assembly is less than 10 percent of the calculated primary daylight zone area for this fenestration, it does not qualify as a daylight zone.
5. Where located in existing buildings, the visible transmittance of the fenestration is no less than 0.20.
6. In parking garages with floor area adjacent to perimeter wall openings, the daylight zone shall include the area within 20 feet of any portion of a perimeter wall that has a net opening to wall ratio of at least 40 percent.
Figure C405.2.4.2(1)
Daylight Zone Adjacent to Fenestration in a Wall
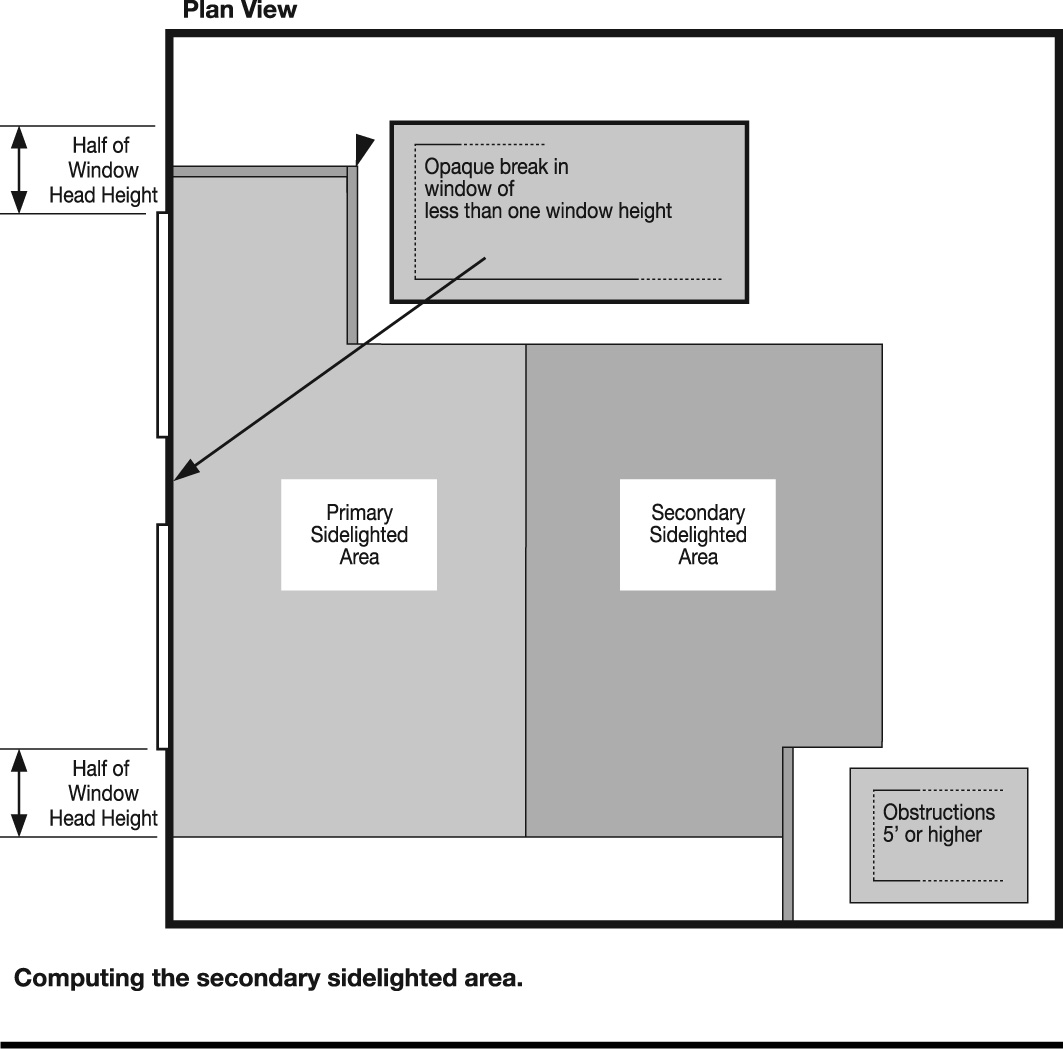 |
Figure C405.2.4.2(2)
Daylight Zone Under a Rooftop Monitor
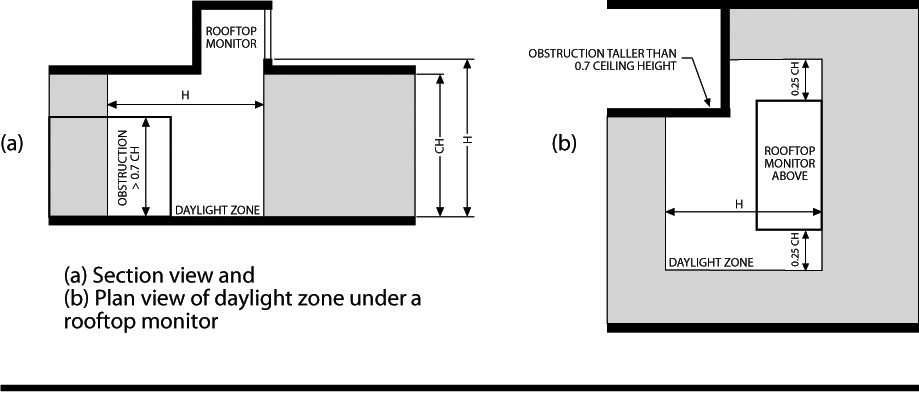 |
Figure C405.2.4.2(3)
Daylight Zone Under a Sloped Rooftop Monitor
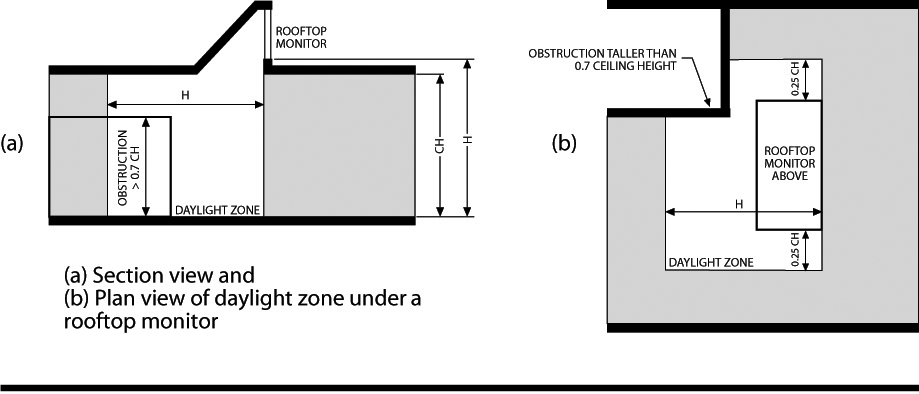 |
Figure C405.2.4.2(4)
Daylight Zone Adjacent to Clerestory Fenestration in a Wall
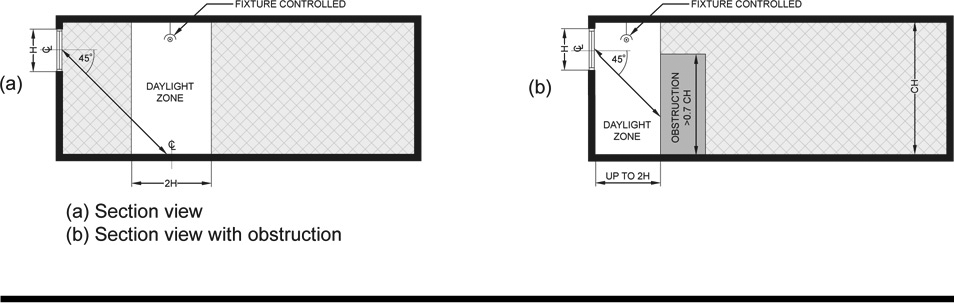 |
C405.2.4.3 Toplight daylight zone. The toplight daylight zone is the floor area underneath a roof fenestration assembly which complies with the following:
1. The toplight daylight zone shall extend laterally and longitudinally beyond the edge of the roof fenestration assembly to the nearest obstruction that is taller than 0.7 times the ceiling height, or up to 0.7 times the ceiling height, whichever is less, as indicated in Figure C405.2.4.3(1).
2. Where toplight daylight zones overlap with sidelight daylight zones, lights within the overlapping area shall be assigned to the toplight daylight zone.
3. Where located in existing buildings, the product of the visible transmittance of the roof fenestration assembly and the area of the rough opening of the roof fenestration assembly, divided by the area of the daylight zone is no less than 0.008.
4. Where located under atrium fenestration, the daylight zone shall include the bottom floor area directly beneath the atrium fenestration, and the top floor directly under the atrium fenestration, as indicated in Figure C405.2.4.3(2). The daylight zone area at the top floor is calculated the same as for a toplight daylight zone. Intermediate levels below the top floor that are not directly beneath the atrium are not included.
Figure C405.2.4.3(1)
Daylight Zone Under a Rooftop Fenestration Assembly
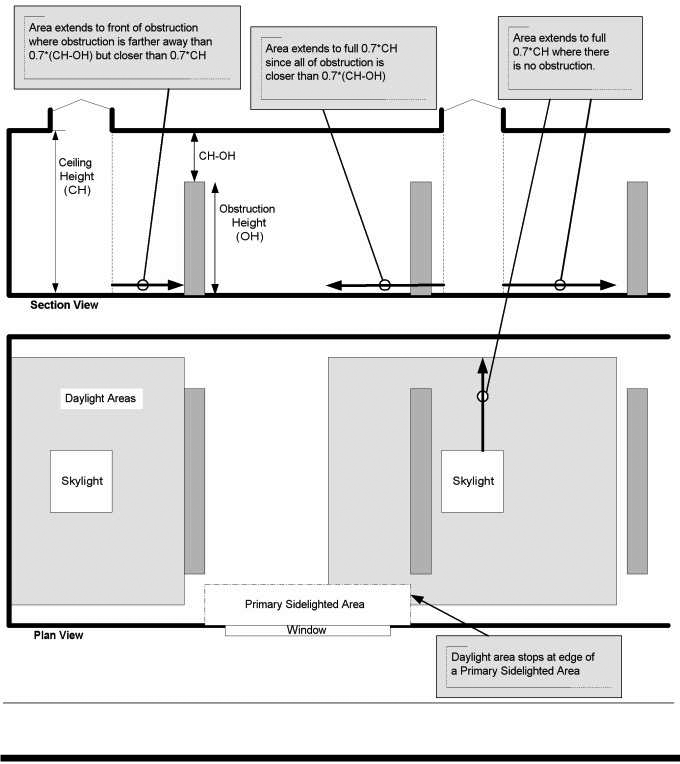 |
Figure C405.2.4.3(2)
Daylight Zone Under Atrium Fenestration
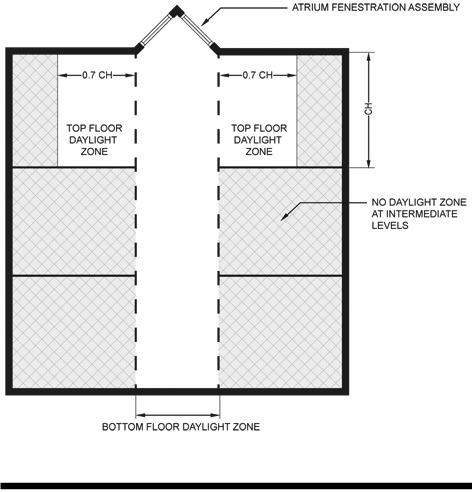 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405025 Section C405.2.5—((Area)) Additional lighting controls.
C405.2.5 ((Area)) Additional lighting controls. ((The maximum lighting power that may be controlled from a single switch or automatic control shall not exceed that which is provided by a 20 ampere circuit loaded to not more than 80 percent. A master control may be installed provided the individual switches retain their capability to function independently. Circuit breakers may not be used as the sole means of switching.
EXCEPTION: | Areas less than 5 percent of the building footprint for footprints over 100,000 ft2.)) |
Specific application lighting controls shall be provided with controls, in addition to controls required by other sections, for the following:
1. Display and accent light shall be controlled by a dedicated control which is independent of the controls for other lighting within the room or space.
2. Lighting in cases used for display case purposes shall be controlled by a dedicated control which is independent of the controls for other lighting within the room or space.
3. Hotel and motel sleeping units and guest suites shall have control device(s) configured to automatically switch off all installed luminaires and switched receptacles within 20 minutes after all occupants leave the room.
EXCEPTION: | Lighting and switched receptacles controlled by captive key systems. |
4. Supplemental task lighting, including permanently installed under-shelf or under-cabinet lighting, shall be automatically shut off whenever that space is unoccupied and shall have a control device integral to the luminaires or be controlled by a wall-mounted control device provided the control device is readily accessible.
5. Lighting for nonvisual applications, such as plant growth and food warming, shall be controlled by a dedicated control which is independent of the controls for other lighting. Each control zone shall be no greater than the area served by a single luminaire or 4,000 square feet, whichever is larger.
6. Lighting equipment that is for sale or for demonstrations in lighting education shall be controlled by a dedicated control which is independent of the controls for other lighting within the room or space.
7. Luminaires serving the exit access and providing means of egress illumination required by Section 1006.1 of the International Building Code, including luminaires that function as both normal and emergency means of egress illumination shall be controlled by a combination of listed emergency relay and occupancy sensors, or signal from another building control system, that automatically shuts off the lighting when the areas served by that illumination are unoccupied.
EXCEPTION: | Means of egress illumination serving the exit access that does not exceed 0.02 watts per square foot of building area is exempt from this requirement. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40526 Section C405.2.6—Digital timer switch.
C405.2.6 Digital timer switch controls. For each of the following space types, when under 300 square feet, digital timer switch controls may be provided in lieu of occupancy sensor controls:
1. Copy/print rooms.
2. Storage rooms.
3. Janitorial closets.
C405.2.6.1 Digital timer switch function. Digital timer switches shall comply with the following:
1. Turn lights on or off with operation of a button, switch or other manual means.
2. Automatically turn lights off within 15 minutes of the lights being turned on. The time delay shall be configurable only by removing the switch faceplate. A switch where the time delay is selected or configurable from the front of the switch faceplate is not permitted.
3. The switch shall provide audible indication of impending shut-off of the lights one minute before shut off.
4. The switch shall provide visible indication of impending shut-off by flashing the lights one minute before shut off.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40527 Section C405.2.7—Exterior lighting controls.
C405.2.7 Exterior lighting controls. Lighting for exterior applications other than emergency lighting that is intended to be automatically off during building operation, lighting specifically required to meet health and life safety requirements or decorative gas lighting systems shall:
1. Be provided with a control that automatically turns off the lighting as a function of available daylight.
2. Where lighting the building façade or landscape, the lighting shall have controls that automatically shut off the lighting as a function of dawn/dusk and a set opening and closing time.
3. Where not covered in Item 2, the lighting shall have controls configured to automatically reduce the connected lighting power by at least 30 percent from no later than 12 midnight to 6 a.m. or from one hour after business closing to one hour before business opening or during any period when no activity has been detected for a time of no longer than 15 minutes.
Time switches shall be capable of retaining programming and the time setting for at least 10 hours without power.
EXCEPTION: | Lighting for covered vehicle entrances or exits from buildings or parking structures where required for safety, security or eye adaption. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40528 Section C405.2.8—Area controls.
C405.2.8 Area controls. The maximum lighting power that may be controlled from a single switch or automatic control shall not exceed that which is provided by a 20 ampere circuit loaded to not more than 80 percent. A master control may be installed provided the individual switches retain their capability to function independently. Circuit breakers may not be used as the sole means of switching.
EXCEPTION: | Areas less than 5 percent of the building footprint for footprints over 100,000 ft2. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40503 ((Section C405.3—))Reserved.
((C405.3 Reserved.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40504 Section ((C405.4)) C405.3—Exit signs.
((C405.4)) C405.3 Exit signs (mandatory). Internally illuminated exit signs shall not exceed 5 watts per side.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40505 Section ((C405.5)) C405.4—Interior lighting power requirements.
((C405.5)) C405.4 Interior lighting power requirements (prescriptive). A building complies with this section if its total connected lighting power calculated under Section ((C405.5.1)) C405.4.1 is no greater than the interior lighting power calculated under Section ((C405.5.2)) C405.4.2.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405051 Section ((C405.5.1)) C405.4.1—Total connected interior lighting power.
((C405.5.1)) C405.4.1 Total connected interior lighting power. The total connected interior lighting power (((watts))) shall be the ((sum of the watts of all interior lighting equipment as determined in accordance with Sections C405.5.1.1 through C405.5.1.4.)) determined in accordance with Equation 4-10.
TCLP = [SL + LV + LTPB + Other]
(Equation 4-10)
Where:
TCLP = Total connected lighting power (watts).
SL = Labeled wattage of luminaires for screw-in lamps.
LV = Wattage of the transformer supplying low-voltage lighting.
LTPB = Wattage of line-voltage lighting tracks and plug-in busways as the specified wattage of the luminaires but at least 50 W/lin. ft., or the wattage limit of the system's circuit breaker, or the wattage limit of other permanent current limiting devices on the system.
Other = The wattage of all other luminaires and lighting, sources not covered above and associated with interior lighting verified by data supplied by the manufacturer or other approved sources.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. The connected power associated with the following lighting equipment is not included in calculating total connected lighting power. |
1.1. Professional sports arena playing field lighting. | |
1.2. Emergency lighting automatically off during normal building operation. | |
1.3. Lighting in spaces specifically designed for use by occupants with special lighting needs including the visually impaired and other medical and age-related issues. | |
1.4. Casino gaming areas. | |
1.5. General area lighting power in industrial and manufacturing occupancies dedicated to the inspection or quality control of goods and products. | |
1.6. Lighting in sleeping units, provided that the lighting complies with Section R404.1. | |
1.7. Mirror lighting in dressing rooms. | |
2. Lighting equipment used for the following shall be exempt provided that it is in addition to general lighting and is controlled by an independent control device: | |
2.1. Task lighting for medical and dental purposes. | |
2.2. Display lighting for exhibits in galleries, museums and monuments. | |
3. Lighting for theatrical purposes, including performance, stage, film production and video production. | |
4. Lighting for photographic processes. | |
5. Lighting integral to equipment or instrumentation and is installed by the manufacturer. | |
6. Task lighting for plant growth or maintenance where the lamp efficacy is not less than 90 lumens per watt. | |
7. Advertising signage or directional signage. | |
8. In restaurant buildings and areas, lighting for food warming or integral to food preparation equipment. | |
9. Lighting equipment that is for sale. | |
10. Lighting demonstration equipment in lighting education facilities. | |
11. Lighting approved because of safety or emergency considerations, inclusive of exit lights. | |
12. Lighting integral to both open and glass enclosed refrigerator and freezer cases. | |
13. Lighting in retail display windows, provided the display area is enclosed by ceiling-height partitions. | |
14. Furniture mounted supplemental task lighting that is controlled by automatic shutoff. | |
15. Lighting used for aircraft painting. |
((C405.5.1.1 Screw lamp holders. The wattage shall be the maximum labeled wattage of the luminaire.
C405.5.1.2 Low-voltage lighting. The wattage shall be the specified wattage of the transformer supplying the system.
C405.5.1.3 Other luminaires. The wattage of all other lighting equipment shall be the wattage of the lighting equipment verified through data furnished by the manufacturer or other approved sources.
C405.5.1.4 Line-voltage lighting track and plug-in busway. The wattage shall be:
1. The specified wattage of the luminaires included in the system with a minimum of 50 W/lin ft. (162 W/lin. m);
2. The wattage limit of the system's circuit breaker; or
3. The wattage limit of other permanent current limiting device(s) on the system.))
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405052 Section ((C405.5.2)) C405.4.2—Interior lighting power requirements.
((C405.5.2)) C405.4.2 Interior lighting power. The total interior lighting power allowance (watts) is determined according to Table ((C405.5.2(1))) C405.4.2(1) using the Building Area Method, or Table ((C405.5.2(2))) C405.4.2(2) using the Space-by-Space Method, for all areas of the building covered in this permit.
C405.4.2.1 Building area method. For the Building Area Method, the interior lighting power allowance is the floor area for each building area type listed in Table ((C405.5.2(1))) C405.4.2(1) times the value from Table ((C405.5.2(1))) C405.4.2(1) for that area. For the purposes of this method, an "area" shall be defined as all contiguous spaces that accommodate or are associated with a single building area type as listed in Table ((C405.5.2(1))) C405.4.2(1). Where this method is used to calculate the total interior lighting power for an entire building, each building area type shall be treated as a separate area.
C405.4.2.2 Space-by-Space Method. For the Space-by-Space Method, the interior lighting power allowance is determined by multiplying the floor area of each space times the value for the space type in Table ((C405.5.2(2))) C405.4.2(2) that most closely represents the proposed use of the space, and then summing the lighting power allowances for all spaces. Tradeoffs among spaces are permitted.
Each area enclosed by partitions that are 80 percent of the ceiling height or taller shall be considered a separate space and assigned the appropriate space type from Table C405.4.2(2). If a space has multiple functions where more than one space type is applicable, that space shall be broken up into smaller subspaces, each using their own space type. Any of these subspaces that are smaller in floor area than 20 percent of the enclosed space and less than 1,000 square feet need not be broken out separately.
C405.4.2.2.1 Additional interior lighting power. Where using the Space-by-Space Method, an increase in the interior lighting power allowance is permitted for specific lighting functions. Additional power shall be permitted only where the specified lighting is installed and automatically controlled separately from the general lighting, to be turned off during nonbusiness hours. This additional power shall be used only for the specified luminaires and shall not be used for any other purpose. An increase in the interior lighting power allowance is permitted for lighting equipment to be installed in sales areas specifically to highlight merchandise, the additional lighting power shall be determined in accordance with Equation 4-11.
(Equation 4-11)
Additional Interior Lighting Power Allowance = 500 watts + (Retail Area 1 × 0.6 W/ft2) + (Retail Area 2 × 0.6 W/ft2) + (Retail Area 3 × 1.4 W/ft2) + (Retail Area 4 × 2.5 W/ft2).
Where:
Retail Area 1 = The floor area for all products not listed in Retail Area 2, 3 or 4.
Retail Area 2 = The floor area used for the sale of vehicles, sporting goods and small electronics.
Retail Area 3 = The floor area used for the sale of furniture, clothing, cosmetics and artwork.
Retail Area 4 = The floor area used for the sale of jewelry, crystal and china.
EXCEPTION: | Other merchandise categories are permitted to be included in Retail Areas 2 through 4, provided that justification documenting the need for additional lighting power based on visual inspection, contrast, or other critical display is approved by the code official. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405053 Table ((C405.5.2(1))) C405.4.2(1)—Interior lighting power allowances—Building area method.
Table ((C405.5.2(1))) C405.4.2(1)
Interior Lighting Power Allowances—Building Area Method
Building Area Type |
LPD (w/ft2) |
((Automotive facility |
0.82 |
Convention center |
1.08 |
Court house |
1.05 |
Dining: Bar lounge/leisure |
0.99 |
Dining: Cafeteria/fast food |
0.90 |
Dining: Family |
0.89 |
Dormitory |
0.61 |
Exercise center |
0.88 |
Fire station |
0.71 |
Gymnasium |
0.95 |
Health care clinic |
0.87 |
Hospital |
1.20 |
Hotel |
1.00 |
Library |
1.18 |
Manufacturing facility |
1.11 |
Motel |
0.88 |
Motion picture theater |
0.83 |
Multifamily |
0.60 |
Museum |
1.00 |
Office |
0.90 |
Parking garage |
0.20 |
Penitentiary |
0.90 |
Performing arts theater |
1.25 |
Police station |
0.90 |
Post office |
0.87 |
Religious building |
1.05 |
Retail |
1.33 |
School/university |
0.99 |
Sports arena |
0.78 |
Town hall |
0.92 |
Transportation |
0.77 |
Warehouse |
0.50 |
Workshop |
1.20)) |
Automotive facility |
0.64 |
Convention center |
0.81 |
Court house |
0.81 |
Dining: Bar lounge/leisure |
0.79 |
Dining: Cafeteria/fast food |
0.72 |
Dining: Family |
0.71 |
Dormitory |
0.46 |
Exercise center |
0.67 |
Fire station |
0.54 |
Gymnasium |
0.75 |
Health care clinic |
0.70 |
Hospital |
0.84 |
Hotel/motel |
0.70 |
Library |
0.94 |
Manufacturing facility |
0.89 |
Motion picture theater |
0.61 |
Multifamily |
0.41 |
Museum |
0.80 |
Office |
0.66 |
Parking garage |
0.16 |
Penitentiary |
0.65 |
Performing arts theater |
1.00 |
Police station |
0.70 |
Post office |
0.70 |
Religious building |
0.80 |
Retail |
1.01 |
School/university |
0.70 |
Sports arena |
0.62 |
Town hall |
0.71 |
Transportation |
0.56 |
Warehouse |
0.04 |
Workshop |
0.95 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405054 Table ((C405.5.5.2(2))) C405.4.2(2)—Interior lighting power allowances—Space-by-space method.
