WSR 17-08-023
PROPOSED RULES
DEPARTMENT OF
LABOR AND INDUSTRIES
[Filed March 28, 2017, 10:59 a.m.]
Original Notice.
Preproposal statement of inquiry was filed as WSR 15-24-101.
Title of Rule and Other Identifying Information: eRules Phase 7 - chapter 296-52 WAC, Safety standards for possession, handling and use of explosives; chapter 296-59 WAC, Safety standards for ski area facilities and operations; chapter 296-78 WAC, Safety standards for sawmills and woodworking operations; chapter 296-79 WAC, Safety standards for pulp, paper and paperboard mills and converters; chapter 296-99 WAC, Grain handling facilities; and chapter 296-115 WAC, Safety requirements for charter boats.
Hearing Location(s): Department of Labor and Industries, Room S119, 7273 Linderson Way S.W., Tumwater, WA 98501, on May 19, 2017, at 10:00 a.m.
Date of Intended Adoption: August 1, 2017.
Submit Written Comments to: Tari Enos, P.O. Box 44620, Olympia, WA 98504-4620, email tari.enos@lni.wa.gov, fax (360) 902-5619, by 5:00 p.m. on May 26, 2017.
Assistance for Persons with Disabilities: Contact Tari Enos by May 5, 2017, at (360) 902-5541.
Purpose of the Proposal and Its Anticipated Effects, Including Any Changes in Existing Rules: No changes in requirements as a result of this rule making.
• | Consistent format for all DOSH safety and health rules. |
• | Easy to access rules for smart phone and tablet users. |
• | Easy navigation in PDF files provided through bookmarks in the rules. |
• | Easier referencing by replacing bullets and dashes with numbers and letters. |
• | Enhanced rule update efficiency for customers through electronic postings. |
Chapters 296-32, 296-36, 296-37, 296-63, and 296-67 WAC were all removed from this rule making. After the CR-101 was filed December 1, 2015, it was determined that these chapters are all being either rewritten and/or reviewed in separate rule-making projects, which will fulfill the requirements of SSB 5679, requiring all of our rules to be reviewed.
Amended Sections
WAC 296-52-60010 through WAC 296-52-809
• | Change bullets, dashes and diamonds to letters or numbers where applicable and renumber/reletter the rest of the section or subsection. |
• | Change uppercase "and" and "or" to lowercase where applicable. |
• | Change "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
Part A - Purpose, Scope and Application
• | Add "definitions" to the title of Part A. |
WAC 296-52-61010 License applicants must provide this information
• | Add "Individual" to beginning of subsection (1). |
• | Remove bulleted item below subsection (1) that said "An individual must provide:" |
• | Add (b) and (c) to subsection (1). |
WAC 296-52-61015 License applicants must complete department forms
• | Add (1) to first sentence in this section. |
WAC 296-52-64005 Responsibility to obtain a blaster's license
• | Add a (1) to the opening paragraph. |
• | Add a (2) to the second paragraph. |
WAC 296-52-65015 Manufacturing site inspections
• | Add a (1) to the beginning of the section and renumber the rest. |
• | Add "The department will…" to new subsection (2). |
WAC 296-52-66015 Storage site inspections
• | Add a (1) to the beginning of the section and renumber the rest. |
• | Add "The department will…" to new subsection (2). |
WAC 296-52-67170 Bulk delivery/mixing vehicles
• | Add (iii) to last paragraph in subsection (2)(e). |
WAC 296-52-70010 Building construction for Type 1 magazines
• | Add a (1) to the opening paragraph of the beginning of the section and then renumber the rest of the section. |
WAC 296-59-001 through 296-59-130
• | Change "the employer" to "you must" where applicable. |
• | Change bullets and dashes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumber/reletter the rest of the section or subsection. |
• | Change "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
WAC 296-59-007 Definitions
• | Remove quotation marks from every definition. |
• | Remove the word "means" from every definition and add a period after the word being defined, making each definition a complete sentence. |
• | Add definitions for "hazardous material system" and "piping system" that were moved from WAC 296-59-080. |
• | Remove definition of "shall" and add definition of "must." |
WAC 296-59-055 Lockout requirements
• | Add letters (i)-(v) to unbulleted list in subsection (10)(a). |
WAC 296-59-080 Installation, inspection and maintenance of pipes, piping systems and hoses
• | Remove definitions of "hazardous material system" and "piping system" from subsection (1) and add them to WAC 296-59-007. |
WAC 296-78-500 through 296-78-84011
• | Change "the employer" to "you must" where applicable. |
• | Change bullets and dashes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumber/reletter the rest of the section or subsection. |
• | Change "shall" to "must" or "will" where applicable. |
• | Remove repetitive "titles" from the beginning of numbered subsections where applicable. |
WAC 296-78-505 Definitions
• | Remove quotation marks and numbers from all definitions. |
• | Remove the word "means" from applicable definitions, and add a period after the word being defined, making each definition a complete sentence. |
WAC 296-78-56505 Boats and mechanical devices on waters
• | Remove the reference to (19) from WAC 296-24-58501 in subsection (8)(h) due to definitions no longer being numbered. |
WAC 296-78-70501 Definitions—Terms, general
• | Remove numbers and quotation marks from definitions and add a period after every word being defined. |
WAC 296-79-010 through 296-79-320
• | Change "the employer" to "you must" where applicable. |
• | Change bullets and dashes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumber/reletter the rest of the section or subsection. |
• | Change "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
• | Remove repetitive "titles" from the beginning of numbered subsections where applicable. |
WAC 296-79-011 Definitions
• | Remove quotation marks from all definitions. |
• | Remove the word "means" from applicable definitions, and add a period after the word being defined, making each definition a complete sentence. |
• | Add definitions of "hazardous material system" and "piping system" that were removed from WAC 296-79-140. |
WAC 296-79-140 Installation, inspection, and maintenance of pipes, piping systems and hoses
• | Remove definitions of "hazardous material system" and "piping system" from subsection (1) and move them to WAC 296-79-011 and renumber the rest of the section. |
WAC 296-79-150 Powered industrial trucks and other equipment
• | Update reference in opening sentence of section from "chapter 296-24 WAC, Part D" to "chapter 296-863 WAC." |
• | Update reference in subsection (14) from "WAC 296-24-230" to "WAC 296-863-40060." |
WAC 296-79-170 Requirements for crawler and truck cranes
• | Add word "below" to subsection (19) to make a complete sentence: "When using visual signals, standard hand signals as illustrated below, must be used for directing crane operators." |
WAC 296-79-210 For conveyors, maintenance and inspection
• | Update reference from "chapter 296-24 WAC, Part D" to "WAC 296-806-420 Conveyors." |
WAC 296-79-230 Confined spaces
• | Update reference in subsection (1) from "chapter 296-62 WAC, Part M" to "chapter 296-809 WAC." |
WAC 296-099-010 through 296-99-085
• | Change "the employer" to "you must" where applicable. |
• | Change bullets/dashes to letters or numbers where applicable. |
WAC 296-99-085 What special requirements apply to inside bucket elevators?
• | Remove definition of "jogging" from subsection (1) and move it to WAC 296-99-005. |
WAC 296-115-025 through 296-115-060
• | Change "The employer" to "You must" where applicable. |
• | Change bullets and dashes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumber/reletter the rest of the section or subsection. |
WAC 296-115-015 Definitions
• | Remove numbers from all definitions. |
• | Remove the word "means" from applicable definitions, and add a period after the word being defined, making each definition a complete sentence. |
New Sections
WAC 296-52-099 Definitions and 296-99-005 What definitions apply to this chapter?
Repealed Sections
WAC 296-52-60130 Definitions and 296-99-020 What definitions apply to this chapter?
Reasons Supporting Proposal: When the agency updated its web site, template DOSH rules in HTML were broken and DOSH began forwarding rule users to the office of the code reviser web site, causing more confusion among customers. This rule package will resolve stakeholder issues that have caused confusion for rule users by bringing one clear and consistent format to all of our rules.
Statute Being Implemented: Chapter 49.17 RCW.
Rule is not necessitated by federal law, federal or state court decision.
Name of Proponent: Department of labor and industries, governmental.
Name of Agency Personnel Responsible for Drafting: Chris Miller, Tumwater, (360) 902-5516; Implementation and Enforcement: Anne Soiza, Tumwater, (360) 902-5090.
No small business economic impact statement has been prepared under chapter 19.85 RCW. According to RCW 19.85.025(3) which references RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d), no small business economic impact statement is required for this rule making.
A cost-benefit analysis is not required under RCW 34.05.328. According to RCW 34.05.328 (5)(iv), no cost-benefit analysis is required for this rule making.
March 28, 2017
Joel Sacks
Director
PART A
DEFINITIONS, PURPOSE, SCOPE, AND APPLICATION
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-52-099 Definitions.
Aerial blaster in charge. A person who:
(a) Is fully qualified, by means of training and experience in explosives use;
(b) Is adequately trained, experienced, and capable of recognizing hazardous conditions throughout the blast area;
(c) Is in charge of:
(i) The blast process; and
(ii) All aspects of explosives and blasting agent storage, handling, and use as recommended by the manufacturer and as required by this chapter.
(d) Is in a position of authority:
(i) To take prompt corrective action in all areas of the blast operation; and
(ii) Over all other blasters at the blast sight.
(e) Has a minimum of five missions under the supervision of a licensed aerial blaster in charge; and
(f) Successfully completes a written exam for aerial blaster in charge.
Alien. Any person who is not a citizen or national of the United States.
American table of distances. The American Table of Distances for Storage of Explosives as revised and approved by Institute of the Makers of Explosives (IME).
Approved storage facility. A facility for the storage of explosive materials which is in compliance with the following sections:
(a) Storage license (WAC 296-52-660);
(b) Storage of explosive materials, Part E of this chapter; and
(c) Magazine construction (WAC 296-52-700).
ATF. The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives.
Attended, as attending explosives. The physical presence of an authorized person within the field of vision of explosives. The said attendant shall be awake, alert, and not engage in activities which may divert their attention so that in case of an emergency the attendant can get to the explosives quickly and without interference, except for brief periods of necessary absence, during which absence simple theft of explosives is not ordinarily possible.
Authorized agent. A person delegated by a licensed purchaser, who possesses a basic knowledge of explosives handling safety, to order and receive explosives on the purchaser's behalf.
Authorized agent list. A current list of agents the purchaser has authorized to order or receive explosives on their behalf.
Authorized, approved, or approval. Authorized, approved, or approval by:
(a) The department;
(b) Any other approving agency; and
(c) An individual as specified in this chapter.
Authorized person. A person approved or assigned by an employer, owner, or licensee to perform a specific type of duty or be at a specific location at the job site.
Avalanche. The sliding or falling of a large amount of snow down a steep slope which has a destructive force due to its mass.
Avalanche control pack. A specially designed and constructed pack for carrying explosives.
Avalanche control route. A route or specific path which is used by an authorized person in order to control the occurrence of avalanches.
Avalauncher. A device like a cannon which is used for avalanche control blasting. It has a rotating base calibrated for pointing and the barrel is mounted on an elevating mechanism. It uses a compressed gas to propel a projectile containing an explosive charge and detonating means. The gas source is connected to the gun by high pressure hose with in-line control valves and pressure gauges ahead of the trigger mechanism.
Barricades.
(a) Barricade. Effectively screening a building containing explosives by means of a natural or artificial barrier from a magazine, another building, a railway, or highway;
(b) Artificial barricade. A barricade of such height that a straight line from the top of any sidewall of the building containing explosives to the eave line of any magazine or other building or to a point twelve feet above the center of a railway or highway shall pass through such barrier, an artificial mound or properly revetted wall of earth with a minimum thickness of three feet;
(c) Natural barricade. Any natural hill, mound, wall, or barrier composed of earth, rock, or other solid material at least three feet thick.
Blast area. The area of a blast that is effected by:
(a) Flying rock missiles;
(b) Gases; and
(c) Concussion.
Blast pattern. The plan of the drill holes laid out and a display of the burden distance, spacing distance, and their relationship to each other.
Blast site. The area where explosive material is handled during loading and fifty feet in all directions from loaded blast holes or holes to be loaded.
Blaster. A person trained and experienced in the use of explosives and licensed by the department.
Blaster in charge. A licensed blaster who is:
(a) Fully qualified, by means of training and experience in explosives use;
(b) Adequately trained, experienced, and capable of recognizing hazardous conditions throughout the blast area;
(c) In charge of:
(i) The blast process;
(ii) All aspects of explosives and blasting agent storage, handling, and use as recommended by the manufacturer and as required by this chapter.
(d) In a position of authority:
(i) To take prompt corrective action in all areas of the blast operation;
(ii) Over all other blasters at the blast area.
Blaster's license. An individual license issued by the department under the provisions of chapter 296-52 WAC.
Blasting agent. Any material or mixture consisting of a fuel and oxidizer:
(a) That is intended for blasting;
(b) Not otherwise defined as an explosive;
(c) If the finished product, as mixed for use or shipment, cannot be detonated by means of a number 8 test blasting cap when unconfined;
(d) A number 8 test blasting cap is one containing two grams of a mixture of eighty percent mercury fulminate and twenty percent potassium chlorate, or a blasting cap of equivalent strength. An equivalent strength cap comprises 0.40-0.45 grams of PETN base charge pressed in an aluminum shell with bottom thickness not to exceed 0.03 of an inch, to a specific gravity of not less than 1.4 g/cc., and primed with standard weights of primer depending on the manufacturer.
Blasting cap or cap. When used in connection with the subject of explosives shall mean detonator.
Blockholing. The breaking of boulders by firing a charge of explosives that has been loaded in a drill hole.
Buildings that are not inhabited. A building(s) which has no one in it while explosives are being made up in an adjacent explosives makeup room or while explosives are being held in an adjacent day box or hand charge storage facility.
Competent person. A person who:
(a) Is capable of identifying existing hazardous and the forecasting of hazards of working conditions which might be unsanitary or dangerous to personnel or property; and
(b) Has authorization to take prompt corrective action to eliminate such hazards.
Consumer fireworks.
(a) Any small firework device:
(i) Designed to produce visible effects by combustion;
(ii) That must comply with the construction, chemical composition, and labeling regulations of the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (Title 16 C.F.R., Parts 1500 and 1507).
(b) A small device designed to produce audible effects which include, but are not limited to:
(i) Whistling devices;
(ii) Ground devices containing 50 mg or less of explosive materials;
(iii) Aerial devices containing 130 mg or less of explosive materials.
Note: | Fused set pieces containing components, which, together, exceed 50 mg of salute powder are not included. |
Conveyance. Any unit used for transporting explosives or blasting agents including, but not limited to:
(a) Trucks;
(b) Trailers;
(c) Rail cars;
(d) Barges;
(e) Vessels.
Day box. A box which:
(a) Is a temporary storage facility for storage of explosive materials;
(b) Is not approved for unattended storage of explosives;
(c) May be used at the worksite during working hours to store explosive materials, provided the day box is:
(i) Constructed as required (WAC 296-52-70065 Explosives day box);
(ii) Marked with the word "explosives";
(iii) Used in a manner that safely separates detonators from other explosives; and
(iv) Guarded at all times against theft.
Dealer. Any person who purchases explosives or blasting agents for the sole purpose of resale and not for use or consumption.
Detonating cord. A round flexible cord containing a center core of high explosive and used to initiate other explosives.
Detonator. Any device containing any initiating or primary explosive that is used for initiating detonation and includes, but is not limited to:
(a) Electric and electronic detonators of instantaneous and delay types;
(b) Detonators for use with safety fuses, detonating cord delay connectors, and nonelectric instantaneous delay detonators which use detonating cord, shock tube, or any other replacement for electric leg wires.
Discharge hose. A hose with an electrical resistance high enough to limit the flow of stray electric currents to safe levels, but not high enough to prevent drainage of static electric charges to the ground. Hose not more than 2 megohms resistance over its entire length and of not less than 5,000 ohms per foot meets the requirement.
Display fireworks. Large fireworks designed primarily to produce visible or audible effects by combustion, deflagration, or detonation, and include, but are not limited to:
(a) Salutes containing more than 2 grains (130 mg) of explosive materials;
(b) Aerial shells containing more than 40 grams of pyrotechnic compositions;
(c) Other display pieces, which exceed the limits of explosive materials for classification as "consumer fireworks";
(d) Fused set pieces containing components, which together exceed 50 mg of salute powder.
Dud. An unexploded deployed charge which still has its initiation system in place.
Electric blasting circuitry. Consists of these items:
(a) Bus wire. An expendable wire used in parallel or series, or in parallel circuits, which are connected to the leg wires of electric detonators;
(b) Connecting wire. An insulated expendable wire used between electric detonators and the leading wires or between the bus wire and the leading wires;
(c) Leading wire. An insulated wire used between the electric power source and the electric detonator circuit;
(d) Permanent blasting wire. A permanently mounted insulated wire used between the electric power source and the electric detonator circuit.
Electric delay detonators. Detonators designed to detonate at a predetermined time after energy is applied to the ignition system.
Electric detonator. A blasting detonator designed for and capable of detonation by means of electric current.
Electronic detonator. A detonator that utilizes stored electrical energy as a means of powering an electronic timing delay element/module that provides initiation energy for firing the base charge.
Emulsion. An explosive material containing:
(a) Substantial amounts of oxidizer dissolved in water droplets, surrounded by an immiscible fuel;
(b) Droplets of an immiscible fuel surrounded by water containing substantial amounts of oxidizer.
Explosive actuated power devices. Any tool or special mechanized device, which is activated by explosives and does not include propellant actuated power devices.
Explosives.
(a) Any chemical compound or mechanical mixture:
(i) Commonly intended or used for the purpose of producing an explosion;
(ii) That contains any oxidizing and combustible units or other ingredients in proportions, quantities or packing that an ignition by fire, friction, concussion, percussion, or detonation of any part of the compound or mixture may cause sudden generation of highly heated gases resulting in gaseous pressures capable of producing destructive effects on contiguous objects or of destroying life or limb.
(b) All material classified as Division 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, or 1.6 explosives by U.S. DOT;
(c) For the purposes of public consumer use, the following are not considered explosives unless they are possessed or used for a purpose inconsistent with small arms use or other legal purposes:
(i) Small arms ammunition;
(ii) Small arms ammunition primers;
(iii) Smokeless powder, not exceeding fifty pounds;
(iv) Black powder, not exceeding five pounds.
Explosives classifications. Explosives classifications include, but are not limited to:
(a) Division 1.1 and Division 1.2 explosives (possess mass explosion or detonating hazard):
(i) Dynamite;
(ii) Nitroglycerin;
(iii) Picric acid;
(iv) Lead azide;
(v) Fulminate of mercury;
(vi) Black powder (exceeding 5 pounds);
(vii) Detonators (in quantities of 1,001 or more);
(viii) Detonating primers.
(b) Division 1.3 explosives (possess a minor blast hazard, a minor projection hazard, or a flammable hazard):
(i) Propellant explosives;
(ii) Smokeless powder (exceeding fifty pounds).
(c) Division 1.4 explosives:
(i) Explosives that present a minor explosion hazard;
(ii) Includes detonators that will not mass detonate in quantities of 1,000 or less.
(d) Division 1.5 explosives:
(i) Explosives with a mass explosion hazard but are so insensitive that there is little probability of initiation;
(ii) ANFO and most other blasting agents are in this division.
(e) Division 1.6 explosives, which are explosives that are extremely insensitive and do not have a mass explosion hazard.
Explosives exemption. The exemption for small arms ammunition, small arms ammunition primers, smokeless powder, not exceeding fifty pounds, and black powder, not exceeding five pounds:
(a) Applies to public consumer use only;
(b) Does not apply to the employer employee relationship covered under the Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act.
Explosives international markings.
(a) The department will accept U.S. DOT and/or ATF international identification markings on explosives and/or explosives containers or packaging;
(b) This exception is under the authority of RCW 70.74.020(3) and in lieu of Washington state designated markings (as defined by RCW 70.74.010(4) (Division 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3) and required by RCW 70.74.300).
Explosives manufacturing building. Any building or structure, except magazines:
(a) Containing explosives where the manufacture of explosives, or any processing involving explosives, is conducted;
(b) Where explosives are used as a component part or ingredient in the manufacture of any article or device.
Explosives manufacturing plant. All lands with buildings used:
(a) In connection with the manufacturing or processing of explosives;
(b) For any process involving explosives;
(c) For the storage of explosives;
(d) To manufacture any article or device where explosives are used as a component part or ingredient in the article or device.
Fireworks. Any composition or device:
(a) Designed to produce a visible or an audible effect by combustion, deflagration, or detonation;
(b) Which meets the definition of "consumer fireworks" or "display fireworks."
Forbidden or not acceptable explosives. Explosives which are forbidden or not acceptable for transportation by common carriers by rail freight, rail express, highway, or water in accordance with the regulations of the Federal Department of Transportation (DOT).
Fuel. A substance, which may react with oxygen to produce combustion.
Fuse (safety). See "safety fuse."
Fuse igniter. A special pyrotechnic device intended to be used to ignite safety fuses.
Hand charge. An explosive charge with a cap and fuse assembly inserted in place.
Handler. Any individual who handles explosives or blasting agents for the purpose of transporting, moving, or assisting a licensed blaster in loading, firing, blasting, or disposal.
Note: | This does not include employees of a licensed manufacturer engaged in manufacturing process, drivers of common carriers, or contract haulers. |
Hand loader. Any person who engages in the noncommercial assembly of small arms ammunition for personal use; specifically, any person who installs new primers, powder, and projectiles into cartridge cases.
Highway. Roads, which are regularly and openly traveled by the general public and includes public streets, alleys, roads, or privately financed, constructed, or maintained roads.
Improvised device. A device, which is:
(a) Fabricated with explosives;
(b) Fabricated with destructive, lethal, noxious, pyrotechnic, or incendiary chemicals, and designed, or has the capacity to disfigure, destroy, distract, and harass.
Inhabited building.
(a) A building which is regularly occupied, in whole or in part, as a habitat for human beings;
(b) Any church, schoolhouse, railroad station, store, or other building where people assemble.
Note: | This does not mean any building or structure occupied in connection with the manufacture, transportation, storage, or use of explosives. |
Low explosives. Explosive materials, which can be caused to deflagrate when, confined. This includes black powder, safety fuses, igniters, igniter cords, fuse lighters, and display fireworks defined as Division 1.2 or Division 1.3 explosives by U.S. DOT (49 C.F.R. Part 173).
Note: | This does not apply to bulk salutes. |
Magazine. Any building, structure, or container approved for storage of explosive materials.
Note: | This does not apply to an explosive manufacturing building. |
Manufacturer. Any person engaged in the business of manufacturing explosive materials for purposes of sale or distribution or for his or her own use.
EXCEPTIONS: | The following exemptions are restricted to materials and components, which are not classified (by U.S. DOT) as explosives until after they are mixed. With this restriction, the definition of manufacturer does not include: |
• Inserting a detonator into a cast booster or a stick of high explosive product to make a primer for loading into a blast hole. | |
• The act of mixing on the blast site, either by hand or by mechanical apparatus, binary components, ammonium nitrate, fuel oil, and/or emulsion products to create explosives for immediate down blast hole delivery. |
Misfire. The complete or partial failure of an explosive charge to explode as planned.
Mudcap (also known as bulldozing and dobying). Covering the required number of cartridges that have been placed on top of a boulder with a three- or four-inch layer of mud, which is free from rocks or other material that could cause a missile hazard.
No-light. The failure of a safety fuse to ignite.
Nonelectric delay detonator. A detonator with an integral delay element in conjunction with and capable of being detonated by a:
(a) Detonation impulse;
(b) Signal from miniaturized detonating cord;
(c) Shock tube.
Oxidizer. A substance that yields oxygen readily to stimulate the combustion of organic matter or other fuel.
Permanent magazines. Magazines that:
(a) Are fastened to a foundation;
(b) Do not exceed permanent magazine capacity limits (RCW 70.74.040);
(c) Are approved and licensed;
(d) Are left unattended.
Person. Any individual, firm, partnership, corporation, company, association, person or joint stock association or trustee, receiver, assignee, or personal representative of that entity.
Person responsible. For an explosives magazine, means:
(a) The person legally responsible for a magazine that actually uses the magazine;
(b) The person is responsible for the proper storage, protection, and removal of explosives, and may be the owner lessee, or authorized operator.
Portable (field) magazines. Magazines that are:
(a) Designed to be unattended;
(b) Not permanently fastened to a foundation;
(c) Constructed or secured to make sure they cannot be lifted, carried, or removed easily by unauthorized persons;
(d) Limited to the capacity of explosives required for efficient blasting operation;
(e) Approved and licensed.
Possess. The physical possession of explosives in one's hand, vehicle, magazine, or building.
Primary blasting. The blasting operation that dislodged the original rock formation from its natural location.
Primer. A unit, package, cartridge, or container of explosives inserted into or attached to a detonator or detonating cord to initiate other explosives or blasting agents.
Propellant actuated power device. Any tool, special mechanized device, or gas generator system, which is actuated by a propellant and releases and directs work through a propellant charge.
Public utility transmission systems.
(a) Any publicly owned systems regulated by:
(i) The utilities and transportation commission;
(ii) Municipalities.
(b) Other public regulatory agencies, which include:
(i) Power transmission lines over 10 kV, telephone cables, or microwave transmission systems;
(ii) Buried or exposed pipelines carrying water, natural gas, petroleum, or crude oil or refined products and chemicals.
Purchaser. Any person who buys, accepts, or receives explosives or blasting agents.
Pyrotechnics (commonly referred to as fireworks). Any combustible or explosive compositions or manufactured articles designed and prepared for the purpose of producing audible or visible effects.
Qualified person. A person who has successfully demonstrated the ability to solve or resolve problems relating to explosives, explosives work, or explosives projects by:
(a) Possession of a recognized degree or certificate;
(b) Professional standing;
(c) Extensive knowledge, training, and experience.
Railroad. Any type of railroad equipment that carries passengers for hire.
Safety fuse (for firing detonators). A flexible cord containing an internal burning medium by which fire is conveyed at a continuous and uniform rate.
Secondary blasting. Using explosives, mudcapping, or blockholing to reduce oversize material to the dimension required for handling.
Shock tube. A small diameter plastic tube:
(a) Used for initiating detonators;
(b) That contains a limited amount of reactive material so energy, transmitted through the tube by means of a detonation wave, is guided through and confined within the walls of the tube.
Small arms ammunition. Any shotgun, rifle, pistol, or revolver cartridge, and cartridges for propellant actuated power devices and industrial guns.
Note: | This does not mean military type ammunition containing explosive bursting incendiary, tracer, spotting, or pyrotechnic projectiles. |
Small arms ammunition primers. Small percussion sensitive explosive charges encased in a detonator or capsule used to ignite propellant power or percussion detonators used in muzzle loaders.
Smokeless powder. Solid chemicals or solid chemical mixtures that function by rapid combustion.
Special industrial explosive devices. Explosive actuated power devices and propellant-actuated power devices.
Special industrial explosives materials. Shaped materials and sheet forms and various other extrusions, pellets, and packages of high explosives, which include:
(a) Dynamite;
(b) Trinitrotoluene (TNT);
(c) Pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN);
(d) Hexahydro-1, 3, 5-trinitro-s-triazine (RDX);
(e) Other similar compounds used for high-energy-rate forming, expanding, and shaping in metal fabrication, and for dismemberment and quick reduction of scrap metal.
Springing. The creation of a pocket in the bottom of a drill hole by the use of a moderate quantity of explosives so that larger quantities of explosives may be inserted.
Sprung hole. A drilled hole that has been enlarged by a moderate quantity of explosives to allow for larger quantities of explosives to be inserted into the drill hole.
Stemming. A suitable inert incombustible material or device used to confine or separate explosives in a drill hole or cover explosives in mudcapping.
Trailer. Semi-trailers or full trailers, as defined by U.S. DOT, which are:
(a) Built for explosives;
(b) Loaded with explosives;
(c) Operated in accordance with U.S. DOT regulations.
U.S. DOT. The United States Department of Transportation.
Vehicle. Any car, truck, tractor, semi-trailer, full trailer, or other conveyance used for the transportation of freight.
Water-gels or emulsion explosives. These explosives:
(a) Comprise a wide variety of materials used for blasting. Two broad classes of water-gels are those which:
(i) Are sensitized by material classed as an explosive, such as TNT or smokeless powder;
(ii) Contain no ingredient classified as an explosive which is sensitized with metals, such as aluminum, or other fuels.
(b) Contain substantial proportions of water and high proportions of ammonium nitrate, some ammonium nitrate is in the solution in the water, and may be mixed at an explosives plant, or the blast site immediately before delivery into the drill hole.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60010 Purpose and intent.
The purpose of this chapter is to define minimum requirements for the prevention and control of hazards related to the possession, handling, and use of explosives in order to:
((•)) (1) Protect the safety and health of the general public;
((•)) (2) Protect the safety and health of explosive industry employees covered under the Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act (chapter 49.17 RCW);
((•)) (3) Develop, support, and maintain safe and healthy use of explosives in Washington state.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-60015 Coverage.
This chapter applies to:
((•)) (1) Any person, partnership, company, corporation, government agency, or other entity;
((•)) (2) All aspects of explosives, blasting agents, and pyrotechnics including:
((–)) (a) Manufacture;
((–)) (b) Sale;
((–)) (c) Possession;
((–)) (d) Purchase;
((–)) (e) Use;
((–)) (f) Storage;
((–)) (g) Transportation;
((–)) (h) Avalanche control.
((•)) (3) Display fireworks.
Note: | Class A and B display fireworks are partially exempt from the requirements of this chapter (see WAC 296-52-60020(5)). |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-08-024, filed 3/24/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-52-60020 Exemptions.
(1) The following are exempt from this chapter:
(a) Explosives or blasting agents transported by railroad, water, highway, or air under the jurisdiction of the Federal Department of Transportation (DOT), the Washington state utilities and transportation commission, and the Washington state patrol.
(b) Laboratories of schools, colleges, and similar institutions if confined to the purpose of instruction or research and if the quantity does not exceed one pound.
(c) Explosives in the forms prescribed by the official United States Pharmacopoeia.
(d) The transportation, storage, and use of explosives or blasting agents in the normal and emergency operations of:
((•)) (i) The United States agencies and departments including the regular United States military departments on military reservations;
((•)) (ii) Arsenals, navy yards, depots, or other establishments owned by, operated by, or on behalf of, the United States;
((•)) (iii) The duly authorized militia of any state; and
((•)) (iv) The emergency operations of any state department or agency, any police, or any municipality or county.
(e) A hazardous devices technician when they are carrying out:
((•)) (i) Normal and emergency operations;
((•)) (ii) Handling evidence;
((•)) (iii) Operating and maintaining a specially designed emergency response vehicle that carries no more than ten pounds of explosive materials;
((•)) (iv) When conducting training and whose employer possesses the minimum safety equipment prescribed by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) for hazardous devices work.
Note: | A hazardous devices technician is a person who is a graduate of the FBI Hazardous Devices School and who is employed by a state, county, or municipality. |
(f) The importation, sale, possession, and use of fireworks, signaling devices, flares, fuses, and torpedoes.
(g) Reserved.
(h) Any violation under this chapter if any existing ordinance of any city, municipality, or county is more stringent.
(i) The transportation and storage of explosive actuated tactical devices, including noise and flash diversionary devices, by local law enforcement tactical response teams and officers in law enforcement department-issued vehicles designated for use by tactical response teams and officers, provided the explosive devices are stored and secured in compliance with regulations and rulings adopted by the federal bureau of alcohol, tobacco, firearms, and explosives.
(2) Noncommercial military explosives. Storage, handling, and use of noncommercial military explosives are exempt from this chapter while they are under the control of the United States government or military authorities.
(3) Import, sale, possession, or use of:
((•)) (a) Consumer fireworks;
((•)) (b) Signaling devices;
((•)) (c) Flares;
((•)) (d) Fuses;
((•)) (e) Torpedoes.
(4) Consumer fireworks. Fireworks classified as Division 1.4 explosives by U.S. DOT and regulated through the state fireworks law (chapter 70.77 RCW) and the fireworks administrative code (chapter 212-17 WAC) by the Washington state fire marshal.
Note: | Consumer fireworks are classified as fireworks UN0336 and UN0337 by U.S. DOT (49 C.F.R. 72.101). |
(5) Partial exemption—Division 1.1, 1.2, or 1.3 display fireworks. Display fireworks are fireworks classified as Division 1.1, 1.2, or 1.3 explosives by US DOT. Users of Division 1.1, 1.2, or 1.3 display fireworks must comply with all storage or storage related requirements (for example, licensing, construction, and use) of this chapter.
Note: | Display fireworks are classified as fireworks UN0333, UN0334, or UN0335 by U.S. DOT (49 C.F.R. 172.101). |
(6) Conditional exemption small arms explosive materials. Public consumers possessing and using:
((•)) (a) Black powder, under five pounds;
((•)) (b) Smokeless powder, under fifty pounds;
((•)) (c) Small arms ammunition;
((•)) (d) Small arms ammunition primers.
((–)) Unless these materials are possessed or used illegally or for a purpose inconsistent with small arms use.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60030 The department.
(1) Administration and enforcement. The director of labor and industries administers and enforces all activities governed by the Washington State Explosives Act through chapter 296-52 WAC using the full resources of the department.
(2) Authority to enter, inspect, and issue penalties. The department may enter and inspect any location, facility, or equipment and issue penalties for any violation whenever the director has reasonable cause to think there are:
((•)) (a) Explosives;
((•)) (b) Blasting agents;
((•)) (c) Explosive materials.
(3) Unlicensed activities. Whenever the director requests an unlicensed person to surrender explosives, improvised devices, or their component parts, he may request the attorney general to apply to the county superior court in which the illegal practice was carried out for a temporary restraining order or other appropriate assistance.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60035 Other government entities.
(1) Law enforcement authorities. The department:
((•)) (a) Acknowledges the legal obligation of other law enforcement agencies to enforce specific aspects or sections of the Washington State Explosives Act under local ordinances and with joint and shared authority granted by RCW 70.74.201.
((•)) (b) Will cooperate with all other law enforcement agencies in carrying out the intent of the Washington State Explosives Act and chapter 296-52 WAC.
(2) Local government authorities.
(a) This chapter does not prevent local jurisdictions from adopting and administering local regulations relating to explosives. Examples of local jurisdictions/regulations include:
((•)) (i) City or county government explosive ordinances;
((•)) (ii) Other government authorities such as the Washington utilities and transportation commission, the Washington state patrol, or Washington administrative codes.
(b) Local regulations must not diminish or replace any regulation of this chapter.
Note: | A nonmandatory sample-blasting ordinance for local jurisdictions is included in Appendix B. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60055 Drug use.
Explosives must not be handled by anyone under the influence of:
((•)) (1) Alcohol;
((•)) (2) Narcotics;
((•)) (3) Prescription drugs and/or narcotics that endanger the worker or others;
((•)) (4) Other dangerous drugs.
Note: | This chapter does not apply to persons taking prescription drugs and/or narcotics as directed by a physician provided their use will not endanger the blaster, workers, or any other people. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60060 License revocation, suspension, and surrender.
(1) Revocation. The department:
(a) Will revoke and not renew the manufacturer, dealer, purchaser, blaster, or storage license of any person as a result of a disqualifying condition identified in WAC 296-52-61040, Applicant disqualifications.
(b) May revoke the license of any person who has:
(i) Repeatedly violated the requirements of this chapter;
(ii) Had a license suspended twice under this chapter.
(2) Suspension. The department may suspend the license of any person for a period up to six months for any violation of this chapter.
(3) Surrender. Revoked or suspended licenses must be surrendered immediately to the department after the chapter violators have been notified.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60080 Entry and access to explosive areas.
Only the owner, owner's authorized agent, the director, or law enforcement officer(s) acting in an official capacity may enter into an:
((•)) (1) Explosives manufacturing building;
((•)) (2) Magazine;
((•)) (3) Vehicle;
((•)) (4) Other common carrier containing explosives.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60095 Fire.
(1) Magazines/buildings. Flame or flame producing devices must not be ignited within fifty feet of any magazine or explosives manufacturing building.
(2) Explosives handling.
(a) All sources of fire or flame, including smoking and matches, are prohibited within one hundred feet of the blast site while explosives are being handled or used.
(b) Explosives must not be handled near:
(i) Open flames;
(ii) Uncontrolled sparks; or
((OR))
(iii) Energized electric circuits.
(3) Fire incident precautions. In the event of a fire:
(a) All employees must be removed to a safe area;
(b) The fire area must be guarded against intruders;
(c) The fire must not be fought where there is danger of contact with explosives.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60115 Explosive industry employers.
In addition to the requirements of this chapter:
(1) Explosive industry employers must comply with other applicable WISHA requirements:
((•)) (a) Chapter 296-800 WAC, Safety and health core rules;
((•)) (b) Chapter 296-24 WAC, General safety and health standards;
((•)) (c) Chapter 296-62 WAC, General occupational health standards;
((•)) (d) Chapter 296-155 WAC, Safety standards for construction;
((•)) (e) Other industry specific standards that may apply.
(2) Manufacturers of explosives or pyrotechnics must comply with WISHA safety standards for process safety management of highly hazardous chemicals, chapter 296-67 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60120 Variance from a chapter requirement.
The director may approve a variance from a chapter requirement pursuant to RCW 49.17.080 or 49.17.090:
((•)) (1) After an application for a variance is received((,));
((•)) (2) After the department has conducted an investigation((,));
((•)) (3) When conditions exist that make the requirement impractical to use((,)); and
((•)) (4) When equivalent means of protection are provided.
Note: | Variance application forms may be obtained from and should be submitted to: Department of Labor and Industries, WISHA Services Division, Post Office Box 44650, Olympia, WA 98504-4650. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-60125 Using standards from national organizations and federal agencies.
To be in compliance with WISHA rules, the information provided in this section must be followed when safety and health standards from national organizations and federal agencies are referenced in WISHA rules.
((•)) (1) The edition of the standard specified in the WISHA rule must be used.
((•)) (2) Any edition published after the edition specified in the WISHA rule may be used.
Note: | The federal and national consensus standards referenced in the WISHA rules are available through the issuing organization and the local or state library. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 08-15-139, filed 7/22/08, effective 12/1/08)
WAC 296-52-61010 License applicants must provide this information.
(1) Individual applicants must provide the following information to the department:
((• An individual must provide:
–)) (a) Their name((,));
(b) Their address((,)); and
(c) Their citizenship.
((•)) (2) A partnership must provide:
((–)) (a) The name, address, and citizenship for each partner;
((–)) (b) The name and address of the applicant.
((•)) (3) An association or corporation must provide:
((–)) (a) The name, address, and citizenship for each officer and director;
((–)) (b) The name and address of the applicant.
(((2))) (4) Applicants must:
((•)) (a) Meet any license specific requirements;
((•)) (c) Provide any information requested by the department before a new or renewal license will be issued.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-61015 License applicants must complete department forms.
(1) Applications must be completed on department forms.
((•)) (2) License application forms may be obtained from and submitted to:
Department of Labor and Industries
WISHA Services Division
Post Office Box 44655((,))
Olympia, WA 98504-4655.
Note: | Purchaser and blaster license applications may also be obtained from explosive dealers or department service locations. (You will find a complete list of L&I service locations at www.lni.wa.gov.) |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 08-15-139, filed 7/22/08, effective 12/1/08)
WAC 296-52-61030 Applicant participation.
(1) Applicants((:
•)) must cooperate and assist the department in all aspects of the application review.
((•)) (2) Applicants must provide all information requested by the department to:
((–)) (a) Verify application statements;
((–)) (b) Help with any questions.
((•)) (3) Applicants must furnish their fingerprints to the department on department forms.
((–)) Fingerprinting and criminal history record information checks are required for management officials directly responsible for explosives operations.
((•)) (4) Applicants must pay the fee to the department for processing the fingerprint card (RCW 70.74.360(1)).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-61040 Reasons why applicants may be disqualified.
(1) Licenses will not be issued for the manufacture, retail sale or purchase of explosives to any applicant who is any of the following:
((•)) (a) Does not provide proof of a valid explosive license or permit issued by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF);
((•)) (b) Under twenty-one years of age;
((•)) (c) Whose license is suspended or revoked, except as provided in this section;
((•)) (d) Convicted in any court of a crime punishable by imprisonment for a term exceeding one year;
((•)) (e) Legally determined at the time of application to be:
((–)) (i) Mentally ill;
((–)) (ii) Insane;
((–)) (iii) Committed to a mental institution;
((–)) (iv) Incompetent due to any mental disability or disease at the time of application.
Note: | The department will not reissue a license until competency has been legally restored. |
((•)) (f) Physically ill or disabled, and cannot use explosives safely. Disqualifying disabilities may include, but are not limited to:
((–)) (i) Blindness;
((–)) (ii) Deafness;
((–)) (iii) Epileptic or diabetic seizures or coma.
Note: | The department will not reissue a license until the applicant's physical ability is verified by a qualified physician through the appeal process (WAC 296-52-60065, Violation appeals). |
((•)) (g) Who is an alien, unless:
((–)) (i) They are lawfully admitted for permanent residence ((–)); and
((–)) (ii) They are in lawful nonimmigrant status.
((•)) (h) Who has been dishonorably discharged from the United States armed forces;
((•)) (i) Who has renounced their citizenship from the United States.
(2) A user (blaster) license will not be issued if the applicant is denied a receiver or employee possessor designation by ATF.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-62010 Dealer applicant information.
The dealer applicant must:
((•)) (1) Give the reason they want to participate in the business of dealing in explosives.
((•)) (2) Provide information required by WAC 296-52-61010, License applicants must provide this information.
((•)) (3) Provide other pertinent information required by the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-62025 Prohibit explosives items from sale or display in these areas.
Explosives, improvised devices, or blasting agents cannot be sold, displayed, or exposed for sale on any:
((•)) (1) Highway;
((•)) (2) Street;
((•)) (3) Sidewalk;
((•)) (4) Public way; or
((OR
•)) (5) Public place.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-62035 Authorized agent information.
A dealer must make sure the purchaser provides a list of people on their authorized agent list with the following information:
((•)) (1) Name;
((•)) (2) Address;
((•)) (3) Driver's license number or valid identification;
((•)) (5) Place of birth;
((•)) (6) Date of birth.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-62040 Verification of customer identity.
(1) Orders.
(a) An order for explosives can be placed:
((•)) (i) In person;
((•)) (ii) By telephone; or
((OR
•)) (iii) In writing.
(b) The dealer must receive proper authorization and identification from the person placing the order to verify the person is either the:
((•)) (i) Purchaser; or
((OR
•)) (ii) Purchaser's authorized agent.
Note: | This requirement does not apply to licensed common carrier companies when the common carrier: |
((•)) 1. Is transferring explosive materials from the seller to the purchaser; and | |
((AND)) | |
((•)) 2. Complies with transfer practices of the state and federal U.S. DOT regulations. |
(2) Deliveries. The dealer must:
(a) Not distribute explosive materials to an unauthorized person((.));
(b) Make sure the recipient is the purchaser or the purchaser's authorized agent((.));
(c) Verify the recipient's identity from a photo identification card (for example, driver's license)((.));
(d) Obtain the:
(i) Purchaser's magazine license number when explosives are delivered to a storage magazine.
(ii) Legal signature of the purchaser or the purchaser's authorized agent on a receipt documenting the explosives were received.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-62045 Recordkeeping and reporting.
(1) Sale documentation. A dealer must document the following information when an explosive materials order is placed. A dealer's record must include the:
((•)) (a) Date explosive materials were sold;
((•)) (b) Purchaser's name and license number;
((•)) (c) Name of the person authorized by the purchaser to physically receive the explosive materials;
((•)) (d) Kind of explosive materials sold;
((•)) (e) Amount of explosive materials sold;
((•)) (f) Date code.
Note: | Black powder sales less than five pounds are not required to be reported to the department. |
(2) Retention of records and receipts. Dealers must keep:
((•)) (a) Signed receipts for a minimum of one year from the date explosives were purchased;
((•)) (b) Records of explosives purchased and sold for a minimum of five years.
(3) Monthly report.
((•)) (a) A monthly report of the dealer's records must be submitted to the department at the following address:
Department of Labor and Industries
WISHA Services Division
Post Office Box 44655
Olympia, WA 98504-4655
((•)) (b) Dealer records must be received by the 10th day of each month.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-63010 Applicant information.
Applicants must provide the following information to the department:
((•)) (1) The reason explosives or blasting agents will be used;
((•)) (2) The location where explosives or blasting agents will be used;
((•)) (3) The kind of explosives or blasting agents to be used;
((•)) (4) The amount of explosives or blasting agents to be used;
((•)) (5) An explosives storage plan:
((–)) (a) Documenting proof of ownership of a licensed storage magazine; or
((OR
–)) (b) With a signed authorization to use another person's licensed magazine; or
((OR
–)) (c) With a signed statement certifying that the explosives will not be stored.
((•)) (6) An authorized agent list, if the purchaser chooses to authorize others to order or receive explosives on their behalf;
((•)) (7) The identity and current license of the purchaser's blaster;
((•)) (8) Information required by WAC 296-52-61010, License applicants must provide this information;
((•)) (9) Any other pertinent information requested by the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-63020 Authorized agents.
(1) Required information.
The purchaser must provide the following written information for people on their authorized agent list:
((•)) (a) Legal name;
((•)) (b) Address;
((•)) (c) Driver's license number or other valid identification;
((•)) (d) Date of birth;
((•)) (e) Place of birth.
(2) List distribution. The purchaser must provide a current authorized agent list to:
((•)) (a) The department when applying for a new or renewal license;
((•)) (b) Any dealer the purchaser plans to order explosive materials from, prior to placing the order.
(3) Notification of list changes. The purchaser must make sure the dealer's and department's authorized agent lists are updated as changes occur.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-63025 Explosive order deliveries.
(1) Receiver identification. Any person receiving explosives purchased from a dealer must:
((•)) (a) Provide proper identification and prove to the satisfaction of the dealer that they are:
((–)) (i) The purchaser; or
((OR
–)) (ii) Their authorized agent.
((•)) (b) Sign their legal signature on the dealer's receipt.
(2) Delivery locations. Explosives must be delivered into:
((•)) (a) Authorized magazines;
((•)) (b) Approved temporary storage; or
((OR
•)) (c) Handling areas.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-63030 Notify the department of blaster changes.
The purchaser must:
((•)) (1) Notify the department when the licensed blaster changes.
((•)) (2) Provide their current blaster's license number to the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-64005 Responsibility to obtain a blaster's license.
(1) No one may conduct a blasting operation without a valid blaster's license issued by the department.
Note: | A blaster's license is not required for a "hand loader." |
(2) Blaster license classifications table. The following information shows classifications for blasting licenses((.)):
((•)) (a) Classification list assignment. Classification list assignment is determined by the use of single or multiple series charges; and the knowledge, training, and experience required to perform the type of blasting competently and safely.
((•)) (b) Multiple list applications. When an applicant wants to apply for multiple classifications and the classifications desired are from two or more classification table lists:
((–)) (i) All classifications must be requested on the application;
((–)) (ii) Qualifying documentation for all classifications being applied for must be included in the applicant's resume (WAC 296-52-64050, Applicant information). Training and experience may fulfill qualification requirements in multiple classifications.
((•)) (c) Request classifications not lists. Applicants must request specific classifications (not list designations) on their blaster application. Licenses are not issued or endorsed for Classification Table lists A, B, or C.
((•)) (d) License additions. To add a classification to an existing license, see WAC 296-52-64085, Changes to a blaster's license classification.
License Classifications Table |
|||||
LIST A |
LIST B |
LIST C |
|||
AB |
Aerial Blasting |
DE |
Demolition |
BT |
Bomb Technician* |
AG |
Agriculture |
SB |
Surface Blasting* |
UL |
Unlimited* |
AV |
Avalanche Control |
UB |
Underground Blasting |
||
ED |
Explosives Disposal* |
UW |
Underwater Blasting |
||
FO |
Forestry* |
||||
LE |
Law Enforcement* |
||||
IO |
Industrial Ordnance |
||||
SE |
Seismographic |
||||
TS |
Transmission Systems |
||||
WD |
Well Drilling |
||||
* | Detailed classification information. |
((•)) (e) Aerial blasting. Will require experience and passing aerial blasting test.
((•)) (f) Bomb technician. Disposal of bombs, illegal fireworks and explosive devices.
((•)) (g) Explosives disposal. Disposal of explosive materials by licensed blasters.
((•)) (h) Forestry. Includes logging, trail building, and tree topping.
((•)) (i) Law enforcement. Diversionary devices, explosive detection K-9 dog handlers, crowd control devices (stingers) requires taking a handlers test. Tactical entry (breaching) requires taking the tactical entry test.
((•)) (j) Surface blasting. Includes construction, quarries, and surface mining.
((•)) (k) Unlimited. Includes all classifications except underground blasting and law enforcement.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-64020 General qualifications for blasters.
(1) Physical condition. An applicant must be in good physical condition.
(2) Drug use. An applicant cannot be addicted to narcotics, intoxicants, or similar types of drugs.
Note: | This rule does not apply to physician prescribed drugs and/or narcotics when taken as directed if their use will not place the blaster, or other employees in danger. |
(3) Knowledge, experience, and performance in transportation, storage, handling, and use of explosives. A blaster applicant must:
((•)) (a) Have working knowledge of state and local explosives laws and regulations;
((•)) (b) Have adequate blaster training, experience, and knowledge;
((•)) (c) Be able to:
((–)) (i) Safely perform the type of blasting to be used; and
((AND
–)) (ii) Recognize hazardous conditions.
((•)) (d) Be competent in the use of each type of blasting method to be used
((•)) (e) Have the ability to understand and give written and oral directions.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-64030 List A qualifications.
To be considered for a blaster's license, limited to one or more List A classifications, an applicant must have a minimum of forty hours documented training accrued during the previous six years.
(1) The training must include a minimum of one of these three requirements:
((•)) (a) Eight hours basic blaster safety classroom training and thirty-two hours classification specific field training experience under a qualified blaster;
((•)) (b) Sixteen hours basic blaster safety classroom training and twenty-four hours classification specific field training experience under a qualified blaster;
((•)) (c) Twelve months classification specific field training experience.
(2) Aerial blasting classification ((shall)) will require:
((•)) (a) Standard avalanche control blaster's license;
((•)) (b) Experience requirement of five missions under the supervision of a licensed aerial blaster;
((•)) (c) Successful completion of a written exam.
Note: | Additional personnel on board with a standard avalanche control blaster's license may log each mission toward the aerial blasting endorsement experience requirement. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-64035 List B qualifications.
To be considered for a blaster's license, which includes one or more List B classifications, the applicant must meet one of the following requirements listed below:
((•)) (1) Eighteen months of documented blasting experience which includes a minimum of twelve months of documented experience in List A and six months documented blasting experience in each classification being applied for in List B;
((•)) (2) Twelve months of documented blasting experience in the past six years in the specific classification being applied for in List B.
Note: | Up to eighty hours of classroom training may be substituted for experience. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-64040 List C qualifications.
(1) Unlimited classification. To be considered for unlimited classification, the applicant must submit a detailed resume documenting:
((•)) (a) Experience in the majority of the classifications in Lists A and B;
((•)) (b) A minimum of five years of continuous full time blasting experience in the explosives industry where blasting has been the applicant's primary responsibility during the previous five years.
(2) Bomb technician. To be considered for a bomb technician classification, the applicant must:
((•)) (a) Submit a copy of the certificate of graduation from the FBI Hazardous Devices School (HDS) basic course in Redstone, Alabama((.));
((•)) (b) Submit a copy of the applicant's FBI Bomb Technician Certification identification card. The FBI Bomb Technician Certification card must bear a date that indicates that it is current at the time of application((.));
((•)) (c) Submit a letter from the applicant's law enforcement agency's head (chief or sheriff) stating that the applicant is a full-time employee assigned to perform bomb technician duties as part of an FBI accredited bomb squad.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-64050 Blaster license applicant information.
An applicant for a blaster's license must provide the following information to the department:
((•)) (1) The application must be signed by the blasting course instructor and the qualified blaster the applicant trained under;
((•)) (2) A detailed resume of blasting training and experience;
((•)) (3) Satisfactory evidence of competency in handling explosives;
((•)) (4) Information required by WAC 296-52-61010, License applicants must provide this information.
Note: | The department may request additional information for the classification being applied for upon review of a blaster's resume. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-64065 Blaster license limits.
(1) A blaster's license documents:
(a) The classifications the blaster is authorized to perform
(b) Any limitations imposed on the licensee.
(2) The licensee cannot:
(a) Perform blasting for which they are not licensed; or
((OR))
(b) Exceed the limits specified on the license.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-64085 Changes to a blaster's license classification.
Additional blaster classifications may be added to a license. Applicants must:
((•)) (1) Submit a detailed resume which documents blasting experience in the specific classification being applied for;
((•)) (2) Pass a written exam prepared and administered by the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-64090 Blaster license renewal.
The following requirements are for license renewal:
((•)) (1) General applicant qualifications, WAC 296-52-64020, General qualifications, apply.
((•)) (2) Renewal qualifications include the requirements of WAC 296-52-64090 License renewal, through WAC 296-52-64100, List C renewal qualifications.
((•)) (3) Training, experience, and responsibility requirements must be accrued during the one year before the application is submitted.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-64095 List A and B renewal qualifications.
The following requirements are for List A and B renewal qualifications:
(1) An application for a license renewal must include documentation of:
((•)) (a) Blasting experience, by providing a minimum of one blast record; or
((OR
•)) (b) Successful completion of eight hours of basic blaster's classroom training. The blasting course instructor must witness the submitted documentation.
(2) List A or B applicants who do not meet the minimum classification qualifications must pass a written exam administered by the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-64100 List C renewal qualifications.
The following requirements are for List C renewal qualifications:
(1) Unlimited classification. To be considered for a renewal of an unlimited license, an applicant must submit a detailed resume documenting:
((•)) (a) Experience in the majority of classification in List A and B;
((•)) (b) Full-time blasting experience in the explosives industry, where blasting has been the applicant's primary responsibility.
(2) Bomb technician. To be considered for a renewal of the bomb technician classification, an applicant must:
((•)) (a) Have continuous employment as a law enforcement bomb technician accrued during the previous year;
((•)) (b) Submit a copy of their FBI Bomb Technician Certification identification card bearing the name of the person making application and an expiration date that indicates that the card is current and valid as of the date of renewal;
((•)) (c) Submit a letter from the applicant's law enforcement agency's head (chief or sheriff) stating that the applicant is a full-time employee assigned to perform bomb technician duties as part of an FBI accredited bomb squad.
Note: | ((•)) If the applicant's card has expired at the time of renewal, they need to show that they are enrolled in the next available course at Redstone, Alabama. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-65010 Manufacturer applicant information.
The manufacturer applicant must provide the following information to the department:
((•)) (1) The reason the applicant wants to manufacture explosives.
((•)) (2) The manufacturing or processing location.
((•)) (3) The kind of explosives manufactured, processed, or used.
((•)) (4) The distance that the explosives manufacturing building is located, or intended to be located, from other buildings, magazines, inhabited buildings, railroads, highways, and public utility transmission systems.
((•)) (5) A site plan. The site plan must:
((–)) (a) Include the distance each manufacturing building is located from:
((♦)) (i) Other buildings on the premises where people are employed;
((♦)) (ii) Other occupied buildings on adjoining property;
((♦)) (iii) Buildings where customers are served;
((♦)) (iv) Public highways;
((♦)) (v) Utility transmission systems.
((–)) (b) Demonstrate compliance with:
((♦)) (i) Applicable requirements of the Washington State Explosives Act;
((♦)) (ii) The separation distance requirements of this chapter.
((–)) (c) Identify and describe all natural or artificial barricades used to influence minimum required separation distances;
((–)) (d) Identify the nature and kind of work being performed in each building;
((–)) (e) Specify the maximum amount and kind of explosives or blasting agents to be permitted in each building or magazine at any one time.
((•)) (6) Information required by WAC 296-52-61010, License applicants must provide this information.
((•)) (7) Other pertinent information required by the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-65015 Manufacturing site inspections.
(1) The department will((:
•)) inspect all manufacturing or processing locations:
((–)) (a) Before they are placed in operation or service; and
((AND
–)) (b) Prior to licensing.
((•)) (2) The department will schedule inspections:
((–)) (a) Once a complete application is received;
((–)) (b) At the earliest available and mutually agreeable date.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-65030 Site plan.
The site plan must include:
(1) A copy of the site plan and manufacturer's license must be posted in the main office of each manufacturing plant.
(2) The site plan must be maintained and updated to reflect the current status of manufacturing facilities, occupancy changes, or other pertinent information.
(3) Notifying the department:
((•)) (a) When a significant change occurs in the site plan;
((•)) (b) For a consultation before changing operations if the change is of such nature or magnitude that compliance with requirements of this chapter is questionable.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-66010 Storage applicant information.
Applicants must provide the following information to the department:
((•)) (1) The address or a legal description of the existing or proposed magazine or mobile storage site must be clearly identified;
((•)) (2) The reason explosive materials will be stored;
((•)) (3) The kind of explosives or blasting agents that will be stored;
((•)) (4) The maximum quantity of explosive materials that are or will be stored;
((•)) (5) Identify the total weight, in pounds, of all explosive materials to be stored on-site;
((•)) (6) The distance that the magazine is located or intended to be located from other magazines, inhabited buildings, explosives manufacturing buildings, railroads, highways, and public utility transmission systems;
((•)) (7) How long the storage license is needed;
((•)) (8) Information required by WAC 296-52-61010, License applicants must provide this information;
((•)) (9) Any other pertinent information requested by the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-66015 Storage site inspections.
(1) The department will((:
•)) inspect magazines, mobile-storage sites, and manufacturing plants:
((–)) (a) Before being placed in operation or service;
((–)) (b) Prior to licensing.
((•)) (2) The department will schedule inspections:
((–)) (a) Once a complete application is received;
((–)) (b) At the earliest available and mutually agreeable date.
Note: | See WAC 296-52-66040, Annual storage inspection, for mobile storage site qualifications. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-66020 Demonstration of handling and storage experience.
Applicants or officers, agents, or employees of the applicant, must demonstrate satisfactory experience in:
((•)) (1) Handling explosives.
((•)) (2) The storage requirements for any type of explosive materials to be stored.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-66053 Altering or destroying a licensed magazine.
(1) When a magazine is altered, the licensee must notify the department with:
((•)) (a) The license number of the magazine((.));
((•)) (b) The specific alterations made to the magazine.