Table ((C405.5.2(2))) C405.4.2(2)
Interior Lighting Power Allowances—Space-by-Space Method
((Common Space-by-Space Types |
LPD (w/ft2) |
|
Atrium - First 40 feet in height |
0.03 per ft. ht. |
|
Atrium - Above 40 feet in height |
0.02 per ft. ht. |
|
Audience/seating area - Permanent |
||
For auditorium |
0.79 |
|
For performing arts theater |
2.43 |
|
For motion picture theater |
1.14 |
|
Classroom/lecture/training |
1.24 |
|
Conference/meeting/multipurpose |
1.23 |
|
Corridor/transition |
0.66 |
|
Dining area |
||
Bar/lounge/leisure dining |
1.31 |
|
Family dining area |
0.89 |
|
Dressing/fitting room performing arts theater |
0.40 |
|
Electrical/mechanical |
0.95 |
|
Food preparation |
0.99 |
|
Laboratory for classrooms |
1.28 |
|
Laboratory for medical/industrial/research |
1.81 |
|
Lobby |
0.90 |
|
Lobby for performing arts theater |
2.00 |
|
Lobby for motion picture theater |
0.52 |
|
Locker room |
0.75 |
|
Lounge recreation |
0.73 |
|
Office - Enclosed |
1.11 |
|
Office - Open plan |
0.98 |
|
Restroom |
0.98 |
|
Sales area |
1.68a |
|
Stairway |
0.69 |
|
Storage |
0.63 |
|
Workshop |
1.59 |
|
Building Specific Space-by-space Types |
||
Automotive - Service/repair |
0.67 |
|
Bank/office - Banking activity area |
1.38 |
|
Convention center |
||
Exhibit space |
1.45 |
|
Audience/seating area |
0.82 |
|
Courthouse/police station/penitentiary |
||
Courtroom |
1.72 |
|
Confinement cells |
1.10 |
|
Judge chambers |
1.17 |
|
Penitentiary audience seating |
0.43 |
|
Penitentiary classroom |
1.34 |
|
Penitentiary dining |
1.07 |
|
Dormitory living quarters |
0.38 |
|
Fire stations |
||
Engine rooms |
0.56 |
|
Sleeping quarters |
0.25 |
|
Gymnasium/fitness center |
||
Fitness area |
0.72 |
|
Gymnasium audience/seating |
0.43 |
|
Playing area |
1.20 |
|
Health care clinic/hospital |
||
Corridors/transition |
0.89 |
|
Emergency |
2.26 |
|
Exam/treatment |
1.66 |
|
Medical supplies |
1.27 |
|
Nursery |
0.88 |
|
Nurse station |
0.87 |
|
Operating room |
1.89 |
|
Patient room |
0.62 |
|
Pharmacy |
1.14 |
|
Physical therapy |
0.91 |
|
Radiology/imaging |
1.32 |
|
Recovery |
1.15 |
|
Hotel |
||
Dining area |
0.82 |
|
Guest rooms |
1.11 |
|
Hotel lobby |
1.06 |
|
Highway lodging dining |
0.88 |
|
Highway lodging guest rooms |
0.75 |
|
Library |
||
Card file and cataloguing |
0.72 |
|
Reading area |
0.93 |
|
Stacks |
1.71 |
|
Manufacturing |
||
Corridors/transition |
0.41 |
|
Detailed manufacturing |
1.29 |
|
Equipment room |
0.95 |
|
Extra high bay (˃ 50-foot floor-ceiling height) |
1.05 |
|
High bay (25 - 50-foot floor-ceiling height) |
1.23 |
|
Low bay (< 25-foot floor-ceiling height) |
1.19 |
|
Museum |
||
General exhibition |
1.05 |
|
Restoration |
1.02 |
|
Parking garage - Garage areas |
0.19 |
|
Post office |
||
Sorting area |
0.94 |
|
Religious building |
||
Audience seating |
1.53 |
|
Fellowship hall |
0.64 |
|
Worship pulpit/choir |
1.53 |
|
Retail |
||
Dressing/fitting area |
0.87 |
|
Mall concourse |
1.10 |
|
Sales area |
1.68a |
|
Sports arena |
||
Audience seating |
0.43 |
|
Court sports area - Class 4 |
0.72 |
|
Court sports area - Class 3 |
1.20 |
|
Court sports area - Class 2 |
1.92 |
|
Court sports area - Class 1 |
3.01 |
|
Ring sports area |
2.68 |
|
Transportation |
||
Air/train/bus baggage area |
0.76 |
|
Airport concourse |
0.36 |
|
Audience seating |
0.54 |
|
Terminal - Ticket counter |
1.08 |
|
Warehouse |
||
Fine material storage |
0.95 |
|
Medium/bulky material |
0.58 |
|
For SI: | 1 foot = 304.8 mm, 1 watt per square foot = 11 W/m2. |
a | Where lighting equipment is specified to be installed to highlight specific merchandise in addition to lighting equipment specified for general lighting and is switched or dimmed on circuits different from the circuits for general lighting, the smaller of the actual wattage of the lighting equipment installed specifically for merchandise, or additional lighting power as determined below shall be added to the interior lighting power determined in accordance with this line item. |
Calculate the additional lighting power as follows:
Additional Interior Lighting Power Allowance |
= |
500 watts + (Retail Area 1 × 0.6 W/ft2) + (Retail Area 2 × 0.6 W/ft2) + (Retail Area 3 × 1.4 W/ft2) + (Retail Area 4 × 2.5 W/ft2). |
Where: |
||
Retail Area 1 |
= |
The floor area for all products not listed in Retail Area 2, 3 or 4. |
Retail Area 2 |
= |
The floor area used for the sale of vehicles, sporting goods and small electronics. |
Retail Area 3 |
= |
The floor area used for the sale of furniture, clothing, cosmetics and artwork. |
Retail Area 4 |
= |
The floor area used for the sale of jewelry, crystal and china. |
EXCEPTION: | Other merchandise categories are permitted to be included in Retail Areas 2 through 4 above, provided that justification documenting the need for additional lighting power based on visual inspection, contrast, or other critical display is approved by the authority having jurisdiction.)) |
Common Space-by-Space Typesa |
LPD (w/ft2) |
|
Atrium - First 40 feet in heighte |
0.02 per ft. ht. |
|
Atrium - Above 40 feet in heighte |
0.03 + 0.02 per ft. in total height |
|
Audience/seating area - Permanent |
||
In an auditorium |
0.50 |
|
In a convention center |
0.66 |
|
In a gymnasium |
0.34 |
|
In a motion picture theater |
0.91 |
|
In a penitentiary |
0.22 |
|
In a performing arts theater |
1.94 |
|
In a religious building |
1.22 |
|
In a sports arena |
0.34 |
|
Otherwise |
0.34 |
|
Banking activity area |
0.81 |
|
Breakroom (see Lounge/breakroom) |
||
Classroom/lecture hall/training room |
||
In a penitentiary |
1.07 |
|
Otherwise |
1.00 |
|
Conference/meeting/multipurpose |
0.98 |
|
Copy/print room |
0.58 |
|
Corridor |
||
In a facility for the visually impaired (and not used primarily by the staff)b |
0.74 |
|
In a hospital |
0.63 |
|
In a manufacturing facility |
0.33 |
|
Otherwise |
0.53 |
|
Courtroom |
1.38 |
|
Computer room |
1.37 |
|
Dining area |
||
In a penitentiary |
0.77 |
|
In a facility for the visually impaired (and not used primarily by the staff)b |
1.52 |
|
In a bar/lounge or leisure dining |
0.86 |
|
In a family dining area |
0.71 |
|
Otherwise |
0.52 |
|
Electrical/mechanical |
0.76 |
|
Emergency vehicle garage |
0.45 |
|
Food preparation |
0.79 |
|
Guest room |
0.38 |
|
Laboratory |
||
In or as a classroom |
1.02 |
|
Otherwise |
1.45 |
|
Laundry/washing area |
0.48 |
|
Loading dock, interior |
0.38 |
|
Lobbyc |
||
In a facility for the visually impaired (and not used primarily by the staff)b |
1.44 |
|
For an elevator |
0.51 |
|
In a hotel |
0.85 |
|
In a motion picture theater |
0.42 |
|
In a performing arts theater |
1.60 |
|
Otherwise |
0.72 |
|
Locker room |
0.60 |
|
Lounge/breakroom |
||
In a health care facility |
0.74 |
|
Otherwise |
0.58 |
|
Officef |
||
Enclosed |
0.89 |
|
Open plan |
0.78 |
|
Parking area, interior |
0.15 |
|
Pharmacy area |
0.91 |
|
Restroom |
||
In a facility for the visually impaired (and not used primarily by the staff)b |
0.97 |
|
Otherwise |
0.78 |
|
Sales area |
1.27 |
|
Seating area, general |
0.43 |
|
Stairway (see space containing stairway) |
||
Stairwell |
0.55 |
|
Storage room |
0.50 |
|
Vehicular maintenance |
0.54 |
|
Workshop |
1.27 |
|
Building Specific Space-by-Space Typesa |
||
Building Specific Space-by-Space Types |
LPDd (w/ft2) |
|
Automotive - (See Vehicular maintenance, above) |
0.54 |
|
Convention center - Exhibit space |
1.16 |
|
Dormitory living quarters |
0.30 |
|
Facility for the visually impairedb |
||
In a chapel (and not used primarily by the staff)b |
1.77 |
|
In a recreation room (and not used primarily by the staff)b |
1.93 |
|
Fire stations - Sleeping quarters |
0.18 |
|
Engine rooms |
0.45 |
|
Gymnasium/fitness center |
||
In an exercise area |
0.58 |
|
In a playing area |
0.96 |
|
Health care facility |
||
In an exam/treatment room |
1.33 |
|
In an imaging room |
1.06 |
|
In a medical supply room |
0.59 |
|
In a nursery |
0.70 |
|
In a nurse's station |
0.57 |
|
In an operating room |
1.51 |
|
In a patient room |
0.50 |
|
In a physical therapy room |
0.73 |
|
In a recovery room |
0.92 |
|
Libraryf |
||
In a reading area |
0.74 |
|
In the stacks |
1.37 |
|
Manufacturing facility |
||
In a detailed manufacturing area |
1.03 |
|
In an equipment room |
0.59 |
|
In an extra high bay area (greater than 50-foot floor-to-ceiling height) |
0.84 |
|
In a high bay area (25 - 50-foot floor-to-ceiling height) |
0.98 |
|
In a low bay (< 25-foot floor-to-ceiling height) |
0.95 |
|
Museum |
||
In a general exhibition area |
0.84 |
|
In a restoration room |
0.82 |
|
Performing arts theater dressing/fitting room |
0.32 |
|
Post office - Sorting area |
0.75 |
|
Religious buildings |
||
In a fellowship hall |
0.51 |
|
In a worship/pulpit/choir |
1.22 |
|
Retail facilities |
||
In a dressing/fitting room |
0.57 |
|
In a mall concourse |
0.88 |
|
Sports arena - Playing area |
||
For a Class 1 facility |
2.41 |
|
For a Class 2 facility |
1.54 |
|
For a Class 3 facility |
0.96 |
|
For a Class 4 facility |
0.58 |
|
Transportation |
||
In a baggage/carousel area |
0.42 |
|
In an airport concourse |
0.29 |
|
At a terminal ticket counter |
0.64 |
|
Warehouse - Storage area |
||
For medium to bulky palletized items |
0.46 |
|
For smaller, hand-carried items |
0.76 |
|
For SI: 1 foot = 304.8 mm, 1 watt per square foot = 11 W/m2. | |
a | In cases where both a common space type and a building area specific space type are listed, the building area specific space type shall apply. |
b | A "Facility for the Visually Impaired" is a facility that is licensed or will be licensed by local or state authorities for senior long-term care, adult daycare, senior support or people with special visual needs. |
c | For spaces in which lighting is specified to be installed in addition to, and controlled separately from, the general lighting for the purpose of highlighting art or exhibits, provided that the additional lighting power shall not exceed 0.5 W/ft2of such spaces. |
d | The watts per square foot may be increased by 2 percent per foot of ceiling height above 20 feet, unless specifically directed otherwise by subsequent footnotes. |
e | Footnote d may not be used for these occupancy types. |
f | The watts per square foot may be increased by 2 percent per foot of ceiling height above 9 feet. Footnote d may not be used for these occupancy types. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40506 Section ((C405.6)) C405.5—Exterior lighting.
((C405.6)) C405.5 Exterior lighting (mandatory). Where the power for exterior lighting is supplied through the energy service to the building, all exterior lighting shall comply with ((Sections C405.6.1 and C405.6.2)) Section C405.5.1.
EXCEPTION: | Where approved because of historical, safety, signage or emergency considerations. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405061 Section ((C405.6.1)) C405.5.1—Exterior building grounds lighting.
((C405.6.1)) C405.5.1 Exterior building grounds lighting. All exterior building grounds luminaires that operate at greater than 100 watts shall ((contain lamps having)) have a minimum efficacy of ((60)) 80 lumens per watt unless the luminaire is controlled by a motion sensor or qualifies for one of the exceptions under Section ((C405.6.2)) C405.5.2.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405062 Section ((C405.6.2)) C405.5.2—Exterior building lighting power.
((C405.6.2)) C405.5.2 Exterior building lighting power. The total exterior lighting power allowance for all exterior building applications is the sum of the base site allowance plus the individual allowances for areas that are to be illuminated and are permitted in Table ((C405.6.2(2))) C405.5.2(2) for the applicable lighting zone. Tradeoffs are allowed only among exterior lighting applications listed in Table ((C405.6.2(2))) C405.5.2(2), Tradable Surfaces section. The lighting zone for the building exterior is determined from Table ((C405.6.2(1))) C405.5.2(1) unless otherwise specified by the local jurisdiction. ((Exterior lighting for all applications (except those included in the exceptions to Section C405.6.2) shall comply with the requirements of Section C405.6.1)).
EXCEPTION: | Lighting used for the following exterior applications is exempt where equipped with a control device independent of the control of the nonexempt lighting: |
1. Specialized signal, directional and marker lighting associated with transportation; | |
2. Advertising signage or directional signage; | |
3. Integral to equipment or instrumentation and is installed by its manufacturer; | |
4. Theatrical purposes, including performance, stage, film production and video production; | |
5. Athletic playing areas; | |
6. Temporary lighting; | |
7. Industrial production, material handling, transportation sites and associated storage areas; | |
8. Theme elements in theme/amusement parks; and | |
9. Used to highlight features of public monuments and registered historic landmark structures or buildings. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405063 Table ((C405.6.2(1))) C405.5.2(1)—Exterior lighting zones.
Table ((C405.6.2(1))) C405.5.2(1)
Exterior Lighting Zones
Lighting Zone |
Description |
1 |
Developed areas of national parks, state parks, forest land, and rural areas |
2 |
Areas predominantly consisting of residential zoning, neighborhood business districts, light industrial with limited nighttime use and residential mixed use areas |
3 |
All other areas not classified as lighting zone 1, 2, or 4 |
4 |
High-activity commercial districts in major metropolitan areas as designated by the local land use planning authority |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-405064 Table ((C405.6.2(2))) C405.5.2(2)—Individual lighting power allowances for building exteriors.
Table ((C405.6.2(2))) C405.5.2(2)
Individual Lighting Power Allowances for Building Exteriors
Lighting Zones |
|||||
Zone 1 |
Zone 2 |
Zone 3 |
Zone 4 |
||
Base Site Allowance (Base allowance is usable in tradable or nontradable surfaces.) |
500 W |
600 W |
750 W |
1300 W |
|
Tradable Surfaces |
Uncovered Parking Areas |
||||
(Lighting power densities for uncovered parking areas, building grounds, building entrances and exits, canopies and overhangs and outdoor sales areas are tradable.) |
Parking areas and drives |
0.04 W/ft2 |
0.06 W/ft2 |
((0.10)) 0.08 W/ft2 |
((0.13)) 0.10 W/ft2 |
Building Grounds |
|||||
Walkways less than 10 feet wide |
0.7 W/linear foot |
0.7 W/linear foot |
0.8 W/linear foot |
1.0 W/linear foot |
|
Walkways 10 feet wide or greater, plaza areas, special feature areas |
0.14 W/ft2 |
0.14 W/ft2 |
0.16 W/ft2 |
0.2 W/ft2 |
|
Stairways |
0.75 W/ft2 |
1.0 W/ft2 |
1.0 W/ft2 |
1.0 W/ft2 |
|
Pedestrian tunnels |
0.15 W/ft2 |
0.15 W/ft2 |
0.2 W/ft2 |
0.3 W/ft2 |
|
Building Entrances and Exits |
|||||
Main entries |
20 W/linear foot of door width |
20 W/linear foot of door width |
30 W/linear foot of door width |
30 W/linear foot of door width |
|
Other doors |
20 W/linear foot of door width |
20 W/linear foot of door width |
20 W/linear foot of door width |
20 W/linear foot of door width |
|
Entry canopies |
0.25 W/ft2 |
0.25 W/ft2 |
0.4 W/ft2 |
0.4 W/ft2 |
|
Sales Canopies |
|||||
Free standing and attached |
0.6 W/ft2 |
0.6 W/ft2 |
0.8 W/ft2 |
1.0 W/ft2 |
|
Outdoor Sales |
|||||
Open areas (including vehicle sales lots) |
0.25 W/ft2 |
0.25 W/ft2 |
0.5 W/ft2 |
0.7 W/ft2 |
|
Street frontage for vehicle sales lots in addition to "open area" allowance |
No Allowance |
10 W/linear foot |
10 W/linear foot |
30 W/linear foot |
|
Nontradable Surfaces (Lighting power density calculations for the following applications can be used only for the specific application and cannot be traded between surfaces or with other exterior lighting. The following allowances are in addition to any allowance otherwise permitted in the "Tradable Surfaces" section of this table.) |
Building facades |
No allowance |
((0.1 W/ft2 for each illuminated wall or surface or 2.5 W/linear foot for each illuminated wall or surface length)) 0.075 W/ft2 of gross above-grade wall area |
((0.15 W/ft2 for each illuminated wall or surface or 3.75 W/linear foot for each illuminated wall or surface length)) 0.113 W/ft2 of gross above-grade wall area |
((0.2 W/ft2 for each illuminated wall or surface or 5.0 W/linear foot for each illuminated wall or surface length)) 0.150 W/ft2 of gross above-grade wall area |
Automated teller machines and night depositories |
270 W per location plus 90 W per additional ATM per location |
270 W per location plus 90 W per additional ATM per location |
270 W per location plus 90 W per additional ATM per location |
270 W per location plus 90 W per additional ATM per location |
|
Entrances and gatehouse inspection stations at guarded facilities |
0.75 W/ft2 of covered and uncovered area |
0.75 W/ft2 of covered and uncovered area |
0.75 W/ft2 of covered and uncovered area |
0.75 W/ft2 of covered and uncovered area |
|
Loading areas for law enforcement, fire, ambulance and other emergency service vehicles |
0.5 W/ft2 of covered and uncovered area |
0.5 W/ft2 of covered and uncovered area |
0.5 W/ft2 of covered and uncovered area |
0.5 W/ft2 of covered and uncovered area |
|
Drive-up windows/doors |
400 W per drive-through |
400 W per drive-through |
400 W per drive-through |
400 W per drive-through |
|
Parking near 24-hour retail entrances |
800 W per main entry |
800 W per main entry |
800 W per main entry |
800 W per main entry |
|
For SI: | 1 foot = 304.8 mm, 1 watt per square foot = W/0.0929 m2 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40507 Section C405.7—Electrical energy consumption.
C405.6 Electrical transformers. Electric transformers shall meet the minimum efficiency requirements of Table C405.6 as tested and rated in accordance with the test procedure listed in DOE 10 C.F.R. 431. The efficiency shall be verified through certification under an approved certification program or, where no certification program exists, the equipment efficiency ratings shall be supported by data furnished by the transformer manufacturer.
EXCEPTION: | The following transformers are exempt: |
1. Transformers that meet the Energy Policy Act of 2005 exclusions based on the DOE 10 C.F.R. 431 definition of special purpose applications. | |
2. Transformers that meet the Energy Policy Act of 2005 exclusions that are not to be used in general purpose applications based on information provided in DOE 10 C.F.R. 431. | |
3. Transformers that meet the Energy Policy Act of 2005 exclusions with multiple voltage taps where the highest tap is at least 20 percent more than the lowest tap. | |
4. Drive transformers. | |
5. Rectifier transformers. | |
6. Auto-transformers. | |
7. Uninterruptible power system transformers. | |
8. Impedance transformers. | |
9. Regulating transformers. | |
10. Sealed and nonventilating transformers. | |
11. Machine tool transformer. | |
12. Welding transformer. | |
13. Grounding transformer. | |
14. Testing transformer. |
Table C405.6
Minimum Nominal Efficiency Levels For 10 C.F.R. 431 Low Voltage Dry-Type Distribution Transformers
Single Phase Transformers |
Three Phase Transformers |
||
kVAa |
Efficiency (%)b |
kVAa |
Efficiency (%)b |
15 |
97.7 |
15 |
97.0 |
25 |
98.0 |
30 |
97.5 |
37.5 |
98.2 |
45 |
97.7 |
50 |
98.3 |
75 |
98.0 |
75 |
98.5 |
112.5 |
98.2 |
100 |
98.6 |
150 |
98.3 |
167 |
98.7 |
225 |
98.5 |
250 |
98.8 |
300 |
98.6 |
333 |
98.9 |
500 |
98.7 |
750 |
98.8 |
||
1000 |
98.9 |
||
a | kiloVolt-Amp rating. |
b | Nominal efficiencies shall be established in accordance with the DOE 10 C.F.R. 431 test procedure for low voltage dry-type transformers. |
C405.7 Electrical energy consumption (mandatory). ((In buildings having individual)) Each dwelling unit((s, provisions shall be made to determine the electrical energy consumed by each tenant by separately metering individual dwelling units)) located in a Group R-2 building shall have a separate electrical meter. A utility tenant meter meets this requirement. See Section C409 for additional requirements for energy metering and energy consumption management.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40508 Section C405.8—Electric motors.
((C405.8 Electric motors. All permanently wired polyphase motors of 1 hp or more, which are not part of an HVAC system, shall comply with Section C403.2.13.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Motors that are an integral part of specialized process equipment. |
2. Where the motor is integral to a listed piece of equipment for which no complying motor has been approved.)) |
C405.8 Electric motor efficiency (mandatory). All electric motors, fractional or otherwise, shall meet the minimum efficiency requirements of Tables C405.8(1) through C405.8(4) when tested and rated in accordance with DOE 10 C.F.R. The efficiency shall be verified through certification under an approved certification program or, where no certification program exists, the equipment efficiency ratings shall be supported by data furnished by the motor manufacturer.
Fractional hp fan motors that are 1/12 hp or greater and less than 1 hp which are not covered by Tables C405.8(3) and C405.8(4) shall be electronically commutated motors or shall have a minimum motor efficiency of 70 percent when rated in accordance with DOE 10 C.F.R. 431. These motors shall also have the means to adjust motor speed for either balancing or remote control. Belt-driven fans may use sheave adjustments for airflow balancing in lieu of a varying motor speed.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Motors that are an integral part of specialized process equipment. |
2. Where the motor is integral to a listed piece of equipment for which no complying motor has been approved. | |
3. Motors used as a component of the equipment meeting the minimum efficiency requirements of Section C403.2.3 and Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(10) provided that the motor input is included when determining the equipment efficiency. | |
4. Motors in the airstream within fan-coils and terminal units that operate only when providing heating to the space served. |
Table C405.8(1)
Minimum Nominal Full-load Efficiency for 60 Hz NEMA General Purpose Electric Motors (Subtype I) Rated 600 Volts or Less (Random Wound)a
NUMBER OF POLES► |
OPEN DRIP-PROOF MOTORS |
TOTALLY ENCLOSED FAN-COOLED MOTORS |
||||
2 |
4 |
6 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
|
SYNCHRONOUS SPEED (RPM)► |
3600 |
1800 |
1200 |
3600 |
1800 |
1200 |
MOTOR HORSEPOWER▼ |
||||||
1 |
77.0 |
85.5 |
82.5 |
77.0 |
85.5 |
82.5 |
1.5 |
84.0 |
86.5 |
86.5 |
84.0 |
86.5 |
87.5 |
2 |
85.5 |
86.5 |
87.5 |
85.5 |
86.5 |
88.5 |
3 |
85.5 |
89.5 |
88.5 |
86.5 |
89.5 |
89.5 |
5 |
86.5 |
89.5 |
89.5 |
88.5 |
89.5 |
89.5 |
7.5 |
88.5 |
91.0 |
90.2 |
89.5 |
91.7 |
91.0 |
10 |
89.5 |
91.7 |
91.7 |
90.2 |
91.7 |
91.0 |
15 |
90.2 |
93.0 |
91.7 |
91.0 |
92.4 |
91.7 |
20 |
91.0 |
93.0 |
92.4 |
91.0 |
93.0 |
91.7 |
25 |
91.7 |
93.6 |
93.0 |
91.7 |
93.6 |
93.0 |
30 |
91.7 |
94.1 |
93.6 |
91.7 |
93.6 |
93.0 |
40 |
92.4 |
94.1 |
94.1 |
92.4 |
94.1 |
94.1 |
50 |
93.0 |
94.5 |
94.1 |
93.0 |
94.5 |
94.1 |
60 |
93.6 |
95.0 |
94.5 |
93.6 |
95.0 |
94.5 |
75 |
93.6 |
95.0 |
94.5 |
93.6 |
95.4 |
94.5 |
100 |
93.6 |
95.4 |
95.0 |
94.1 |
95.4 |
95.0 |
125 |
94.1 |
95.4 |
95.0 |
95.0 |
95.4 |
95.0 |
150 |
94.1 |
95.8 |
95.4 |
95.0 |
95.8 |
95.8 |
200 |
95.0 |
95.8 |
95.4 |
95.4 |
96.2 |
95.8 |
250 |
95.0 |
95.8 |
95.4 |
95.8 |
96.2 |
95.8 |
300 |
95.4 |
95.8 |
95.4 |
95.8 |
96.2 |
95.8 |
350 |
95.4 |
95.8 |
95.4 |
95.8 |
96.2 |
95.8 |
400 |
95.8 |
95.8 |
95.8 |
95.8 |
96.2 |
95.8 |
450 |
95.8 |
96.2 |
96.2 |
95.8 |
96.2 |
95.8 |
500 |
95.8 |
96.2 |
96.2 |
95.8 |
96.2 |
95.8 |
a Nominal efficiencies shall be established in accordance with DOE 10 C.F.R. 431. |
||||||
Table C405.8(2)
Minimum Nominal Full-load Efficiency of General Purpose Electric Motors (Subtype II) And All Design B Motors Greater Than 200 Horsepowera
NUMBER OF POLES► |
OPEN DRIP-PROOF MOTORS |
TOTALLY ENCLOSED FAN COOLED MOTORS |
||||||
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
|
SYNCHRONOUS SPEED (RPM)► |
3600 |
1800 |
1200 |
900 |
3600 |
1800 |
1200 |
900 |
MOTOR HORSEPOWER▼ |
||||||||
1 |
NR |
82.5 |
80.0 |
74.0 |
75.5 |
82.5 |
80.0 |
74.0 |
1.5 |
82.5 |
84.0 |
84.0 |
75.5 |
82.5 |
84.0 |
85.5 |
77.0 |
2 |
84.0 |
84.0 |
85.5 |
85.5 |
84.0 |
84.0 |
86.5 |
82.5 |
3 |
84.0 |
86.5 |
86.5 |
86.5 |
85.5 |
87.5 |
87.5 |
84.0 |
5 |
85.5 |
87.5 |
87.5 |
87.5 |
87.5 |
87.5 |
87.5 |
85.5 |
7.5 |
87.5 |
88.5 |
88.5 |
88.5 |
88.5 |
89.5 |
89.5 |
85.5 |
10 |
88.5 |
89.5 |
90.2 |
89.5 |
89.5 |
89.5 |
89.5 |
88.5 |
15 |
89.5 |
91.0 |
90.2 |
89.5 |
90.2 |
91.0 |
90.2 |
88.5 |
20 |
90.2 |
91.0 |
91.0 |
90.2 |
90.2 |
91.0 |
90.2 |
89.5 |
25 |
91.0 |
91.7 |
91.7 |
90.2 |
91.0 |
92.4 |
91.7 |
89.5 |
30 |
91.0 |
92.4 |
92.4 |
91.0 |
91.0 |
92.4 |
91.7 |
91.0 |
40 |
91.7 |
93.0 |
93.0 |
91.0 |
91.7 |
93.0 |
93.0 |
91.0 |
50 |
92.4 |
93.0 |
93.0 |
91.7 |
92.4 |
93.0 |
93.0 |
91.7 |
60 |
93.0 |
93.6 |
93.6 |
92.4 |
93.0 |
93.6 |
93.6 |
91.7 |
75 |
93.0 |
94.1 |
93.6 |
93.6 |
93.0 |
94.1 |
93.6 |
93.0 |
100 |
93.0 |
94.1 |
94.1 |
93.6 |
93.6 |
94.5 |
94.1 |
93.0 |
125 |
93.6 |
94.5 |
94.1 |
93.6 |
94.5 |
94.5 |
94.1 |
93.6 |
150 |
93.6 |
95.0 |
94.5 |
93.6 |
94.5 |
95.0 |
95.0 |
93.6 |
200 |
94.5 |
95.0 |
94.5 |
93.6 |
95.0 |
95.0 |
95.0 |
94.1 |
250 |
94.5 |
95.4 |
95.4 |
94.5 |
95.4 |
95.0 |
95.0 |
94.5 |
300 |
95.0 |
95.4 |
95.4 |
NR |
95.4 |
95.4 |
95.0 |
NR |
350 |
95.0 |
95.4 |
95.4 |
NR |
95.4 |
95.4 |
95.0 |
NR |
400 |
95.4 |
95.4 |
NR |
NR |
95.4 |
95.4 |
NR |
NR |
450 |
95.8 |
95.8 |
NR |
NR |
95.4 |
95.4 |
NR |
NR |
500 |
95.8 |
95.8 |
NR |
NR |
95.4 |
95.8 |
NR |
NR |
a Nominal efficiencies shall be established in accordance with DOE 10 C.F.R. 431. NR - No requirement. |
||||||||
Table C405.8(3)
Minimum Average Full Load Efficiency for Polyphase Small Electric Motorsa
OPEN MOTORS |
|||
NUMBER OF POLES ==> |
2 |
4 |
6 |
SYNCHRONOUS SPEED (RPM) |
3600 |
1800 |
1200 |
MOTOR HORSEPOWER |
|||
0.25 |
65.6 |
69.5 |
67.5 |
0.33 |
69.5 |
73.4 |
71.4 |
0.50 |
73.4 |
78.2 |
75.3 |
0.75 |
76.8 |
81.1 |
81.7 |
1 |
77.0 |
83.5 |
82.5 |
1.5 |
84.0 |
86.5 |
83.8 |
2 |
85.5 |
86.5 |
N/A |
3 |
85.5 |
86.9 |
N/A |
a Average full load efficiencies shall be established in accordance with 10 C.F.R. 431. |
|||
Table C405.8(4)
Minimum Average Full Load Efficiency For Capacitor-start Capacitor-run and Capacitor-start Induction-run Small Electric Motorsa
OPEN MOTORS |
|||
NUMBER OF POLES ==> |
2 |
4 |
6 |
SYNCHRONOUS SPEED (RPM) |
3600 |
1800 |
1200 |
MOTOR HORSEPOWER |
|||
0.25 |
66.6 |
68.5 |
62.2 |
0.33 |
70.5 |
72.4 |
66.6 |
0.50 |
72.4 |
76.2 |
76.2 |
0.75 |
76.2 |
81.8 |
80.2 |
1 |
80.4 |
82.6 |
81.1 |
1.5 |
81.5 |
83.8 |
N/A |
2 |
82.9 |
84.5 |
N/A |
3 |
84.1 |
N/A |
N/A |
a Average full load efficiencies shall be established in accordance with 10 C.F.R. 431. |
|||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40509 Section C405.9—((Transformers)) Vertical and horizontal transportation systems.
((C405.9 Transformers. The minimum efficiency of a low voltage dry-type distribution transformer shall be the Class I Efficiency Levels for distribution transformers specified in Table 4-2 of NEMA TP-1.)) C405.9 Vertical and horizontal transportation systems and equipment. Vertical and horizontal transportation systems and equipment shall comply with this section.
C405.9.1 Elevator cabs. For the luminaires in each elevator cab, not including signals and displays, the sum of the lumens divided by the sum of the watts shall be no less than 35 lumens per watt. Ventilation fans in elevators that do not have their own air conditioning system shall not consume more than 0.33 watts/cfm at the maximum rated speed of the fan. Controls shall be provided that will de-energize ventilation fans and lighting systems when the elevator is stopped, unoccupied and with its doors closed for over 15 minutes.
C405.9.2 Escalators and moving walks. Escalators and moving walks shall comply with ASME A17.1/CSA B44 and shall have automatic controls configured to reduce speed to the minimum permitted speed in accordance with ASME A17.1/CSA B44 or applicable local code when not conveying passengers.
EXCEPTION: | A power factor controller that reduces operating voltage in response to light loading conditions may be provided in place of the variable speed function. |
C405.9.2.1 Regenerative drive. An escalator designed either for one-way down operation only or for reversible operation shall have a variable frequency regenerative drive that supplies electrical energy to the building electrical system when the escalator is loaded with passengers whose combined weight exceeds 750 pounds.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40510 Section C405.10—((Walk-in coolers and freezers)) Controlled receptacles.
((C405.10 Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers. Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers shall comply with all of the following:
1. Lights shall use light sources with an efficacy of 40 lumens per watt or more, including ballast losses (if any). Light sources with an efficacy of less than 40 lumens per watt, including ballast losses (if any), may be used in conjunction with a timer or device that turns off the lights within 15 minutes of when the walk-in cooler or walk-in freezer is not occupied by people.)) C405.10 Controlled receptacles. At least 50 percent of all 125 volt 15- and 20-ampere receptacles installed in private offices, open offices, conference rooms, rooms used primarily for printing and/or copying functions, break rooms, individual workstations and classrooms, including those installed in modular partitions and modular office workstation systems, shall be controlled as required by this section. In rooms larger than 200 square feet (19 m2), a controlled receptacle shall be located within 72 inches (1.8 m) of each uncontrolled receptacle. Controlled receptacles shall be visibly differentiated from standard receptacles and shall be controlled by one of the following automatic control devices:
1. An occupant sensor that turns receptacle power off when no occupants have been detected for a maximum of 20 minutes.
2. A time-of-day operated control device that turns receptacle power off at specific programmed times and can be programmed separately for each day of the week. The control device shall be configured to provide an independent schedule for each portion of the building not to exceed 5,000 square feet (2,323 m2) and not to exceed one full floor. The device shall be capable of being overridden for periods of up to two hours by a timer accessible to occupants. Any individual override switch shall control the controlled receptacles for a maximum area of 5,000 square feet (465 m2). Override switches for controlled receptacles are permitted to control the lighting within the same area.
EXCEPTION: | Receptacles designated for specific equipment requiring 24-hour operation, for building maintenance functions, or for specific safety or security equipment are not required to be controlled by an automatic control device and are not required to be located within 72 inches (1.8 m) of a controlled receptacle. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40511 ((Section C405.11—Refrigerated warehouse coolers and freezers.)) Reserved.
((C405.11 Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers. Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers shall comply with all of the following:
1. Lights shall use light sources with an efficacy of 40 lumens per watt or more, including ballast losses (if any). Light sources with an efficacy of less than 40 lumens per watt, including ballast losses (if any), may be used in conjunction with a timer or device that turns off the lights within 15 minutes of when the refrigerated warehouse cooler or refrigerated warehouse freezer is not occupied by people.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40512 ((Section C405.12—Escalators and moving walks.)) Reserved.
((C405.12 Escalators and moving walks.
C405.12.1 Variable speed escalators. Where variable speed escalators and moving walks are permitted by the administrative authority, all escalators and moving walks shall reduce their operating speed to no more than 15 feet per minute when no passengers have been detected for a period of time not exceeding three times the amount of time required to transfer a passenger between landings. Such escalators and moving walks shall comply with the requirements of ANSI/ASME A17.1 for variable speed escalators and moving walks.
EXCEPTION: | A power factor controller that reduces operating voltage in response to light loading conditions may be provided in place of the variable speed function. |
C405.12.2 Regenerative drive. Escalators designed either for one-way down operation only or for reversible operation shall have variable frequency regenerative drives that supply electrical energy to the building electrical system when loaded with more than 5 passengers.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40600 Section C406—Additional efficiency package options.