(2) When a magazine is destroyed, the licensee must notify the department with the license number of the magazine.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-66057 Transfer, sale or lease of a magazine or mobile storage site.
(1) When a magazine or mobile storage site is leased, the owner of the magazine or mobile storage site must notify the department with:
(a) The magazine license number or site license number;
(b) The name of the individual or company leasing the magazine or mobile storage site.
(2) When a magazine or mobile storage site is transferred or sold from one entity to another, the previous owner/licensee ((shall)) must notify the department with:
(a) The magazine license number or site license number;
(b) The date of the sale or transfer;
(c) The name of the individual or company to whom the magazine or mobile storage site was sold or transferred to;
(d) Who will be licensing the magazine or mobile storage site;
(e) The name of the contact person and phone number.
(3) A new owner/licensee of a magazine or mobile storage site((:
(a))) is responsible for the safe operation of the magazine or mobile storage site (((b))). They must also:
((•)) (a) Submit a magazine storage application to the department;
((•)) (b) Pay the license fee for a minimum of one year;
((•)) (c) Obtain a storage license prior to storing explosive materials in the magazine or at the mobile storage site.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67010 Blaster in charge responsibilities.
The blaster in charge is responsible for all aspects of explosives use and must:
(1) Carry a current license with the correct blaster classification for the type of blasting being performed.
(2) Comply with all federal, state, and local government regulations.
(3) Meet the general license qualifications identified in WAC 296-52-64020, General qualifications.
(4) Use every reasonable precaution to ensure the safety of the general public and workers. Reasonable precautions include the use of:
(a) Blast area surveys.
(b) Warning signal posters, which must be posted in suitable locations. Table T-1 shows the information that must be on the poster.
TABLE T-1 |
|
WARNING SIGNAL |
A 1 minute series of long blasts 5 minutes prior to blast signal. |
BLAST SIGNAL |
A series of short blasts 1 minute prior to the shot. |
ALL CLEAR SIGNAL |
A prolonged blast following the inspection of the blast. |
(c) Flags and barricades.
(d) Blasting mats or other suitable protective material.
(5) Exercise and apply independent professional judgment regarding blasting activities, when following instructions from others could result in an illegal act or affect the outcome of a blast.
(6) Blast operation activities. The blaster in charge must:
((•)) (a) Have authority over all blasters and be able to promptly correct all actions taken in any area of the blast operation;
((•)) (b) Manage the blast operation properly for any type of blasting being performed;
((•)) (c) Control blast activities associated with a blast;
((•)) (d) Supervise explosive material activities, which include:
((–)) (i) Keeping a running inventory of all explosives and blasting agents stored at the blast area;
((–)) (ii) Supervising all on-site transportation, storage, loading, and firing of explosives.
((•)) (e) Notify local jurisdictions when blasting may affect them;
((•)) (f) Designate safe locations for personnel during the blast;
((•)) (g) Designate a method to determine when all personnel are accounted for in designated safe locations;
((•)) (h) Make sure blast observers are able to communicate with the blaster in charge;
((•)) (i) Make sure all possible exits to the blast site are observed immediately prior to each blast;
((•)) (j) Distribute explosives in the shot;
((•)) (k) Be present when a charge is detonated;
((•)) (l) Personally detonate the charge or give an order to a designated blaster to detonate the charge.
(7) Notification - Blast incidents. The blaster in charge must notify the department within twenty-four hours when:
(a) A misfire is not cleared;
(b) Vibration and air blast limits cause injury or property damage;
(c) Flyrock causes injury or property damage.
(8) Blast records. The blaster in charge must:
(a) Keep an accurate inventory of all explosives and blasting agents stored at the blast operation;
(b) Keep a blast record with the following information:
((•)) (i) Name of the company or contractor;
((•)) (ii) Exact location of the blast;
((•)) (iii) Date and time of detonation;
((•)) (iv) Name, signature, and license number of the blaster in charge;
((•)) (v) Type of material blasted;
((•)) (vi) Type of explosives used;
((•)) (vii) Number of holes, burden, and spacing;
((•)) (viii) Diameter and depth of holes;
((•)) (ix) Total amount of each type of explosives used;
((•)) (x) Maximum amount of explosives per delay period within eight milliseconds;
((•)) (xi) Maximum number of hole per delay period within eight milliseconds;
((•)) (xii) Method of firing;
((•)) (xiii) Type of circuit;
((•)) (xiv) Direction, distance in feet, and identification of the nearest dwelling, house, public building, school, church, or commercial/institutional building not owned or leased by the blaster in charge conducting the blasting;
((•)) (xv) Weather conditions;
((•)) (xvi) Type and height (or length) of stemming;
((•)) (xvii) A statement indicating whether blast mats or other flyrock protection were used;
((•)) (xviii) Type of initiation system used;
((•)) (xix) Type of delay periods used.
((•)) (c) Have seismograph records and readings, if required or used, that must accurately identify the:
((–)) (i) Name of the person and business analyzing the record;
((–)) (ii) Exact location of the seismograph;
((–)) (iii) Distance of the seismograph from the blast.
((• Sketch)) (d) Have sketches of the blast pattern. The sketch must include the:
((–)) (i) Number of hole;
((–)) (ii) Burden;
((–)) (iii) Spacing distance delay pattern.
((• Sketch)) (e) Have sketches of the hole profile if decking was used;
((•)) (f) Have general comments which include:
((–)) (i) Unusual conditions/situations during the blast;
((–)) (ii) The calculated scale distance number;
((–)) (iii) Misfires.
((•)) (g) Complete and sign each blast record;
((•)) (h) Retain blast records for a minimum of three years;
((•)) (i) Make sure blast records are available for department inspection.
Note: | A nonmandatory sample blast record can be found in Appendix B. You may use this format or create your own but all the information in this section must be included. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67045 Handling explosives.
Explosives must:
((•)) (1) Be handled by only competent and authorized personnel.
((•)) (2) Be delivered and issued only to a purchaser or a purchaser's authorized agent.
((•)) (3) Be delivered into authorized magazines, approved temporary storage, or handling areas.
((•)) (4) Be carried to the blast site from the main storage magazines by the blaster or blaster's helper in special insulated containers, day boxes, or original U.S. DOT shipping containers.
((•)) (5) Never be carried in pockets or clothing, including detonators.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67050 Trainee supervision.
Trainees and inexperienced personnel must work under the direct supervision of a fully qualified licensed blaster who knows the ((sites)) site's:
((•)) (1) Blasting method;
((•)) (2) Safety procedures;
((•)) (3) Blasting signals.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67060 Extraneous electricity and radio frequency (RF) transmitters.
Precautions must be taken to prevent unintended electric detonator discharge from extraneous electricity and radio frequency (RF) transmitters. The following are sources of common hazards for extraneous electricity and RF transmissions:
(1) Extraneous electricity. Common hazardous sources of extraneous electricity include:
((•)) (a) Adjacent power lines;
((•)) (b) Dust storms;
((•)) (c) Lightning storms.
(2) RF transmission sources. Common hazardous sources of RF transmissions include:
((•)) (a) Mobile transmitters:
((–)) (i) Citizen band (CB);
((–)) (ii) Side band radio;
((–)) (iii) VHF (FM) radio;
((–)) (iv) UHF cellular telephones;
((–)) (v) Radar.
((•)) (b) Fixed location transmitters:
((–)) (i) Base stations for CB;
((–)) (ii) Side band or FM radio communications;
((–)) (iii) UHF cellular telephone transmitters and service extension repeater systems;
((–)) (iv) AM and FM (commercial) radio broadcast transmitters;
((–)) (v) TV broadcast transmitters and repeater system transmitters;
((–)) (vi) Surface scan and radio navigation beacons.
((•)) (c) Low flying aircraft (in particular military aircraft) create the most common serious RF exposures. These highly unpredictable mobile transmitters are very powerful and transmit on a broad spectrum of frequencies, which include, but are not limited to:
((–)) (i) Radar;
((–)) (ii) Laser;
((–)) (iii) All common communications bands.
Note: | The two most dangerous examples are: |
– Low flying automatic terrain following guidance systems | |
– Airplanes which are equipped to jam all common radar and communications frequencies for a distance of several miles around the airborne transmitters. |
(3) Transportation. Transportation of explosives must meet these requirements:
((•)) (a) Public highways. The Washington utilities and transportation commission (UTC) and Washington state department of transportation (WSDOT) require compliance with ANSI D6.1-1988, Uniform Traffic Control Devices;
((•)) (b) Private roads. You do not have to comply with ANSI on private roads under department jurisdiction if required warning signs are properly placed when electric detonators are present.
(4) Site survey. The blaster in charge must conduct or assign a designated appointee to conduct an accurate survey of the entire blast area, to determine:
((•)) (a) The clearance points where roads or right of ways enter and exit the required clearance zone;
((•)) (b) If the one thousand-foot clearance zone needs adjusting to maintain the permissible clearance zone at all times, if the blast area moves as the job progresses.
(5) Clearance zones.
Required clearance zones for: |
Number of feet |
Construction operations |
1000 feet |
Demolition operations |
1000 feet |
General industry operations, not subject to construction requirements |
350 feet |
(6) RF-transmitter warning signs.
RF-TRANSMITTER WARNING SIGNS
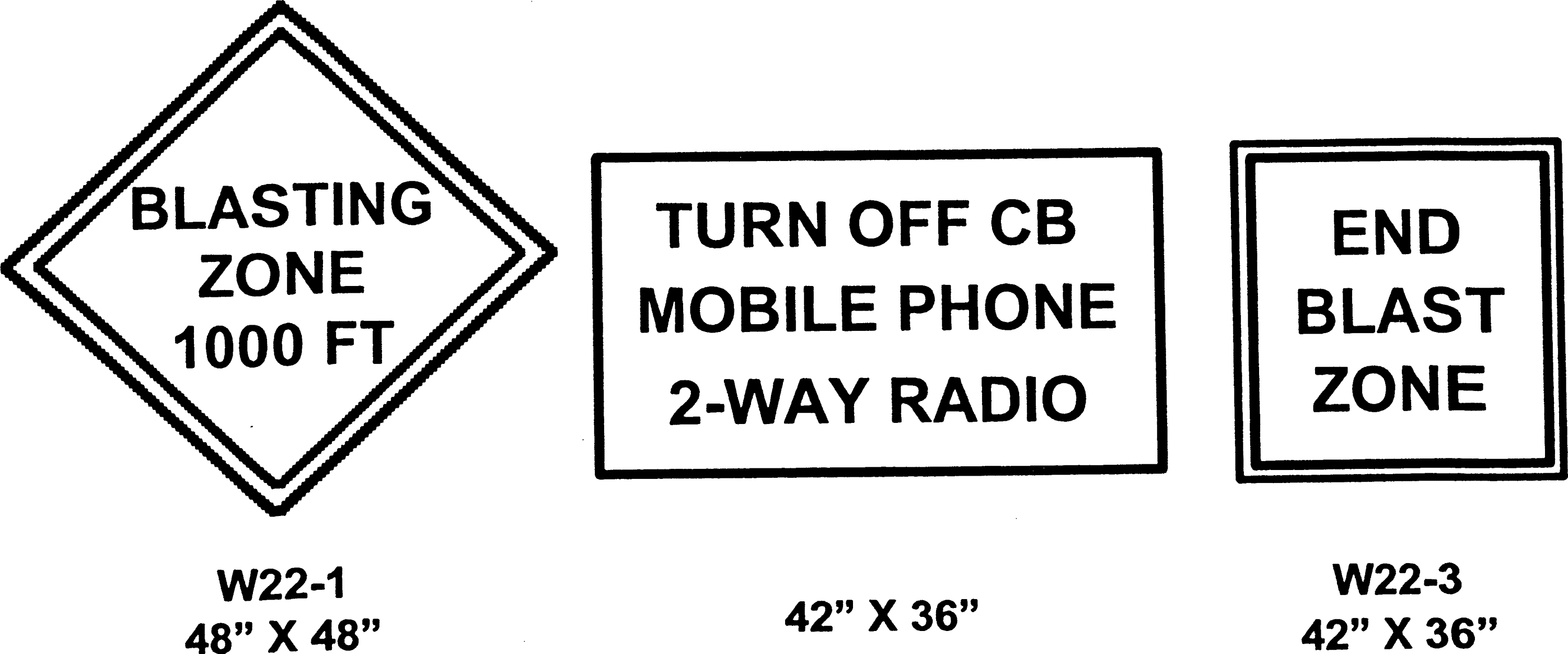 |
(a) RF-transmitter warning-sign specifications.
Signs must:
((•)) (i) Be a specific size. See the signs above for sign dimensions;
((•)) (ii) Have a "construction" orange background;
((•)) (iii) Have black letters and borders;
((•)) (iv) Use all upper case letters that are at least the size shown above.
Note: | Larger signs may be required where the highway speed limit is more than fifty-five miles per hour. |
(b) Posting warning signs must:
((•)) (i) Be adequately placed to warn:
((–)) (A) All transmitter users against the use of:
((•)) (I) Radio frequency transmitters;
((•)) (II) CBs;
((•)) (III) Mobile phones;
((•)) (IV) Two-way radios.
((•)) (B) All users of routes into the electric detonator clearance zone.
((•)) (ii) Be prominently displayed when an electric detonator initiation system is being used during blasting operations and when the electric detonators have been removed from the original U.S. DOT approved shipping container;
((•)) (iii) Be posted at the beginning of the blast zone minimum clearance point saying:
"TURN OFF CB, MOBILE PHONE, 2-WAY RADIO"
(c) Blast zone signs.
((•)) (i) The "BLAST ZONE 1,000 FEET" sign must be posted one thousand feet before the "TURN OFF CB, MOBILE PHONE, 2-WAY RADIO" sign;
((•)) (ii) The one thousand-foot separation distance limit may be reduced (not less than three hundred feet) in very slow vehicle travel zones (such as off-road construction right of ways, rock pits, or quarries).
(d) An "END BLAST ZONE" sign must be posted outside the blasting zone clearance limits.
(e) Signs must be covered or removed when blasting operations are not being conducted.
(7) Voltage identification. Electrical transmission and distribution line voltage must be accurately identified.
(8) System clearance identification. The required clearance for each system must be accurately identified.
(9) RF transmitters. Mobile RF transmitters must be deenergized or disconnected when they are less than one hundred feet from electric detonators that are not fully contained in their original U.S. DOT shipping containers.
Note: | Fixed location RF transmitters represent a higher level of hazard to both storage and blasting operations involving electric detonators because the transmitters are more powerful and transmit dangerous levels of RF exposure over much greater distances. |
(10) Prevention of radio frequency hazards:
(a) Electric detonators in storage or at blasting operations must meet the appropriate distance table requirements published in the IME Publication Number 20, 1988, "Safety Guide for the Prevention of Radio Frequency Hazards in the Use of Commercial Electric Detonators (Blasting Caps)."
(b) If it is necessary to conduct blasting operations inside the required separation distances specified in the IME Pamphlet Number 20, 1988:
((•)) (i) Storage and use of electric detonators is prohibited on the site;
((•)) (ii) Only detonating cord, safety fuse, shock tube, or other approved nonelectric systems can be used.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67070 Storage at blast sites.
(1) Packaging materials. Empty boxes, paper, and fiber packing materials that have previously contained explosive materials must be:
((•)) (a) Disposed of in a safe manner; or
((OR
•)) (b) Reused in accordance with U.S. DOT hazardous materials regulations.
(2) Opening fiberboard cases. Nonsparking metallic slitters may be used for opening fiberboard cases.
(3) Deteriorating explosives. Deteriorating explosives must be carefully set aside and disposed of according to the manufacturer's specifications.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-67080 Drilling.
(1) Unexploded charges.
(a) Drilling cannot begin:
(i) When there is danger of drilling into a charged or misfired hole.
(ii) Until all remaining butts of old holes are examined for unexploded charges.
(b) Unexploded charges must be refired before work proceeds.
(2) Distance limits during drilling. Blasters cannot load or use explosives closer than:
(a) The length of the steel being used for drilling; or
((OR))
(b) Within fifty feet of drilling operations, whichever is greater.
(3) Prior to loading drill holes.
(a) Holes must be checked prior to loading to determine depth and conditions.
(b) Drill holes that have contained explosives or blasting agents cannot be deepened.
(c) Drill holes must be large enough to allow unobstructed or free insertion of explosive cartridges.
(4) Enlarging or springing a drill hole.
(a) A drill hole cannot be sprung when it is near a loaded hole.
(b) A minimum of two hours must pass after a charge has exploded in a drill hole that was enlarged or "sprung," before loading another charge of explosives into the hole.
Note: | You do not have to wait two hours if the sprung hole is thoroughly wet down with water before it is loaded. |
(c) Flashlight batteries cannot be used as a power source for springing holes.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67085 Loading blast holes.
(1) Power lines and portable electric cables. Power lines and portable electric cables must be kept at a safe distance from explosives or blasting agents being loaded into drill holes.
(2) Equipment, machinery, and tools.
((•)) (a) Any machine or tool not being used to load holes must be removed from the immediate loading area.
((•)) (b) Equipment cannot be operated within fifty feet of loaded holes except when:
((–)) (i) It is needed to add burden or mats;
((–)) (ii) Tracking drills out of the loading area.
(3) Holes that may be loaded. Only holes that will be fired in the next blasting round may be loaded.
(4) Tamping.
(a) A primer must never be tamped.
(b) Tamping must be done with wood rods or approved plastic tamping poles that do not have exposed metal parts.
(c) Nonsparking metal connectors may be used for jointed poles.
(d) Violent tamping must be avoided.
(5) Pneumatic loading. When loading blasting agents pneumatically over primed boosters:
((•)) (a) A semiconductive delivery hose must be used;
((•)) (b) Equipment must be bonded and grounded.
(6) Stemming. All blast holes in open work must be stemmed to:
(a) The collar((.
OR)); or
(b) A point, which will confine the charge.
(7) Attendance of holes. Loaded holes must be attended or protected.
(8) Unused explosives. After loading, all remaining explosives and detonators must be immediately returned to an authorized magazine or day box.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-67090 Initiation systems.
(1) General initiation rules.
(a) Training and supervision.
(i) The blaster in charge must provide adequate on-the-job training and supervision in the safe use of initiation systems.
(ii) All members of the blasting crew must be instructed, by the blaster in charge, in the safe use of the initiation system to be used and its system components.
(b) Manufacturer recommendations. All initiation systems and system components must be used in accordance with manufacturer recommendations and instructions.
(c) Vehicle use precautions.
(i) Explosives bulk trucks or other vehicles operated on a blast site cannot tread on:
(A) Tubing;
(B) Connectors; or
((OR))
(C) Any surface delay component.
(ii) If a vehicle must pass over loaded blast holes. Precautions must be made to consolidate tubing, connectors, or any surface delay component at the collar of the hole to prevent vehicle contact.
(d) Connecting the firing line. Firing lines cannot be connected to the blast initiating device until all personnel are:
(i) Accounted for;
(ii) Removed from the blast danger area; or
((OR
Are)) (iii) In a blast shelter or other location that provides equivalent protection.
(e) Visual inspection. The blaster in charge must visually inspect the initiation system to make sure it is assembled according to the manufacturer's recommendations, before firing the shot.
(f) Explosives not used:
(i) Unused detonators or short capped fuses cannot be placed in holes that may be used for blasting.
(ii) Unused detonators must be removed from the work area and disposed of or stored in a licensed magazine.
(iii) Loose cartridges of explosives, detonators, primers, and capped fuses that are not used by the end of the work shift must be returned to and locked in their magazines.
(2) Nonelectric initiation systems.
(a) Shock tube lines. When a nonelectric shock tube initiation system is used:
(i) Spools of shock tube lines cannot be spooled from trucks or equipment.
(ii) The shock tube line must:
(A) Be free of knots and tight kinks;
(B) Be free of cuts or abrasions that could expose the core to moisture;
(C) Not be stretched;
(D) Be neat and orderly.
(iii) Tie ins must be kept neat and clean.
(iv) Unused lead line must be sealed to prevent moisture and dirt from entering the tube.
(v) Care must be taken to avoid hitting the tube with a shovel when the shock tube is being covered.
(vi) The end of the detonator must be pointed toward the front of the shot to minimize the chance of shrapnel flying to the rear of the blast where the shock tube will be lit.
(b) Surface connector blocks. Nonelectrical tubes must:
(i) Be secured properly in surface connector blocks.
(ii) Never exceed the rated capacity of tubes in surface connector blocks.
(c) Splicing line. A knot must be tied in the tubes to take the strain off of the splice.
(d) Detonator cord. If a detonator cord is used for surface tie in:
(i) All lines must be kept taut.
(ii) Connections to nonelectrical units must be at ninety degree angles.
(e) Equipment and personnel.
(i) Equipment cannot roll over shock tubes.
(ii) All unnecessary equipment and personnel must be removed from the blast area during loading.
(3) Electric initiating systems.
(a) Survey of extraneous currents. A survey to evaluate extraneous currents must be conducted:
(i) By the blaster in charge before adopting any system of electrical firing.
(ii) To eliminate all currents before holes are loaded.
(b) Detonator compatibility, style, function, and manufacture. In any single blast using electric detonators, all detonators must be:
(i) Compatible with each other.
(ii) Of the same style or function.
(iii) From the same manufacturer.
(c) Wire capacity and gauge.
(i) Connecting wires and lead wires must:
(A) Be insulated single solid wires with sufficient current carrying capacity.
(B) Not be less than twenty gauge (American wire gauge) solid core insulated wire.
(ii) Firing line or lead wires must:
(A) Be made of solid single wires with sufficient current carrying capacity.
(B) Not be less than fourteen gauge (American wire gauge) solid core insulated wire.
Note: | Bus wires, depends on the size of the blast, fourteen gauge (American wire gauge) copper is recommended. |
(d) Lead wires.
(i) Shunting. You must shunt the ends of lead wires that will be connected to a firing device by twisting them together before they are connected to leg or connecting wires.
(ii) Control. The blaster in charge must keep control of shunted lead wires until loading is completed and the leg wires are attached.
(iii) Attachment. Lead wires must be attached by the blaster in charge when it is time to fire the shot.
(e) Detonator leg wires. Electric detonator leg wires must:
(i) Be kept shunted (short circuited) until they are connected into the circuit for firing.
(ii) Not be separated (except for testing) until all holes are loaded and the loader is ready to connect the leg wires to the connecting or lead wires.
(f) Circuits.
(i) Blasting circuits or power circuits must be used in electric blasting and according to the electric detonator manufacturer's recommendations.
(ii) Care must be taken to make sure an adequate quantity of delivered current is available according to the manufacturer's recommendations, when firing a circuit of electric detonators.
(iii) A power circuit used for firing electric detonators cannot be grounded.
(iv) The firing switch must be designed so the firing lines to the detonator circuit automatically short circuit when the switch is in the "off" position.
(v) The firing switch must be locked in the "open" or "off" position at all times, except when firing from a power circuit.
(g) Firing line insulation. The insulation on all firing lines must be adequate and in good condition when firing electrically.
(h) Testing.
(i) The firing line must be checked at the terminals with an approved testing device before being connected to the blasting machine or other power sources.
(ii) The circuit, including all detonators, must be tested with an approved testing device before being connected to the firing line.
(i) Switch keys. The blaster in charge is the only person who is allowed to have firing switch keys in their possession.
(j) Blasting machines. A nonelectric system must be used if these requirements cannot be satisfied:
(i) Blasting machines must be in good condition.
(ii) The efficiency of the blasting machine must be tested periodically to make sure it delivers power at its rated capacity.
(iii) Responsible person.
((•)) (A) The blaster in charge must be in charge of blasting machines.
((•)) (B) The blaster in charge must connect the lead wires to the blasting machine and must fire the shot.
(iv) Connections.
((•)) (A) When firing with blasting machines, connections must be made according to the manufacturer of the electric detonator's recommendations.
((•)) (B) All connections must be made from the drill hole back to the source of the firing current.
((•)) (C) Lead wires must remain shunted and not connected to the blasting machine or other source of current until the charge is ready to fire.
((•)) (D) The number of electric detonators connected to a blasting machine cannot exceed the blasting machine's rated capacity.
(v) Series circuit. In primary blasting, a series circuit cannot contain more detonators than the manufacturer's recommended limits for electric detonators.
(vi) Circuit testing. A blaster in charge must use blasting testers specifically designed to test circuits to charged holes.
(vii) Blasting near power lines. Whenever lead or blasting wires could be thrown over live overhead powerlines, communication lines, utility services, or other services or structures by the force of an explosion, care must be taken to make sure:
(A) The total length of wires are short enough so they will not hit the lines.
(B) The wires are securely anchored to the ground.
(C) The owners or operators of the utilities in the blast area are notified.
(viii) Disconnecting lead wires. After firing an electric blast from a blasting machine, lead wires must be immediately disconnected from the machine and short-circuited.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67100 Use of detonating cord.
(1) Cord selection. Care must be taken to select a detonating cord consistent with the:
((•)) (a) Type and physical condition of the drill hole;
((•)) (b) Stemming;
((•)) (c) Type of explosives used.
(2) Handling. A detonating cord must be handled and used with:
((•)) (a) The same respect and care given to other explosives;
((•)) (b) Care to avoid damaging or severing the cord during and after loading and hooking up.
(3) Calculating quantity and distance.
((•)) (a) For quantity and distance purposes, a detonating fuse (up to sixty grains per foot) should be calculated as equivalent to nine pounds of high explosives per one thousand feet;
((•)) (b) Heavier cord loads should be rated proportionally.
(4) Trunk lines.
((•)) (a) Detonators for firing the trunk line cannot be brought to the loading area or attached to the detonating cord until everything else is ready for the blast;
((•)) (b) All detonating cord trunk lines and branch lines must be free of loops, sharp kinks, or angles that direct the cord back toward the oncoming line of detonation;
((•)) (c) Trunk lines in multiple row blasts must make one or more complete loops, with cross ties between loops at intervals less than two hundred feet.
(5) Connections.
(a) Detonating cord. All detonating cords must be:
(i) Competent and positive in accordance with the manufacturer's recommended specifications.
(ii) Kept at right angles to the trunk lines.
(iii) Inspected before firing the blast.
(b) Knots.
(i) Knot or other cord-to-cord connections must be made with a detonating cord where the explosive core is dry.
(ii) All detonator cord knots must be tight.
(c) Connecting detonators.
(i) A detonator or electric detonator must be taped or securely attached along the side or end of the detonating cord. The detonator end containing the explosive charge must be pointed in the direction of the detonation.
(ii) Manufacturer's recommendations must be followed when short interval delay electric detonators are used with a detonating cord.
(iii) Manufacturer's recommendations must be followed when detonating cord millisecond delay connectors are used with a detonating cord.
(iv) The line of detonating cord extending from a drill hole or a charge must be cut from the supply spool before loading the remainder of the drill hole or placing additional charges.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67110 Precautions after firing.
(1) Immediately after firing. Immediately after firing, the blaster in charge must:
(a) Disconnect the firing line from the blasting machine.
(b) Lock the power switches in the "open" or "off" position.
(c) Carefully trace all wires and search for unexploded charges.
(2) Post blast inspection. The blaster in charge must perform an inspection of the area and surrounding rubble to determine if all charges have been exploded before employees are allowed to return to the operation.
(3) Misfires.
(a) Misfire found. Misfires must be:
(i) Immediately reported to their supervisor.
(ii) Recorded on the blast record.
(iii) Reported to the department within twenty-four hours if not cleared.
(b) Responsible person. A blaster in charge must be present and direct the handling of all misfires.
(c) Termination of work.
(i) All work must stop, except activities needed to remove the misfire hazard.
(ii) Drilling, digging, or picking is not permitted until:
(A) All misfired holes have been detonated; or
((OR))
(B) The blaster in charge determines work can proceed.
(d) Evacuation precautions. The following evacuation precautions must be taken in the event of a misfire:
(i) If a misfire is found, the blaster in charge must make sure safeguards are in place to keep all employees or other personnel from the danger zone, except those needed to remove the misfire hazard.
(ii) Workers cannot return to misfired holes for at least:
(A) Thirty minutes when electric blasting caps are used;
(B) One hour when detonators and fuses are used.
(e) Charged or misfired holes.
(i) Attempts cannot be made to remove explosives from any charged or misfired hole.
(ii) A new primer must be connected and the hole refired.
(f) Refiring hazard. If refiring a misfired hole presents a hazard, explosives may be:
(i) Removed by washing out the explosives with water; or
((OR))
(ii) Removed with air, if the misfire is under water.
(4) Burning holes.
(a) Everyone in the endangered area must move to a safe location when explosives are suspected of burning in a hole.
(b) No one, under any circumstances, may return to the hole:
(i) Until the danger has passed; or
((OR))
(ii) For at least one hour after the hole has been found.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67115 Excavation work in pressurized air locks.
(1) Receiving, handling, storing, and transportation.
(a) The blaster in charge or powder person is responsible for the receipt, unloading, storage, and on-site transportation of explosives and detonators.
(b) Explosives in transit cannot be left unattended.
(c) Detonators and explosives for each round must be taken directly from the magazines to the blasting zone and immediately loaded.
(2) Wet holes. Explosives appropriate for use in wet holes must be:
(a) Water resistant; and
((AND))
(b) Fume Class 1 or other approved explosives.
(3) Bonding. All metal pipes, rails, air locks, and steel tunnel linings must be:
(a) Electrically bonded together and grounded at or near the portal or shaft.
(b) Cross bonded together at not less than one thousand-foot intervals throughout the length of the tunnel.
(4) Air locks.
(a) No one is allowed to enter the air lock when detonators or explosives are brought in, except:
(i) The blaster in charge.
(ii) The powder person.
(iii) The lock tender.
(iv) Employees needed to carry explosive materials.
(b) Primers, detonators, and explosives must be taken separately into pressure working locks.
(c) Material, supplies, or equipment cannot be brought into air locks with explosive materials.
(d) Detonators and explosives not used after loading a round must be removed from the working chamber before connecting the connecting wires.
(5) Grounding. Each air supply pipe must be grounded at its delivery end.
(6) Mixed face.
(a) Light charges and light burdens must be used for each hole when tunnel excavation in rock face is approaching or is in mixed face.
(b) Advance drilling must be done when tunnel excavation in rock face approaches mixed face to determine the:
(i) General nature and extent of rock cover; and
((AND))
(ii) Distance to soft ground as excavation advances.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67130 Fixed location mixing.
(1) Building location. Buildings or other facilities used for manufacturing blasting agents must meet the separation distance requirements of Table H-21 for inhabited buildings, passenger railroads, and public highways.
(2) Building construction. Buildings used for mixing blasting agents must be constructed of noncombustible material or sheet metal on wood studs and be well ventilated.
(3) Determining distance. When determining the distances separating highways, railroads, and inhabited buildings from potential explosions (Table H-20), the sum of all masses that may propagate (i.e., lie at distances less than specified in Table H-22) from either individual or combined donor masses are included in the sum. However, when the ammonium nitrate is included, only fifty percent of its weight must be used because of its reduced blast effects.
(4) Heat sources.
(a) Internal heating units. Properly designed and located heating units that do not depend on combustion processes may be used in the building.
(b) External heating units. All direct sources of heat must be located outside the mixing building.
(5) Mixing plant floors must be made of nonabsorbent materials such as concrete.
(6) Electrical equipment.
(a) Electrical switches, controls, motors, and lights located in the mixing room must:
(i) Comply with the requirements of WAC 296-800-280.
(ii) Be located outside the mixing room.
(b) The frame of the mixer and all other equipment must be:
(i) Electrically bonded.
(ii) Provided with a continuous path to ground.
(7) Internal combustion engines.
(a) Location. All internal combustion engines used for electric power generation must be:
(i) Located outside the mixing plant building((.
OR)); or
(ii) Properly ventilated and isolated by a firewall.
(b) Exhaust systems. Engine exhaust systems must be positioned so spark emission does not become a hazard to any material in or adjacent to the plant.
(8) Mixing equipment. Equipment used for mixing blasting agents must comply with the following:
(a) Design. The design of the mixer must:
((•)) (i) Minimize the possibility of frictional heating, compaction, and confinement;
((•)) (ii) Have the bearings and drive assemblies mounted outside the mixer and protected against the accumulation of dust;
((•)) (iii) Have the surfaces accessible for cleaning.
(b) Construction. Mixing and packaging equipment must be constructed of materials compatible with the fuel ammonium nitrate composition.
(c) Fire precautions. The following fire precautions must be followed:
(i) Mixer fuel oil flow. In case of fire:
(A) Appropriate means to prevent the flow of fuel oil to the mixer must be provided.
(B) An automatic spring-loaded shutoff valve with fusible link must be installed in gravity flow systems.
(ii) Flame/spark producing devices. Smoking, matches, open flames, spark-producing devices, and firearms (except firearms carried by law enforcement bomb squad members or qualified guards), are not allowed inside or within fifty feet of any facility used for mixing blasting agents.
(9) Blasting agent compositions. The following are requirements for determining blasting agent compositions:
(a) Determining sensitivity. The sensitivity of the blasting agent must be determined by means of a Number 8 test detonator at regular intervals and after every change in formulation.
(b) Handling precautions. Precautions must be taken when handling:
((•)) (i) Small particle oxidizers, such as crushed ammonium nitrate prills or fines, may be more sensitive than coarser products and must be handled with greater care;
((•)) (ii) Solid fuels must be used in a manner to minimize dust explosion hazards;
((•)) (iii) Metal powders, such as aluminum, must be:
((–)) (A) Kept dry; or
((OR
–)) (B) Stored in moisture resistant or weather tight containers or bins.
(c) Use restrictions. The following cannot be used:
(i) Crude and crankcase oil;
(ii) Hydrocarbon liquid fuel with a flash point lower than the 125°F minimum for Number 2 diesel fuel oil; or
((OR))
(iii) Peroxides and chlorates.
(10) Fuel oil storage.
(a) Facilities. Fuel oil storage facilities must be:
(i) Independent structures; or
((OR))
(ii) Located at a site away from the manufacturing building.
(b) Surrounding area. In order to prevent oil from draining toward a manufacturing building in the event of a tank rupture, the surrounding grounds must slope away from the building.
(11) Safety precautions. Safety precautions at mixing plants must include these requirements:
(a) Floor construction. Floors must be constructed to eliminate floor drains and piping where molten materials could flow and be confined, in case of fire.
(b) Mixing/packaging room. The floors and equipment of the mixing and packaging room must be cleaned regularly and thoroughly to prevent accumulation of oxidizers, fuels, and other sanitizers.
(c) Housekeeping. The following housekeeping requirements must be followed:
(i) Mixing plant. The mixing and packaging plant must:
(A) Be cleaned regularly and thoroughly to prevent excessive accumulation of dust.
(B) Safely dispose of empty ammonium nitrate bags daily.
(ii) Surrounding area. The land surrounding the mixing plant must be kept clear of brush, dried grass, leaves, and other materials for a minimum of twenty-five feet.
(d) Welding.
(i) Welding or open flames are not permitted in or around the mixing or storage area of the plant unless:
(A) The equipment or area has been completely washed; and
((AND))
(B) All oxidizer material has been removed.
(ii) Before welding or repairing hollow shafts:
(A) Oxidizer materials must be removed from the inside and outside of the shaft; and
((AND))
(B) The shaft must be vented with a minimum 1/2-inch diameter opening.
(e) Explosives. Explosives are not permitted inside or within fifty feet of any facility used for mixing blasting agents.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67135 Bulk delivery/mixing vehicles.
Note: | This section applies to both off-highway operations and public highway transportation. |
(1) Vehicles. These vehicle requirements must be followed:
(a) Strength. A bulk delivery vehicle must be strong enough to carry a load without difficulty.
(b) Mechanical condition. A bulk delivery vehicle must be in good mechanical condition.
(c) Body. A bulk vehicle body for delivering and mixing blasting agents must:
(i) Be constructed of noncombustible materials.
(ii) Have closed bodies if they are used to transport bulk premixed blasting agents.
(d) Mixing system parts.
(i) All moving parts of the mixing system must be designed to prevent heat buildup.
(ii) Shafts or axles which contact the product must have outboard bearings with a minimum of one-inch clearance between the bearings and the outside of the product container. Special attention must be given to the clearances on all moving parts.
(e) Welding.
(i) Welding or open flames are not permitted in or around the mixing or storage area of the plant unless the equipment or area has been completely washed and all oxidizer material removed.
(ii) Before welding or repairing hollow shafts:
(A) All oxidizer material must be removed from the inside and outside of the shaft; and
((AND))
(B) The shaft must be vented with a minimum 1/2-inch diameter opening.
(2) Vehicle operation. Operation of bulk delivery and mixing vehicles must comply with WAC 296-52-680, Transportation of explosive material, U.S. DOT placard requirements, and these requirements:
(a) Driver training. The vehicle driver must be:
(i) Trained in the safe operation of the vehicle, mixing, conveying, and related equipment.
(ii) Familiar with the load being delivered and general procedures for handling emergencies.
(b) Cargo and containers. Cargo and containers must:
(i) Haul either detonators or other explosives, but not both, it is permitted on bulk trucks provided a special wood or nonferrous-lined container is installed for explosives.
(ii) Be U.S. DOT specified shipping containers, according to 49 C.F.R. Chapter 1.
(c) Moving a vehicle in the blast area. When moving a vehicle in the blast area:
(i) The driver must exercise caution to avoid driving the vehicle onto or dragging hoses over firing lines, cap wires, or explosive materials; and
((AND))
(ii) A second person must help guide the vehicle driver's movements.
(3) Pneumatic loading. Pneumatic loading from bulk delivery vehicles into blast holes primed with electric detonators or other static sensitive systems must comply with these requirements:
(a) A positive grounding device must be used to prevent accumulation of static electricity.
(b) A discharge hose must:
(i) Have a resistance range that will prevent conducting stray currents; or
((OR))
(ii) Be conductive, to bleed off static buildup.
(c) A qualified person must evaluate all static sensitive systems to determine if they will adequately dissipate static under potential field conditions.
(4) Repairs. Bulk delivery vehicle repair must comply with the requirements of this section.
(5) Prohibited activities. The following are prohibited:
(a) In-transit mixing of materials.
(b) While in or about bulk vehicles in the process of the mixing, transferring or down-the-hole loading of water-gels at or near the blasting site:
(i) Smoking; and
((AND))
(ii) Carrying flame producing devices including matches and firearms near bulk vehicles in the process of mixing, transferring, or down-the-hole loading of water-gels, at or near the blast site.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67140 Bulk storage bins.
(1) Construction. A bin, including supports, must be:
(a) Waterproof.
(b) Constructed of compatible materials.
(c) Adequately supported and braced to withstand the combined force of all loads, including impact from product movement within the bin and accidental vehicle contact with the support legs.
(2) Discharge gates. A bin discharge gate must be designed to lock and close tightly to prevent leakage of the stored product and to lock.
(3) Loading manways. Bin loading manways or access hatches must be hinged or attached to the bin and designed to lock.
(4) Electric conveyors. An electrically driven conveyor used for loading or unloading bins must:
(a) Comply with the requirements of WAC 296-800-280, Basic electrical rules.
(b) Be designed to minimize corrosion damage.
(5) Separation distances. The following separation distances must be followed:
(a) Blasting agent bins. Bins containing blasting agents must meet the distance requirements of:
(i) Table H-20, in reference to separation from inhabited buildings, passenger railroads, and public highways; or
((OR))
(ii) Table H-22, in reference to separation from other explosives and blasting agent storage facilities.
(b) Ammonium nitrate bins. Bins containing ammonium nitrate must meet the distance requirements of Table H-22 in reference to separation of blasting agent and explosives storage.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-67165 Fixed location mixing.
(1) Buildings.
(a) Locations.
(i) Separation distance tables. Buildings or other facilities used for manufacturing emulsions and water-gels must meet the separation distance requirements of Table H-21 for:
(A) Inhabited buildings;
(B) Passenger railroads;
(C) Public highways.
(ii) Determining distance. When determining the distances separating highways, railroads, and inhabited buildings from potential explosions (Table H-20), the sum of all masses that may propagate (i.e., lie at distances less than specified in Table H-22) from either individual or combined donor masses are included in the sum. However, when ammonium nitrate must be included, only fifty percent of its weight must be used because of its reduced blast effects.
(b) Construction. Buildings used for the manufacture of water-gels or emulsions must:
(i) Be constructed of noncombustible material or sheet metal on wood studs.
(ii) Have mixing plant floors made of nonabsorbent materials, such as concrete.
(iii) Be well ventilated.
(c) Heat sources. Heating units that are designed to be independent of the combustion process within the heating unit, may be used within processing buildings or compartments if they:
(i) Have temperature and safety controls; and
((AND))
(ii) Are located away from combustible materials and the finished product.
(d) Internal combustion engines.
(i) Location. All internal combustion engines used for electric power generation must be:
(A) Located outside the mixing plant building; or
((OR))
(B) Properly ventilated and isolated by a firewall.
(ii) Exhaust systems. Engine exhaust systems must be located to prevent spark emissions from becoming a hazard to any materials, in or near the plant.
(e) Fuel oil storage.
(i) Facilities. Fuel oil storage facilities must be:
(A) Independent structures;
(B) Located away from the manufacturing building.
(ii) Surrounding area. In order to prevent oil from draining toward a manufacturing building in the event of a tank rupture, the surrounding grounds must slope away from the building.
(2) Storage of water-gel and emulsion ingredients.
(a) Explosive ingredients. Ingredients must be stored with compatible materials.
(b) Nitrate water solutions.
(i) Nitrate water solutions can be stored in tank cars, tank trucks, or fixed tanks without quantity or distance limitations.
(ii) Spills or leaks which may contaminate combustible materials must be cleaned up immediately.
(c) Metal powders. Metal powders, for example, aluminum, must be:
(i) Kept dry; and
((AND))
(ii) Stored in containers or bins that are moisture resistant or weather tight.
(d) Solid fuels. Solid fuels must be used in a way that minimizes dust explosion hazards.
(e) Peroxides and chlorates. Peroxides and chlorates cannot be used.
(3) Mixing equipment. Mixing equipment must comply with these requirements:
(a) Design. The design of processing equipment, including mixers, pumps, valves, conveying, and other related equipment, must:
(i) Be compatible with the relative sensitivity of other materials being handled.
(ii) Minimize the possibility of frictional heating, compaction, overloading, and confinement.
(iii) Prevent the introduction of foreign objects or materials.
(iv) Be designed to permit regular and periodic flushing, cleaning, dismantling, and inspection.
(b) Handling procedures. Equipment handling procedures must be designed to prevent the introduction of foreign objects or materials.
(c) Housekeeping.
(i) A cleaning and collection system for dangerous residues must be provided.
(ii) The mixing, loading, and ingredient transfer areas, where residues or spilled materials may accumulate, must be cleaned periodically.
(d) Electrical equipment. Electrical equipment must:
(i) Comply with the requirements of WAC 296-800-280, Basic electrical rules, including wiring, switches, controls, motors, and lights.
(ii) Have appropriate overload protection devices for all electric motors and generators.
(iii) Be electrically bonded with electrical generators, motors, proportioning devices, and all other electrical enclosures.
(iv) Have grounding conductors effectively bonded to:
(A) The service entrance ground connection; or
((OR))
(B) All equipment ground connections in a manner to provide a continuous path to ground.
(4) Mixing facility fire prevention. Mixing facilities must comply with these fire prevention requirements:
(a) All direct sources of heat must only come from units located outside of the mixing building.
(b) A daily visual inspection must be made of the mixing, conveying, and electrical equipment to make sure they are in good operating condition.
(c) A systematic maintenance program must be conducted on a regular schedule.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67170 Bulk delivery/mixing vehicles.
(1) Vehicle design. The design of bulk delivery/mixing vehicles must comply with these requirements:
(a) Public highways. Vehicles used for the bulk transportation of emulsion, water-gels, or ingredients classified as dangerous commodities on public highways, must meet:
(i) U.S. DOT regulations, including placard requirements; and
((AND))
(ii) WAC 296-52-680, Transportation of explosive materials.
(b) Power supply. When electric power is supplied by a self-contained motor generator located on the vehicle, the generator must be separate from where the water-gel is discharged.
(c) Parking brakes and chocks. The following are requirements for parking breaks and chocks:
(i) A positive action parking brake, which will engage the wheel brakes on at least one axle, must be:
(A) Provided on vehicles equipped with air brakes;
(B) Used during bulk delivery operations.
(ii) Wheel chocks must supplement parking brakes whenever conditions require.
(2) Vehicle operation. Operation of bulk delivery and mixing vehicles must comply with these requirements:
(a) Driver training. The vehicle driver must be:
(i) Trained in the safe operation of the vehicle and mixing, conveying, and related equipment.
(ii) Familiar with the supplies being delivered and emergency procedures.
Pneumatic loading.
(b) Cargo and containers.
(i) Hauling either detonators or other explosives is permitted on bulk trucks provided a special wood or nonferrous lined container is installed for explosives.
(ii) Detonators and explosives must be in U.S. DOT specified shipping containers, according to 49 C.F.R. Chapter 1.
(c) Moving a vehicle in the blast area. When moving a vehicle in the blasting area:
(i) The driver must exercise caution to avoid driving the vehicle onto or dragging hoses over firing lines, cap wires, or explosive materials((.
AND)); and
(ii) A second person must help guide the vehicle driver's movements.
(d) Transfer locations. The location chosen to transfer water-gel or other ingredients from a support vehicle to the drill hole loading vehicle, must be removed from the blast hole site if the drill holes are loaded or are in the process of being loaded.
(e) Prohibited activities. The following are prohibited:
(i) In-transit mixing of materials((.));
(ii) Smoking((.
AND)); and
(iii) Carrying flame-producing devices including matches and firearms near bulk vehicles in the process of mixing, transferring, or down-the-hole loading of water-gels, at or near the blast site.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67230 Initiating systems.
(((1))) Electric systems.
(((a))) (1) Safety switch. A safety switch must be:
(((i))) (a) Placed at intervals in the permanent firing line when firing from a power circuit.
(((ii))) (b) Made:
(((A))) (i) So it can only be locked in the "off position"; or
((OR
(B))) (ii) With a short-circuiting arrangement of the firing lines to the detonator circuit.
(((b))) (2) Lighting gap. A lighting gap must be:
(((i))) (a) At least five feet ahead (in the firing system) of the main firing switch, between the switch and power source.
(((ii))) (b) Bridged by a flexible jumper cord just before firing the blast.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-67245 High speed tunneling: Central primer house.
Note: | The following requirements apply when primers are made up at a central primer house for use in high speed tunneling: |
(1) Primers.
(a) Only enough primer must be made for each round of blasting.
(b) Primers must be placed in separate containers and bins, categorized by the degree of delay in preventing physical impact.
(2) Separation of explosives in magazines. Explosives transported in the same magazine must be separated by:
(a) One-quarter inch steel; and
((AND))
(b) Covered on each side by four inches of hardwood planking or equivalent protection.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68010 Public highways.
Transportation of explosives on public highways are:
((•)) (1) Regulated by:
((–)) (a) United States Department of Transportation (U.S. DOT) (49 C.F.R., Parts 100 - 199);
((–)) (b) The Washington utilities and transportation commission.
((•)) (2) Administered and enforced by the Washington state patrol.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68015 Job sites and off-highway roads.
The transportation rules in this chapter apply to:
((•)) (1) On job sites and off highway roads.
((•)) (2) Privately financed, constructed, or maintained roads.
Note: | These rules do not apply to state or interstate highway systems. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68020 Safety precautions.
No one may:
((•)) (1) Smoke or carry matches, or any other flame producing device, while in or near a vehicle transporting explosives.
((•)) (2) Carry firearms or ammunition while in or near a vehicle transporting explosives, except guards or commissioned law enforcement officers.
((•)) (3) Drive, load, or unload a vehicle transporting explosives in a careless or reckless manner.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68030 Cargo.
Materials and supplies cannot be placed in the cargo space of vehicles or conveyance containing:
((•)) (1) Explosives;
((•)) (2) Detonating cord; or
((OR
•)) (3) Detonators.
Note: | It is okay to transport safety fuses and properly secured nonsparking equipment in cargo spaces. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68040 Vehicle strength and condition.
All vehicles used for transporting explosives must:
((•)) (1) Be strong enough to carry the load without difficulty;
((•)) (2) Be in good mechanical condition;
((•)) (3) Have a tight floor in the cargo compartment(s);
((•)) (4) Not have any exposed spark producing metal inside the vehicle, which could come in contact with explosives.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68045 Open top vehicles.
(1) Locations of use. While loaded with explosives, open top vehicles must only be used on:
((•)) (a) The job site; or
((OR
•)) (b) Roads that are closed to public travel.
(2) Containers. Explosives being transported in open top vehicles or trailers must be transported in:
((•)) (a) The original U.S. DOT approved shipping container or box; or
((OR
•)) (b) A day box or portable magazine that complies with the requirements of this chapter.
(3) Securing containers. Explosive containers, boxes, day boxes, or portable magazines must be fastened to the bed of the vehicle or trailer.
(4) Loading. Packages of explosives cannot be loaded above the sides on open top vehicles.
(5) Tarpaulins (tarps).
((•)) (a) If an explosives transportation vehicle or trailer does not have a fully enclosed cargo area with nonsparking interior, the cargo bed and all explosive cargo must be covered with a flame and moisture proof tarp or other effective protection against moisture and sparks.
((•)) (b) Whenever tarps are used for covering explosives, both the tarp and the explosives container must be fastened to the body of the truck bed with rope, wire, or other equally efficient tie downs.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68050 Vehicle placards.
All vehicles transporting explosives material must have placards. They must:
((•)) (1) Be displayed as specified by U.S. DOT;
((•)) (2) Remain on the vehicle until all explosives have been removed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68055 Vehicle fire protection.
(1) Fire extinguishers.
((•)) (a) Driver training. The driver must be trained to use the fire extinguishers on the vehicle;
((•)) (b) Equipment specifications. Vehicles used for transporting explosive materials must be equipped with fire extinguishers according to the gross vehicle weight:
((–)) (i) Less than 14,000 pounds: A minimum of two multipurpose dry-chemical extinguishers having a combined capacity of at least 4-A:20-B:C;
((–)) (ii) 14,000 pounds or greater: A minimum of two multipurpose drychemical extinguishers having a combined capacity of at least 4-A:70-B:C.
((•)) (c) Laboratory approval. Only fire extinguishers approved by a nationally recognized testing laboratory can be used on vehicles carrying explosives;
((•)) (d) Condition and location. Fire extinguishers must be filled, ready for immediate use, and easily reached;
((•)) (e) Inspection. A competent person must inspect fire extinguishers periodically. You must comply with the requirements of WAC 296-800-30020, Inspect and test all portable fire extinguishers.
(2) Vehicle inspection. Any motor vehicle used for transporting explosives must have a safety inspection. The inspection must verify that:
((•)) (a) Fire extinguishers are filled and in working order;
((•)) (b) All electrical wiring is protected and securely fastened to prevent short circuiting;
((•)) (c) Chassis, motor, pan, and underside of body are reasonably clean and free of excess oil and grease;
((•)) (d) Fuel tank and feedline are secure and have no leaks;
((•)) (e) Tires are checked for proper inflation and defects;
((•)) (f) Brakes, lights, horn, windshield wipers, and steering apparatus are functioning properly;
((•)) (g) The vehicle is in proper condition in every other respect and acceptable for handling explosives.
(3) Vehicle repair/servicing. Motor vehicles or conveyances carrying explosives, blasting agents, or blasting supplies cannot be repaired or serviced inside a garage or shop when carrying explosive material.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-06-073, filed 3/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-52-68060 Operation of vehicles transporting explosives.
(1) Authorized explosives transportation. Explosives may only be transported by a:
((•)) (a) Licensed manufacturer;
((•)) (b) Blaster;
((•)) (c) Purchaser, seller, or their designated representative; or
((OR
•)) (d) Contract carrier for hire who complies with all requirements for transportation of hazardous materials.
(2) Driver qualifications.
(a) Vehicles transporting explosives must be driven by a responsible licensed driver who is:
((•)) (i) At least twenty-one years old;
((•)) (ii) Physically fit;
((•)) (iii) Careful;
((•)) (iv) Capable;
((•)) (v) Reliable;
((•)) (vi) Able to read and write the English language;
((•)) (vii) Not addicted to or under the influence of intoxicants, narcotics, or other dangerous drugs. (This does not apply to people taking prescription drugs and/or narcotics as directed by a physician, as long as use of the prescription drug does not endanger the worker or others.)
(b) The driver must be:
((•)) (i) Familiar with all:
((–)) (A) Traffic regulations;
((–)) (B) Department of Transportation (U.S. DOT) and other state laws in the transportation of explosives and hazardous material laws.
((•)) (ii) Aware of:
((–)) (A) What they are carrying;
((–)) (B) Safety precautions for the explosives being transported.
(3) Parking - Division 1.1 or 1.2 explosives. A vehicle that contains Division 1.1 or 1.2 explosives cannot be parked:
((•)) (a) On or within five feet of the traveled portion of a public street or highway;
((•)) (b) On private property, including fueling or eating facilities, without the knowledge and consent of the person. The person in charge must be aware of the hazardous materials in the vehicle; or
((OR
•)) (c) Within three hundred feet of a bridge, tunnel, dwelling, building, or place where people work, congregate, or assemble.
Exemption: | These restrictions do not apply when: |
– Routine operations require the vehicle be parked for a brief period of time. | |
– It is impractical to park the vehicle any other place. |
(4) Vehicle attendance. A vehicle transporting any quantity of Division 1.1 or 1.2 explosives must be attended at all times by a driver or other representative of the vehicle carrier, exceptions are:
((•)) (a) A vehicle containing explosive materials may be left unattended for a period not to exceed forty-eight hours provided((:
–)) the vehicle is parked in a designated parking lot, which complies with NFPA Std. 498 and the appropriate distance table for the type and quantity of explosives.
((•)) (b) The parking lot must:
((–)) (i) Be correctly bermed, walled, or fenced, and gated to prevent unauthorized entry;
((–)) (ii) Be inspected and approved by the department;
((–)) (iii) Provide a full-time, continuous security patrol when explosives are present.
((•)) (c) An explosives delivery truck does not need to be attended when it only contains Division 1.5 and no high explosives, provided the:
((–)) (i) Vehicle is locked so it cannot be moved;
((–)) (ii) Cargo compartments are locked to prevent theft;
((–)) (iii) Vehicle is parked according to all applicable storage distance requirements;
((–)) (iv) Vehicle is located in a secured area that restricts entry of unauthorized personnel.
(5) Attendant.
(a) An authorized attendant must be physically present and able to see the explosives at all times.
(b) In an emergency, the attendant must be able to quickly get to the explosives without interference.
(c) The attendant must:
((•)) (i) Be awake;
((•)) (ii) Be alert;
((•)) (iii) Not be engaged in activities, which could divert their attention;
((•)) (iv) Be aware of the division of the explosive material and its dangers;
((•)) (v) Be instructed in the methods and procedures used to protect the public;
((•)) (vi) Be familiar with the particular vehicle being driven;
((•)) (vii) Be trained in the use of the vehicle;
((•)) (viii) Have authorization and be able to move the vehicle if required.
(6) Loading precautions. A vehicle must comply with U.S. DOT loading regulations in order to transport explosives in the same vehicle body with the following items:
((•)) (a) Spark producing metal;
((•)) (b) Spark producing tools;
((•)) (c) Oils;
((•)) (d) Matches;
((•)) (e) Firearms;
((•)) (f) Electric storage batteries;
((•)) (g) Flammable substances;
((•)) (h) Acids;
((•)) (i) Oxidizing materials; or
((OR
•)) (j) Corrosive compound.
(7) Congested areas. Vehicles transporting explosives must avoid congested areas and heavy traffic.
(8) Disabled vehicles.
((•)) (a) A qualified person must be present before explosives can be transferred from a disabled vehicle to another vehicle;
((•)) (b) If a vehicle becomes disabled in a congested area, you must promptly notify local fire and police authorities. In a remote area they may be notified if necessary.
(9) Explosives delivery and issue. Delivery and issue of explosives must be made:
((•)) (a) Only by and to authorized people;
((•)) (b) Into authorized magazines or authorized temporary storage or handling areas.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68065 Transporting detonators and explosives in the same vehicle.
(1) Fuse type detonators, detonators with a safety fuse, or detonators with a metal clad mild detonating fuse, cannot be transported in the same vehicle or trailer with other explosives, unless they comply with U.S. DOT hazardous material regulations for:
((•)) (a) Packaging;
((•)) (b) Separation;
((•)) (c) Transportation.
(2) Detonators rated as nonmass detonating by U.S. DOT may be transported in the same vehicle or trailer with other explosives when the:
((•)) (a) Detonators are carried in U.S. DOT approved shipping containers; or
((OR
•)) (b) Truck or trailer complies with the requirements of IME Safety Library Publication Number 22, May 1993.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68075 Powder cars, vehicles, and conveyances.
In underground blasting operations, explosives and blasting agents must be hoisted, lowered, or transported in a powder car.
(1) State approval. A state-approved powder car or conveyance must be used underground.
(2) Two-unit compartments. Compartments for transporting detonators and explosives together on the same conveyance must be physically separated by a:
((•)) (a) Distance of twenty-four inches; or
((OR
•)) (b) Solid partition a minimum of six inches thick.
(3) Auxiliary lights prohibited. Auxiliary lights that are powered by an electrical system on a truck bed are prohibited.
(4) Daily inspection. The powder car or conveyance must be inspected daily for:
((•)) (a) Properly working lights;
((•)) (b) Properly working brakes;
((•)) (c) External damage to electrical circuitry.
(5) Weekly inspection. Weekly inspections must:
((•)) (a) Be conducted on the electrical system, to assess electrical hazards;
((•)) (b) Include a written inspection certification record that:
((–)) (i) Contains the date of inspection, the serial number, or other positive identification of the unit being inspected, and the signature of the person performing the inspection;
((–)) (ii) Is kept on file for the duration of the job.
(6) Explosives warning sign. Powder cars or conveyance built for transporting explosives or blasting agents must have signs posted on each side of the car that:
((•)) (a) State "EXPLOSIVES";
((•)) (b) Use letters a minimum of four inches high;
((•)) (c) Have a background color that sharply contrasts with the letters.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-68085 Underground transportation.
(1) Explosives and blasting agents. These requirements must be followed when transporting explosives and blasting agents underground:
((•)) (a) Companion items.
((–)) (i) Explosives or blasting agents cannot be transported in the same shaft conveyance with other materials, supplies, or equipment;
((–)) (ii) Detonators and other explosives cannot be transported in the same shaft conveyance;
((•)) (b) Manual transportation. Explosives or blasting agents that are not in their original containers must be placed in a suitable container when transported manually;
((•)) (c) Car or conveyance. The car or conveyance containing explosives or blasting agents must be pulled and not pushed;
((•)) (d) Locomotives. Explosives or blasting agents must:
((–)) (i) Not be transported on any locomotive;
((–)) (ii) Be separated by a minimum of two car lengths from the locomotive.
((•)) (e) Riding on a conveyance. When transporting explosives or blasting agents, no one can ride on:
((–)) (i) A shaft conveyance; or
((OR
–)) (ii) Any other conveyance, except the operator, helper, or powder person.
((•)) (f) Crew haul trips. Explosives or blasting agents cannot be transported on a crew haul trip;
((•)) (g) Disposition at arrival. All explosives or blasting agents that are transported underground must immediately be taken to the place of use or storage.
(2) Quantity limit. The quantity of explosives or blasting agents taken to an underground loading area cannot exceed the amount estimated to be necessary for the blast.
(3) Unloading primers at the blast site. Primers must be:
((•)) (a) Unloaded after drilling has been completed and the holes in the round are ready for loading;
((•)) (b) Unloaded from the powder car at the face or heading;
((•)) (c) Removed from the powder car for only the exact number being used for the round;
((•)) (d) The powder car must be removed from the tunnel after the charge has been loaded.
(4) Electric detonators. Wires on electric detonators must be kept shunted until wired to the bus wires.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-06-073, filed 3/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-52-69010 Explosives.
All Division 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, and 1.4 explosives, special industrial explosives, and any newly developed unclassified explosives, must be kept in magazines that meet the requirements of RCW 70.74.120 and this chapter, unless the explosives are:
((•)) (1) In the manufacturing process;
((•)) (2) Being physically handled;
((•)) (3) Being used at the blast site; or
((OR
•)) (4) Being transported to a place of storage or use.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69025 Quantity and distance tables.
All explosive manufacturing buildings and magazines that store explosives or blasting agents (except small arms ammunition and smokeless powder), must meet the requirements as specified in:
((•)) (1) Table H-20, Distances for Storage of Explosives;
((•)) (2) Table H-21, Distance Table for Separation between Magazines;
((•)) (3) Table H-22, Separation Distance of Ammonium Nitrate and Blasting Agent from Explosives or Blasting Agents.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69030 Storage within magazines.
(1) Storage materials. Magazines cannot be used for storage of metal tools or any commodity other than:
((•)) (a) Explosives;
((•)) (b) Blasting agents;
((•)) (c) Blasting supplies.
(2) Black powder.
((•)) (a) Black powder must be stored separately from other explosives in a magazine.
((•)) (b) Kegs must be stored on end, bungs down, on sides, seams down.
(3) Age/or date mark. Explosives that are not already age/or date marked by the manufacturer, must be marked with the manufacturing date before being stored in the magazine.
Note: | Unidentified explosives confiscated by law enforcement may be marked with the confiscation date, if the manufacturer's date is unknown. |
(4) Grades and brands.
((•)) (a) Identical grades and brands of explosives must be stored together, with the brands and grade marks showing.
((•)) (b) Explosive materials must be stored so they can be easily checked and counted.
(5) Package placement. Explosive packages must be:
((•)) (a) Placed right side up;
((•)) (b) Stacked so they are stable.
(6) Ventilation. Explosive material cannot be:
((•)) (a) Stored where they could interfere with ventilation; or
((OR
•)) (b) Placed less than two inches from the interior walls.
Note: | Nonsparking lattice or other nonsparking material may be used to prevent contact of stored explosive material with interior walls. |
(7) Housekeeping.
((•)) (a) Magazine floors must be:
((–)) (i) Regularly swept and the sweepings properly disposed of;
((–)) (ii) Kept clean and dry;
((–)) (iii) Free of grit, paper, and used packages or rubbish.
((•)) (b) Brooms and other cleaning tools cannot have any spark producing metal parts.
((•)) (c) Floors stained with nitroglycerin must be cleaned according to the manufacturer's instructions.
(8) Unpacking or repacking explosives.
((•)) (a) Containers of explosives (except for fiberboard or other nonmetal containers) cannot be unpacked or repacked:
((–)) (i) In a magazine;
((–)) (ii) Within fifty feet of a magazine; or
((OR
–)) (iii) Near other explosives.
((•)) (b) Opened packages of explosives must be securely closed before returning them to a magazine.
((•)) (c) Tools used for opening packages of explosives must be constructed of nonsparking materials.
((•)) (d) A wood wedge and a fiber, rubber, or wood mallet must be used for opening or closing wooden crates of explosives.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 11-01-124, filed 12/20/10, effective 2/1/11)
WAC 296-52-69040 Notification of fire safety authority.
Any person who stores explosive material must notify the local fire safety authority, who has jurisdiction over the area where the explosive material is stored.
(1) The local fire safety authority must be notified:
((•)) (a) Orally, on the first day explosive materials are stored;
((•)) (b) In writing, within forty-eight hours, from the time the explosive material was stored;
((•)) (c) In writing when an explosive storage license is renewed.
(2) The notification must include the following for each site where explosive material is stored:
((•)) (a) Type of explosives;
((•)) (b) Magazine capacity;
((•)) (c) Location.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69045 Magazine repairs.
Before beginning repair activities that could cause sparks or fire:
((•)) (1) All explosives must be removed from the magazine under repair and placed in another magazine or a safe distance away;
((•)) (2) Explosives must be properly guarded until they are returned to the magazine;
((•)) (3) The floor must be cleaned before beginning repairs inside a magazine.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69050 Inventory.
(1) A qualified person must be:
((•)) (a) Responsible for the magazine at all times;
((•)) (b) At least twenty-one years old;
((•)) (c) Held responsible for the enforcement of all safety requirements.
(2) Explosives must:
((•)) (a) Be accounted for at all times;
((•)) (b) Be kept in a locked magazine when not in use;
((•)) (c) Not be easily accessed by unauthorized persons.
(3) Inventory and use records must be kept up to date for all explosives.
(4) Any person responsible for explosives who discovers a theft or loss of explosives must report the incident to local law enforcement within twenty-four hours.
(5) Law enforcement agencies must report a theft or loss of explosives to the department immediately.
(6) Other people who know of attempted or actual unauthorized magazine entry must report this information to local law enforcement.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69055 Inspection.
(1) Weekly inspection.
(a) The person or company responsible for the contents of the magazine must inspect the magazine at least every seven days to determine whether there has been an unauthorized:
((•)) (i) Attempted entry into the magazine; or
((OR
•)) (ii) Removal of explosives from the magazine.
(b) The person doing the inspection must be familiar with the magazine and its contents.
Note: | This inspection does not need to be an inventory. |
(2) Inspection documentation.
(a) The person doing the inspection must sign one of the following documents after completing the inspection:
((•)) (i) A weekly inspection log;
((•)) (ii) An inventory sheet; or
((OR
•)) (iii) Other record.
(b) Weekly inspection records must be kept for at least one year.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69060 Precautions for areas surrounding magazine.
(1) Firearms. Only qualified guards and qualified law enforcement officers are allowed to carry firearms inside or within fifty feet of a magazine.
(2) Area maintenance. The area surrounding magazines must:
((•)) (a) Be kept clear of rubbish, brush, dry grass, or trees, except live trees more than ten feet tall, for a minimum of twenty-five feet in all directions;
((•)) (b) Be free of volatile materials for a minimum of fifty feet from outdoor magazine;
((•)) (c) Have the ground around storage facilities slope away for drainage; living foliage does not need to be removed.
(3) Fire sources. Smoking, matches, open flames, and spark producing devices are not permitted:
((•)) (a) In any magazine;
((•)) (b) Within fifty feet of an outdoor magazine; or
((OR
•)) (c) In any room containing an indoor magazine.
(4) Warning sign.
(a) Access routes. All normal access routes to explosive material storage facilities, except Class 3 (1.4) magazines, must be posted with warning signs that read:
DANGER
NEVER FIGHT EXPLOSIVE FIRES
EXPLOSIVES ARE STORED ON THIS SITE
CALL
(b) Sign specifications and placement. Signs must:
(i) Be contrasting in color;
(ii) Have the pin stroke of the letters a minimum of three inches (75 mm) high and one-half inch (12.5 mm) wide;
(iii) Be placed so a bullet passing through the sign will not strike a magazine;
(iv) Not be attached to magazines.
(c) Transportation placards. Placards required by the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) (49 C.F.R.) for transporting blasting agents must be displayed on all Class 5 magazines where blasting agents are stored.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69065 Deteriorated explosives.
((•)) (1) Explosives must be immediately destroyed, according to the manufacturer's recommendations, whenever they are suspected of deteriorating to the point they are:
((–)) (a) Unstable;
((–)) (b) Dangerous;
((–)) (c) Leaking nitroglycerine.
((•)) (2) Only a licensed blaster may destroy explosives.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69070 Explosives recovered from misfires.
((•)) (1) Storage. Explosives recovered from misfires must be placed in a separate licensed magazine until they can be disposed of according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
((•)) (2) Detonator use. Detonators suspected of being defective cannot be reused.
((•)) (3) Disposal. The blaster in charge must dispose of explosives and detonators according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69080 Blast site storage.
(1) Location. Temporary storage for explosives at blast sites must be located away from:
((•)) (a) Inhabited buildings;
((•)) (b) Railways;
((•)) (c) Highways;
((•)) (d) Other magazines.
(2) Separation distance. A distance must be maintained between magazines and the blast site. This distance must be a minimum of:
((•)) (a) One hundred fifty feet when the quantity of explosives is greater than twenty-five pounds;
((•)) (b) Fifty feet when the quantity of explosives is twenty-five pounds or less.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69085 Multiple magazines.
(1) Separation distance. When two or more storage magazines are located on the same property, each magazine must comply with the minimum quantity of explosives and separation distance requirements for:
((•)) (a) Magazines (Table H-21);
((•)) (b) Inhabited buildings, railways, and highways (Table H-20).
(2) Distances that do not meet requirements. If the separation distance between two or more magazines is less than the distance required (Table H-21), the magazines must:
((•)) (a) Be considered one magazine; and
((AND
•)) (b) Comply with the minimum distance requirements for inhabited buildings, railways, and highways (Table H-20).
(3) Distance of grouped magazines to other magazines. Each magazine in a group must comply with minimum magazine distance requirements (Table H-21) in relation to other magazines not considered part of the group.
(4) Quantity of explosives.
(a) Magazine group. The total quantity of explosives stored in a magazine group (two or more) must:
((•)) (i) Be considered one magazine;
((•)) (ii) Not exceed the requirements of Table H-21 for one magazine.
(b) Detonator magazine. The quantity of explosives contained in a detonator magazine takes precedence over the minimum magazine distance requirements (Table H-21) when determining the separation distance required between a detonator magazine and magazines that contain other types of explosives.
(c) Detonator strength. Strengths of blasting and electric detonators:
((•)) (i) Up to #8 detonators must be rated as one and one-half pounds of explosives per one thousand detonators;
((•)) (ii) Detonators greater than #8 must be computed on the combined weight of explosives.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69090 Blasting agents and supplies.
(1) Storage.
Note: | You may store blasting agents with nonexplosive blasting supplies. |
(a) When stored with explosives, blasting agents or ammonium nitrate must be stored as required in magazine construction.
(b) When computing the total quantity of explosives, the mass of blasting agents and one-half the mass of ammonium nitrate must be included when determining the distance requirements.
(c) When stored separately from explosives, blasting agents and ammonium nitrate must be stored as required in this chapter; or
((OR))
Warehouses which are:
((•)) (i) One story without basements;
((•)) (ii) Noncombustible or fire resistant;
((•)) (iii) Constructed so there are no open floor drains and piping where molten materials could flow and be trapped in case of fire;
((•)) (iv) Weather resistant;
((•)) (v) Well ventilated;
((•)) (vi) Equipped with a strong door which is securely locked except when open for business.
(d) Semi-trailer or full trailer vans used for highway or on-site transportation of blasting agents. They must:
((•)) (i) Comply with location requirements for inhabited buildings, passenger railways, and public highways in Table H-20;
((•)) (ii) Be in accordance with the distance requirements in Table H-22;
((•)) (iii) Have substantial means for locking and the trailer doors must be kept locked except during the time of placement or removal of blasting agents.
(e) Storage warehouses for blasting agents:
((•)) (i) Must comply with the location requirements for inhabited buildings, passenger railways, and public highways in Table H-20;
((•)) (ii) Must be in accordance with the distance requirements in Table H-22.
(f) Combustible materials, flammable liquids, corrosive acids, chlorates, or nitrates cannot be stored in warehouses used for blasting agents unless they are separated by a fire resistant wall with a minimum of one-hour fire resistance.
(g) A competent person, at least twenty-one years old, must supervise every warehouse used for the storage of blasting agents.
(2) Combustible materials. These activities and items are prohibited within fifty feet (15.2 m) of any warehouse used for storing blasting agents:
((•)) (a) Smoking;
((•)) (b) Matches;
((•)) (c) Open flames;
((•)) (d) Spark producing devices;
((• Fire-arms)) (e) Firearms.
(3) Housekeeping. The interiors of warehouses used for storing blasting agents must be:
((•)) (a) Kept clean, and free from debris and empty containers;
((•)) (b) All spilled materials must be promptly cleaned.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-52-69095 Ammonium nitrate.
(1) Storage.
(a) Ammonium nitrate storage requirements do not apply to:
((•)) (i) The transportation of ammonium nitrates while under the jurisdiction of and in compliance with U.S. DOT regulations (see 49 C.F.R., Part 173);
((•)) (ii) The storage of ammonium nitrates while under the jurisdiction of and in compliance with U.S. Coast Guard (see 49 C.F.R., Parts 146-149);
((•)) (iii) The storage of ammonium nitrate and ammonium nitrate mixtures, which are more sensitive than allowed by the bulletin:
"Definition and test procedures for ammonium nitrate fertilizers" from the Fertilizer Institute, 501 2nd Street N.E., Washington, D.C. 20006.
This definition limits the contents of organic materials, metals, sulfur, etc., in products that may be classified ammonium nitrate fertilizer.
((•)) (iv) The production of ammonium nitrate or the storage of ammonium nitrate on the premises of the producing plant, if no hazards are created to the employees or public;
((•)) (v) The standards for ammonium nitrate (nitrous oxide grade) that are found in the:
"Specifications, properties and recommendations for packaging, transportation, storage and use of ammonium nitrate," from the Compressed Gas Association, Inc., 1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Suite 1004, Arlington, VA 22202-4100.
(b) Ammonium nitrate storage requirements apply to:
((•)) (i) Anyone, in addition to the owner or lessee of any building, premises, or structure having or storing ammonium nitrate in quantities of one thousand pounds (425 kg) or more;
((•)) (ii) Ammonium nitrate in the form of crystals, flakes, grains, or prills including fertilizer grade, dynamite grade, nitrous oxide grade, technical grade, and other mixtures containing sixty percent or more ammonium nitrate by weight.
Note: | The approval of large quantity storage is based on the fire and explosion hazards, including exposure to toxic vapors from burning or decomposing ammonium nitrate. |
(c) Storage buildings housing ammonium nitrate must:
((•)) (i) Have adequate ventilation or be self-ventilating in the event of a fire;
((•)) (ii) Have fire resistant walls when the exposed side of a storage building is within fifty feet (15.2 m) of a combustible building, forest, piles of combustible materials, and similar exposure hazards. Other suitable means of exposure protection such as a freestanding wall may be used instead of a fire resistant wall;
((•)) (iii) Have roof coverings that are Division 1.4 or better as defined in Roof Coverings, NFPA 203M-1970;
((•)) (iv) Have flooring of noncombustible material or be protected against saturation by ammonium nitrate. In case of fire, the floor must not have open drains, traps, tunnels, pits, or pockets into which molten ammonium nitrate could flow and be confined;
((•)) (v) Be dry and free from water seepage through the roof, walls, and floors;
((•)) (vi) Not have basements, unless the basements are open on at least one side;
((•)) (vii) Not be over one story in height.
Note: | The continued use of an existing storage building or structure may be approved in cases where continued use will not constitute a hazard to life or adjoining property. |
Bags, drums, and other containers of ammonium nitrate must:
(d) Comply with specifications and standards required for use in interstate commerce (see 49 C.F.R., Chapter 1). Containers used on the premises in the actual manufacturing or processing do not need to comply((.));
((•)) (i) Not be used for storage when the temperature of the ammonium nitrate exceeds 130°F (54.4°C);
((•)) (ii) Not be stored within thirty inches (76 cm) of the storage building walls and partitions;
((•)) (iii) Not be stacked higher than twenty feet (6.1 m) in height, twenty feet (6.1 m) in width, and fifty feet (15.2 m) in length. When buildings are constructed of noncombustible materials or protected by automatic sprinklers, there are no stacking height restrictions;
((•)) (iv) Never be stacked closer than thirty-six inches (.09 m) below the roof or overhead supporting and spreader beams;
((•)) (v) Be separated by aisles a minimum of three feet wide. There must be one main aisle in the storage area a minimum of four feet (1.2 m) wide.
(e) Bulk ammonium nitrate must be stored:
((•)) (i) In warehouses with adequate ventilation or be capable of adequate ventilation in case of fire;
((•)) (ii) In structures that are not more than forty feet (12.2 m) high, unless:
((–)) (A) They are constructed of noncombustible material; or
((OR
–)) (B) Have adequate facilities for fighting a roof fire.
((•)) (iii) In clean bins that are free of materials that could cause contamination;
((•)) (iv) In bins or piles that are clearly identified by signs reading "AMMONIUM NITRATE" in letters a minimum of two inches (5 cm) high;
((•)) (v) In bins or piles sized and arranged so all material is moved periodically to minimize the possibility of caking;
((•)) (vi) Adequately separated from easily combustible fuels. Bins cannot be made of galvanized iron, copper, lead, and zinc because of the:
((–)) (A) Corrosive and reactive properties of ammonium nitrate; and
((AND
–)) (B) To avoid contamination.
((•)) (vii) In tightly constructed wooden and aluminum bins that are protected against saturation from ammonium nitrate;
((•)) (viii) In tightly constructed partitions that divide the ammonium nitrate from other products to avoid contamination;
((•)) (ix) Where the temperature of the product does not exceed 130°F (54.4°C);
((•)) (x) No higher than thirty-six inches (0.9 m) below the roof or overhead supporting and spreader beams if stacked in piles. Stack limits (height and depth), should be determined by the pressure setting tendency of the product.
(f) Bulk ammonium nitrate when caked, cannot be broken up or loosed by the use of dynamite, other explosives or blasting agents.
(g) Bulk ammonium nitrate cannot be stored with:
((•)) (i) LP Gas on the premises except when such storage complies with WAC 296-24-475, Storage and handling of liquefied petroleum gases;
((•)) (ii) Sulfur and finely divided metals in the same building except when such storage complies with this chapter and NFPA standard 495, Explosives Materials Code;
((•)) (iii) Explosives and blasting agents in the same building except on the premises of manufacturers, distributors, and user of explosives or blasting agents;
((•)) (iv) When explosives or blasting agents are stored in separate buildings, other than on the approval of manufacturers, distributors, and user, they must be separated from the ammonium nitrate by the distances and/or barricades specified in Table H-22 or a minimum of fifty feet (15.2 m);
((•)) (v) With flammable liquids, such as gasoline, kerosene, solvents, and light fuel oils on the premises except when such storage conforms to WAC 296-24-330, Flammable liquids, and when walls, sills or curbs are provided in accordance with WAC 296-52-69095, Ammonium nitrate.
(2) Contaminants must be stored in a separate building from ammonium nitrate
((OR)) or be separated by an approved firewall of not less that one-hour fire resistance rating which should extend to the underside of the roof. Alternatively, the contaminants may be separated by a minimum of thirty feet (9.1 m), instead of using walls. These contaminants are:
((•)) (a) Organic chemicals;
((•)) (b) Acids;
((•)) (c) Other corrosive materials;
((•)) (d) Materials that may require blasting during processing or handling;
((•)) (e) Compressed flammable gases;
((•)) (f) Flammable and combustible materials;
((•)) (g) Other substances including:
Animal fats |
Baled cotton |
Baled rags |
Baled scrap paper |
Bleaching powder |
Burlap or cotton bags |
Caustic soda |
Coal |
Coke |
Charcoal |
Cork |
Camphor |
Excelsior |
Fibers of any kind |
Fish oil |
Fish meal |
Foam rubber |
Hay |
Lubricating oil |
Linseed oil |
Other oxidizable or drying oils |
Naphthalene |
Oakum |
Oiled clothing |
Oiled paper |
Oiled textiles |
Paint |
Straw |
Sawdust |
Wood shavings |
Vegetable oil |
(3) Housekeeping requirements must have:
((•)) (a) Electrical installations, which meet the requirements of chapter 296-24 WAC, Part L, Electrical, and WAC 296-800-280, Basic electrical rules, for ordinary locations and be designed to minimize damage from corrosion;
((•)) (b) Adequate lightning protections in areas where lightning storms are prevalent (see NFPA 78-1992, Lightning Protection Code);
((•)) (c) Procedures to prevent unauthorized personnel from entering the ammonium nitrate storage area.
(4) Fire protection must provide:
((•)) (a) Water supplies and fire hydrants;
((•)) (b) Suitable fire control devices, such as a small hose or portable fire extinguishers, throughout the warehouse and in the loading/unloading areas. These devices must comply with the requirements of WAC 296-800-300, Portable fire extinguishers, and WAC 296-24-602, Standpipe and hose systems;
((•)) (c) Approved sprinkler systems installed according to WAC 296-24-607, Automatic sprinkler systems;
((•)) (d) Two thousand five hundred tons (two thousand two hundred seventy metric) or less of bagged ammonium nitrate may be stored in a structure that does not have an automatic sprinkler system.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-69110 Table H-21—Quantity and distance table for separation between magazines.
Note: | This table applies to the permanent storage of commercial explosives only. It does not apply to: |
((•)) 1. Explosives handling; | |
((•)) 2. Explosives transportation; | |
((•)) 3. Temporary storage of explosives; | |
((•)) 4. Bombs, projectiles, or other heavily encased explosives. |
Magazines containing detonators and electric detonators must be separated from:
(1) Other magazines with similar contents((.
OR)); or
(2) Magazines containing explosives.
Note: | Definitions of barricade including artificial and natural barricade can be found in WAC 296-52-60130, Definitions. |
Table H-21
QUANTITY AND DISTANCE TABLE FOR SEPARATION BETWEEN MAGAZINES CONTAINING EXPLOSIVES |
Separation Distance in Feet Between Magazines |
||||||
Pounds Over |
Pounds Not Over |
Not Barricaded |
Barricaded |
||||
2 |
5 |
12 |
6 |
||||
5 |
10 |
16 |
8 |
||||
10 |
20 |
20 |
10 |
||||
20 |
30 |
22 |
11 |
||||
30 |
40 |
24 |
12 |
||||
40 |
50 |
28 |
14 |
||||
50 |
75 |
30 |
15 |
||||
75 |
100 |
32 |
16 |
||||
100 |
125 |
36 |
18 |
||||
125 |
150 |
38 |
19 |
||||
150 |
200 |
42 |
21 |
||||
200 |
250 |
46 |
23 |
||||
250 |
300 |
48 |
24 |
||||
300 |
400 |
54 |
27 |
||||
400 |
500 |
58 |
29 |
||||
500 |
600 |
62 |
31 |
||||
600 |
700 |
64 |
32 |
||||
700 |
800 |
66 |
33 |
||||
800 |
900 |
70 |
35 |
||||
900 |
1,000 |
72 |
36 |
||||
1,000 |
1,200 |
78 |
39 |
||||
1,200 |
1,400 |
82 |
41 |
||||
1,400 |
1,600 |
86 |
43 |
||||
1,600 |
1,800 |
88 |
44 |
||||
1,800 |
2,000 |
90 |
45 |
||||
2,000 |
2,500 |
98 |
49 |
||||
2,500 |
3,000 |
104 |
52 |
||||
3,000 |
4,000 |
116 |
58 |
||||
4,000 |
5,000 |
122 |
61 |
||||
5,000 |
6,000 |
130 |
65 |
||||
6,000 |
7,000 |
136 |
68 |
||||
7,000 |
8,000 |
144 |
72 |
||||
8,000 |
9,000 |
150 |
75 |
||||
9,000 |
10,000 |
156 |
78 |
||||
10,000 |
12,000 |
164 |
82 |
||||
12,000 |
14,000 |
174 |
87 |
||||
14,000 |
16,000 |
180 |
90 |
||||
16,000 |
18,000 |
188 |
94 |
||||
18,000 |
20,000 |
196 |
98 |
||||
20,000 |
25,000 |
210 |
105 |
||||
25,000 |
30,000 |
224 |
112 |
||||
30,000 |
35,000 |
238 |
119 |
||||
35,000 |
40,000 |
248 |
124 |
||||
40,000 |
45,000 |
258 |
129 |
||||
45,000 |
50,000 |
270 |
135 |
||||
50,000 |
55,000 |
280 |
140 |
||||
55,000 |
60,000 |
290 |
145 |
||||
60,000 |
65,000 |
300 |
150 |
||||
65,000 |
70,000 |
310 |
155 |
||||
70,000 |
75,000 |
320 |
160 |
||||
75,000 |
80,000 |
330 |
165 |
||||
80,000 |
85,000 |
340 |
170 |
||||
85,000 |
90,000 |
350 |
175 |
||||
90,000 |
95,000 |
360 |
180 |
||||
95,000 |
100,000 |
370 |
185 |
||||
100,000 |
110,000 |
380 |
195 |
||||
110,000 |
120,000 |
410 |
205 |
||||
120,000 |
130,000 |
430 |
215 |
||||
130,000 |
140,000 |
450 |
225 |
||||
140,000 |
150,000 |
470 |
235 |
||||
150,000 |
160,000 |
490 |
245 |
||||
160,000 |
170,000 |
510 |
255 |
||||
170,000 |
180,000 |
530 |
265 |
||||
180,000 |
190,000 |
550 |
275 |
||||
190,000 |
200,000 |
570 |
285 |
||||
200,000 |
210,000 |
590 |
295 |
||||
210,000 |
230,000 |
630 |
315 |
||||
230,000 |
250,000 |
670 |
335 |
||||
250,000 |
275,000 |
720 |
360 |
||||
275,000 |
300,000 |
770 |
385 |
||||
Note: | With site-specific department approval, a stand of mature timber may qualify as a natural barricade. The timber must be dense enough so the area requiring protection cannot be seen from the magazine when the trees are bare of leaves. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-06-073, filed 3/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-52-69125 Table H-24—Low explosives.
(1) Use Table H-24 for((:)) magazines that are restricted to:
((•)) (a) Division 1.2 or 1.3;
((•)) (b) Division 1.4, low explosives;
((•)) (c) Low explosives classified by BATF.
(2) Detonators cannot be stored with low explosives.
Table H-24
TABLE OF DISTANCES FOR STORAGE OF LOW EXPLOSIVES
Pounds |
From inhabited building distance (feet) |
From public railroad and highway distance (feet) |
From above ground magazine (feet) |
|
Over |
Not Over |
|||
0 |
1,000 |
75 |
75 |
50 |
1,000 |
5,000 |
115 |
115 |
75 |
5,000 |
10,000 |
150 |
150 |
100 |
10,000 |
20,000 |
190 |
190 |
125 |
20,000 |
30,000 |
215 |
215 |
145 |
30,000 |
40,000 |
235 |
235 |
155 |
40,000 |
50,000 |
250 |
250 |
165 |
50,000 |
60,000 |
260 |
260 |
175 |
60,000 |
70,000 |
270 |
270 |
185 |
70,000 |
80,000 |
280 |
280 |
190 |
80,000 |
90,000 |
295 |
295 |
195 |
90,000 |
100,000 |
300 |
300 |
200 |
100,000 |
200,000 |
375 |
375 |
250 |
200,000 |
300,000 |
450 |
450 |
300 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-70005 Type 1 magazines: Permanent storage facilities.
A Type 1 storage facility must be:
((•)) (1) A permanent structure such as:
((–)) (a) A building;
((–)) (b) An igloo;
((–)) (c) An army-type structure;
((–)) (d) A tunnel; or
((OR
–)) (e) A dugout.
((•)) (2) Bullet resistant, fire resistant, weather resistant, theft resistant, and well ventilated.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-70010 Building construction for Type 1 magazines.
(1) All building-type storage facilities must:
((•)) (a) Be constructed of masonry, wood, metal, or a combination of these materials;
((•)) (b) Have no openings except for entrances and ventilation;
((•)) (c) Have the ground around the facility slope away for drainage.
(((1))) (2) Wall construction.
(a) Masonry wall construction. Masonry wall construction must:
((•)) (i) Consist of brick, concrete, tile, cement block, or cinder block;
((•)) (ii) Be at least eight inches thick.
(b) Hollow masonry construction. Hollow masonry construction must:
((•)) (i) Have all hollow spaces filled with well tamped coarse dry sand; or
((OR
•)) (ii) Have weak concrete (a mixture of one part cement to eight parts sand with enough water to dampen the mixture) while tamping in place; and
((AND
•)) (iii) Have interior walls covered with a nonsparking material.
(c) Fabricated metal wall construction.
((•)) (i) Metal wall construction must be securely fastened to a metal framework and consist of one of the following types of metal:
((–)) (A) Sectional sheets of steel (at least number 14 gauge); or
((OR
–)) (B) Aluminum (at least number 14 gauge).
((•)) (ii) Metal wall construction must:
((–)) (A) Be lined with brick, solid cement blocks, and hardwood at least four inches thick or material of equivalent strength;
((–)) (B) Have a minimum of six-inch sand fill between interior and exterior walls;
((–)) (C) Have interior walls constructed of or covered with a nonsparking material.
(d) Wood frame wall construction.
((•)) (i) Exterior wood walls must be covered with iron or aluminum at least number 26 gauge;
((•)) (ii) Inner walls, made of nonsparking materials must be constructed with a space:
((–)) (A) A minimum of six inches between the outer and inner walls; and
((AND
–)) (B) Filled with coarse dry sand or weak concrete.
(((2))) (3) Floors. Floors must be:
(a) Constructed of a nonsparking material.
(b) Strong enough to hold the weight of the maximum quantity to be stored.
(((3))) (4) Foundation.
((•)) (a) Foundations must be constructed of brick, concrete, cement block, stone, or wood posts.
((•)) (b) If piers or posts are used instead of a continuous foundation, the space under the building must be enclosed with metal.
(((4))) (5) Roof.
(a) Roofs must be covered with no less than number 26 gauge iron or aluminum fastened to a 7/8-inch sheathing, except for buildings with fabricated metal roofs.
(b) If it is possible for a bullet to be fired directly through the roof at such an angle that it would strike a point below the top of the inner walls, storage facilities must be protected by one of the following two methods:
((•)) (i) A sand tray must be:
((–)) (A) Located at the top of the inner wall covering the entire ceiling area, except the area necessary for ventilation((.));
((–)) (B) Lined with a layer of building paper((.));
((–)) (C) Filled with at least four inches of coarse dry sand.
((•)) (ii) A fabricated metal roof must be constructed of 3/16-inch plate steel lined with four inches of hardwood or material of equivalent strength. For each additional 1/16-inch of plate steel, the hardwood or material of equivalent strength lining may be decreased one inch.
(((5))) (6) Doors and hinges.
(a) All doors must be constructed of 1/4-inch plate steel and lined with three inches of hardwood or material of equivalent strength.
(b) Hinges and hasps must be installed so they cannot be removed when the doors are closed and locked by:
((•)) (i) Welding;
((•)) (ii) Riveting; or
((OR
•)) (iii) Bolting nuts on the inside of the door.
(((6))) (7) Locks.
(a) Each door must be equipped with:
((•)) (i) Two mortise locks;
((•)) (ii) Two padlocks fastened in separate hasps and staples;
((•)) (iii) A combination of a mortise lock and a padlock;
((•)) (iv) A mortise lock that requires two keys to open; or
((OR
•)) (v) A three-point lock.
(b) Padlocks must:
((•)) (i) Have a minimum of five tumblers;
((•)) (ii) Have a case hardened shackle at least 3/8 inches in diameter;
((•)) (iii) Be protected with a minimum of 1/4-inch steel hoods, constructed to prevent sawing or lever action on the locks, hasps, and staples.
Note: | These requirements do not apply to magazine doors that are adequately secured on the inside by means of a bolt, lock, or bar that cannot be operated from the outside. |
(((7))) (8) Ventilation.
((•)) (a) A two-inch air space must be left around ceilings and the perimeter of floors, except in doorways;
((•)) (b) Foundation ventilators must be at least four inches by six inches;
((•)) (c) Vents in the foundation, roof, or gables must be screened and offset.
(((8))) (9) Exposed metal.
((•)) (a) Sparking metal construction cannot be exposed below the tops of walls in storage facilities;
((•)) (b) All nails must be blind nailed, countersunk, or nonsparking.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-70015 Igloos, army-type structures, tunnels, and dugouts.
These storage facilities must:
((•)) (1) Be constructed of reinforced concrete, masonry, metal, or a combination of these materials.
((•)) (2) Have an earth mound covering of at least twenty-four inches on the top, sides, and rear unless the magazine meets the requirements of WAC 296-52-70010 (4)(b), Building construction for roofs.
((•)) (3) Have interior walls and floors covered with a nonsparking material.
((•)) (4) Be constructed according to the requirements of WAC 296-52-70005, Type 1 magazines: Permanent storage facilities, through WAC 296-52-70060((,)) construction.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-70020 Type 2 magazines: Portable field storage.
A Type 2 storage facility must:
((•)) (1) Be a box, trailer, semi-trailer, or other mobile facility. When an unattended vehicular magazine is used, the wheels must be removed or it must be effectively immobilized by kingpin locking devices or other methods approved by the department.
((•)) (2) Be bullet resistant, fire resistant, weather resistant, theft resistant, and well ventilated.
((•)) (3) Be a minimum of one cubic yard.
((•)) (4) Be supported to prevent direct contact with the ground.
((•)) (5) Have the ground around the magazine slope away for drainage or provide for other adequate drainage.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-70025 Construction for Type 2 magazines.
(1) Exterior, doors, and top openings.
(a) The exterior and doors must be constructed of at least 1/4-inch steel and lined with a minimum of three-inch hardwood.
(b) Magazines with top openings must have lids with water resistant seals or lids that overlap the sides by a minimum of one inch when closed.
(2) Hinges and hasps. Hinges and hasps must be installed so they cannot be removed when the doors are closed and locked by:
((•)) (a) Welding;
((•)) (b) Riveting; or
((OR
•)) (c) Bolting nuts on the inside of the door.
(3) Locks.
(a) Each door must be equipped with:
((•)) (i) Two mortise locks;
((•)) (ii) Two padlocks fastened in separate hasps and staples;
((•)) (iii) A combination of mortise lock and a padlock;
((•)) (iv) A mortise lock that requires two keys to open; or
((OR
•)) (v) A three-point lock.
(b) Padlocks must have:
((•)) (i) A minimum of five tumblers and a case hardened shackle with a minimum of 3/8-inch diameter;
((•)) (ii) A minimum of 1/4-inch steel hoods constructed to prevent sawing or lever action on the locks, hasps, and staples.
Note: | These requirements do not apply to magazine doors that are adequately secured on the inside by means of a bolt, lock, or bar that cannot be operated from the outside. |
(4) Ventilation.
((•)) (a) A two-inch air space must be left around ceilings and the perimeter of floors, except at doorways;
((•)) (b) Foundation ventilators must be at least four inches by six inches;
((•)) (c) Vents in the foundation, roof, or gables must be screened and offset.
(5) Exposed metal.
((•)) (a) Sparking metal cannot be exposed below the top of walls in the storage facilities;
((•)) (b) All nails must be blind nailed, countersunk, or nonsparking.
Note: | The following are nonmandatory construction alternatives for magazine exteriors: |
((–)) 1. All steel and wood dimensions shown are actual thickness; | |
((–)) 2. The manufacturer's represented thickness may be used to meet the concrete block and brick dimensions. |
3/16
((•)) (c) 3/16-inch steel lined with an interior of 4-inch hardwood.
((•)) (d) 3/16-inch steel lined with:
(i) An interior of 7 inches of softwood; or
((OR))
(ii) 6 3/4 inches of plywood.
((•)) (e) 3/16-inch steel lined with:
(i) An intermediate layer of 3-inch hardwood; and
((AND))
(ii) An interior lining of 3/4-inch plywood.
1/8
((•)) (f) 1/8-inch steel lined with an interior of 5-inch hardwood.
((•)) (g) 1/8-inch steel lined with an interior of 9-inch softwood.
((•)) (h) 1/8-inch steel lined with:
(i) An intermediate layer of 4-inch hardwood; and
((AND))
(ii) An interior lining of 3/4-inch plywood.
((•)) (i) Reserved.
(j) 1/8-inch steel lined with:
(i) A first intermediate layer of 3/4-inch plywood((.));
(ii) A second intermediate layer of 3 5/8 inches well-tamped dry sand; or
((OR))
(iii) Sand/cement mixture.
(6) An interior lining of 3/4-inch plywood.
((•)) (a) 5/8-inch steel lined with an interior of any type of nonsparking material.
((•)) (b) 1/2-inch steel lined with an interior of at least 3/8-inch plywood.
((•)) (c) 3/8-inch steel lined with an interior of 2-inch hardwood.
((•)) (d) 3/8-inch steel lined with an interior of:
(i) 3 inches softwood; or
((OR))
(ii) 2 1/4 inches of plywood.
((•)) (e) 1/4-inch steel lined with:
(i) An interior of 5 inches of softwood; or
((OR))
(ii) 5 1/4 inches of plywood.
((•)) (f) Any type of structurally sound fire resistant material lined with:
(i) An intermediate layer of 4-inch solid concrete block; or
((OR))
(ii) 4-inch solid brick or concrete; and
((AND))
(iii) An interior lining of 1/2-inch plywood placed securely against the masonry lining.
((•)) (g) Standard 8-inch concrete block with voids filled with well tamped sand/cement mixture.
((•)) (h) Standard 8-inch solid brick.
((•)) (i) Reserved.
(j) Any type of structurally sound fire resistant material lined with an intermediate 6-inch space filled with:
(i) Well tamped dry sand; or
((OR))
(ii) Well tamped sand/cement mixture.
((•)) (k) Any type of fire resistant material lined with:
(i) A first intermediate layer of 3/4-inch plywood((,));
(ii) A second intermediate layer of 3 5/8-inch well tamped dry sand; or
((OR))
(iii) Sand/cement mixture((,));
(iv) A third intermediate layer of 3/4-inch plywood((,));
(v) A fourth intermediate layer of 2-inch hardwood; or
((OR))
(vi) 14 gauge steel and an interior lining of 3/4-inch plywood((,));
(vii) 8-inch thick solid concrete.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-70030 Type 3 magazines: Indoor storage facilities.
((•)) (1) Detonators in quantities of one thousand or less;
((•)) (2) Ammonium perchlorate rocket motors in 62.5 gram amounts or greater, but not to exceed fifty pounds in total weight of explosives((.)); or
((OR
•)) (3) Diversionary devices intended for law enforcement use only, but not to exceed fifty pounds in total weight of explosives.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-70035 Storage facilities for detonators.
Storage facilities for detonators in quantities of one thousand or less:
((•)) (1) Must be fire resistant and theft resistant;
((•)) (2) Must be locked in an uninhabited building;
((•)) (3) May be less than one cubic yard;
((•)) (4) Must be painted red and have an identification label in case of fire.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-70045 Type 4 magazines: Blasting agent, low explosive, or nonmass detonating detonator storage facilities.
A Type 4 storage facility must:
((•)) (1) Be a building, an igloo, an army-type structure, a tunnel, a dugout, a box, a trailer, semi-trailer, or other mobile facility;
((•)) (2) Be fire resistant, weather resistant, and theft resistant;
((•)) (3) Have the ground around the facility slope away for drainage;
((•)) (4) Have the wheels removed or effectively immobilized by kingpin locking devices or other methods approved by the department, when an unattended vehicular magazine is used.
Note: | Test results show that electric detonators are not affected by sympathetic detonation. Therefore, a Type 4 storage facility meets the necessary requirements for storage of electric detonators. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-70050 Construction for Type 4 magazines.
(1) These magazines must be constructed of masonry, metal covered wood, fabricated metal, or a combination of these materials.
(2) Foundations. Foundations must be constructed of:
((•)) (a) Brick;
((•)) (b) Concrete;
((•)) (c) Cement block;
((•)) (d) Stone;
((•)) (e) Metal; or
((OR
•)) (f) Wood posts.
(3) The space under the building must be enclosed with fire resistant material, if piers or posts replace continuous foundation.
(4) The walls and floors must be made or covered with a nonsparking material or lattice work.
(5) Doors must be metal or solid wood covered with metal.
(6) Hinges and hasps must be installed so they cannot be removed when the doors are closed and locked by:
((•)) (a) Welding;
((•)) (b) Riveting; or
((OR
•)) (c) Bolting nuts on the inside of the door.
(7) Locks.
(a) Each door must be equipped with:
((•)) (i) Two mortise locks;
((•)) (ii) Two padlocks fastened in separate hasps and staples;
((•)) (iii) A combination of a mortise lock and a padlock;
((•)) (iv) A mortise lock that requires two keys to open; or
((OR
•)) (v) A three-point lock.
(b) Padlocks must:
((•)) (i) Have a minimum of five tumblers;
((•)) (ii) Have a case hardened shackle of a minimum of 3/8-inch diameter;
((•)) (iii) Be protected with a minimum of 1/4-inch steel hoods constructed to prevent sawing or lever action on the locks, hasps, and staples.
Note: | These requirements do not apply to magazine doors that are adequately secured on the inside by means of a bolt, lock, or bar that cannot be operated from the outside. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-70055 Type 5 magazines: Blasting agent storage facilities.
A Type 5 storage facility must:
((•)) (1) Be a building, an igloo, an army-type structure, a tunnel, a dugout, a box, or a trailer, semi-trailer, or other mobile facility;
((•)) (2) Be weather resistant and theft resistant;
((•)) (3) Have the ground around the facility slope away for drainage;
((•)) (4) Have the wheels removed or be effectively immobilized by kingpin locking devices or other methods approved by the department, when the unattended vehicular magazine is used.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-08-110, filed 4/5/05, effective 6/1/05)
WAC 296-52-70060 Construction for Type 5 magazines.
(1) Doors must be constructed of solid wood or metal.
(2) Hinges and hasps must be installed so they cannot be removed when the doors are closed and locked by:
((•)) (a) Welding;
((•)) (b) Riveting; or
((OR
•)) (c) Bolting nuts on the inside of the door.
(3) Locks.
(a) Each door must be equipped with:
((•)) (i) Two mortise locks;
((•)) (ii) Two padlocks fastened in separate hasps and staples;
((•)) (iii) A combination of a mortise lock and a padlock;
((•)) (iv) A mortise lock that requires two keys to open; or
((OR
•)) (v) A three-point lock.
(b) Padlocks must have:
((•)) (i) A minimum of five tumblers;
((•)) (ii) A case hardened shackle of a minimum of 3/8-inch diameter;
((•)) (iii) Padlocks must be protected with a minimum of 1/4-inch steel hoods constructed to prevent sawing or lever action on the locks, hasps, and staples.
Note: | Trailers, semi-trailers, and similar vehicular magazines. Each door may be locked with one 3/8-inch diameter steel padlock and does not need to be protected by a steel hood, if the door hinges and lock hasp are securely fastened to the magazine and to the doorframe. These requirements do not apply to magazine doors that are adequately secured on the inside by means of a bolt, lock, or bar that cannot be operated from the outside. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-70065 Explosives day box.
(1) A day box for explosives must:
((•)) (a) Be fire, weather, and theft resistant;
((•)) (b) Be used in a manner that safely separates detonators from other explosives;
((•)) (c) Be constructed of a minimum of number 12 gauge (.1046 inches) steel;
((•)) (d) Be lined with at least either 1/2-inch plywood or 1/2-inch masonite-type hardboard;
((•)) (e) Have doors that overlap the sides by a minimum of one inch;
((•)) (f) Have appropriate ground slope for drainage.
(2) Hinges and hasps must be attached by:
((•)) (a) Welding;
((•)) (b) Riveting; or
((OR
•)) (c) Bolting nuts on the inside of the door.
(3) One steel padlock, which does not need to be protected by a steel hood, having a minimum of five tumblers and a case hardened shackle of a minimum of 3/8-inch diameter is sufficient for locking purposes.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-70070 Detonator day box.
A detonator day box is a temporary storage facility for detonators in quantities of one thousand or less.
(1) Construction materials. Sides, bottoms, and covers must be:
((•)) (a) Constructed of number 12 gauge metal;
((•)) (b) Lined with a nonsparking material.
(2) Hinges and hasps must be attached by:
((•)) (a) Welding;
((•)) (b) Riveting; or
((OR
•)) (c) Bolting nuts on the inside of the door.
(3) A single five tumbler lock must be used to lock the detonator day box.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-70080 Magazine heating system requirements.
Magazine heating system requirements and the following apply:
(1) Heat sources. Magazines requiring heat must be heated by either:
((•)) (a) Hot water radiant heating; or
((OR
•)) (b) Air directed into the magazine building by hot water or low pressure steam (15 psig) coils located outside the magazine building.
(2) Heating systems. Magazine heating systems must meet the following requirements:
(a) The radiant heating coils in the building must be installed where explosive materials or their containers cannot touch the coils and air is free to circulate between the coils and the explosive material containers.
(b) The heating ducts must be installed where the hot air released from a duct is not directed toward the explosive material or containers.
(c) The heating device used in connection with a magazine must have controls, to prevent the building temperature from exceeding 130°F.
(d) The electric fan or pump used in the heating system for a magazine must be:
((•)) (i) Mounted outside;
((•)) (ii) Separate from the wall of the magazine;
((•)) (iii) Grounded.
(e) Electric motor, device controls, and electric switch gear.
(i) The electric fan motor and the controls for electrical heating devices used in heating water or steam must have overloads and disconnects which comply with the National Electrical Code, (NFPA Number 70-1992).
(ii) All electrical switch gear must be located a minimum distance of twenty-five feet from the magazine.
(f) Water or steam heating source.
(i) A heating source for water or steam must be separated from a magazine by a distance of at least:
((•)) (A) Twenty-five feet when the heating source is electrical;
((•)) (B) Fifty feet when the heating source is fuel fired.
(ii) The area between a heating unit and a magazine cannot contain combustible materials.
(g) The storage of explosive material containers in the magazine must allow for uniform air circulation, so temperature uniformity can be maintained throughout the explosive materials.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-70085 Lighting.
(1) Battery activated safety lights or lanterns may be used in explosive storage magazines.
(2) National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Standards.
(a) Electric lighting used in an explosive storage magazine must meet National Electric Code (NEC) standards (NFPA 70-1992) for all magazine conditions.
(b) All electrical switches must:
((•)) (i) Be located outside the magazine;
((•)) (ii) Meet NEC standards.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-71025 Separation from flammable materials.
Small arms ammunition must be separated from flammable liquids, flammable solids (as classified in 49 C.F.R. Part 172), and oxidizing materials by a:
((•)) (1) Fire resistant wall with a one-hour rating; or
((OR
•)) (2) Distance of twenty-five feet.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-06-073, filed 3/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-52-71040 Shipping container.
((•)) (1) Small arms smokeless powder (Division 1.2 or 1.3) must be packed, stored, and transported in U.S. DOT approved shipping containers.
((•)) (2) All smokeless powder must be stored in shipping containers made for smokeless powder (as required by 49 C.F.R. 173.93).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-06-073, filed 3/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-52-71045 Storage.
(1) Private residence or car.
((•)) (a) Twenty-five pounds or less of small arms smokeless powder, no restrictions;
((•)) (b) Twenty-five to fifty pounds of small arms smokeless powder, they must be stored in a strong box or cabinet constructed of a minimum of 3/4-inch plywood or equivalent material, on all sides, top, and bottom.
(2) Commercial stocks.
((•)) (a) Over twenty pounds but not more than one hundred pounds of small arms smokeless powder must be stored in portable wooden boxes with a minimum of one-inch thick walls;
((•)) (b) Small arms smokeless powder not exceeding one hundred fifty pounds, must be stored in a nonportable storage cabinet with a minimum of one-inch thick wood walls.
(3) Dealer's warehouse.
((•)) (a) A dealer's warehouse cannot hold more then one hundred fifty pounds of small arms smokeless powder;
((•)) (b) Twenty to one hundred pounds of small arms smokeless powder must be stored in a minimum of one-inch thick portable or fixed wooden boxes.
(4) Dealer's display.
((•)) (a) The dealer's display cannot exceed more then seventy-five pounds of small arms smokeless powder;
((•)) (b) Small arms smokeless powder must be stored in one-pound containers.
(5) Magazines. Small arms smokeless powder that exceed one hundred fifty pounds must be stored in approved licensed magazines. See Storage licensing, WAC 296-52-660, Storage of explosive materials, WAC 296-52-690, and Magazine construction, WAC 296-52-700.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-71060 Separation from flammable materials.
Primers must be separate from flammable liquids, flammable solids, and oxidizing materials by a:
((•)) (1) Fire resistant wall with a one hour rating; or
((OR
•)) (2) Distance of twenty-five feet.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-71065 Storage.
(1) Private residence. The maximum small arms ammunition primers permitted is ten thousand primers. No restrictions apply.
(2) Private car. The maximum small arms ammunition primers permitted is twenty-five thousand primers. No restrictions apply.
(3) Dealer's display. The maximum small arms ammunition primers permitted is ten thousand primers. No restrictions apply.
(4) Dealer's warehouse. ((•)) The maximum small arms ammunition primers permitted is seven hundred fifty thousand primers.
((–)) (a) No more than one hundred thousand small arms ammunition primers may be stored in one stack;
((–)) (b) Stacks must be separated by at least fifteen feet.
(5) Magazines. If there are more than seven hundred fifty thousand small arms ammunition primers, they must be stored in approved licensed magazines (see Storage licensing, WAC 296-52-660, Storage of explosive material, WAC 296-52-690, and Magazine construction, WAC 296-52-700).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-71095 Hours of transfer.
Explosives cannot be received between sunset and sunrise from any:
((•)) (1) Railway station;
((•)) (2) Truck terminal;
((•)) (3) Pier;
((•)) (4) Wharf;
((•)) (5) Harbor facility; or
((OR
•)) (6) Airport terminal.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-71100 Storage in route.
Explosives waiting for delivery or further transit at a railway facility, truck terminal, pier, wharf, harbor facility, or airport terminal must be:
((•)) (1) Stored in a safe place;
((•)) (2) Isolated as much as practical;
((•)) (3) In a manner that allows quick and easy removal.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-71105 Railway cars.
(1) Use of railway cars.
Explosives cannot be kept in a railway car unless:
((•)) (a) An emergency exists;
((•)) (b) Permission has been granted by the local authority;
((•)) (c) The railway car, its contents, and methods of loading are in compliance with U.S. DOT regulations (49 C.F.R. Chapter 1).
(2) Warning signs for railway cars not in transit.
((•)) (a) Any railway car containing explosives must have warning signs attached to every side of the car when it is:
((–)) (i) Stopped in transit; or
((OR
–)) (ii) At its designation; and
((AND
–)) (iii) No longer considered in interstate commerce.
((•)) (b) Warning signs must read "EXPLOSIVES—HANDLE CAREFULLY—KEEP FIRE AWAY."
The letters must be:
((–)) (i) Red;
((–)) (ii) At least one and one-half inches high;
((–)) (iii) On a white background.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-125, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-52-720 Appendix A, sample explosives-blasting ordinance for local jurisdictions, nonmandatory.
Explosives-blasting ordinance for local jurisdictions
Be it ordained by the ____________________ (jurisdiction name).
Section 1: Permit required.
(1) A current and valid blasting permit issued by _____________________ (jurisdiction name) is required by companies or individuals who:
((•)) (a) Possess explosive materials (as defined by chapter 296-52 WAC, Safety standards for possessions and handling of explosives);
((•)) (b) Conduct an operation or activity requiring the use of explosive materials; or
((OR
•)) (c) Perform, order, or supervise the loading and firing of high explosive materials.
(2) Anyone in ______________________ (jurisdiction name) who does not have a valid blasting permit cannot transport, sell, give, deliver, or transfer explosive materials.
(3) A blasting permit is required for every individual project requiring blasting explosives.
(4) A permit issued to any person, company, or corporation under this ordinance is nontransferable to any other person, company, or corporation.
(5) All blasting permits issued by _____________________ (jurisdiction name) must follow all federal, state, county, and city laws and regulations that apply to these activities with explosive materials:
((•)) (a) Obtaining;
((•)) (b) Owning;
((•)) (c) Transporting;
((•)) (d) Storing;
((•)) (e) Handling;
((•)) (f) Using.
Section 2: Application contents.
(1) The proper administrative authority ( name ) or their designee, has the power and authority to issue blasting permits and requires persons, companies, or corporations who are issued permits to file an application that includes:
(a) A completed application form provided by ____________________ (jurisdiction name) specifying the name and address of the person, company or corporation applying for the permit, and the name and address of the blast site or the person who will actually supervise the blasting.
(b) A current and valid explosives license issued by the state of Washington department of labor and industries to one or more individuals working on the specific blasting project.
(c) A transportation plan according to Section 8.
(d) A blasting plan according to Section 10(1).
(e) A traffic control plan according to Section 10(2).
(f) A preblast; notification, inspection, and monitoring plan according to Section 10(3).
(g) Proof of insurance must be provided according to Section 4.
(2) ____________________ (jurisdiction name) will issue a permit within fourteen days of receiving an application that includes acceptable documentation of the above items 1 a through g through 7. If the permit is denied, it must be done within fourteen days of administering authority receipt and must include a list of reasons for denial as well as instructions for reapplication.
Section 3: Fee.
A permit fee is required for each permit issued. It should be:
((•)) (1) Valid for twelve months;
((•)) (2) Follow the local fee schedule;
((•)) (3) Renewable.
Section 4: Liability insurance required.
(1) If the ____________________ (jurisdiction name) design requires approval, then coverage of one million dollars or more is required or other reasonable amount depending on the circumstances as determined by ________________________ (name of the proper administrative authority).
(2) The certificate must also state that the insurance company must give ____________________ (jurisdiction name) a minimum of ten days notice of cancellation of the liability insurance coverage.
(3) The ____________________ (name of the proper administrative authority) has the power and authority to limit the level of blasting. After examining all pertinent circumstances surrounding the proposed blasting, they may refuse to issue a permit, or suspend, or revoke an existing permit.
Section 5: Revocation.
The ___________________ (name of the proper administrative authority) has the power to revoke any permit if the permit holder does not follow the requirements of this chapter. The permit holder has twenty-four hours to remove all explosive materials after being notified that their permit has been revoked.
Section 6: Denial or revocation appeal.
Any person, company, or corporation whose blasting permit application is denied, suspended, or revoked by ____________ (name of proper authority), may file a notice of appeal within ten days to __________________ (name of the legislative body with jurisdiction over the administrator).
– The legislative body must schedule an appeals hearing within fourteen days.
Section 7: ____________________ (jurisdiction name) not to assume liability.
______________________ (jurisdiction name) is not responsible for any damage caused by the person, company, or corporation blasting with ___________________ (jurisdiction name).
Section 8: Transportation of explosives (transportation plan).
(1) You must include a transportation plan that addresses the transportation of explosive materials within ____________________ (jurisdiction name) with your application for a blasting permit.
(2) The transportation plan must include the following information:
(a) Route used for deliveries and returns
(b) Hours of transportation
(c) Maximum quantities of explosives being transported
(d) Types of vehicles being used. Vehicles must be in compliance with federal and state transportation regulations for transportation of explosive material.
Section 9: Storage of explosives.
(1) No overnight storage of explosive material is permitted within the limits of ____________________ (jurisdiction area) without specific amendments to the permit allowing storage. Blast holes loaded with explosives are to be shot on the day they are loaded.
(2) The required method of handling explosives in ____________________ (jurisdiction area) is as follows:
(a) Same day delivery
(b) Stand by during loading
(c) Return of all unused explosive materials.
Section 10: Use of explosives.
(1) Blasting plan. A blasting plan for each project must be submitted to ____________________ and approved by the ____________________ (name of the proper administrative authority) or their designee prior to issuing a blasting permit. The plan must include additional documentation for the proposed blasting operation. For example, maps, site plans, and excavation drawings. The plan must include:
(a) The location where the blast will occur
(b) The approximate total amount of material to be blasted
(c) The incremental volumes, per blast, of material to be blasted
(d) The types and packaging of explosive materials to be used
(e) The drill hole diameters, depths, patterns, subdrilling depths and drill hole orientation to be used
(f) The initiation system, the incremental delay times, and the location of the primers in the explosive column
(g) The stemming depths and stemming material for the various estimated depths of drill holes to be blasted
(h) The approximate powder factors anticipated
(i) The flyrock control procedures and equipment to be used
(j) The maximum number of blasts that will be made in one day
(k) The blast warning sound system and equipment to be used
(l) The scheduled start date and finish date of blasting operations
(m) Additional requirements as needed.
(2) Traffic control plan. A traffic control plan acceptable to ____________________ (jurisdiction name) detailing signing, flagging, temporary road closures, and detour routes for blasting operations must be filed before the blasting permit is issued.
(3) Preblast notification plan. A plan outlining preblast public notifications, structural inspections, and blast effect monitoring within a specified distance of the blasting is required before the blasting permit is issued.
(a) Separation distance. The distances from the blasting where the notification, preblast structural inspection, and blast monitoring is required must be determined by the scaled distance formulas described below. Blasting will not be permitted until the notification and inspection requirements are completed.
(b) Scaled distance formulas.
(i) The distance from the blast within which:
((•)) (A) Notification of all occupied structures is required: Da = 90 w;
((•)) (B) Inspection of all occupied structures is required: Db = 75 w;
((•)) (C) Monitoring of selected structures is required: Dc = 60 w.
(ii) In the above formulas:
((•)) (A) Da, Db, and Dc are the actual distances in feet from the closest point in the blast.
((•)) (B) w is the square root of the maximum weight of the explosives in pounds detonated with a minimum 8 millisecond from another detonation event.
(c) Notification letter. The preblast notification must consist of a letter advising all residents within the distance (specified in WAC 296-52-720 section 10 (3)(b)) of the blasts. The letter must include the intent of the blasting program, its anticipated impact on local residents, the proposed duration of blasting activities, and provide telephone numbers for public contact. Distribution of this notification must be made a minimum of seven days before the start of blasting. The source of the chart is 121.8507, Bureau of Mines, U.S. Department of Interior, 1980.