((Sections C406.1 through C406.4 are not adopted.)) C406.1 Requirements. Buildings shall comply with no less than two of the following:
1. More efficient HVAC performance in accordance with Section C406.2.
2. Reduced lighting power in accordance with Section C406.3.
3. Enhanced lighting controls in accordance with Section C406.4.
4. On-site supply of renewable energy in accordance with Section C406.5.
5. Provision of a dedicated outdoor air system for certain HVAC equipment in accordance with Section C406.6.
6. High-efficiency service water heating in accordance with Section C406.7.
7. Enhanced envelope performance in accordance with Section C406.8.
8. Reduced air infiltration in accordance with Section C406.9.
C406.1.1 Tenant spaces. Tenant spaces shall comply with Section C406.2, C406.3, C406.4, or C406.7, where applicable. Where an entire building complies with Section C406.5, C406.8 or C406.9, tenant spaces within the building shall be deemed to comply with this section.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40602 Section C406.2—HVAC option.
C406.2 More efficient HVAC equipment and fan performance. Buildings shall comply with Sections C406.2.1 through C406.2.3.
C406.2.1 HVAC system selection. No less than 90 percent of the total HVAC capacity serving the building shall be provided by equipment that is listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(9) or a combination thereof.
C406.2.2 Minimum equipment efficiency. Equipment shall exceed the minimum efficiency requirements listed in Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(7) by 15 percent, in addition to the requirements of Section C403. Where multiple performance requirements are provided, the equipment shall exceed all requirements by 15 percent.
C406.2.3 Minimum fan efficiency. Stand-alone supply, return and exhaust fans designed for operating with motors over 750 watts (1 hp) shall have an energy efficiency classification of not less than FEG 71 as defined in AMCA 205. The total efficiency of the fan at the design point of operation shall be within 10 percentage points of either the maximum total efficiency of the fan or the static efficiency of the fan.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40603 Section C406.3—LPA option.
C406.3 Reduced lighting power. Buildings shall comply with Sections C406.3.1 and, where applicable, C406.3.2.
C406.3.1 Reduced lighting power density. The total interior lighting power (watts) of the building shall be determined by using 75 percent of the lighting power values specified in Table C405.4.2(1) times the floor area for the building types, or by using 75 percent of the interior lighting power allowance calculated by the Space-by-Space Method in Section C405.4.2.
C406.3.2 Lamp fraction. Not less than 95 percent of the interior lighting power (watts) from lamps in permanently installed light fixtures in dwelling units and sleeping units shall be provided by lamps with a minimum efficacy of 60 lumens per watt.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40604 Section C406.4—Lighting controls option.
C406.4 Enhanced digital lighting controls. Interior lighting shall be located, scheduled and operated in accordance with Section C405.2.2 and no less than 90 percent of the total installed interior lighting power shall be configured with the following enhanced control functions.
1. Luminaires shall be configured for continuous dimming.
2. Each luminaire shall be individually addressed.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Multiple luminaires mounted on no more than 12 linear feet of a single lighting track and addressed as a single luminaire. |
2. Multiple linear luminaires that are ganged together to create the appearance of a single longer fixture and addressed as a single luminaire, where the total length of the combined luminaires is not more than 12 feet. | |
3. Not more than eight luminaires within a daylight zone are permitted to be controlled by a single daylight responsive control. | |
4. Luminaires shall be controlled by a digital control system configured with the following capabilities: | |
4.1. Scheduling and illumination levels of individual luminaires and groups of luminaires are capable of being reconfigured through the system. | |
4.2. Load shedding. | |
4.3. In open and enclosed offices, the illumination level of overhead general illumination luminaires are configured to be individually adjusted by occupants. | |
4.4. Occupancy sensors and daylight responsive controls are capable of being reconfigured through the system. | |
5. Construction documents shall include submittal of a Sequence of Operations, including a specification outlining each of the functions required by this section. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40605 Section C406.5—On-site renewable energy option.
C406.5 On-site renewable energy. Buildings shall be provided with on-site renewable energy systems with a total system rating per square foot of conditioned floor area of the building of not less than the value specified in Table C406.5.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40606 Section C406.6—DOAS option.
C406.6 Dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS). For buildings not subject to the provisions of Section C403.2.6.1, provide DOAS in accordance with Section C403.2.6.1.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40607 Section C406.7—Service water heating option.
C406.7 Reduced energy use in service water heating. Buildings shall comply with Sections C406.7.7 and C406.7.2.
C406.7.1 Building type. Not less than 90 percent of the conditioned floor area shall be of the following types:
1. Group R-1: Boarding houses, hotels or motels.
2. Group I-2: Hospitals, psychiatric hospitals and nursing homes.
3. Group A-2: Restaurants and banquet halls or buildings containing food preparation areas.
4. Group F: Laundries.
5. Group R-2: Buildings with residential occupancies.
6. Group A-3: Health clubs and spas.
7. Buildings with a service hot water load of 10 percent or more of total building energy loads, as shown with an energy analysis as described in Section C407.
C406.7.1 Load fraction. Not less than 60 percent of the annual building service hot water energy use, or not less than 100 percent of the annual building service hot water heating energy use in buildings subject to the requirements of Section C403.6.4, shall be provided by one or more of the following:
1. Service hot water system delivering heating requirements using heat pump technology with a minimum COP of 3.0.
2. Waste heat recovery from service hot water, heat recovery chillers, building equipment, process equipment, a combined heat and power system, or other approved system.
3. Solar water-heating systems.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40608 Section C406.8—Envelope option.
C406.8 Enhanced envelope performance. The total UA of the building thermal envelope shall be 15 percent lower than the maximum allowable UA for a building of identical configuration and fenestration area in accordance with Section C402.1.4, where UA equals the sum of the U-values of each distinct envelope assembly multiplied by the area in square feet of that assembly.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-40609 Section C406.9—Air infiltration option.
C406.9 Reduced air infiltration. Air infiltration shall be verified by whole building pressurization testing conducted in accordance with ASTM E779 or ASTM E1827 by an independent third party. The measured air leakage rate of the building envelope shall not exceed 0.25 cfm/ft2 (2.0 L/s•m2) under a pressure differential of 0.3 in. water (75 Pa), with the calculated surface area being the sum of the above and below grade building envelope. A report that includes the tested surface area, floor area, air by volume, stories above grade, and leakage rates shall be submitted to the code official and the building owner.
EXCEPTION: | Where the conditioned floor area of the building is not less than 250,000 ft2 (25,000 m2), air leakage testing shall be permitted to be conducted on representative above grade sections of the building provided the conditioned floor area of tested areas is no less than 25 percent of the conditioned floor area of the building and are tested in accordance with this section. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40702 Section C407.2—Mandatory requirements.
C407.2 Mandatory requirements. Compliance with this section requires that the criteria of Sections ((C402.4)) C402.5, C403.2, C404 and C405 be met.
The building permit application for projects utilizing this method shall include in one submittal all building and mechanical drawings and all information necessary to verify that the building envelope and mechanical design for the project corresponds with the annual energy analysis. If credit is proposed to be taken for lighting energy savings, then an electrical permit application shall also be submitted and approved prior to the issuance of the building permit. If credit is proposed to be taken for energy savings from other components, then the corresponding permit application (e.g., plumbing, boiler, etc.) shall also be submitted and approved prior to the building permit application. Otherwise, components of the project that would not be approved as part of a building permit application shall be modeled the same in both the proposed building and the standard reference design and shall comply with the requirements of this code.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40703 Section C407.3—Performance-based compliance.
C407.3 Performance-based compliance. Compliance based on total building performance requires that a proposed building (proposed design) be shown to have an annual energy consumption based on site energy expressed in Btu and Btu per square foot of conditioned floor area that is less than or equal to ((the annual energy consumption of)) 87 percent of that of the standard reference design.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-122, filed 12/3/14, effective 1/3/15)
WAC 51-11C-40705 Section C407.5—Calculation procedure.
C407.5 Calculation procedure. Except as specified by this section, the standard reference design and proposed design shall be configured and analyzed using identical methods and techniques.
C407.5.1 Building specifications. The standard reference design and proposed design shall be configured and analyzed as specified by Table C407.5.1(1). Table C407.5.1(1) shall include by reference all notes contained in Table ((C402.2)) C402.1.4.
C407.5.2 Thermal blocks. The standard reference design and proposed design shall be analyzed using identical thermal blocks as specified in Section C407.5.2.1, C407.5.2.2 or C407.5.2.3.
C407.5.2.1 HVAC zones designed. Where HVAC zones are defined on HVAC design drawings, each HVAC zone shall be modeled as a separate thermal block.
EXCEPTION: | Different HVAC zones shall be allowed to be combined to create a single thermal block or identical thermal blocks to which multipliers are applied provided: |
1. The space use classification is the same throughout the thermal block. | |
2. All HVAC zones in the thermal block that are adjacent to glazed exterior walls face the same orientation or their orientations are within 45 degrees (0.79 rad) of each other. | |
3. All of the zones are served by the same HVAC system or by the same kind of HVAC system. |
C407.5.2.2 HVAC zones not designed. Where HVAC zones have not yet been designed, thermal blocks shall be defined based on similar internal load densities, occupancy, lighting, thermal and temperature schedules, and in combination with the following guidelines:
1. Separate thermal blocks shall be assumed for interior and perimeter spaces. Interior spaces shall be those located more than 15 feet (4572 mm) from an exterior wall. Perimeter spaces shall be those located closer than 15 feet (4572 mm) from an exterior wall.
2. Separate thermal blocks shall be assumed for spaces adjacent to glazed exterior walls: A separate zone shall be provided for each orientation, except orientations that differ by no more than 45 degrees (0.79 rad) shall be permitted to be considered to be the same orientation. Each zone shall include floor area that is 15 feet (4572 mm) or less from a glazed perimeter wall, except that floor area within 15 feet (4572 mm) of glazed perimeter walls having more than one orientation shall be divided proportionately between zones.
3. Separate thermal blocks shall be assumed for spaces having floors that are in contact with the ground or exposed to ambient conditions from zones that do not share these features.
4. Separate thermal blocks shall be assumed for spaces having exterior ceiling or roof assemblies from zones that do not share these features.
C407.5.2.3 Multifamily ((Group R)) residential buildings. ((Group R)) Residential spaces shall be modeled using one thermal block per space except that those facing the same orientations are permitted to be combined into one thermal block. Corner units and units with roof or floor loads shall only be combined with units sharing these features.
C407.5.3 Equipment efficiencies. All HVAC equipment in the standard reference design shall be modeled at the minimum efficiency levels, both part load and full load, in accordance with Section C403.2.3. Chillers shall use Path A efficiencies as shown in Table C403.2.3(7). Where efficiency ratings include supply fan energy, the efficiency rating shall be adjusted to remove the supply fan energy. For Baseline Systems HVAC Systems 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10 and 11, calculate the minimum COPnfcooling and COPnfheating using the equation for the applicable performance rating as indicated in Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(3). Where a full- and part-load efficiency rating is provided in Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(3), use Equation 4-12.
(Equation 4-12)
COPnfcooling = 7.84E-8 x EER x Q + 0.338 x EER
COPnfcooling = -0.0076 x SEER2 + 0.3796 x SEER
COPnfheating = 1.48E-7 x COP47 x Q + 1.062 x COP47(applies to heat-pump heating efficiencies only)
COPnfheating = -0.0296 x HSPF2 + 0.7134 x HSPF
Where:
COPnfcooling = The packaged HVAC equipment cooling energy efficiency.
COPnfheating = The packaged HVAC equipment heating energy efficiency.
Q = The AHRI-rated cooling capacity in Btu/h.
EER, SEER, COP and HSPF shall be at AHRI test conditions. Fan energy shall be modeled separately according to Table C407.5.1(1).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-407051 Table C407.5.1(1)—Specifications for the standard reference and proposed design.
Table C407.5.1(1)
Specifications for the Standard Reference and Proposed Designs
Building Component Characteristics |
Standard Reference Design |
Proposed Design |
|
Space use classification |
Same as proposed |
The space use classification shall be chosen in accordance with Table ((C405.5.2)) C405.4.2 for all areas of the building covered by this permit. Where the space use classification for a building is not known, the building shall be categorized as an office building. |
|
Roofs |
Type: Insulation entirely above deck |
As proposed |
|
Gross area: Same as proposed |
As proposed |
||
U-factor: From Table ((C402.1.2)) C402.1.4 |
As proposed |
||
Solar absorptance: 0.75 |
As proposed |
||
Emittance: 0.90 |
As proposed |
||
Walls, above-grade |
Type: Mass wall if proposed wall is mass; otherwise steel-framed wall |
As proposed |
|
Gross area: Same as proposed |
As proposed |
||
U-factor: From Table ((C402.1.2)) C402.1.4 |
As proposed |
||
Solar absorptance: 0.75 |
As proposed |
||
Emittance: 0.90 |
As proposed |
||
Walls, below-grade |
Type: Mass wall |
As proposed |
|
Gross area: Same as proposed |
As proposed |
||
U-Factor: From Table ((C402.1.2)) C402.1.4 with insulation layer on interior side of walls |
As proposed |
||
Floors, above-grade |
Type: Joist/framed floor |
As proposed |
|
Gross area: Same as proposed |
As proposed |
||
U-factor: From Table ((C402.1.2)) C402.1.4 |
As proposed |
||
Floors, slab-on-grade |
Type: Unheated |
As proposed |
|
F-factor: From Table ((C402.1.2)) C402.1.4 |
As proposed |
||
Opaque Doors |
Type: Swinging |
As proposed |
|
Area: Same as proposed |
As proposed |
||
U-factor: From Table ((C402.2)) C402.1.4 |
As proposed |
||
Vertical Fenestration Other than opaque doors |
Area |
As proposed |
|
1. The proposed vertical fenestration area; where the proposed vertical fenestration area is less than 30 percent of above-grade wall area. |
|||
2. 30 percent of above-grade wall area; where the proposed vertical fenestration area is 30 percent or more of the above-grade wall area. |
|||
U-factor: From Table ((C402.3)) C402.4 for the same framing material as proposed |
As proposed |
||
SHGC: From Table ((C402.3)) C402.4 except that for climates with no requirement (NR) SHGC = 0.40 shall be used |
As proposed |
||
External shading and PF: None |
As proposed |
||
Skylights |
Area |
As proposed |
|
1. The proposed skylight area; where the proposed skylight area is less than 3 percent of gross area of roof assembly. |
|||
2. 3 percent of gross area of roof assembly; where the proposed skylight area is 3 percent or more of gross area of roof assembly. |
|||
U-factor: From Table ((C402.3)) C402.4 |
As proposed |
||
SHGC: From Table ((C402.3)) C402.4 except that for climates with no requirement (NR) SHGC = 0.40 shall be used |
As proposed |
||
Air leakage |
For infiltration, the air leakage rate as determined below shall be modeled at 100% when the building fan system is off, and at 25% when the building fan system is on, unless otherwise approved by the building official for unusually pressurized buildings. Per PNNL Report 18898, Infiltration Modeling Guidelines for Commercial Building Energy Analysis, the building air leakage rates as determined in accordance with Section C402.5.1.2 at 0.30 in. w.g. (75 Pa) shall be converted for modeling in annual energy analysis programs by being multiplied by 0.112 unless other multipliers are approved by the building official (e.g., a tested air leakage of 0.40 cfm/ft2 of total building envelope area at 0.30 in. w.g. (75 Pa) would be calculated at 0.045 cfm/ft2 of building envelope area). The calculated infiltration rate shall be normalized to the input required by the modeling software. |
The Proposed Design air-leakage rate shall be the same as the Standard Design. |
|
Lighting, interior |
The interior lighting power shall be determined in accordance with Table ((C405.5.2. Where the occupancy of the building is not known, the lighting power density shall be 1.0 watt per square foot (10.73 W/m2) based on the categorization of buildings with unknown space classification as offices)) C405.4.2. As proposed when the occupancy of the space is not known. |
As proposed; where the occupancy of the space is not known, the lighting power density shall be based on the space classification as offices in Table C405.4.2(1). |
|
Automatic lighting controls (e.g., programmable controls or automatic controls for daylight utilization) shall be modeled in the standard reference design as required by Section C405. |
|||
Lighting, exterior |
The lighting power shall be determined in accordance with Table ((C405.6.2(2))) C405.5.2(2). Areas and dimensions of tradable and nontradable surfaces shall be the same as proposed. |
As proposed |
|
Internal gains |
Same as proposed |
Receptacle, motor and process loads shall be modeled and estimated based on the space use classification. All end-use load components within and associated with the building shall be modeled to include, but not be limited to, the following: Exhaust fans, parking garage ventilation fans, exterior building lighting, swimming pool heaters and pumps, elevators, escalators, refrigeration equipment and cooking equipment. |
|
Schedules |
Same as proposed |
Operating schedules shall include hourly profiles for daily operation and shall account for variations between weekdays, weekends, holidays and any seasonal operation. Schedules shall model the time-dependent variations in occupancy, illumination, receptacle loads, thermostat settings, mechanical ventilation, HVAC equipment availability, service hot water usage and any process loads. The schedules shall be typical of the proposed building type as determined by the designer and approved by the jurisdiction. |
|
((Mechanical ventilation)) Outdoor airflow rates |
((Same as proposed, except when modeling demand-control ventilation in the proposed design when its use is not required by Section C403.2.5.1 or occupancy sensor ventilation controls when their use is not required by Section C403.2.5.2.)) Same as proposed, or no higher than those allowed by Section C403.2.6 (without exception 1), whichever is less. |
As proposed, in accordance with Section ((C403.2.5)) C403.2.6. |
|
Demand control ventilation: Shall be modeled as required by Section C403.2.6.1 including reduction to the minimum ventilation rate when unoccupied. |
As proposed |
||
Heating systems |
Fuel type: Same as proposed design |
As proposed |
|
Equipment typea: From Tables C407.5.1(2) ((and)), C407.5.1(3), and C407.5.1(4) |
As proposed |
||
Efficiency: From Tables C403.2.3(2), C403.2.3(3), C403.2.3(4) and C403.2.3(5) |
As proposed |
||
Preheat coils: ((If the HVAC system in the proposed design has a preheat coil and a preheat coil can be modeled in the standard reference design, the standard reference design shall be modeled with a preheat coil controlled in the same manner as the proposed design)) For HVAC system numbers 1 through 4, a preheat coil shall be modeled controlled to a fixed setpoint 20°F less than the design room heating temperature setpoint. |
|||
Capacityb: Sized proportionally to the capacities in the proposed design based on sizing runs, i.e., the ratio between the capacities used in the annual simulations and the capacities determined by the sizing runs shall be the same for both the proposed design and standard reference design, and shall be established such that no smaller number of unmet heating load hours and no larger heating capacity safety factors are provided than in the proposed design. |
As proposed |
||
Weather conditions used in sizing runs to determine standard reference design equipment capacities may be based either on hourly historical weather files containing typical peak conditions or on design days developed using 99.6% heating design temperatures and 1% dry-bulb and 1% wet-bulb cooling design temperatures. |
|||
Cooling systems |
Fuel type: Same as proposed design |
As proposed |
|
Equipment typec: From Tables C407.5.1(2) ((and)), C407.5.1(3), and C407.5.1(4) |
As proposed |
||
Efficiency: From Tables C403.2.3(1), C403.2.3(2) and C403.2.3(3). Chillers shall use Path A efficiency. |
As proposed |
||
Capacityb: Sized proportionally to the capacities in the proposed design based on sizing runs, i.e., the ratio between the capacities used in the annual simulations and the capacities determined by the sizing runs shall be the same for both the proposed design and standard reference design, and shall be established such that no smaller number of unmet cooling load hours and no larger cooling capacity safety factors are provided than in the proposed design. |
As proposed |
||
Economizerd: Same as proposed, in accordance with Section ((C403.4.1)) C403.3. The high-limit shutoff shall be a dry-bulb switch with a setpoint as determined by Table ((C403.3.1.1.3(2))) C403.3.3.3. |
As proposed |
||
Energy recovery |
Standard reference design systems shall be modeled where required in Section ((C403.2.6)) C403.5. |
As proposed |
|
Fan systems |
Airflow rate: System design supply airflow rates for the standard reference design shall be based on a supply-air-to-room-air temperature difference of 20°F or the required ventilation air or makeup air, whichever is greater. If return or relief fans are specified in the proposed design, the standard reference design shall also be modeled with fans serving the same functions and sized for the standard reference design system supply fan air quantity less the minimum outdoor air, or 90% of the supply fan air quantity, whichever is larger. |
As proposed |
|
Motor brake horsepower: System fan electrical power for supply, return, exhaust, and relief (excluding power to fan-powered VAV boxes) shall be calculated using the following formulas: For systems ((8 and 10)) in Table C407.5.1(4), Pfan = CFMS × 0.3 For all other systems, including DOAS, Pfan = bhp × 746/Fan Motor Efficiency Where: Pfan = Electric power to fan motor (watts) bhp = Brake horsepower of standard reference design fan motor from Table ((C403.2.10.1(1))) C403.2.12.1(1) – Option 2 Fan motor = The efficiency from Tables ((C403.2.13)) C405.8(1) through C405.8(4) for the efficiency next motor size greater than the bhp using the enclosed motor at 1800 rpm CFMS = The standard reference design system maximum design supply fan airflow rate in cfm DOAS fan power shall be calculated separately from the brake horsepower allowance. |
As proposed |
||
On-site renewable energy |
No on-site renewable energy shall be modeled in the standard reference design. |
As proposed. ((On-site renewable energy sources energy shall not be considered to be consumed energy and shall not be included in the proposed building performance.)) |
|
Shading from adjacent structures/terrain |
Same as proposed. |
For the standard reference design and the proposed building, shading by permanent structures and terrain shall be taken into account for computing energy consumption whether or not these features are located on the building site. A permanent fixture is one that is likely to remain for the life of the proposed design. |
|
Service water heating |
Fuel type: Same as proposed |
As proposed |
|
Efficiency: From Table C404.2 |
As proposed |
||
Capacity: Same as proposed |
|||
Demand: Same as proposed |
((Demand:)) Service hot-water energy consumption shall be calculated explicitly based upon the volume of service hot water required and the entering makeup water and the leaving service hot water temperatures. Entering water temperatures shall be estimated based upon the location. Leaving temperatures shall be based upon the end-use requirements. Service water loads and usage shall be the same for both the standard reference design and the proposed design and shall be documented by the calculation procedures recommended by the manufacturer's specifications or generally accepted engineering methods. |
||
Where no service water hot water system exists or is specified in the proposed design, no service hot water heating shall be modeled. |
As proposed |
||
Drain water heat recovery: Not required. |
As proposed Drain water heat recovery modeling shall take into account manufacturer's rated efficiencies per C404.9, quantity of connected drains, the proportional flow rates between the waste stream and the preheated stream. Reductions in service water heating energy use for drain water heat recovery shall be demonstrated by calculations. |
||
a | Where no heating system exists or has been specified, the heating system shall be modeled as fossil fuel. The system characteristics shall be identical in both the standard reference design and proposed design. |
b | The ratio between the capacities used in the annual simulations and the capacities determined by sizing runs shall be the same for both the standard reference design and proposed design. |
c | Where no cooling system exists or no cooling system has been specified, the cooling system shall be modeled as an air-cooled single-zone system, one unit per thermal zone. The system characteristics shall be identical in both the standard reference design and proposed design. |
d | ((Reserved.)) If an economizer is required in accordance with Section C403.3 and where no economizer exists or is specified in the proposed design, then an air economizer shall be provided in the standard reference design in accordance with Section C403.3. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-24-122, filed 12/3/14, effective 1/3/15)
WAC 51-11C-407052 Table C407.5.1(2)/(3)—HVAC systems map.
Table C407.5.1(2)
HVAC Systems Map for Buildings Governed by Section C403.2.6.1d
Condenser Cooling Sourcea |
Heating System Classificationb |
Standard Reference Design HVAC System Typec |
|
Single-Zone Group R System |
All Other |
||
Electric resistance |
System 5 |
System 5 |
|
Water/ground |
Heat pump |
System 6 |
System 6 |
Fossil fuel |
System 7 |
System 7 |
|
Electric resistance |
System 8 |
System 9 |
|
Air/none |
Heat pump |
System 8 |
System 9 |
Fossil fuel |
System 10 |
System 11 |
|
a | Select "water/ground" if the proposed design system condenser is water or evaporatively cooled; select "air/none" if the condenser is air cooled. Closed-circuit dry coolers shall be considered air cooled. Systems utilizing district cooling shall be treated as if the condenser water type were "water." If no mechanical cooling is specified or the mechanical cooling system in the proposed design does not require heat rejection, the system shall be treated as if the condenser water type were "Air." For proposed designs with ground-source or groundwater-source heat pumps, the standard reference design HVAC system shall be water-source heat pump (System 6). |
b | Systems utilizing district heating (steam or hot water) or district cooling and systems with no heating capability shall be treated as if the heating system type were "fossil fuel" for the purpose of Standard Reference Design HVAC system selection. Otherwise, select the path that corresponds to the proposed design heat source: Electric resistance, heat pump (including air source and water source), or fuel fired. For systems with mixed fuel heating sources, the system or systems that use the secondary heating source type (the one with the smallest total installed output capacity for the spaces served by the system) shall be modeled identically in the standard reference design and the primary heating source type shall be used to determine standard reference design HVAC system type. |
c | Select the standard reference design HVAC system category: The system under "single-zone Group R system" shall be selected if the HVAC system in the proposed design is a single-zone system and serves a residential space. The system under "single-zone other than Group R system" shall be selected if the HVAC system in the proposed design is a single-zone system and serves other than Group R spaces. The system under "all other" shall be selected for all other cases. |
d | This table covers those building types required by Section C403.2.6.1 to install Dedicated Outdoor Air Systems: Office, retail, education, libraries and fire stations. |
Table C407.5.1(3)
HVAC Systems Map for All Other Buildings
Standard Reference Design HVAC System Typec |
||||
Condenser Cooling Sourcea |
Heating System Classificationb |
Single-Zone Group R System |
Single-Zone Other than Group R System |
All Other |
Electric resistance |
System 5 |
System 5 |
System 1 |
|
Water/ground |
Heat pump |
System 6 |
System 6 |
System 6 |
Fossil fuel |
System 7 |
System 7 |
System 2 |
|
Electric resistance |
System 8 |
System 9 |
System 3 |
|
Air/none |
Heat pump |
System 8 |
System 9 |
System 3 |
Fossil fuel |
System 10 |
System 11 |
System 4 |
|
a | Select "water/ground" if the proposed design system condenser is water or evaporatively cooled; select "air/none" if the condenser is air cooled. Closed-circuit dry coolers shall be considered air cooled. Systems utilizing district cooling shall be treated as if the condenser water type were "water." If no mechanical cooling is specified or the mechanical cooling system in the proposed design does not require heat rejection, the system shall be treated as if the condenser water type were "Air." For proposed designs with ground-source or groundwater-source heat pumps, the standard reference design HVAC system shall be water-source heat pump (System 6). |
b | Systems utilizing district heating (steam or hot water) or district cooling and systems with no heating capability shall be treated as if the heating system type were "fossil fuel" for the purpose of Standard Reference Design HVAC system selection. Otherwise, select the path that corresponds to the proposed design heat source: Electric resistance, heat pump (including air source and water source), or fuel fired. For systems with mixed fuel heating sources, the system or systems that use the secondary heating source type (the one with the smallest total installed output capacity for the spaces served by the system) shall be modeled identically in the standard reference design and the primary heating source type shall be used to determine standard reference design HVAC system type. |
c | Select the standard reference design HVAC system category: The system under "single-zone Group R system" shall be selected if the HVAC system in the proposed design is a single-zone system and serves a residential space. The system under "single-zone other than Group R system" shall be selected if the HVAC system in the proposed design is a single-zone system and serves other than Group R spaces. The system under "all other" shall be selected for all other cases. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-407053 Table ((C407.5.1(3))) C407.5.1(4)—Specifications for the standard reference design HVAC system description.