(d) Preblast inspection. A preblast inspection of resident's property must be offered to all residents within the distance (specified in WAC 296-52-720 section 10 (3)(b) above) of the blasting at no cost to the resident and will be preformed by a qualified third party who is not an employee of the contractor. A copy of the individual inspection reports and a log of all photos taken are to be provided to ____________________ (jurisdiction name). Where inspections are not allowed by the resident or are not possible for other reasons, a certified letter must be sent to the occupant/owner at the unsurveyed address advising them of their right to a preblast inspection and the possible consequences of denying an inspection. The preblast inspection program for residences within the specified distance must be complete two days prior to the start of blasting and the ____________________ (name of the proper administrative authority) should be notified.
(4) Blast-plan compliance inspections. Blast-plan compliance inspections may be required for every blast until the operator can demonstrate an ability to safely blast according to the blast plan and control the extraneous effects of blasting such as flyrock, noise/air blast, and ground vibration. If more than two blasting inspections are required, an additional fee of ____________________ (insert dollar amount) per blast inspection will be assessed.
(5) Monitoring. All blasts which require monitoring by section 10 (3)(b) are to be monitored using blast monitoring equipment designed for the purpose and carrying a certificate of calibration dated within the previous twelve months. The blast monitors must record peak particle velocity and frequency in three orthogonal directions and air over pressure. Monitored shots in which the pounds detonated per an 8-millisecond time increment is less than ten pounds, one blast monitor is required. When ten or more pounds is detonated per an 8-millisecond time interval, two or more blast monitors are required. All blast-monitoring records are to be signed and submitted to ____________________ (jurisdiction name) within twenty-four hours of each blast.
(6) Maximum peak particle velocity. The maximum peak particle velocity in any seismic trace at the dominant frequency allowed on any residential, business or public structure designed for human occupancy is to be determined by the chart in WAC 296-52-67065(1).
(7) Air blast. The maximum air blast over pressure permitted at the closest residential, business or public structure designed for human occupancy is not to exceed 133 dBL @ 2.0 Hz hi pass system per WAC 296-52-67065(3). The source of this regulation is 121.8485, Bureau of Mines, U.S. Department of Interior, 1980.
(8) Utilities. Whenever blasting is being conducted in close proximity to existing utilities, the utility owner must be notified a minimum of twenty-four hours in advance of blasting.
(9) Blast report. A signed blast report, on a form approved by the ____________________ (name of the proper administrative authority) or their designee, needs to be filed with ____________________ (jurisdiction name) within twenty-four hours of the blast. The report must include the following blast information:
(a) Date, time, and location of the blast
(b) Number of drill holes
(c) Maximum, minimum and average drill hole depth
(d) Drill hole diameter
(e) Subdrill depth
(f) Total pounds of each type of explosive used
(g) A drill hole section schematic showing the loading of a typical hole
(h) Amount and type of stemming material
(i) Schematic showing the drill hole pattern
(j) Initiated delayed sequence
(k) Maximum pounds of explosives detonated in any eight millisecond time interval
(l) Type and size of any flyrock protection devices used, if any
(m) Comment regarding the outcomes of the blast.
(10) ____________________ (jurisdiction name) must be notified immediately of any unplanned or unusual events that resulted from the blast. The permittee must also report any incident, damage claim, or neighbor annoyance report brought to the permittee's attention within twenty-four hours.
Section 11:
This ordinance will be in effect to preserve the health, peace, and safety of the citizens of ____________________ (jurisdiction name).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-800 Avalanche control.
(1) General.
(a) During periods of high avalanche danger, areas in avalanche paths ((shall)) must not be opened for use until trained personnel have evaluated conditions and determined whether avalanche control work is necessary.
(b) When avalanche control work is deemed necessary, areas in the potential avalanche path ((shall)) must be closed until the risk of avalanches has been reduced to a level determined appropriate by trained personnel.
(c) An avalanche ((shall)) must not be purposely released until the avalanche path and potential runout zone are clear of personnel and vehicles.
(d) Avalanche guards, signs, and/or barricades ((shall)) must be positioned at normal entrances to the avalanche path if there is any chance that personnel and vehicles will enter the danger zone during intentional release activities.
(e) During very unstable snow conditions, release of one avalanche may trigger sympathetic releases over a wide area. Avalanche workers ((shall)) must consider such possibility and clear the appropriate areas of personnel and vehicles.
(2) Personnel and equipment.
(a) The avalanche control crew ((shall)) must be adequately trained and physically capable for tasks which can be anticipated in their individual job assignments.
(b) No person ((shall)) must accept or be given a job assignment which is beyond the individual's physical ability or training.
(c) On-slope assignments which include potential exposure to avalanche hazards ((shall)) must only be conducted by fully qualified and fully equipped control crew members.
(d) The control crew may be split up into smaller groups (teams) to work on multiple areas simultaneously provided that each team consists of at least two qualified members.
(e) Each avalanche control crew or team ((shall)) must have one or more designated rescue coordinators as is deemed necessary to maintain communications. Compliance with this requirement may be achieved by designating control crew teams to serve as each others' rescue coordinator provided that the teams are reasonably proximate to each other and do in fact maintain frequent communications.
(f) Each avalanche control crew member ((shall)) must be equipped for continuous two-way communications to the avalanche crew coordinators.
(g) The avalanche crew or teams ((shall)) must not be assigned to on-slope areas where they cannot maintain communications with their designated coordinator. This requirement may be met by the use of a relay person; however, if any team completely loses communications, they ((shall)) must return directly to base via the safest route available.
(h) Each person on an avalanche control team ((shall)) must be equipped with a shovel and an electronic transceiver before commencing on-slope control work. The transceiver ((shall)) must be in the transmit position whenever personnel are performing on-slope job assignments.
(3) Avalanche rescue plan. All employers with avalanche control personnel ((shall)) must have a written avalanche rescue plan. The plan ((shall)) must require:
(a) All rescue personnel who will be assigned to on-slope activities ((shall)) must:
(i) Be competent skiers;
(ii) Have a current first-aid card;
(iii) Be thoroughly trained in the rescue plan details;
(b) A specific list of required equipment for rescue crew personnel including:
(i) Probes;
(ii) Belaying rope;
(iii) Shovels;
(iv) Two-way communication radios;
(v) Electronic transceivers;
(c) A list of rescue equipment locations;
(d) Specific rescue procedures to be followed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-803 Storage, makeup, and use of explosives for avalanche control blasting.
(1) General.
(a) The storage, handling, and use of explosives and blasting agents used in avalanche control practices ((shall)) must comply with this chapter and chapter 70.74 RCW.
(b) The minimum requirements published in chapter 296-52 WAC, Part H, ((shall)) must be applicable to the storage, handling, and use of explosives and blasting agents in the endeavor of avalanche control.
(2) Management responsibility.
(a) Explosives and blasting agents ((shall)) must not be stored in any regularly occupied areas or buildings except in compliance with this chapter.
(b) Explosives and blasting agents ((shall)) must not be assembled or combined to form armed charges in any regularly occupied area or building except in compliance with this chapter.
(3) Personnel.
(a) Only fully qualified and licensed blasters ((shall)) must be permitted to assemble or arm explosives components.
(b) Training ((shall)) must include avalanche blasting experience so that the problems encountered in cold weather blasting are known factors.
(c) All training activities ((shall)) must be conducted under the attended supervision of a fully qualified and licensed blaster.
(4) General requirements.
(a) Initiating systems for hand-placed or hand-thrown charges.
(i) The ignition system on single-unit hand-thrown charges ((shall)) must consist of a nonelectric cap or shock tube and approved initiation system.
(ii) Multiple units combined to form a single hand-placed charge may use the above system, an approved detonating cord system or shock tube system. No other ignition system ((shall)) must be permissible without specific approval by the department.
(iii) When using a shock tube system, after all charges are in place, connected to the shock tube trunk line and ready for initiation, the shock tube initiation tool ((shall)) must be attached for firing.
(b) Multiple charge blasts.
(i) Detonating cord or shock tube system ((shall)) must be used in lieu of blasting wire to connect multiple charge blasts.
(ii) When using detonating cord systems, after all charges are placed, connected to the detonating cord, and the charges are ready to be ignited, a safety fuse and cap ((shall)) must be attached to the detonating cord. A fuse igniter may then be attached to ignite the safety fuse.
(c) Blasting caps ((shall)) must be no larger than No. 8 except when recommended by the explosives manufacturer for a particular explosive used within a specific application.
(d) Electric blasting caps are not permitted.
(e) Safety fuse and shock tube.
(i) Only the highest quality safety fuse with excellent water resistance and flexibility ((shall)) must be used.
(ii) Shock tube systems may be used in place of fuse cap and safety fuse systems.
(f) Fuse length.
(i) Safety fuse length ((shall)) must be selected to permit the control team adequate escapement time from the blast area under all reasonable contingencies (falls, release of bindings, etc.)
(ii) In no instance ((shall)) must a fuse length with less than ninety seconds burn time be permitted.
(iii) The burn time of each roll of safety fuse ((shall)) must be checked prior to use.
(iv) Checked rolls ((shall)) must be marked with the tested burn time.
(v) It is recommended that all hand charges be prepared for ignition with either one safety fuse and igniter or a double safety fuse and igniters.
Note: | Standard safety fuse burns at a rate of forty to fifty-five seconds at two thousand five hundred meters elevation. This rate equates to approximately twenty-four inches fuse length for ninety second hand charge fuses at normal avalanche control elevations, but fuse burn rate should be checked before each use. |
(5) Explosives.
(a) Explosives chosen ((shall)) must have a safe shelf life of at least one operating season in the storage facilities in which it will be stored.
(b) Explosives chosen ((shall)) must have excellent water and freezing resistance.
(c) Industrial primers (or boosters) that consist mainly of TNT or gelatin are the recommended explosives.
(6) Transporting explosives and hand charges.
(a) Hand charges or explosives components ((shall)) must be transported in approved type avalanche control packs, in United States Department of Transportation-approved shipping containers or in licensed magazines.
(b) Criteria for avalanche control packs.
(i) The pack ((shall)) must be constructed of water resistant material.
(ii) Packs ((shall)) must be constructed with sufficient individual compartments to separate hand charges or explosives components from tools or other equipment or supplies which may be carried in the pack.
(iii) Each compartment used for hand charges or explosives components ((shall)) must have an independent closure means.
(iv) If fuse igniters will be permitted to be carried on the avalanche control pack, a separate compartment with individual closure means ((shall)) must be attached to the outside of the exterior of the pack.
(c) Use of avalanche control packs.
(i) Packs ((shall)) must be inspected daily, prior to loading, for holes or faulty compartment closures. Defective packs ((shall)) must not be used until adequately repaired.
(ii) Tools or other materials ((shall)) must not be placed in any compartment which contains hand charges or explosives components.
(iii) Fuse igniters ((shall)) must never be placed anywhere inside the pack when the pack contains hand charges or other explosives components.
(iv) Fuse igniters may be carried in a separate compartment attached to the outside of the pack exterior but preferably in a compartment attached to the front of the carrying harness. Another acceptable alternative is to carry the igniters in a jacket pocket completely separate from the pack.
(v) Hand charges or explosives components ((shall)) must not be stored or left unattended in avalanche control packs. Unused hand charges ((shall)) must be promptly disassembled at the end of individual control routes and all components returned to approved storage.
(vi) Individual control team members ((shall)) must not carry more than thirty-five pounds of hand charges in avalanche control packs.
(vii) A hand charge or cap and fuse assembly which has a fuse igniter attached ((shall)) must never be placed in an avalanche control pack for any reason.
(d) Whenever explosives or explosives components are transported in or on any vehicle powered by an internal combustion engine, provisions ((shall)) must be made to ensure that said explosives or containers cannot come into contact with the hot exhaust system.
(e) Hand charges or explosives components ((shall)) must not be transported in spark-producing metal containers.
(f) Hand charges ((shall)) must not be transported on public roads and highways when such roads or highways are open to the public. Explosives components ((shall)) must only be transported on public roads or highways in compliance with United States Department of Transportation regulations.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-805 Hand charge makeup methods.
General. The department ((shall)) must recognize two permissible methods concerning hand charges for avalanche control blasting. The descriptions and requirements for each method are contained in this section.
Note: | A well-designed and constructed hand charge makeup room can enhance the correct assembly of explosive components and reduce the incidences of misfires from incorrect makeup or moisture. |
(1) Method I. Makeup at the blast site.
(a) The ignition system ((shall)) must consist of a nonelectrical blasting cap and highest quality water resistant safety fuse, or detonating cord, assembled as recommended by the manufacturer.
(b) Detonating cord ((shall)) must be used to connect separated multiple-charge blasts.
(c) No other ignition system ((shall)) must be permissible on hand-placed or hand-thrown avalanche control charges unless variance is granted by the department.
(d) Caps ((shall)) must be installed on correct length fuses prior to being transported out onto control routes.
(e) Caps ((shall)) must only be crimped with a crimper tool approved for that purpose.
(f) Assembling caps and fuses ((shall)) must be done in a warm, dry, well-lighted environment. The location used for assembly ((shall)) must not have flammable fuels, flammable gases, or explosives present where accidental detonation of the caps could create a secondary ignition or detonation hazard.
(g) Each cap ((shall)) must be protected by a styrofoam shield or the equivalent before being placed in an avalanche control pack for transportation.
(h) A fuse igniter ((shall)) must never be attached to a fuse until the fuse and cap assembly is installed in the hand charge at the blast site and the control crew is fully prepared to ignite the charge.
(i) All 1.1 explosives ((shall)) must be attended as defined in this chapter at all times when the explosive is out of the Type 1 or 2 storage magazine.
(j) Disbursement of explosive charges from the Type 1 or 2 storage magazine into avalanche control packs ((shall)) must be done outside the storage magazine. Records ((shall)) must be maintained for all explosives disbursed.
(k) Caps, cap and fuse assemblies, armed hand charges, or fuse igniters ((shall)) must not be carried into or stored in a Type 1 or 2 magazine which contains 1.1 explosives.
(2) Method II. Hand charge makeup room. This method is different from method I primarily in that the fuse and cap assembly is installed in the explosive charge while inside a special makeup room. The assembly procedure ((shall)) must be as follows:
(a) Install caps on correct length fuses with an approved crimper tool before explosives are brought into the makeup room.
(b) The cap and fuse assemblies ((shall)) must not be combined with explosives to form hand charges until just before the intended time of distribution.
(c) Only nonsparking skewers ((shall)) must be used to punch holes in an explosives cartridge.
(d) The fuse ((shall)) must be laced or taped in position after inserting the cap in the charge.
(e) Each hand charge ((shall)) must be placed in an explosives box or avalanche control pack immediately after assembly is completed.
(f) No spark-producing metal tools ((shall)) must be used to open explosives containers.
(g) Fuse igniters ((shall)) must never be attached to a fuse or a hand charge until the hand charge is at the blast site and the control crew is fully prepared to ignite the charge.
(3) Makeup room requirements, procedures.
(a) Construction requirements.
(i) Makeup rooms located in accordance with the American Standard Quantity and Distance Tables for storage ((shall)) must not require construction of reinforced concrete walls, floors, and doors. All other requirements of this chapter ((shall)) must be applicable for such facilities.
(ii) Floors and walls. The floor and walls ((shall)) must be constructed of reinforced concrete not less than eight inches thick. The rebar ((shall be not)) must not be less than one-half inch diameter and ((shall)) must be spaced on twelve-inch vertical and horizontal centers. The rebar ((shall)) must be bent at a ninety degree angle and extend a minimum of twenty-four inches into the adjoining floor or wall to secure each floor and wall joint.
(iii) Roof. The roof is not limited to specific materials but ((shall)) must provide both weather protection and standard snow loading protection for the region.
(iv) Access door(s).
(A) If a hinged door mounting is utilized, the hinge ((shall)) must be mounted on the inside so that the door opens into the makeup room. In the fully closed position, in position to be locked, the door ((shall)) must be a minimum of two inches larger than the access opening on all sides.
(B) If a flush door mounting is utilized, the door ((shall)) must be mounted with a two-inch decreasing taper on all sides of both the door and the concrete access opening to form a wedge seal.
(C) If a sliding door mounting is utilized, the mounting apparatus ((shall)) must be on the inside of the makeup room and the door ((shall)) must be a minimum of two inches larger than the access opening when the door is fully closed.
(D) Makeup room door may be either:
(I) Constructed to the same structural integrity and mounting requirements of (A) through (C) of this subsection; or
(II) Constructed of plywood not less than two inches thick and overlaid on the outside with a steel plate not less than one-eighth inch thick.
(III) If a door which complies with (II) of this subsection is used, a berm or barricade ((shall)) must be installed within six feet of the door. The berm or barricade ((shall)) must extend at least as high as the top of the door and ((shall)) must be a minimum of two feet wider than the door on both sides of the door.
(E) For security purposes, one steel padlock having at least five tumblers and a case hardened shackle of at least three-eighths inch diameter is sufficient for locking purposes. Hinges and hasps ((shall)) must be attached so that they cannot be removed from the outside when in the closed position and with the lock in place.
(v) Interior finish. The inside of all makeup rooms ((shall)) must be finished and equipped to the following minimum requirements:
(A) Construction ((shall)) must be fire resistant and nonsparking up to the top of the walls. Nails or screws ((shall)) must be countersunk, blind nailed, or covered.
(B) Lighting ((shall)) must be by N.E.C. explosion-proof rated fixtures and all wiring ((shall)) must be in sealed conduit.
(C) Control switches ((shall)) must be outside the makeup room.
(D) No electrical outlet boxes are permissible inside the room.
(b) Restrictions.
(i) Smoking, matches, open flames, or flame- or spark-producing devices ((shall)) must not be permitted inside the makeup room.
(ii) Flammable liquids or flammable compressed gases ((shall)) must not be stored in the makeup room.
(iii) Signs limiting entry to authorized personnel ((shall)) must be posted on the door(s).
(iv) A sign stating the occupancy rules ((shall)) must be posted inside the makeup room where it is clearly legible upon entering the room. The sign ((shall)) must post the following rules:
(A) Occupancy ((shall)) must be restricted to specifically authorized personnel;
(B) Smoking, matches, flame- or spark-producing devices, tools or equipment ((shall)) must not be permitted in the room at any time when explosives or explosive components are present; and
(C) Flammable fuels or compressed gases ((shall)) must not be permitted inside the room nor stored within fifty feet of the room.
(v) Heating units ((shall)) must be limited to:
(A) Forced air systems with the heating unit located outside the room.
(B) Steam systems of 15 psig or less.
(C) Hot water systems of 130°F or less.
(D) The radiant heating coils and piping for steam or hot water systems ((shall)) must be protected so that explosives cannot come into contact with them.
(E) Heating ducts ((shall)) must be installed so that the hot air does not discharge directly on explosives.
(F) The heating system used in a makeup room ((shall)) must have controls which prevent the ambient room temperature from exceeding 130°F.
(vi) The makeup room ((shall)) must be equipped with a portable fire extinguisher of at least 2A-20BC rating.
Note: | For additional requirements relating to portable fire extinguishers see WAC 296-800-300. |
(vii) Ventilation.
(A) The makeup room ((shall)) must be equipped with a ventilation system capable of maintaining a minimum rate of three air exchanges per hour during all times when explosives are present in the room.
(B) Fans and controls ((shall)) must be located outside the makeup room and ((shall)) must be of a type approved for this service.
(C) The lighting circuit control ((shall)) must also activate the ventilation fan and the ventilation fan ((shall)) must be operated whenever personnel are in the room.
(D) Exhaust ventilation ((shall)) must be arranged to discharge into outside air, not into an enclosed structure.
(viii) The floor or exterior walls may be constructed with duct openings for heating and ventilation purposes provided that:
(A) Each duct opening is not greater in volume than seventy-two square inches;
(B) The combined number of duct openings ((shall)) must not exceed three;
(C) Duct openings ((shall)) must be located within twelve inches of the floor or ceiling;
(D) The exhaust duct opening ((shall)) must not be located on the wall above the makeup workbench.
(c) Practices and procedures.
(i) When explosives are present in the makeup room, entry into the makeup room ((shall)) must be restricted to trained and authorized personnel.
(ii) The access door(s) to the makeup room ((shall)) must be kept locked or bolted from the inside while employees are assembling explosives.
(iii) The entire makeup room ((shall)) must be kept clean, orderly, and free of burnable rubbish.
(iv) Brooms and other cleaning utensils ((shall)) must not have any spark-producing metal parts if used when explosives are present.
(v) Sweepings and empty explosives containers ((shall)) must be disposed of as recommended by the explosives supplier.
(vi) Repair activities which utilize spark-producing tools ((shall)) must not be conducted on any part of the makeup room while explosives are present.
(d) Storage of explosives.
(i) A makeup room ((shall)) must not be used for the unattended storage of 1.1 explosives.
(ii) A makeup room which meets all requirements of this chapter may contain a Type 3 storage facility, for one thousand or less blasting caps.
(iii) A Type 3 storage facility ((shall)) must be constructed according to the requirements in WAC 296-52-70030 through 296-52-70040.
(A) A Type 3 storage facility ((shall)) must be fire resistant and theft resistant. It does not need to be bullet resistant and weather resistant if the locked makeup room provides protection from weather and bullet penetration.
(B) Sides, bottoms, and covers ((shall)) must be constructed of not less than number twelve gauge metal and lined with a nonsparking material.
(C) Hinges and hasps ((shall)) must be attached so that they cannot be removed from the outside.
(D) One steel padlock having at least five tumblers and a case-hardened shackle of at least three-eighths inch diameter is sufficient for locking purposes. The lock and hasp is not required to be equipped with a steel hood.
(e) Location.
(i) The makeup room ((shall)) must be located in accordance with the American Quantity and Distance Separation Tables as adopted in chapter 70.74 RCW, Washington State Explosives Act and this chapter except under conditions as indicated in this section.
(ii) Where locating the makeup room in accordance with the quantity and distance separation table is impractical because of bad weather accessibility, rough terrain, or space availability:
(A) Upon application the department will issue a variance enabling location of the makeup room, by mutual agreement, at the safest possible location within the limitation of the individual base area.
(B) The safest possible location will be the location most isolated from assembly areas and buildings that are inhabited with application of additional protection measures such as:
(I) Berming.
(II) Locating natural obstructions or buildings that are not inhabited between the makeup room and assembly areas and buildings that are inhabited.
(III) Limitations on the total quantity of explosives in the makeup room at any one time.
(iii) Makeup rooms designed to hold the boxes of explosives awaiting makeup and the madeup explosives in avalanche control packs awaiting distribution may be located using the total quantity of explosives allowed at the makeup table at any one time as the referenced quantity of explosives provided.
(A) The makeup room is located in accordance with the American Quantity and Distance Separation Tables as adopted in chapter 70.74 RCW, Washington State Explosives Act and this chapter for the referenced quantity of explosives at the makeup table.
(I) This separation ((shall)) must apply only to human proximity to the makeup room and only at such time as there are explosives in the makeup room.
(II) When the makeup room does not contain explosives the separation tables ((shall)) must not apply.
(B) The concrete walls of the room are designed to withstand the explosion of the total amount of the referenced explosives.
(I) The concrete walls must be constructed in accordance with specifications designed and certified by a licensed engineer; or
(II) The concrete walls must be constructed to the specifications of Department of the Army TM5-1300 "Structures to Resist the Effects of Accidental Explosions" designed to produce walls which will withstand explosion of the referenced quantity explosives.
(C) The boxes of explosives awaiting makeup and the madeup explosives in avalanche control packs awaiting distribution are located behind separate concrete debris barrier walls which will ensure that detonation of these explosives will not occur if the explosives at the makeup table detonate.
(I) The concrete debris barrier wall must be constructed in accordance with specifications designed and certified by a licensed engineer; or
(II) The concrete debris barrier wall must be constructed to the specifications of Department of the Army TM5-1300 "Structures to Resist the Effects of Accidental Explosions" to produce a barrier which will not allow detonation of the explosives awaiting makeup and distribution should the referenced quantity of explosives detonate.
(III) Access from the makeup table to the area behind the concrete debris barrier walls ((shall)) must not be doored. The concrete debris barrier walls will be designed so that the access way from the makeup table to the area behind the concrete debris barrier wall will deflect debris from an explosive blast by inherent design.
(D) The roof ((shall)) must be designed so that the resistance to an interior explosive blast will be negligible.
(iv) A full containment makeup room may be located anywhere and must meet the following requirements:
(A) The makeup room must be constructed in accordance with a licensed explosive engineer's approved design.
(B) The total amount of explosives in the room at any time must not exceed the design limit of the room.
(C) The makeup room cannot be used for storage.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-807 Avalanche control blasting.
(1) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that all members of avalanche control blasting crews are competent ski mountaineers in good physical and mental condition.
(2) Each avalanche control blasting crew or team ((shall)) must consist of a qualified and licensed blaster and at least one trained assistant.
(3) Untrained personnel may accompany blasting crews for training purposes but ((shall)) must not participate in actual firing of charges until trained and authorized.
(4) The blaster in charge of each crew or team ((shall)) must be responsible for all phases of preparation and placement of charges.
(5) Avalanche control blasting should be conducted during daylight hours whenever possible.
(6) Escape route.
(a) The avalanche control crew or team ((shall)) must preplan the escape route before igniting any charge.
(b) The escape route ((shall)) must be as safe and foolproof as possible and ((shall)) must culminate behind a terrain barrier or at least one hundred feet from the blast site by the time of detonation.
(7) Hand-thrown charges.
(a) A blaster ((shall)) must only work with one charge at a time.
(b) Before attaching the igniter, the blaster must:
(i) Be at the start of the escape route;
(ii) Check the runout zone for personnel;
(iii) Check the blast area for personnel.
(c) After the blaster attaches and activates the igniter:
(i) The blaster ((shall)) must check to see that the fuse is ignited;
(ii) If the fuse did not ignite, no attempt ((shall)) must be made to relight it. The blaster ((shall)) must immediately remove the fuse cap from the charge to sidearm it. The fuse cap ((shall)) must be treated as a misfire and be put in an appropriately safe place separate from all other explosive components. It ((shall)) must not be approached for at least thirty minutes, after which time it ((shall)) must be properly disposed of;
(iii) The practice of double fusing hand charges ((shall)) must be allowed. An attempt ((shall)) must be made to light both fuses. If only one of the two fuses lights, the charge ((shall)) must be deployed as normal;
(iv) As soon as the fuse is ignited, the blaster ((shall)) must promptly throw the charge into the target area;
(v) All personnel ((shall)) must be in a safe place when the charge detonates.
(d) Where hand-thrown charges will slide down the hill on hard frozen snow or ice surface, charges ((shall)) must be belayed with light cord.
(8) Hand charges thrown from ski lifts or trams.
(a) The number of charges thrown from ski lifts or trams ((shall)) must be kept to a minimum.
(b) The lift operating crew ((shall)) must be informed of the blasting plans.
(c) The lift crew ((shall)) must stand by for emergency procedures such as transfer of lift onto auxiliary power, evacuation, etc.
(d) The lift crew and the blaster in charge ((shall)) must be in direct radio contact at all times during the blasting operations.
(e) Only the avalanche control blasting crew and the essential lift operating personnel ((shall)) must be on a lift or tram during blasting operations.
(f) The avalanche control blasting crew ((shall)) must be traveling up slope when a charge is thrown.
(g) A charge ((shall)) must always be thrown down slope and to the side, away from towers, haulropes and other equipment or facilities.
(h) The minimum distance from the blast target to the closest point of the lift ((shall)) must be sixty feet.
(i) Hand charges ((shall)) must not exceed 4.5 pounds of TNT equivalent.
(j) Fuses ((shall)) must be timed and cut to such length that all personnel on the lift will have moved a minimum of three hundred feet from the blast target by the time of detonation.
(k) Precautions ((shall)) must be taken to avoid tossing charges into any of the lift equipment, moving chairs, cables, towers, etc.
(9) Aerial avalanche control blasting.
(a) Blasting from aircraft ((shall)) will require a written program approved by the Federal Aviation Administration and the director, or designee of the department of labor and industries.
(b) A written program ((shall)) must include the following:
(i) Written procedures to be followed including provisions for safety in the avalanche runout zone and emergency rescue plans.
(ii) Hand charge makeup and handling procedures.
(iii) The type of explosives to be used.
(iv) The qualifications of all avalanche control personnel involved in aerial blasting must meet the requirements of WAC 296-52-64030.
(v) The specific locations where aircraft blasting is to take place.
(c) An aerial avalanche control team ((shall)) must be established consisting of (at minimum) a pilot, a blaster in charge and an observer/controller.
(d) Blasting from an aircraft ((shall)) must require the blaster in charge to be a licensed avalanche blaster with an endorsement for aerial blasting. The blaster in charge will be on board during each aerial blasting mission.
Note: | Blasting from aircraft should only be used when it is determined that conventional methods are not the safest means to mitigate the existing avalanche hazard. |
(10) Avalauncher requirements.
(a) Management ((shall)) must develop a written training program and ensures that every person who will be authorized to work on an avalauncher firing team is thoroughly trained. Training ((shall)) must include:
(i) All operating instructions;
(ii) Safety precautions;
(iii) Emergency procedures;
(iv) Securing requirements for the equipment.
(b) ((Each employer shall)) You must have a list of authorized operators listed on a posted operator's list.
(c) Only trained and authorized personnel ((shall)) must be permitted to point and fire an avalauncher with explosive rounds.
(d) During firing of explosive loaded rounds, the firing team ((shall)) must consist of two qualified operators and not more than one adequately trained helper.
(e) Operators must have a current state blasting license.
(f) Each operator ((shall)) must individually check the elevation, pointing and pressure settings of the gun before each shot is fired.
(g) Operators ((shall)) must attempt to determine and record whether or not each round which is fired actually explodes on contact.
(h) The approximate location of all known misfired explosives (or duds) ((shall)) must be recorded.
(i) Initial shooting coordinates for each avalauncher mount ((shall)) must be made during periods of good visibility.
(j) Testing ((shall)) must include test firing in various wind conditions.
(k) The correct coordinates for the various conditions encountered ((shall)) must be carefully recorded.
(l) When spotter personnel are used in the target area, shooting ((shall)) must be conducted with nonexplosive projectiles.
(m) Firing of explosive avalauncher rounds ((shall)) must only be conducted when personnel are not in the target area.
(n) The avalauncher apparatus ((shall)) must be stored in a nonfunctional condition when not in use. This ((shall)) must be accomplished by:
(i) Locking out the firing mechanism or gas source in accordance with the lockout requirements of this chapter; or
(ii) Disassembly of functional components rendering the gun inoperable and separate storage of components removed; or
(iii) Removal of the entire gun to secure storage.
(o) With established avalauncher mounts, each autumn when reinstalling guns, the following procedures ((shall)) must be accomplished before the gun is considered operable:
(i) All components ((shall)) must be carefully inspected by qualified personnel;
(ii) After assembly and installation, the gun ((shall)) must first be test fired using a nonexplosive projectile;
(iii) The established firing coordinates ((shall)) must be checked by test firing.
(11) Cornice control requirements.
(a) Cornice buildup hazards ((shall)) must be evaluated regularly by qualified personnel, particularly after heavy snowfall periods which are accompanied by high wind or other snow transport weather conditions.
(b) Cornice hazards ((shall)) must be controlled whenever the buildup appears to offer potential hazard to areas accessible by personnel.
(c) The control team ((shall)) must establish the tension breakline of the cornice roof as accurately as conditions permit before starting any other control work on the cornice.
(d) The tension breakline ((shall)) must be marked when necessary.
(e) Small lightly packed cornices may be kicked off with a ski, ski pole, or shovel by an unbelayed control team member if the ridgeline can be clearly established and all work can be done from the safe side of the ridgeline.
(f) When working along an anticipated cornice breakline, control team members ((shall)) must retreat back from the breakline to change work positions rather than traverse along the breakline.
(g) The following factors ((shall)) must be given careful consideration before commencing control activities on any relatively larger cornice:
(i) The older and larger a cornice becomes, the more densely it compacts. Densely packed cornices release into larger blocks offering a higher level of danger to an extended runout zone. The control team leader ((shall)) must therefore take highest level of precautions to assure that the runout zone is clear of personnel;
(ii) Larger size cornices result in increased suspended weight and leverage which may cause the breakline release fracture to occur behind the actual ridgeline. The actual ridgeline may also be obscured by the simple mass of larger cornices. Control team members ((shall)) must stay off the cornice roof and must be protected by a secure belay when working near the suspected breakline;
(iii) All large cornices ((shall)) must be released by explosives. Explosives ((shall)) must be transported, made up and fired in accordance with the following requirements:
(A) The ignition system for single hand charge blasts ((shall)) must be safety fuse and cap or a system approved by the department.
(B) Detonating cord or shock tube ((shall)) must be used to connect multiple charge blasts.
(C) When detonating cord is used, one end ((shall)) must be securely anchored where premature cornice collapse will not disturb the anchor. The fuse and cap ((shall)) must be attached to the free end of the detonating cord after all charges are connected to the detonating cord.
(D) Safety fuse length ((shall)) must be sufficient to permit adequate escapement time for all personnel from the area influenced by the blast. Safety fuse ((shall)) must be not less than three feet long, approximately two minutes and twenty seconds, in all instances.
(h) Cornice control work on large cornices ((shall)) must be conducted during daylight hours and preferably during favorable weather conditions. As a minimum, clear visibility ((shall)) must exist across the full length of any cornice which the control team is attempting to release.
(12) Belaying practices.
(a) Belay rope ((shall)) must be standard 11 mm mountaineering rope or the equivalent.
(i) Belay rope ((shall)) must be inspected at not less than thirty-day intervals and maintained in excellent condition.
(ii) Defective belay rope ((shall)) must not be used for belaying purposes.
(b) Adequate trees or other suitable natural belay anchors ((shall)) must be used in preference to a human belay anchor when such natural anchors are available.
(c) The belay anchor position ((shall)) must be as near to ninety degrees from the tension breakline as the terrain conditions will permit.
(d) With either a natural belay anchor or human belay anchor, the belay line ((shall)) must be tended to keep slack out of the line.
(e) When either the belayed person or belay anchor needs to change position, the belayed person ((shall)) must retreat back from the cornice to a safe position until the belay anchor is reestablished.
(f) When a human belay anchor is used:
(i) The belay anchor person ((shall)) must establish the anchor position as far back away from the cornice as conditions permit;
(ii) The anchor person ((shall)) must remain in a seated position with their legs pointed toward the belayed person until such time as the belayed person has retreated back from the cornice to a position considered to be safe.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-52-809 Retrieving misfired explosives (duds).
(1) The following requirements ((shall)) must apply to all kinds of avalanche control blasting:
(a) Each person who ignites a charge or propels a charged projectile with any kind of apparatus ((shall)) must note whether or not the charge actually detonates.
(b) A conscientious effort ((shall)) must be made to promptly retrieve any misfired explosives.
(i) If conditions make it impractical or dangerous to promptly retrieve a misfired explosive, a search ((shall)) must be conducted as soon as conditions permit.
(ii) Any area which contains a misfired explosive ((shall)) must be closed to entry to all personnel except the search team until such time as the area has been searched and pronounced safe by the designated search leader.
(c) When searching for a misfired explosive on an uncontrolled avalanche slope (a slope which has not released), the procedures used ((shall)) must be consistent with good mountaineering practices.
(d) A hand charge misfire ((shall)) must not be approached for at least thirty minutes.
(e) A hand charge or avalauncher misfired explosive may be blown up with a secondary charge where they are found or may be disarmed at that location by fully trained and qualified personnel.
(f) Military warhead misfired explosives ((shall)) must not be moved. They ((shall)) must be blown up where they are found by secondary charges except that trained military personnel may disarm and transport such misfired explosives when approved by the governmental branch having jurisdiction.
(2) Records.
(a) Accurate records ((shall)) must be maintained for every explosive device which does not detonate.
(b) Misfired explosives records ((shall)) must include the following information:
(i) The suspected location;
(ii) A description of the misfired explosive;
(iii) The date the misfired explosive was lost;
(iv) The date the misfired explosive was found and disposed of.
(3) Misfired explosive frequency.
(a) Misfired explosive frequency should be maintained below one misfired explosive for every five hundred detonating attempts.
(b) All employers who do not maintain a misfired explosive frequency below one misfired explosive per five hundred detonation attempts ((shall)) must investigate all aspects of the blasting program and take prompt corrective actions as indicated.
(4) Misfired explosives warning signs.
(a) Requirements for warning signs. Ski area operations which use any form of explosive device for avalanche control ((shall)) must display warning, information placards and/or signs as found in this chapter, Part H.
(b) Signs ((shall)) must be posted at readily visible locations and in such a manner as to give both employees and the public ample opportunity to be informed of the potential existence of misfired explosive avalanche charges. Locations may include, but are not limited to:
(i) Ticket sales and lift loading areas;
(ii) Food and beverage service facilities;
(iii) Restrooms and locker rooms;
(iv) Safety bulletin boards;
(v) Along general access routes.
(c) Signs ((shall)) must be distinctive in appearance from the surrounding background where they are posted.
(d) Signs ((shall)) must be maintained in legible condition.
(e) Signs ((shall)) must include the following information:
(i) The word "WARNING" or "DANGER" at the top of the sign in the largest lettering on the sign;
(ii) The words "EXPLOSIVES ON THE MOUNTAIN";
(iii) A colored pictorial illustration which also provides information on dimensions of each type of explosive device used in the area;
(iv) The sign wording ((shall)) must conclude with specific instructions to be followed by anyone who locates an unexploded explosive device.
REPEALER
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
WAC 296-52-60130 |
Definitions. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-59-001 Foreword.
(1) This vertical standard is promulgated in accordance with applicable provisions of the Washington State Administrative Procedure Act, chapter 34.04 RCW, and the Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act, chapter 49.17 RCW.
(2) The requirements of this chapter ((shall)) must be applied through the department of labor and industries, division of industrial safety and health, in accordance with administrative procedures provided for in chapter 49.17 RCW, and chapters 296-27, 296-360, 296-800, and 296-900 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-59-003 Scope and application.
(1) The rules of this chapter are applicable to all persons, firms, corporations, or others engaged in the operation of organized ski areas and facilities within the jurisdiction of the department of labor and industries. These rules ((shall)) must augment the WAC general horizontal standards, specifically referenced WAC vertical standards, and specifically referenced national standards or manuals.
(2) In the event that specific provisions of this chapter may conflict with any other WAC chapter, national standard, or manual, the provisions of this chapter ((shall)) must prevail.
(3) The rules of this chapter ((shall)) must not be applied to rescue crews during the time that rescue procedures are in process provided that reasonably prudent methods, equipment, and processes are employed. Personnel directly engaged in rescue operations ((shall)) must not be subjected to the immediate restraint provisions of RCW 49.17.130.
(4) Nothing herein contained ((shall)) must prevent the use of existing ski lift and tow equipment during its lifetime unless specific requirements of this chapter require retrofitting or modifications, provided that it ((shall)) must be in conformance with applicable national or state code requirements at the time of manufacture and be maintained in good condition to conform with safety factors for the materials and method of manufacture used.
(5) Severability. If any provision of this chapter, or its application to any person, firm, corporation, or circumstance is held invalid under state (RCW) or national (Public Law) laws, the remainder of this chapter, or the application of the provision to other persons or circumstances is not affected.
(6) Variance and procedure. Recognizing that conditions may exist which do not exactly meet the literal requirements of this or other applicable Title 296 WAC standards, pursuant to RCW 49.17.080 and 49.17.090, the director of the department of labor and industries or his/her authorized representative may permit a variance when other means of providing an equivalent measure of protection are afforded. The specific requirements and procedures for variance application are contained in chapter 296-900 WAC, Administrative rules. Application forms may be obtained from the assistant director for safety and health or from regional departmental offices.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-59-005 Incorporation of other standards.
(1) Lifts and tows ((shall)) must be designed, installed, operated, and maintained in accordance with American National Standard Institute (ANSI) B77.1-1982, Standards for Passenger Tramways—Aerial Tramways and Lifts, Surface Lifts, and Tows—Safety Requirements.
(2) Future revised editions of ANSI B77.1-1982 may be used for new installations or major modifications of existing installations, as recommended or approved by the equipment manufacturer or a qualified design engineer, except that, where specific provisions exist, variances ((shall)) must be requested from the department.
(3) Reserved.
(4) The use of military type weapons for avalanche control ((shall)) must comply with all requirements of the United States government and/or the military branch having jurisdiction. Compliance ((shall)) must include qualification of employees, security requirements, and storage and handling of ammunition.
(5) ((The employer shall)) You must develop and maintain a hazard communication program as required by WAC 296-901-140, which will provide information to all employees relative to hazardous chemicals or substances to which they are exposed, or may become exposed, in the course of their employment.
(6) When employees perform activities such as construction work or logging, the WAC chapter governing the specific activity ((shall)) must apply, e.g., chapter 296-155 or 296-54 WAC, et seq.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-59-007 Definitions.
(("))Aerial work platform((" means)). Any form of work platform, work chair, or workbasket designed to lift or carry workmen to an elevated work position.
(("))ANSI((" means)). The American National Standards Institute.
(("))Approved((" means)). Approved by the director of the department of labor and industries except where this code requires approval by another specific body or jurisdiction authority.
(("))ASME((" means)). The American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
(("))Authorized person((" means)). A person approved or assigned by the employer to perform specific duties or to be at specific restricted locations.
(("))Avalanche((" means)). The sliding or falling of a large amount of snow down a steep slope which has a destructive force due to its mass.
(("))Belay((" means)). To provide an anchor for a safety line when a person is working in a position exposed to falling or sliding, the mountaineering term.
(("Designated" means appointed or authorized by the highest management authority available at the site.
"))Department((" means)). The department of labor and industries, division of industrial safety and health, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise.
(("))Designated. Appointed or authorized by the highest management authority available at the site.
Director((" means)). The director of the department of labor and industries or his/her designated representative.
(("))Hazard((" means)). That condition, potential or inherent, which might cause injury, death, or occupational disease.
(("))Hazardous material system. Any system within the following classifications:
(a) Flammable or explosive. Any system containing materials which are hazardous because they are easily ignited and create a fire or explosion hazard, defined by NFPA as Class I liquids;
(b) Chemically active or toxic. Any system containing material which offers corrosion or toxic hazard in itself or can be productive of harmful gases upon release, defined by NFPA 704M as Class 3 and 4 materials;
(c) Thermally hazardous. Any system above 130°F which exposes persons to potential thermal burns;
(d) Pressurized. Any gaseous system above two hundred psig or liquid system above five hundred psig.
Lift certificate to operate((" means)). An operating certificate issued by the Washington state parks and recreation commission pursuant to chapter 70.88 RCW subsequent to annual inspections as required by chapter 352-44 WAC.
((")) Must. Indicates a mandatory requirement.
N.E.C.((" means)). The National Electric Code, as published by either the National Fire Protection Association or ANSI.
(("))Occupied building((" means)). A building regularly occupied in whole or in part as a habitation for human beings, or any church, schoolhouse, railroad station, store, or other building where people are accustomed to assemble.
((")) Piping system. Any fixed piping, either rigid pipe or flexible hose, including all fittings and valves, in either permanent or temporary application.
Qualified((" means)). One who, by possession of a recognized degree, certificate, license, or professional standing, has successfully demonstrated the personal ability to solve or resolve problems relating to the subject matter, the work, or the project.
(("))RCW((" means)). The Revised Code of Washington, legislative law.
(("))ROPS((" means)). Rollover protective structure.
(("))S.A.E.((" means)) The society of automotive engineers.
(("))Safety factor((" means)). The ratio of ultimate breaking strength of any member or piece of material or equipment to the actual working stress or safe load when in use.
(("Shall" indicates a mandatory requirement.
"))Should((")). Indicates a recommended practice.
(("))WAC((" means)). The Washington Administrative Code.
(("))WISHA((" means)). Washington industrial safety and health administration.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-59-010 Safe place standards.
The safe place requirements of the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-110, ((shall)) must be applicable within the scope of chapter 296-59 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-19-074, filed 9/19/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-59-015 General requirements.
(1) The use of any machinery, tool, material, or equipment which is not in compliance with any applicable requirement of this chapter is prohibited. Such machine, tool, material, or equipment ((shall)) must either be identified as unsafe by tagging or locking the controls to render them inoperable or ((shall)) must be physically removed from its place of operation.
(2) ((The employer shall)) You must permit only those employees qualified by training or experience to operate equipment and machinery.
(3) Employees ((shall)) must use safeguards provided for their protection.
(4) Loose or ragged clothing, scarfs, or ties ((shall)) must not be worn while working around moving machinery.
(5) Workers should not be assigned or permitted to occupy work locations directly under other workers. When such practice is unavoidable, all parties ((shall)) must be made aware of the potential hazard and adequate protective measures ((shall)) must be taken. When adequate protective measures are not available, one party ((shall)) must be moved to eliminate the potential exposure.
(6) Employees ((shall)) must report to their employers the existence of any unsafe equipment or method, or any other hazard which, to their knowledge, is unsafe. Where such unsafe equipment or method or other hazard exists in violation of this chapter it ((shall)) must be corrected.
(7) Housekeeping.
(a) All places of employment ((shall)) must be kept clean to the extent that the nature of the work allows.
(b) The floor of every workroom ((shall)) must be maintained so far as practicable in a dry condition. Where wet processes are used, drainage ((shall)) must be maintained. Where necessary or appropriate, waterproof footgear ((shall)) must be worn.
(c) To facilitate cleaning, every floor, working place, and passageway ((shall)) must be kept free from protruding nails, splinters, loose boards, unnecessary holes and openings or other tripping hazards.
(d) Cleaning and sweeping ((shall)) must be done in such a manner as to minimize the contamination of the air with dust and so far as is practical, ((shall)) be done outside of working hours.
(8) Requirements for warning signs. Ski area operations which use any form of explosive device for avalanche control ((shall)) must display warning, information placards and/or signs as found in chapter 296-52 WAC, Part G.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-59-020 Management's responsibility.
The "safe work environment" section of the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-110, ((shall)) will be applicable within the scope of chapter 296-59 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-59-025 Employee's responsibility.
The "employee responsibilities" section of the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-120, ((shall)) will be applicable within the scope of chapter 296-59 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 88-14-108, filed 7/6/88)
WAC 296-59-027 Work activities which include skiing.
Management ((shall)) must develop a written safety program for all employees whose job duties include skiing. The program ((shall)) must include but is not limited to the following:
(1) The skiing ability and physical condition of individuals ((shall)) must be considered when determining individual job assignments;
(2) The ski equipment used ((shall)) must be appropriate for the individual when performing any given job assignment;
(3) The condition of all ski equipment ((shall)) must be checked by a qualified individual at the beginning of each ski season;
(4) Employees ((shall)) must be instructed not to use ski equipment until it has been checked and approved;
(5) Employees ((shall)) must be instructed to ski within their ability and in control at all times;
(6) Employees ((shall)) must be required to check all ski equipment, including adjustments, before starting work each day;
(7) Employees ((shall)) must be instructed not to use ski equipment which is defective or out of adjustment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-59-030 Safety bulletin board.
The "safety bulletin board" requirements of the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-190, ((shall)) will be applicable within the scope of chapter 296-59 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-05-071, filed 2/17/09, effective 4/1/09)
WAC 296-59-050 Personal protective equipment, general requirements.
(1) Application.
(a) Protective equipment, including personal protective equipment for eyes, face, head, and extremities, protective clothing, respiratory devices, and protective shields and barriers, ((shall)) must be provided at no cost to the employee, used, and maintained in a sanitary and reliable condition wherever it is indicated by reason of hazards of processes or environment, chemical hazards, radiological hazards, or mechanical irritants encountered in a manner capable of causing injury or impairment in the function of any part of the body through absorption, inhalation, or physical contact.
(b) Employee-owned equipment. Where employees provide their own protective equipment, ((the employer shall)) you must be responsible to ((assure)) ensure its adequacy, including proper maintenance, and sanitation of such equipment.
(c) Design, construction, testing, and use of personal protective equipment ((shall)) must comply with the requirements of the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-160; the Occupational health standards—Safety standards for carcinogens, chapter 296-62 WAC; or the currently applicable ANSI standard.
(2) Eye and face protection. Eye and face protective equipment ((shall)) must be provided and worn where there is exposure in the work process or environment to hazard of injury, which can be prevented by such equipment.
(3) Occupational head protection. Employees working in areas where there is a possible danger of head injury from impact, or from falling or flying objects, or from electrical shock and burns, ((shall)) must be protected by protective helmets, i.e., a lift operator would not be required to use a hardhat while operating the lift. However, if that same person is assisting with maintenance operations and is working under a tower where overhead work is being done, that operator would now be required to wear an approved helmet.
(a) Helmets for the protection of employees against impact and/or penetration of falling and flying objects ((shall)) must meet the specifications contained in American National Standards Institute, Z89.1-1986, Safety Requirements for Industrial Head Protection.
(b) Helmets for the head protection of employees exposed to high voltage electrical shock and burns ((shall)) must meet the specifications contained in American National Standards Institute, Z89.2-1971, Safety Requirements for Industrial Protective Helmets for Electrical Workers, Class B.
(c) Approved head protection ((shall)) must be worn by operators of snowmobiles and other mobile oversnow equipment which is not equipped with a rigid metal operator's cab.
(4) Occupational foot protection.
(a) Substantial footwear appropriate for the work conditions encountered ((shall)) must be worn by all employees.
(b) Where the job assignment includes exposure to slipping hazards, soles and heels of footwear ((shall)) must be of such material and design as to reduce the hazard of slipping.
(5) Safety belts, lifelines, lanyards, and nets.
(a) Safety belts, lifelines, and lanyards which meet the requirements of ANSI A10.14 ((shall)) must be provided and used whenever employees are working in locations which expose them to a fall of more than ten feet. The particular work location and application ((shall)) must dictate which type of belt or harness and length of lanyard is used.
(b) Lifelines ((shall)) must be secured to an anchorage or structural member capable of supporting a minimum dead weight of five thousand four hundred pounds.
(c) Lifelines used on rock scaling applications or in areas where the lifeline may be subjected to cutting or abrasion ((shall)) must be a minimum of seven-eighths inch wire core manila rope or equivalent. For all other lifeline applications, three-fourths inch manila rope or equivalent with a minimum break strength of five thousand four hundred pounds may be used.
(d) Each safety belt lanyard ((shall)) must be a minimum of one-half inch nylon, or equivalent, with a minimum of five thousand four hundred pounds breaking strength.
(e) Employees will not be required to wear a safety belt and lanyard while riding on a standard lift chair while seated in the normal riding position.
(f) Safety nets meeting the requirements of ANSI A10.11 ((shall)) must be used when other acceptable forms of fall protection are not useable. When used, safety nets ((shall)) must extend a minimum of eight feet beyond the edge offering exposure, ((shall)) must be hung with sufficient clearance to prevent user's contact with surfaces or objects below, and ((shall)) must not be more than twenty-five feet below the fall exposure edge.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 88-14-108, filed 7/6/88)
WAC 296-59-055 Lockout requirements.
(1) ((Each employer shall)) You must develop a formal written policy and procedure for lockout requirements. The policy ((shall)) must embody the principles of subsection (2) of this section and ((shall)) must clearly state that the procedures must be applied in all instances.
(a) The lockout policy ((shall)) must be posted on all required employee bulletin boards.
(b) The lockout policy and procedures ((shall)) must be made a part of new employee orientation and employee training programs.
(c) Supervisors and crew leadpersons ((shall)) must assure compliance with the published policy and procedures in all instances.
(2) Whenever the unexpected start up of machinery, the energizing of electrical circuits, the flow of material in piping systems, or the removal of guards would endanger workers, such exposure ((shall)) must be prevented by deactivating and locking out the controls as required by this section.
(3) Equipment requirements.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must provide and each employee ((shall)) must use as many padlocks, tags, chains, or devices as are necessary to implement these requirements.
(b) Provisions ((shall)) must be made whereby the source of power or exposure can be locked out in accordance with the requirements of this section.
(c) On electrically powered equipment, "stop/start" control switches ((shall)) must not be used as lockout switches. Lockout switches must be the primary circuit disconnects and must adequately separate both the power source and any auxiliary power unit from the prime mover so that accidental start up of the equipment being locked out is precluded.
(d) Keyed-alike locks, which all open with identical keys, ((shall)) must not be issued as personal lockout locks.
(4) Training requirements.
(a) Each person who will be given authority to implement these requirements ((shall)) must first be thoroughly trained in the requirements and procedures.
(b) Before being given authority to deactivate and lockout a particular system or piece of equipment, authorized personnel ((shall)) must be made fully aware of all power sources and/or material entry sources which may offer exposure.
(c) Checklists ((shall)) must be used to implement effective lockout procedures for complex systems or equipment.
(i) Complex is identified as those systems or equipment which require the locking out of four or more controls to assure isolation or which have controls remote from the immediate work area.
(ii) Checklists ((shall)) must identify all controls necessary to achieve isolation at the intended worksite(s).
(iii) Checklists ((shall)) must provide a space after each listed control to be used for the identity of the person(s) who performed the lockout and required postlockout tests of each control.
(iv) Checklists ((shall)) must be prepared by qualified personnel and approved by the responsible area supervisor before each use.
(5) Control procedure.
(a) Each person who could be exposed to the hazard ((shall)) must apply a personal padlock on each control mechanism. Padlocks ((shall)) must be applied in such a manner as to physically block the controls from being moved into the operating position. Each lock ((shall)) must be personally identified or an information tag identifying the owner ((shall)) must be attached to the lock.
(b) Padlocks used in lockout procedures may only be removed by the person identified on the lock, except, when it is positively determined that the owner/user of the lock has left the premises without removing a lock, the job supervisor may remove the lock in accordance with a specific procedure formulated by the local plant labor management safety committee or approved by the department.
(6) Testing after lockout or tagout. After tagging or locking out equipment, a test ((shall)) must be conducted to ascertain that the equipment has been made inoperative or the flow of material has been positively stopped. Precautions ((shall)) must be taken to ascertain that persons will not be subjected to any hazard while conducting the test if the power source or flow of material is not shut off.
(7) Temporary or alternate power to be avoided. Whenever possible, temporary or alternate sources of power to the equipment being worked on ((shall)) must be avoided. If the use of such power is necessary, all affected employees ((shall)) must be informed and the source of temporary or alternate power ((shall)) must be identified.
(8) Where tags or signs are required to implement the lockout and control procedures, the tag and attachment device ((shall)) must be constructed of such material that it will not be likely to deteriorate in the environment that it will be subjected to.
(9) Provisional exception. Electrical lighting and instrument circuits of two hundred forty volts or less on single phase systems or two hundred seventy-seven volts on three-phase systems may be exempted from the lockout requirements of subsection (5)(a) of this section provided that:
(a) An information tag meeting the requirements of subsection (8) of this section is used in lieu of a padlock.
(b) The information tag ((shall)) must be placed on the switch or switch cover handle in such a manner as to easily identify the deactivated switchgear.
(10) Deactivating piping systems.
(a) Hazardous material systems are defined as:
(i) Gaseous systems that are operated at more than two hundred psig;
(ii) Systems containing any liquid at more than five hundred psig;
(iii) Systems containing any material at more than 130°F;
(iv) Systems containing material which is chemically hazardous as defined by NFPA 704 M Class 3 and 4; and
(v) Systems containing material classified as flammable or explosive as defined in NFPA Class I.
(b) Lockout of piping systems ((shall)) must provide isolation to the worksite, including backflow where such potential exists and where the system is classified as a hazardous material system. The required method ((shall)) must be applied based on the content of the system as specified below:
(i) Nonhazardous systems ((shall)) must be deactivated by locking out either the pump or a single valve.
(ii) Hazardous material systems ((shall)) must be deactivated by one of the following methods:
(A) Locking out both the pump and one valve between the pump and the worksite;
(B) Locking out two valves between the hazard source and the worksite;
(C) Installing and locking out a blank flange between the hazard source and worksite.
Exception: | Aerial tramways and lifts, surface lifts and tows. It is recognized that some inspection, testing, running adjustments, and maintenance tasks cannot be accomplished on this equipment while using standard lockout procedures, particularly when using a work platform suspended from the haulrope. Management of each ski area shall therefore develop a specific written procedure to be used in any instance where any potentially exposed personnel cannot personally lock the controls. The procedure for each area shall meet the following minimum requirements: |
(I) The controls ((shall)) must be attended by a qualified operator at all times when personnel are in potentially exposed work positions and the controls are not padlocked out.
(II) Direct communication capability between the control operator and remote work crew ((shall)) must be maintained at all times.
(III) All personnel involved ((shall)) must be thoroughly trained in the exact procedures to be followed.
(IV) Extension tools which minimize personnel exposure ((shall)) must be used where possible.
(V) The equipment ((shall)) must be operated at the slowest speed possible consistent with the task at hand.
(VI) This exception ((shall)) must not be used by more than one workcrew at more than one remote location on any single piece of equipment or system.
(VII) This exception is limited to work on the haulrope, towers, and replacing bullwheel liners. For all other work on the bullwheels or drive operations, the master disconnect ((shall)) must be deactivated and locked out.
Note: | See Appendix 1 for illustrative example. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 95-04-007, filed 1/18/95, effective 3/1/95)
WAC 296-59-060 Vessel or confined area requirements.
The requirements of WAC 296-62-145 through 296-62-14529, general occupational health standards for permit - Required confined spaces, ((shall)) will be applicable within the scope of chapter 296-59 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-59-065 Fire protection and ignition sources.
The requirements of WAC 296-24-585 and 296-800-300, et seq., relating to fire protection requirements, ((shall)) will be applicable within the scope of chapter 296-59 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-59-070 Illumination.
(1) Sufficient illumination required. All areas ((shall)) must be sufficiently illuminated in order that persons in the area can safely perform their assigned duties. The recommended levels of illumination specified in the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-210, ((shall)) must be followed. When areas are not specifically referred to in chapter 296-800 WAC and the adequacy of illumination for the area or task performed is questionable, a determination of the amount of illumination needed may be made by the division of industrial safety and health.
(2) Emergency or secondary lighting system required.
(a) There ((shall)) must be an emergency or secondary lighting system which can be actuated immediately upon failure of the normal power supply system. The emergency or secondary lighting system ((shall)) must provide illumination in the following areas:
(i) Wherever it is necessary for workers to remain at their machine or station to shut down equipment in case of power failure;
(ii) At stairways and passageways or aisleways used by workers as an emergency exit in case of power failure;
(iii) In all plant first-aid and/or medical facilities;
(iv) In emergency power and control room, i.e., in emergency generator rooms unless arranged to start automatically in the event of power failure, or on ski lift motor drive rooms where it would be necessary for employees to switch on the emergency drive system during night skiing.
(b) Emergency lighting facilities ((shall)) must be checked at least every thirty days for mechanical defects. Defective equipment ((shall)) must be given priority for repair schedule.
(3) Extension cord type lights. All extension cord type lights ((shall)) must be provided with proper guards.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 88-14-108, filed 7/6/88)
WAC 296-59-075 Electrical equipment and distribution.
(1) National Electrical Code to prevail. All electrical installations and electrical utilization equipment ((shall)) must comply with the National Electrical Code requirements.
Exception: | In instances where (N.E.C.) conflicts with ANSI B77.1 with respect to tramways, surface lifts, or tows, ANSI B77.1 shall prevail. |
(2) Authorized personnel to do electrical work. Only those persons who are qualified to do the work assigned and are authorized by ((the employer shall)) you, must be allowed to perform electrical work on any electrical equipment or wiring installations.
(3) High voltage areas to be guarded. Motor rooms, switch panel rooms, or other areas where persons may come in contact with high voltages ((shall)) must be fenced off or be enclosed in a separate area. The gate, door, or access to such area ((shall)) must be posted with a notice stating that only authorized persons are allowed in the area.
(4) Control panels. In areas where mobile equipment operates, floor stand panels ((shall)) must be protected from being struck by moving equipment. Start or run handles and buttons ((shall)) must be protected from accidental actuation.
(5) Switches or control devices. Switches, circuit breakers, or other control devices ((shall)) must be ((so)) located so that they are readily accessible for activation or deactivation and ((shall)) must be marked to indicate their function or machine which they control. The positions of ON and OFF ((shall)) must be marked or indicated and provision ((shall)) must be made for locking out the circuit.
(6) Starting requirements for electrically driven equipment after power failure. Electrically driven equipment ((shall)) must be ((so)) designed so that it will not automatically start upon restoration of power after a power failure if it will create a hazard to personnel.
(7) Posting equipment automatically activated or remotely controlled. Equipment which is automatically activated or remotely controlled ((shall)) must be posted, warning persons that machine may start automatically if it will create a hazard to personnel.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 88-14-108, filed 7/6/88)
WAC 296-59-080 Installation, inspection, and maintenance of pipes, piping systems, and hoses.
(1) ((Definitions applicable to this section.
(a) "Hazardous material system" is any system within the following classifications:
(i) "Flammable or explosive" - any system containing materials which are hazardous because they are easily ignited and create a fire or explosion hazard, defined by NFPA as Class I liquids;
(ii) "Chemically active or toxic" - any system containing material which offers corrosion or toxic hazard in itself or can be productive of harmful gases upon release, defined by NFPA 704M as Class 3 and 4 materials;
(iii) "Thermally hazardous" - any system above 130°F which exposes persons to potential thermal burns;
(iv) "Pressurized" - any gaseous system above two hundred psig or liquid system above five hundred psig.
(b) "Piping system" - any fixed piping, either rigid pipe or flexible hose, including all fittings and valves, in either permanent or temporary application.
(2))) Design and installation. All new piping systems intended to be used in hazardous material service ((shall)) must be designed and installed in accordance with applicable provisions of the ASME Code for Pressure Piping or in accordance with applicable provisions of ANSI B31.1 through B31.8. The referenced edition in effect at the time of installation ((shall)) must be utilized.
Note: | Both referenced standard have identical requirements. |
(((3))) (2) Inspection and maintenance.
(a) Management ((shall)) must develop a formal program of inspections for all hazardous material piping systems. The program ((shall)) must be based on sound maintenance engineering principles and ((shall)) must demonstrate due consideration for the manufacturing specifications of the pipe, hose, valves, and fittings, the ambient environment of the installation and the corrosive or abrasive effect of the material handled within the system.
(b) Type and frequency of tests and/or inspections and selection of inspection sites ((shall)) must be adequate to give indications that minimum safe design operating tolerances are maintained. The tests may include visual and nondestructive methods.
(c) ((All employers shall submit their)) You must submit your formal program of initial and ongoing inspections to the department for approval within one year after the effective date of this requirement.
(d) All existing hazardous material systems ((shall)) must be inspected to the criteria of this section prior to two years after effective date, or in accordance with a schedule approved by the department.
(((4))) (3) Inspection records.
(a) Results of inspections and/or tests ((shall)) must be maintained as a record for each system.
(b) Past records may be discarded provided the current inspection report and the immediate preceding two reports are maintained.
(c) When a system is replaced, a new record ((shall)) must be established and all past records may be discarded.
(d) The records for each system ((shall)) must be made available for review by the department upon request.
(e) ((The employer)) You may omit the inspection requirements for portions of existing systems that are buried or enclosed in permanent structures in such a manner as to prevent exposure to employees even in the event of a failure.
(((5))) (4) Systems or sections of systems found to be below the minimum design criteria requirements for the current service ((shall)) must be repaired or replaced with component parts and methods which equal the requirements for new installations.
(((6))) (5) Identification of piping systems.
(a) Pipes containing hazardous materials ((shall)) must be identified. It is recommended that USAS A13.1 "Scheme for Identification of Piping Systems" be followed.
(b) Positive identification of piping system content ((shall)) must be identified by lettered legend giving the name of the content in full or abbreviated form, or a commonly used identification system. Such identification ((shall)) must be made and maintained at suitable intervals and at valves, fittings, and on both sides of walls or floors. Arrows may be used to indicate the direction of flow. Where it is desirable or necessary to give supplementary information such as hazard of use of the piping system content, this may be done by additional legend or by color applied to the entire piping system or as colored bands. Legends may be placed on colored bands.
Examples of legends which may give both positive identification and supplementary information regarding hazards or use are:
Ammonia . . . . |
Hazardous liquid or gas |
|
Chlorine . . . . |
Hazardous liquid or gas |
|
Liquid caustic . . . . |
Hazardous liquid |
|
Sulphuric acid . . . . |
Hazardous liquid |
|
Natural gas . . . . |
Flammable/explosive gas |
|
Note: | Manual L-1, published by Chemical Manufacturers Association, Inc., is a valuable guide in respect to supplementary legend. |
(c) When color, applied to the entire piping system or as colored bands, is used to give supplementary information it should conform to the following:
CLASSIFICATION |
PREDOMINANT COLOR |
F-Fire-protection equipment . . . . |
Red |
D-Dangerous materials . . . . |
Yellow (or orange) |
S-Safe materials . . . . |
Green (or the achromatic colors, white, black, gray, or aluminum) |
And, when required, P-Protective materials . . . . |
Bright blue |
(d) Legend boards showing the color and identification scheme in use ((shall)) must be prominently displayed at each plant. They ((shall)) must be located so that employees who may be exposed to hazardous material piping systems will have a frequent reminder of the identification program.
(e) All employees who work in the area of hazardous material piping systems ((shall)) must be given training in the color and identification scheme in use.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-59-085 Scaffolds, construction, use, and maintenance.
(1) Whenever work must be performed at a height which cannot be reached from the floor or permanent platform and where it would not be a safe practice to use a ladder, a properly constructed scaffold ((shall)) must be provided and used.
(2) Scaffolds ((shall)) must be constructed and used in compliance with WAC 296-24-860 through 296-24-862.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-11-060, filed 5/19/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-59-090 Mobile equipment and lift trucks.
(1) Mobile equipment ((shall)) must be designed, constructed, maintained, and used in accordance with this section and appropriate ANSI and/or S.A.E. requirements.
(2) Operator training.
(a) Methods ((shall)) must be devised by management to train personnel in the safe operation of mobile equipment.
(b) Training programs for all mobile equipment ((shall)) must include the manufacturer's operating instructions when such instructions are available.
(c) Only trained and authorized operators ((shall)) must be permitted to operate such vehicles.
(3) Special duties of operator. Special duties of the operator of a power-driven vehicle ((shall)) must include the following:
(a) Test brakes, steering gear, lights, horns, warning devices, clutches, etc., before operating vehicle;
(b) Not move a vehicle while an unauthorized rider is on the vehicle;
(c) Slow down and sound horn upon approaching blind corners or other places where vision or clearance is limited;
(d) Comply with all speed and traffic regulations and other applicable rules;
(e) Have the vehicle being operated under control at all times so that he can safely stop the vehicle in case of emergency; and
(f) Keep the load on the uphill side when driving a forklift vehicle on a grade.
(4) Operator to be in proper position. Control levers of lift trucks, front end loaders, or similar types of equipment ((shall)) must not be operated except when the operator is in ((his)) their proper operating position.
(5) Raised equipment to be blocked. Employees ((shall)) must not work below the raised bed of a dump truck, raised buckets of front end loaders, raised blades of tractors or in similar positions without blocking the equipment in a manner that will prevent it from falling. When working under equipment suspended by use of jacks, safety stands or blocking ((shall)) must be used in conjunction with the jack.
(6) Precautions to be taken while inflating tire. Unmounted split rim wheels ((shall)) must be placed in a safety cage or other device ((shall)) must be used which will prevent a split rim from striking the worker if it should dislodge while the tire is being inflated.
(7) Reporting suspected defects. If, in the opinion of the operator, a power-driven vehicle is unsafe, the operator ((shall)) must report the suspected defect immediately to the person in charge. Any defect which would make the vehicle unsafe to operate under existing conditions ((shall)) must be cause for immediate removal from service. The vehicle ((shall)) must not be put back into use until it has been made safe.
(8) Safe speed. Vehicles ((shall)) must not be driven faster than a safe speed compatible with existing conditions.
(9) Unobstructed view.
(a) Vehicle operators ((shall)) must have a reasonably unobstructed view of the direction of travel. Where this is not possible, the operator ((shall)) must be directed by a person or by a safe guidance means or device.
(b) Where practical, mirrors ((shall)) must be installed at blind corners or intersections which will allow operators to observe oncoming traffic.
(c) It is recommended that vehicles operating in congested areas be provided with an automatic audible or visual alarm system.
(10) Passengers to ride properly.
(a) Passengers ((shall)) must not be permitted to ride with legs or arms extending outside the running lines of the cab, FOPS, or ROPS of any vehicle.
(b) Passengers on mobile oversnow equipment ((shall)) must ride within the cab unless exterior seating is provided. The exterior seating may include the cargo bed provided that the bed is equipped with sideboards and a tailgate at least ten inches high. If passengers are permitted to stand in the bed, adequate handholds ((shall)) must be provided.
(c) The number of passengers and seating arrangements within the cab on any mobile equipment ((shall)) must not interfere with the operator's ability to safely operate the equipment.
(d) Exterior passengers ((shall)) must not be permitted on mobile oversnow equipment which has snow grooming equipment mounted on the bed or when the machine is towing any kind of equipment, sleds, etc.
(e) Operators ((shall)) must use good judgment with respect to speed and terrain when carrying exterior passengers.
(11) Horns and lights.
(a) Every vehicle ((shall)) must be provided with an operable horn distinguishable above the surrounding noise level.
(b) Any vehicle required to travel away from an illuminated area ((shall)) must be equipped with a light or lights which adequately illuminate the direction of travel.
(12) Brakes on power-driven vehicles. Vehicles ((shall)) must be equipped with brakes and devices which will hold a parked vehicle with load on any grade on which it may be used. The brakes and parking devices ((shall)) must be kept in proper operating condition at all times.
(13) Cleaning vehicles. All vehicles ((shall)) must be kept free of excessive accumulations of dust and grease which may present a hazard.
(14) Lifting capacity of vehicle to be observed. At no time ((shall)) must a load in excess of the manufacturer's maximum lifting capacity rating be lifted or carried. Such lifting capacity may only be altered with the approval of the equipment manufacturer or a qualified design engineer.
(15) Posting rated capacity. The maximum rated lifting capacity of all lift trucks ((shall at all times)) must be posted at all times on the vehicle in such a manner that it is readily visible to the operator.
(16) Carrying loose material. Lift trucks ((shall)) must not be used to carry loose loads of pipe, steel, iron, lumber, palletized material, rolls of paper, or barrels unless adequate clearance is provided and the loads are stabilized.
(17) Position of lift forks or clamps. The forks or clamps of lift trucks ((shall)) must be kept as low as possible while the vehicle is moving. They ((shall)) must be lowered to the ground or floor when the vehicle is parked.
(18) Walking under loads prohibited. No person ((shall)) will be allowed under the raised load of a lift truck, backhoe, or front end loader.
(19) Hoisting of personnel on vehicle forks prohibited. Personnel ((shall)) must not be hoisted by standing directly on the forks of vehicles.
(20) Using forklifts as elevated work platforms. A platform or structure built specifically for hoisting persons may be used providing the following requirements are met:
(a) The structure must be securely attached to the forks and ((shall)) must have standard guardrails and toeboards installed on all sides;
(b) The hydraulic system ((shall)) must be so designed that the lift mechanism will not drop faster than one hundred thirty-five feet per minute in the event of a failure in any part of the system. Forklifts used for elevating work platforms ((shall)) must be identified that they are so designed;
(c) A safety strap ((shall)) must be installed or the control lever ((shall)) must be locked to prevent the boom from tilting;
(d) An operator ((shall)) must attend the lift equipment while workers are on the platform;
(e) The operator ((shall)) must be in the normal operating position while raising or lowering the platform. A qualified operator ((shall)) must remain in attendance whenever an employee is on the work platform;
(f) The vehicle ((shall)) must not travel from point to point while workers are on the platform except that inching or maneuvering at very slow speed is permissible; and
(g) The area between workers on the platform and the mast ((shall)) must be adequately guarded to prevent contact with chains or other shear points.
(21) Overhead guards on lift trucks. All lift trucks ((shall)) must be equipped with an overhead guard constructed and installed to conform to USAS B56.1-1969 "Safety Code for Powered Industrial Trucks." This guard may be removed only when it cannot be used due to the nature of the work being performed in which case loads ((shall)) must be maintained so as not to create a hazard to the operator.
(22) Protection from exhaust system. Any exhaust system which might be exposed to contact ((shall)) must be properly insulated or isolated to protect personnel. Exhaust systems on lift trucks and jitneys ((shall)) must be constructed to discharge either within twenty inches from the floor or eighty-four inches or more above the floor. The exhausted gases ((shall)) must be directed away from the operator. The equipment ((shall)) must be designed in such a manner that the operator will not be exposed to the fumes.
(23) Emergency exit from mobile equipment. Mobile equipment with an enclosed cab ((shall)) must be provided with an escape hatch or other method of exit in case the regular exit cannot be used.
(24) Vehicle wheels chocked. When driving mobile equipment onto the bed of a vehicle, the wheels of the vehicle ((shall)) must be chocked.
(25) Prevent trailer from tipping. Suitable methods ((shall)) must be used or devices installed which will prevent the trailer from tipping while being loaded or unloaded.
(26) Refueling. Gasoline or LPG engines ((shall)) must be shut off during refueling.
(27) Close valve on LPG container. Whenever vehicles using LP gas as a fuel are parked overnight or stored for extended periods of time indoors, with the fuel container in place, the service valve of the fuel container ((shall)) must be closed.
(28) LPG tanks. LPG vehicle fuel tanks ((shall)) must be installed and protected in a manner which will minimize the possibility of damage to the tank.
(29) Inspecting and testing of LPG containers. LPG containers ((shall)) must be inspected and tested as required by chapter 296-24 WAC.
(30) Spinners on steering wheels. The use of spinners on steering wheels ((shall)) must be prohibited unless an antikick device is installed or the equipment has a hydraulic steering system.
(31) The requirements of chapter 296-817 WAC, Hearing loss prevention (noise), apply to mobile equipment operation.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 88-14-108, filed 7/6/88)
WAC 296-59-095 Requirements for cranes and hoists—General safety and health standards to prevail.
All applicable rules for design, construction, maintenance, operation, and testing of cranes and hoists contained in the General safety and health standards, chapter 296-24 WAC, ((shall)) must be met.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 88-14-108, filed 7/6/88)
WAC 296-59-115 Ski lift facilities and structures.
(1) Existing ski lift facilities and structures ((shall)) must not be required to be retrofitted with standard construction work platforms, walkways, stairs or guardrails on exterior surfaces when such features would add significantly to snow loading considerations. When such standard protective features are omitted, alternative personal protective measures ((shall)) must be used where possible. Examples include but are not limited to: Safety belt and lanyard, ladder climbing safety devices, temporary work platforms or scaffolds, temporary or removable handrails, guardrails, or walkways.
(2) Snow removal.
(a) During the operating season, standard guardrails which would interfere with snow removal may be omitted in areas where it can be anticipated that frequent snow removal will be necessary to maintain operability of ski lift apparatus. Examples could include but are not limited to the motor house roof or loading and unloading areas.
(b) Personnel barricades, signs, or other devices ((shall)) must be used to deflect traffic or warn personnel of existing fall hazards.
(3) All ski lift towers installed after the effective date of this standard ((shall)) must be equipped with permanent ladders or steps which meet the following minimum requirements:
(a) The minimum design live load ((shall)) must be a single concentrated load of two hundred pounds.
(b) The number and position of additional concentrated live load units of two hundred pounds each as determined from anticipated usage of the ladder ((shall)) must be considered in the design.
(c) The live loads imposed by persons occupying the ladder ((shall)) must be considered to be concentrated at such points as will cause the maximum stress in the structural member being considered.
(d) The weight of the ladder and attached appurtenances together with the live load ((shall)) must be considered in the design of rails and fastenings.
(e) All rungs ((shall)) must have a minimum diameter of three-fourths inch.
(f) The distance between rungs on steps ((shall)) must not exceed twelve inches and shall be uniform throughout the ladder length. The top rung ((shall)) must be located at the level of the landing or equipment served by the ladder.
(g) The minimum clear length of rungs or steps ((shall)) must be sixteen inches on new installations.
(h) Rungs, cleats, and steps ((shall)) must be free of sharp edges, burrs, or projections which may be a hazard.
(i) The rungs of an individual-rung ladder ((shall)) must be so designed that the foot cannot slide off the end. (A suggested design is shown in Figure D-1, at the end of this section.)
(j) Side rails which might be used as a climbing aid ((shall)) must be of such cross sections as to afford adequate gripping surface without sharp edges or burrs.
(k) Fastenings((. Fastenings shall)) must be an integral part of fixed ladder design.
(l) All splices made by whatever means ((shall)) must meet design requirements as noted in (a) of this subsection. All splices and connections ((shall)) must have smooth transition with original members and with no sharp or extensive projections.
(m) Adequate means ((shall)) must be employed to protect dissimilar metals from electrolytic action when such metals are joined.
(n) ((Welding.)) All welding ((shall)) must be in accordance with the "Code for Welding in Building Construction" (AWS D1.0-1966).
(o) Protection from deterioration. Metal ladders and appurtenances ((shall)) must be painted or otherwise treated to resist corrosion and rusting when location demands.
(4) Installation and clearance.
(a) Pitch.
(i) The preferred pitch of fixed ladders is between the range of seventy-five degrees and ninety degrees with the horizontal (Figure D-4).
(ii) Substandard pitch. Fixed ladders ((shall)) must be considered as substandard if they are installed within the substandard pitch range of forty-five and seventy-five degrees with the horizontal. Substandard fixed ladders are permitted only where it is found necessary to meet conditions of installation. This substandard pitch range is considered as a critical range to be avoided, if possible.
(iii) Pitch greater than ninety degrees. Ladders having a pitch in excess of ninety degrees with the horizontal are prohibited.
(b) Clearances.
(i) The perpendicular distance from the centerline of the rungs to the nearest permanent object on the climbing side of the ladder ((shall)) must be thirty-six inches for a pitch of seventy-six degrees, and thirty inches for a pitch of ninety degrees (Figure D-2), with minimum clearances for intermediate pitches varying between these two limits in proportion to the slope.
(ii) A clear width of at least fifteen inches ((shall)) must be provided each way from the centerline of the ladder in the climbing space.
(iii) The side rails of through or side-step ladder extensions ((shall)) must extend three and one-half feet above parapets and landings.
(A) For through ladder extensions, the rungs ((shall)) must be omitted from the extension and ((shall)) must have not less than eighteen nor more than twenty-four inches clearance between rails.
(B) For side-step or offset fixed ladder sections, at landings, the side rails and rungs ((shall)) must be carried to the next regular rung beyond or above the three and one-half feet minimum.
(iv) Grab bars ((shall)) must be spaced by a continuation of the rung spacing when they are located in the horizontal position. Vertical grab bars ((shall)) must have the same spacing as the ladder side rails. Grab bar diameters ((shall)) must be the equivalent of the round-rung diameters.
(v) Clearance in back of ladder. The distance from the centerline of rungs, cleats, or steps to the nearest permanent object in back of the ladder ((shall)) must be not less than seven inches, except that when unavoidable obstructions are encountered, minimum clearances as shown in Figure D-3 shall be provided.
(vi) Clearance in back of grab bar. The distance from the centerline of the grab bar to the nearest permanent object in back of the grab bars ((shall)) must be not less than four inches. Grab bars ((shall)) must not protrude on the climbing side beyond the rungs of the ladder which they serve.
(c) The step-across distance from the nearest edge of a ladder to the nearest edge of the equipment or structure ((shall be)) must not be more than twelve inches, or less than two and one-half inches. However, the step-across distance may be as much as twenty inches provided:
(i) The climber is wearing a safety belt and lanyard; and
(ii) The lanyard is attached to the tower structure before the climber steps off the ladder.
(5) Ski lift towers are not required to be equipped with ladder cages, platforms or landings.
(6) Maintenance and use.
(a) All ladders ((shall)) must be maintained in a safe condition. All ladders ((shall)) must be inspected regularly, with the intervals between inspections being determined by use and exposure.
(b) When ascending or descending, the climber must face the ladder.
(c) Personnel ((shall)) must not ascend or descend ladders while carrying tools or materials which could interfere with the free use of both hands.
(7) Personnel ((shall)) must be provided with and ((shall)) must use ladder safety devices or safety belts and lanyards whenever feasible.
(8) Personnel ((shall)) must not place mobile equipment or personal equipment such as skis, ski poles, or large tools within the falling radius of the lift tower while climbing or working on the lift tower.
(9) Ski lift towers and terminals are not required to be equipped with sheave guards on the haulrope wheels.
(10) Ski lift towers are not required to be equipped with work platforms.
(11) Personnel ((shall)) must use personal protective equipment such as ((a)) safety belts and lanyards when working at unprotected elevated locations. Exception to this requirement ((shall)) must only be permitted for emergency rescue or emergency inspection if a safety belt and lanyard is not immediately available. Required personal protective equipment ((shall)) must be made available as quickly as possible.
(12) When fixed ladders on towers do not reach all the way down to the ground or snow level, a specifically designed and constructed portable ladder ((shall)) must be used for access to and from the fixed ladder. Portable ladders ((shall)) must be constructed and maintained to the following requirements:
(a) The portable ladder ((shall)) must be constructed in accordance with applicable provisions of subsection (3) of this section.
(b) The portable ladder ((shall)) must be constructed with a minimum of two attachment hooks near the top to be utilized for securing the portable ladder onto the fixed ladder.
(c) The attachment hooks ((shall)) must be installed to support the portable ladder near the fixed ladder ((siderails)) side rails.
(d) Rungs or steps on the portable ladder ((shall)) must be spaced to be identical with rungs or steps on the fixed ladder when the portable ladder is attached for use. The design criteria ((shall be to)) must achieve a horizontal plane relationship on the top (walking surface) portion of both steps when overlapping is necessary.
(e) The portable ladder ((shall)) must be equipped with a hold-out device near the bottom to assure clearance behind the steps as required by subsection (4)(b)(v) of this section.
 |
FIGURE D-1 |
 |
FIGURE D-2 Minimum Ladder Clearance |
 |
FIGURE D-3 Clearance for Unavoidable Obstruction at Rear of Fixed Ladder. |
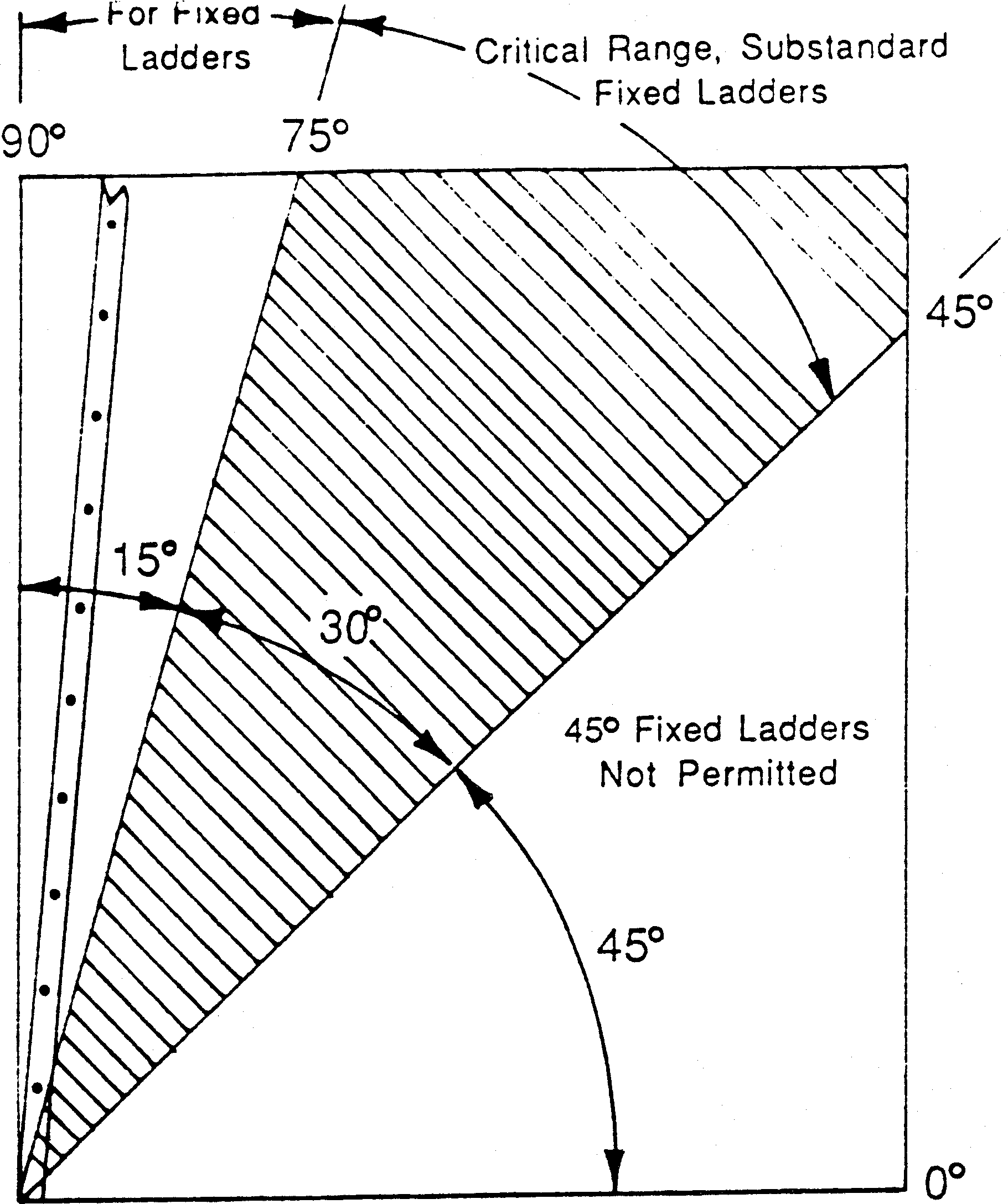 |
FIGURE D-4 Fixed Ladder Range |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 88-14-108, filed 7/6/88)
WAC 296-59-120 Ski lift operations.
(1) Operators.
(a) Only trained and qualified lift operators ((shall)) must be permitted to operate any lift while it is carrying passengers.
(b) Management designated trainees ((shall)) must only be permitted to operate a lift while under the direct supervision of a qualified operator or trainer.
(c) Initial training of operators ((shall)) must be accomplished when the lift is not carrying passengers.
(d) Operator training ((shall)) must include:
(i) Standard and emergency start up procedures;
(ii) Standard and emergency stopping procedures;
(iii) Lockout procedures;
(iv) Corrective actions for operating malfunctions;
(v) Specific instructions on who to contact for different kinds of rescue emergencies;
(vi) Specific instructions on standard operating procedures with respect to the hazard of loading or unloading passengers proximate to the moving lift chairs.
(2) Operators and helpers ((shall)) must prepare and maintain the loading and unloading work stations in a leveled condition and, to the extent possible, free from slipping hazards caused by ice, ruts, excessive snow accumulation, tools, etc.
(3) Daily start up procedure.
(a) Loading station operators ((shall)) must test all operating controls and stopping controls before permitting any personnel or passengers to load on the lift.
(b) The lift must travel a distance of two times the longest tower span before any employee can load on a chair to go to the remote station.
(c) A qualified operator ((shall)) must be the first passenger on each lift each day.
Exception: | The avalanche control team and the emergency rescue team may use any operable lift at anytime for that work. They may use lifts without a remote operator provided that direct communications are maintained to the operator and the operator has successfully completed normal daily safety and operating control checks at the operating station in use. |
(d) ((Enroute)) En route to the remote station, the remote operator ((shall)) must visually inspect each tower as the chair or gondola proceeds to the remote station.
(e) The remote operator ((shall)) must stop the system when he/she has reached the remote control station. The operator ((shall)) must then conduct the daily safety and operating control checks on the remote station.
(f) The remote operator ((shall)) must ensure that the unloading area is groomed to adequately accommodate normal unloading.
(g) When all controls are checked and functioning correctly and the unloading area is prepared, the remote operator ((shall)) must communicate to the operator that the system can be placed in normal operation.
(4) Operators ((shall)) must report to their work station wearing adequate clothing for inclement weather which may be encountered. This requirement ((shall)) must include reasonably water resistant footwear which ((shall)) must have a slip resistant sole tread.
(5) While the lift is in operation and carrying passengers, operators ((shall)) must not permit any activity in the loading/unloading areas which could distract their attention from the principle duty of safely loading or unloading passengers.
(6) Means of communication ((shall)) must be maintained between the top operator and bottom operator stations.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 88-14-108, filed 7/6/88)
WAC 296-59-125 Ski lift aerial work platforms.
(1) Construction and loading.
(a) All aerial work platforms ((shall)) must be constructed to sustain the permissible loading with a safety factor of four. The load permitted ((shall)) must be calculated to include:
(i) The weight of the platform and all suspension components;
(ii) The weight of each permitted occupant calculated at two hundred fifty pounds per person including limited handtools;
(iii) The weight of any additional heavy tools, equipment, or supplies for tasks commonly accomplished from the work platform.
(b) The floor of the platform ((shall)) must not have openings larger than two inches in the greatest dimension.
(c) The platform ((shall)) must be equipped with toeboards at least four inches high on all sides.
(d) Guardrails.
(i) The platform ((shall)) must be equipped with standard height and strength guardrails where such guardrails will pass through the configuration of all lifts on which it is intended to be used.
(ii) Where guardrails must be less than thirty-six inches high in order to clear carriages, guideage, etc., guardrails ((shall)) must be as high as will clear the obstructions but never less than twelve inches high.
(iii) If the work platform is equipped with an upper work level, the upper level platform ((shall)) must be equipped with a toeboard at least four inches high.
(iv) Each platform ((shall)) must be equipped with a lanyard attachment ring for each permissible occupant to attach a safety belt lanyard.
(v) Each lanyard attachment ring ((shall)) must be of such strength as to sustain five thousand four hundred pounds of static loading for each occupant permitted to be attached to a specific ring.
(vi) Attachment rings ((shall)) must be permanently located as close to the center balance point of the platform as is practical.
(vii) The rings may be movable, for instance, up and down a central suspension rod, but ((shall)) must not be completely removable.
(e) Platform attachment.
(i) The platform ((shall)) must be suspended by either a standard wire rope four part bridle or by solid metal rods, bars, or pipe.
(ii) The attachment means chosen ((shall)) must be of a type which will prevent accidental displacement.
(iii) The attachment means ((shall)) must be adjusted so that the platform rides level when empty.
(f) Maintenance.
(i) Every aerial work platform ((shall)) must be subjected to a complete annual inspection by qualified personnel.
(ii) The inspection ((shall)) must include all structural members, welding, bolted or treaded fittings, and the suspension components.
(iii) Any defect noted ((shall)) must be repaired before the platform is placed back in service.
(iv) A written record ((shall)) must be kept for each annual inspection. The record ((shall)) must include:
(A) The inspector identification;
(B) All defects found;
(C) The identity of repair personnel;
(D) Identity of the postrepair inspector who accepted the platform for use.
(g) The platform ((shall)) must be clearly identified as to the number of permissible passengers and the weight limit of additional cargo permitted.
(i) Signs ((shall)) must be applied on the outside of each side panel.
(ii) Signs ((shall)) must be maintained in clearly legible condition.
(h) Unless the side guardrail assembly is at least thirty-six inches high on all sides, signs ((shall)) must be placed on the inside floor or walls to clearly inform all passengers that they must use a safety belt and lanyard at all times when using the platform.
(2) Work platform use.
(a) Platforms ((shall)) must be attached to the haulrope with an attachment means which develops a four to one strength factor for the combined weight of the platform and all permissible loading.
(b) The haulrope attachment means ((shall)) must be designed to prevent accidental displacement.
(c) Trained and competent personnel ((shall)) must attach and inspect the platform before each use.
(d) Passengers ((shall)) must be provided with and ((shall)) must use the correct safety harness and lanyard for the intended work.
(e) Any time a passenger's position is not protected by a standard guardrail at least thirty-six inches high, the individual ((shall)) must be protected by a short lanyard which will not permit free-fall over the platform edge.
(f) When personnel are passengers on a work platform and their work position requires the use of a safety harness and lanyard, the lanyard ((shall)) must be attached to the work platform, not to the haulrope or tower.
(g) Work platform passengers ((shall)) must face in the direction of travel when the lift is moving.
(h) Tools, equipment and supplies ((shall)) must be loaded on the platform in such a fashion that the loaded platform can safely pass all towers and appurtenances.
(i) Heavy tools, equipment or supplies ((shall)) must be secured in place if they could fall over or roll within the platform and create a hazard for passengers.
(j) When the work crew is traveling on the work platform, the lift ((shall)) must be operated at a speed which is safe for that particular system and the conditions present.
Note: | See Appendix 2 for operating procedure requirements. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-59-130 Ski lift machinery guarding.
(1) Moving machine parts that are located within normal reach ((shall)) must be fitted with safety guards in compliance with chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
(a) The coupling apparatus for the ski lift emergency drive may be provided with a removable or swing guard.
(b) When removable or swing guards are used, the guard and mounting means ((shall)) must be so designed and constructed as to sustain a two hundred fifty pound weight loading without displacement.
(2) All guards ((shall)) must be maintained in good condition and ((shall)) must be secured in place when the equipment is in operation except for inspection and adjustment purposes.
(3) The drive machinery and primary control apparatus ((shall)) must be installed in a facility which can prevent access by unauthorized personnel. The access door ((shall)) must have a sign which states that entry is restricted to authorized personnel.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-78-500 Foreword.
(1) General requirements. The chapter 296-78 WAC ((shall)) will apply to and include safety requirements for all installations where the primary manufacturing of wood building products takes place. The installations may be a permanent fixed establishment or a portable operation. These operations ((shall)) will include, but are not limited to, log and lumber handling, sawing, trimming and planing, plywood or veneer manufacturing, canting operations, waste or residual handling, operation of dry kilns, finishing, shipping, storage, yard and yard equipment, and for power tools and affiliated equipment used in connection with such operation. WAC 296-78-450 shall apply to shake and shingle manufacturing. The provisions of WAC 296-78-500 through 296-78-84011 are also applicable in shake and shingle manufacturing except in instances of conflict with the requirements of WAC 296-78-705. (Rev. 1-28-76.)
(2) This standard ((shall)) will augment the Washington state general safety and health standards, general occupational health standards, electrical workers safety rules, and any other standards which are applicable to all industries governed by chapter 80, Laws of 1973, Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act. In the event of any conflict between any portion of this chapter and any portion of any of the general application standards, the provisions of this chapter 296-78 WAC, ((shall)) will apply.
(3) In exceptional cases where compliance with specific provisions of this chapter can only be accomplished to the serious detriment and disadvantage of an operation, variance from the requirement may be permitted by the director of the department of labor and industries after receipt of application for variance which meets the requirements of chapter 296-900 WAC.
(4) No safety program will run itself. To be successful, the wholehearted interest of the employees' group (labor unions) and management must not only be behind the program, but the fact must also be readily apparent to all.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-505 Definitions applicable to this chapter.
(((1) "))A-frame((" means)). A structure made of two independent columns fastened together at the top and separated at the bottom for stability.
(((2) "))Annealing((")). Heating then cooling to soften and render less brittle.
(((3) "))Binder((")). A hinged lever assembly used to connect the ends of a wrapper to tighten the wrapper around the load of logs or materials.
(((4) "))Boom((")). Logs or timbers fastened together end to end and used to contain floating logs. The term includes enclosed logs.
(((5) "))Brow log((")). A log placed parallel to a roadway at a landing or dump to protect vehicles while loading or unloading.
(((6) "))Bunk((")). A cross support for a load.
(((7) "))Cant((")). A log slabbed on one or more sides.
(((8) "))Carriage((")) (log carriage). A framework mounted on wheels which runs on tracts or in grooves in a direction parallel to the face of the saw, and which contains apparatus to hold a log securely and advance it toward the saw.
(((9) "))Carrier((")). An industrial truck so designed and constructed that it straddles the load to be transported with mechanisms to pick up the load and support it during transportation.
(((10) "))Chipper((")). A machine which cuts material into chips.
(((11) "))Chock,((" "))bunk block,((")) and (("))cheese block((")). A wedge that prevents logs or loads from moving.
(((12) "))Cold deck((")). A pile of logs stored for future removal.
(((13) "))Crotch lines((")). Two short lines attached to a hoisting line by a ring or shackle, the lower ends being attached to loading hooks.
(((14) "))Dog((")) (carriage dog). A steel tooth or assembly of steel teeth, one or more of which are attached to each carriage knee to hold log firmly in place on carriage.
(((15) "))Drag saw((")). A power-driven, reciprocating cross-cut saw mounted on suitable frame and used for bucking logs.
(((16) "))Head block((")). That part of a carriage which holds the log and upon which it rests. It generally consists of base, knee, taper set, and mechanism.
(((17) "))Head rig((")). A combination of head saw and log carriage used for the initial breakdown of logs into timbers, cants, and boards.
(((18) "))Hog((")). A machine for cutting or grinding slabs and other coarse residue from the mill.
(((19) "))Husk((")). A head saw framework on a circular mill.
(((20) "))Industrial truck((")). A mobile, power-driven vehicle used to carry, push or pull material. It is designed for "in-plant" or "on-site" use rather than highway use.
(((21) "))Kiln tender((")). The operator of a kiln.
(((22) "))Lift truck((")). An industrial truck used for lateral transportation and equipped with a power-operated lifting device, usually in the form of forks, for piling or unpiling lumber units or packages.
(((23) "))Live rolls((")). Cylinders of wood or metal mounted on horizontal axes and rotated by power, which are used to convey slabs, lumber, and other wood products.
(((24) "))Loading boom((")). Any structure projecting from a pivot point and intended to be used for lifting and guiding loads for the purpose of loading or unloading.
(((25) "))Log((")). A portion of a tree, usually a minimum of twelve feet in length, capable of being further processed into a variety of wood products.
(((26) "))Log deck((")). A platform in the sawmill on which the logs remain until needed for sawing.
(((27) "))Log haul((")). A conveyor for transferring logs to mill.
(((28) "))Lumber dimensions((")). The nominal size of surfaced lumber, unless otherwise stated.
(((29) "))Lumber hauling truck((")). An industrial truck, other than a lift truck or a carrier, used for the transport of lumber.
(((30) "))Package((")). A unit of lumber.
(((31) "))Peavy((")). A stout wooden handle fitted with a spike and hook and used for rolling logs.
(((32) "))Peeler block((")). A portion of a tree usually bucked in two foot intervals plus trim, to be peeled in a lathe or sliced in a slicer into veneer for further processing into plywood.
(((33) "))Pike pole((")). A long pole whose end is shod with a sharp pointed spike.
(((34) "))Pitman rod((")). Connecting rod.
(((35) "))Resaw((")). Band, circular, or sash gang saws used to break down slabs, cants, or flitches into lumber.
(((36) "))Running line((")). Any moving rope as distinguished from a stationary rope such as a guyline.
(((37) "))Safety factor((")). A calculated reduction factor which may be applied to laboratory test values to obtain safe working stresses for wooden beams and other mechanical members; ratio of breaking load to safe load.
(((38) "))Saw guide((")). A device for steadying a circular or bandsaw.
(((39) "))Setwork((")). A mechanism on a sawmill carriage which enables an operator to move the log into position for another cut.
(((40) "))Sorting gaps((")). The areas on a log pond enclosed by boom sticks into which logs are sorted.
(((41) "))Spreader wheel((")). A metal wheel that separates the board from the log in back of circular saws to prevent binding.
(((42) "))Splitter((")). A knife-type, nonrotating spreader.
(((43) "))Sticker((")). A strip of wood or other material used to separate layers of lumber.
(((44) "))Stiff boom((")). The anchored, stationary boom sticks which are tied together and on which boom persons work.
(((45) "))Swifter((" is a)). The tying of boom sticks together to prevent them from spreading while being towed.
(((46) "))Telltale((")). A device used to serve as a warning for overhead objects.
(((47) "))Top saw((")). The upper of two circular saws on a head rig, both being on the same husk.
(((48) "))Tramway((")). A way for trams, usually consisting of parallel tracks laid on wooden beams.
(((49) "))Trestle((")). A braced framework of timbers, piles or steelwork for carrying a road or railroad over a depression.
(((50) "))Wrapper((")). A chain, strap or wire rope assembly used to contain a load of logs or materials.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-510 Education and first-aid standards.
It ((shall)) must be the duty of every employer to comply with such standards and systems of education for safety as ((shall)) must be, from time to time, prescribed for such employer by the director of labor and industries through the division of industrial safety and health or by statute.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 15-11-066, filed 5/19/15, effective 7/1/15)
WAC 296-78-515 Management's responsibility.
(1) It ((shall)) must be the responsibility of management to establish, supervise, and enforce, in a manner which is effective in practice:
(a) A safe and healthful working environment.
(b) An accident prevention program as required by these standards.
(c) Training programs to improve the skill and competency of all employees in the field of occupational safety and health. Such training ((shall)) must include the on-the-job instructions on the safe use of powered materials handling equipment, machine tool operations, use of toxic materials and operation of utility systems prior to assignments to jobs involving such exposures.
(2) ((The employer shall)) You must develop and maintain a hazard communication program as required by WAC 296-901-140, which will provide information to all employees relative to hazardous chemicals or substances to which they are exposed, or may become exposed, in the course of their employment.
(3) Management ((shall)) must not assign mechanics, millwrights, or other persons to work on equipment by themselves when there is a probability that the person could fall from elevated work locations or equipment or that a person could be pinned down by heavy parts or equipment so that they could not call for or obtain assistance if the need arises.
Note: | This subsection does not apply to operators of motor vehicles, watchperson or certain other jobs which, by their nature, are singular employee assignments. However, a definite procedure for checking the welfare of all employees during their working hours shall be instituted and all employees so advised. |
(4) After the emergency actions following accidents that cause serious injuries that have immediate symptoms, a preliminary investigation of the cause of the accident ((shall)) must be conducted. The investigation ((shall)) must be conducted by a person designated by ((the employer)) you, the immediate supervisor of the injured employee, witnesses, employee representative if available and any other person with the special expertise required to evaluate the facts relating to the cause of the accident. The findings of the investigation ((shall)) must be documented by ((the employer)) you for reference at any following formal investigation.
(5) Reporting and recording requirements. ((The employer)) You must comply with chapter 296-27 WAC for recording work-related injuries and illnesses and reporting to the department any work-related fatality, inpatient hospitalization, amputation, or the loss of an eye.
(6) ((The employer)) You must comply with the accident investigation requirements in WAC 296-800-320.
(7) Personal protective equipment required by this standard ((shall)) must be provided at no cost to employees.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-520 Employee's responsibility.
(1) Employees ((shall)) must coordinate and cooperate with all other employees in an attempt to eliminate accidents.
(2) Employees ((shall)) must study and observe all safe practices governing their work.
(3) Employees should offer safety suggestions, wherein such suggestions may contribute to a safer work environment.
(4) Employees ((shall)) must apply the principles of accident prevention in their daily work and ((shall)) must use proper safety devices and protective equipment as required by their employment or employer.
(5) Employees ((shall)) must properly care for all personal protective equipment.
(6) Employees ((shall)) must make a prompt report to their immediate supervisor, of each industrial injury or occupational illness, regardless of the degree of severity.
(7) Employees ((shall)) must not wear torn or loose clothing while working around machinery.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 94-20-057, filed 9/30/94, effective 11/20/94)
WAC 296-78-525 Accident-prevention programs.
Each employer ((shall)) must develop a formal accident-prevention program, tailored to the needs of the particular plant or operation and to the type of hazards involved. The department may be contacted for assistance in developing appropriate programs.
(1) The following are the minimal program elements for all employers:
(a) A safety orientation program describing the employer's safety program and including:
(i) How and when to report injuries, including instruction as to the location of first-aid facilities.
(ii) How to report unsafe conditions and practices.
(iii) The use and care of required personal protective equipment.
(iv) The proper actions to take in event of emergencies including the routes of exiting from areas during emergencies.
(v) Identification of the hazardous gases, chemicals or materials involved along with the instructions on the safe use and emergency action following accidental exposure.
(vi) A description of the ((employers)) employer's total safety program.
(vii) An on-the-job review of the practices necessary to perform the initial job assignments in a safe manner.
(b) A designated safety and health committee consisting of management and employee representatives with the employee representatives being elected or appointed by fellow employees.
(2) Each accident-prevention program ((shall)) must be outlined in written format.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-530 Safety and health committee plan.
(1) All employers of eleven or more employees((, shall)) must have a designated safety committee composed of employer and employee elected members.
(a) The terms of employee-elected members ((shall)) must be a maximum of one year. Should a vacancy occur on the committee, a new member ((shall)) must be elected prior to the next scheduled meeting.
(b) The number of employer-selected members ((shall)) must not exceed the number of employee-elected members.
(2) The safety committee ((shall)) must have an elected chairperson.
(3) The safety committee ((shall)) must be responsible for determining the frequency of committee meetings.
Note: | If the committee vote on the frequency of safety meetings is stalemated, the division's regional safety educational representative may be consulted for recommendations. |
(a) The committee ((shall)) must be responsible for determining the date, hour and location of the meetings.
(b) The length of each meeting ((shall)) must not exceed one hour except by majority vote of the committee.
(4) Minutes of each committee meeting ((shall)) must be prepared and filed for a period of at least one year and ((shall)) be made available for review by noncompliance personnel of the division of industrial safety and health.
(5) Safety and health committee meetings ((shall)) must address the following:
(a) A review of the safety and health inspection reports to assist in correction of identified unsafe conditions or practices.
(b) An evaluation of the accident investigations conducted since the last meeting to determine if the cause of the unsafe acts or unsafe conditions involved was properly identified and corrected.
(c) An evaluation of the accident or illness prevention program with the discussion of recommendation for improvement where indicated.
(d) The attendance ((shall)) must be documented.
(e) The subject(s) discussed ((shall)) must be documented.
(6) All employers of ten or less employees and employers of eleven or more employees where the employees are segregated on different shifts or in widely dispersed locations in crews of ten or less employees, may elect to have foreman-crew meetings in lieu of a safety and health committee plan provided:
(a) Foreman-crew safety meetings be held at least once a month, however, if conditions require, weekly or semimonthly meetings ((shall)) must be held to discuss safety problems as they arise.
(b) All items under subsection (5) of this section ((shall)) must be covered.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-535 Safety bulletin board.
There ((shall)) must be installed and maintained in every fixed establishment, a safety bulletin board sufficient in size to display and post safety bulletins, newsletters, posters, accident statistics and other safety educational material. It is recommended that safety bulletin boards be painted green and white.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-07-160, filed 3/23/04, effective 5/1/04)
WAC 296-78-540 First-aid training and certification.
((The employer)) You must ensure that first-aid trained personnel are available to help employees who are injured or who become acutely ill on the job. ((The employer)) You must meet this requirement by maintaining first-aid trained staff on the job site. ((The employer)) You must ensure that:
(1) Each person in charge of employees has first-aid training; or another person with first-aid training is present or available to the employees. Such training must be successfully completed every two years;
(2) Documentation of first-aid training is kept;
(3) Emergency telephone numbers are adequately posted.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-560 Safe place standards.
(1) Each employer ((shall)) must furnish to each of his employees a place of employment free from recognized hazards that are causing or likely to cause serious injury or death to his employees.
(2) Every employer ((shall)) must furnish and use safety devices and safeguards, and ((shall)) adopt and use practices, means, methods, operations, and processes which are reasonably adequate to render such employment and place of employment safe. Every employer ((shall)) must do every other thing reasonably necessary to protect the life and safety of employees.
(3) ((No employer shall)) Employers must not require any employee to go or be in any employment or place of employment which is not safe.
(4) No employer ((shall)) must fail or neglect:
(a) To provide and use safety devices and safeguards.
(b) To adopt and use methods and processes reasonably adequate to render the employment and place of employment safe.
(c) To do every other thing reasonably necessary to protect the life and safety of employees.
(5) No employer, owner, or lessee of any real property ((shall)) must construct or cause to be constructed any place of employment that is not safe.
(6) No person ((shall)) must do any of the following:
(a) Remove, displace, damage, destroy or carry off any safety device, safeguard, notice, or warning, furnished for use in any employment or place of employment.
(b) Interfere in any way with the use thereof by any other person.
(c) Interfere with the use of any method or process adopted for the protection of any employee, including himself, in such employment, or place of employment.
(d) Fail or neglect to do every other thing reasonably necessary to protect the life and safety of employees.
(e) Intoxicating beverages and narcotics ((shall)) must not be permitted or used in or around work sites. Workers under the influence of alcohol or narcotics ((shall)) must not be permitted on the work site. This rule does not apply to persons taking prescription drugs and or narcotics as directed by a physician, providing such use ((shall)) does not endanger the worker or others.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-03-124, filed 1/23/02, effective 3/1/02)
WAC 296-78-56501 Log dumps and ponds.
(1) Log dumps, booms, ponds or storage areas, if used at night, ((shall)) must be illuminated in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-800-210, safety and health core rules.
(2) A log dump ((shall)) must be constructed at each log pond or decking ground. Log trucks ((shall)) must not be unloaded by use of peavies or by hand.
(a) The roadbed ((shall)) must be of hard packed gravel, heavy planking or equivalent material and ((shall)) be maintained at all times. Roadbeds at log dumps ((shall)) must be of width and evenness to ((insure)) ensure safe operation of equipment.
(b) A mechanical unloading device ((shall)) must be provided and used for unloading logs. Log unloading areas ((shall)) must be arranged and maintained to provide a safe working area.
(c) Signs prohibiting unauthorized foot or vehicle traffic in log unloading and storage areas ((shall)) must be posted.
(d) At no time ((shall)) will one person be permitted to work alone on a log dump, a booming or rafting grounds, or a log pond.
(3) Water log dumps. Ungrounded electrically powered hoists using handheld remote control in grounded locations, such as log dumps or mill log lifts, ((shall)) must be actuated by circuits operating at less than 50 volts to ground.
(4)(((a))) A brow log, skid timbers or the equivalent ((shall)) must be installed on all log dumps.
(((b))) (a) Where logs are unloaded onto skids, sufficient space ((shall)) must be provided between the top of the skids and the ground to accommodate the body of a person.
(((c))) (b) All truck dumps ((shall)) must be built with not more than six inches variation of level from side to side.
(5)(((a))) All truck log dumps ((shall)) must be equipped with a positive safeguard to prevent logs from leaving the load on the side opposite the brow log. Jill pokes ((shall)) must not be used on truck log dumps.
(((b))) (a) Unloading lines ((shall)) must be attached and tightened or other positive safeguard in place before binder chains are released at any log dump.
(((c))) (b) Stakes and chocks which trip ((shall)) must be constructed in such manner that the tripping mechanism that releases the stake or chocks is activated at the opposite side of the load being tripped.
(((d))) (c) Binders ((shall)) must be released only from the side on which the unloader operates, except when released by remote control devices or except when person making release is protected by racks or stanchions or other equivalent means.
(((e))) (d) Loads on which a binder is fouled by the unloading machine ((shall)) must have an extra binder or metal band of equal strength placed around the load, or the load ((shall)) must be otherwise secured so that the fouled binder can be safely removed.
(((f))) (e) Unloading lines, crotch lines, or equally effective means ((shall)) must be arranged and used in a manner to minimize the possibility of any log swinging or rolling back.
(6)(((a))) In unloading operations, the operator of the unloading machine ((shall)) must have an unobstructed view of the vehicle and the logs being unloaded.
(((b))) (7) Unloading lines ((shall)) must be arranged so that it is not necessary for the employees to attach them from the pond or dump site of the load except when entire loads are lifted from the log-transporting vehicle.
(((7))) (8) All log dumps ((shall)) must be kept reasonably free of bark and other debris.
(((8))) (9) Employees ((shall)) must remain in the clear until all moving equipment has come to a complete stop.
(((9))) (10) Artificial log ponds subject to unhealthy stagnation ((shall)) must be drained, cleansed, and water changed at least once every six months.
(((10))) (11) All employees whose regular work requires walking on logs ((shall)) must wear spiked or calked shoes, except when working in snow.
(((11))) (12) Employees whose duties require them to work from boats, floating logs, boom sticks, or walkways along or on water must be provided with and must wear appropriate buoyant devices while performing such duties.
(a) Employees are not considered exposed to the danger of drowning:
(i) When working behind standard height and strength guardrails;
(ii) When working inside operating cabs or stations which eliminate the possibility of accidentally falling into the water;
(iii) When wearing approved safety belts with lifeline attached so as to preclude the possibility of falling into the water.
(b) Prior to and after each use, personal floating devices ((shall)) must be inspected for defects which would reduce their designed effectiveness. Defective personal flotation devices ((shall)) must not be used.
(c) To meet the approved criteria required by this subsection (((11))) (12), a personal flotation device ((shall)) must be approved by the United States Coast Guard as a Type I PFD, Type II PFD, Type III PFD, or Type V PFD, or their equivalent, pursuant to 46 C.F.R. 160 (Coast Guard lifesaving equipment specifications) and 33 C.F.R. 175.23 (Coast Guard table of devices equivalent to personal flotation devices). Ski belt or inflatable type personal flotation devices are specifically prohibited.
(((12)(a))) (13) Wooden pike poles ((shall)) must be of continuous, straight grained No. 1 material. Defective poles, blunt or dull pikes ((shall)) must not be used.
(((b))) (14) Aluminum or other metal poles ((shall)) must not be used where hazard of coming in contact with live electric wires exists.
(((13)(a))) (15) Walkways and floats ((shall)) must be provided and security anchored to provide safe passage for workers.
(((b))) (a) Permanent cable swifters ((shall)) must be so arranged that it will not be necessary to roll boom sticks in order to attach or detach them.
(((c))) (b) Inspection of cable or dogging lines ((shall)) must be made as necessary to determine when repair or removal from service is necessary.
(((14)(a))) (16) Decks of floats or other walkways ((shall)) must be kept above the waterline at all times and ((shall)) be capable of supporting four times the load to be imposed.
(((b))) (17) Floating donkeys or other power-driven machinery used on booms ((shall)) must be placed on a raft or float with enough buoyancy to keep the deck above water.
(((15)(a))) (18) All regular boom sticks and foot logs ((shall)) must be reasonably straight, have all protruding knots and bark removed, and ((shall)) must be capable of supporting above the waterline at either end, any necessary weight of workers and equipment.
(((b))) (a) Stiff booms ((shall)) must be two float logs wide secured by boom chains or other connecting devices, and of a width adequate for the working needs. Walking surfaces ((shall)) must be free of loose material and maintained in good repair.
(((c))) (b) Boom sticks ((shall)) must be fastened together with crossties or couplings.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-56503 Log hauls.
(1) Every log haul used as a walkway ((shall)) must have at least one walkway with standard railing to enable workers to stand clear of the logs in the chute. Cleats ((shall)) must be installed to provide safe footing on sloping walkways.
(2) Workers ((shall)) must not stand under or dangerously near to logs that are being hoisted vertically to the log deck.
(3)(((a))) Log haul gears and bull chain drive mechanism ((shall)) must be adequately guarded for the protection of employees.
(((b))) (a) Log haul bull chains or cable ((shall)) must be designed, installed, and maintained to provide a four to one safety factor for the intended load.
(((c))) (b) Troughs for the return strand of log haul chains ((shall)) must be provided over passageways.
(((d))) (c) Overhead protection ((shall)) must be provided for employees working below logs being moved to the log deck.
(4) Log haul controls ((shall)) must be arranged to operate from a position where the operator will at all times be in the clear of logs, machinery lines and rigging. Such controls ((shall)) must operate mechanism only when moved toward the log slip or deck.
(5) Where possible, an automatic stop ((shall)) must be installed on all log hauls. A positive stop ((shall)) must be installed on all log hauls to prevent logs from traveling too far ahead in the mill.
(6)(((a))) Slip persons ((shall)) must handle pike poles in such manner as to be in the clear in case of a slip back.
(((b))) (a) All sorting gaps ((shall)) must have a stiff boom on each side.
(((c))) (b) The banks of the log pond in the vicinity of the log haul ((shall)) must be reinforced to prevent caving in.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-06-076, filed 3/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-78-56505 Boats and mechanical devices on waters.
(1) The applicable provisions of the Standard for Fire Protection for Motorcraft, NFPA No. 302-1994, ((shall)) must be complied with. Prior to starting the boat motor, any spilled fuel ((shall)) must be removed and vapors ((shall)) must be exhausted from any area in which they may accumulate.
(2) The bilge area ((shall)) must be kept clean and oil, grease, fuel, or highly combustible materials ((shall)) must not be allowed to accumulate.
(3) Adequate ventilation equipment ((shall)) must be provided and used for the bilge area to prevent the accumulation of toxic or explosive gases or vapors.