Table ((C407.5.1(3))) C407.5.1(4)
Specifications for the Standard Reference Design HVAC System Descriptions
System No. |
System Type |
Fan Control |
Cooling Type |
Heating Type |
1 |
Variable air volume with parallel fan-powered boxesa |
VAVd |
Chilled watere |
Electric resistance |
2 |
Variable air volume with reheatb |
VAVd |
Chilled watere |
Hot water fossil fuel boilerf |
3 |
Packaged variable air volume with parallel fan-powered boxesa |
VAVd |
Direct expansionc |
Electric resistance |
4 |
Packaged variable air volume with reheatb |
VAVd |
Direct expansionc |
Hot water fossil fuel boilerf |
5 |
Two-pipe fan coil |
Constant volumei,j |
Chilled watere |
Electric resistance |
6 |
Water-source heat pump |
Constant volumei,j |
Direct expansionc |
Electric heat pump and boilerg |
7k |
Four-pipe fan coil |
Constant volumei,j |
Chilled watere |
Hot water fossil fuel boilerf |
8k |
Packaged terminal heat pump |
Constant volumei,j |
Direct expansionc |
Electric heat pumph |
9k |
Packaged rooftop heat pump |
Constant volumei,j |
Direct expansionc |
Electric heat pumph |
10k |
Packaged terminal air conditioner |
Constant volumei,j |
Direct expansion |
Hot water fossil fuel boilerf |
11k |
Packaged rooftop air conditioner |
Constant volumei,j |
Direct expansion |
Fossil fuel furnace |
For SI: | 1 foot = 304.8 mm, 1 cfm/ft2 = 0.0004719, 1 Btu/h = 0.293/W, °C = [(°F) -32/1.8]. |
a | VAV with parallel boxes: Fans in parallel VAV fan-powered boxes shall be sized for 50 percent of the peak design flow rate and shall be modeled with 0.35 W/cfm fan power. Minimum volume setpoints for fan-powered boxes shall be equal to the minimum rate for the space required for ventilation consistent with Section ((C403.4.5)) C403.4.4, Exception ((5)) 4. Supply air temperature ((setpoint shall be constant at the design condition)) shall be reset based on zone demand. Design airflow rates shall be sized for the maximum reset supply air temperature. The air temperature for cooling shall be reset higher by 5°F under the minimum cooling load conditions. |
b | VAV with reheat: Minimum volume setpoints for VAV reheat boxes shall be 0.4 cfm/ft2 of floor area. Supply air temperature shall be reset based on zone demand ((from the design temperature difference to a 10°F temperature difference under minimum load conditions)). Design airflow rates shall be sized for the maximum reset supply air temperature((, i.e., a 10°F temperature difference)). The air temperature for cooling shall be reset higher by 5°F under the minimum cooling load conditions. |
c | Direct expansion: The fuel type for the cooling system shall match that of the cooling system in the proposed design. |
d | VAV: When the proposed design system has a supply, return or relief fan motor horsepower (hp) requiring variable flow controls as required by Section ((C403.2.12)) C403.2.11.5, the corresponding fan in the VAV system of the standard reference design shall be modeled assuming a variable speed drive. For smaller fans, a forward-curved centrifugal fan with inlet vanes shall be modeled. If the proposed design's system has a direct digital control system at the zone level, static pressure setpoint reset based on zone requirements in accordance with Section ((C403.4.2)) C403.4.1 shall be modeled. |
e | Chilled water: For systems using purchased chilled water, the chillers are not explicitly modeled. Otherwise, the standard reference design's chiller plant shall be modeled with chillers having the number as indicated in Table ((C407.5.1(4))) C407.5.1(5) as a function of standard reference building chiller plant load and type as indicated in Table ((C407.5.1(5))) C407.5.1(6) as a function of individual chiller load. Where chiller fuel source is mixed, the system in the standard reference design shall have chillers with the same fuel types and with capacities having the same proportional capacity as the proposed design's chillers for each fuel type. Chilled water supply temperature shall be modeled at 44°F design supply temperature and 56°F return temperature. Piping losses shall not be modeled in either building model. Chilled water supply water temperature shall be reset in accordance with Section ((C403.4.3.4)) C403.4.2.4. Pump system power for each pumping system shall be the same as the proposed design; if the proposed design has no chilled water pumps, the standard reference design pump power shall be 22 W/gpm (equal to a pump operating against a 75-foot head, 65-percent combined impeller and motor efficiency). The chilled water system shall be modeled as primary-only variable flow with flow maintained at the design rate through each chiller using a bypass. Chilled water pumps shall be modeled as riding the pump curve or with variable-speed drives when required in Section ((C403.4.3.4)) C403.4.2.4. The heat rejection device shall be an axial fan cooling tower with variable speed fans if required in Section ((C403.4.4 or Section C403.2.12)) C403.4.3. Condenser water design supply temperature shall be 85°F or 10°F approach to design wet-bulb temperature, whichever is lower, with a design temperature rise of 10°F. The tower shall be controlled to maintain a 70°F leaving water temperature where weather permits, floating up to leaving water temperature at design conditions. Pump system power for each pumping system shall be the same as the proposed design; if the proposed design has no condenser water pumps, the standard reference design pump power shall be 19 W/gpm (equal to a pump operating against a 60-foot head, 60-percent combined impeller and motor efficiency). Each chiller shall be modeled with separate condenser water and chilled water pumps interlocked to operate with the associated chiller. |
f | Fossil fuel boiler: For systems using purchased hot water or steam, the boilers are not explicitly modeled. Otherwise, the boiler plant shall use the same fuel as the proposed design and shall be natural draft. The standard reference design boiler plant shall be modeled with a single boiler if the standard reference design plant load is 600,000 Btu/h and less and with two equally sized boilers for plant capacities exceeding 600,000 Btu/h. Boilers shall be staged as required by the load. Hot water supply temperature shall be modeled at 180°F design supply temperature and 130°F return temperature. Piping losses shall not be modeled in either building model. Hot water supply water temperature shall be reset in accordance with Section ((C403.4.3.4)) C403.4.2.4. Pump system power for each pumping system shall be the same as the proposed design; if the proposed design has no hot water pumps, the standard reference design pump power shall be 19 W/gpm (equal to a pump operating against a 60-foot head, 60-percent combined impeller and motor efficiency). The hot water system shall be modeled as primary only with continuous variable flow. Hot water pumps shall be modeled as riding the pump curve or with variable speed drives when required by Section ((C403.4.3.4)) C403.4.2.4. |
g | Electric heat pump and boiler: Water-source heat pumps shall be connected to a common heat pump water loop controlled to maintain ((temperatures between)) a heating setpoint of 60°F and cooling setpoint of 90°F. Heat rejection from the loop shall be provided by an axial fan closed-circuit evaporative fluid cooler with variable speed fans if required in Section ((C403.4.2)) C403.4.2.1 or ((Section C403.2.12)) C403.2.13. Heat addition to the loop shall be provided by a boiler that uses the same fuel as the proposed design and shall be natural draft. If no boilers exist in the proposed design, the standard reference building boilers shall be fossil fuel. The standard reference design boiler plant shall be modeled with a single boiler if the standard reference design plant load is 600,000 Btu/h or less and with two equally sized boilers for plant capacities exceeding 600,000 Btu/h. Boilers shall be staged as required by the load. Piping losses shall not be modeled in either building model. Pump system power shall be the same as the proposed design; if the proposed design has no pumps, the standard reference design pump power shall be 22 W/gpm, which is equal to a pump operating against a 75-foot head, with a 65-percent combined impeller and motor efficiency. Loop flow shall be variable with flow shutoff at each heat pump when its compressor cycles off as required by Section ((C403.4.3.3)) C403.4.2.3. Loop pumps shall be modeled as riding the pump curve or with variable speed drives when required by Section ((C403.4.3.4)) C403.4.2.4. |
h | Electric heat pump: Electric air-source heat pumps shall be modeled with electric auxiliary heat and an outdoor air thermostat. The system shall be controlled ((with a multistage space thermostat and an outdoor air thermostat wired)) to energize auxiliary heat only ((on the last thermostat stage and)) when outdoor air temperature is less than 40°F. ((In heating operation the system shall be controlled to operate the heat pump as the first stage of heating, before energizing the electric auxiliary heat,)) The air-source heat pump shall be modeled to continue to operate while auxiliary heat is energized. The air-source heat pump shall be modeled to operate down to a minimum outdoor air temperature of 35°F for System No. 8 or ((17°F)) 0°F for System No. 9. If the Proposed Design utilizes the same system type as the Standard Design (PTHP or PSZ-HP), the Proposed Design shall be modeled with the same minimum outdoor air temperature for heat pump operation as the Standard Design. For temperatures below the stated minimum outdoor air temperatures, the electric auxiliary heat shall be controlled to provide the full heating load. |
i | Constant volume: For building types governed by Section C403.2.6.1, fans shall be controlled ((in the same manner as in the proposed design; i.e., fan operation whenever the space is occupied or)) to cycle with load; i.e., fan operation cycled on calls for heating and cooling. If the fan is modeled as cycling and the fan energy is included in the energy efficiency rating of the equipment, fan energy shall not be modeled explicitly. For all other buildings, fans shall be controlled in the same manner as in the proposed design; i.e., fan operation whenever the space is occupied or fan operation cycled on calls for heating and cooling. If the fan is modeled as cycling and the fan energy is included in the energy efficiency rating of the equipment, fan energy shall not be modeled explicitly. |
j | Fan speed control: Fans shall operate as one- or two-speed as required by Section C403.2.11.5, regardless of the fan speed control used in the proposed building. |
k | Outside air: For building types governed by Section C403.2.6.1, outside air shall be supplied by a separate dedicated outside air system (DOAS) operating in parallel with terminal equipment. The terminal equipment fan system cycle calls for heating and cooling. DOAS shall include an Energy Recovery Ventilation System with a minimum effectiveness in accordance with Section C403.5. |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-407054 Table ((C407.5.1(4))) C407.5.1(5)—Number of chillers.
Table ((C407.5.1(4))) C407.5.1(5)
Number of Chillers
Total Chiller Plant Capacity |
Number of Chillers |
≤ 300 tons |
1 |
˃ 300 tons, < 600 tons |
2, sized equally |
≥ 600 tons |
2 minimum, with chillers added so that no chiller is larger than 800 tons, all sized equally |
For SI: | 1 ton = 3517 W. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-407055 Table ((C407.5.1(5))) C407.5.1(6)—Water chiller types.
Table ((C407.5.1(5))) C407.5.1(6)
Water Chiller Types
Individual Chiller Plant Capacity |
Electric-Chiller Type |
Fossil Fuel Chiller Type |
≤ 100 tons |
Water-cooled Reciprocating |
Single-effect absorption, direct fired |
˃ 100 tons, < 300 tons |
Water-cooled Screw |
Double-effect absorption, direct fired |
≥ 300 tons |
Water-cooled Centrifugal |
Double-effect absorption, direct fired |
For SI: | 1 ton = 3517 W. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40706 Section C407.6—Calculation software tool.
C407.6 Calculation software tools. Calculation procedures used to comply with this section shall be software tools capable of calculating the annual energy consumption of all building elements that differ between the standard reference design and the proposed design and shall include the following capabilities.
1. Building operation for a full calendar year (8,760 hours).
2. Climate data for a full calendar year (8,760 hours) and shall reflect approved coincident hourly data for temperature, solar radiation, humidity and wind speed for the building location.
3. Ten or more thermal zones.
4. Thermal mass effects.
5. Hourly variations in occupancy, illumination, receptacle loads, thermostat settings, mechanical ventilation, HVAC equipment availability, service hot water usage and any process loads.
6. Part-load performance curves for mechanical equipment.
7. Capacity and efficiency correction curves for mechanical heating and cooling equipment.
8. Printed code official inspection checklist listing each of the proposed design component characteristics from Table C407.5.1(1) determined by the analysis to provide compliance, along with their respective performance ratings (e.g., R-value, U-factor, SHGC, HSPF, AFUE, SEER, EF, etc.).
9. Air-side economizers with integrated control.
10. Standard reference design characteristics specified in Table C407.5.1(1).
C407.6.1 Specific approval. Performance analysis tools meeting the applicable subsections of Section C407 and tested according to ASHRAE Standard 140 shall be permitted to be approved. Tools are permitted to be approved based on meeting a specified threshold for a jurisdiction. The code official shall be permitted to approve tools for a specified application or limited scope.
C407.6.2 Input values. Where calculations require input values not specified by Sections C402, C403, C404 and C405, those input values shall be taken from an approved source.
C407.6.3 Exceptional calculation methods. ((When)) Where the simulation program does not model a design, material, or device of the proposed design, an Exceptional Calculation Method shall be used if approved by the ((building)) code official. If there are multiple designs, materials, or devices that the simulation program does not model, each shall be calculated separately and Exceptional Savings determined for each. ((At no time shall)) The total Exceptional Savings shall not constitute more than half of the difference between the baseline building performance and the proposed building performance. ((All)) Applications for approval of an exceptional method shall include:
1. Step-by-step documentation of the Exceptional Calculation Method performed detailed enough to reproduce the results;
2. Copies of all spreadsheets used to perform the calculations;
3. A sensitivity analysis of energy consumption when each of the input parameters is varied from half to double the value assumed;
4. The calculations shall be performed on a time step basis consistent with the simulation program used; and
5. The Performance Rating calculated with and without the Exceptional Calculation Method.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40801 Section C408.1—General.
C408.1 General. ((This section covers the commissioning of the building)) A building commissioning process led by a certified commissioning professional shall be completed for mechanical systems in Section C403, service water heating systems in Section C404, electrical power and lighting systems in Section C405 and energy metering in Section C409.
EXCEPTION: | Buildings, or portions thereof, which are exempt from Sections C408.2 through C408.6 may be excluded from the commissioning process. |
C408.1.1 Commissioning in construction documents. Construction document notes shall clearly indicate provisions for commissioning and completion requirements in accordance with this section and are permitted to refer to specifications for further requirements.
C408.1.2 Commissioning plan. A commissioning plan shall be developed by the project's certified commissioning professional and shall outline the organization, schedule, allocation of resources, and documentation requirements of the commissioning process. Items 1 through 4 shall be included with the construction documents, and items 5 through 8 shall be submitted prior to the first mechanical inspection. For projects where no mechanical inspection is required, items 5 through 8 shall be submitted prior to the first electrical inspection.
1. A narrative description of the activities that will be accomplished during each phase of commissioning, including the personnel intended to accomplish each of the activities.
2. Roles and responsibilities of the commissioning team, including statement of qualifications of the commissioning professional in accordance with Section C408.1.1.
3. A schedule of activities including systems testing and balancing, functional performance testing, and verification of the building documentation requirements in Section C103.6.
4. Where the certified commissioning professional is an employee of one of the registered design professionals of record or an employee or subcontractor of the project contractor, an In-House Commissioning Disclosure and Conflict Management Plan shall be submitted with the commissioning plan. This plan shall disclose the certified commissioning professional's contractual relationship with other team members and provide a conflict management plan demonstrating that the certified commissioning professional is free to identify any issues discovered and report directly to the owner.
5. A listing of the specific equipment, appliances or systems to be tested and a description of the tests to be performed.
6. Functions to be tested.
7. Conditions under which the test will be performed.
8. Measurable criteria for performance.
C408.1.3 Final commissioning report. A final commissioning report shall be completed and certified by the certified commissioning professional and delivered to the building owner or owner's authorized agent. The report shall be organized with mechanical, lighting, service water heating and metering findings in separate sections to allow independent review. The report shall record the activities and results of the commissioning process and be developed from the final commissioning plan with all of its attached appendices. The report shall include:
1. Results of functional performance tests.
2. Disposition of deficiencies found during testing, including details of corrective measures used or proposed.
3. Functional performance test procedures used during the commissioning process including measurable criteria for test acceptance, provided herein for repeatability.
EXCEPTION: | Deferred tests which cannot be performed at the time of report preparation due to climatic conditions. |
C408.1.4. Commissioning process completion requirements. Prior to ((passing)) the final mechanical, plumbing and electrical inspections or obtaining a certificate of occupancy, the ((registered design)) certified commissioning professional or approved agency shall provide evidence of systems commissioning and completion in accordance with the provisions of this section.
Copies of all documentation shall be given to the owner and made available to the code official upon request in accordance with Section((s C408.1.2 and C408.1.3.
C408.1.1 Commissioning plan. A commissioning plan shall be developed by a registered design professional or approved agency and shall include the following items:
1. A narrative description of the activities that will be accomplished during each phase of commissioning, including the personnel intended to accomplish each of the activities.
2. Roles and responsibilities of the commissioning team.
3. A schedule of activities including systems testing and balancing, functional testing, and supporting documentation.
4. A listing of the specific equipment, appliances or systems to be tested and a description of the tests to be performed.
5. Functions to be tested.
6. Conditions under which the test will be performed.
7. Measurable criteria for performance.
C408.1.2 Preliminary commissioning report.)) C408.1.4.3.
C408.1.4.1 Commissioning progress report for code compliance. A preliminary report of commissioning test procedures and results shall be completed and certified by the ((registered design)) certified commissioning professional or approved agency and provided to the building owner or owner's authorized agent. The report shall be organized with mechanical, lighting, service water heating and metering findings in separate sections to allow independent review. The report shall be identified as "Preliminary Commissioning Report" and shall identify:
1. Itemization of deficiencies found during testing required by this ((section)) code that have not been corrected at the time of report preparation.
2. Deferred tests that cannot be performed at the time of report preparation because of climatic conditions, with anticipated date of completion.
3. Climatic conditions required for performance of the deferred tests.
4. ((Record of progress and completion of operator training.
C408.1.2.1)) Status of the project's record documents, manuals and systems operation training with respect to requirements in Section C103.6.
C408.1.4.2 Acceptance of report. Buildings, or portions thereof, shall not ((pass the final mechanical and electrical inspections or obtain a certificate of occupancy, until such time as the)) be considered acceptable for a final inspection pursuant to Section C104.3 until the code official has received a letter of transmittal from the building owner acknowledging that the building owner or owner's authorized agent has received the Preliminary Commissioning Report. Completion of the Commissioning Compliance Checklist (Figure ((C408.1.2.1)) C408.1.4.2) is deemed to satisfy this requirement.
((C408.1.2.2)) C408.1.4.3 Copy of report. The code official shall be permitted to require that a copy of the Preliminary Commissioning Report be made available for review by the code official.
((C408.1.3 Documentation requirements. The construction documents shall specify that the documents described in this section be provided to the building owner within 90 days of the date of receipt of the certificate of occupancy.
C408.1.3.1 Record documents. Construction documents shall be updated to convey a record of the alterations to the original design. Such updates shall include updated mechanical, electrical and control drawings red-lined, or redrawn if specified, that show all changes to size, type and locations of components, equipment and assemblies.
C408.1.3.2 Manuals. An operating and maintenance manual shall be provided and include all of the following:
1. Submittal data stating equipment size and selected options for each piece of equipment requiring maintenance.
2. Manufacturer's operation manuals and maintenance manuals for each piece of equipment requiring maintenance, except equipment not furnished as part of the project. Required routine maintenance actions shall be clearly identified.
3. Name and address of at least one service agency.
4. Controls system maintenance and calibration information, including wiring diagrams, schematics, record documents, and control sequence descriptions. Desired or field-determined setpoints shall be permanently recorded on control drawings at control devices or, for digital control systems, in system programming instructions.
5. A narrative of how each system is intended to operate, including recommended setpoints. Sequence of operation is not acceptable for this requirement.
C408.1.3.3 System balancing report. A written report describing the activities and measurements completed in accordance with Section C408.2.2.
C408.1.3.4 Final commissioning report. A report of test procedures and results identified as "Final Commissioning Report" shall be delivered to the building owner and shall include:
1. Results of functional performance tests.
2. Disposition of deficiencies found during testing, including details of corrective measures used or proposed.
3. Functional performance test procedures used during the commissioning process including measurable criteria for test acceptance, provided herein for repeatability.
EXCEPTION: | Deferred tests which cannot be performed at the time of report preparation due to climatic conditions. |
C408.1.4 Systems operation training. Training of the maintenance staff for equipment included in the manuals required by Section C408.1.3.2 shall include at a minimum:
1. Review of systems documentation.
2. Hands-on demonstration of all normal maintenance procedures, normal operating modes, and all emergency shutdown and start-up procedures.
3. Training completion report.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-408012 Figure ((C408.1.2.1)) C408.1.4.2—Commissioning compliance checklist.
Figure ((C408.1.2.1)) C408.1.4.2
Commissioning Compliance Checklist
((Project Name: |
||||
Project Information |
Project Address: |
|||
Commissioning Authority: |
||||
Commissioning Plan |
□ |
Commissioning Plan was used during construction and included items below |
||
(Section 408.1.1) |
• |
A narrative description of activities and the personnel intended to accomplish each one |
||
• |
Measurable criteria for performance |
|||
• |
Functions to be tested |
|||
Systems Balancing |
□ |
Systems Balancing has been completed |
||
(Section C408.2.2) |
• |
Air and Hydronic systems are proportionately balanced in a manner to first minimize throttling losses. |
||
• |
Test ports are provided on each pump for measuring pressure across the pump. |
|||
Functional Testing |
□ |
HVAC Systems Equipment Testing has been completed (Section C408.2.3.1) |
||
(Section C408.2.3, C408.3.1, C408.4.1, C408.4.1.3 and C408.5.1) |
HVAC equipment has been tested to demonstrate the installation and operation of components, systems and system-to-system interfacing relationships in accordance with approved plans and specifications |
|||
□ |
HVAC Controls Functional Testing has been completed (Section C408.2.3.2) |
|||
HVAC controls have been tested to ensure that control devices are calibrated, adjusted and operate properly. Sequences of operation have been functionally tested to ensure they operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications |
||||
□ |
Economizers Functional Testing has been completed (Section C408.2.3.3) |
|||
Economizers operate in accordance with manufacturer's specifications |
||||
□ |
Lighting Controls Functional Testing has been completed (Section C408.3.1) |
|||
Lighting controls have been tested to ensure that control devices, components, equipment, and systems are calibrated, adjusted and operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications |
||||
□ |
Service Water Heating System Functional Testing has been completed (Section C408.4.1) |
|||
Service water heating equipment has been tested to ensure that control devices, components, equipment, and systems are calibrated, adjusted and operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications |
||||
□ |
Pool and Spa Functional Testing has been completed (Section C408.4.1.3) |
|||
Pools and spas have been tested to ensure that service water heating equipment, time switches and heat recovery equipment are calibrated, adjusted and operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications |
||||
□ |
Metering System Functional Testing has been completed (Section C408.5.1) |
|||
Energy source meters, energy end-use meters, the energy metering data acquisition system and required display are calibrated adjusted and operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications |
||||
Supporting Documents |
□ |
Manuals, record documents and training have been completed or are scheduled |
||
(Section 408.1.3.2) |
• |
System documentation has been provided to the owner or scheduled date: |
||
• |
Record documents have been submitted to owner or scheduled date: |
|||
• |
Training has been completed or scheduled date: |
|||
Commissioning Report |
□ |
Preliminary Commissioning Report submitted to Owner and includes items below |
||
(Section C408.1.2) |
• |
Deficiencies found during testing required by this section which have not been corrected at the time of report preparation |
||
• |
Deferred tests, which cannot be performed at the time of report preparation due to climatic conditions |
|||
Certification |
□ |
I hereby certify that all requirements for Commissioning have been completed in accordance with the Washington State Energy Code, including all items above |
||
Building Owner or Owner's Representative |
Date)) |
|||
Project Name: |
||||
Project Information |
Project Address: |
|||
Certified Commissioning Professional: |
||||
Certifying Body: |
||||
Commissioning Plan (Section 408.1.2) |
□ |
Commissioning Plan was used during construction |
||
Commissioned Systems |
□ |
Mechanical Systems were included in the Commissioning Process (Section C408.2) |
||
(Section C408.2, C408.3, C408.4 and C408.6) |
Building mechanical systems have been tested to demonstrate the installation and operation of components, systems and system-to-system interfacing relationships in accordance with approved plans and specifications |
|||
□ |
There are unresolved deficiencies with the mechanical systems. These are described in the Preliminary Commissioning Report submitted to the owner. The following items are not in compliance with the energy code: |
|||
□ |
Electrical Power or Lighting Systems were included in the Commissioning Process (Section C408.4) |
|||
Electrical power and automatic lighting controls have been tested to demonstrate the installation and operation of components, systems and system-to-system interfacing relationships in accordance with approved plans and specifications |
||||
□ |
There are unresolved deficiencies with the electrical power and/or automatic lighting controls. These are described in the Preliminary Commissioning Report submitted to the owner. The following items are not in compliance with the energy code: |
|||
□ |
Service Water Heating Systems were included in the Commissioning Process (Section C408.5) |
|||
Service water heating systems have been tested to demonstrate that control devices, components, equipment and systems are calibrated, adjusted and operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications |
||||
□ |
There are unresolved deficiencies with the service water heating systems. These are described in the Preliminary Commissioning Report submitted to the owner. The following items are not in compliance with the energy code: |
|||
□ |
Additional Systems included in the Commissioning Process (Section C408.5) |
|||
□ |
There are unresolved deficiencies with systems required by Section C406 or Section C407. These are described in the Preliminary Commissioning Report submitted to the owner. The following items are not in compliance with the energy code: |
|||
□ |
Metering Systems were included in the Commissioning Process (Section C408.6) |
|||
Energy source meters, energy end-use meters, the energy metering data acquisition system and required display are calibrated, adjusted and operate to minimally meet code requirements |
||||
□ |
There are unresolved deficiencies with the metering system. These are described in the Preliminary Commissioning Report submitted to the owner. The following items are not in compliance with the energy code: |
|||
Supporting Documents |
□ |
Manuals, record documents and training have been completed or are scheduled |
||
(Section C103.6) |
• |
System documentation has been provided to the owner or scheduled date: |
||
• |
Record documents have been submitted to owner or scheduled date: |
|||
• |
Training has been completed or scheduled date: |
|||
Preliminary Commissioning Report |
□ |
Preliminary Commissioning Report submitted to owner and includes items below |
||
(Section C408.1.4.1) |
□ |
Itemization of deficiencies found during testing that are part of the energy code and that have not been corrected at the time of report preparation |
||
□ |
Deferred tests, which cannot be performed at the time of report preparation, with anticipated date of completion |
|||
□ |
Status of the project's record documents, manuals and systems operation training with respect to requirements in Section C103.6 |
|||
Certification |
□ |
I hereby certify that all requirements for Commissioning have been completed in accordance with the Washington State Energy Code, including all items above |
||
Building Owner or Owner's Authorized Agent |
Date |
|||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40802 Section C408.2—Mechanical systems commissioning ((and completion requirements)).
C408.2 Mechanical systems commissioning ((and completion requirements)). Mechanical equipment and controls subject to Section C403 shall ((comply with Section C408.2.
Construction document notes shall clearly indicate provisions for commissioning and completion requirements in accordance with this section and are permitted to refer to specifications for further requirements. Exception: Systems which (a) qualify as simple systems using the criteria in Section C403.3, (b) are not required to have an economizer per Section C403.3.1, and (c) where the building total mechanical equipment capacity is less than 480,000 Btu/h (140,690 W) cooling capacity and 600,000 Btu/h (175,860 W) heating capacity.)) be included in the commissioning process required by Section C408.1. The commissioning process shall minimally include all energy code requirements for which the code states that equipment or controls shall "be capable of" or "configured to" perform specific functions.
EXCEPTION: | Mechanical systems are exempt from the commissioning process where the building's total mechanical equipment capacity is less than 240,000 Btu/h cooling capacity and less than 300,000 Btu/h heating capacity. |
C408.2.1 Reserved.
C408.2.2 Systems adjusting and balancing. HVAC systems shall be balanced in accordance with generally accepted engineering standards. Air and water flow rates shall be measured and adjusted to deliver final flow rates within the tolerances provided in the ((product)) project specifications. Test and balance activities shall include air system and hydronic system balancing.
C408.2.2.1 Air systems balancing. Each supply air outlet and zone terminal device shall be equipped with means for air balancing in accordance with the requirements of Chapter 6 of the International Mechanical Code. Discharge dampers used for air system balancing are prohibited on constant volume fans and variable volume fans with motors 10 hp (18.6 kW) and larger. Air systems shall be balanced in a manner to first minimize throttling losses then, for fans with system power of greater than 1 hp (0.74 kW), fan speed shall be adjusted to meet design flow conditions.
EXCEPTION: | Fans with fan motors of 1 hp (0.74 kW) or less. |
C408.2.2.2 Hydronic systems balancing. Individual hydronic heating and cooling coils shall be equipped with means for balancing and measuring flow. Hydronic systems shall be proportionately balanced in a manner to first minimize throttling losses, then the pump impeller shall be trimmed or pump speed shall be adjusted to meet design flow conditions. Each hydronic system shall have either the capability to measure pressure across the pump, or test ports at each side of each pump.
EXCEPTION((S)): | The following equipment is not required to be equipped with means for balancing or measuring flow: |
1. Pumps with pump motors of 5 hp (3.7 kW) or less. | |
2. Where throttling results in no greater than five percent of the nameplate horsepower draw above that required if the impeller were trimmed. |
C408.2.3 Functional performance testing. Functional performance testing specified in Sections C408.2.3.1 through C408.2.3.3 shall be conducted. Written procedures which clearly describe the individual systematic test procedures, the expected systems' response or acceptance criteria for each procedure, the actual response or findings, and any pertinent discussion shall be followed. ((At a minimum,)) Testing shall affirm operation during actual or simulated winter and summer design conditions and during full outside air conditions.
C408.2.3.1 Equipment. Equipment functional performance testing shall demonstrate the installation and operation of components, systems, and system-to-system interfacing relationships in accordance with approved plans and specifications such that operation, function, and maintenance serviceability for each of the commissioned systems is confirmed. Testing shall include all modes and sequence of operation, including under full-load, part-load and the following emergency conditions:
1. All modes as described in the sequence of operation;
2. Redundant or automatic back-up mode;
3. Performance of alarms; and
4. Mode of operation upon a loss of power and restoration of power.
C408.2.3.2 Controls. HVAC control systems shall be tested to document that control devices, components, equipment, and systems are calibrated((,)) and adjusted and operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications. Sequences of operation shall be functionally tested to document they operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications.
C408.2.3.3 Economizers. Air economizers shall undergo a functional test to determine that they operate in accordance with manufacturer's specifications.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-23-096, filed 11/20/13, effective 4/1/14)
WAC 51-11C-40803 Section C408.3—Lighting system ((functional testing)) commissioning.
((C408.3 Lighting system functional testing. Controls for automatic lighting systems shall comply with Section C408.3.1.)) C408.3 Electrical power and lighting systems commissioning. Electrical power and lighting systems subject to Section C405 shall be included in the commissioning process required by Section C408.1. The commissioning process shall minimally include all energy code requirements for which the code requires specific daylight responsive controls, "control functions," and where the code states that equipment shall be "configured to" perform specific functions.
EXCEPTION: | Lighting control systems are exempt from the commissioning process in buildings where ((the total installed lighting load is less than 20kW and less than 10kW of lighting is controlled by occupancy sensors or automatic daylighting controls.)): |
1. The total installed lighting load is less than 20 kW. | |
2. Where the lighting load controlled by occupancy sensors or automatic daylighting controls is less than 10 kW. |
C408.3.1 Functional testing. ((Testing shall ensure that control hardware and software are calibrated, adjusted, programmed and in proper working condition in accordance with the construction documents and manufacturer's installation instructions. Written procedures which clearly describe the individual systematic test procedures, the expected systems' response or acceptance criteria for each procedure, the actual response or findings, and any pertinent discussion shall be followed. At a minimum, testing shall affirm operation during normally occupied daylight conditions. The construction documents shall state the party who will conduct the required functional testing.
Where occupant sensors, time switches, programmable schedule controls, photosensors or daylighting controls are installed, the following procedures shall be performed:
1. Confirm that the placement, sensitivity and time-out adjustments for occupant sensors yield acceptable performance.
2. Confirm that the time switches and programmable schedule controls are programmed to turn the lights off.
3. Confirm that the placement and sensitivity adjustments for photosensor controls reduce electric light based on the amount of usable daylight in the space as specified.)) Prior to passing final inspection, the certified commissioning professional shall provide evidence that the lighting control systems have been tested to ensure that control hardware and software are calibrated, adjusted, programmed and in proper working condition in accordance with the construction documents and manufacturer's instructions. Written procedures which clearly describe the individual systematic test procedures, the expected systems' response or acceptance criteria for each procedure, the actual response or findings, and any pertinent discussion shall be followed. Functional testing shall comply with Section C408.3.1.1 through C408.3.1.3 for the applicable control type.
C408.3.1.1 Occupant sensor controls. Where occupancy sensors are provided, the following procedures shall be performed:
1. Certify that the occupancy sensor has been located and aimed in accordance with manufacturer recommendations.
2. For projects with seven or fewer occupancy sensors, each sensor shall be tested. For projects with more than seven occupancy sensors, testing shall be done for each unique combination of sensor type and space geometry. Where multiples of each unique combination of sensor type and space geometry are provided, no fewer than the greater of one or 10 percent of each combination shall be tested unless the code official or design professional requires a higher percentage to be tested. Where 30 percent or more of the tested controls fail, all remaining identical combinations shall be tested.