(4) Adequate ventilation equipment ((shall)) must be provided and used for the cabin area on enclosed cabin-type boats to prevent an accumulation of harmful gases or vapors.
(5) Deck and cabin lighting ((shall)) must be provided and used where necessary to provide safe levels of illumination aboard boats. Boats operated during the period from sunset to sunrise, or in conditions of restricted visibility, ((shall)) must display navigation lights as required by the United States Coast Guard. Searchlights or floodlights ((shall)) must be provided to facilitate safe navigation and to illuminate working or boarding areas adjacent to the craft.
(6) Decks of pond boats ((shall)) must be covered with nonslip material. On craft used by workers wearing calked shoes, all areas where the operator or workers must stand or walk ((shall)) must be made of or be covered with wood or other suitable matting or nonslip material and such covering ((shall)) must be maintained in good condition.
(7) Each boat ((shall)) must be provided with a fire extinguisher and life ring with at least fifty feet of one-fourth inch line attached.
Note: | For additional requirements relating to portable fire extinguishers see WAC 296-800-300. |
(8)(((a))) Along docks, walkways, or other fixed installations on or adjacent to open water more than five feet deep, approved life rings with at least ninety feet of one-fourth inch line attached, ((shall)) must be provided. The life rings ((shall)) must be spaced at intervals not to exceed two hundred feet and ((shall be)) kept in easily visible and readily accessible locations.
(((b))) (a) When employees are assigned work at other casual locations where exposure to drowning exists, at least one approved life ring with at least ninety feet of line attached, ((shall)) must be provided in the immediate vicinity of the work assigned.
(((c))) (b) When work is assigned over water where the vertical drop from the accidental fall would exceed fifty feet, special arrangements ((shall)) must be made with and approved by the department of labor and industries prior to such assignment.
(((d))) (c) Lines attached to life rings on fixed locations ((shall)) must be at least ninety feet in length, at least one-fourth inch in diameter, and have a minimum breaking strength of five hundred pounds. Similar lines attached to life rings on boats ((shall)) must be at least fifty feet in length.
(((e))) (d) Life rings must be United States Coast Guard approved thirty-inch size.
(((f))) (e) Life rings and attached lines ((shall)) must be provided and maintained to retain their buoyancy and strength.
(((g))) (f) Log broncs, boomscooters, and boomboats ((shall)) must not be loaded with personnel or equipment so as to adversely affect their stability or seaworthiness.
(((h))) (g) Boats ((shall)) must not be operated at an excessive speed or handled recklessly.
(((i))) (h) Boat fuel ((shall)) must be transported and stored in approved containers. Refer to WAC 296-24-58501(((19))) for definition of approved.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-56507 Log decks.
(1) Dry deck storage.
(a) Dry deck storage areas ((shall)) must be kept orderly and ((shall)) must be maintained in a condition which is conducive to safe operation of mobile equipment.
(b) Logs ((shall)) must be stored in stabilized piles, and roadways and traffic lanes ((shall)) must be maintained at a width adequate for safe travel of log handling equipment.
(c) Logs ((shall)) must be arranged to minimize the chance of accidentally rolling from the deck.
(2)(((a))) Employees ((shall)) must not spool cable on winch or drums with their hands.
(((b))) (3) Log wells ((shall)) must be provided with safeguard to prevent logs from rolling back into well off log deck.
(((3))) (4) Jump skids on log decks ((shall)) must be installed in grooves in a manner that they cannot work out onto the carriage way.
(((4)(a))) (5) Log decks ((shall)) must be provided with effective means to prevent logs from accidentally rolling down the deck onto the carriage or its runway.
(((b) Swing saws.)) (a) Swing saws on log decks ((shall)) must be equipped with a barricade and stops for protection of employees who may be on the opposite side of the log haul chute.
(((c))) (b) Drag saws. Where reciprocating log cutoff saws (drag saws) are provided, they ((shall)) must not project into walkway or aisle.
(((d))) (c) Circular cutoff saws. Circular log bucking or cutoff saws ((shall)) must be so located and guarded as to allow safe entrance to and exit from the building.
(((e))) (d) Entrance doorway. Where the cutoff saw partially blocks the entrance from the log haul runway the entrance ((shall)) must be guarded.
(((5))) (6) A barricade or other positive stop ((shall)) must be erected between the sawyer's stand and the log deck to protect the sawyer from rolling logs. Such barricade or stop ((shall)) must be of sufficient strength to stop any log.
(((6))) (7) Chains from overhead canting gear or other equipment ((shall)) must not be allowed to hang over the log deck in such manner as to endanger workers.
(((7))) (8) Canting gear control levers ((shall)) must be ((so)) arranged so that they move away from the carriage to operate.
(((8))) (9) Moving parts or equipment on or about log decks ((shall)) must be guarded.
(((9))) (10) Peavies, canthooks and other hand tools ((shall)) must be kept in good repair at all times.
(((10))) (11) Workers ((shall)) must not go below logs on decks that are likely to roll or be rolled. Means of access ((shall)) must be provided to the head rig which does not subject employees to the hazard of moving logs or equipment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-56509 Mechanical barkers.
(1) Rotary barkers. Rotary barking devices ((shall)) must be ((so)) guarded so as to protect employees from flying chips, bark, or other extraneous material.
(2) Elevating ramp. If an elevating ramp or gate is used, it ((shall)) must be provided with a safety chain, hook, or other means of suspension while employees are underneath.
(3) Area around barkers. The hazardous area around ring barkers and their conveyors ((shall)) must be fenced off or posted as a prohibited area for unauthorized persons.
(4) Enclosing hydraulic barkers. Hydraulic barkers ((shall)) must be enclosed with strong baffles at the inlet and outlet. The operator ((shall)) must be protected by adequate safety glass or equivalent.
(5) ((Holddown rolls.)) Holddown rolls ((shall)) must be installed at the infeed and outfeed sections of mechanical ring barkers to control the movement of logs.
(6) If such holddown rolls have a tendency to throw logs or chunks, horseshoe or equivalent type guards ((shall)) must be installed to contain the logs or chunks.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-56511 Head rigs and feed works.
(1) A clear walkway ((shall)) must be provided along the upper side of the log deck and around the head rig unless an overhead walkway is provided.
(2) The sawyer ((shall)) must be primarily responsible for the safety of the carriage crew and off-bearers. ((He shall)) They must exercise due care in the operation of the carriage and log turning devices.
(3) Feedworks and log turning control levers ((shall)) must be ((so)) arranged so that they may be securely locked when not in use and ((shall)) must be guarded against accidental contact.
(4)(((a))) A positive means ((shall)) must be provided to prevent unintended movement of the carriage. This ((shall)) must involve a control locking device, a carriage tie-down, or both.
(((b))) (5) An emergency control or equally effective means ((shall)) must be provided so that the sawyer may stop the head rig section of the mill without leaving the operator station.
(((5))) (6) An effective method of disengaging the head rig saws from the power unit ((shall)) must be installed on all head rigs where the power unit is not directly controlled by the sawyer. The saws ((shall)) must be disengaged from the source of power while repairs or changes are made.
(((6))) (7) A shield of lexan, makrolon, merlon, plestar, or equivalent transparent material, ((shall)) must be installed between the sawyer's stand and the head saws in all circular mills. In band mills and chipper type installations, a wire screen of not less than twelve gauge wire, one-half inch mesh, mounted in a frame in compliance with chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety, is an acceptable substitute for the type shield required in circular mills.
(((7))) (8) Safety glasses, safety shields or other suitable eye protection ((shall)) must be provided for and use by head rig off-bearers.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-17-056, filed 8/20/96, effective 10/15/96)
WAC 296-78-56513 Log carriages.
(1) Carriages upon which employees are required to work ((shall)) must be solidly decked over.
(2) Dogs. Dogging devices ((shall)) must be adequate to secure logs, cants, or boards, during sawing operations.
(3) The feed control lever of friction or belt driven carriage feed works ((shall)) must be arranged to operate away from the saws or carriage track.
(4) A quick action valve, controlled from the sawyer's stand, ((shall)) must be located in the steam line to any steam operated feed works. The valve ((shall)) must be tested daily.
(5) Valves in steam feeds ((shall)) must be closed and locked in a neutral position before the sawyer leaves his station. Leaking steam valves or piping ((shall)) must not be used on carriage drives.
(6)(((a))) Where employees ride the headrig carriage, clearance of the rear edge of the carriage ((shall be)) must either not be more than two inches or ((shall be)) not less than thirty inches from the side wall of the building. The side wall ((shall)) must be boarded over smoothly to a height of not less than six feet six inches from the setter's platform and for at least the length of the carriage travel.
(a) Where the clearance is thirty inches or more the floor between the back side of the setter's platform and the wall ((shall)) must be raised to the level of the platform. The clearance between the floor edge and the platform ((shall)) must not be more than two inches.
(b) Barriers and warning signs. A barrier ((shall)) must be provided to prevent employees from entering the space necessary for travel of the carriage, with headblocks fully receded, for the full length and extreme ends of carriage runways. Warning signs ((shall)) must be posted at possible entry points to this area.
(7) Safe access to the head rig ((shall)) must be provided.
(8) No roof truss or roof timber or other obstruction ((shall)) must be located within six feet six inches of the upper surface of the setter's platform on any carriage.
(9) Doors which lead onto a passageway at the end or side of the carriage runway ((shall)) must be provided with a handrail opposite such doorway. Handrail ((shall)) must not be less than eighteen inches from the carriage run. A warning sign ((shall)) must be posted on the entrance side of such doorways.
(10) A stop or bumper capable of stopping the loaded carriage at operating speed ((shall)) must be installed at each end of the carriage run.
(11) Rail sweeps ((shall)) must be installed in front of the front wheels in the direction of travel. Such sweeps ((shall)) must extend to within one-fourth inch of the rail.
(12) Where power operated log turners are used, carriage knees ((shall)) must be provided with goosenecks or other means of protecting the carriage crew from climbing logs.
(13) Employees ((shall)) must use a stick or wire brush to clear head blocks of debris.
(14) All weakened or broken carriage boards ((which)) that will not support the load ((to)) and will be imposed with a safety factor of 4, ((shall)) must be immediately replaced.
(15) Carriage control. A positive means ((shall)) must be provided to prevent unintended movement of the carriage. This may involve a control locking device, a carriage tie-down, or both.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-17-056, filed 8/20/96, effective 10/15/96)
WAC 296-78-570 Band saws—Saws.
(1) Band head rigs ((shall)) must be given a thorough daily inspection and any deficiency reported and corrected.
(2) Any band saw found to have developed a crack greater than one-tenth the width of the saw ((shall)) must be removed from service until the width of the saw is reduced to eliminate the crack, the cracked section is removed, or the development of the crack is arrested by welding.
(3) Band saws ((shall)) must not be continued in use of the head rig for which they have been designed after they have been reduced forty percent in width.
(4) Leather gloves, or equivalent hand protection, ((shall)) must be worn by employees while changing band saws.
(5) All head band saw wheels ((shall)) must have a minimum rim thickness of five-eighths inch, except for a distance of not to exceed one inch from the front edge of the wheel.
(6) Provisions ((shall)) must be made for alerting and warning employees before starting band head saws, and measures ((shall)) must be taken to ((insure)) ensure that all persons are in the clear.
(7) No band saw ((shall)) must be run at a peripheral speed in excess of that recommended by the manufacturer. The manufacturer's recommended maximum speed ((shall)) must be stamped in plainly legible figures on some portion of the assembly.
(8) A band wheel that has developed a crack in the rim ((shall)) must be immediately removed from service. If a crack has developed in a spoke, the wheel ((shall)) must be removed from service until repaired.
(9) All band wheels ((shall)) must be completely encased or guarded on both sides. The exposed part of the saw blade on the uptravel between the two wheels ((shall)) must be encased, and no portion of the blade exposed, except such part of the cutting edge as is essential for sawing the material at hand.
(10) All band wheel guards ((shall)) must be constructed of not less than ten U.S. gauge metal, or not less than two inch wood material or equivalent, attached to the frames. Ventilating ports ((shall)) must not exceed 2 x 4 inches in size. Openings necessary for lubrication or repair of the saw ((shall)) must have doors or gates of equivalent strength to the remainder of the guard, and such doors or gates ((shall)) must be securely closed during operation.
(11) Every band mill ((shall)) must be equipped with a saw catcher, rest or guard of substantial construction.
(12) All band saws other than head mills ((shall)) must be enclosed or guarded except the working side of the blade between the guide and the table. The guard for the portion of the saw between the sliding guide and the upper saw wheel guard ((shall)) must be adjusted with the guide.
(13) Each gang ripper of band or straight saw type ((shall)) must have the cutting edges of the saw guarded by a hood or screen secured to the framework of the machine.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-575 Circular saws.
(1) Single circular head saws. Circular head saws ((shall)) must not be operated at speeds in excess of those specified by the manufacturer. Maximum speed ((shall)) must be etched on the saw.
(2) On all circular saw mills, the horizontal distance from the side of the saw to the nearest post of the husk or frame ((shall)) must be at least one inch greater than the clear vertical distance between the collars of the top and bottom saws.
(3) Circular head saws ((shall)) must be equipped with safety guides that can be readily adjusted without use of wrench or other hand tools. Brackets or edging supports ((shall)) must be installed between the saw and the side of the husk.
(4) The upper saw of a double circular mill ((shall)) must be provided with a hood or guard. A screen or other suitable device ((shall)) must be placed so as to protect the sawyer from flying particles.
(5) All circular sawmills, where live rolls are not used behind the head saw ((shall)), must be equipped with an effective spreader or splitter. In any mill where the head saw is used for edging lumber, the splitter ((shall)) must be solid and stationary and ((shall)) must extend above the head blocks.
(6) Drag saws or circular cut-off saws ((shall)) must be ((so)) arranged ((that)) so they will not project into any passageway. When existing installations do not leave clear passage, saws ((shall)) must be fenced off in order to make it impossible for anyone to walk into them. Means to securely hold material being sawed ((shall)) must be provided wherever such material creates a hazard.
(7) All employees ((shall)) must be in the clear before starting operation of drag or swing cut-off saws.
(8) Twin circular head saws. Twin circular head saw rigs such as ((scrag)) scragg saws, ((shall)) must meet the specifications for single circular head saws in subsection (1) of this section, where applicable.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-17-056, filed 8/20/96, effective 10/15/96)
WAC 296-78-580 Edgers.
(1) Edgers ((shall)) must be guarded by a metal housing of ten gauge sheet metal, ten gauge by one-half inch mesh wire, screen, or by a baffle of not less than two inch wood material.
(2) Openings in end frames ((shall)) must be enclosed with sheet metal, wire screen or wood and may be hinged or arranged to permit oiling and removal of saws.
(3) The top of the edger ((shall)) must be guarded to prevent contact by employees or debris being thrown and all chains and gears fully enclosed as required by WAC 296-78-710 of this chapter.
(4) Vertical arbor edgers installed ahead of the main saw ((shall)) must be ((so)) located and guarded ((that)) so an employee cannot contact any part of the edger saws from his normal operating position.
(5) Edgers ((shall)) must not be located in the main roll case behind the head saw.
(6) All edgers ((shall)) must be equipped with pressure feed rolls. The controls ((shall)) must be installed and located so that from the normal work station the operator can quickly stop the infeed drive without releasing the hold down tension of the pressure rolls.
(7) All edgers ((shall)) must be provided with a method of preventing or guarding against kickbacks. Finger units or dogs installed at the edger, or hinged steel plates suspended across the feed table may be used for this purpose. A kickback barricade, in line with the edger, if fenced off may be used.
(8) Pressure and feed rolls on edgers ((shall)) must be guarded against accidental contact by means of roll covers, bars or strips. The pressure rolls ((shall)) must not be lifted while stock is being run, or while any person is in line with the feed side of the saws.
(9) Edger men ((shall)) must not raise feed rolls and reach between saws while edger is in operation.
(10) Edger men ((shall)) must not put their hands on cants being run through the edger.
(11) Live rolls and rotating powered tailing devices in back of the edger ((shall)) must operate at a speed not less than the speed of the edger feed rolls.
(12) Tables in back of edgers ((shall)) must be kept clear of cants, edgings and unnecessary debris.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-585 Equalizer saws.
(1) Equalizer saws for bolts, staves, heading, etc., ((shall)) must have the saws encased, except that portion immediately adjacent to the feeding device.
(2) Feeding devices on all such equipment ((shall)) must be provided with guards to prevent contact with the feeding device by employees.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-590 Gang saws and ((re-saws)) resaws.
(1) Gang saws and ((re-saws shall)) resaws must be fully guarded or housed in accordance with conditions. Cranks, pitman rods, and other moving parts ((shall)) must be guarded.
(2) Feed rolls ((shall)) must be enclosed by a cover over the top, front, and open ends except where guarded by location. Drive mechanism to feed rolls ((shall)) must be enclosed.
(3) Feed rolls ((shall)) must be enclosed and if the operator stands within thirty inches of the feed rolls, they ((shall)) must be so guarded as to prevent operator coming into contact with them.
(4) Circular ((re-saws)) resaws or rip saws, except power feed rip saws with a roller or wheel back of the saw, ((shall)) must be provided with splitters or spreaders.
(5) A hood of metal or wood of sufficient strength to give protection against splinters or flying teeth ((shall)) must be provided over all circular rip saws.
(6) That portion of the saw extending below the table ((shall)) must be ((so)) guarded so as to prevent contact.
(7) Circular rip saws ((shall)) must be equipped with a standard anti-kickback device.
(8) Carriage cradles of whole-log sash gang saws, Swedish gangs ((shall)) must be of height to prevent logs from kicking out while being loaded.
(9) ((Band re-saws.)) Band ((re-saws shall)) resaws must meet the specifications for band head saws as required in WAC 296-78-570(7).
(10) Circular gang ((re-saws)) resaws.
(a) Banks of circular gang ((re-saws shall)) resaws must be guarded by a hood to contain teeth or debris which can be thrown by the saws.
(b) Circular gang ((re-saws shall)) resaws must be provided with safety fingers or other anti-kickback devices.
(c) Circular gang ((re-saws shall)) resaws must not be operated at speeds exceeding those recommended by the manufacturer.
(d) Feed belts and drive pulleys ((shall)) must be guarded in accordance with chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
(e) Each circular gang ((re-saw)) resaw, except self-feed saws with a live roll or wheel at back of saw, ((shall)) must be provided with spreaders.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-595 Jump saws.
(1) Jump saws ((shall)) must have guards below the top of the table or roll case. A guard ((shall)) must be placed over the roll casing to prevent persons from walking into or over the saw.
(2) Jump saws, underhung swing saws, or bed trimmers ((shall)) must be ((so)) arranged ((that)) so the saws are fully enclosed when not in actual use.
(3) A positive stop ((shall)) must be installed to prevent the saw from passing the front edge of the roll case or table. The throat in the table or roll case ((shall)) must be only wide enough to permit unobstructed operation of the saw.
(4) Guards constructed of not less than two inch wood material or of heavy wire mesh mounted in a steel frame ((shall)) must be placed in front of jump saw trimmers. Stops ((shall)) must be installed to prevent timber from being thrown off the roll case.
(5) Foot treadle operated saws ((shall)) must be provided with safeguards to prevent accidental contact.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-600 Trimmer and slasher saws.
(1) Trimmer ((of [and])) and slasher saws ((shall)) must be guarded in front by a flat or round steel framework with a rigid metal screen or light iron bars attached thereto, or by wood baffles of not less than two inch wood material securely bolted to the frame.
Maximum speed. Trimmer saws ((shall)) must not be run at peripheral speeds in excess of those recommended by the manufacturer.
(2) Front guards for a series of saws ((shall)) must be set as close to the top of the feed table as is practical when considering the type of machine in use and the material being cut. The end saws of a series ((shall)) must be guarded or fenced off.
(3) The rear of a series of saws ((shall)) must have a stationary or swinging guard of not less than two inch wood material or equivalent the full width of the saws and as much wider as is necessary to protect persons at the rear of the trimmer.
(4) Safety stops. Automatic trimmer saws ((shall)) must be provided with safety stops or hangers to prevent saws from dropping on table.
(5) Feed chains ((shall)) must be stopped while employees are on the feed table.
(6) Spotters for trimmers or slashers ((shall)) must be provided with goggles or other eye protection when conditions so warrant.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-605 Swing saws.
(1) Manually operated swing cut-off saws of the following types ((shall)) must be set up, guarded and operated in accordance with chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety:
((•)) (a) Saws into which materials to be cut are fed or positioned and/or held in position by hand pressure during the cutting stroke; ((and/or •))
(b) Saws on which the cutting stroke is propelled by hand pressure; and/or
((•)) (c) Saws on which the operator is within arm's reach of the blade when the operator is standing at the operator's control station and the blade is fully extended to the limit of operating travel.
(2) Operators of hand operated swing saws ((shall)) must not stand directly in front of saw while making a cut.
(3) Swing cut-off saws which are fed by powered live rolls, conveyor chains and/or belts and which are operated from a remote operator's station (defined as being beyond arm's reach of the blade when the blade is fully extended to the limit of operating travel) ((shall)) must be set up, guarded and operated in accordance with the following:
(a) Overhead swing cut-off saws ((shall)) must be guarded by a hood, which ((shall)) must cover the upper half of the cutting edge at least to the depth of the teeth.
(b) The driving belts on overhead swing cut-off saws, where exposed to contact, ((shall)) must be provided with guards as required by WAC 296-78-71505.
(c) Saws ((shall)) must be completely enclosed when in idle position.
(d) Power operated swing saws ((shall)) must have controls so arranged that the operators will not stand directly in front of saw when making cut.
(e) All swing saws ((shall)) must be equipped with a counter balance which ((shall)) must be permanently fastened to the frame of the saw and so arranged or adjusted that it will return the saw beyond the rear edge of the table or roll case without a rebounding motion. Wire rope, chain or nonmetallic rope running to a weight over a sheave ((shall)) must not be used for attaching counter balance.
(f) No swing cut-off or trim saw ((shall)) must be located directly in line with stock coming from an edger.
(g) Swing limit stops ((shall)) must be provided and so adjusted that at no time ((shall)) the forward swing of the saw extends the cutting edge of the saw beyond a line perpendicular with the edge of the saw table, roll case, guard or barrier.
(h) Saws that are fed into the cut by means of air, steam, hydraulic cylinders, or other power device or arrangement ((shall)) must be designed so they can be locked or rendered inoperative.
(i) Foot treadle operated saws ((shall)) must be provided with safeguards to prevent accidental contact.
(j) Swing saws on log decks ((shall)) must be equipped with a positive stop for the protection of persons who may be on the opposite side of the log haul chute.
(k) Tables or roll casings for swing saws ((shall)) must be provided with stops or lineup rail to prevent material being pushed off on opposite side.
(4) Operators of hand operated swing saws ((shall)) must not stand directly in front of saw while making cut.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-610 Circular saws, speeds, repairs.
(1) Circular saws ((shall)) must not be operated at speeds in excess of that specified by the manufacturer. Speeds ((shall)) must be etched on all new saws. When saws are repaired, remanufactured or retensioned in any way to change their operating speeds, such change of speed ((shall)) must be etched on the saw. These etched speeds ((shall)) must not be exceeded.
(2) Circular saws ((shall)) must be inspected for cracks each time that the teeth are filed or set.
(3) A circular saw ((shall)) must be discontinued from use until properly repaired when found to have developed a crack equal to the length indicated in the following table:
Length of Crack |
Diameter |
|||
1/2 - |
inch. . . . |
Up to 12" |
||
1 - |
inch. . . .Over |
12" to 24" |
||
1-1/2 - |
inch. . . .Over |
24" to 36" |
||
2 - |
inch. . . .Over |
36" to 48" |
||
2-1/2 - |
inch. . . .Over |
48" to 60" |
||
3 - |
inch. . . . |
Over 60" |
||
(4) Welding or slotting of cracked saws ((shall)) must be done by a sawsmith under a procedure recommended by the saw manufacturer. Holes ((shall)) must not be drilled in saws as a means of arresting cracks. After saws are repaired they ((shall)) must be retensioned. Unless a sawsmith is employed, saws ((shall)) must be returned to the manufacturer for welding or tensioning.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-615 Saw filing and grinding rooms and equipment.
(1) Approaches to filing rooms ((shall)) must be kept free from material and equipment at all times.
(2) Enclosed grinding and filing rooms ((shall)) must be ventilated as specified in the general occupational health standard, WAC 296-62-110 through 296-62-11019.
(3) Each filing and grinding room ((shall)) must be provided with two exits so arranged as to permit easy escape in case of fire.
(4) Floors ((shall)) must be cleaned regularly and ((shall)) must be kept free from oil, grease and other materials that might cause employees to slip or fall.
(5) Flooring around machines ((shall)) must be kept in good repair at all times.
(6) Saw grinding machine belts ((shall)) must be provided with guards where these belts pass through the frame of the machine.
(7) All grinding wheels on such machines ((shall)) must be provided with a metal retaining hood which ((shall)) also covers the arbor ends if they are exposed to contact.
(8) Filing room employees ((shall)) must be provided with goggles, face shields, or other necessary protective equipment and are required to wear the same.
(9) Guarding and mounting of abrasive wheels ((shall)) must be in accordance with chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-17-056, filed 8/20/96, effective 10/15/96)
WAC 296-78-620 Miscellaneous woodworking machines—Planers, stickers, molders, matchers.
(1) Each planing, molding, sticking and matching machine ((shall)) must have all cutting heads, and saws if used, covered by a solid metal guard. If such guard is constructed of sheet metal, the material used ((shall)) must be not less than one-sixteenth inch in thickness, and if cast iron is used, it ((shall)) must be not less than three-sixteenths inch in thickness.
(2) Planers, stickers, molding, sticking and matching machines ((shall)) must be provided with exhaust fans, hoods and dust conveyors to remove the harmful dusts, etc., from the vicinity of the operator. Such hoods may be arranged to serve as guards for cutting heads.
(3) Planers and other machinery or equipment ((shall)) must not be oiled while in motion, unless provided with guards or other devices to permit oiling without any possibility of contact with moving parts of machinery.
(4) Feed rolls ((shall)) must be guarded by means of roll covers, bars or strips, attached to the roll frame in such manner as to remain in adjustment for any thickness of lumber.
(5)(((a))) Levers or controls ((shall)) must be ((so)) arranged or guarded so as to prevent accidental operation of machines.
(((b))) (a) Foot treadle operated machines ((shall)) must have a treadle guard fastened over the treadle.
(((c))) (b) Locks, blocks, or other devices ((shall)) must be provided for positive immobilization of machine controls while repairs or adjustments are being made.
(6) Side head hoods ((shall)) must be of sufficient height to safeguard the head set screw.
(7) Side heads ((shall)) must not be adjusted while the machine is in operation, except when extension adjusting devices are provided.
(8) Side belt and pulley guards ((shall)) must be kept in place at all times the machine is in motion.
(9) All universal joints ((shall)) must be enclosed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-625 Planers (stave and headings).
(1) Each planer (stave and heading) ((shall)) must have all cutting heads, and saws if used, covered by a solid metal guard.
(2) Stave and heading planers ((shall)) must be provided with exhaust fans, hoods and dust conveyors to remove the harmful dusts, etc., from the vicinity of the operator. Such hoods may be arranged to serve as guards for cutting heads.
(3) Sectional feed rolls should be provided. Where solid feed rolls are used, a sectional finger device (or other means equally effective) ((shall)) must be provided to prevent kickbacks.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-630 Stave croziers.
(1) Stave croziers ((shall)) must have the heads guarded completely by the exhaust hood or other device, except that portion which actually ((inbeds)) embeds itself in the stock.
(2) Each stave crozier ((shall)) must have all feed chains and sprockets completely enclosed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-17-056, filed 8/20/96, effective 10/15/96)
WAC 296-78-635 Jointers.
(1) Each hand feed jointer or buzz planer with horizontal head ((shall)) must be provided with an automatic guard over the cutting head both in front of and in back of the guide.
(2) Each jointer or buzz planer with horizontal head ((shall)) must be equipped with a cylindrical cutting head, the throat of which ((shall)) must not exceed three-eighths inch in depth or one-half inch in width. The knife projection ((shall)) must not exceed one-eighth inch beyond the cylindrical body of the head.
(3) The opening in the table ((shall)) must be kept as small as possible. The clearance between the edge of the rear table and the cutter head ((shall)) must be not more than one-eighth inch. The table throat opening ((shall)) must be not more than two and one-half inches when tables are set or aligned with each other for zero cut.
(4) Each jointer or buzz planer with vertical head ((shall)) must be guarded by an exhaust hood or other approved device which ((shall)) completely encloses the revolving head except for a slot sufficiently wide to permit the application of material. The guard ((shall)) must effectively protect the operator's hand from coming in contact with the revolving knives. The guard ((shall)) must automatically adjust itself to cover the unused portion of the head and ((shall)) must remain in contact with the material at all times.
(5) Push sticks ((shall)) must be provided and used for feeding stock through hand operated jointers or buzz planers.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-640 Jointers (stave and heading).
(1) Stave and heading jointers and matchers ((shall)) must have the heads guarded completely by the exhaust hood or other device, except that portion where the stock is applied.
(2) Foot power stave jointing machines ((shall)) must have the knife effectively guarded to prevent the operator's fingers from coming in contact with it.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-645 Wood shapers.
(1) The cutting head of each wood shaper, hand feed panel raiser, or other similar machine not automatically fed, ((shall)) must be guarded with a cage or pulley guard or other device so designed as to keep the operator's hands away from the cutting edge. In no case ((shall)) will a warning device of leather or other material attached to the spindle be acceptable. Cylindrical heads ((shall)) must be used wherever the nature of the work permits. The diameter of circular shaper guards ((shall)) must be not less than the greatest diameter of the cutter.
(2) All double spindle shapers ((shall)) must be provided with a spindle starting and stopping device for each spindle or provision ((shall)) must be made that only one spindle operate at any one time.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-650 Boring and mortising machines.
(1) Boring and mortising machines ((shall)) must be provided with safety bit chucks without projecting set screws. Automatic machines ((shall)) must be provided with point of operation guards. When necessary to prevent material from revolving with the bit, clamps or stops ((shall)) must be provided and used to hold material firmly against the guides.
(2) The requirements of WAC 296-806-48048, Make sure boring and mortising machines meet these requirements, ((shall)) must be applicable to boring and mortising machines.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-655 Tenoning machines.
(1) Each tenoning machine ((shall)) must have all cutting heads, saws if used, and all exposed moving parts guarded. In the case of cutting heads and saws, the guard ((shall)) must be of solid metal.
(2) If sheet metal is used, it ((shall be)) must not be less than ten U.S. gauge in thickness. If cast metal is used, it ((shall be)) must not be less than three-sixteenths inch thick, or if aluminum is used, it ((shall be)) must not be less than five-eighths inch thick. The hood of the exhaust system may form part or all of the guard. When so used, the hood ((shall)) must be constructed of metal of a thickness not less than that specified herein.
(3) Feed chains and sprockets of all double end tenoning machines ((shall)) must be completely enclosed, except that portion of chain used for conveying stock. At rear ends of frames over which the feed conveyors run, sprockets and chains ((shall)) must be guarded at the sides by plates projecting beyond the periphery of sprockets and ends of lugs.
(4) The rear end of the frame over which the feed conveyors run ((shall)) must be so extended that the material as it leaves the machine will be guided to a point within easy reach of the person removing stock at the rear of the tenoner.
(5) Single end tenoners, hand fed, ((shall)) must have a piece of sheet metal placed so that the operator's hands cannot slip off the lever handle into the tool in passing. Such guard ((shall)) must be fastened to the lever.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-660 Lathe (pail and barrel).
(1) Each profile, swing-head and back-knife lathe ((shall)) must have all cutting heads covered by a solid metal guard.
(2) If sheet metal is used, it ((shall)) must be not less than ten U.S. gauge in thickness. If cast metal is used, it ((shall)) must be not less than three-sixteenths inch thick, or if aluminum is used, it ((shall be)) must not be less than five-eighths inch thick. The hood of the exhaust system may form part or all of the guard. When so used, the hood ((shall)) must be constructed of metal of a thickness not less than that specified above.
(3) Pail and barrel lathes ((shall)) must be guarded in accordance with the specifications for profile and back-knife lathes insofar as they are applicable.
(4) The requirements of WAC 296-806-450, Lathes, ((shall)) must be applicable to pail and barrel lathes.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-20-055, filed 10/3/05, effective 12/1/05)
WAC 296-78-665 Sanding machines.
(1) Each belt sanding machine ((shall)) must have both pulleys enclosed in such a manner as to guard the points where the belt runs onto the pulleys. The edges of the unused run of belt ((shall)) must be enclosed or otherwise guarded from contact by employees.
(2) Each drum sanding machine ((shall)) must be provided with a guard so arranged as to completely enclose the revolving drum except such portion required for the application of the material to be finished. Guards with hinges to facilitate the insertion of sandpaper may be installed. The exhaust hood may form part or all of this guard. When so used, the hood ((shall)) must conform to the specifications as given under exhaust systems in WAC 296-78-710.
(3) All standard stationary sanding machines ((shall)) must be provided with exhaust systems in conformity with the section of this code dealing with exhaust systems.
(4) All portable sanding machines ((shall)) must be provided with means of removing excessive dust, or employees using equipment ((shall)) must be provided with such necessary respiratory protective equipment as will conform to the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators.
(5) The requirements of WAC 296-806-475, sanding machines, ((shall)) must be applicable to sanding machines.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-78-670 Glue machines.
(1) Personal protective equipment as required by the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-160, and the general occupational health standard, WAC 296-62-11021, and proper washing facilities with noncaustic soap and sterilizers, ((shall)) must be provided for all employees handling glue. Rubber gloves and other personal equipment must be sterilized when transferred from one person to another.
(2) Glue spreaders ((shall)) must be enclosed on the in-running side, leaving only sufficient space to insert the stock.
(3) All glue spreaders ((shall)) must be equipped with a panic bar or equivalent type device that can be reached from either the infeed or outfeed side of the spreader to shut off the power in an emergency situation. Such device ((shall)) must be installed on existing glue spreaders no later than April 1, 1982, and be standard equipment on any glue spreader purchased after January 1, 1982.
(4) All glue mixing and handling rooms where located above work areas ((shall)) must have water tight floors.
(5) All glue rooms ((shall)) must be provided with ventilation in accordance with WAC 296-62-110 through 296-62-11013, of the general occupational health standard.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-675 Lath mills.
(1) Lath mills ((shall)) must be so arranged that stock pickers ((shall)) must be protected from slabs and blocks from slasher and trimmers.
(2) Bolters and lath machines ((shall)) must be provided with a wall or shield of not less than two inch wood material or equivalent, constructed in front of the machines, to protect stock pickers and passing employees from kickbacks.
(3) Lath bolters and lath mills ((shall)) must have all feed rolls, belts, gears and moving parts provided with approved guards. Feed chains ((shall)) must be guarded to as low a point as the maximum height of the stock will permit.
(4)(((a))) Lath bolters and lath mill saws ((shall)) must be provided with a sheet metal guard not less than one-eighth inch thick, or a cast iron guard not less than three-sixteenths inch thick, or equivalent. These hoods may be hinged so that they can be turned back to permit changing of the saws.
(((b))) (5) A metal plate baffle, finger device or other device, ((shall)) must be installed to prevent kickbacks.
(((5)(a))) (6) The feed rolls on bolters or lath mills ((shall)) must not be raised while any employee is in line with the saws.
(((b))) (7) The stock ((shall)) must be pushed through the saws with another piece of stock or push stick.
(((6)(a))) (8) The lath trimmer ((shall)) must be provided with guards on the ends, the top and the rear so designed as to contain debris and prevent employee contact with the saw. The belt drive ((shall)) must be provided with guards as required by WAC 296-78-710.
(((b))) (9) The entire top half of all trimmer saws ((shall)) must be provided with guards. The guards ((shall)) must be so adjusted as to prevent employees from accidentally contacting saws.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-680 Veneer and plywood plants—Peeling and barking.
(1) Where peeling or barking pits are located directly under the log cranes, logs ((shall)) must not be moved over workers.
(2) Single spiked hooks without a bell ((shall)) must not be used for handling logs. Hooks ((shall)) must be equipped with hand holds and ((shall)) must be maintained in condition to safely perform the job application.
(3) Mechanical barking devices ((shall)) must be ((so)) guarded so as to protect employees from flying chips, bark or other matter.
(4) Logs ((shall)) must not be removed from the barker until the barking head has ceased to revolve, unless the barker is so designed and arranged that the barking head will not create or constitute a hazard to employees.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-685 Veneer lathe.
(1) The elevating ramp (gate) ((shall)) must be provided with a safety chain and hook or other positive means of suspension while employees are working underneath same.
(2) The area under the tipple from lathe to stock trays ((shall)) must be provided with railings or other suitable means of preventing employees from entering this area, if access is not prevented by the construction of the machine and employees can enter this area.
(3) Catwalks ((shall)) must be provided along stock trays so that employees will not have to climb on the sides of trays to straighten stock.
(4) Any section of stock trays ((shall)) must be locked out or ((shall)) must have an operator stationed at starting controls while stock is being removed or adjusted.
(5) Guards which will cover the cutting edge of veneer lathe and clipper blades ((shall)) must be provided and used while such blades are being transported about premises.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-690 Veneer slicer and cutter.
(1) Each veneer slicer and each rotary veneer cutter ((shall)) must have all revolving and other moving knives provided with guards.
(2) The requirements of chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety, ((shall)) must be applicable to veneer slicers and cutters.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-695 Veneer clipper.
(1) Each veneer clipper ((shall)) must have either automatic feed or ((shall)) must be provided with a guard ((which)) that will make it impossible to place any portion of the hand under the knife while feeding stock. Where practicable, such guard ((shall)) must be of the vertical finger type.
(2) The rear of each manually operated clipper ((shall)) must be guarded either by a screen or vertical finger guard which ((shall)) must make it impossible for any portion of the hand to be placed under the knife while removing clipped stock.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-700 Veneer wringer (swede).
The entry side of each veneer wringer other than glue spreader ((shall)) must be enclosed, leaving only sufficient space to insert stock. A guard ((shall)) must be provided to prevent the veneer from overriding the top roll and kicking back.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-705 The shake and shingle industry.
The following terms and standards ((shall)) will apply only in the manufacturing of shakes and shingles and these requirements ((shall)) will take precedence over other sawmill and woodworking standards.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-70501 Definitions—Terms, general.
(((1) "))Block(s)((" -)). Those sections of a log cut in various lengths.
(((2) "))Block(s)((")) and (("))bolt(s)((")). May be considered to be synonymous.
(((3) "))Clipper saw((" -)). A circular saw used to trim manufactured shingles.
(((4) "))Groover((" -)). A cylinder-type knife (knives) similar to a planer knife (knives), used to cut grooves into the face surface of shakes or shingles.
(((5) "))Hip((")) and (("))ridge saw((" -)). A circular saw used to cut various angles on the side edge of shakes or shingles.
(((6) "))Johnson bar((" -)). A shaft used to control the feed of the carriage.
(((7) "))Knee bolter circular saw((" -)). A stationary circular saw used to trim and debark blocks (the blocks are manually maneuvered onto a carriage and fed into a saw).
(((8) "))Log haul((" -)). A power conveyor used to move logs to mill.
(((9) "))Packers((" -)). Employees who pack the manufactured shakes or shingles into bundles.
(((10) "))Panagraph power splitter((" -)). A hydraulically operated wedge, manually positioned into place, used to split blocks.
(((11) "))Power saw splitter((" -)). A stationary circular saw used to split (saw) blocks, (the blocks are manually maneuvered onto a carriage and fed into the saw).
(((12) "))Set works((" -)). A component of the shingle machine, located on the machine frame, used to control the thickness of each shingle being manufactured.
(((13) "))Shake machine((" -)). A band saw used to cut shake blanks into manufactured shakes.
(((14) "))Shake splitter((" -)). A stationary hydraulically operated wedge, manually controlled, used to split shake blocks into shake blanks or boards.
(((15) "))Shim saw((" -)). A circular saw used to ((re-cut)) recut manufactured shingles into narrow widths.
(((16) "))Shingle machine((" -)). A machine used to manufacture shingles; composed of a feed, set works, and carriage system, all functioning in relation to a circular saw.
(((17) "))Shingle saw((" -)). A circular saw used to cut shingles from blocks.
(((18) "))Spault((" -)). The first and last section(s) of a block as it is cut into shingles.
(((19) "))Spault catcher((" -)). A device located on the shingle machine next to the solid feed rolls, used to hold the last section of each block being cut (called a spault), in place.
(((20) "))Track or swing cutoff saw((" -)). A circular saw used to cut blocks from a log.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-70503 Shake and shingle machinery—General.
(1) Track or swing cutoff circular saw.
(a) Manually operated track or swing circular cutoff saws of the following types ((shall)) must be set up, guarded and operated in accordance with chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety:
((•)) (i) Saws into which materials to be cut are fed or positioned and/or held in position by hand pressure during the cutting stroke; ((and •))
(ii) Saws on which the cutting stroke is propelled by manual (hand) pressure; and
((•)) (iii) Saws on which the operator is within arm's reach of the blade when the blade is fully extended to the limit of operating travel and the operator is standing at the operator's normal control station/location.
(b) Large track or swing circular cutoff saws into which materials to be cut are fed by powered live rolls, conveyor belts and/or chains and which are operated from a remote operator's control station, defined as beyond arm's reach when the blade is fully extended to the limit of operating travel, ((shall)) must be set up, guarded and operated in accordance with the following:
(i) A power operated track or swing cutoff circular saw ((shall)) must have controls so arranged that operators are not positioned directly in front of the saw while making a cut.
(ii) All track or swing cutoff circular saws ((shall)) must be completely encased or guarded when the saw is in the retract position, except for that portion of the guard that must be left open for the operation of the saw.
(iii) Track or swing cutoff circular saw guards ((shall)) must be constructed of sheet metal not less than one-eighth inch thick, or a wood guard of not less than nominal two inch thick wood material, or equivalent.
Hinged or removable doors or gates will be permitted where necessary to permit adjusting and oiling.
(iv) The driving belt(s) on the track or swing cutoff circular saw ((shall)) must be guarded in accordance with chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
(v) A safety catch ((shall)) must be provided to prevent the track cutoff saw from leaving the track.
(2) Overhead deck splitter - Panagraph.
(a) Panagraph splitters ((shall)) must have a shroud incorporated on the upper pressure plate to eliminate the possibility of the splitter moving from the operating area. This shroud ((shall)) must be constructed of solid design with a minimum width of three inches and a minimum thickness of three-eighths inch.
(b) Mechanically operated overhead splitters ((shall)) must have handles moving opposite the stroke of the piston.
(c) When the leading edge of the panagraph splitter is completely extended, the maximum clearance from the deck to the splitting edge ((shall)) must be two inches.
(3) Power splitter saw. Power splitters ((shall)) must have spreaders behind the saw to prevent materials from squeezing the saw or being thrown back on the operator. The top of the saw ((shall)) must be completely covered.
(4) Knee bolter circular saw.
(a) A safety catch ((shall)) must be provided to prevent the bolter carriage from leaving the track.
(b) Bolter saws ((shall)) must be provided with a canopy guard of sheet metal not less than one-eighth inch thick, or cast iron guard not less than three-sixteenths inch thick or a wood guard of not less than nominal four inch thick wood material or equivalent.
The bolter canopy guard ((shall)) must completely enclose the rear portion of the saw. It ((shall)) must be so arranged and adjusted as to cover the front of the saw; not to exceed twenty inches from the top of the carriage to the bottom of the guard on sixteen inch and eighteen inch block and twenty-six inches on twenty-four inch blocks, of the material being cut.
(c) Bolter saws ((shall)) must be provided with wipers of belting or other suitable material. These wipers ((shall)) must be installed on both sides of the saw in such a manner as to deflect knots, chips, slivers, etc., that are carried by the saw.
(d) A positive device ((shall)) must be provided and used to manually lock and hold the feed table in the neutral position when not in use.
(e) That portion of all bolter saws which is below and behind the saw table ((shall)) must be guarded by the exhaust hood or other device. Hinged or removable doors or gates will be permitted where necessary to permit adjusting and oiling.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-70505 Shake machinery.
(1) Shake splitters.
(a) A positive deenergizing device ((shall)) must be provided within ready reach of each shake splitter operator.
(b) Each shake splitter ((shall)) must be provided with an adjustable stroke limiter to eliminate the splitting blade from striking the table.
(c) All splitters ((shall)) must have a maximum clearance of four inches, from the splitting edge to the table surface, when the splitter is in the extended position.
(d) All splitter tables ((shall)) must have a friction surface to reduce kick out of the material being split.
(e) Shake splitters ((shall)) must not be operated at a speed that would cause chunks to be thrown in such a manner as to create a hazard.
(f) The use of foot pedal (treadle) mechanisms ((shall)) must be provided with protection to prevent unintended operation from falling or moving objects or by accidental stepping onto the pedal.
(i) The pedal ((shall)) must have a nonslip surface.
(ii) The pedal return spring ((shall)) must be of the compression type, operating on a rod or guided within a hole or tube, or designed to prevent interleaving of spring coils in event of breakage.
(iii) If pedal counterweights are provided, the path of the travel of the weight ((shall)) must be enclosed.
(2) Shake saw guards.
(a) Every shake band saw ((shall)) must be equipped with a saw guard on both sides of the blade down to the top side of the guide.
(b) The outside saw guard ((shall)) must extend a minimum of three and one-half inches below the bottom edge of the saw guide.
(c) The maximum opening between the saw guide and table rolls ((shall)) must be fifteen inches.
(3) Shake saw band wheel guards.
(a) The band wheels on all shake band saws ((shall)) must be completely encased or guarded on both sides. The guards ((shall)) must be constructed of not less than No. 14 U.S. gauge metal or material equal in strength.
(b) The metal doors((,)) on such guards((, shall)) must have a wood liner of a minimum thickness of one-half inch.
(4) Shake saw band wheel speeds and maintenance.
(a) No band wheel ((shall)) must be run at a peripheral speed in excess of that recommended by the manufacturer.
(b) Each band wheel ((shall)) must be carefully inspected at least once a month by management.
Any band wheel in which a crack is found in the rim or in a spoke ((shall)) must be immediately discontinued from service until properly repaired.
(c) Each band saw frame ((shall)) must be provided with a tension indicator.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-70507 Upright shingle machine.
(1) Upright shingle saw guard.
(a) Every shingle machine carriage ((shall)) must be equipped with a hand guard which:
(i) Projects at least one inch beyond the cutting edge of the saw.
(ii) ((Shall)) Must be located not more than one-half inch from the side of the saw blade.
(b) Shingle saw guards ((shall)) must have a rim guard ((so)) designed and installed ((as)) to prevent chips and knots from flying from the saws. Such guards ((shall)) must cover the edge of the saw to at least the depth of the teeth, except such part of the cutting edge as is essential for sawing the material.
(c) Saw arbors and couplings ((shall)) must be guarded to prevent contact.
(d) Every part of a clipper saw blade, except ((that)) the part which is exposed to trim shingles, ((shall)) must be enclosed by a guard((, so)) designed and installed to prevent contact with the clipper saw. An additional guard ((shall)) must be installed not more than four inches above the clipper board and not more than one-half inch from the vertical plane of the saw.
(e) The underside of clipper saw boards ((shall)) must be equipped with a finger guard to effectively protect the operator's fingers. The guard ((shall)) must be a minimum of five inches long and one and one-quarter inches deep.
(2) Upright carriage guards.
(a) Automatic revolving cam set works and rocker arms, on machine frame, ((shall)) must be guarded where exposed to contact.
(b) The spault catchers ((shall be)) must not be less than three-sixteenths inch thick and kept sharp at all times. Missing teeth ((shall)) must be replaced.
(3) Carriage feed works.
(a) The pinion gear, bull wheel and Johnson bar, operating the saw carriage, ((shall)) must be guarded where exposed to contact.
(b) Each shingle machine clutch treadle ((shall)) must be arranged so that it is necessary to manually operate the treadle to start the machine. Devices which start the machine when the jaw treadle is released ((shall)) must not be installed or used. The carriage ((shall)) must have a brake to hold it in a neutral position.
(c) Carriage speed ((shall)) must not exceed thirty-four strokes per minute.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-70509 Related shake and shingle sawing machinery.
(1) Flat or taper saw. A wood or metal guard or its equivalent ((shall)) must be secured to the sliding table at the side nearest the sawyer to protect him from contact with the cutting edge of the saw when a block is not in the cut.
(2) Hip and ridge saws. The hip and ridge saws ((shall)) must be guarded with a hood-like device. This guard ((shall)) must cover that portion of the saw not needed to cut the material, located above the cutting table.
(a) The remaining portion of the saw, located below the table, ((shall)) must be guarded to prevent contact by employees.
(b) The hip and ridge guarding standard is applicable to both shake and shingle hip and ridge saws.
(3) Shim stock saws. The top ends and sides of the shim stock saws ((shall)) must be guarded. All shim stock saw power transmission mechanism ((shall)) must be guarded.
(4) Shake or shingle groover. The top ends and sides of the groover, ((to include)) including the press rolls, ((shall)) must be guarded to contain material or debris which can be thrown and to prevent contact. All groover machine power transmission mechanism ((shall)) must be guarded in compliance with WAC 296-78-710.
(5) Circular saws, speeds and repairs.
(a) Maximum allowable speeds.
(i) No circular saw ((shall)) must be run at a speed in excess of that recommended by the manufacturer.
(ii) Such speed ((shall)) must be etched or otherwise permanently marked on the blade, and that speed ((shall)) must not be exceeded.
(b) Repairs and reconditions.
(i) Shingle saws, when reduced in size to less than forty inches in diameter ((shall)), must be discontinued from service as shingle saws on upright or vertical machines.
(ii) Shingle saws may be reconditioned for use as clipper saws provided the surface is reground and the proper balance attained.
(iii) Shingle saws may be used to no less than thirty-six inches on flat or taper saw machines.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-70511 Safety rules.
(1) General.
(a) Workers ((shall)) must not leave shingle machines unattended while the carriage is in motion.
(b) Shingle blocks ((shall)) must not be piled more than one tier high on tables or roll cases. Chunks may be placed horizontally one tier high on top of shingle blocks. Shingle blocks ((shall)) must be piled in a stable manner, not more than seventy-two inches high, within the immediate working area of the shingle sawyer or the area ((shall)) must be barricaded.
(c) Provisions ((shall)) must be made to prevent blocks from falling into the packing area.
(d) On each machine operated by electric motors, positive means ((shall)) must be provided for rendering such controls or devices inoperative while repairs or adjustments are being made to the machines they control.
(e) Workers ((shall)) must not stand on top of blocks while in the process of splitting other blocks into bolts.
(2) Jointers (shingle). Shingle jointers ((shall)) must have the front, or cutting face of the knives, housed except for a narrow slot through which the shingles may be fed against the knives.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-16-020, filed 7/24/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-78-71001 General.
(1) Construction when not specifically covered in these standards ((shall)), must be governed by such other standards adopted by the department of labor and industries as may apply.
(2) All buildings, docks, tramways, walkways, log dumps and other structures ((shall be so)) must be designed, constructed, and maintained ((as)) to provide a safety factor of four. This means that all members ((shall)) must be capable of supporting four times the maximum load to be imposed. This provision refers to buildings, docks and so forth designed and constructed subsequent to the effective date of these standards and also refers in all cases where either complete or major changes or repairs are made to such buildings, docks, tramways, walkways, log dumps and other structures.
(3) Basements on ground floors under mills ((shall)) must be evenly surfaced, free from unnecessary obstructions and debris, and provided with lighting facilities in compliance with the requirements of the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-210.
(4) All engines, motors, transmission machinery or operating equipment installed in mill basements or ground floors ((shall)) must be equipped with standard safeguards for the protection of workers.
(5) Flooring of buildings, ramps and walkways not subject to supporting motive equipment ((shall be of)) must not be of less than two-inch wood planking or material of equivalent structural strength.
(6) Flooring of buildings, ramps, docks, trestles and other structures required to support motive equipment ((shall be of)) must not be of less than full two and one-half inch wood planing or material of equivalent structural strength. However, where flooring is covered by steel floor plates, two inch wood planking or material or equivalent structural strength may be used.
(7) Walkways, docks, and platforms.
(a) Walkways, docks and platforms ((shall)) must be constructed and maintained in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-24-735 through 296-24-75011 and WAC 296-800-270.
(b) Maintenance. Walkways ((shall)) must be evenly floored and kept in good repair.
(c) Where elevated platforms are used, they ((shall)) must be equipped with stairways or ladders in accordance with WAC 296-24-765 through 296-24-81013, WAC 296-800-250 and chapter 296-876 WAC, Ladders, portable and fixed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-78-71003 Floor and wall openings.
(1) All floor and wall openings, either temporary or permanent, ((shall)) must be protected as required by WAC 296-24-750 through 296-24-75011 and WAC 296-800-260.
(2) The area under floor openings ((shall)) must, where practical, be fenced off. When this is not practical, the areas ((shall)) must be plainly marked with yellow lines and telltails ((shall)) must be installed to hang within five and one-half feet of the ground or floor level.
(3) Where floor openings are used to drop materials from one level to another, audible warning systems ((shall)) must be installed and used to indicate to employees on the lower level that material is to be dropped.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-71005 Floors, docks, platforms and runways.
(1) Faces of docks except on loading and unloading sides of rail and truck loading platforms, and runways used for the operation of lift trucks and other vehicles ((shall)) must have a guard or shear timber eight by eight inches set over three inch blocks and securely fastened to the floor by bolts of not less than five-eighths inch diameter.
(2) The flooring of buildings, docks and passageways ((shall)) must be kept in good repair at all times. When a hazardous condition develops that cannot be immediately repaired, the area shall be fenced off and not used until adequate repairs are made.
(3) All working areas ((shall)) must be kept free from unnecessary obstruction and debris.
(4) Floors around machines and other places where workers are required to stand ((shall)) must be provided with effective means to prevent slipping.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-71007 Footwalks and passageways.
(1) All footwalks and passageways subject to slipping hazards due to peculiarities of conditions or processes of the operation ((shall)) must be provided with nonslip surfaces.
(2) Walkways in accordance with WAC 296-78-71001(8) ((shall)) must be provided over roll casings, transfer tables, conveyors or other moving parts except ((where)) when stepping over such equipment is not in connection with usual and necessary traffic.
(3) Walkways alongside of sorting tables ((shall)) must be of sufficient width to provide a safe working area. Such walkways ((shall)) must be evenly floored and kept in good repair at all times. They ((shall)) must be kept free from obstructions and debris.
(4) When employees are required to clear plug-ups in veneer trays or lumber sorting trays, adequate walkways with standard guardrails ((shall)) must be provided for access to the trays whenever possible. When walkways are not provided, safety belts or harnesses with lanyards, tied off to substantial anchorages, ((shall)) must be provided and used at all times.
(5) Walkways and stairways with standard hand rails ((shall)) must be provided wherever space will permit, for oilers and other employees whose duties require them to go consistently to elevated and hazardous locations.
(a) Where such passageways are over walkways or work areas, standard toeboards ((shall)) must be provided.
(b) Protection, as required by chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety, ((shall)) must be provided against contact with transmission machinery or moving conveyors.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-16-020, filed 7/24/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-78-71009 Stairways and ladders.
(1) Stairways ((shall)) must be used in preference over ladders wherever possible. Stairways or ladders, whichever is used, ((shall)) must be constructed and maintained in accordance with the provisions of WAC 296-24-75009 through 296-24-81013, WAC 296-800-250 and chapter 296-876 WAC, Ladders, portable and fixed.
(2) Doors ((shall)) must not open directly on a flight of stairs.
(3) Permanent ladders ((shall)) must be fastened securely at both the top and the bottom.
(4) Portable ladders ((shall)) must not be used upon footing other than a suitable type.
(5) Hooks or other means of securing portable ladders when in use((, shall)) must be provided.
(6) Portable ladders ((shall)) must not be used for oiling machinery which is in motion.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-78-71011 Egress and exit.
(1) In all enclosed buildings, means of egress ((shall)) must be provided in accordance with the provisions of WAC 296-800-310.
(2) All swinging doors ((shall)) must be provided with windows, the bottom of which ((shall be)) must not be more than forty-eight inches above the floor. One window ((shall)) must be provided for each section of double swinging doors. All such windows ((shall)) must be of shatter proof or safety glass unless otherwise protected against breakage.
(3) Outside exits ((shall)) must open outward. ((Where)) When sliding doors are used as exits, an inner door not less than two feet six inches by six feet ((shall)) must be cut inside each of the main doors and arranged to open outward.
(4) At least two fire escapes or substantial outside stairways((, shall)) must be provided for mill buildings where the floor level is more than eight feet above the ground.
(a) Buildings over one hundred fifty feet in length ((shall)) must have at least one additional fire escape or substantial outside stairway for each additional one hundred fifty feet of length or fraction thereof.
(b) Passageways to fire escapes or outside stairways ((shall)) must be marked and kept free of obstructions at all times.
(c) Fire protection. The requirements of chapter 296-24 WAC, Part G-3 of the general safety and health standard, and WAC 296-800-300 of the safety and health core rules, and chapter 296-811 WAC, Fire brigades, ((shall)) must be complied with in providing the necessary fire protection for sawmills.
(d) Fire drills ((shall)) must be held at least quarterly and ((shall)) must be documented.
(5) Where a doorway opens upon a roadway, railroad track, or upon a tramway or dock over which vehicles travel, a barricade or other safeguard and a warning sign ((shall)) must be placed to prevent workers from stepping directly into moving traffic.
(6) Tramways and trestles ((shall)) must be substantially supported by piling or framed bent construction, which ((shall)) must be frequently inspected and maintained in good repair at all times. Tramways or trestles used both for vehicular and pedestrian traffic ((shall)) must have a walkway with standard hand rail at the outer edge and shear timber on the inner edge, and ((shall)) must provide three feet clearance to vehicles. When walkways cross over other thoroughfares, they ((shall)) must be solidly fenced at the outer edge to a height of forty-two inches over such thoroughfares.
(7) Where tramways and trestles are built over railroads, they ((shall)) must have a vertical clearance of twenty-two feet above the top of the rails. When constructed over carrier docks or roads, they ((shall)) must have a vertical clearance of not less than six feet above the drivers foot rest on the carrier, and in no event ((shall)) must this clearance be less than twelve feet from the surface of the lower roadway or dock.
(8) Walkways (either temporary or permanent) ((shall)) must be not less than twenty-four inches wide and two inches thick, nominal size, securely fastened at each end. When such walkways are used on an incline the angle ((shall)) must not be greater than twenty degrees from horizontal.
(9) Walkways from the shore or dock to floats or barges ((shall)) must be securely fastened at the shore end only and clear space provided for the other end to adjust itself to the height of the water.
(10) Cleats of one by four inch material ((shall)) must be fastened securely across walkways at uniform intervals of eighteen inches whenever the grade is sufficient to create a slipping hazard.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-71013 Cableways.
(1)(((a))) Inclined cableways ((shall)) must have a central line between the rails in practical alignment with the center of the hoisting drums. A substantial bumper ((shall)) must be installed at the foot of each incline.
(((b))) (2) Barricades or warning signs ((shall)) must be installed to warn pedestrians to stand clear of the cables on inclined cableways. The cables ((shall)) must not be put into motion without activating an alarm system, either audible or visible, which will inform anyone on the tracks to stand clear.
(((2))) (3) Employees ((shall)) must not ride on or stand below the cars on an inclined cableway.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-78-71015 Tanks and chemicals.
(1) All open vats and tanks into which workers may fall ((shall)) must be guarded with standard railings or screen guards in all cases where such guarding is possible with regard to practical operation.
(2) Foundations of elevated tanks ((shall)) must be accessible for inspections. When the tank platform is more than five feet above the ground a stairway or ladder ((shall)) must be permanently attached.
(3) Every open tank over five feet in height ((shall)) must be equipped with fixed standard ladders both inside and out, extending from the bottom to the rim of the tank arranged to be accessible to each other, so far as local conditions permit.
(4) The use of chemicals for treating of lumber for prevention of sap stain or mold or as preservatives, ((shall)) must conform to the requirements of chapter 296-835 WAC, Dipping and coating operations (dip tanks).
(a) Storage, handling, and use of chemicals. Threshold limits. Employees ((shall)) must not be exposed to airborne concentration of toxic dusts, vapors, mists or gases that exceed the threshold limit values set forth in chapter 296-62 WAC, Part H, and chapter 296-841 WAC, Airborne contaminants.
(b) Protective equipment. The use of chemicals ((shall)) must be controlled ((so as)) to protect employees from harmful exposure to toxic materials. Where necessary, employees ((shall)) must be provided with and are required to wear such protective equipment ((as)) that will afford adequate protection against harmful exposure as required by WAC 296-800-160, and chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators.
(5)(((a))) Means ((shall)) must be provided and used to collect any excess of chemicals used in treating lumber so as to protect workers from accidental contact with harmful concentrations of toxic chemicals or fumes.
(((b))) (a) Dip tanks containing flammable liquids ((shall)) must be constructed, maintained and used in accordance with chapter 296-835 WAC, Dipping and coating operations (dip tanks).
(((c))) (b) An evacuation plan ((shall)) must be developed and implemented for all employees working in the vicinity of dip tanks using flammable liquids. A copy of the plan ((shall)) must be available at the establishment for inspection at all times. Every employee ((shall)) must be made aware of the evacuation plan and know what to do in the event of an emergency and be evacuated in accordance with the plan. The plan ((shall)) must be reviewed with employees at least quarterly and documented.
(((d))) (c) When automatic foam, automatic carbon dioxide or automatic dry chemical extinguishing systems are used, an alarm device ((shall)) must be activated to alert employees in the dip tank area before and during the activation of the system. The following combinations of extinguishment systems when used in conjunction with the evacuation plan as stated above will be acceptable in lieu of bottom drains:
(i) A dip tank cover with an automatic foam extinguishing system under the cover, or an automatic carbon dioxide system, or an automatic dry chemical extinguishing system, or an automatic water spray extinguishing system;
(ii) An automatic dry chemical extinguishing system with an automatic carbon dioxide system or a second automatic dry chemical extinguishing system or an automatic foam extinguishing system;
(iii) An automatic carbon dioxide system with a second automatic carbon dioxide system or an automatic foam extinguishing system.
(((e))) (d) The automatic water spray extinguishing systems, automatic foam extinguishing systems, and dip tank covers ((shall)) must conform with the requirements of chapter 296-835 WAC, Dipping and coating operations (dip tanks). The automatic carbon dioxide systems and dry chemical extinguishing system ((shall)) must conform with the requirements of WAC 296-24-615 and 296-24-620.
(6) Where workers are engaged in the treating of lumber with chemicals or are required to handle lumber or other materials so treated, the workers ((shall)) must be provided with, at no cost to the worker, and required to use such protective equipment ((as)) that will provide complete protection against contact with toxic chemicals or fumes therefrom.
(7) Sanitation requirements. The requirements of WAC 296-800-220 and 296-800-230 (safety and health core rules), ((shall)) must govern sanitation practices.
(8) The sides of steam vats and soaking pits, unless otherwise guarded ((shall)), must extend forty-two inches above the floor level. The floor adjacent thereto ((shall)) must be of nonslip construction.
(9) Large steam vats or soaking pits, divided into sections, ((shall)) must be provided with substantial walkways between each section, each walkway to be provided with standard railings which may be removable if necessary.
(10) Covers ((shall)) must be removed only from that portion of the steaming vats on which workers are working and a portable railing ((shall)) must be placed at this point to protect the operators.
(11) Workers ((shall)) must not ride or step on logs in steam vats.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-16-020, filed 7/24/06, effective 12/1/06)
WAC 296-78-71017 Dry kilns.
(1) Dry kilns ((shall)) must be ((so)) constructed upon solid foundations so that tracks will not sag. Dry kilns ((shall)) must be provided with suitable walkways. Each kiln ((shall)) must have doors that operate from the inside and be provided with escape doors of adequate height and width to accommodate an average size man, that also operates from the inside, and ((shall)) must be located in or near the main door. Escape doors ((shall)) must swing in the direction of the exit. Kiln doors and door carriers ((shall)) must be fitted with safety devices to prevent the doors or carriers from falling.
(2) Ladders. A fixed ladder, in accordance with the requirements of chapter 296-876 WAC, Ladders, portable and fixed, or other means ((shall)) must be provided to permit access to the roof. Where controls and machinery are mounted on the roof, a permanent stairway with standard handrail ((shall)) must be installed in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-800-250.
(3) A heated room ((shall)) must be provided for the use of the kiln operator in inclement weather. ((He)) They should remain in such room for at least ten minutes after leaving a hot kiln before going to cold outside air.
(4) Where operating pits are used, they ((shall)) must be well ventilated, drained and lighted. Substantial gratings ((shall)) must be installed at the kiln floor line. Steam lines ((shall)) must be provided with insulation wherever exposed to contact by employees. Fans ((shall)) must be enclosed by standard safeguards.
(5) Mechanical equipment. All belts, pulleys, blowers, and other exposed moving equipment used in or about kilns ((shall)) must be guarded in accordance with chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-78-71019 Exhaust systems.
(1) Air requirements in buildings, where persons are habitually employed, ((shall)) must meet the requirements of the general occupational health standard, WAC 296-62-100 through 296-62-11013.
(2) Where the natural ventilation is not sufficient to remove dust, fumes or vapors that create or constitute a hazard, additional means of removal ((shall)) must be provided.
(3) All mills containing one or more machines whose operations create dust, shavings, chips or slivers during a period of time equal to or greater than one-fourth of the working day or shift, ((shall)) must be equipped with a collecting system either continuous or automatic in action and of sufficient strength and capacity to thoroughly remove such refuse from the points of operation of the machines and the work areas.
(4) Each woodworking machine that creates dust, shavings, chips, or slivers ((shall)) must be equipped with an exhaust or conveyor system located and adjusted to remove the maximum amount of refuse from the point of operation and immediate vicinity.
(5) Blower, collecting and exhaust systems ((shall)) must be designed, constructed and maintained in accordance with American National Standards Z33.1 - 1961 (for the installation of blower and exhaust systems for dust, stock and vapor removal or conveying) and Z12.20 - 1962 (R1969) (code for the prevention of dust explosions in woodworking and wood flour manufacturing plants).
(6) Fans used for ventilating ((shall)) must be of ample capacity, as evidenced by the performance schedules of the manufacturers, and ((shall)) must be guarded when exposed to contact. Hoods, dust conveyors, dust collectors and other accessary equipment ((shall)) must be large enough to insure free intake and discharge.
(7) The outlet or discharge of all ventilating equipment ((shall)) must be ((so)) arranged so that at no time will the dust, vapors, gases or other air borne impurities discharged, create or constitute a hazard.
(8) Where a hood is used to form a part or all of the guard required on a given machine, it ((shall)) must be constructed of ((not)) no less than ten U.S. gauge sheet metal, or if of cast iron it ((shall be)) must not be less than three-sixteenths inches in thickness.
(9) All exhaust pipes ((shall)) must be of such construction and internal dimensions as to minimize the possibility of clogging. They ((shall)) must be readily accessible for cleaning.
(10) All exhaust pipes ((shall)) must empty into settling or dust chambers which ((shall)) must effectively prevent the dust or refuse from entering any work area. Such settling or dust chambers ((shall)) must be so designed and operated as to reduce to a minimum the danger of fire or dust explosions.
(11) In lieu of a general ventilating system, exhaust or blower units may be installed on the dust or fume producing machine, provided the required protection is secured thereby.
(12) When proper ventilation is not provided, and temporary hazardous conditions are therefore encountered, ((the employer shall)) you must furnish approved respiratory and visual equipment: Provided, however, That the exposure to such hazard ((shall)) must not be for more than two hours duration. Protective measures and equipment ((shall)) must meet the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators.
(13) Provisions for the daily removal of refuse ((shall)) must be made in all operations not required to have an exhaust system, or having refuse too heavy, or bulky, or otherwise unsuitable to be handled by an exhaust system.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-71021 Spray painting.
All spray painting operations ((shall)) must be carried on in accordance with the requirements of the general safety and health standard, WAC 296-24-370 through 296-24-37027 and the general occupational health standard, WAC 296-62-11019.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-78-71023 Lighting.
The lighting and illumination requirements of the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-210, ((shall)) must apply.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-71025 Gas piping and appliances.
All gas piping and appliances ((shall)) must be installed in accordance with the American National Standard Requirements for Gas Appliances and Gas Piping Installations, Z21.30 - 1964.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-71501 General provisions.
(1) All machinery or other equipment located or used on the premises of the operation or in the processes incidental thereto, ((shall)) must be provided and maintained with approved standard safeguards, irrespective of ownership.
(2) Machines ((shall)) must be ((so)) located so that each operator will have sufficient space in which to handle material with the least possible interference from or to other workers or machines.
(3) Machines ((shall)) must be so placed that it will not be necessary for the operator to stand where passing traffic creates a hazard.
(4) Aisles of sufficient width to permit the passing of vehicles or employees without crowding ((shall)) must be provided in all work areas and stock or storage rooms.
(5) All metal decking around machinery ((shall)) must be equipped to effectively prevent slipping.
(6) All machinery or equipment started by a control so located as to create impaired vision of any part of such machinery or equipment ((shall)) must be provided with an audible warning device, where such machinery or equipment is exposed to contact at points not visible to the operator. Such devices ((shall)) must be sounded before starting up unless positive mechanical or electrical interlocking controls are provided which will prevent starting until all such posts are cleared.
(7) A mechanical or electrical power control device ((shall)) must be provided at each machine which will make it possible for the operator to stop the machine feed without leaving his position at the point of operation.
(8) All machines operated by means of treadles, levers, or other similar devices, ((shall)) must be provided with positive and approved nonrepeat devices except where such machine is being used as an automatic repeating device.
(9) Operating levers and treadles on all machines or machinery ((shall)) must be ((so)) located and protected ((that)) so they cannot be shifted or tripped accidentally.
(10) All power driven machinery ((shall)) must be stopped and brought to a complete standstill before any repairs or adjustments are made or pieces of material or refuse removed, except where motion is necessary to make adjustments.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-78-71505 Mechanical power transmission apparatus.
(1) Machines and other equipment ((shall)) must not be oiled while in motion, unless provided with guards or other devices to permit oiling without any possibility of contact with moving parts of machinery.
(2) Inspections ((shall)) must be made to ((assure)) ensure that shaftings, bearings and machines are in proper alignment at all times and that bolts in shaft hangars, couplings and boxes are tight.
(3) Isolated bearings or other equipment not reached by walkway ((shall)) must be served by a ladder or other means of safe access.
(4) Running belts under power on or off pulleys ((shall)) must be accomplished by mechanical means which will not expose employees to moving elements of the operation.
(5) Counterweights located on or near passageways or work areas ((shall)) must be provided with enclosures. Overhead counterweights ((shall)) must be provided with substantial safety chains or cables, or otherwise secured against falling.
(6) The construction, operation, and maintenance of all mechanical power-transmission apparatus ((shall)) must be in accordance with chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
(7) Baffles ((shall)) must be erected, where necessary, to protect employees from breaking belts, chains, ropes or cables.
(8) Overhead horizontal belts, chains or rope drives ((shall)) must be provided with guards.
(9) Hydraulic systems. Means ((shall)) must be provided to block, chain, or otherwise secure equipment normally supported by hydraulic pressure so as to provide for safe maintenance.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-720 Boiler and pressure vessels.
Boilers and pressure vessels ((shall)) must be constructed, maintained and inspected in accordance with the provisions of the boiler and unfired pressure vessel law, chapter 70.79 RCW, and chapter 296-104 WAC as administered by the boiler inspection section of the department of labor and industries.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-17-056, filed 8/20/96, effective 10/15/96)
WAC 296-78-725 Nonionizing radiation.
(1) Only qualified and trained employees ((shall)) must be assigned to install, operate, adjust, and maintain laser equipment. Proof of qualification of the laser equipment operator ((shall)) must be available and in possession of operator at all times.
(2) Employees, when working in areas in which a potentially hazardous exposure (see WAC 296-62-09005(4)) to direct or reflected laser radiation exists, ((shall)) must be provided with antilaser eye protection devices specified in WAC 296-62-09005, general occupational health standards.
(3) Areas in which lasers are used ((shall)) must be posted with standard laser warning placards.
(4) Beam shutters or caps ((shall)) must be utilized, or the laser turned off, when laser transmission is not actually required. When the laser is left unattended for a substantial period of time, such as during lunch hour, overnight, or at change of shifts, the laser ((shall)) must be turned off or shutters or caps ((shall)) must be utilized.
(5) The laser beam ((shall)) must not be directed at employees.
(6) Only mechanical or electronic means ((shall)) must be used as a detector for guiding the internal alignment of the laser.
(7) The laser equipment ((shall)) must bear such labels, logos and data placards to indicate maximum output and class designation as required of the manufacturer at time of sale, by I.A.W. Part 1040, C.F.R. Title 21. Such labels, logos, data placards, etc., ((shall)) must be maintained in a legible condition.
(8) When it is raining or snowing, or when there is dust or fog in the air, and it is impracticable to cease laser system operation, employees ((shall)) must be kept out of range of the area of source and target during such weather conditions.
(9) Employees ((shall)) must not be exposed to light intensities in excess of:
(a) Direct staring: One micro-watt per square centimeter;
(b) Incidental observing: One milliwatt per square centimeter; or
(c) Diffused reflected light: Two and one-half watts per square centimeter.
(10) The laser equipment ((shall)) must not be modified, except by the manufacturer.
(11) Laser unit in operation ((shall)) must be set up above the heads of the employees, when possible.
(12) Employees ((shall)) must not be exposed to radio frequency/microwave radiation in excess of the permissible exposure limits specified in WAC 296-62-09005.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-78-730 Electrical service and equipment.
(1) Electrical service and equipment ((shall)) must be constructed, maintained, inspected and operated according to chapter 296-24 WAC, General safety and health standards, Part L, and WAC 296-800-280 of the safety and health core rules.
(2) Repairs. Electrical repairs ((shall)) must be made only by authorized and qualified personnel.
(3) Identification. Marks of identification on electrical equipment ((shall)) must be clearly visible.
(4) Protective equipment. Rubber protective equipment ((shall)) must be provided as required by WAC 296-800-160 of the safety and health core rules.
(5) Open switches. Before working on electrical equipment, switches ((shall)) must be open and ((shall)) must be locked out.
(6) Concealed conductors. Where electrical conductors are known to be concealed, no work ((shall)) must be performed until such conductors are located.
(7) Overload relays. Overload relays ((shall)) must be reset by authorized qualified personnel only.
(8) Passageways to panels. Passageways to switch centers or panels ((shall at all times)) must be kept free from obstruction at all times. Not less than three feet of clear space ((shall)) must be maintained in front of switch centers or panels at all times.
(9) Bridging fuses. Fuses ((shall)) must not be doubled or bridged.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-78-735 Elevators, moving walks.
Elevators, moving walks and other lifting devices intended for either passenger or freight service ((shall)) must be constructed, maintained, inspected and operated in accordance with the provisions of chapter 70.87 RCW, WAC 296-24-875 through 296-24-90009 of the general safety and health standards, and those specific standards which are applicable from the division of building and construction safety inspection services, elevator section.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-740 Transportation—Lumber handling equipment—Cranes—Construction.
(1) All apparatus ((shall)) must be designed throughout, with not less than the following factors of safety, under static full rated load stresses, based on ultimate strength of the material used:
Material |
Factor of Safety |
||
Cast iron. . . . |
12 |
||
Cast steel. . . . |
8 |
||
Structural steel. . . . |
5 |
||
Forged steel. . . . |
5 |
||
Cables. . . . |
5 |
||
(2) A notice ((shall)) must be placed on every crane and hoist showing the maximum allowable load in pounds or tons. This notice ((shall)) must be placed in such a manner as to be clearly legible from the floor.
(3) Cranes ((shall)) must be of what is known as "all steel construction." No cast iron ((shall)) will be used in parts subject to tension except in drums, trolley sides, bearings, brackets and brake shoes.
(4) The construction of cranes ((shall)) must be such that all parts may be safely lubricated and inspected when cranes are not in operation.
(5) Bolts subject to stress ((shall)) must be of the through type and all bolts ((shall)) must be equipped with approved protection so that the bolt will not work loose or nuts work off.
(6) Outside crane cages ((shall)) must be enclosed. There ((shall)) must be windows on three sides of the cage and windows in the front, and the side opposite the door ((shall)) must be the full width of the cage.
(7) Where a tool box or receptacle is used for the storing of oil cans, tools, etc., it ((shall)) must be permanently secured in the cage or on the foot-walk of outside cranes and on the foot-walk of inside cranes. Tool boxes of hot metal cranes ((shall)) must be constructed of metal.
(8) All gears on cranes ((shall)) must be provided with standard guards.
(9) Keys projecting from revolving shafts ((shall)) must be guarded.
(10) A braking apparatus ((shall)) must be provided on every type of crane and ((shall)) must be so designed and installed as to be capable of effectually braking a weight of at least one and one-half times the full rated load.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-745 Electrical equipment.
(1) All exposed current-carrying parts except conductors, connected to circuits above three hundred volts to ground ((shall)) must be ((so)) isolated, insulated, or guarded so that no employee can come in contact with them. Exposed parts less than 300 volts ((shall)) must be protected in some suitable way against possible accidental contact. Exposed metallic parts of conduit armored cable or molding ((shall)) must be permanently grounded.
(2) Guards for the current-carrying parts of unisolated electrical equipment, such as controllers, motors, transformers, automatic cutouts, circuit breakers, switches, and other devices ((shall)) must consist of cabinets, casings, or shields of permanently grounded metal or of insulating material.
(3) All parts of electrical equipment, such as fuses and the handles and arc chutes of circuit breakers, ((shall)) must be ((so)) isolated or guarded so that the liability of employees being struck or burned by sparking, flashing or movement during operation is reduced to a minimum.
(4) All exposed noncurrent carrying metal parts of electrical equipment ((shall)) must be permanently grounded. The ground connection through well bonded track rails will be considered satisfactory.
(5) The metallic parts of portable cranes, derricks, hoists, and similar equipment on which wires, cables, chains, or other conducting objects are maintained ((shall)) must be provided with an effective protective ground, where operated in the vicinity of supply lines.
(6) Readily accessible means ((shall)) must be provided whereby all conductors and equipment located in cranes can be disconnected entirely from the source of energy at a point as near as possible to the main current collectors.
(7) Means ((shall)) must be provided to prevent the starting and operation of equipment by unauthorized persons.
(8) The control levers of traveling cranes ((shall)) must be ((so)) located so that the operator can readily face the direction of travel.
(9) A hoist limiting device ((shall)) must be provided for each hoist.
(10) All fuses ((shall)) must be of the enclosed arcless type.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-17-056, filed 8/20/96, effective 10/15/96)
WAC 296-78-750 Chains, wire rope, cables and fiber rope.
(1) Ropes, cables, slings, and chains.
(a) Safe usage. Ropes, cables, slings, and chains ((shall)) must be used in accordance with safe use practices recommended by the manufacturer or within safe limits recommended by the equipment manufacturer when used in conjunction with it.
(b) Work by qualified persons. Installation, inspection, maintenance, repair, and testing of ropes, cables, slings, and chains ((shall)) must be done only by persons qualified to do such work.
(((b))) (c) Proof testing. ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that before use, each new, repaired, or reconditioned alloy steel chain sling, including all welded components in the sling assembly, ((shall be)) is proof tested by the sling manufacturer or equivalent entity, in accordance with paragraph 5.2 of the American Society of Testing and Materials Specification A391.65 (ANSI G61.1-1968). ((The employer shall)) You must retain the certificate of the proof test and ((shall)) must make it available for examination. When a chain sling assembly is made up of segments of proof tested alloy chain and proof tested individual components such as mechanical coupling links, hooks and similar devices; it is not necessary to test the assembled unit, when appropriate test certification of individual components is available and the assembled sling is appropriately tagged by the manufacturer or equal entity. The sling ((shall)) must not be used in excess of the rated capacity of the weakest component.
(((c) Slings.)) (d) Slings and their fittings and fastenings, when in use, ((shall)) must be inspected daily for evidence of overloading, excessive wear, or damage. Slings found to be defective ((shall)) must be removed from service.
(2) Proper storage ((shall)) must be provided for slings while not in use.
(3) Protection ((shall)) must be provided between the sling and sharp unyielding surfaces of the load to be lifted.
(4) Hooks. No open hook ((shall)) must be used in rigging to lift any load where there is hazard from relieving the tension on the hook from the load or hook catching or fouling.
(5) Ropes or cables. Wire rope or cable ((shall)) must be inspected when installed and once each day thereafter, when in use. It ((shall)) must be removed from hoisting or load-carrying service when kinked or when one of the following conditions exist:
(a) When three broken wires are found in one lay of 6 by 6 wire rope.
(b) When six broken wires are found in one lay of 6 by 19 wire rope.
(c) When nine broken wires are found in one lay of 6 by 37 wire rope.
(d) When eight broken wires are found in one lay of 8 by 19 wire rope.
(e) When marked corrosion appears.
(f) Wire rope of a type not described herein ((shall)) must be removed from service when four percent of the total number of wires composing such rope are found to be broken in one lay.
(g) Condemned. When wire rope, slings or cables deteriorate through rust, wear, broken wires, kinking or other conditions, to the extent there is a reasonable doubt that the necessary safety factor is maintained, the use of such equipment ((shall)) must be discontinued.
(6) Wire rope removed from service due to defects ((shall)) must be plainly marked or identified as being unfit for further use on cranes, hoists, and other load-carrying devices.
(7) The ratio between the rope diameter and the drum, block, sheave, or pulley tread diameter ((shall)) must be such that the rope will adjust itself to the bend without excessive wear, deformation, or injury. In no case ((shall)) must the safe value of drums, blocks, sheaves, or pulleys be reduced when replacing such items unless compensating changes are made for rope used and for safe loading limits.
(8) ((Drums, sheaves, and pulleys.)) Drums, sheaves, and pulleys ((shall)) must be smooth and free from surface defects liable to injure rope. Drums, sheaves, or pulleys having eccentric bores or cracked hubs, spokes, or flanges ((shall)) must be removed from service.
(9) ((Connections.)) Connections, fittings, fastenings, and other parts used in connection with ropes and cables ((shall)) must be of the quality, size and strength recommended by the manufacturer for the use intended. These connections ((shall)) must be installed in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations.
(10) Socketing, splicing, and seizing.
(a) Socketing, splicing, and seizing of cables ((shall)) must be performed only by qualified persons.
(b) All eye splices ((shall)) must be made in a manner recommended by the manufacturer and wire rope thimbles of proper size ((shall)) must be fitted in the eye, except that in slings the use of thimbles ((shall)) will be optional.
(11) Wire rope clips attached with U-bolts ((shall)) must have these bolts on the dead or short end of the rope. The U-bolt nuts ((shall)) must be retightened immediately after initial load carrying use and at frequent intervals thereafter. The number and spacing of clips ((shall)) must be as follows:
Improved Plow Steel Diameter of Rope |
Number of Clips (Drop Forged) |
Required Other Material |
Minimum Space Between Clips |
|||
3/8 to 5/8 |
" |
3 |
4 |
3-3/4 |
" |
|
3/4 |
" |
4 |
5 |
4-1/2 |
" |
|
7/8 |
" |
4 |
5 |
5-1/4 |
" |
|
1 |
" |
5 |
6 |
6 |
" |
|
1-1/8 |
" |
6 |
6 |
6-3/4 |
" |
|
1-1/4 |
" |
6 |
7 |
7-1/2 |
" |
|
1-3/8 |
" |
7 |
7 |
8-1/4 |
" |
|
1-1/2 |
" |
7 |
8 |
9 |
" |
|
(a) When a wedge socket-type fastening is used, the dead or short end of the cable ((shall)) must be clipped with a U-bolt or otherwise made secure against loosening.
(b) Fittings. Hooks, shackles, rings, pad eyes, and other fittings that show excessive wear or that have been bent, twisted, or otherwise damaged ((shall)) must be removed from service.
(12) Running lines. Running lines of hoisting equipment located within six feet six inches of the ground or working level ((shall)) must be boxed off or otherwise guarded, or the operating area ((shall)) must be restricted.
(13) Preventing abrasion. The reeving of a rope ((shall)) must be so arranged as to minimize chafing or abrading while in use.
(14) Sheave guards. Bottom sheaves ((shall)) must be protected by close fitting guards to prevent cable from jumping the sheave.
(15) There ((shall be)) must not be less than two full wraps of hoisting cable on the drums of cranes and hoists at all times of operation.
(16) Where the cables are allowed to pile on the drums of cranes, the drums ((shall)) must have a flange at each end to prevent the cables from slipping off the drum.
(17) ((Chains.)) Chains used in load carrying service ((shall)) must be inspected before initial use and weekly thereafter.
If at any time any three-foot length of chain is found to have stretched one-third the length of a link it ((shall)) must be discarded.
(18) Chains ((shall)) must be spliced in compliance with the requirements of the general safety and health standard, WAC 296-24-29413.
(19) Wherever annealing of chains is attempted, it ((shall)) must be done in properly equipped annealing furnaces and under the direct supervision of a competent person thoroughly versed in heat treating.
Chains ((shall)) must be normalized or annealed periodically as recommended by the manufacturer.
(20) Fiber rope.
(a) Frozen fiber rope ((shall)) must not be used in load carrying service.
(b) Fiber rope that has been subjected to acid ((shall)) must not be used for load carrying purposes.
(c) Fiber rope ((shall)) must be protected from abrasion by padding where it is fastened or drawn over square corners or sharp or rough surfaces.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-755 Natural and synthetic fiber rope slings.
(1) Sling use.
(a) Fiber rope slings made from conventional three strand construction fiber rope ((shall)) must not be used with loads in excess of the rated capacities prescribed in Tables D-16 through D-19 of Part "D" of the general safety and health standards, chapter 296-24 WAC.
(b) Slings not included in these tables ((shall)) must be used only in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations.
(2) Safe operating temperatures. Natural and synthetic fiber rope slings, except for wet frozen slings, may be used in a temperature range from minus 20°F to plus 180°F without decreasing the working load limit. For operations outside this temperature range and for wet frozen slings, the sling manufacturer's recommendations ((shall)) must be followed.
(3) Splicing. Spliced fiber rope slings ((shall)) must not be used unless they have been spliced in accordance with the following minimum requirements and in accordance with any additional recommendations of the manufacturer:
(a) In manila rope, eye splices ((shall)) must consist of at least three full tucks, and short splices ((shall)) must consist of at least six full tucks, three on each side of the splice center line.
(b) In synthetic fiber rope, eye splices ((shall)) must consist of at least four full tucks, and short splices ((shall)) must consist of at least eight full tucks, four on each side of the center line.
(c) Strand end tails ((shall)) must not be trimmed flush with the surface of the rope immediately adjacent to the full tucks. This applies to all types of fiber rope and both eye and short splices. For fiber rope under one inch in diameter, the tail ((shall)) must project at least six rope diameters beyond the last full tuck. For fiber rope one inch in diameter and larger, the tail ((shall)) must project at least six inches beyond the last full tuck. Where a projecting tail interferes with the use of the sling, the tail ((shall)) must be tapered and spliced into the body of the rope using at least two additional tucks (which will require a tail length of approximately six rope diameters beyond the last full tuck).
(d) Fiber rope slings ((shall)) must have a minimum clear length of rope between eye splices equal to ten times the rope diameter.
(e) Knots ((shall)) must not be used in lieu of splices.
(f) Clamps not designed specifically for fiber ropes ((shall)) must not be used for splicing.
(g) For all eye splices, the eye ((shall)) must be of such size to provide an included angle of not greater than sixty degrees at the splice when the eye is placed over the load or support.
(4) End attachments. Fiber rope slings ((shall)) must not be used if end attachments in contact with the rope have sharp edges or projections.
(5) Removal from service. Natural and synthetic fiber rope slings ((shall)) must be immediately removed from service if any of the following conditions are present:
(a) Abnormal wear.
(b) Powdered fiber between strands.
(c) Broken or cut fibers.
(d) Variations in the size or roundness of strands.
(e) Discoloration or rotting.
(f) Distortion of hardware in the sling.
(6) Repairs. Only fiber rope slings made from new rope ((shall)) must be used. Use of repaired or reconditioned fiber rope slings is prohibited.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-760 Synthetic web slings.
(1) Sling identification. Each sling ((shall)) must be marked or coded to show the rated capacities for each type of hitch and type of synthetic web material.
(2) Webbing. Synthetic webbing ((shall)) must be of uniform thickness and width and selvage edges ((shall)) must not be split from the webbing's width.
(3) ((Fittings.)) Fittings ((shall)) must be:
(a) Of a minimum breaking strength equal to that of the sling; and
(b) Free of all sharp edges that could in any way damage the webbing.
(4) Attachment of end fittings to webbing and formation of eyes. Stitching ((shall)) must be the only method used to attach end fittings to webbing and to form eyes. The thread ((shall)) must be in an even pattern and contain a sufficient number of stitches to develop the full breaking strength of the sling.
(5) Sling use. Synthetic web slings illustrated in Figure D-6 ((shall)) must not be used with loads in excess of the rated capacities specified in Tables D-20 through D-22. Slings not included in these tables ((shall)) must be used only in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations.
(6) Environmental conditions. When synthetic web slings are used, the following precautions ((shall)) must be taken:
(a) Nylon web slings ((shall)) must not be used where fumes, vapors, sprays, mists or liquids of acids or phenolics are present.
(b) Polyester and polypropylene web slings ((shall)) must not be used where fumes, vapors, sprays, mists or liquids of caustics are present.
(c) Web slings with aluminum fittings ((shall)) must not be used where fumes, vapors, sprays, mists or liquids of caustics are present.
(7) Safe operating temperatures. Synthetic web slings of polyester and nylon ((shall)) must not be used at temperatures in excess of 180°F. Polypropylene web slings ((shall)) must not be used at temperatures in excess of 200°F.
(8) Repairs.
(a) Synthetic web slings which are repaired ((shall)) must not be used unless repaired by a sling manufacturer or an equivalent entity.
(b) Each repaired sling ((shall)) must be proof tested by the manufacturer or equivalent entity to twice the rated capacity prior to its return to service. ((The employer shall)) You must retain a certificate of the proof test and make it available for examination.
(c) Slings, including webbing and fittings, which have been repaired in a temporary manner ((shall)) must not be used.
(9) Removal from service. Synthetic web slings ((shall)) must be immediately removed from service if any of the following conditions are present:
(a) Acid or caustic burns;
(b) Melting or charring of any part of the sling surface;
(c) Snags, punctures, tears or cuts;
(d) Broken or worn stitches; or
(e) Distortion of fittings.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-765 Floor operated cranes.
(1) An unobstructed aisle not less than three feet wide ((shall)) must be maintained for travel of the operator except in such cases where the control handles are hung from the trolleys of traveling cranes.
(2) The controller or controllers, if rope operated, ((shall)) must automatically return to the "off" position when released by the operator.
(3) Pushbuttons((,)) in pendant stations((, shall return)) must be returned to the "off" position when pressure is released by the crane operator.
(4) All pushbuttons ((shall)) must be marked to indicate their purpose.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-770 Operators.
(1) Cranes ((shall)) must be operated only by regular crane operators, authorized substitutes who have had adequate experience and training under the supervision of a competent operator, or by crane repair person or inspectors.
(2) No person under the age of eighteen years ((shall)) will be permitted to operate a crane.
(3) Operators ((shall)) will be required to pass a practical examination limited to the specific type of equipment to be operated. Operators ((shall)) must meet the following physical qualifications:
(a) Have vision of at least 20/30 Snellen in one eye, and 20/50 in the other, with or without corrective lenses.
(b) Be able to distinguish red, green, and yellow, regardless of position of colors, if color differentiation is required for operation.
(c) Hearing, with or without hearing aid, must be adequate for the specific operation.
(d) A history of epilepsy or an uncorrected disabling heart condition ((shall)) must be cause for a doctor decision to determine qualifications to operate a crane.
(4) Hands ((shall)) must be kept free when going up and down ladders. Articles which are too large to go into pockets or belts ((shall)) must be lifted to or lowered from the crane by hand line. (Except where stairways are provided.)
(5) Cages ((shall)) must be kept free of clothing and other personal belongings. Tools, extra fuses, oil cans, waste and other articles necessary in the crane cage ((shall)) must be stored in a tool box and not left loose on or about the crane.
(6) The ((operator shall)) operator(s) must familiarize ((himself)) themselves fully with all crane rules and with the crane mechanism and its proper care. If adjustments or repairs are necessary, ((he shall)) they must report the same at once to the proper authority.
(7) The operator ((shall)) must not eat, smoke or read while actually engaged in the operation of the crane.
(8) The operator or someone especially designated ((shall)) must lubricate all working parts of the crane.
(9) Cranes ((shall)) must be examined for loose parts or defects each day on which they are in use.
(10) Sawdust, oil or other debris ((shall)) must not be allowed to accumulate to create a fire, health or slipping hazard.
(11) Operators ((shall)) must avoid, as far as possible, carrying loads over workers. Loads ((shall)) must not be carried over employees without sounding an audible warning alarm.
(12) Whenever the operator finds the main or emergency switch open, ((he shall)) they must not close it, even when starting on regular duty, until ((he has)) they have made sure that no one is on or about the crane. ((He shall)) They must not oil or repair the crane unless the main switch is open.
(13) If the power goes off, the operator ((shall)) must immediately throw all controllers to the "off" position until the power is again available.
(14) Before closing the main switch the operator ((shall)) must make sure that all controllers are in the "off" position until the power is again available.
(15) The operator ((shall)) must pay special attention to the block, when long hitches are made, to avoid tripping the limit switch.
(16) The operator ((shall)) must recognize signals only from the person who is supervising the lift except for emergency stop signals. Operating signals ((shall)) must follow established standard crane signals as illustrated in WAC 296-78-830 of this chapter. Whistle signals may be used where one crane only is in operation. Cranes ((shall)) must have audible warning device which ((shall)) must be sounded in event of emergency.
(17) Before starting to hoist, the operator ((shall)) must place the trolley directly over the load to avoid swinging it when being hoisted.
(18) The operator ((shall)) must not make side pulls with the crane except when especially instructed to do so by the proper authority.
(19) When handling maximum loads, the operator ((shall)) must test the hoist brakes after the load has been lifted a few inches. If the brakes do not hold, the load ((shall)) must be lowered at once and the brakes adjusted or repaired.
(20) Bumping into runway stops or other cranes ((shall)) must be avoided. When the operator is ordered to engage with or push other cranes, ((he shall)) they must do so with special care for the safety of persons on or below cranes.
(21) When lowering a load, the operator ((shall)) must proceed carefully and make sure ((that he has)) they have the load under safe control.
(22) When leaving the cage, the operator ((shall)) must throw all controllers to the "off" position and open the main switch.
(23) If the crane is located out of doors, the operator ((shall)) must lock the crane in a secure position to prevent it from being blown along or off the track by a severe wind.
(24) Railroad cars ((shall)) must not be pulled along the tracks with sidepulls on an overhead crane.
(25) Operators ((shall)) must not move the crane or a load unless floor signals are clearly understood.
(26) The rated lifting capacity of a crane ((shall)) must not be exceeded. If any doubt exists about the weight of a load which might exceed the rated capacity, the foreman in charge must be contacted before any attempt is made to lift the load. The foreman ((shall)) must determine that the load is within the rated capacity of the crane or the load ((shall)) must not be lifted.
(27) Crane operators and floorpersons ((shall)) must coordinate their activities on every lift or movement of the crane. Both the operator and signalperson ((shall)) must clearly understand any problem a movement might create with regard to surrounding materials, structures, equipment or personnel.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-775 Signalpersons.
(1) Signalpersons ((shall)) must give all the signals to the operator in accordance with established standard signals as illustrated in WAC 296-78-830 of this chapter.
(2) A designated person ((shall)) must be responsible for the condition and use of all hoisting accessories and for all hitches.
(3) Before an operator moves a crane upon which an empty chain or cable sling is hanging, both ends of the sling ((shall)) must be placed on the hook.
(4) Signalpersons, where necessary, ((shall)) must walk ahead of the moving load and warn people to keep clear of it. They ((shall)) must see that the load is carried high enough to clear all obstructions.
(5) Signalpersons ((shall)) must notify the person in charge in advance when an extra heavy load is to be handled.
(6) No person ((shall)) will be permitted to stand or pass under an electric magnet in use.
(7) The electrical circuit for electric magnets ((shall)) must be maintained in good condition. Means for taking up the slack cable ((shall)) must be provided.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-780 Repairpersons.
(1) When repairs are necessary, repairpersons ((shall)) must have the crane run to a location where the repair work will least interfere with the other cranes and with operations on the floor.
(2) Before starting repairs, repairpersons ((shall)) must see that all controllers are thrown to the "off" position, and that main or emergency switches are opened; one of these ((shall)) must be locked out in compliance with WAC 296-78-715(11) of this chapter.
(3) Repairpersons ((shall)) must immediately place warning signs or "Out of Order" signs on a crane to be repaired and also on the floor beneath or hanging from the crane so that it can easily be seen from the floor. If other cranes are operated on the same runway, repairpersons ((shall)) must also place rail stops at a safe distance or make other safe provisions.
(4) When repairing runways, repairpersons ((shall)) must place rail stops and warning signs or signals so as to protect both ends of the section to be repaired.
(5) Repairpersons ((shall)) must take care to prevent loose parts from falling or being thrown upon the floor beneath.
(6) Repairs ((shall)) will not be considered complete until all guards and safety devices have been put in place and the block and tackle and other loose material have been removed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-785 Construction requirements.
(1) Calculations for wind pressure on outside overhead traveling cranes ((shall)) must be based on not less than 30 pounds per square foot of exposed surface.
(2) No overhung gears ((shall)) must be used unless provided with an effective means of keeping them in place, and keys ((shall)) must be secured to prevent gears working loose.
(3) Safety lugs or brackets ((shall)) must be provided on the trolley frames and bridge ends of overhead traveling cranes, so that in the event of a broken axle or wheel the trolley or bridge proper will not have a drop greater than one inch.
(((3))) (4) Where there are no members over an outside overhead crane suitable for attaching blocks for repair work, and a locomotive crane is not available, a structural steel outrigger of sufficient strength to lift the heaviest part of the trolley ((shall)) must be provided.
(((4))) (5) Outside overhead traveling cranes ((shall)) must be equipped with wind indicators and rail clamps as required by the general safety and health standards, WAC 296-24-23503.
(((5))) (6) Foot brakes, or other effective means ((shall)) must be provided to control the bridge travel of all overhead traveling cranes.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-790 Crane platforms and footwalks.
(1) Platforms ((shall)) must be provided when changing and repairing truck wheels on end trucks.
(2) A platform or footwalk ((shall)) must be located on a crane or crane runway to give access to the crane cage, and it ((shall)) must be accessible from one or more stairways or fixed ladders. This platform or footwalk ((shall)) must be not less than eighteen inches in width.
(3) Where stairways are used to give access to platforms, they ((shall)) must make an angle of not more than fifty degrees with the horizontal and ((shall)) must be equipped with substantial railing. If ladders are used to give access to platforms they ((shall)) must extend not less than thirty-six inches above the platform. Railed stairways or ladders to be used as a means of ingress and egress to crane cages ((shall)) must be located at either or both ends.
(4) A footwalk ((shall)) must be placed along the entire length of the bridge on the motor side, and a short platform twice the length of the trolley placed at one end of the girder on the opposite side, with a vertical clearance of a least six feet six inches where the design of crane or building permits, but in no case ((shall)) must there be less than four feet clearance. For hand operated cranes the footwalk ((shall)) must not be required to be installed on the bridge of the crane, but there ((shall)) must be a repair platform equal in strength and design to that required for motor operated cranes, installed on the wall of the building or supported by the crane runway at a height equal to the lower edge of the bridge girder to facilitate necessary repairs.
(5) Clear width of footwalks ((shall)) must not be less than eighteen inches except around the bridge motor where it may be reduced to fifteen inches.
(6) Footwalks ((shall)) must be of substantial construction and rigidly braced. Footwalks for outside service ((shall)) must be constructed so as to provide proper drainage, but the cracks between the boards ((shall)) must not be wider than one-fourth inch.
(7) Every footwalk ((shall)) must have a standard railing and toeboard at all exposed edges. Railings and toeboards ((shall)) must conform in construction and design with the following requirements:
(a) Railings ((shall)) must be not less than thirty-six inches nor more than forty-two inches in height, with an additional rail midway between the top rail and the floor.
(b) Pipe railings ((shall)) must be not less than one and one-fourth inch inside diameter if of iron or be not less than one and one-half inches outside diameter if of brass tubing.
(c) Metal rails other than pipe ((shall)) must be at least equal in strength to that of one and one-half by three-sixteenths inch angle and ((shall)) must be supported by uprights of equal strength.
(d) Posts or uprights ((shall)) must be spaced not more than eight feet center to center.
(e) Toeboards ((shall)) must be not less than four inches in height.
(f) Toeboards ((shall)) must be constructed in a permanent and substantial manner of metal, wood, or other material equivalent thereto in strength. Where of wood, toeboards ((shall)) must be at least equal in cross section to one inch by four inches; where of steel at least one-eighth inch by four inches; where of other construction at least equal to the requirements for steel. Perforations up to one-half inch are permissible in metal toeboards.
(8) No openings ((shall)) must be permitted between the bridge footwalk and the crane girders. Where wire mesh is used to fill this opening the mesh openings ((shall be)) must not be greater than one-half inch.
(9) All footwalks and platforms ((shall)) must be ((so)) designed ((as)) to be capable of sustaining a concentrated load of one hundred pounds per lineal foot.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-78-795 Crane cages.
(1) Safe means of escape ((shall)) must be provided for operators of all cranes in all operating locations. Rope ladders ((shall)) must not be used as a regular means of access but may be installed as an emergency escape device to be used in the event of fire, mechanical breakdown or other emergency.
(2) The operator's cage ((shall)) must be located at a place from which signals can be clearly distinguishable, and ((shall)) must be securely fastened in a place and well braced to minimize vibration. It ((shall)) must be large enough to allow ample room for the control equipment and the operator. The operator ((shall)) must not be required to step over an open space of more than eighteen inches when entering the cage.
(3) Cab operated cranes ((shall)) must be equipped with a portable fire extinguisher which meets the requirements of WAC 296-24-590 through 296-24-59007 and WAC 296-800-300.
(4) In establishments where continuous loud noises prevail such as caused by the operation of pneumatic tools, steam exhausts from boilers, etc., adequate signals ((shall)) must be installed on cranes or one or more employees ((shall)) must be placed on the floor for each crane operated to give warning to other employees of the approach of a crane with a load. Where there are more than two cranes on the same runway or within the same building structure, signaling devices are required to give warning to other employees of the approach of a crane with a load.
(5) Cages of cranes subjected to heat from below ((shall)) must be of noncombustible construction and ((shall)) must have a steel plate shield not less than one-eighth inch thick, placed not less than six inches below the bottom of the floor of the cage.
(6) Outside crane cages ((shall)) must be enclosed. There ((shall)) must be windows on three sides of the cage. The windows in the front and the side opposite the door ((shall)) must be the full width of the cage.
(7) The floor of the cage on ((out-door)) outdoor cranes ((shall)) must be extended to form an entrance landing which ((shall)) must be equipped with a handrail and toeboard constructed to the specifications of WAC 296-78-790 of this chapter.
(8) A copy of the rules for operators ((shall)) must be permanently posted in the cages of all cage-operated cranes.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-17-056, filed 8/20/96, effective 10/15/96)
WAC 296-78-800 Crane rail stops, bumpers and fenders.
(1) Rail stops ((shall)) must be provided at both ends of the crane runway and at ends of the crane bridge. When two trolleys are operated on the same bridge rails, bumpers ((shall)) must be provided to prevent collision of trolleys.
(2) Bumpers and rail stops ((shall)) must extend at least as high as the centers of the wheel.
(3) Rail stops ((shall)) must be fastened to the girders or girders and rails, but not to the rails alone. This does not apply to portable rail stops. Portable rail stops ((shall)) must not be used as permanent rail stops.
(4) Rail stops ((shall)) must be built up of plates and angles or be made of cast steel.
(5) Fenders ((shall)) must be installed which extend below the lowest point of the treads of gantry type crane wheels. They ((shall)) must be of a shape and form that will tend to push or raise an employee's hand, arm or leg off the rail and away from the wheel.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-805 Crawler locomotive and truck cranes.
Crawler locomotives and truck cranes ((shall)) must be constructed, maintained, inspected and operated in accordance with the provisions of WAC 296-24-240 through 296-24-24019 of the general safety and health standards.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-810 Chain and electric hoists.
(1) Chain and electric hoists ((shall)) must be of what is known as "all steel construction." No cast iron ((shall)) must be used in parts subject to tension except drums, bearings or brake shoes.
(2) The chains ((shall)) must be made of the best quality steel or iron with welded links.
(3) Chain and electric hoists ((shall)) must have a factor of safety of at least five.
(4) Chain and electric hoists ((shall)) must be equipped with a device which will automatically lock the load when hoisting is stopped.
(5) Electric hoists ((shall)) must be provided with a limit stop to prevent the hoist block from traveling too far in case the operating handle is not released in time.
(6) Workers ((shall)) must not ride the load of any chain or electric hoist. If necessary to balance the load manually, it ((shall)) must be done from a safe distance.
(7) The rated capacity of the hoist ((shall)) must be posted on both the hoist and the jib or rail.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-815 Monorail hoists.
(1) No attempt ((shall)) must be made with a monorail hoist to lift or move an object by a side pull, unless designed for that purpose.
(2) A stop ((shall)) must be provided at all switches and turntables which will prevent the trolley from running off should the switch be turned or be left in the open position.
(3) All monorail hoists operating on swivels ((shall)) must be equipped with one or more safety catches which will support the load should a suspension pin fail. All trolley frames ((shall)) must be safeguarded against spreading.
(4) Rail stops ((shall)) must be provided at the ends of crane runways. Such rail stops ((shall)) must extend at least as high as the centers of the wheels.
(5) All monorail hoists ((shall)) must have the rated capacity posted on both the hoist and the rail.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-820 Air hoists.
(1) To prevent piston rod lock nuts from becoming loose and allowing rods to drop when supporting a load, lock nuts ((shall)) must be secured to piston rods by a castellated nut and cotter-pin.
(2) A clevis, "D" strap or other means ((shall)) must be used to prevent the hoist cylinder becoming detached from the hanger.
(3) All air hoists ((shall)) must have their rated capacity posted on both the hoist and the jib or rail.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-825 Jib, pillar, and portable floor cranes, crabs, and winches.
(1) Side pulls ((shall)) must not be made with jib or pillar cranes. The arm or boom ((shall)) must be directly over the load when making a lift.
(2) The gears of all cranes ((shall)) must be enclosed, and if hand operated by means of a crab or winch, a locking dog ((shall)) must be provided to hold load when the handle is released.
(3) Some form of brake or safety lowering device ((shall)) must be provided on all crabs, winches, and jib cranes.
(4) A hoist limiting device ((shall)) must be provided on all jib cranes of ten or more tons capacity.
(5) The rated capacity of the hoisting device ((shall)) must be posted on the hoist and the arm or boom.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-830 Standard crane hand signals—Illustrations.
(1) The following hand signals ((shall)) must be used for crawler, locomotive, and truck cranes and a copy ((shall)) must be posted in the cab at the operator's station.
CRAWLER, LOCOMOTIVE, AND TRUCK CRANES
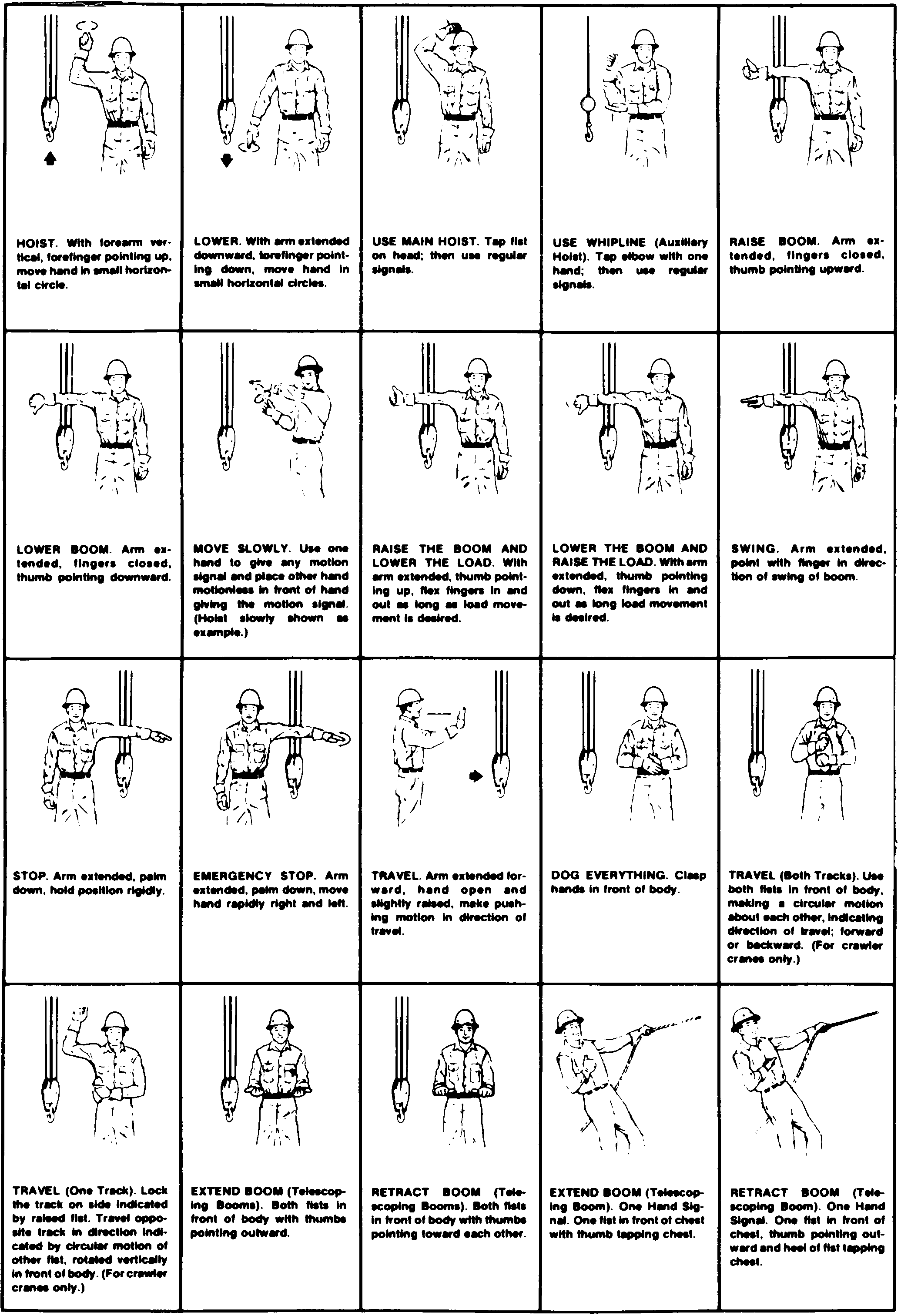 |
(2) The following hand signals ((shall)) must be used for overhead and gantry cranes and a copy ((shall)) must be posted in the cab at the operator's station.
STANDARD HAND SIGNALS FOR CONTROLLING OVERHEAD AND GANTRY CRANES
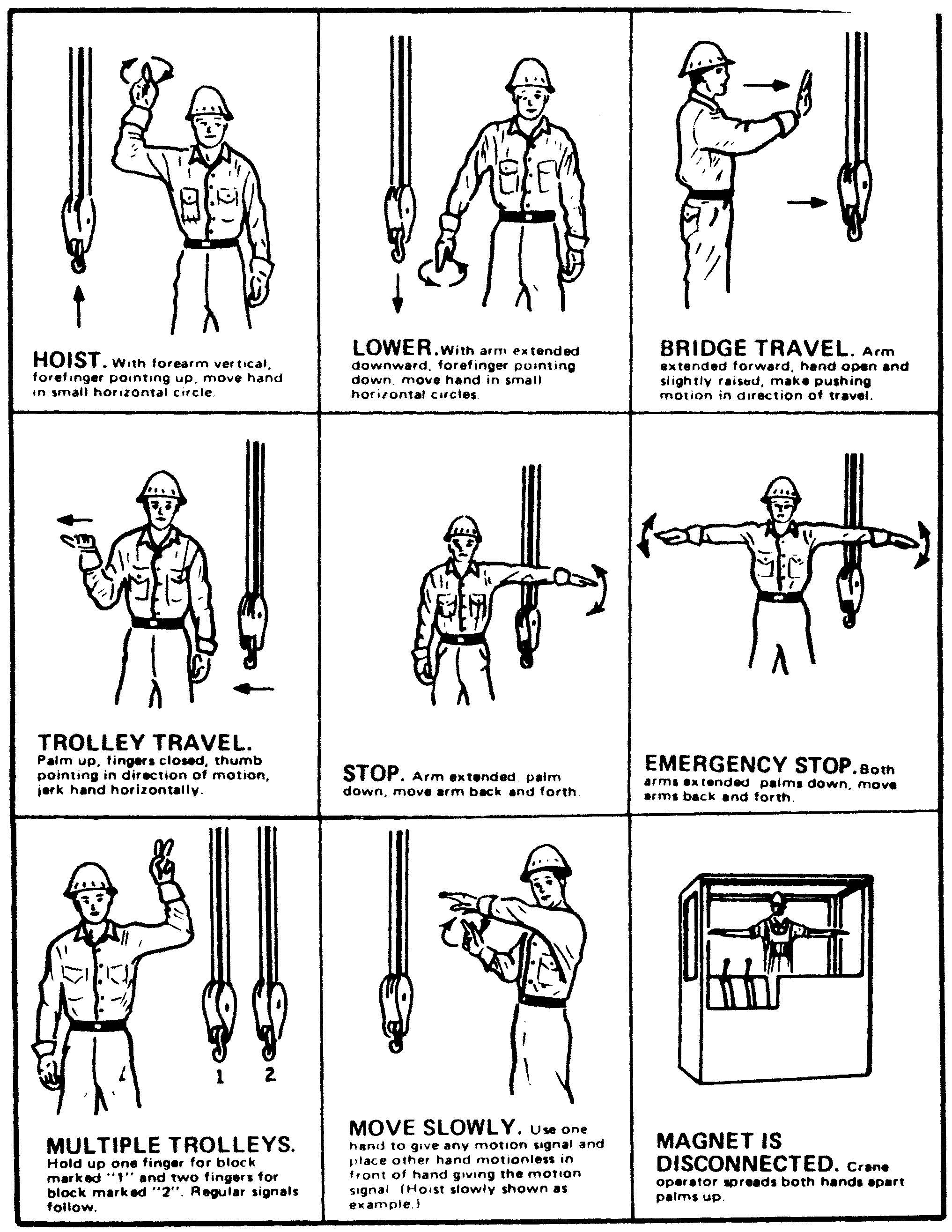 |
(3) The following hand signals ((shall)) must be used for derricks and a copy ((shall)) must be posted in the cab at the operator's station.