3. For each occupancy sensor to be tested, verify the following:
3.1. Where occupancy sensors include status indicators, verify correct operation.
3.2. The controlled lights turn off or down to the permitted level within the required time.
3.3. For auto-on occupancy sensors, the lights turn on to the permitted level within the required time.
3.4. For manual on sensors, the lights turn on only when manually activated.
3.5. The lights are not incorrectly turned on by movement in adjacent areas or by HVAC operation.
C408.3.1.2 Time switch controls. Where automatic time switches are provided, the following procedures shall be performed:
1. Confirm that the automatic time switch control is programmed with accurate weekday, weekend and holiday schedules, and set-up and preference program settings.
2. Provide documentation to the owner of automatic time switch programming, including weekday, weekend, holiday schedules and set-up and preference program settings.
3. Verify the correct time and date in the time switch.
4. Verify that any battery backup is installed and energized.
5. Verify that the override time limit is set to not more than two hours.
6. Simulate occupied conditions. Verify and document the following:
6.1. All lights can be turned on and off by their respective area control switch.
6.2. The switch only operates lighting in the enclosed space in which the switch is located.
7. Simulate unoccupied condition. Verify the following:
7.1. All nonexempt lighting turns off.
7.2. Manual override switch allows only the lights in the enclosed space where the override switch is located to turn on or remain on until the next scheduled shut off occurs.
8. Additional testing as specified by the certified commissioning professional.
C408.3.1.3 Daylight responsive controls. Where daylight responsive controls are provided, the following procedures shall be performed:
1. All control devices have been properly located, field-calibrated and set for accurate setpoints and threshold light levels.
2. Daylight controlled lighting loads adjusted to light level setpoints in response to available daylight.
3. The locations of calibration adjustment equipment are readily accessible only to authorized personnel.
C408.3.2 Documentation requirements. The construction documents shall specify that documents certifying that the installed lighting controls meet documented performance criteria of Section C405 be provided to the building owner within 90 days from the date of receipt of the certificate of occupancy.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40804 Section C408.4—Service water heating systems commissioning ((and completion requirements)).
C408.4 Service water heating systems commissioning and completion requirements. Service water heating equipment and controls ((shall comply with Section C408.4. Construction document notes shall clearly indicate provisions for commissioning and completion requirements in accordance with this section and are permitted to refer to specifications for further requirements.
EXCEPTION: | The following systems are exempt from the commissioning requirements: |
1. Service water heating systems in buildings where the largest service water heating system capacity is less than 200,000 Btu/h (58,562 W) and where there are no pools or in-ground permanently installed spas.)) |
subject to Section C404 shall be included in the commissioning process required by Section C408.1. The commissioning process shall minimally include all energy code requirements for which the code states that equipment or controls shall "be capable of" or "configured to" perform specific functions.
EXCEPTION: | Service water heating systems are exempt from the commissioning process in buildings where the largest service water heating system capacity is less than 200,000 Btu/h (58.6 W) and where there are no pools or permanent spas. |
C408.4.1 Functional performance testing. Functional performance testing specified in Sections C408.4.1.1 through C408.4.1.3 shall be conducted. Written procedures which clearly describe the individual systematic test procedures, the expected systems' response or acceptance criteria for each procedure, the actual response or findings, and any pertinent discussion shall be followed. ((At a minimum,)) Testing shall affirm operation with the system under 50 percent water heating load.
C408.4.1.1 Equipment. Equipment functional performance testing shall demonstrate the installation and operation of components, systems, and system-to-system interfacing relationships in accordance with approved plans and specifications such that operation, function, and maintenance serviceability for each of the commissioned systems is confirmed. Testing shall include all modes and sequence of operation, including under full-load, part-load and the following emergency conditions:
1. Redundant or automatic back-up mode;
2. Performance of alarms; and
3. Mode of operation upon a loss of power and restoration of power.
C408.4.1.2 Controls. Service water heating controls shall be tested to document that control devices, components, equipment, and systems are calibrated, adjusted and operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications. Sequences of operation shall be functionally tested to document they operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications.
C408.4.1.3 Pools and spas. Service water heating equipment, time switches, and heat recovery equipment which serve pools and ((in-ground permanently installed)) permanent spas shall undergo a functional test to determine that they operate in accordance with manufacturer's specifications.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-408045 Section C408.5—Other systems commissioning.
C408.5 Systems installed to meet Section C406 or C407. Equipment, components, controls or configuration settings for mechanical, service water heating, electrical power or lighting systems which are included in the project to comply with Section C406 or C407 shall be included in the commissioning process required by Section C408.1.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40805 Section ((C408.5)) C408.6—Metering system commissioning.
((C408.5)) C408.6 Metering system commissioning. Energy metering systems required by Section C409 shall comply with Section ((C408.5)) C408.6 and be included in the commissioning process required by Section C408.1. ((Construction documents shall clearly indicate provisions for commissioning in accordance with Section C408 and are permitted to refer to specifications for further requirements)) The commissioning process shall include all energy metering equipment and controls required by Section C409.
((C408.5.1)) C408.6.1 Functional performance testing. Functional performance testing shall be conducted by following written procedures which clearly describe the individual systematic test procedures, the expected systems' response or acceptance criteria for each procedure, the actual response or findings, and any pertinent discussion. Functional testing shall document that energy source meters, energy end-use meters, the energy metering data acquisition system, and required energy consumption display are calibrated, adjusted and operate in accordance with approved plans and specifications. At a minimum, testing shall confirm that:
1. The metering system devices and components work properly under low and high load conditions.
2. The metered data is delivered in a format that is compatible with the data collection system.
3. The energy display is accessible to building operation and management personnel.
4. The energy display meets code requirements regarding views required in Section C409.4.3. The display shows energy data in identical units (e.g., kWh).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40901 Section C409.1—General.
C409.1 General. New buildings and additions with a gross conditioned floor area over 50,000 square feet shall comply with Section C409. Buildings shall be equipped to measure, monitor, record and display energy consumption data for each energy source and end use category per the provisions of this section, to enable effective energy management.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Tenant spaces smaller than 50,000 square feet within buildings if the tenant space has its own utility service and utility meters. |
2. Buildings in which there is no gross conditioned floor area over 25,000 square feet, including building common area, that is served by its own utility services and meters. |
C409.1.1 Alternate metering methods. Where approved by the building official, energy use metering systems may differ from those required by this section, provided that they are permanently installed and that the source energy measurement, end use category energy measurement, data storage and data display have similar accuracy to and are at least as effective in communicating actionable energy use information to the building management and users, as those required by this section.
C409.1.2 Conversion factor. Any threshold stated in kW shall include the equivalent BTU/h heating and cooling capacity of installed equipment at a conversion factor of 3,412 Btu per kW at 50 percent demand.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40903 Section C409.3—End-use metering.
C409.3 End-use metering. Meters shall be provided to collect energy use data for each end-use category listed in Sections C409.3.1 through C409.3.2. These meters shall collect data for the whole building or for each separately metered portion of the building where not exempted by the exception to Section C409.1. Multiple meters may be used for any end-use category, provided that the data acquisition system totals all of the energy used by that category.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. HVAC and water heating equipment serving only an individual dwelling unit or sleeping unit does not require end-use metering. |
2. Separate metering is not required for fire pumps, stairwell pressurization fans or other life safety systems that operate only during testing or emergency. | |
3. End use metering is not required for individual tenant spaces not exceeding 2,500 square feet in floor area when a dedicated source meter meeting the requirements of Section C409.4.1 is provided for the tenant space. |
C409.3.1 HVAC system energy use. This category shall include all energy including electrical, gas, liquid fuel, district steam and district chilled water that is used by boilers, chillers, pumps, fans and other equipment used to provide space heating, space cooling, dehumidification and ventilation to the building, but not including energy that serves process loads, water heating or miscellaneous loads as defined in Section C409.3. Multiple HVAC energy sources, such as gas, electric and steam, are not required to be summed together.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. All 120 volt equipment. |
2. 208/120 volt equipment in a building where the main service is 480/277 volt power. | |
3. Electrical energy fed through variable frequency drives that are connected to the energy metering data acquisition center. |
C409.3.2 Water heating energy use. This category shall include all energy used for heating of domestic and service hot water, but not energy used for space heating.
EXCEPTION: | Water heating energy use less than 50 kW does not require end-use metering. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-40905 Section C409.5—Metering for existing buildings.
C409.5 Metering for existing buildings.
C409.5.1 Existing buildings that were constructed subject to the requirements of this section. Where new or replacement systems or equipment are installed in an existing building that was constructed subject to the requirements of this section, metering shall be provided for such new or replacement systems or equipment so that their energy use is included in the corresponding end-use category defined in Section C409.2. This includes systems or equipment added in conjunction with additions or alterations to existing buildings.
C409.5.1.1 Small existing buildings. Metering and data acquisition systems shall be provided for additions over 25,000 square feet to buildings that were constructed subject to the requirement of this section, in accordance with the requirements of sections C409.2 and C409.3.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-41000 Section C410—Refrigeration system requirements.
C410.1 General (prescriptive). Walk-in coolers, walk-in freezers, refrigerated warehouse coolers, refrigerated warehouse freezers, and refrigerated display cases shall comply with this Section.
C410.1.1 Refrigeration equipment performance. Refrigeration equipment shall have an energy use in kWh/day not greater than the values of Tables C410.2(1) and C410.2(2) when tested and rated in accordance with AHRI Standard 1200. The energy use shall be verified through certification under an approved certification program or, where a certification program does not exist, the energy use shall be supported by data furnished by the equipment manufacturer.
Table C410.1.1(1)
Minimum Efficiency Requirements: Commercial Refrigeration
EQUIPMENT TYPE |
APPLICATION |
ENERGY USE LIMITS (kWh per day)a |
TEST PROCEDURE |
Refrigerator with solid doors |
Holding Temperature |
0.10 x V + 2.04 |
AHRI 1200 |
Refrigerator with transparent doors |
0.12 x V + 3.34 |
||
Freezers with solid doors |
0.40 x V + 1.38 |
||
Freezers with transparent doors |
0.75 x V + 4.10 |
||
Refrigerator/freezers with solid doors |
The greater of 0.12 x V + 3.34 or 0.70 |
||
Commercial refrigerators |
Pulldown |
0.126 x V + 3.51 |
|
a V = Volume of the chiller for frozen compartment as defined in AHAM-HRF-1. |
|||
Table C410.1.1(2)
Minimum Efficiency Requirements: Commercial Refrigerators and Freezers
EQUIPMENT TYPE |
ENERGY USE LIMITS (kWh per day)a,b |
TEST PROCEDURE |
|||
Equipment Classc |
Family Code |
Operating Mode |
Rating Temperature |
||
VOP.RC.M |
Vertical open |
Remote condensing |
Medium |
0.82 x TDA + 4.07 |
AHRI 1200 |
SVO.RC.M |
Semivertical open |
Remote condensing |
Medium |
0.83 x TDA + 3.18 |
|
HZO.RC.M |
Horizontal open |
Remote condensing |
Medium |
0.35 x TDA + 2.88 |
|
VOP.RC.L |
Vertical open |
Remote condensing |
Low |
2.27 x TDA + 6.85 |
|
HZO.RC.L |
Horizontal open |
Remote condensing |
Low |
0.57 x TDA + 6.88 |
|
VCT.RC.M |
Vertical transparent door |
Remote condensing |
Medium |
0.22 x TDA + 1.95 |
|
VCT.RC.L |
Vertical transparent door |
Remote condensing |
Low |
0.56 x TDA + 2.61 |
|
SOC.RC.M |
Service over counter |
Remote condensing |
Medium |
0.51 x TDA + 0.11 |
|
VOP.SC.M |
Vertical open |
Self-contained |
Medium |
1.74 x TDA + 4.71 |
|
SVO.SC.M |
Semivertical open |
Self-contained |
Medium |
1.73 x TDA + 4.59 |
|
HZO.SC.M |
Horizontal open |
Self-contained |
Medium |
0.77 x TDA + 5.55 |
|
HZO.SC.L |
Horizontal open |
Self-contained |
Low |
1.92 x TDA + 7.08 |
|
VCT.SC.I |
Vertical transparent door |
Self-contained |
Ice cream |
0.67 x TDA + 3.29 |
|
VCS.SC.I |
Vertical solid door |
Self-contained |
Ice cream |
0.38 x V + 0.88 |
|
HCT.SC.I |
Horizontal transparent door |
Self-contained |
Ice cream |
0.56 x TDA + 0.43 |
|
SVO.RC.L |
Semivertical open |
Remote condensing |
Low |
2.27 x TDA + 6.85 |
|
VOP.RC.I |
Vertical open |
Remote condensing |
Ice cream |
2.89 x TDA + 8.7 |
|
SVO.RC.I |
Semivertical open |
Remote condensing |
Ice cream |
2.89 x TDA + 8.7 |
|
HZO.RC.I |
Horizontal open |
Remote condensing |
Ice cream |
0.72 x TDA + 8.74 |
|
VCT.RC.I |
Vertical transparent door |
Remote condensing |
Ice cream |
0.66 x TDA + 3.05 |
|
HCT.RC.M |
Horizontal transparent door |
Remote condensing |
Medium |
0.16 x TDA + 0.13 |
|
HCT.RC.L |
Horizontal transparent door |
Remote condensing |
Low |
0.34 x TDA + 0.26 |
|
HCT.RC.I |
Horizontal transparent door |
Remote condensing |
Ice cream |
0.4 x TDA + 0.31 |
|
VCS.RC.M |
Vertical solid door |
Remote condensing |
Medium |
0.11 x V + 0.26 |
|
VCS.RC.L |
Vertical solid door |
Remote condensing |
Low |
0.23 x V + 0.54 |
|
VCS.RC.I |
Vertical solid door |
Remote condensing |
Ice cream |
0.27 x V + 0.63 |
|
HCS.RC.M |
Horizontal solid door |
Remote condensing |
Medium |
0.11 x V + 0.26 |
|
HCS.RC.L |
Horizontal solid door |
Remote condensing |
Low |
0.23 x V + 0.54 |
|
HCS.RC.I |
Horizontal solid door |
Remote condensing |
Ice cream |
0.27 x V + 0.63 |
|
SOC.RC.L |
Service over counter |
Remote condensing |
Low |
1.08 x TDA + 0.22 |
|
SOC.RC.I |
Service over counter |
Remote condensing |
Ice cream |
1.26 x TDA + 0.26 |
|
VOP.SC.L |
Vertical open |
Self-contained |
Low |
4.37 x TDA + 11.82 |
|
VOP.SC.I |
Vertical open |
Self-contained |
Ice cream |
5.55 x TDA + 15.02 |
|
SVO.SC.L |
Semivertical open |
Self-contained |
Low |
4.34 x TDA + 11.51 |
|
SVO.SC.I |
Semivertical open |
Self-contained |
Ice cream |
5.52 x TDA + 14.63 |
|
HZO.SC.I |
Horizontal open |
Self-contained |
Ice cream |
2.44 x TDA + 9.0 |
|
SOC.SC.I |
Service over counter |
Self-contained |
Ice cream |
1.76 x TDA + 0.36 |
|
HCS.SC.I |
Horizontal solid door |
Self-contained |
Ice cream |
0.38 x V + 0.88 |
|
a | V = Volume of the case, as measured in accordance with Appendix C of AHRI 1200. | ||
b | TDA = Total display area of the case, as measured in accordance with Appendix D of AHRI 1200. | ||
c | Equipment class designations consist of a combination [(in sequential order separated by periods (AAA).(BB).(C))] of: | ||
(AAA) An equipment family code where: | |||
VOP = Vertical open | |||
SVO = Semi-vertical open | |||
HZO = Horizontal open | |||
VCT = Vertical transparent doors | |||
VCS = Vertical solid doors | |||
HCT = Horizontal transparent doors | |||
HCS = Horizontal solid doors | |||
SOC = Service over counter | |||
(BB) An operating mode code: | |||
RC = Remote condensing | |||
SC = Self-contained | |||
(C) A rating temperature code: | |||
M = Medium temperature (38°F) | |||
L = Low temperature (0°F) | |||
I = Ice cream temperature (15°F) | |||
For example, "VOP.RC.M" refers to the "vertical-open, remote-condensing, medium-temperature" equipment class. | |||
C410.2 Walk-in coolers, walk-in freezers, refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers. Refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers shall comply with this section. Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers that are not either site assembled or site constructed shall comply with the following:
1. Be equipped with automatic door-closers that firmly close walk-in doors that have been closed to within 1 inch (25 mm) of full closure.
EXCEPTION: | Automatic closers are not required for doors more than 45 inches (1143 mm) in width or more than 7 feet (2134 mm) in height. |
2. Doorways shall have strip doors, curtains, spring-hinged doors or other method of minimizing infiltration when doors are open.
3. Walk-in coolers and refrigerated warehouse coolers shall contain wall, ceiling, and door insulation of not less than R-25 or have wall, ceiling and door assembly U-factors no greater than U-0.039. Walk-in freezers and refrigerated warehouse freezers shall contain wall, ceiling and door insulation of not less than R-32 or have wall, ceiling and door assembly U-factors no greater than U-0.030.
EXCEPTION: | Glazed portions of doors or structural members need not be insulated. |
4. The floor of walk-in freezers shall contain floor insulation of not less than R-28 or have a floor assembly U-factor no greater than U-0.035.
5. Transparent reach-in doors for walk-in freezers and windows in walk-in freezer doors shall be of triple-pane glass, either filled with inert gas or with heat-reflective treated glass.
6. Windows and transparent reach-in doors for walk-in coolers doors shall be of double-pane or triple-pane, inert gas-filled, heat-reflective treated glass.
7. Evaporator fan motors that are less than 1 hp (0.746 kW) and less than 460 volts shall use electronically commutated motors, brushless direct-current motors, or 3-phase motors.
8. Condenser fan motors that are less than 1 hp (0.746 kW) shall use electronically commutated motors, permanent split capacitor-type motors or 3-phase motors.
9. Where antisweat heaters without antisweat heater controls are provided, they shall have a total door rail, glass and frame heater power draw of not more than 7.1 W/ft2 (76 W/m2) of door opening for walk-in freezers and 3.0 W/ft2 (32 W/m2) of door opening for walk-in coolers.
10. Where antisweat heater controls are provided, they shall reduce the energy use of the antisweat heater as a function of the relative humidity in the air outside the door or to the condensation on the inner glass pane.
11. Lights in walk-in coolers, walk-in freezers, refrigerated warehouse coolers and refrigerated warehouse freezers shall either use light sources with an efficacy of not less than 40 lumens per watt, including ballast losses, or shall use light sources with an efficacy of not less than 40 lumens per watt, including ballast losses, in conjunction with a device that turns off the lights within 15 minutes when the space is not occupied.
C410.2.1 Walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers. Site-assembled or site-constructed walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers shall comply with the following:
1. Automatic door closers shall be provided that fully close walk-in doors that have been closed to within 1 inch (25 mm) of full closure.
EXCEPTION: | Closers are not required for doors more than 45 inches (1143 mm) in width or more than 7 feet (2134 mm) in height. |
2. Doorways shall be provided with strip doors, curtains, spring-hinged doors or other method of minimizing infiltration when the doors are open.
3. Walk-in cooler walls, ceilings and doors shall be provided with insulation having a thermal resistance of not less than R-25 or have wall, ceiling and door assembly U-factors no greater than U-0.039. Walk-in freezers walls, ceilings and doors shall be provided with insulation having a thermal resistance of not less than R-32 or have wall, ceiling, door and slab assembly U-factors no greater than U-0.030.
EXCEPTION: | Insulation is not required for glazed portions of doors or at structural members associated with the walls, ceiling or door frame. |
4. The floor of walk-in freezers shall be provided with insulation having a thermal resistance of not less than R-28 or have a floor assembly U-factor no greater than U-0.035.
5. Transparent reach-in doors for and windows in opaque walk-in freezer doors shall be provided with triple-pane glass having the interstitial spaces filled with inert gas or provided with heat-reflective treated glass.
6. Transparent reach-in doors for and windows in opaque walk-in cooler doors shall be double-pane heat-reflective treated glass having the interstitial space gas filled.
7. Evaporator fan motors that are less than 1 hp (0.746 kW) and less than 460 volts shall be electronically commutated motors or 3-phase motors.
8. Condenser fan motors that are less than 1 hp (0.746 kW) in capacity shall be of the electronically commutated or permanent split capacitor-type or shall be 3-phase motors.
EXCEPTION: | Fan motors in walk-in coolers and walk-in freezers combined in a single enclosure greater than 3,000 square feet (279 m2) in floor area are exempt. |
9. Antisweat heaters that are not provided with antisweat heater controls shall have a total door rail, glass and frame heater power draw not greater than 7.1 W/ft2 (76 W/m2) of door opening for walk-in freezers, and not greater than 3.0 W/ft2 (32 W/m2) of door opening for walk-in coolers.
10. Antisweat heater controls shall be capable of reducing the energy use of the antisweat heater as a function of the relative humidity in the air outside the door or to the condensation on the inner glass pane.
11. Light sources shall have an efficacy of not less than 40 lumens per watt, including any ballast losses, or shall be provided with a device that automatically turns off the lights within 15 minutes of when the walk-in cooler or walk-in freezer was last occupied.
C410.2.2 Refrigerated display cases. Site-assembled or site-constructed refrigerated display cases shall comply with the following:
1. Lighting and glass doors in refrigerated display cases shall be controlled by one of the following:
1.1. Time switch controls to turn off lights during nonbusiness hours. Timed overrides for display cases shall turn the lights on for up to 1 hour and shall automatically time out to turn the lights off.
1.2. Motion sensor controls on each display case section that reduce lighting power by at least 50 percent within 3 minutes after the area within the sensor range is vacated.
2. Low-temperature display cases shall incorporate temperature-based defrost termination control with a time-limit default. The defrost cycle shall terminate first on an upper temperature limit breach and second upon a time limit breach.
3. Antisweat heater controls shall reduce the energy use of the antisweat heater as a function of the relative humidity in the air outside the door or to the condensation on the inner glass pane.
C410.3 Refrigeration systems. Refrigerated display cases, walk-in coolers or walk-in freezers that are served by remote compressor and remote condensers not located in a condensing unit, shall comply with Sections C410.4.1 and C410.4.2.
EXCEPTION: | Systems where the working fluid in the refrigeration cycle goes through both subcritical and supercritical states (transcritical) or that use ammonia refrigerant are exempt. |
C410.3.1 Condensers serving refrigeration systems. Fan-powered condensers shall comply with the following:
1. The design saturated condensing temperatures for air-cooled condensers shall not exceed the design dry-bulb temperature plus 10°F (5.6°C) for low-temperature refrigeration systems, and the design dry-bulb temperature plus 15°F (8°C) for medium temperature refrigeration systems where the saturated condensing temperature for blend refrigerants shall be determined using the average of liquid and vapor temperatures as converted from the condenser drain pressure.
2. Condenser fan motors that are less than 1 hp (0.75 kW) shall use electronically commutated motors, permanent split-capacitor-type motors or 3-phase motors.
3. Condenser fans for air-cooled condensers, evaporatively cooled condensers, air- or water-cooled fluid coolers or cooling towers shall reduce fan motor demand to not more than 30 percent of design wattage at 50 percent of design air volume, and incorporate one of the following continuous variable speed fan control approaches:
3.1. Refrigeration system condenser control for air-cooled condensers shall use variable setpoint control logic to reset the condensing temperature setpoint in response to ambient dry-bulb temperature.
3.2. Refrigeration system condenser control for evaporatively cooled condensers shall use variable setpoint control logic to reset the condensing temperature setpoint in response to ambient wet-bulb temperature.
4. Multiple fan condensers shall be controlled in unison.
5. The minimum condensing temperature setpoint shall be not greater than 70°F (21°C).
C410.3.2 Compressor systems. Refrigeration compressor systems shall comply with the following:
1. Compressors and multiple-compressor system suction groups shall include control systems that use floating suction pressure control logic to reset the target suction pressure temperature based on the temperature requirements of the attached refrigeration display cases or walk-ins.
EXCEPTION: | Controls are not required for the following: |
1. Single-compressor systems that do not have variable capacity capability. | |
2. Suction groups that have a design saturated suction temperature of 30°F (-1.1°C) or higher, suction groups that comprise the high stage of a two-stage or cascade system, or suction groups that primarily serve chillers for secondary cooling fluids. |
2. Liquid subcooling shall be provided for all low-temperature compressor systems with a design cooling capacity equal to or greater than 100,000 Btu/hr (29.3 kW) with a design-saturated suction temperature of -10°F (-23°C) or lower. The subcooled liquid temperature shall be controlled at a maximum temperature setpoint of 50°F (10°C) at the exit of the subcooler using either compressor economizer (interstage) ports or a separate compressor suction group operating at a saturated suction temperature of 18°F (-7.8°C) or higher.
2.1. Insulation for liquid lines with a fluid operating temperature less than 60°F (15.6°C) shall comply with Table C403.2.10.
3. Compressors that incorporate internal or external crankcase heaters shall provide a means to cycle the heaters off during compressor operation.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-50000 Chapter 5 [CE]—((Referenced standards)) Existing buildings.
((This chapter lists the standards that are referenced in various sections of this document. The standards are listed herein by the promulgating agency of the standard, the standard identification, the effective date and title, and the section or sections of this document that reference the standard. The application of the referenced standards shall be as specified in Section 106.
AAMA |
American Architectural Manufacturers Association |
||
1827 Walden Office Square |
|||
Suite 550 |
|||
Schaumburg, IL 60173-4268 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
AAMA/WDMA/CSA 101/I.S.2/A C440—11 |
North American Fenestration Standard/Specifications for Windows, Doors and Unit Skylights |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4.3 |
AHAM |
Association of Home Appliance Manufacturers |
||
1111 19th Street, N.W., Suite 402 |
|||
Washington, D.C. 20036 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ANSI/AHAM RAC-1—2008 |
Room Air Conditioners |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(3) |
AHRI |
Air Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute |
||
4100 North Fairfax Drive, Suite 200 |
|||
Arlington, VA 22203 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE |
|||
13256-1 (2005) |
Water-source Heat Pumps - Testing and Rating for Performance - Part 1: Water-to-air and Brine-to-air Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(2) |
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE |
|||
13256-2 (1998) |
Water-source Heat Pumps - Testing and Rating for Performance - Part 2: Water-to-water and Brine-to-water Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(2) |
210/240—08 |
Unitary Air Conditioning and Air-source Heat Pump Equipment |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(1), Table C403.2.3(2) |
310/380—04 |
Standard for Packaged Terminal Air Conditioners and Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(3) |
340/360—2007 |
Commercial and Industrial Unitary Air-conditioning and Heat Pump Equipment |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(1), Table C403.2.3(2) |
365—09 |
Commercial and Industrial Unitary Air-conditioning Condensing Units |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(1), Table C403.2.3(6) |
390—03 |
Performance Rating of Single Package Vertical Air Conditioners and Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(3) |
400—01 |
Liquid to Liquid Heat Exchangers with Addendum 2 |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(9) |
440—08 |
Room Fan Coil |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.8 |
460—05 |
Performance Rating Remote Mechanical Draft Air-cooled Refrigerant Condensers |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(8) |
550/590—03 |
Water Chilling Packages Using the Vapor Compression Cycle—with Addenda |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.3.1, Table C403.2.3(7), Table C406.2(6) |
560—00 |
Absorption Water Chilling and Water-heating Packages |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(7) |
1160—08 |
Performance Rating of Heat Pump Pool Heaters |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C404.2 |
AMCA |
Air Movement and Control Association International |
||
30 West University Drive |
|||
Arlington Heights, IL 60004-1806 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
500D—10 |
Laboratory Methods for Testing Dampers for Rating |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.4.5.1, C402.4.5.2 |
ANSI |
American National Standards Institute |
||
25 West 43rd Street |
|||
Fourth Floor |
|||
New York, NY 10036 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ANSI/ASME A17.1-2010 |
Safety code for elevators and escalators |
. . . . . . . . |
C405.12.1 |
Z21.10.3/CSA 4.3—04 |
Gas Water Heaters, Volume III—Storage Water Heaters with Input Ratings Above 75,000 Btu per Hour, Circulating Tank and Instantaneous |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C404.2 |
Z21.47/CSA 2.3—06 |
Gas-fired Central Furnaces |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4), Table C406.2(4) |
Z83.8/CSA 2.6—09 |
Gas Unit Heaters, Gas Packaged Heaters, Gas Utility Heaters and Gas-fired Duct Furnaces |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4), Table C406.2(4) |
ASHRAE |
American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. |
||
1791 Tullie Circle, N.E. |
|||
Atlanta, GA 30329-2305 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ANSI/ASHRAE/ACCA |
|||
Standard 127-2007 |
Method of Testing for Rating Computer and Data Processing Room Unitary Air Conditioners |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.4.1 |
Standard 183—2007 |
Peak Cooling and Heating Load Calculations in Buildings, Except Low-rise Residential Buildings |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.1 |
ASHRAE—2004 |
ASHRAE HVAC Systems and Equipment Handbook—2004 |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.1 |
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE |
|||
13256-1 (2005) |
Water-source Heat Pumps—Testing and Rating for Performance— Part 1: Water-to-air and Brine-to-air Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(2) |
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE |
|||
13256-2 (1998) |
Water-source Heat Pumps—Testing and Rating for Performance—Part 2: Water-to-water and Brine-to-water Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(2) |
90.1—2010 |
Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-rise Residential Buildings (ANSI/ASHRAE/IESNA 90.1—2010) |
. . . . . . . . |
C401.2, C401.2.1, C402.1.1, Table C402.1.2, Table C402.2, Table C407.6.1 |
119—88 (RA 2004) |
Air Leakage Performance for Detached Single-family Residential Buildings |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C405.5.2(1) |
140—2010 |
Standard Method of Test for the Evaluation of Building Energy Analysis Computer Programs |
. . . . . . . . |
C407.6.1 |
146—2006 |
Testing and Rating Pool Heaters |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C404.2 |
ASTM |
ASTM International |
||
100 Barr Harbor Drive |
|||
West Conshohocken, PA |
|||
19428-2859 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
C 90—08 |
Specification for Load-bearing Concrete Masonry Units |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.2 |
C 1371—04 |
Standard Test Method for Determination of Emittance of Materials Near Room Temperature Using Portable Emissometers |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.2.1.1 |
C 1549—04 |
Standard Test Method for Determination of Solar Reflectance Near Ambient Temperature Using A Portable Solar Reflectometer |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C405.2.1.1 |
D 1003—07e1 |
Standard Test Method for Haze and Luminous Transmittance of Transparent Plastics |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.3.2.2 |
E 283—04 |
Test Method for Determining the Rate of Air Leakage Through Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls and Doors Under Specified Pressure Differences Across the Specimen |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.2.1.1, C402.4.1.2.2, Table C402.4.3, C402.4.4, C402.4.8 |
E 408—71 (2002) |
Test Methods for Total Normal Emittance of Surfaces Using Inspection-meter Techniques |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.2.1.1 |
E 779—03 |
Standard Test Method for Determining Air Leakage Rate by Fan Pressurization |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.4.1.2.3 |
E 903—96 |
Standard Test Method Solar Absorptance, Reflectance and Transmittance of Materials Using Integrating Spheres (Withdrawn 2005) |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.2.1.1 |
E 1677—05 |
Standard Specification for an Air-retarder (AR) Material or System for Low-rise Framed Building Walls |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.4.1.2.2 |
E 1918—97 |
Standard Test Method for Measuring Solar Reflectance of Horizontal or Low-sloped Surfaces in the Field |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.2.1.1 |
E 1980—(2001) |
Standard Practice for Calculating Solar Reflectance Index of Horizontal and Low-sloped Opaque Surfaces |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.2.1.1 |
E 2178—03 |
Standard Test Method for Air Permanence of Building Materials |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.4.1.2.1 |
E 2357—05 |
Standard Test Method for Determining Air Leakage of Air Barrier Assemblies |
. . . . . . . . |
C404.1.2.2 |
CSA |
Canadian Standards Association |
||
5060 Spectrum Way |
|||
Mississauga, Ontario, Canada L4W 5N6 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
AAMA/WDMA/CSA 101/I.S.2/A440—11 |
North American Fenestration Standard/Specification for Windows, Doors and Unit Skylights |
. . . . . . . . |
R402.4.3 |
CTI |
Cooling Technology Institute |
||
2611 FM 1960 West, Suite A-101 |
|||
Houston, TX 77068 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ATC 105 (00) |
Acceptance Test Code for Water Cooling Tower |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(8) |
STD 201—09 |
Standard for Certification of Water Cooling Towers Thermal Performances |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(8) |
DASMA |
Door and Access Systems Manufacturers Association |
||
1300 Sumner Avenue |
|||
Cleveland, OH 44115-2851 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
105—92 (R2004) |
Test Method for Thermal Transmittance and Air Infiltration of Garage Doors |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4.3 |
DOE |
U.S. Department of Energy |
||
c/o Superintendent of Documents |
|||
U.S. Government Printing Office |
|||
Washington, D.C. 20402-9325 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
10 C.F.R., Part 430—1998 |
Energy Conservation Program for Consumer Products: |
||
Test Procedures and Certification and Enforcement Requirement for Plumbing Products; and Certification and Enforcement Requirements for Residential Appliances; Final Rule |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4), Table C403.2.3(5), Table C404.2, Table C406.2(4), Table C406.2(5) |
|
10 C.F.R., Part 430, Subpart B, Appendix N—1998 |
Uniform Test Method for Measuring the Energy Consumption of Furnaces and Boilers |
||
. . . . . . . . |
C202 |
||
10 C.F.R., Part 431—2004 |
Energy Efficiency Program for Certain Commercial and Industrial Equipment: Test Procedures and Efficiency Standards; Final Rules |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(5), Table C406.2(5) |
NAECA 87—(88) |
National Appliance Energy Conservation Act 1987 [(Public Law 100-12 (with Amendments of 1988-P.L. 100-357)] |
. . . . . . . . |
Tables C403.2.3 (1), (2), (4) |
IAPMO |
International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials |
||
4755 E. Philadelphia Street |
|||
Ontario, CA 91761 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
UPC—2012 |
Uniform Plumbing Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C201.3 |
ICC |
International Code Council, Inc. |
||
500 New Jersey Avenue, N.W., |
|||
6th Floor |
|||
Washington, DC 20001 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
IBC—12 |
International Building Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C201.3, C303.2, C402.4.4 |
IFC—12 |
International Fire Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C201.3 |
IFGC—12 |
International Fuel Gas Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C201.3 |
IMC—12 |
International Mechanical Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.5, C403.2.5.1, C403.2.6, C403.2.7, C403.2.7.1, C403.2.7.1.1, C403.2.7.1.2, C403.2.7.1.3, C403.4.5, C408.2.2.1 |
IESNA |
Illuminating Engineering Society of North America |
||
120 Wall Street, 17th Floor |
|||
New York, NY 10005-4001 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ANSI/ASHRAE/IESNA 90.1—2010 |
Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-rise Residential Buildings |
. . . . . . . . |
C401.2, C401.2.1, C402.1.1, Table C402.1.2, Table C402.2, Table C407.6.1 |
ISO |
International Organization for Standardization |
||
1, rue de Varembe, Case postale 56, CH-1211 |
|||
Geneva, Switzerland |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE 13256-1 (2005) |
Water-source Heat Pumps—Testing and Rating for Performance—Part 1: Water-to-air and Brine-to-air Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.3(2) |
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE 13256-2 (1998) |
Water-Source Heat Pumps—Testing and Rating for Performance—Part 2: Water-to-water and Brine-to-water Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.3(2) |
NEMA |
National Electric Manufacturers Association |
||
1300 North 17th Street |
|||
Suite 1752 |
|||
Rosslyn, VA 22209 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
TP-1-2002 |
Guide for Determining Energy Efficiency for Distribution Transformers |
. . . . . . . . |
C405.9 |
NFRC |
National Fenestration Rating Council, Inc. |
||
6305 Ivy Lane, Suite 140 |
|||
Greenbelt, MD 20770 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
100—2010 |
Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product U-factors |
. . . . . . . . |
C303.1.2, C402.2.1 |
200—2010 |
Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product Solar Heat Gain Coefficients and Visible Transmittance at Normal Incidence |
. . . . . . . . |
C303.1.3, C402.3.1.1 |
400—2010 |
Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product Air Leakage |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4.3 |
SMACNA |
Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning Contractors National Association, Inc. |
||
4021 Lafayette Center Drive |
|||
Chantilly, VA 20151-1209 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
SMACNA—85 |
HVAC Air Duct Leakage Test Manual |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.7.1.3 |
UL |
Underwriters Laboratories |
||
333 Pfingsten Road |
|||
Northbrook, IL 60062-2096 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
727—06 |
Oil-fired Central Furnaces—with Revisions through April 2010 |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4), Table C406.2(4) |
731—95 |
Oil-fired Unit Heaters—with Revisions through April 2010 |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4), Table C406.2(4) |
US-FTC |
United States-Federal Trade Commission |
||
600 Pennsylvania Avenue N.W. |
|||
Washington, DC 20580 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
C.F.R. Title 16 (May 31, 2005) |
R-value Rule |
. . . . . . . . |
C303.1.4 |
WDMA |
Window and Door Manufacturers Association |
||
1400 East Touhy Avenue, Suite 470 |
|||
Des Plaines, IL 60018 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
AAMA/WDMA/CSA 101/I.S.2/A440—11 |
North American Fenestration Standard/Specification for Windows, Doors and Unit Skylights |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4.3)) |
C501 General.
C501.1 Scope. The provisions of this chapter shall control the alteration, repair, addition and change of occupancy of existing buildings and structures.
C501.2 Existing buildings. Except as specified in this chapter, this code shall not be used to require the removal, alteration or abandonment of, nor prevent the continued use and maintenance of, an existing building or building system lawfully in existence at the time of adoption of this code.
C501.3 Maintenance. Buildings and structures, and parts thereof, shall be maintained in a safe and sanitary condition. Devices and systems which are required by this code shall be maintained in conformance with the code edition under which installed. The owner or the owner's authorized agent shall be responsible for the maintenance of buildings and structures. The requirements of this chapter shall not provide the basis for removal or abrogation of energy conservation, fire protection and safety systems and devices in existing structures.
C501.4 Compliance. Alterations, repairs, additions and changes of occupancy to, or relocation of, existing buildings and structures shall comply with the provisions for alterations, repairs, additions and changes of occupancy or relocation, respectively, in the International Building Code, International Fire Code, International Fuel Gas Code, International Mechanical Code, Uniform Plumbing Code, and NFPA 70.
C501.5 New and replacement materials. Except as otherwise required or permitted by this code, materials permitted by the applicable code for new construction shall be used. Like materials shall be permitted for repairs, provided no hazard to life, health or property is created. Hazardous materials shall not be used where the code for new construction would not permit their use in buildings of similar occupancy, purpose and location.
C501.6 Historic buildings. The building official may modify the specific requirements of this code for historic buildings and require alternate provisions which will result in a reasonable degree of energy efficiency. This modification may be allowed for those buildings or structures that are listed in the state or national register of historic places; designated as a historic property under local or state designation law or survey; certified as a contributing resource with a national register listed or locally designated historic district; or with an opinion or certification that the property is eligible to be listed on the national or state registers of historic places either individually or as a contributing building to a historic district by the state historic preservation officer or the keeper of the national register of historic places.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency.
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-50200 Section C502—Additions.
C502.1 General. Additions to an existing building, building system or portion thereof shall conform to the provisions of this code as they relate to new construction without requiring the unaltered portion of the existing building or building system to comply with this code. Additions shall not create an unsafe or hazardous condition or overload existing building systems. An addition shall be deemed to comply with this code if the addition alone complies or if the existing building and addition comply with this code as a single building. Additions shall comply with Section C502.2.
C502.2 Prescriptive compliance. Additions shall comply with Sections C502.2.1 through C502.2.6.2.
C502.2.1 Vertical fenestration. Additions with vertical fenestration that results in a total building vertical fenestration area less than or equal to that specified in Section C402.4.1 shall comply with Section C402.4. Additions with vertical fenestration that results in a total building vertical fenestration area greater than that specified in Section C402.4.1 shall comply with one of the following:
1. Vertical fenestration alternate per Section C402.4.1.1 or C402.4.1.3 for the addition only.
2. Component performance option with target area adjustment per Section C402.1.5 or the total building performance option in Section C407 for the whole building.
C502.2.2 Skylight area. Additions with skylights that result in a total building skylight area less than or equal to that specified in Section C402.4.1 shall comply with Section C402.4. Additions with skylights that result in a total building skylight area greater than that specified in Section C402.4.1 shall comply with the component performance option with the target area adjustment per Section C402.1.5 or the total building performance option in Section C407 for the whole building.
C502.2.3 Building mechanical systems. New mechanical systems and equipment serving the building heating, cooling or ventilation needs, that are part of the addition, shall comply with Section C403.
C502.2.4 Service water heating systems. New service water-heating equipment, controls and service water heating piping shall comply with Section C404.
C502.2.5 Pools and permanent spas. New pools and permanent spas shall comply with Section C404.11.
C502.2.6 Lighting and power systems. New lighting systems that are installed as part of the addition shall comply with Section C405.
C502.2.6.1 Interior lighting power. The total interior lighting power for the addition shall comply with Section C405.4.2 for the addition alone, or the existing building and the addition shall comply as a single building.
C502.2.6.2 Exterior lighting power. The total exterior lighting power for the addition shall comply with Section C405.5.1 for the addition alone, or the existing building and the addition shall comply as a single building.
C502.2.7 Refrigeration systems. New refrigerated spaces and refrigeration equipment shall comply with Section C410.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-50300 Section C503—Alterations.
C503.1 General. Alterations to any building or structure shall comply with the requirements of the code for new construction. Alterations shall be such that the existing building or structure is no less conforming with the provisions of this code than the existing building or structure was prior to the alteration. Alterations to an existing building, building system or portion thereof shall conform to the provisions of this code as they relate to new construction without requiring the unaltered portions of the existing building or building system to comply with this code. Alterations shall not create an unsafe or hazardous condition or overload existing building systems.
EXCEPTION: | The following alterations need not comply with the requirements for new construction provided the energy use of the building is not increased: |
1. Storm windows installed over existing fenestration. | |
2. Surface applied window film installed on existing single pane fenestration assemblies to reduce solar heat gain provided the code does not require the glazing fenestration to be replaced. | |
3. Existing ceiling, wall or floor cavities exposed during construction provided that these cavities are insulated to full depth with insulation having a minimum nominal value of R-3.0 per inch installed per Section C402. | |
4. Construction where the existing roof, wall or floor cavity is not exposed. | |
5. Roof recover. | |
6. Air barriers shall not be required for roof recover and roof replacement where the alterations or renovations to the building do not include alterations, renovations or repairs to the remainder of the building envelope. | |
7. Replacement of existing doors that separate conditioned space from the exterior shall not require the installation of a vestibule or revolving door, provided however that an existing vestibule that separates a conditioned space from the exterior shall not be removed. |
C503.2 Change in space conditioning. Any nonconditioned space that is altered to become conditioned space or semi-heated space shall be required to be brought into full compliance with this code. Any semi-heated space that is altered to become conditioned space shall be required to be brought into full compliance with this code.
EXCEPTION: | Where the component performance building envelope option in Section C402.1.5 is used to comply with this Section, the Proposed UA is allowed to be up to 110 percent of the Target UA. Where the total building performance option in Section C407 is used to comply with this section, the annual energy consumption of the proposed design is allowed to be 110 percent of the annual energy consumption otherwise allowed by Section C407.3. |
C503.3 Building envelope. New building envelope assemblies that are part of the alteration shall comply with Sections C402.1 through C402.5 as applicable.
EXCEPTION: | Air leakage testing is not required for alterations and repairs, unless the project includes a change in space conditioning according to Section C503.2 or a change of occupancy or use according to Section C505.1. |
C503.3.1 Roof replacement. Roof replacements shall comply with Table C402.1.3 or C402.1.4 where the existing roof assembly is part of the building thermal envelope and contains insulation entirely above the roof deck.
C503.3.2 Vertical fenestration. The addition of vertical fenestration that results in a total building vertical fenestration area less than or equal to that specified in Section C402.4.1 shall comply with Section C402.4. Alterations that result in a total building vertical fenestration area greater than specified in Section C402.4.1 shall comply with one of the following:
1. Vertical fenestration alternate per Section C402.1.3 for the new vertical fenestration added.
2. Vertical fenestration alternate per Section C402.4.1.1 for the area adjacent to the new vertical fenestration added.
3. Component performance option with target area adjustment per Section C402.1.5 or the total building performance option in Section C407 for the whole building.
C503.3.2.1 Application to replacement fenestration products. Where some or all of an existing fenestration unit is replaced with a new fenestration product, including sash and glazing, the replacement fenestration unit shall meet the applicable requirements for U-factor and SHGC in Table C402.4.
EXCEPTION: | An area-weighted average of the U-factor of replacement fenestration products being installed in the building for each fenestration product category listed in Table C402.4 shall be permitted to satisfy the U-factor requirements for each fenestration product category listed in Table C402.4. Individual fenestration products from different product categories listed in Table C402.4 shall not be combined in calculating the area-weighted average U-factor. |
C503.3.3 Skylight area. The addition of skylights that results in a total building skylight area less than or equal to that specified in Section C402.4.1 shall comply with Section C402.4. Alterations that result in a total building skylight area greater than that specified in Section C402.4.1 shall comply with the component performance option with target area adjustment per Section C402.1.5 or the total building performance option in Section C407 for the whole building.
C503.4 Mechanical systems. Those parts of systems which are altered or replaced shall comply with Section C403. Additions or alterations shall not be made to an existing mechanical system that will cause the existing mechanical system to become out of compliance.
All new systems in existing buildings, including packaged unitary equipment and packaged split systems, shall comply with Section C403.
Where mechanical cooling is added to a space that was not previously cooled, the mechanical system shall comply with either Section C403.2.6.1 or C403.3.
EXCEPTIONS: | 1. Alternate designs that are not in full compliance with this code may be approved when the code official determines that existing building constraints including, but not limited to, available mechanical space, limitations of the existing structure, or proximity to adjacent air intakes/exhausts make full compliance impractical. Alternate designs shall provide alternate energy savings strategies including, but not limited to, Demand Control Ventilation or increased mechanical cooling or heating efficiency above that required by Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(10). |
2. Qualifying small equipment: This exception shall not be used for unitary cooling equipment installed outdoors or in a mechanical room adjacent to the outdoors. This exception is allowed to be used for other cooling units and split systems serving one zone with a total cooling capacity rated in accordance with Section C403.2.3 of less than 33,000 Btu/h (hereafter referred to as qualifying small systems) provided that these are high-efficiency cooling equipment with SEER and EER values more than 15 percent higher than minimum efficiencies listed in Tables C403.2.3 (1) through (3), in the appropriate size category, using the same test procedures. Equipment shall be listed in the appropriate certification program to qualify for this exception. The total capacity of all qualifying small equipment without economizers shall not exceed 72,000 Btu/h per building, or 5 percent of its air economizer capacity, whichever is greater. That portion of the equipment serving Group R occupancies is not included in determining the total capacity of all units without economizers in a building. Redundant units are not counted in the capacity limitations. This exception shall not be used for the shell-and-core permit or for the initial tenant improvement or for Total Building Performance. | |
3. Chilled water terminal units connected to systems with chilled water generation equipment with IPLV values more than 25 percent higher than minimum part load efficiencies listed in Table C403.2.3(7), in the appropriate size category, using the same test procedures. Equipment shall be listed in the appropriate certification program to qualify for this exception. The total capacity of all systems without economizers shall not exceed 480,000 Btu/h per building, or 20 percent of its air economizer capacity, whichever is greater. That portion of the equipment serving Group R occupancy is not included in determining the total capacity of all units without economizers in a building. This exception shall not be used for the initial permit (this includes any initial permit for the space including, but not limited to, the shell-and-core permit, built-to-suit permit, and tenant improvement permit) or for Total Building Performance Method. |
Alterations to existing mechanical cooling systems shall not decrease economizer capacity unless the system complies with either Section C403.2.6 or C403.3. In addition, for existing mechanical cooling systems that do not comply with either Section C403.2.6 or C403.3, including both the individual unit size limits and the total building capacity limits on units without economizer; other alterations shall comply with Table C503.4.
When space cooling equipment is replaced, controls shall comply with all requirements under Section C403.2.6 and related subsections or provide for integrated operation with economizer in accordance with Section C403.3.1.
Existing equipment currently in use may be relocated within the same floor or same tenant space if removed and reinstalled within the same permit.
Table C503.4
Economizer Compliance Options for Mechanical Alterations
Option A |
Option B (alternate to A) |
Option C (alternate to A) |
Option D (alternate to A) |
|
Unit Type |
Any alteration with new or replacement equipment |
Replacement unit of the same type with the same or smaller output capacity |
Replacement unit of the same type with a larger output capacity |
New equipment added to existing system or replacement unit of a different type |
1. Packaged Units |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,3 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,3 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,4 |
2. Split Systems |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32 |
Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capability |
Only for new units < 54,000 Btuh replacing unit installed prior to 1991 (one of two): Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Economizer: 50%6 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,4 |
For units > 54,000 Btuh or any units installed after 1991: Option A |
||||
3. Water Source Heat Pump |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32 |
(two of three): Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Flow control valve7 Economizer: 50%6 |
(three of three): Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Flow control valve7 Economizer: 50%6 (except for certain pre-1991 systems8) |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,4 (except for certain pre-1991 systems8) |
4. Hydronic Economizer using Air-Cooled Heat Rejection Equipment (Dry Cooler) |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: 14332 |
Efficiency: + 10/5%5 Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Option A |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,4 |
5. Air-Handling Unit (including fan coil units) where the system has an air-cooled chiller |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32 |
Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Option A (except for certain pre-1991 systems8) |
Option A (except for certain pre-1991 systems8) |
6. Air-Handling Unit (including fan coil units) and Water-cooled Process Equipment, where the system has a water-cooled chiller10 |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32 |
Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Option A (except for certain pre-1991 systems8 and certain 1991-2004 systems9) |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,4 (except for certain pre-1991 systems8 and certain 1991-2015 systems9) |
7. Cooling Tower |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32 |
No requirements |
Option A |
Option A |
8. Air-Cooled Chiller |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32 |
Efficiency: + 5%11 Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency (two of two): (1) + 10%12 and (2) multistage Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,4 |
9. Water-Cooled Chiller |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32 |
Efficiency (one of two): (1) + 10%13 or (2) plate frame heat exchanger15 Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency (two of two): (1) + 15%14 and (2) plate-frame heat exchanger15 Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,4 |
10. Boiler |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32 |
Efficiency: + 8%16 Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency: + 8%16 Economizer: shall not decrease existing economizer capacity |
Efficiency: min.1 Economizer: C403.32,4 |
1 | Minimum equipment efficiency shall comply with Section C403.2.3 and Tables C403.2.3(1) through C403.2.3(10). | |
2 | System and building shall comply with Section C403.3 (including both the individual unit size limits and the total building capacity limits on units without economizer). It is acceptable to comply using one of the exceptions to Section C403.3 or C504.3.4. | |
3 | All equipment replaced in an existing building shall have air economizer complying with Section C403.3 unless both the individual unit size and the total capacity of units without air economizer in the building is less than that allowed in Exception 2 to Section C503.4. | |
4 | All separate new equipment added to an existing building shall have air economizer complying with Section C403.3 unless both the individual unit size and the total capacity of units without air economizer in the building is less than that allowed in Exception 3 to Section C503.4. | |
5 | Equipment shall have a capacity-weighted average cooling system efficiency: | |
a. | For units with a cooling capacity below 54,000 Btuh, a minimum of 10% greater than the requirements in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2). | |
b. | For units with a cooling capacity of 54,000 Btuh and greater, a minimum of 5% greater than the requirements in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2). | |
6 | Minimum of 50% air economizer that is ducted in a fully enclosed path directly to every heat pump unit in each zone, except that ducts may terminate within 12 inches of the intake to an HVAC unit provided that they are physically fastened so that the outside air duct is directed into the unit intake. If this is an increase in the amount of outside air supplied to this unit, the outside air supply system shall be configured to provide this additional outside air and equipped with economizer control. | |
7 | Have flow control valve to eliminate flow through the heat pumps that are not in operation with variable speed pumping control complying with Section C403.4.2 for that heat pump. | |
- When the total capacity of all units with flow control valves exceeds 15% of the total system capacity, a variable frequency drive shall be installed on the main loop pump. | ||
- As an alternate to this requirement, have a capacity-weighted average cooling system efficiency that is 5% greater than the requirements in note 5 (i.e., a minimum of 15%/10% greater than the requirements in Tables C403.2.3(1) and C403.2.3(2)). | ||
8 | Systems installed prior to 1991 without fully utilized capacity are allowed to comply with Option B, provided that the individual unit cooling capacity does not exceed 90,000 Btuh. | |
9 | Economizer not required for systems installed with water economizer plate and frame heat exchanger complying with previous codes between 1991 and June 2016, provided that the total fan coil load does not exceed the existing or added capacity of the heat exchangers. | |
10 | For water-cooled process equipment where the manufacturers specifications require colder temperatures than available with waterside economizer, that portion of the load is exempt from the economizer requirements. | |
11 | The air-cooled chiller shall have an IPLV efficiency that is a minimum of 5% greater than the IPLV requirements in Table C403.2.3(7). | |
12 | The air-cooled chiller shall: | |
a. | Have an IPLV efficiency that is a minimum of 10% greater than the IPLV requirements in Table C403.2.3(7); and | |
b. | Be multistage with a minimum of two compressors. | |
13 | The water-cooled chiller shall have an IPLV efficiency that is a minimum of 10% greater than the IPLV requirements in Table C403.2.3(7). | |
14 | The water-cooled chiller shall have an IPLV efficiency that is a minimum of 15% greater than the IPLV requirements in Table C403.2.3(7). | |
15 | Economizer cooling shall be provided by adding a plate-frame heat exchanger on the waterside with a capacity that is a minimum of 20% of the chiller capacity at standard AHRI rating conditions. | |
16 | The replacement boiler shall have an efficiency that is a minimum of 8% higher than the value in Table C403.2.3(5), except for electric boilers. | |
C503.5 Service hot water systems. New service hot water systems that are part of the alteration shall comply with Section C404.
C503.6 Lighting and motors. Alterations that replace 50 percent or more of the luminaires in a space enclosed by walls or ceiling-height partitions, replace 50 percent or more of parking garage luminaires, or replace 50 percent or more of the total installed wattage of exterior luminaires shall comply with Sections C405.4 and C405.5. Where less than 50 percent of the fixtures in an interior space enclosed by walls or ceiling-height partitions or parking garage are new, or 50 percent or more of the installed exterior wattage is altered, the installed lighting wattage shall be maintained or reduced.
Where new wiring is being installed to serve added fixtures and/or fixtures are being relocated to a new circuit, controls shall comply with Sections C405.2.2.3, C405.2.4, C405.2.5, C405.3, and as applicable C408.3. In addition, office areas less than 300 ft2 enclosed by walls or ceiling-height partitions, and all meeting and conference rooms, and all school classrooms, shall be equipped with occupancy sensors that comply with Section C405.2.1 and C408.3. Where a new lighting panel (or a moved lighting panel) with all new raceway and conductor wiring from the panel to the fixtures is being installed, controls shall also comply with the other requirements in Sections C405.2 and C408.3.
Where new walls or ceiling-height partitions are added to an existing space and create a new enclosed space, but the lighting fixtures are not being changed, other than being relocated, the new enclosed space shall have controls that comply with Sections C405.2.1, C 405.2.2, C405.2.4 and C408.3.
Those motors which are altered or replaced shall comply with Section C405.8.
C503.7 Refrigeration systems. Those parts of systems which are altered or replaced shall comply with Section C410. Additions or alterations shall not be made to an existing refrigerated space or system that will cause the existing mechanical system to become out of compliance. All new refrigerated spaces or systems in existing buildings, including refrigerated display cases, shall comply with Section C410.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-50400 Section C504—Repairs.
C504.1 General. Buildings and structures, and parts thereof, shall be repaired in compliance with Section C501.3 and this section. Work on nondamaged components that is necessary for the required repair of damaged components shall be considered part of the repair and shall not be subject to the requirements for alterations in this chapter. Routine maintenance required by Section C501.3, ordinary repairs exempt from permit, and abatement of wear due to normal service conditions shall not be subject to the requirements for repairs in this section.
C504.2 Application. For the purposes of this code, the following shall be considered repairs.
1. Glass only replacements in an existing sash and frame.
2. Roof repairs.
3. Air barriers shall not be required for roof repair where the repairs to the building do not include alterations, renovations or repairs to the remainder of the building envelope.
4. Replacement of existing doors that separate conditioned space from the exterior shall not require the installation of a vestibule or revolving door, provided however that an existing vestibule that separates a conditioned space from the exterior shall not be removed.
5. Repairs where only the bulb and/or ballast within the existing luminaires in a space are replaced provided that the replacement does not increase the installed interior lighting power.
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-50500 Section C505—Change of occupancy or use.
C505.1 General. Spaces undergoing a change in occupancy shall be brought up to full compliance with this code in the following cases:
1. Any space that is converted from an F, S or U occupancy to an occupancy other than F, S or U.
2. Any space that is converted to a Group R dwelling unit or portion thereof, from another use or occupancy.
3. Any Group R dwelling unit or portion thereof permitted prior to July 1, 2002, that is converted to a commercial use or occupancy.
Where the use in a space changes from one use in Table C405.4.2 (1) or (2) to another use in Table C405.4.2 (1) or (2), the installed lighting wattage shall comply with Section C405.4.
EXCEPTION: | Where the component performance alternative in Section C402.1.5 is used to comply with this section, the proposed UA is allowed to be up to 110 percent of the target UA. Where the total building performance option in Section C407 is used to comply with this section, the annual energy consumption of the proposed design is allowed to be 110 percent of the annual energy consumption otherwise allowed by Section C407.3. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-600000 Chapter 6 [CE]—Referenced standards.
This chapter lists the standards that are referenced in various sections of this document. The standards are listed herein by the promulgating agency of the standard, the standard identification, the effective date and title, and the section or sections of this document that reference the standard. The application of the referenced standards shall be as specified in Section C106.
AAMA |
American Architectural Manufacturers Association |
||
1827 Walden Office Square |
|||
Suite 550 |
|||
Schaumburg, IL 60173-4268 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
AAMA/WDMA/CSA 101/I.S.2/A C440—11 |
North American Fenestration Standard/Specifications for Windows, Doors and Unit Skylights |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4.2 |
AHAM |
Association of Home Appliance Manufacturers |
||
1111 19th Street, N.W., Suite 402 |
|||
Washington, D.C. 20036 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ANSI/AHAM RAC-1—2008 |
Room Air Conditioners |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(3) |
AHAM HRF-1-2007 |
Energy, Performance and Capacity of Household Refrigerators, Refrigerator-Freezers and Freezers |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C410.1(1) |
AHRI |
Air Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute |
||
4100 North Fairfax Drive, Suite 200 |
|||
Arlington, VA 22203 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE |
|||
13256-1 (2011) |
Water-source Heat Pumps - Testing and Rating for Performance - Part 1: Water-to-air and Brine-to-air Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(2) |
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE |
|||
13256-2 (2011) |
Water-source Heat Pumps - Testing and Rating for Performance - Part 2: Water-to-water and Brine-to-water Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(2) |
210/240—08 with Addenda 1 and 2 |
Unitary Air Conditioning and Air-source Heat Pump Equipment |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(1), Table C403.2.3(2) |
310/380—04 |
Standard for Packaged Terminal Air Conditioners and Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(3) |
340/360—2007 with Addendum 2 |
Commercial and Industrial Unitary Air-conditioning and Heat Pump Equipment |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(1), Table C403.2.3(2) |
365—09 |
Commercial and Industrial Unitary Air-conditioning Condensing Units |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(1), Table C403.2.3(6) |
390—03 |
Performance Rating of Single Package Vertical Air Conditioners and Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(3) |
400—01 |
Liquid to Liquid Heat Exchangers with Addendum 2 |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(9) |
440—08 |
Room Fan Coil |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.8 |
460—05 |
Performance Rating Remote Mechanical Draft Air-cooled Refrigerant Condensers |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(8) |
550/590—2011 with Addendum 1 |
Water Chilling Packages Using the Vapor Compression Cycle—with Addenda |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.3.1, Table C403.2.3(7), Table C406.2(6) |
560—00 |
Absorption Water Chilling and Water-heating Packages |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(7) |
1160—08 |
Performance Rating of Heat Pump Pool Heaters |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C404.2 |
1200-2010 |
Performance Rating of Commercial Refrigerated Display Merchandisers and Storage Cabinets |
. . . . . . . . |
C410.1,Table C410.1(1), Table C410.1(2) |
AMCA |
Air Movement and Control Association International |
||
30 West University Drive |
|||
Arlington Heights, IL 60004-1806 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
205-12 |
Energy Efficiency Classification for Fans |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.11.3 |
220-8 (2012) |
Laboratory Methods for Testing Air Curtain Units for Aerodynamic Performance Rating |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.5.7 |
500D—12 |
Laboratory Methods for Testing Dampers for Rating |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.4.5.1, C402.4.5.2 |
ANSI |
American National Standards Institute |
||
25 West 43rd Street |
|||
Fourth Floor |
|||
New York, NY 10036 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ANSI/ASME A17.1-2010 |
Safety code for elevators and escalators |
. . . . . . . . |
C405.12.1 |
Z21.10.3/CSA 4.3—11 |
Gas Water Heaters, Volume III—Storage Water Heaters with Input Ratings Above 75,000 Btu per Hour, Circulating Tank and Instantaneous |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C404.2 |
Z21.47/CSA 2.3—12 |
Gas-fired Central Furnaces |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4) |
Z83.8/CSA 2.6—09 |
Gas Unit Heaters, Gas Packaged Heaters, Gas Utility Heaters and Gas-fired Duct Furnaces |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4) |
APSP |
The Association of Pool and Spa Professionals |
||
2111 Eisenhower Avenue |
|||
Alexandria, VA 22314 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
14-11 |
American National Standards for Portable Electric Spa Efficiency |
. . . . . . . . |
C404.12 |
ASHRAE |
American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. |
||
1791 Tullie Circle, N.E. |
|||
Atlanta, GA 30329-2305 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ANSI/ASHRAE/ACCA |
|||
Standard 127-2007 |
Method of Testing for Rating Computer and Data Processing Room Unitary Air Conditioners |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(9) |
Standard 183—2007 |
Peak Cooling and Heating Load Calculations in Buildings, Except Low-rise Residential Buildings |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.1 |
ASHRAE—2012 |
ASHRAE HVAC Systems and Equipment Handbook—2012 |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.1 |
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE |
|||
13256-1 (2011) |
Water-source Heat Pumps—Testing and Rating for Performance— Part 1: Water-to-air and Brine-to-air Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(2) |
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE |
|||
13256-2 (2011) |
Water-source Heat Pumps—Testing and Rating for Performance—Part 2: Water-to-water and Brine-to-water Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(2) |
90.1—2013 |
Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-rise Residential Buildings (ANSI/ASHRAE/IESNA 90.1—2010) |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.1.3, Table C402.1.4, C406.2 Table C407.6.1 |
140—2011 |
Standard Method of Test for the Evaluation of Building Energy Analysis Computer Programs |
. . . . . . . . |
C407.6.1 |
146—2011 |
Testing and Rating Pool Heaters |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C404.2 |
ASME |
American Society of Mechanical Engineers |
||
Two Park Avenue |
|||
New York, NY 10016-5990 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ASME A17.1/CSA B44-2013 |
Safety Code for Elevators and Escalators |
. . . . . . . . |
C405.9.2 |
ASTM |
ASTM International |
||
100 Barr Harbor Drive |
|||
West Conshohocken, PA |
|||
19428-2859 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
C 90—13 |
Specification for Load-bearing Concrete Masonry Units |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.1.3 |
C1363-11 |
Standard Test Method for Thermal Performance of Building Materials and Envelope Assemblies by Means of a Hot Box Apparatus |
. . . . . . . . |
C303.1.4.1, Table C402.1.4 |
C 1371—04a(2010)e1 |
Standard Test Method for Determination of Emittance of Materials Near Room Temperature Using Portable Emissometers |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4 |
C 1549—09 |
Standard Test Method for Determination of Solar Reflectance Near Ambient Temperature Using A Portable Solar Reflectometer |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4 |
D 1003—11e1 |
Standard Test Method for Haze and Luminous Transmittance of Transparent Plastics |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.4.2.2 |
E 283—04 |
Test Method for Determining the Rate of Air Leakage Through Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls and Doors Under Specified Pressure Differences Across the Specimen |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.5.1.2.2 |
E 408—71 (2008) |
Test Methods for Total Normal Emittance of Surfaces Using Inspection-meter Techniques |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4 |
E 779—10 |
Standard Test Method for Determining Air Leakage Rate by Fan Pressurization |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.5.1.2.3 |
E 903—96 |
Standard Test Method Solar Absorptance, Reflectance and Transmittance of Materials Using Integrating Spheres (Withdrawn 2005) |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4 |
E 1677—11 |
Standard Specification for an Air-retarder (AR) Material or System for Low-rise Framed Building Walls |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.5.1.2.2 |
E 1918—06 |
Standard Test Method for Measuring Solar Reflectance of Horizontal or Low-sloped Surfaces in the Field |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4 |
E 1980—11 |
Standard Practice for Calculating Solar Reflectance Index of Horizontal and Low-sloped Opaque Surfaces |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.2.1.1 |
E 2178—13 |
Standard Test Method for Air Permanence of Building Materials |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.4 |
E 2357—11 |
Standard Test Method for Determining Air Leakage of Air Barrier Assemblies |
. . . . . . . . |
C402.5.1.2.2 |
CSA |
Canadian Standards Association |
||
5060 Spectrum Way |
|||
Mississauga, Ontario, Canada L4W 5N6 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
AAMA/WDMA/CSA 101/I.S.2/A440—11 |
North American Fenestration Standard/Specification for Windows, Doors and Unit Skylights |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4.2 |
CTI |
Cooling Technology Institute |
||
2611 FM 1960 West, Suite A-101 |
|||
Houston, TX 77068 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ATC 105 (00) |
Acceptance Test Code for Water Cooling Tower |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(8) |
ATC 105S—11 |
Acceptance Test Code for Closed Circuit Cooling Towers |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(8) |
ATC 106—11 |
Acceptance Test Code for Mechanical Draft Evaporative Vapor Condensers |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(8) |
STD 201—11 |
Standard for Certification of Water Cooling Towers Thermal Performances |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(8) |
DASMA |
Door and Access Systems Manufacturers Association |
||
1300 Sumner Avenue |
|||
Cleveland, OH 44115-2851 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
105—92 (R2004)—13 |
Test Method for Thermal Transmittance and Air Infiltration of Garage Doors |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4.2 |
DOE |
U.S. Department of Energy |
||
c/o Superintendent of Documents |
|||
U.S. Government Printing Office |
|||
Washington, D.C. 20402-9325 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
10 C.F.R., Part 430—1998 |
Energy Conservation Program for Consumer Products: |
||
Test Procedures and Certification and Enforcement Requirement for Plumbing Products; and Certification and Enforcement Requirements for Residential Appliances; Final Rule |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4), Table C403.2.3(5), Table C404.2 |
|
10 C.F.R., Part 430, Subpart B, Appendix N—1998 |
Uniform Test Method for Measuring the Energy Consumption of Furnaces and Boilers |
. . . . . . . . |
C202 |
10 C.F.R., Part 431—2004 |
Energy Efficiency Program for Certain Commercial and Industrial Equipment: Test Procedures and Efficiency Standards; Final Rules |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(5), Table C406.2(5) |
NAECA 87—(88) |
National Appliance Energy Conservation Act 1987 [(Public Law 100-12 (with Amendments of 1988-P.L. 100-357)] |
. . . . . . . . |
Tables C403.2.3 (1), (2), (4) |
IAPMO |
International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials |
||
4755 E. Philadelphia Street |
|||
Ontario, CA 91761 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
UPC—2015 |
Uniform Plumbing Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C201.3, C501.4 |
ICC |
International Code Council, Inc. |
||
500 New Jersey Avenue, N.W., |
|||
6th Floor |
|||
Washington, D.C. 20001 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
IBC—15 |
International Building Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C201.3, C303.2, C402.4.3 |
IFC—15 |
International Fire Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C201.3, C501.4 |
IFGC—15 |
International Fuel Gas Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C201.3, C501.4 |
IMC—15 |
International Mechanical Code |
. . . . . . . . |
C106.3, C201.3, C402.5.3, C403.2.4.3, C403.2.6, C403.2.6.2, C403.2.6.4, C403.2.6.4.1, C403.2.8.2, C403.2.8.3, C403.2.8.3.1, C403.2.8.3.2, C403.2.11.4, C403.2.11.5, C403.4.4, C403.4.4.3, C403.5.1, C408.2.2.1, C501.4 |
IEEE |
The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers, Inc. |
||
3 Park Avenue |
|||
New York, NY 10016 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
IEEE 515.1—2012 |
IEEE Standard for the Testing, Design, Installation and Maintenance of Electrical Resistance Trace Heating for Commercial Applications |
. . . . . . . . |
C404.6.2 |
IESNA |
Illuminating Engineering Society of North America |
||
120 Wall Street, 17th Floor |
|||
New York, NY 10005-4001 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ANSI/ASHRAE/IESNA 90.1—2013 |
Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-rise Residential Buildings |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.1.3, Table C402.1.4, Table C407.5.1 |
ISO |
International Organization for Standardization |
||
1, rue de Varembe, Case postale 56, CH-1211 |
|||
Geneva, Switzerland |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE 13256-1 (2011) |
Water-source Heat Pumps—Testing and Rating for Performance—Part 1: Water-to-air and Brine-to-air Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.3(2) |
ISO/AHRI/ASHRAE 13256-2 (2011) |
Water-Source Heat Pumps—Testing and Rating for Performance—Part 2: Water-to-water and Brine-to-water Heat Pumps |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.3(2) |
NEMA |
National Electric Manufacturers Association |
||
1300 North 17th Street |
|||
Suite 1752 |
|||
Rosslyn, VA 22209 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
TP-1-2002 |
Guide for Determining Energy Efficiency for Distribution Transformers |
. . . . . . . . |
C405.9 |
MGI—1993 |
Motors and Generators |
. . . . . . . . |
C202 |
NFRC |
National Fenestration Rating Council, Inc. |
||
6305 Ivy Lane, Suite 140 |
|||
Greenbelt, MD 20770 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
100—2009 |
Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product U-factors |
. . . . . . . . |
C303.1.2, C402.2.2 |
200—2009 |
Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product Solar Heat Gain Coefficients and Visible Transmittance at Normal Incidence |
. . . . . . . . |
C303.1.3, C402.4.1.1 |
400—2009 |
Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product Air Leakage |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4.2 |
SMACNA |
Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning Contractors National Association, Inc. |
||
4021 Lafayette Center Drive |
|||
Chantilly, VA 20151-1209 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
SMACNA—2012 |
HVAC Air Duct Leakage Test Manual |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.8.1.3 |
UL |
Underwriters Laboratories |
||
333 Pfingsten Road |
|||
Northbrook, IL 60062-2096 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
710—12 |
Exhaust Hoods for Commercial Cooking Equipment |
. . . . . . . . |
C403.2.8 |
727—06 |
Oil-fired Central Furnaces—with Revisions through April 2010 |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4) |
731—95 |
Oil-fired Unit Heaters—with Revisions through April 2010 |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C403.2.3(4) |
US-FTC |
United States-Federal Trade Commission |
||
600 Pennsylvania Avenue N.W. |
|||
Washington, D.C. 20580 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
C.F.R. Title 16 (May 31, 2005) |
R-value Rule |
. . . . . . . . |
C303.1.4 |
WDMA |
Window and Door Manufacturers Association |
||
1400 East Touhy Avenue, Suite 470 |
|||
Des Plaines, IL 60018 |
|||
Standard reference number |
Title |
Referenced in code section number |
|
AAMA/WDMA/CSA 101/I.S.2/A440—11 |
North American Fenestration Standard/Specification for Windows, Doors and Unit Skylights |
. . . . . . . . |
Table C402.4.2 |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-61011 Section A101.1—Scope.
A101.1 Scope. The following defaults shall apply to Chapter 4 of both the (RE) and (CE) sections of the ((IECC)) WSEC. This chapter includes tables of seasonal average heat loss coefficients for specified nominal insulation.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-61015 Section A101.5—Building materials.
A101.5 Building materials. Default R-values used for building materials shall be as shown in Table A101.5.
Table A101.5
Default R-values for Building Materials
Material |
Nominal Size (in.) |
Actual Size (in.) |
R-Value (Heat Capacityc) |
Air cavity (unventilated), between metal studs at 16 inches on centera |
- |
- |
0.79 |
Air cavity (unventilated), all other depths and framing materials1 |
- |
- |
0.91 |
Airfilm, exterior surfacesb |
- |
- |
0.17 |
Airfilm, interior horizontal surfaces, heat flow upb |
- |
- |
0.61 |
Airfilm, interior horizontal surfaces, heat flow downb |
- |
- |
0.92 |
Airfilm, interior vertical surfacesb |
- |
- |
0.68 |
Brick at R-0.12/in. (face brick, 75% solid/25% core area, 130 lbs/ft3) |
4 |
3.5 |
0.32 (5.9) |
Carpet and rubber pad |
- |
- |
1.23 |
Concretec at R-0.0625/in., heavyweight (144 lbs/ft3) |
- |
2 |
0.13 (HC-4.8) |
- |
4 |
0.25 (HC-9.6) |
|
- |
6 |
0.38 (HC-14.4) |
|
- |
8 |
0.50 (HC-19.2) |
|
- |
10 |
0.63 (HC-24.0) |
|
- |
12 |
0.75 (HC-28.8) |
|
((Concrete masonry units, solid grouted, lightweight (95 lbs/ft3) |
6 |
- |
0.80 (HC-11.4) |
Concrete masonry units, solid grouted, normal weight (135 lbs/ft3) |
6 |
- |
0.51 (HC-13.2) |
Concrete masonry units, partly grouted, lightweight (95 lbs/ft3) |
6 |
- |
1.33 (HC-6.7) |
Concrete masonry units, partly grouted, normal weight (135 lbs/ft3) |
6 |
- |
0.82 (HC-9.0) |
Concrete masonry units, solid grouted, lightweight (95 lbs/ft3) |
8 |
- |
1.05 (HC-15.5) |
Concrete masonry units, solid grouted, normal weight (135 lbs/ft3) |
8 |
- |
0.69 (HC-17.9) |
Concrete masonry units, partly grouted, lightweight (95 lbs/ft3) |
8 |
- |
1.44 (HC-9.6) |
Concrete masonry units, partly grouted, normal weight (135 lbs/ft3) |
8 |
- |
0.98 (HC-12.0) |
Concrete masonry units, solid grouted, lightweight (95 lbs/ft3) |
10 |
- |
1.30 (HC-19.7) |
Concrete masonry units, solid grouted, normal weight (135 lbs/ft3) |
10 |
- |
0.87 (HC-22.6) |
Concrete masonry units, partly grouted, lightweight (95 lbs/ft3) |
10 |
- |
1.61 (HC-11.9) |
Concrete masonry units, partly grouted, normal weight (135 lbs/ft3) |
10 |
- |
1.11 (HC-14.8) |
Concrete masonry units, solid grouted, lightweight (95 lbs/ft3) |
12 |
- |
1.53 (HC-23.9) |
Concrete masonry units, solid grouted, normal weight (135 lbs/ft3) |
12 |
- |
1.06 (HC-27.2) |
Concrete masonry units, partly grouted, lightweight (95 lbs/ft3) |
12 |
- |
1.75 (HC-14.2) |
Concrete masonry units, partly grouted, normal weight (135 lbs/ft3) |
12 |
- |
1.23 (HC-17.5))) |
Flooring, wood subfloor |
- |
0.75 |
0.94 |
Gypsum board |
- |
0.5 |
0.45 |
- |
0.625 |
0.56 |
|
Metal deck |
- |
- |
0 |
Roofing, built-up |
- |
0.375 |
0.33 |
Sheathing, vegetable fiber board, 0.78 in. |
- |
0.78 |
2.06 |
Soil at R-0.104/in. |
- |
12 |
1.25 |
Steel, mild |
1 |
0.0031807 |
|
Stucco |
- |
0.75 |
0.08 |
a | There is no credit for cavities that are open to outside air. |
b | Air films do not apply to air cavities within an assembly. |
c | For heat capacity for concrete ((and)) with densities other than these values or other concrete masonry materials ((with densities other than the values listed in Table A101.5)), see Tables A103.3.7.1(1) through (3) or Tables A3.1B and A3.1C in ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-61022 Section A102.2—Component description.
A102.2 Component description. The four types of ceilings are characterized as follows:
A102.2.1 Ceilings below a vented attic. Attic insulation is assumed to be blown-in, loose-fill fiberglass with a K-value of 2.6 h • ft2 • °F/Btu per inch. Full bag count for specified R-value is assumed in all cases. Ceiling dimensions for flat ceiling calculations are 45 by 30 feet, with a gabled roof having a 4/12 pitch. The attic is assumed to vent naturally at the rate of 3 air changes per hour through soffit and ridge vents. A void fraction of 0.002 is assumed for all attics with insulation baffles. Standard-framed, unbaffled attics assume a void fraction of 0.008.
Attic framing is either standard or advanced. Standard framing assumes tapering of insulation depth around the perimeter with resultant decrease in thermal resistance. An increased R-value is assumed in the center of the ceiling due to the effect of piling leftover insulation. Advanced framing assumes full and even depth of insulation extending to the outside edge of exterior walls. Advanced framing does not change from the default value.
U-factors for flat ceilings below vented attics with standard framing may be modified with the following table:
U-Factor for Standard Framing |
|||
Roof Pitch |
R-30 |
R-38 |
|
4/12 |
0.036 |
0.031 |
|
5/12 |
0.035 |
0.030 |
|
6/12 |
0.034 |
0.029 |
|
7/12 |
0.034 |
0.029 |
|
8/12 |
0.034 |
0.028 |
|
9/12 |
0.034 |
0.028 |
|
10/12 |
0.033 |
0.028 |
|
11/12 |
0.033 |
0.027 |
|
12/12 |
0.033 |
0.027 |
|
Vented scissors truss attics assume a ceiling pitch of 2/12 with a roof pitch of either 4/12 or 5/12. Unbaffled standard framed scissors truss attics are assumed to have a void fraction of 0.016.
A102.2.2 Vaulted ceilings. Insulation is assumed to be fiberglass batts installed in roof joist cavities. In the vented case, at least 1.5 inches between the top of the batts and the underside of the roof sheathing is left open for ventilation in each cavity. A ventilation rate of 3.0 air changes per hour is assumed. In the unvented or dense pack case, the ceiling cavity is assumed to be fully packed with insulation, leaving no space for ventilation.
A102.2.3 Roof decks. Rigid insulation is applied to the top of roof decking with no space left for ventilation. Roofing materials are attached directly on top of the insulation. Framing members are often left exposed on the interior side.
A102.2.4 Metal truss framing. Overall system tested values for the roof/ceiling Uo for metal framed truss assemblies from approved laboratories shall be used, when such data is acceptable to the building official.
Alternatively, the Uo for roof/ceiling assemblies using metal truss framing may be obtained from Tables A102.2.4(1) through A102.2.4(5).
A102.2.5 Metal building roof. Table A102.2.5: The base assembly is a roof where the insulation is compressed when installed beneath metal roof panels attached to the steel structure (purlins). Additional assemblies include continuous insulation, uncompressed and uninterrupted by framing.
U-factors for metal building roofs shall be taken from Table A102.2.5, provided the average purlin spacing is at least 52 inches and the R-value of the thermal spacer block is greater than or equal to the thermal spacer block R-value indicated in Table A107.2.5 for the assembly. It is not acceptable to use the U-factors in Tables A102.2.6(1), A102.2.6(2) and A102.2.6(3) if additional insulated sheathing is not continuous.
A102.2.5.1 Single layer. The rated R-value of insulation is for insulation installed perpendicular to and draped over purlins and then compressed when the metal roof panels are attached. A minimum R-3 (R-0.5) thermal spacer block between the purlins and the metal roof panels is required, unless compliance is shown by the overall assembly U-factor.
A102.2.5.2 Double layer. The first rated R-value of insulation is for insulation installed perpendicular to and draped over purlins. The second rated R-value of insulation is for unfaced insulation installed above the first layer and parallel to the purlins and then compressed when the metal roof panels are attached. A minimum R-3 (R-0.5) thermal spacer block between the purlins and the metal roof panels is required, unless compliance is shown by the overall assembly U-factor.
A102.2.5.3 Continuous insulation. For continuous insulation (e.g., insulation boards or blankets), it is assumed that the insulation is installed below the purlins and is uninterrupted by framing members. Insulation exposed to the conditioned space or semi-heated space shall have a facing, and all insulation seams shall be continuously sealed to provide a continuous air barrier.
A102.2.5.4 Liner system (Ls). A continuous membrane is installed below the purlins and uninterrupted by framing members. Uncompressed, unfaced insulation rests on top of the membrane between the purlins. For multilayer installations, the last rated R-value of insulation is for unfaced insulation draped over purlins and then compressed when the metal roof panels are attached. A minimum R-3 (R-0.5) thermal spacer block between the purlins and the metal roof panels is required, unless compliance is shown by the overall assembly U-factor.
A102.2.5.5 Filled cavity. The first rated R-value of insulation is for faced insulation installed parallel to the purlins. The second rated R-value of insulation is for unfaced insulation installed above the first layer, parallel to and between the purlins and compressed when the metal roof panels are attached. The facer of the first layer of insulation is of sufficient width to be continuously sealed to the top flange of the purlins and to accommodate the full thickness of the second layer of insulation. A supporting structure retains the bottom of the first layer at the prescribed depth required for the full thickness of the second layer of insulation being installed above it. A minimum R-5 (R-0.9) thermal spacer block between the purlins and the metal roof panels is required, unless compliance is shown by the overall assembly U-factor.
A102.2.6 Roofs with insulation entirely above deck (uninterrupted by framing). Tables A102.2.6(1) through A102.2.6(3): The base assembly is continuous insulation over a structural deck. ((Added insulation is continuous and uninterrupted by framing. For the insulation, the first column lists the R-value for continuous insulation with a uniform thickness; the second column lists the comparable area-weighted average R-value for continuous insulation provided that the insulation thickness is never less than R-5 (except at roof drains) and that the slope is)) These tables indicate effective U-factors for tapered roof insulation, sloped from a maximum R-value (Rmax) at the peak of the slope to a minimum R-value (Rmin) at the low point of the slope. The rows of the tables represent the rated R-value of the insulation at the minimum conditions (except at roof drains) and the columns of the table represent the rated R-value of the insulation at the maximum conditions. The slope of the tapered insulation shall be no greater than 1/4 inch per foot.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-610226 Tables A102.2.6—Assembly U-factors for roofs with insulation entirely above deck.
((Table A102.2.6
Assembly U-factors for Roofs with Insulation Entirely above Deck
(Uninterrupted by Framing)
Rated R-Value of Insulation Alone: Minimum Throughout, Unsloped |
Rated R-Value of Insulation Alone: Average (R-5 minimum), Sloped (1/4 inch per foot maximum) |
Overall U-Factor for Entire Assembly |
R-0 |
Not Allowed |
U-1.282 |
R-1 |
Not Allowed |
U-0.562 |
R-2 |
Not Allowed |
U-0.360 |
R-3 |
Not Allowed |
U-0.265 |
R-4 |
Not Allowed |
U-0.209 |
R-5 |
Not Allowed |
U-0.173 |
R-6 |
R-7 |
U-0.147 |
R-7 |
R-8 |
U-0.129 |
R-8 |
R-9 |
U-0.114 |
R-9 |
R-10 |
U-0.102 |
R-10 |
R-12 |
U-0.093 |
R-11 |
R-13 |
U-0.085 |
R-12 |
R-15 |
U-0.078 |
R-13 |
R-16 |
U-0.073 |
R-14 |
R-18 |
U-0.068 |
R-15 |
R-20 |
U-0.063 |
R-16 |
R-22 |
U-0.060 |
R-17 |
R-23 |
U-0.056 |
R-18 |
R-25 |
U-0.053 |
R-19 |
R-27 |
U-0.051 |
R-20 |
R-29 |
U-0.048 |
R-21 |
R-31 |
U-0.046 |
R-22 |
R-33 |
U-0.044 |
R-23 |
R-35 |
U-0.042 |
R-24 |
R-37 |
U-0.040 |
R-25 |
R-39 |
U-0.039 |
R-26 |
R-41 |
U-0.037 |
R-27 |
R-43 |
U-0.036 |
R-28 |
R-46 |
U-0.035 |
R-29 |
R-48 |
U-0.034 |
R-30 |
R-50 |
U-0.032 |
R-35 |
R-61 |
U-0.028 |
R-40 |
R-73 |
U-0.025 |
R-45 |
R-86 |
U-0.022 |
R-50 |
R-99 |
U-0.020 |
R-55 |
R-112 |
U-0.018 |
R-60 |
R-126 |
U-0.016)) |
Table A102.2.6(1)
Assembly U-factors for Roofs with Tapered Insulation Entirely Above Deck Single Slope Rectangular to One-sided,e,f,g,h
(Uninterrupted by Framing)
 |
Rated R-value of Insulation at Maximum Condition (Rmaxc) |
||||||||||||||
1 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
45 |
50 |
55 |
60 |
||
Rated R-value of insulation at a Minimum Condition (Rminb) |
1 |
0.562 |
0.306 |
0.213 |
0.168 |
0.140 |
0.121 |
0.107 |
0.097 |
0.088 |
0.081 |
0.075 |
0.070 |
0.066 |
5 |
- |
0.173 |
0.125 |
0.101 |
0.086 |
0.076 |
0.068 |
0.062 |
0.057 |
0.053 |
0.049 |
0.046 |
0.044 |
|
10 |
- |
- |
0.093 |
0.076 |
0.066 |
0.058 |
0.053 |
0.048 |
0.045 |
0.042 |
0.039 |
0.037 |
0.035 |
|
15 |
- |
- |
- |
0.063 |
0.055 |
0.049 |
0.045 |
0.041 |
0.038 |
0.036 |
0.034 |
0.032 |
0.030 |
|
20 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.048 |
0.043 |
0.039 |
0.036 |
0.034 |
0.032 |
0.030 |
0.028 |
0.027 |
|
25 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.039 |
0.035 |
0.033 |
0.031 |
0.029 |
0.027 |
0.026 |
0.025 |
|
30 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.032 |
0.030 |
0.028 |
0.026 |
0.025 |
0.024 |
0.023 |
|
35 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.028 |
0.026 |
0.025 |
0.023 |
0.022 |
0.021 |
|
40 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.025 |
0.023 |
0.022 |
0.021 |
0.020 |
|
45 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.022 |
0.021 |
0.020 |
0.019 |
|
50 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.020 |
0.019 |
0.018 |
|
55 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.018 |
0.017 |
|
60 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.016 |
|
Table A102.2.6(2)
Assembly U-factors for Roofs with Tapered Insulation Entirely Above Deck Sloped Triangle (Roof with Center Drain)e,f,g,h,i
(Uninterrupted by Framing)
 |
Rated R-value of Insulation at Maximum Condition (Rmaxc) |
||||||||||||||
1 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
45 |
50 |
55 |
60 |
||
Rated R-value of insulation at a Minimum Condition (Rminb) |
1 |
0.526 |
0.242 |
0.146 |
0.106 |
0.083 |
0.068 |
0.058 |
0.051 |
0.045 |
0.040 |
0.036 |
0.033 |
0.031 |
5 |
- |
0.173 |
0.112 |
0.084 |
0.068 |
0.057 |
0.049 |
0.044 |
0.039 |
0.035 |
0.032 |
0.030 |
0.028 |
|
10 |
- |
- |
0.093 |
0.071 |
0.059 |
0.050 |
0.044 |
0.039 |
0.035 |
0.032 |
0.029 |
0.027 |
0.025 |
|
15 |
- |
- |
- |
0.063 |
0.053 |
0.045 |
0.040 |
0.035 |
0.032 |
0.029 |
0.027 |
0.025 |
0.023 |
|
20 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.048 |
0.042 |
0.037 |
0.033 |
0.030 |
0.027 |
0.025 |
0.024 |
0.022 |
|
25 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.039 |
0.034 |
0.031 |
0.028 |
0.026 |
0.024 |
0.022 |
0.021 |
|
30 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.032 |
0.029 |
0.027 |
0.025 |
0.023 |
0.021 |
0.020 |
|
35 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.028 |
0.026 |
0.024 |
0.022 |
0.021 |
0.019 |
|
40 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.025 |
0.023 |
0.021 |
0.020 |
0.019 |
|
45 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.022 |
0.020 |
0.019 |
0.018 |
|
50 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.020 |
0.018 |
0.017 |
|
55 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.018 |
0.017 |
|
60 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.016 |
|
Table A102.2.6(3)
Assembly U-factors for Roofs with Tapered Insulation Entirely Above Deck Sloped Triangle (Roof with Perimeter Drains)e,f,g,h,i
(Uninterrupted by Framing)
 |
Rated R-value of Insulation at Maximum Condition (Rmaxc) |
||||||||||||||
1 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
45 |
50 |
55 |
60 |
||
Rated R-value of insulation at a Minimum Condition (Rminb) |
1 |
0.562 |
0.242 |
0.146 |
0.106 |
0.083 |
0.068 |
0.058 |
0.051 |
0.045 |
0.040 |
0.036 |
0.033 |
0.031 |
5 |
- |
0.173 |
0.122 |
0.084 |
0.068 |
0.057 |
0.049 |
0.044 |
0.039 |
0.035 |
0.032 |
0.030 |
0.028 |
|
10 |
- |
- |
0.093 |
0.071 |
0.059 |
0.050 |
0.044 |
0.039 |
0.035 |
0.032 |
0.029 |
0.027 |
0.025 |
|
15 |
- |
- |
- |
0.063 |
0.053 |
0.045 |
0.040 |
0.035 |
0.032 |
0.029 |
0.027 |
0.025 |
0.024 |
|
20 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.048 |
0.042 |
0.037 |
0.033 |
0.030 |
0.027 |
0.025 |
0.024 |
0.022 |
|
25 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.039 |
0.034 |
0.031 |
0.028 |
0.026 |
0.024 |
0.022 |
0.021 |
|
30 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.032 |
0.029 |
0.027 |
0.025 |
0.023 |
0.021 |
0.020 |
|
35 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.028 |
0.026 |
0.024 |
0.022 |
0.021 |
0.019 |
|
40 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.025 |
0.023 |
0.021 |
0.020 |
0.019 |
|
45 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.022 |
0.020 |
0.019 |
0.018 |
|
50 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.020 |
0.018 |
0.017 |
|
55 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.018 |
0.017 |
|
60 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.016 |
|
Footnotes to Tables A102.2.6(1), A102.2.6(2), and A102.2.6(3): | |
a Rmax and Rmin are determined along the linearly tapered cross section for the 6. respective minimum and maximum thickness values for the roof section being analyzed. For triangular roof sections. | |
b Rmax refers to the insulation value along the long edge of the triangle and Rmin to the insulation at the point of the triangle which assumes that the insulation slopes to the center. | |
c Rmax refers to the insulation value at the point of the triangle and Rmin to the insulation along the long edge of the triangle which assumes that the insulation slopes to the perimeter. | |
d Effective U-factor for rectangular tapered insulation is calculated as follows: | |
Reff | = | Rmax – Rmin |
Ln[Rmax/Rmin] |
e Effective U-factor for triangular tapered insulation is calculated as follows: | |
Reff = [2/(Rmax – Rmin) [1 + (Rmin/Rmax – Rmin)ln(Rmin/Rmax)]]-1 | |
f Assembly U-factors include an exterior air film (R=0.17) and an interior air film, horizontal with heat flow up (R=0.61). | |
g For effective U-factors of roof assemblies with different Rmax or Rmin values not listed in the tables interpolation is allowed. | |
h This table shall only be applied to tapered insulation that is tapered along only one axis. | |
i In areas of differing insulation slopes/configurations, individual U-values shall be calculated and an area weighted U-value calculation shall be used to determine the effective value of the roof. |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-20-120, filed 10/1/13, effective 11/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-61031 Section A103.1—General.
A103.1 General. The tables in this section list heat loss coefficients for the opaque portion of above-grade wood stud frame walls, metal stud frame walls and concrete masonry walls (Btu/h • ft2 • °F). They are derived from procedures listed in the ASHRAE Fundamentals Handbook. For intermediate floor slabs which penetrate the insulated wall, use the concrete wall U-factors in Table A103.3.7.1(1).
Insulation is assumed to uniformly fill the entire cavity and to be installed as per manufacturer's directions. All walls are assumed to be finished on the inside with 1/2 inch gypsum wallboard, and on the outside with either beveled wood siding over 1/2 inch plywood sheathing or with 5/8 inch T1-11 siding. Insulated sheathing (either interior or exterior) is assumed to cover the entire opaque wall surface, except where modified in accordance with footnote ((h)) g to Table ((C402.1.1)) C402.1.3.
Metal building walls have a different construction and are addressed in Table A103.3.6.3.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-610337 Section A103.3.7—Concrete and masonry walls.
A103.3.7 Concrete and masonry walls.
A103.3.7.1 Concrete masonry walls. The nominal R-values in Tables A103.3.7.1(1), A103.3.7.1(2) and A103.3.7.1(3) may be used for purposes of calculating concrete masonry wall section U-factors in lieu of the ASHRAE isothermal planes calculation method as provided in Chapter 27 of the ASHRAE Fundamentals Handbook.
Table A103.3.7.1(1)
Default U-factors for Concrete ((and)) Masonry Walls
((8" Concrete Masonry
CORE TREATMENT |
||||
Partial Grout with Ungrouted Cores |
||||
Loose-fill insulated |
||||
Wall Description |
Empty |
Perlite |
Vermiculite |
Solid Grout |
Exposed Block, Both Sides |
0.40 |
0.23 |
0.24 |
0.43 |
R-5 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
0.14 |
0.11 |
0.12 |
0.15 |
R-6 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
0.14 |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.14 |
R-10.5 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
0.11 |
0.09 |
0.09 |
0.11 |
R-8 Interior Insulation, Metal Clips |
0.11 |
0.09 |
0.09 |
0.11 |
R-6 Exterior Insulation |
0.12 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
0.12 |
R-10 Exterior Insulation |
0.08 |
0.07 |
0.07 |
0.08 |
R-9.5 Rigid Polystyrene Integral Insulation, Two Webbed Block |
0.11 |
0.09 |
0.09 |
0.12 |
12" Concrete Masonry
CORE TREATMENT |
||||
Partial Grout with Ungrouted Cores |
||||
Loose-fill insulated |
||||
Wall Description |
Empty |
Perlite |
Vermiculite |
Solid Grout |
Exposed Block, Both Sides |
0.35 |
0.17 |
0.18 |
0.33 |
R-5 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
0.14 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
0.13 |
R-6 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
0.13 |
0.09 |
0.10 |
0.13 |
R-10.5 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
0.11 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.10 |
R-8 Interior Insulation, Metal Clips |
0.10 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.09 |
R-6 Exterior Insulation |
0.11 |
0.09 |
0.09 |
0.11 |
R-10 Exterior Insulation |
0.08 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.08 |
R-9.5 Rigid Polystyrene Integral Insulation, Two Webbed Block |
0.11 |
0.08 |
0.09 |
0.12 |
8" Clay Brick))
8-inch Medium-Weight (115 lb/CF) CMU |
|||||||||
All Cells Grouted |
Grout @ 16-inches OC |
Grout @ 32 inches OC |
Grout @ 48 inches OC |
No Grout (unreinforced) |
|||||
Additional Insulation |
Cores Empty |
Cores Filled |
Cores Empty |
Cores Filled |
Cores Empty |
Cores Filled |
Cores Empty |
Cores Filled |
|
None |
0.58 |
0.52 |
0.43 |
0.48 |
0.35 |
0.46 |
0.27 |
0.43 |
0.21 |
R-5 continuous insulation |
0.15 |
0.14 |
0.14 |
0.14 |
0.12 |
0.14 |
0.11 |
0.14 |
0.10 |
R-10 continuous insulation |
0.09 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.07 |
0.08 |
0.07 |
0.08 |
0.07 |
R-15 continuous insulation |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
R-19 continuous |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
R-13 insulation 2x4 wood studs |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.07 |
0.08 |
0.07 |
R-21 insulation 2x6 wood studs |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
R-13 insulation 3-5/8" metal studs |
0.16 |
0.15 |
0.14 |
0.14 |
0.13 |
0.14 |
0.12 |
0.14 |
0.11 |
R-19 insulation 6" metal studs |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.11 |
0.10 |
R-21 insulation 5.5" metal studs |
0.12 |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.11 |
0.09 |
0.11 |
0.09 |
12-inch Medium-Weight (115 lb/CF) CMU |
|||||||||
All Cells Grouted |
Grout @ 16 inches OC |
Grout @ 32 inches OC |
Grout @ 48 inches OC |
No Grout (unreinforced) |
|||||
Additional Insulation |
Cores Empty |
Cores Filled |
Cores Empty |
Cores Filled |
Cores Empty |
Cores Filled |
Cores Empty |
Cores Filled |
|
None |
0.47 |
0.44 |
0.34 |
0.42 |
0.28 |
0.41 |
0.21 |
0.40 |
0.15 |
R-5 continuous insulation |
0.14 |
0.14 |
0.12 |
0.14 |
0.11 |
0.13 |
0.10 |
0.13 |
0.09 |
R-10 continuous insulation |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.07 |
0.08 |
0.07 |
0.08 |
0.06 |
R-15 continuous insulation |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
R-19 continuous |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
R-13 insulation 2x4 wood studs |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.07 |
0.08 |
0.07 |
0.08 |
0.06 |
R-21 insulation 2x6 wood studs |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
R-13 insulation 3-5/8" metal studs |
0.15 |
0.14 |
0.13 |
0.14 |
0.12 |
0.14 |
0.11 |
0.14 |
0.11 |
R-19 insulation 6" metal studs |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.11 |
0.10 |
R-21 insulation 5.5" metal studs |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.11 |
0.09 |
0.11 |
0.08 |
0.11 |
0.09 |
Notes: 1. Interpolation is allowed between 8-inch and 12-inch CMU values (for 10-inch CMU). 2. Interpolation is allowed between 16 and 32-inch grout spacing (for 24-inch spacing). 3. Interpolation is allowed between 32 and 48-inch grout spacing (for 40-inch spacing). 4. "Cores filled" means that all cores not grouted are filled with perlite or vermiculite insulation. 5. Values are based on stud spacing of 16 inches on center. 6. Values are based on horizontal grout spacing of 48 inches OC. 7. Stud wall values include one layer of gypsum board on the interior. |
|||||||||
Table A103.3.7.1(2)
Default U-factors for 80-Inch Clay Brick Masonry Walls
CORE TREATMENT |
||||
Partial Grout with Ungrouted Cores |
||||
Loose-fill insulated |
||||
Wall Description |
Empty |
Perlite |
Vermiculite |
Solid Grout |
Exposed Block, Both Sides |
0.50 |
0.31 |
0.32 |
0.56 |
R-5 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
0.15 |
0.13 |
0.13 |
0.16 |
R-6 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
0.15 |
0.12 |
0.12 |
0.15 |
R-10.5 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
0.12 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
0.12 |
R-8 Interior Insulation, Metal Clips |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
0.11 |
R-6 Exterior Insulation |
0.12 |
0.11 |
0.11 |
0.13 |
R-10 Exterior Insulation |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
0.09 |
((6" Concrete Poured or Precast))
Table A103.3.7.1(3)
Default U-factors for 6-Inch Concrete Poured
or Precast Masonry Walls
CORE TREATMENT |
||||
Partial Grout with Ungrouted Cores |
||||
Loose-fill insulated |
||||
Wall Description |
Empty |
Perlite |
Vermiculite |
Solid Grout |
Exposed Concrete, Both Sides |
NA |
NA |
NA |
0.61 |
R-5 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
NA |
NA |
NA |
0.16 |
R-6 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
NA |
NA |
NA |
0.15 |
R-10.5 Interior Insulation, Wood Furring |
NA |
NA |
NA |
0.12 |
R-8 Interior Insulation, Metal Clips |
NA |
NA |
NA |
0.12 |
R-6 Exterior Insulation |
NA |
NA |
NA |
0.13 |
R-10 Exterior Insulation |
NA |
NA |
NA |
0.09 |
Notes for Tables A103.3.7.1(2) and A103.3.7.1(3):
1. Grouted cores at 40" x 48" on center vertically and horizontally in partial grouted walls.
2. Interior insulation values include 1/2" gypsum board on the inner surface.
3. Furring and stud spacing is 16" on center. Insulation is assumed to fill furring space and is not compressed.
4. Intermediate values may be interpolated using this table. Values not contained in this table may be computed using the procedures listed in the ASHRAE Fundamentals Handbook.
((5. Concrete Masonry Unit (CMU) assembly U-values are based on local test data for Washington state CMU block material using the ASTM C-236-87 steady state thermal conductance test. Tests included an 8"x8"x16" CMU with all cells filled with vermiculite (1995) and 8"x8"x16" CMU with all cells filled with polymaster foam in place insulation (1996). Refer to ASHRAE Standard 90.1 for additional nationally recognized data on the thermal performance of CMU block walls.))
Table A103.3.7.1(2)
Default U-Factors for Concrete and Masonry Wallsa, b, c, d
Framing Type and Depth |
Rated R-value of Insulation Alone |
Assembly U-factors for Solid Concrete Walls |
Assembly U-factors for Concrete Block Walls: Solid Grouted |
Assembly U-factors for Concrete Block Walls: Partially Grouted (Cores Uninsulated Except Where Specified) |
Base Wall only |
||||
No Framing |
R-0 |
U-0.740 |
U-0.580 |
U-0.480 |
Ungrouted Cores Filled with Loose-Fill Insulation |
N.A. |
N.A. |
U-0.350 |
|
Continuous Wood Framing |
||||
0.75 in. |
R-3.0 |
U-0.247 |
U-0.226 |
U-0.210 |
1.5 in. |
R-6.0 |
U-0.160 |
U-0.151 |
U-0.143 |
2.0 in. |
R-10.0 |
U-0.116 |
U-0.111 |
U-0.107 |
3.5 in. |
R-11.0 |
U-0.094 |
U-0.091 |
U-0.088 |
3.5 in. |
R-13.0 |
U-0.085 |
U-0.083 |
U-0.080 |
3.5 in. |
R-15.0 |
U-0.079 |
U-0.077 |
U-0.075 |
5.5 in. |
R-19.0 |
U-0.060 |
U-0.059 |
U-0.058 |
5.5 in. |
R-21.0 |
U-0.057 |
U-0.055 |
U-0.054 |
Continuous Metal Framing at 24 in. on center horizontally |
||||
1.0 in. |
R-0.0 |
U-0.414 |
U-0.359 |
U-0.318 |
1.0 in. |
R-3.8 |
U-0.325 |
U-0.290 |
U-0.263 |
1.0 in. |
R-5.0 |
U-0.314 |
U-0.281 |
U-0.255 |
1.0 in. |
R-6.5 |
U-0.305 |
U-0.274 |
U-0.249 |
1.5 in. |
R-11.0 |
U-0.267 |
U-0.243 |
U-0.223 |
2.0 in. |
R-7.6 |
U-0.230 |
U-0.212 |
U-0.197 |
2.0 in. |
R-10.0 |
U-0.219 |
U-0.202 |
U-0.188 |
2.0 in. |
R-13.0 |
U-0.210 |
U-0.195 |
U-0.182 |
3.0 in. |
R-11.4 |
U-0.178 |
U-0.167 |
U-0.157 |
3.0 in. |
R-15.0 |
U-0.168 |
U-0.158 |
U-0.149 |
3.0 in. |
R-19.0 |
U-0.161 |
U-0.152 |
U-0.144 |
3.5 in. |
R-11.0 |
U-0.168 |
U-0.158 |
U-0.149 |
3.5 in. |
R-13.0 |
U-0.161 |
U-0.152 |
U-0.144 |
3.5 in. |
R-15.0 |
U-0.155 |
U-0.147 |
U-0.140 |
4.5 in. |
R-17.1 |
U-0.133 |
U-0.126 |
U-0.121 |
4.5 in. |
R-22.5 |
U-0.124 |
U-0.119 |
U-0.114 |
4.5 in. |
R-25.2 |
U-0.122 |
U-0.116 |
U-0.112 |
5.0 in. |
R-19.0 |
U-0.122 |
U-0.117 |
U-0.112 |
5.0 in. |
R-25.0 |
U-0.115 |
U-0.110 |
U-0.106 |
5.0 in. |
R-28.0 |
U-0.112 |
U-0.107 |
U-0.103 |
5.0 in. |
R-32.0 |
U-0.109 |
U-0.105 |
U-0.101 |
5.5 in. |
R-19.0 |
U-0.118 |
U-0.113 |
U-0.109 |
5.5 in. |
R-20.9 |
U-0.114 |
U-0.109 |
U-0.105 |
5.5 in. |
R-21.0 |
U-0.113 |
U-0.109 |
U-0.105 |
5.5 in. |
R-27.5 |
U-0.106 |
U-0.102 |
U-0.099 |
5.5 in. |
R-30.8 |
U-0.104 |
U-0.100 |
U-0.096 |
6.0 in. |
R-22.8 |
U-0.106 |
U-0.102 |
U-0.098 |
6.0 in. |
R-30.0 |
U-0.099 |
U-0.095 |
U-0.092 |
6.0 in. |
R-33.6 |
U-0.096 |
U-0.093 |
U-0.090 |
6.5 in. |
R-24.7 |
U-0.099 |
U-0.096 |
U-0.092 |
7.0 in. |
R-26.6 |
U-0.093 |
U-0.090 |
U-0.087 |
7.5 in. |
R-28.5 |
U-0.088 |
U-0.085 |
U-0.083 |
8.0 in. |
R-30.4 |
U-0.083 |
U-0.081 |
U-0.079 |
1 in. Metal Clips at 24 in. on center horizontally and 16 in. vertically (also, where allowed by Section ((C402.1.2)) C402.1.3, for assemblies with a ratio of metal penetration area/mass wall area of < 0.0004 or < 0.04% of the mass wall area) See ASHRAE Fundamentals for determination of U-factors for assemblies that include metal other than screws and nails. |
||||
1.0 in. |
R-3.8 |
U-0.210 |
U-0.195 |
U-0.182 |
1.0 in. |
R-5.0 |
U-0.184 |
U-0.172 |
U-0.162 |
1.0 in. |
R-5.6 |
U-0.174 |
U-0.163 |
U-0.154 |
1.5 in. |
R-5.7 |
U-0.160 |
U-0.151 |
U-0.143 |
1.5 in. |
R-7.5 |
U-0.138 |
U-0.131 |
U-0.125 |
1.5 in. |
R-8.4 |
U-0.129 |
U-0.123 |
U-0.118 |
2.0 in. |
R-7.6 |
U-0.129 |
U-0.123 |
U-0.118 |
2.0 in. |
R-10.0 |
U-0.110 |
U-0.106 |
U-0.102 |
2.0 in. |
R-11.2 |
U-0.103 |
U-0.099 |
U-0.096 |
2.5 in. |
R-9.5 |
U-0.109 |
U-0.104 |
U-0.101 |
2.5 in. |
R-12.5 |
U-0.092 |
U-0.089 |
U-0.086 |
2.5 in. |
R-14.0 |
U-0.086 |
U-0.083 |
U-0.080 |
3.0 in. |
R-11.4 |
U-0.094 |
U-0.090 |
U-0.088 |
3.0 in. |
R-15.0 |
U-0.078 |
U-0.076 |
U-0.074 |
3.0 in. |
R-16.8 |
U-0.073 |
U-0.071 |
U-0.069 |
3.5 in. |
R-13.3 |
U-0.082 |
U-0.080 |
U-0.077 |
3.5 in. |
R-17.5 |
U-0.069 |
U-0.067 |
U-0.065 |
3.5 in. |
R-19.6 |
U-0.064 |
U-0.062 |
U-0.061 |
4.0 in. |
R-15.2 |
U-0.073 |
U-0.071 |
U-0.070 |
4.0 in. |
R-20.0 |
U-0.061 |
U-0.060 |
U-0.058 |
4.0 in. |
R-22.4 |
U-0.057 |
U-0.056 |
U-0.054 |
5.0 in. |
R-28.0 |
U-0.046 |
U-0.046 |
U-0.045 |
6.0 in. |
R-33.6 |
U-0.039 |
U-0.039 |
U-0.038 |
7.0 in. |
R-39.2 |
U-0.034 |
U-0.034 |
U-0.033 |
8.0 in. |
R-44.8 |
U-0.030 |
U-0.030 |
U-0.029 |
9.0 in. |
R-50.4 |
U-0.027 |
U-0.027 |
U-0.026 |
10 in. |
R-56.0 |
U-0.024 |
U-0.024 |
U-0.024 |
11 in. |
R-61.6 |
U-0.022 |
U-0.022 |
U-0.022 |
Continuous Insulation Uninterrupted by Framing |
||||
No Framing |
R-1.0 |
U-0.425 |
U-0.367 |
U-0.324 |
R-2.0 |
U-0.298 |
U-0.269 |
U-0.245 |
|
R-3.0 |
U-0.230 |
U-0.212 |
U-0.197 |
|
R-4.0 |
U-0.187 |
U-0.175 |
U-0.164 |
|
R-5.0 |
U-0.157 |
U-0.149 |
U-0.141 |
|
No Framing |
R-6.0 |
U-0.136 |
U-0.129 |
U-0.124 |
R-7.0 |
U-0.120 |
U-0.115 |
U-0.110 |
|
R-8.0 |
U-0.107 |
U-0.103 |
U-0.099 |
|
R-9.0 |
U-0.097 |
U-0.093 |
U-0.090 |
|
R-10.0 |
U-0.088 |
U-0.085 |
U-0.083 |
|
No Framing |
R-11.0 |
U-0.081 |
U-0.079 |
U-0.076 |
R-12.0 |
U-0.075 |
U-0.073 |
U-0.071 |
|
R-13.0 |
U-0.070 |
U-0.068 |
U-0.066 |
|
R-14.0 |
U-0.065 |
U-0.064 |
U-0.062 |
|
R-15.0 |
U-0.061 |
U-0.060 |
U-0.059 |
|
No Framing |
R-16.0 |
U-0.058 |
U-0.056 |
U-0.055 |
R-17.0 |
U-0.054 |
U-0.053 |
U-0.052 |
|
R-18.0 |
U-0.052 |
U-0.051 |
U-0.050 |
|
R-19.0 |
U-0.049 |
U-0.048 |
U-0.047 |
|
R-20.0 |
U-0.047 |
U-0.046 |
U-0.045 |
|
No Framing |
R-21.0 |
U-0.045 |
U-0.044 |
U-0.043 |
R-22.0 |
U-0.043 |
U-0.042 |
U-0.042 |
|
R-23.0 |
U-0.041 |
U-0.040 |
U-0.040 |
|
R-24.0 |
U-0.039 |
U-0.039 |
U-0.038 |
|
R-25.0 |
U-0.038 |
U-0.037 |
U-0.037 |
|
No Framing |
R-30.0 |
U-0.032 |
U-0.032 |
U-0.031 |
R-35.0 |
U-0.028 |
U-0.027 |
U-0.027 |
|
R-40.0 |
U-0.024 |
U-0.024 |
U-0.024 |
|
R-45.0 |
U-0.022 |
U-0.021 |
U-0.021 |
|
R-50.0 |
U-0.019 |
U-0.019 |
U-0.019 |
|
R-55.0 |
U-0.018 |
U-0.018 |
U-0.018 |
|
R-60.0 |
U-0.016 |
U-0.016 |
U-0.016 |
|
Brick cavity wall with continuous insulation |
||||
No Framing |
R-0.0 |
U-0.337 |
U-0.299 |
U-0.270 |
No Framing |
R-3.8 |
U-0.148 |
U-0.140 |
U-0.133 |
No Framing |
R-5.0 |
U-0.125 |
U-0.120 |
U-0.115 |
No Framing |
R-6.5 |
U-0.106 |
U-0.102 |
U-0.098 |
No Framing |
R-7.6 |
U-0.095 |
U-0.091 |
U-0.088 |
No Framing |
R-10.0 |
U-0.077 |
U-0.075 |
U-0.073 |
No Framing |
R-10.5 |
U-0.079 |
U-0.077 |
U-0.075 |
No Framing |
R-11.4 |
U-0.070 |
U-0.068 |
U-0.066 |
No Framing |
R-15.0 |
U-0.056 |
U-0.055 |
U-0.053 |
No Framing |
R-16.5 |
U-0.054 |
U-0.053 |
U-0.052 |
No Framing |
R-19.0 |
U-0.046 |
U-0.045 |
U-0.044 |
No Framing |
R-22.5 |
U-0.041 |
U-0.040 |
U-0.039 |
No Framing |
R-28.5 |
U-0.033 |
U-0.032 |
U-0.032 |
Continuous Insulation Uninterrupted by Framing with Stucco and Continuous Metal Framing at 24 in. on center horizontally |
||||
1.0 in. |
R-0.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.047 |
U-0.046 |
U-0.045 |
1.0 in. |
R-3.8 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.045 |
U-0.044 |
U-0.044 |
1.0 in. |
R-5.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.045 |
U-0.044 |
U-0.043 |
1.0 in. |
R-6.5 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.045 |
U-0.044 |
U-0.043 |
1.5 in. |
R-11.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.044 |
U-0.043 |
U-0.043 |
2.0 in. |
R-7.6 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.043 |
U-0.042 |
U-0.041 |
2.0 in. |
R-10.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.042 |
U-0.041 |
U-0.041 |
2.0 in. |
R-13.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.042 |
U-0.041 |
U-0.041 |
3.0 in. |
R-11.4 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.041 |
U-0.040 |
U-0.039 |
3.0 in. |
R-15.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.040 |
U-0.039 |
U-0.039 |
3.0 in. |
R-19.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.040 |
U-0.039 |
U-0.038 |
3.5 in. |
R-11.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.040 |
U-0.039 |
U-0.039 |
3.5 in. |
R-13.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.040 |
U-0.039 |
U-0.038 |
5.0 in. |
R-19.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.037 |
U-0.036 |
U-0.036 |
5.0 in. |
R-25.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.036 |
U-0.035 |
U-0.035 |
5.0 in. |
R-32.5 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.035 |
U-0.035 |
U-0.034 |
5.5 in. |
R-19.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.036 |
U-0.036 |
U-0.035 |
5.5 in. |
R-21.0 + R-19 c.i. |
U-0.035 |
U-0.035 |
U-0.035 |
Note for Default Table A103.3.7.1(2):
a. | It is acceptable to use the U-factors in Table A103.3.7.1(2) for all concrete and masonry walls, provided that the grouting is equal to or less than that specified. |
- For ungrouted walls, use the partially grouted column. | |
- For metal studs and z-furring, use the continuous-metal-framing category. | |
- For discontinuous metal clips 1 inch square or smaller, use the metal-clip category. | |
- For insulation that is attached without any framing members (e.g. glued), use the continuous-insulation uninterrupted-by-framing category. Continuous insulation may be installed on the interior or exterior of masonry walls, or between stand-alone walls in multilayer masonry walls, or on the interior or exterior of the concrete. | |
b. | For Table A103.3.7.1(2), the U-factor includes R-0.17 for exterior air film and R-0.68 for interior air film-vertical surfaces. For insulated walls, the U-factor also includes R-0.45 for 0.5 in. gypsum board. U-factors are provided for the following configurations: |
(1) Concrete wall: 8-in. normal weight concrete wall with a density of 145 lb/ft3. | |
(2) Solid grouted concrete block wall: 8-in. medium weight ASTM C90 concrete block with a density of 115 lb/ft3 and solid grouted cores. | |
(3) Partially grouted concrete block wall: 8-in. medium weight ASTM C90 concrete block with a density of 115 lb/ft3 having reinforcing steel every 32 in. vertically and every 48 in. horizontally, with cores grouted in those areas only. Other cores are filled with insulating material only if there is no other insulation. | |
c. | For walls with insulation contained in a framing layer, the U-factors in Table A103.3.7.1(2) assume contact (and thermal bridging) between the mass wall and other framing. For wall assemblies with multiple layers where the wood or metal framing layer does not contact the concrete or masonry layer (i.e., walls with an airspace between the stud wall layer and the mass wall layer), it is acceptable to use the appropriate wood or metal frame wall default U-factors in Tables A103.3.1 or A103.3.6.1. Note: It is acceptable to use this approach where the insulation extends beyond the framing and is in contact with the mass wall layer (e.g. a nominal four-inch metal stud containing insulation that is nominally six inches thick and therefore extends two inches beyond the back of the metal stud). |
d. | Except for wall assemblies qualifying for note 3, if not taken from Table A103.3.7.1(2), mass wall U-factors shall be determined in accordance with ASHRAE 90.1, Appendix A, Section A3.1 and Tables A3.1A to A3.1D, or Section A9.4. |
A103.3.7.2 Peripheral edges of intermediate concrete floors. See Table A103.3.7.2.
Table A103.3.7.2
Default U-factors for Peripheral Edges of Intermediate Concrete Floorsa, b, c, d
Average Thickness of Wall above and below |
||||
Slab Edge Treatment |
6 inches |
8 inches |
10 inches |
12 inches |
Exposed Concrete |
0.816 |
0.741 |
0.678 |
0.625 |
R-5 Exterior Insulation |
0.161 |
0.157 |
0.154 |
0.152 |
R-6 Exterior Insulation |
0.138 |
0.136 |
0.134 |
0.132 |
R-7 Exterior Insulation |
0.122 |
0.120 |
0.118 |
0.116 |
R-8 Exterior Insulation |
0.108 |
0.107 |
0.106 |
0.104 |
R-9 Exterior Insulation |
0.098 |
0.097 |
0.095 |
0.094 |
R-10 Exterior Insulation |
0.089 |
0.088 |
0.087 |
0.086 |
R-11 Exterior Insulation |
0.082 |
0.081 |
0.080 |
0.079 |
R-12 Exterior Insulation |
0.076 |
0.075 |
0.074 |
0.074 |
R-13 Exterior Insulation |
0.070 |
0.070 |
0.069 |
0.068 |
R-14 Exterior Insulation |
0.066 |
0.065 |
0.065 |
0.064 |
R-15 Exterior Insulation |
0.062 |
0.061 |
0.061 |
0.060 |
Note for Table A103.3.7.2:
a. | Exterior insulation values listed above are continuous R-values on the exterior side of the concrete floor. |
b. | For conditions with an exterior wall above the peripheral edge of intermediate concrete floor but with no wall below the intermediate concrete floor this table may be used as long as the code minimum insulation is applied to the floor slab below the concrete floor. |
c. | Typical conditions where conditioned space building envelope wall thermal insulation values are broken concrete floors include, but are not limited to, the following examples: |
1. Elevator hoistway shafts that serve the conditioned building and pass through unconditioned floors such as parking garage levels; | |
2. Stairwell enclosures that serve the conditioned building and pass through unconditioned floors such as parking garage levels; | |
3. Walls between interior and exterior building envelope that separate the interior conditioned space from an exterior courtyard or roofdeck; | |
4. Walls between interior and exterior building envelope that separate the interior conditioned space from an exterior unconditioned space on parking garage levels. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 13-04-056, filed 2/1/13, effective 7/1/13)
WAC 51-11C-61051 Section A105.1—General.
A105.1 General. Tables A105.1(1), A105.1(2) and A105.1(3) list heat loss coefficients for floors over unconditioned spaces in units of Btu/h • ft2 • °F.
They are derived from procedures listed in the ASHRAE Fundamentals Handbook, assuming an average outdoor temperature of 45°F, an average indoor temperature of 65°F and a crawlspace area of 1350 ft2 and 100 feet of perimeter. The crawlspace is assumed to be 2.5 feet high, with 24 inches below grade and 6 inches above grade.
Table A105.1(1)
Default U-factors for Wood-Framed Floors
over Vented Crawlspace or
Unheated Basement
Nominal R-value |
U-factor |
|||
Floor |
Perimeter |
Post & Beam |
Joists |
|
0 |
0 11 19 30 |
0.112 0.100 0.098 0.093 |
0.134 0.116 0.114 0.107 |
|
11 |
0 11 |
0.052 0.048 |
0.056 0.052 |
|
19 |
0 11 |
0.038 0.036 |
0.041 0.038 |
|
22 |
0 11 |
0.034 0.033 |
0.037 0.035 |
|
25 |
0 11 |
0.032 0.031 |
0.034 0.033 |
|
30 |
0 11 |
0.028 0.027 |
0.029 0.028 |
|
38 |
0 11 |
0.024 0.024 |
0.025 0.024 |
|
Table A105.1(2)
Default U-factors for Wood-Framed Floors over Heated Plenum Crawlspaces
Nominal R-value Perimeter |
U-factor |
11 |
0.085 |
19 |
0.075 |
30 |
0.069 |
Note: | Crawlspaces used as heated plenums have approximately 30 percent higher heat loss rate than unvented crawlspaces with the same assumed ACH. Default U-factors in Table A105.1(2) reflect this higher rate of heat loss. |
Table A105.1(3)
Default U-factors for Exposed Floors
Nominal R-value |
U-factor |
||
Concrete |
Wood Joist |
Metal Joist |
|
R-11 |
0.077 |
0.088 |
0.14 |
R-15 |
0.059 |
0.076 |
0.12 |
R-19 |
0.048 |
0.062 |
0.11 |
R-21 |
0.043 |
0.057 |
0.11 |
R-25 |
0.037 |
0.051 |
0.10 |
R-30 |
0.031 |
0.040 |
0.09 |
R-38 |
0.025 |
0.034 |
0.08 |
NEW SECTION
WAC 51-11C-80500 Appendix D—Renewable energy.
AE101.1 On-site renewable energy systems. Each new commercial building or addition larger than 5,000 square feet of gross conditioned floor area shall include a renewable energy generation system consisting of at least 70 watts rated peak photovoltaic energy production, or 240 kBtu of annual solar water heating energy production, per 1,000 square feet of conditioned floor area or fraction thereof. For buildings over 5 stories in height, the conditioned area for this calculation shall be based on the conditioned area of the largest 5 above-grade stories in the building. If the on-site renewable energy option in C406 is selected, this energy shall be in addition to that required by C406.
EXCEPTION: | The code official can approve an alternative approach to achieve the on-site renewable energy requirements. |