STANDARD HAND SIGNALS FOR CONTROLLING DERRICKS
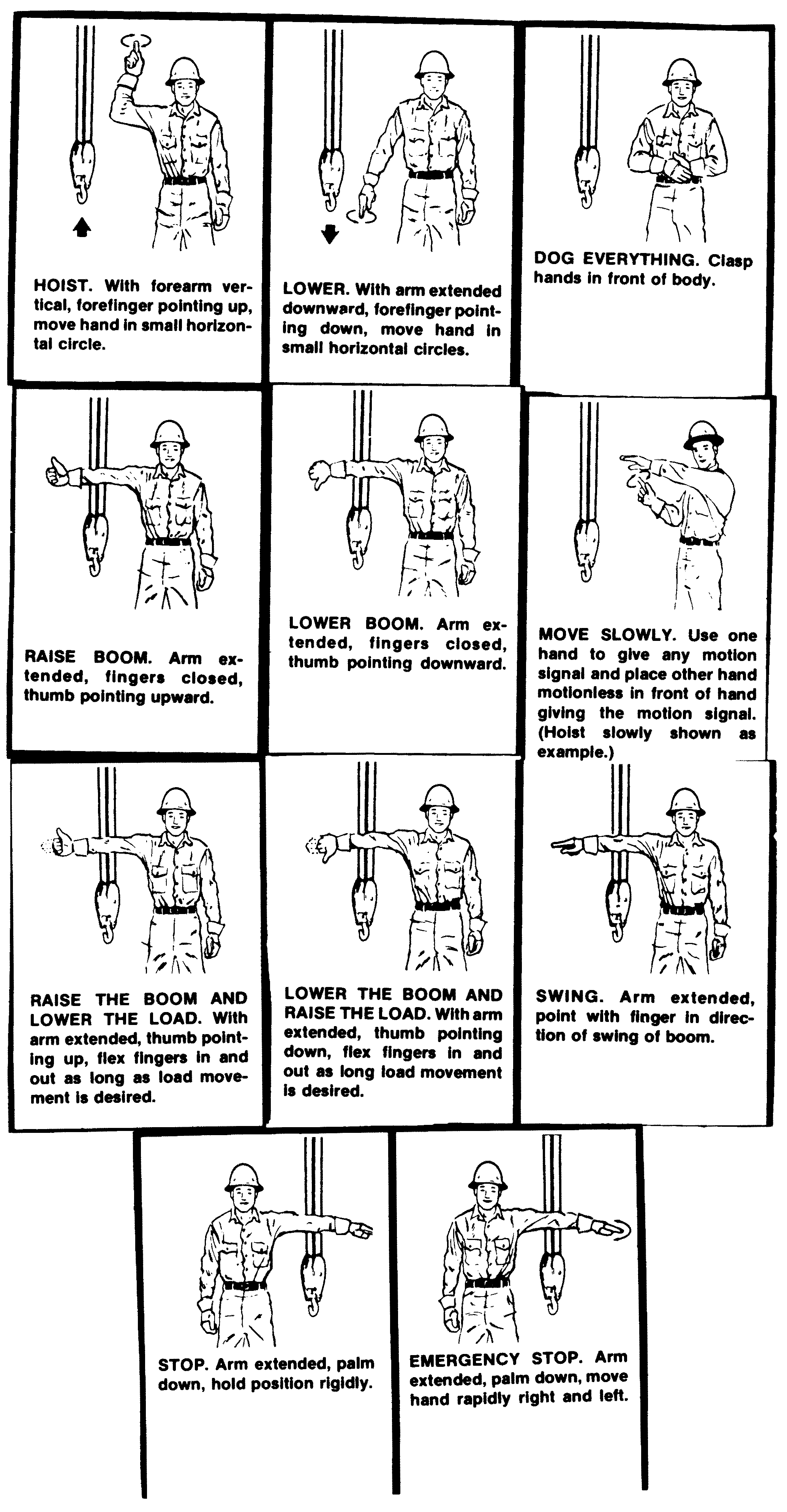 |
(4) The following hand signals ((shall)) must be used for portal, tower, and pillar cranes and a copy ((shall)) must be posted in the cab at the operator's station.
STANDARD HAND SIGNALS FOR CONTROLLING PORTAL, TOWER AND PILLAR CRANES
 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-78-835 Vehicles.
(1) Vehicles.
(a) Scope. Vehicles ((shall)) must include all mobile equipment normally used in sawmill, planing mill, storage, shipping, and yard operations, including log sorting yards.
(b) ((Lift trucks.)) Lift trucks ((shall)) must be designed, constructed, maintained and operated in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-24-230 through 296-24-23035 of the general safety and health standards.
(c) Carriers. Drive chains on lumber carriers ((shall)) must be adequately guarded to prevent contact at the pinch points.
(d)(((i))) Lumber carriers ((shall)) must be ((so)) designed and constructed so that the operator's field of vision ((shall)) will not be unnecessarily restricted.
(((ii))) (e) Carriers ((shall)) must be provided with ladders or equivalent means of access to the operator's platform or cab.
(((e))) (f) Lumber hauling trucks.
(((i))) On trucks where the normal operating position is ahead of the load in the direction of travel, the cab ((shall)) must be protected by a barrier at least as high as the cab. The barrier ((shall)) must be capable of stopping the weight of the load capacity of the vehicle if the vehicle were to be stopped suddenly while traveling at its normal operating speed. The barrier ((shall)) must be constructed in such a manner that individual pieces of a normal load will not go through openings in the barrier.
(((ii))) (i) Stakes, stake pockets, racks, tighteners, and binders ((shall)) must provide a positive means to secure the load against any movement during transit.
(((iii))) (ii) Where rollers are used, at least two ((shall)) must be equipped with locks which shall be locked when supporting loads during transit.
(2) Warning signals and spark arrestors. All vehicles ((shall)) must be equipped with audible warning signals and where practicable ((shall)) must have spark arrestors.
(3) Flywheels, gears, sprockets and chains and other exposed parts that constitute a hazard to workers ((shall)) must be enclosed in standard guards.
(4) All vehicles operated after dark or in any area of reduced visibility ((shall)) must be equipped with head lights and backup lights which adequately illuminate the direction of travel for the normal operating speed of the vehicle. The vehicle ((shall)) must also be equipped with tail lights which are visible enough to give sufficient warning to surrounding traffic at the normal traffic operating speed.
(5) All vehicles operated in areas where overhead hazards exist ((shall)) must be equipped with an overhead guard for the protection of the operator.
(6) Where vehicles are so constructed and operated that there is a possibility of the operator being injured by backing into objects, a platform guard ((shall)) must be provided and so arranged as not to hinder the exit of the driver.
(7) Trucks, lift trucks and carriers ((shall)) must not be operated at excessive rates of speed. When operating on tramways or docks more than six feet above the ground or lower level they ((shall)) must be limited to a speed of not more than twelve miles per hour. When approaching blind corners they ((shall)) must be limited to four miles per hour.
(8) Vehicles ((shall)) must not be routed across principal thoroughfares while employees are going to or from work unless pedestrian lanes are provided.
(a) Railroad tracks and other hazardous crossings ((shall)) must be plainly posted.
(b) Restricted overhead clearance. All areas of restricted side or overhead clearance ((shall)) must be plainly marked.
(c) Pickup and unloading points. Pickup and unloading points and paths for lumber packages on conveyors and transfers and other areas where accurate spotting is required, ((shall)) must be plainly marked and wheel stops provided where necessary.
(d) ((Aisles, passageways, and roadways.)) Aisles, passageways, and roadways ((shall)) must be sufficiently wide to provide safe side clearance. One-way aisles may be used for two-way traffic if suitable turnouts are provided.
(9) Where an operator's vision is impaired by the vehicle or load it is carrying, ((he shall)) they must move only on signal from someone so stationed as to have a clear view in the direction the vehicle is to travel.
(10) Reserved.
(11) Load limits. No vehicle ((shall)) must be operated with loads exceeding its safe load capacity.
(12) Vehicles with internal combustion engines ((shall)) must not be operated in enclosed buildings or buildings with ceilings less than sixteen feet high unless the buildings have ventilation adequate to maintain air quality as required by the general occupational health standard, chapter 296-62 WAC.
(13) Vehicles ((shall)) must not be refueled while motor is running. Smoking or open flames ((shall)) must not be allowed in the refueling area.
(14) No employee other than trained operators or mechanics ((shall)) must start the motor of, or operate any log or lumber handling vehicle.
(15) All vehicles ((shall)) must be equipped with brakes capable of holding and controlling the vehicle and capacity load upon any grade or incline over which they may operate.
(16) Unloading equipment and facilities.
(a) Machines used for hoisting, unloading, or lowering logs ((shall)) must be equipped with brakes capable of controlling or holding the maximum load in midair.
(b) The lifting cylinders of all hydraulically operated log handling machines, or where the load is lifted by wire rope, ((shall)) must be equipped with a positive device for preventing the uncontrolled lowering of the load or forks in case of a failure in the hydraulic system.
(c) A limit switch ((shall)) must be installed on powered log handling machines to prevent the lift arms from traveling too far in the event the control switch is not released in time.
(d) When forklift-type machines are used to load trailers, a means of securing the loading attachment to the fork ((shall)) must be installed and used.
(e) A-frames and similar log unloading devices ((shall)) must have adequate height to provide safe clearance for swinging loads and to provide for adequate crotch lines and spreader bar devices.
(f) Log handling machines used to stack logs or lift loads above operator's head ((shall)) must be equipped with overhead protection.
(g) Unloading devices ((shall)) must be equipped with a horn or other plainly audible signaling device.
(h) Movement of unloading equipment ((shall)) must be coordinated by audible or hand signals when operator's vision is impaired or operating in the vicinity of other employees.
Lift trucks regularly used for transporting peeler blocks or cores ((shall)) must have tusks or a similar type hold down device to prevent the blocks or cores from rolling off the forks.
(17) Where spinners are used on steering wheels, they ((shall)) must be of the automatic retracting type or ((shall)) must be built into the wheel in such a manner as not to extend above the plane surface of the wheel. Vehicles equipped with positive antikickback steering are exempted from this requirement.
(18) Mechanical stackers and unstackers ((shall)) must have all gears, sprockets and chains exposed to the contact of workers, fully enclosed by guards as required by WAC 296-78-710 of this chapter.
(19) Manually operated control switches ((shall)) must be properly identified and so located as to be readily accessible to the operator. Main control switches ((shall)) must be ((so)) designed ((that)) so they can be locked in the open position.
(20) Employees ((shall)) must not stand or walk under loads being lifted or moved. Means ((shall)) must be provided to positively block the hoisting platform when employees must go beneath the stacker or unstacker hoist.
(21) No person ((shall)) must ride any lift truck or lumber carrier unless a suitable seat is provided, except for training purposes.
(22) Unstacking machines ((shall)) must be provided with a stopping device which ((shall at all times)) must be accessible at all times to at least one employee working on the machine.
(23) Floor of the unstacker ((shall)) must be kept free of broken stickers and other debris. A bin or frame ((shall)) must be provided to allow for an orderly storage of stickers.
(24) Drags or other approved devices ((shall)) must be provided to prevent lumber from running down on graders.
(25) Liquified petroleum gas storage and handling. Storage and handling of liquified petroleum gas ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-24-475 through 296-24-47517 of the general safety and health standards.
(26) ((Flammable liquids.)) Flammable liquids ((shall)) must be stored and handled in accordance with WAC 296-24-330 through 296-24-33019 of the general safety and health standards.
(27) Guarding side openings. The hoistway side openings at the top level of the stacker and unstacker ((shall)) must be protected by enclosures of standard railings.
(28) Guarding hoistway openings. When the hoist platform or top of the load is below the working platform, the hoistway openings ((shall)) must be guarded.
(29) Guarding lower landing area. The lower landing area of stackers and unstackers ((shall)) must be guarded by enclosures that prevent entrance to the area or pit below the hoist platform. Entrances should be protected by electrically interlocked gates which, when open, will disconnect the power and set the hoist brakes. When the interlock is not installed, other positive means of protecting the entrance ((shall)) must be provided.
(30) ((Lumber lifting devices.)) Lumber lifting devices on all stackers ((shall)) must be designed and arranged so as to minimize the possibility of lumber falling from such devices.
(31) Inspection. At the start of each work shift, equipment operators ((shall)) must inspect the equipment they will use for evidence of failure or incipient failure. Equipment found to have defects which might affect the operating safety ((shall)) must not be used until the defects are corrected.
(32) Cleaning pits. Safe means of entrance and exit ((shall)) must be provided to permit cleaning of pits.
(33) Preventing entry to hazardous area. Where the return of trucks from unstacker to stacker is by mechanical power or gravity, adequate signs, warning devices, or barriers ((shall)) must be erected to prevent entry into the hazardous area.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-84001 Loading, piling, storage and conveying—General.
(1) Units or loads of lumber built up for transportation by overhead cranes, lift trucks, auto trucks, or manually or mechanically operated transfers ((shall)) must be provided with at least one set of stickers for each eighteen inches in height of unit or load. One set of stickers ((shall)) must be not more than six inches from the top of units of lumber up to three inch dimension. Where dimension of material is greater than three inches, a set of stickers ((shall)) must be placed under the top layer. Stickers ((shall)) must extend the full width of the package, ((shall)) must be uniformly spaced, and ((shall)) must be aligned one above the other. Stickers may be lapped with a minimum overlapping of twelve inches. Stickers ((shall)) must not protrude more than two inches beyond the sides of the package.
(2) Lumber loading. Loads ((shall)) must be built and secured to insure stability in transit.
(3) Units or loads of lumber ((shall)) must not be lifted or moved until all workers are in the clear.
(4) Gradient of roll sets or roll cases over which units of lumber are to be moved ((shall)) must not exceed three percent. The movement of units ((shall)) must be under control at all times.
(5) Stacking of lumber in yards, either by units or in block piles, ((shall)) must be conducted in a safe and orderly manner.
(6) Foundations for piling lumber in yards ((shall)) must be capable of supporting the maximum applied load without tipping or sagging.
(7) The height of stacked units in storage areas ((shall)) must not exceed seven of the usual four foot units, subject to the following qualifications:
(a) Units of lumber ((shall)) must not be stacked more than four high unless two or more stacks of units are tied together with ties.
(b) Long units of lumber ((shall)) must not be stacked upon shorter packages except where a stable pile can be made with the use of package separators.
(c) In unit package piles, substantial polsters or unit separators ((shall)) must be placed between each package directly over the stickers.
(8) Wooden horses used for loading preformed loads of lumber ((shall)) must be of material not less than four by six inches in cross section net measure.
(9) Unstable piles. Piles of lumber which have become unstable ((shall)) must be immediately made stable or removed.
(10) Lift boards or pallets ((shall)) must be loaded in such a manner as to prevent material from spilling or the material ((shall)) must be secured with a binder.
(11) Packing rooms ((shall)) must be kept free of debris and chutes ((shall)) must be equipped with a means of slowing down the materials.
(12) Sorting chains ((shall)) must be provided with a stopping device which ((shall at all times)) must be readily accessible at all times to at least one employee working on the chain.
(13) The inside of the walkway of all green chains and sorting tables shall be provided with a standard toeboard.
(14) Rollers or other devices ((shall)) must be provided for removing heavy dimension lumber from the cabin or table.
(15) Roll casings and transfer tables ((shall)) must be cleaned regularly and ((shall be)) kept reasonably free from debris.
(16) In all permanent installations, green chains and sorting tables ((shall)) must be roofed over to provide protection from inclement weather. Normal work stations ((shall)) must be provided with a drained work surface which is evenly floored of nonslip material.
(17) Power driven rolls ((shall)) must be operated in a manner to prevent end collisions.
(18) The space between live rolls ((shall)) must be filled in on either side of crosswalks with material of structural strength to withstand the load imposed with a four to one safety factor.
(19) The driving mechanism of live rolls ((shall)) must be guarded wherever exposed to contact.
(20) Live rolls ((shall)) must be replaced when their surface develops a break or hole.
(21) Guarding. Spiked live rolls ((shall)) must be guarded.
(22) Ramps or skidways used to transfer lumber or materials from one level to another ((shall)) must be provided with all safeguards necessary for the protection of workers.
(23) Landings on a lower level where lumber or timbers are discharged over ramps or skidways ((shall)) must be provided with a solid bumper not less than six inches in height at the outer edge. Such landing ((shall)) must be maintained in good repair at all times.
(24) Ramps or skidways ((shall)) must be ((so)) arranged so that the person putting lumber down ((shall have)) has a clear view of the lower landing. Lumber or timbers ((shall)) must not be put down until all workers are in the clear.
(25)(((a))) The under face of all ramp or skidway landings ((shall)) must be fenced off or other positive means provided to prevent persons from walking out under dropping timber.
(((b))) (26) Return strands of sorting table ramp chains ((shall)) must be supported by troughs of sufficient strength to support the weight of a broken chain.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-84003 Conveyors.
(1) Construction, operation, and maintenance of conveyors ((shall)) must be in accordance with American National Standard B20.1 - 1957, Safety Code for Conveyors, Cableways and related equipment.
(2) Conveyor troughs in which the working strands of a conveyor operate ((shall)) must be of ample dimension and strength to carry a broken chain and ((shall)) must afford effective protection to all employees.
(3) When the return strand of a conveyor operates within seven feet of the floor there ((shall)) must be a trough provided of sufficient strength to carry the weight resulting from a broken chain.
(4) When the return strands of a conveyor pass over passageways or work areas such guards ((shall)) must be placed under them as they will effectively protect workers.
(5) When the working strand of a conveyor crosses within three feet of the floor level in passageways, the trough in which it works ((shall)) must be bridged the full width of the passageway.
(6) Where conveyor, idler pulleys or other equipment is located over or dangerously near burning refuse, any worker going to such location ((shall)) must use a safety line which ((shall)) must be securely fastened to his body and tended by a helper.
(7) Conveyors ((shall)) must be provided with an emergency panic-type stopping device which can be reached by a person in a sitting position on the conveyor. Such devices ((shall)) must be located near the material entrance to each barker, chipper, hog, saw, or similar type of equipment except where the conveyor leading into such equipment is under constant control of an operator who has full view of the material entrance and is located or restrained where he/she cannot possibly fall onto the conveyor. The device ((shall)) must stop the conveyor a sufficient distance away from the hazard to prevent injury or further injury by the hazard.
(8) Screw or auger type conveyor troughs and boxes ((shall)) must be equipped with covers. If it is not practical to cover the troughs or boxes, other equivalent type guards ((shall)) must be provided.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-20-055, filed 10/3/05, effective 12/1/05)
WAC 296-78-84005 Dry kilns.
(1) Transfer, kiln and dolly tracks ((shall)) must be properly maintained at all times and ((shall)) must have a grade of not more than one and one-fourth percent. Bumpers or stops ((shall)) must be installed at the ends of all tracks capable of stopping a normal load for which the track is installed. A means ((shall)) must be provided for chocking or blocking cars.
(2) Doors.
(a) ((Main kiln doors.)) Main kiln doors ((shall)) must be provided with a method of holding them open while kiln is being loaded.
(b) Counterweights on vertical lift doors ((shall)) must be boxed or otherwise guarded.
(c) Means ((shall)) must be provided to firmly secure main doors, when they are disengaged from carriers and hangers, to prevent toppling.
(3) Kilns whose operation requires inside inspection ((shall)) must be maintained with not less than eighteen inches clearance between loaded cars and the walls of the kiln. The requirements for personal protective equipment specified in WAC 296-800-160, safety and health core rules, and chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators, ((shall)) must be complied with.
(4) Kiln loads ((shall)) must be equipped or arranged for easy attachment and detachment of transfer cables. Means for stopping kiln cars ((shall)) must be available at all times.
(5) Cars ((shall)) must not be moved until tracks are clear and workers are out of the bight of transfer lines.
(6) When kiln or dolly loads of lumber are permitted to coast through or adjacent to any work area, an audible warning ((shall)) must be given.
(7) Stickers ((shall)) must not be allowed to protrude more than two inches from the sides of kiln stacks.
(8) Yards and storage areas ((shall)) must be kept reasonably free of debris and unnecessary obstruction. Warning signs ((shall)) must be conspicuously posted wherever there is danger from moving vehicles or equipment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-17-056, filed 8/20/96, effective 10/15/96)
WAC 296-78-84007 Chippers and hogs.
(1) Chippers. The feed system to the chipper ((shall)) must be arranged so the operator does not stand in direct line with the chipper spout (hopper). The chipper spout ((shall)) must be enclosed to a height or distance of not less than forty inches from the floor or the operator's station. A safety belt and lifeline ((shall)) must be worn by workers when working at or near the spout unless the spout is guarded. The lifeline ((shall)) must be short enough to prevent workers from falling into the chipper.
(2) Hog mills ((shall)) must be provided with feed chutes ((so)) designed and arranged so that from no position on the rim of the chute ((shall)) will the distance to the knives or feed roll be less than forty inches. Baffles ((shall)) must be provided which ((shall)) must effectively prevent material from being thrown from the mill.
(3) Employees feeding hog mills ((shall)) must be provided with safety belts and lines, which they ((shall be)) are required to use at all times, unless otherwise protected from any possibility of falling into the mill.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-84009 Bins and bunkers.
(1) Bins, bunkers, hoppers, and fuel houses. Guarding. Open bins, bunkers, and hoppers whose upper edges extend less than three feet above working level ((shall)) must be equipped with standard handrails and toeboards, or have their tops covered by a substantial grill or grating with openings small enough to prevent a person from falling through.
(2) Fuel hoppers ((shall)) must be provided with doors that may be remotely operated.
(3) Fuel hoppers ((shall)) must be provided with platforms with standard railings and adequately lighted for the protection of workers taking out fuel.
(4)(((a))) Fuel bins ((shall)) must be provided with an approved railed platform or walkway near the top or other approved means, for the use of employees engaged in dislodging congested fuel. No employee ((shall)) must enter any fuel bin except where adequately safeguarded.
(((b))) (a) Recognizing however, the varying designs of fuel storage vaults and the type of fuel handled and certain peculiar local conditions, the adequacy of safety devices ((shall)) must be determined by a duly authorized representative of the department of labor and industries, division of industrial safety and health.
(((c))) (b) During operations when the flow of normal fuel is interrupted but dust from operating sanders is received in the bin, workers ((shall)) must not enter the fuel bin until the flow of sander dust has been discontinued and the dust has settled.
(((d))) (c) Use of wheeled equipment to load bins. Where automotive or other wheeled equipment is used to move materials into bins, bunkers, and hoppers, adequate guard rails ((shall)) must be installed along each side of the runway, and a substantial bumper stop provided when necessary.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 81-18-029, filed 8/27/81)
WAC 296-78-84011 Burners.
(1) Burners and smoke stacks, other than the self-supporting type ((shall)), must be adequately guyed. Buckle guys ((shall)) must be installed if a burner or stack is more than fifty feet in height.
(2) Runway. The conveyor runway to the burner ((shall)) must be equipped with a standard handrail. If the runway crosses a roadway or thoroughfare, standard toeboards ((shall)) must be provided in addition.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-79-010 Scope and application.
(1) This chapter applies to establishments, firms, persons and corporations that manufacture, process, store, finish, or convert pulp, paper or paperboard and includes all buildings, machinery, and equipment.
(2) This chapter ((shall)) will augment the Washington state general safety and health standards (chapter 296-24 WAC), general occupational health standards (chapter 296-62 WAC), and safety and health core rules (chapter 296-800 WAC). In the event of any conflict between any portion of this chapter and any portion of any of the general application standards, the provisions of this chapter 296-79 WAC, ((shall)) will prevail.
(3) The rules contained in this chapter are minimum requirements and the use of additional guards, or other means, methods or procedures may be needed to make the work or place of work safe.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-011 Definitions.
(("))Authorized((" - One)). A person who is qualified by reason of training and to whom the responsibility to perform a specific assignment has been given by the employer.
(("))Guarded((" -)). The means to remove the likelihood of approach or contact by persons or objects to a point of danger.
((")) Hazardous material system. Any system within the following classifications:
(a) Flammable or explosive - Any system containing materials which are hazardous because they are easily ignited and create a fire or explosion hazard, defined by NFPA as Class I liquids;
(b) Chemically active or toxic - Any system containing material which offers corrosion or toxic hazard in itself or can be productive of harmful gases upon release, defined by NFPA 704M as Class 3 and 4 materials;
(c) Thermally hazardous - Any system above 130°F which exposes persons to potential thermal burns;
(d) Pressurized - Any gaseous system above 200 psig or liquid system above 500 psig.
Knowledgeable((" -)). The demonstrated ability to communicate the safe work practices required to perform a job or task correctly.
(("))Piping system. Any fixed piping, either rigid pipe or flexible hose, including all fittings and valves, in either permanent or temporary application.
Qualified((" - One)). A person who is familiar with the construction and operation of the equipment and the duties of the position they may be filling. This includes being aware of the hazards of the job and the means and procedures necessary to eliminate or control those hazards.
(("Training" - The procedure that must establish and document the employee's competency in the work practices that they are required to perform.
"))Shall((")) or (("))must((")). As used in this standard means the requirement is compulsory.
(("May" or "should")) Should or may. A as used in this standard to identify recommendations or suggestions only.
Training. The procedure that must establish and document the employee's competency in the work practices that they are required to perform.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-79-020 General requirements.
(1) Housekeeping.
(((a))) Floors must be kept reasonably clear of spilled or leaking oil, grease, water, broke, etc., that may cause slipping, tripping or falling. Nonskid type surfacing must be installed in vehicular or pedestrian traffic areas where slipping hazards otherwise would exist.
(a) In areas where it is not possible to keep the floor free of materials which cause a slipping hazard, mats, cleats, or other suitable materials which will effectively minimize or eliminate the hazard must be installed.
(b) Hoses, cords, slings or similar items or equipment must be stored in such a manner that they will not create a hazard.
(2) Storage and transportation of materials. Materials, objects or equipment must be stored or transported by methods which will prevent them from falling, tipping or rolling.
(3) Warning of open manholes or excavations. Open manholes or excavations must be:
((•)) (a) Roped off, barricaded, or adequately safeguarded when located in or adjacent to walkways, aisleways, or roadways.
((•)) (b) Provided with warning lights or lanterns during periods of darkness or reduced visibility.
(4) Training. Employees must receive proper instruction and be familiar with safe operating procedures:
(a) Before they supervise the operation, or make adjustments to any machine or equipment.
(b) To be able to cope with emergencies arising from breaks, ruptures, or spills which would create a hazardous condition.
(c) For lifting and moving objects. Mechanical devices should be used or employees should ask for assistance in lifting or moving heavy objects.
(d) On prompt reporting of any faulty equipment or hazardous condition to the person in charge.
(5) Working alone. When an employee is assigned to work alone in a remote or isolated area, procedures must be developed to ensure:
((•)) (a) That the employee reports by use of radio or telephone to someone periodically; or
((•)) (b) That at reasonable intervals a designated person must check on the employee; and
((•)) (c) That all persons involved in working alone are advised of the procedures to be followed.
(6) Exits from hazardous areas. Where physically and reasonably possible, there must be at least two unobstructed exits from any hazardous area. Such exits should be on opposite walls.
(7) Safe work area. Sufficient clearance must be maintained between machines to allow employees a safe work area.
(8) Protection from overhead hazard. Warning signs/devices must be:
((•)) (a) Placed in conspicuous locations below areas where overhead work is being done; and
((•)) (b) Removed promptly when work is completed and the overhead hazard no longer exists.
(9) Welding areas protected.
(a) Areas in which welding is being done must be screened or barricaded to protect persons from flash burns, when practical.
(b) If the welding process cannot be isolated, all persons who may be exposed to the hazard of arc flash must be properly protected.
(10) Testing safety devices. Brakes, back stops, anti-runaway devices, overload releases, emergency stops, and other safety devices must be inspected and tested frequently to ensure that all are operative and maintained in good repair.
(11) Starting and stopping devices.
((•)) (a) Electrically or manually operated power starting or stopping devices must be provided within easy reach of the operator from the normal operating position.
((•)) (b) If necessary for safety of the operation, the machine must be so equipped that retarding or braking action can be applied at the time of or after the source of power is deactivated.
(12) Interlocks:
(a) Interlocks that affect the safety of employees must not be bypassed except where ((the employer)) you demonstrate((s that)) alternate procedures or devices that provide a level of safety for employees equivalent to ((that)) those provided by the safety interlock. Interlocks are considered to be bypassed anytime the designed control strategy is bypassed by means including, but not limited to, a temporary wiring change, physical interference or a temporary software change of "force."
(b) Prior to bypassing a safety interlock ((the employer)) you must:
((•)) (i) Develop a written procedure detailing how the bypass will be accomplished and the alternate means of protecting employees((.));
((•)) (ii) Inform affected employees of all pertinent information including at a minimum the reason for the change, the date of the change, who is responsible for the change, and approximately how long the change will be in effect((.)); and
((•)) (c) Post appropriate warning of the change on the equipment or area.
(13) Designing control systems. ((Employers)) You must ensure that all control systems are designed to:
((•)) (a) Ensure that the system does not create an unsafe state that endangers personnel((.));
((•)) (b) Ensure that when control systems fail, the equipment being controlled fails to a safe state((.)); and
((•)) (c) Have an independent method to safely stop the process or equipment, such as a hardwired emergency stop button or other controls that deenergize the system, or independent methods to force the system to a safe state.
(14) Compressed air.
(a) Compressed air must not be used for cleaning clothing that is being worn, or if it will endanger persons in the area.
(b) Sections of high pressure air hoses must be properly coupled and have safety chains or equivalent safety device attached between the sections (30 psi or more is high pressure air).
(15) Punch bars. Open pipes must not be used as punch bars if the use would create a hazard.
(16) Saw table limit stop or extension. Employees must be protected from contact with the front edge of a circular saw by:
((•)) (a) A limit stop which will prevent the forward swing of the cutting edge from extending beyond the edge of the table; or
((•)) (b) Installation of a table extension.
(17) Powder-actuated tools.
((•)) (a) Powder-actuated tool design, construction, operation and use ((shall)) must comply with all requirements specified in "safety requirements for powder actuated fastening systems," (see chapter 296-24 WAC, Part H-1).
((•)) (b) A careful check must be made to ensure that no cartridges or charges are left where they could enter equipment or be accidentally discharged in any area where they could create a fire or explosion hazard.
(18) Ladders required on waterfront docks. ((Employers)) You must ensure that either permanent ladders or portable ladders:
((•)) (a) Are readily available for emergency use on all waterfront docks((.));
((•)) (b) Extend from the face of the dock to the water line at its lowest elevation((.));
((•)) (c) Are installed at intervals not to exceed 400 feet((.));
((•)) (d) Are noticeable by painting the dock area immediately adjacent to the ladder with a bright color which contrasts with the surrounding area((.)); and
((•)) (e) Have been secured with a suitable method.
Note: | When working on or around water also see WAC 296-800-160. |
(19) Prevent overhang while removing materials. Extreme care must be taken to prevent material from creating an overhang while removing the materials from piles or bins.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-79-030 Guards and guarding.
For additional guarding requirements see chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
(1) Safeguarding specific areas, machines or conditions. Certain equipment, tools, machines, and areas present definite hazards and must be safeguarded by compliance with the following requirements:
(a) Broke shredder((s.)) cutting heads must be completely enclosed except for opening at feed side sufficient only to permit entry of stock. The enclosure must be:
((•)) (i) Bolted or locked in place((,)); and
((•)) (ii) Of solid material or with mesh or other openings not exceeding 1/2 inch.
(b) Stitching or sewing machine. Carton or bag stitching machines must be properly safeguarded to prevent persons from coming in contact with the stitching head and other pinch or nip points.
(c) Beaters and pulpers.
(i) A guardrail of standard height must be installed when the top edge of vessels or tubs is less than standard height guardrails above the floor or operator's platform. If necessary for the protection of the person feeding equipment, an intermediate guardrail or other suitable protection shall be installed.
(ii) Beater rolls must be provided with covers.
(d) First dryer. A permanent guard or apron guard, or both, must be installed to protect workers from any exposed ingoing nip of the first dryer drum in each section if the area is accessible to workers while the dryer is in operation.
(e) Floor and drain openings. Floor and drain openings in walkways and general work areas must be covered with material or gratings with openings no larger than 2" in the narrow dimension.
(f) Mechanical devices to dump chip cars, trucks or trailers.
((•)) (i) When using mechanical equipment to elevate the front end of the chip containers for dumping into a hopper, the shear area between the floor and the elevated section must be safeguarded.
((•)) (ii) The pit area must be adequately safeguarded or barricaded.
((•)) (iii) Safeguards must be installed around the exposed sides of a chip hopper.
(2) Replacing guards. All permanent guards must be replaced or adequate temporary safeguards provided before a machine is put into operation.
(3) Protection from moving materials. When material, such as chunks, slivers, cants, or logs, could be thrown or flipped by a saw, barker, or other machines, adequate barricades, screens, netting, or other safeguards must be provided and maintained.
(4) Protection for areas where guards are impractical. When normal guarding is impractical:
((•)) (a) The hazard must be reduced to a minimum by use of safety chains, lifelines, signs or other reasonable means((,)); and
((•)) (b) Areas which present a hazard which cannot be reasonably safeguarded must be identified by use of paint or other materials.
(5) Knives and scissors.
(a) Knives used for chip or hog fuel machines, or guillotine cutters, must be secured in properly constructed containers during transportation.
(b) Workers must be furnished properly designed and constructed sheaths for safely carrying knives and scissors used for cutting or trimming pulp and paper.
(c) Tables where paper is being cut must be equipped with sheaths or shelves for safe storage of knives and scissors.
(d) Sharp edged slitter knives subject to accidental contact must be effectively guarded. Carriers must be provided and used when transporting or carrying sharp edged slitter knives.
(e) Hand knives and sharpening steels used in paper preparation, must be provided with guards at the junction of the handle and the blade. Utility knives with blade exposure two and one-half inches or less are exempted from this requirement.
(6) Safeguard for foot operated treadle switch used to activate power driven equipment. Foot operated treadle switches used for activation of power driven equipment must be protected by a stirrup type guard or equivalent protection must be provided to prevent accidental activation.
(7) Automatic pressure actuated stopping devices. Hand fed machines and other moving equipment which create shear or pinch points which cannot be reasonably guarded may be safeguarded by the installation of pressure activated bars or sensing devices which, when contacted, will automatically stop the machine or equipment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-79-050 Personal protection clothing and equipment.
See WAC 296-800-160 for additional personal protective equipment requirements.
(1) Rings or other jewelry that could create a hazard should not be worn by employees while in the performance of their work.
(2) Protective footwear.
((•)) (a) Employees who work in areas where there is a possibility of foot injury due to falling or rolling objects must wear safety type footwear.
((• Employers)) (b) You will supply shoe guards and toe protectors.
((• Employers)) (c) You must also make safety shoes available for purchase by employees at not more than actual cost to ((the employer)) you.
(3) Calks or other suitable footwear that will afford reasonable protection from slipping must be:
((•)) (a) Worn while working on logs((.)); and
((•)) (b) Made available at not more than actual cost to the employer.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-070 Illumination.
(1) Illumination required. Lighting that is adequately adjusted to provide a margin of safety for all work tasks must be provided and maintained.
(a) The minimum level of task lighting for all indoor activities must be an average of ten-foot candles measured thirty inches above the floor or at the task.
(b) The minimum level of task lighting for all outdoor activities must be an average of five-foot candles measured thirty inches above the working surface or at the task.
(2) If general lighting is not provided throughout the work area, ((the employer)) you must provide illumination which is adequately adjusted to provide visibility of nearby objects that might be potential hazards or to see to operate emergency control or other equipment. The minimum level of nontask lighting for all indoor and outdoor activities must be an average of three-foot candles measured thirty inches above the floor or working surface.
Note: | This section establishes minimal levels of illumination for safety purposes only. Guidelines pertaining to optimal levels of lighting and illumination may be found in practice for Industrial Lighting, ANSI/IES RP7-1979. The minimum levels specified in subsections (1) and (2) of this section represent averages with the lowest level in an area to be no less than fifty percent of the indicated value. |
(3) Emergency or secondary lighting system required.
(a) There must be an emergency or secondary lighting system that can be actuated immediately upon failure of the normal power supply system. The emergency or secondary lighting system must provide illumination in the following areas:
((•)) (i) Wherever it is necessary for workers to remain at their machine or station to shut down equipment in case of power failure.
((•)) (ii) At stairways and passageways or aisleways used by workers as an emergency exit in case of power failure.
(b) Emergency lighting facilities must be checked at least every 30 days for mechanical defects. Defective equipment must be given priority for repair schedule.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-110 Elevated runways and ramps used by vehicles.
(1) Runways and ramps must:
(a) Be cleated, grooved, rough surfaced, or covered with a material that will minimize the danger of skidding((.)); and
(b) Not have a maximum incline exceeding 20° from horizontal if used for wheeled equipment.
(2) Guarding exposed sides.
((•)) (a) Elevated ramps or runways used for the travel of wheeled equipment must have exposed sides guarded with a substantial bull rail or shear rail of sufficient height to prevent wheeled equipment from going over the rail.
((•)) (b) If elevated ramps or runways are used by pedestrians, standard guardrails must be installed on runways wherever the height exceeds 4 feet above the adjacent area except where used for loading or unloading purposes.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-12-098, filed 6/5/02, effective 8/1/02)
WAC 296-79-140 Installation, inspection, and maintenance of pipes, piping systems, and hoses.
(1) ((Definitions applicable to this section.
"Hazardous material system" - Any system within the following classifications:
• Flammable or explosive - Any system containing materials which are hazardous because they are easily ignited and create a fire or explosion hazard, defined by NFPA as Class I liquids;
• Chemically active or toxic - Any system containing material which offers corrosion or toxic hazard in itself or can be productive of harmful gases upon release, defined by NFPA 704M as Class 3 and 4 materials;
• Thermally hazardous - Any system above 130°F which exposes persons to potential thermal burns;
• Pressurized - Any gaseous system above 200 psig or liquid system above 500 psig.
"Piping system" - Any fixed piping, either rigid pipe or flexible hose, including all fittings and valves, in either permanent or temporary application.
(2))) Design and installation. All new piping systems intended to be used in hazardous material service must be designed and installed in accordance with applicable provisions of the ASME Code for Pressure Piping or in accordance with applicable provisions of ANSI B31.1-1995 through B31.8-1995.
(((3))) (2) Inspection and maintenance.
(a) ((The employer)) You must develop a formal program of installation inspections and maintenance for all hazardous material piping systems. The program must be:
((•)) (i) Based on sound maintenance engineering principle((, and));
((•)) (ii) Demonstrate due consideration for the manufacturing specifications of the pipe, hose, valves and fittings, the ambient environment of the installation and the corrosive or abrasive effect of the material handled within the system((.)); and
(b) Type and frequency of tests and/or inspections and selection of inspection sites must be adequate to give indications that minimum safe design operating tolerances are maintained. The tests may include visual or nondestructive methods.
(((4))) (3) Inspection records.
(a) Results of inspections and/or tests must be maintained as a record for each system. Portions of systems that are buried or enclosed in permanent structures in such a manner as to prevent exposure to employees even in the event of a failure, may be exempted from the inspection requirements only.
((•)) (i) Past records may be discarded provided the current inspection report and the immediately preceding two reports are maintained.
((•)) (ii) When a system is replaced, a new record must be established and all past records may be discarded.
(b) Upon request the records for each system must be made available for review by the department of labor and industries.
(((5))) (4) Systems or sections of systems found to be below the minimum design criteria requirements for the current service must be repaired or replaced with component parts and methods which equal the requirements for new installations.
(((6))) (5) Identification of piping systems. (((a))) USAS A13.1-1956, "Scheme for Identification of Piping Systems," must be followed.
(6) Positive identification of a piping system content:
((•)) (a) Must have a lettered legend giving the name of the content in full or abbreviated form, or a commonly used identification system((.));
((•)) (b) Must be made and maintained at suitable intervals and at valves, fittings, and on both sides of walls or floors as needed((.));
((•)) (c) May have arrows to indicate the direction of flow((.)); and
((•)) (d) May provide necessary supplementary information, such as hazard of use. This may be done by additional legend or by color applied to the entire piping system or as colored bands. Legends may be placed on colored bands.
(7) Examples of legend which may give both positive identification and supplementary information regarding hazards or use are:
Ammonia . . . . |
Hazardous liquid or gas |
Chlorine . . . . |
Hazardous liquid or gas |
Chlorine dioxide . . . . |
Hazardous liquid or gas |
Sulphur dioxide . . . . |
Hazardous gas |
Liquid caustic . . . . |
Hazardous liquid |
Liquid sulphur . . . . |
Hazardous liquid |
Sulphuric acid . . . . |
Hazardous liquid |
Sodium chlorate . . . . |
When dry, danger of fire or explosion |
Note: | Manual L-1, published by Chemical Manufacturers Association, Inc., is a valuable guide in respect to supplementary legend. |
((•)) (a) When color, applied to the entire piping system or as colored bands, is used to give supplementary information it should conform to the following:
CLASSIFICATION |
PREDOMINANT COLOR |
|||
F—Fire-protection equipment . . . . |
Red |
|||
D—Dangerous materials . . . . |
Yellow |
|||
(or orange) |
||||
S—Safe materials . . . . |
Green |
|||
(or the achromatic |
||||
colors, white, black, |
||||
gray or aluminum) |
||||
and, when required, |
||||
P—Protective materials . . . . |
Bright blue |
|||
(b) When legend systems are used, legend boards showing the color and identification scheme in use must be prominently displayed at each plant. They must be located so that employees who may be exposed to hazardous material piping systems will have a frequent reminder of the identification program.
(c) All employees who work in the area of hazardous material piping systems must be given training in the color and identification scheme in use.
(((7))) (8) Steam hoses. Steam hoses must be specifically designed to safely carry steam at any pressures to which they may be subjected.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-150 Powered industrial trucks and other equipment.
Additional requirements on mobile equipment and lift trucks are in chapter ((296-24 WAC, Part D)) 296-863 WAC.
(1) The operator of a power-driven vehicle must test the brakes, steering gear, lights, horns, warning devices, clutches, etc., before operating vehicle.
(2) Control levers of lift trucks, front end loaders, or similar types of equipment must not be operated except when the operator is in the proper operating position.
(3) No person may be permitted to ride on a powered hand truck unless it is so designed by the manufacturer. A limit switch must be on the operating handle—30 degrees each way from a 45-degree angle up and down.
(4) Employees must not work below the raised bed of a dump truck, raised buckets of front end loaders, raised blades of tractors or in similar positions without blocking the equipment in a manner that will prevent it from falling.
(5) Reporting suspected defects. If, in the opinion of the operator, a power-driven vehicle is unsafe, the operator must report the suspected defect immediately to the person in charge. Any defect that would make the vehicle unsafe to operate under existing conditions will be cause to take the vehicle out of service and it must not be put back into use until it has been made safe.
(6) Vehicle operators must have a reasonably unobstructed view of the direction of travel, or, where this is not possible, the operator must be directed by a person or by a safe guidance means or device. Where practical, mirrors must be installed at blind corners or intersections that will allow operators to observe oncoming traffic.
(7) Vehicles in congested areas must operate with a warning light.
(8) Passengers must not be permitted to ride with legs or arms extending outside any vehicle nor must they be permitted to ride unless a passenger seat or other protective device is provided.
(9) Guard on operator's platform. Every power truck operated from an end platform or standing position must be:
((•)) (a) Equipped with a platform extending beyond the operator's position((,)); and
((•)) (b) Strong enough to withstand a compression load equal to the weight of the loaded vehicle applied along the longitudinal axis of the truck with the outermost projection of the platform against the flat vertical surface.
(10) Cleaning vehicles. All vehicles must be kept free of excessive accumulations of dust and grease that may present a hazard.
(11) Vehicles must be controlled manually while being pushed or towed except when a tow bar is used. Pushing of vehicles or railroad cars with the forks or clamps of a lift truck is prohibited.
(12) Aisles or passageways should be at least three feet wider than the widest vehicle or load traveling the aisle or passageway. When this clearance cannot be maintained, adequate precautions must be taken.
(13) The forks, clamps, or attachments of lift trucks must be kept as low as possible while the vehicle is moving.
(14) The hoisting of personnel by lift trucks must meet the requirements in WAC ((296-24-230)) 296-863-40060.
(15) Exhaust systems on lift trucks and jitneys shall be constructed to discharge either within 20 inches from the floor or 84 inches or more above the floor.
(16) Mobile equipment with an enclosed cab must be provided with an escape hatch or other method of exit in case the regular exit cannot be used.
(17) Suitable methods must be used or devices installed which will prevent the trailer from tipping while being loaded or unloaded.
(18) Whenever vehicles using LP gas as a fuel are parked overnight or stored for extended periods of time indoors, with the fuel container in place, the service valve of the fuel container must be closed.
(19) The use of spinners on steering wheels must be prohibited unless an anti-kick device is installed or the equipment has a hydraulic steering system.
(20) Rolls transported with a grab or clamp attachment must be carried with the core in a vertical position.
(21) When traveling empty with a grab or clamp attachment, the jaws or blades of those attachments must remain within the running lines of the lift truck.
(22) When transporting two or more rolls with a roll grab attachment, the bottom roll will have at least sixty percent of the grab attachment on it.
(23) When transporting two or more rolls or bales with a grab or clamp attachment, there must be no rolls or bales unsecured if there is risk of part or all of the load shifting or falling.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-170 Requirements for crawler and truck cranes.
(1) Boom length indicated. The length must be plainly marked on each boom section of a mobile crane having a sectioned boom.
(2) Radius or boom angle indicator. A radius or boom angle indicator must be installed where it is readily visible to the operator's normal operating position on all cranes having a movable working boom.
(3) Safety device for light fixtures. Any light fixtures attached to a crane boom or machinery house must have a safety strap or other device attached which will prevent the fixture from falling.
(4) Boom stops. Boom stops must be:
((•)) (a) Installed to govern the upward travel of the boom to a safe limit((.)); and
((•)) (b) Of adequate strength to prevent the boom from traveling past the vertical position.
(5) Controls marked. Crane operating controls must be marked or an explanation of the controls' functions must be posted in full view of the operator.
(6) Locking hydraulic outriggers. Hydraulic outriggers must be:
((•)) (a) Equipped with a pilot operated check valve; or
((•)) (b) Installed with a mechanical lock which will prevent outriggers from retracting in case of failure of the hydraulic system.
(7) Top of boom painted. The top six feet of the boom or jib must be painted bright yellow or other bright contrasting color if the boom is yellow.
(8) Warning devices. All cranes must be equipped with a suitable warning device such as a horn or whistle.
(9) Hook safety device. All hooks must be equipped with a safety device or other effective means must be used to prevent accidental unhooking of the load.
(10) Counterweight limited. The amount of crane counterweight must not exceed the maximum amount specified by the crane manufacturer.
(11) Use proper size wire rope for sheaves. The size and diameter of sheaves and wire rope must be compatible and follow the recommendations by the manufacturer, published by the Wire Rope Institute or other acceptable engineering practices.
(12) Loading or unloading gear. Unloading gear such as grapples, tongs, and buckets, must not be left suspended when not in use or whenever the machine is unattended.
(13) No one under load. Personnel must not position themselves under crane loads and such loads must not be carried over workers.
(14) Operating clearance from stationary objects. Where the area is accessible to workers:
((•)) (a) A distance of 30 inches must be maintained between the outermost part of a revolving crane and any stationary object within the swing radius of the crane; or
((•)) (b) The hazardous area must be temporarily guarded or barricaded.
(15) See WAC 296-24-960 when working around energized lines.
(16) Operators must avoid contacting overhead obstructions which may damage the boom or adversely affect stability. In instances where the operator may have difficulty in observing clearances, a signal person must be stationed where they can observe clearances and signal the operator.
(17) Safe travel across thoroughfares or railroad tracks.
((•)) (a) When moving cranes, shovels or similar types of equipment across thoroughfares or railroad tracks and the operator does not have a clear vision of approaching traffic, a ((flagperson)) flag person must be used.
((•)) (b) The flag person must be stationed where the equipment operator can be signaled and other traffic can be controlled.
(18) Only a designated member of the crew may give signals to the crane operator. Exception: Anyone may give an emergency stop signal.
(19) Standard hand signals. When using visual signals, standard hand signals as illustrated below, must be used for directing crane operators.
CRAWLER, LOCOMOTIVE, AND TRUCK CRANES
STANDARD HAND SIGNALS FOR CRANES
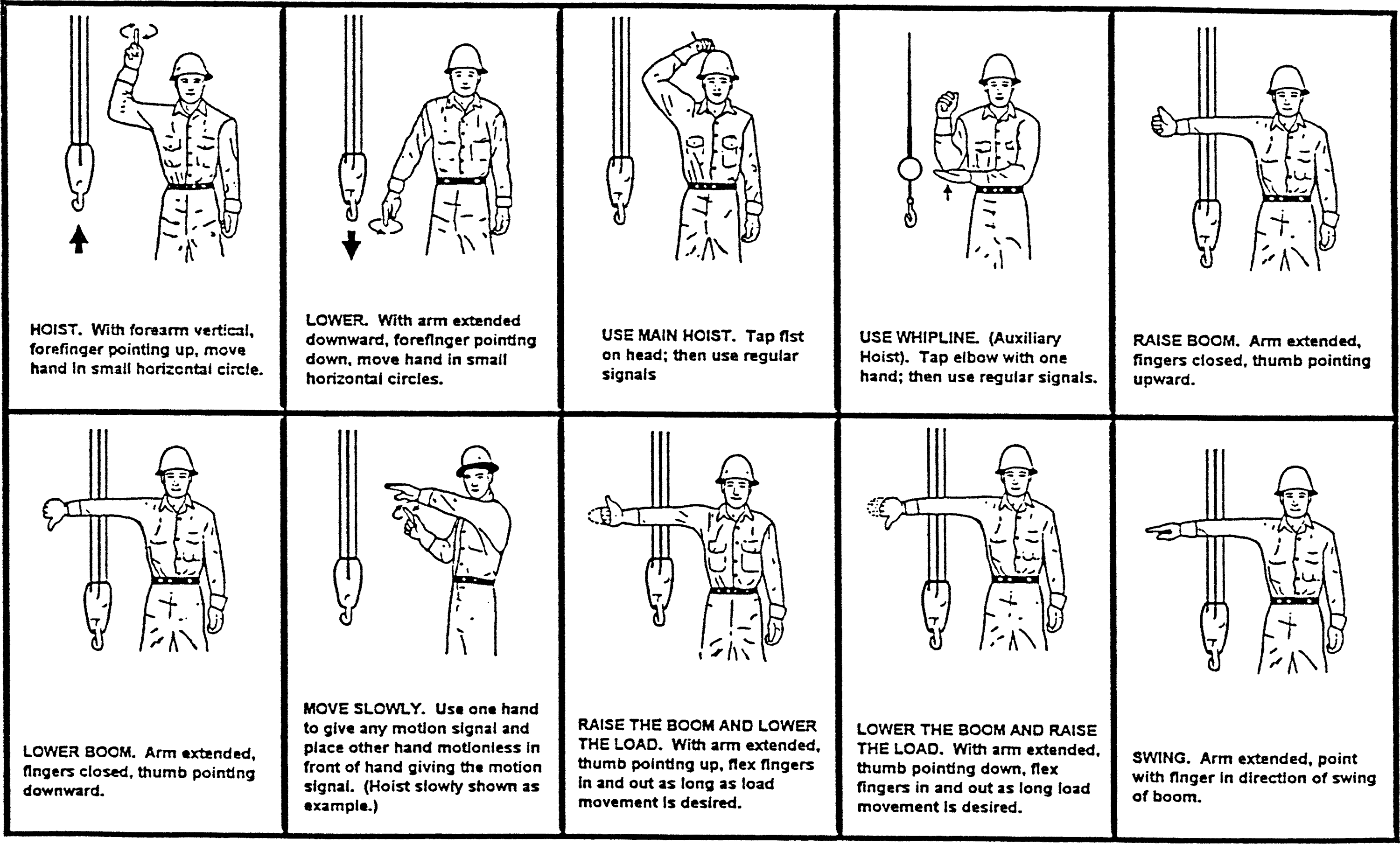 |
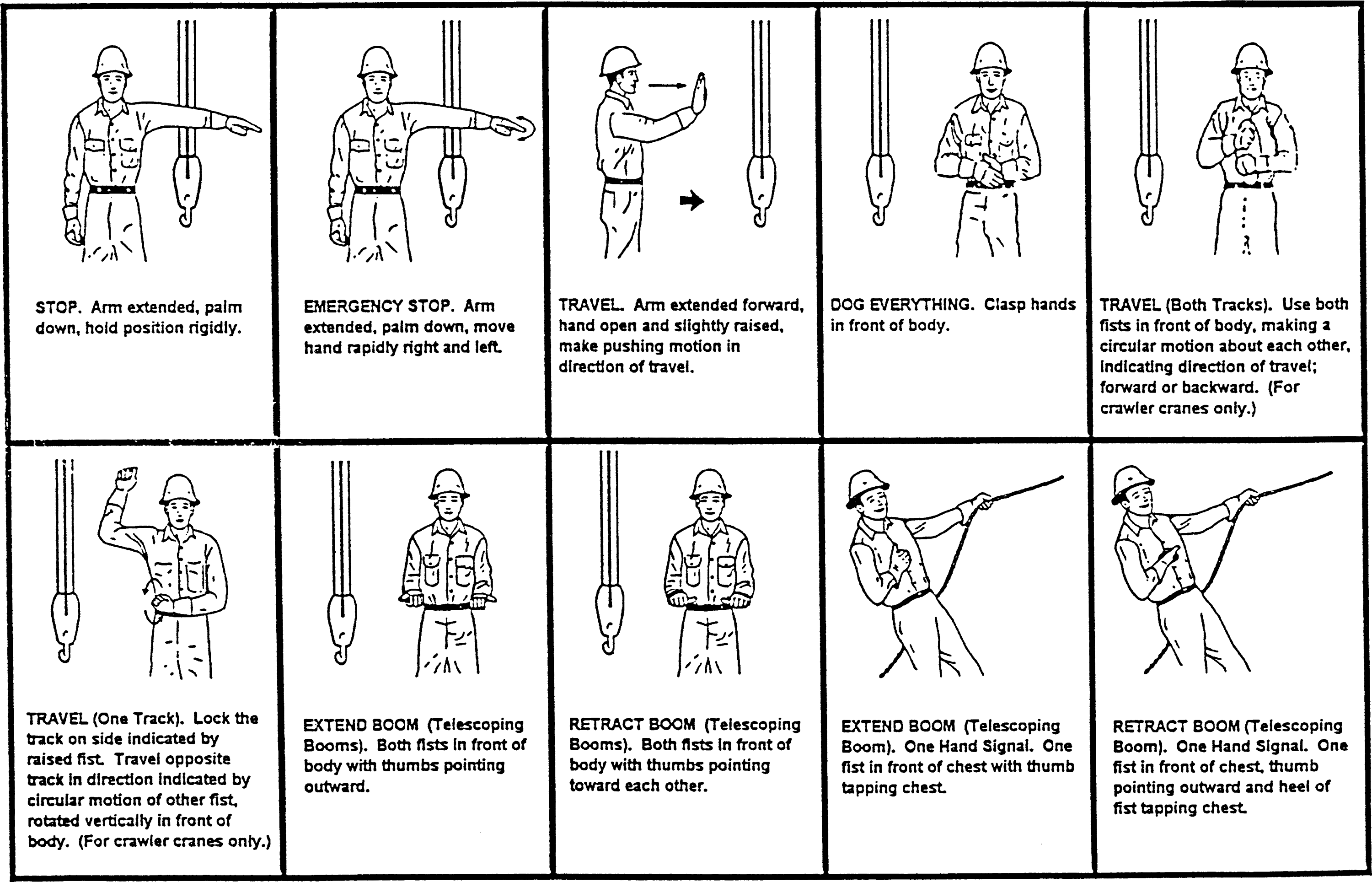 |
STANDARD HAND SIGNALS FOR CONTROLLING OVERHEAD AND GANTRY CRANES
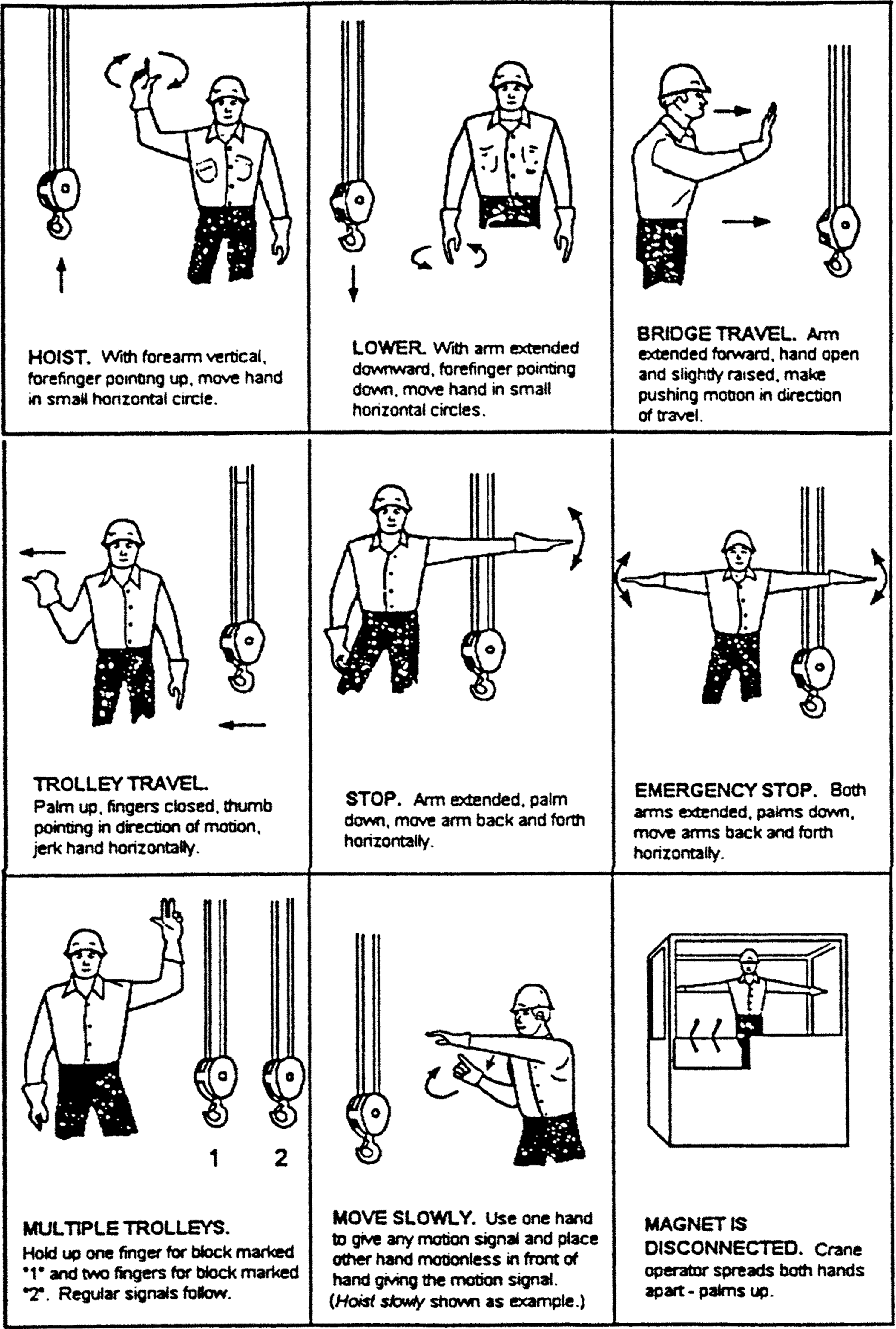 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-180 Privately owned standard gauge railroad operations.
(1) Blue flag or light for railroad operations.
((•)) (a) A blue signal (blue flag or blue light for nonilluminated areas) must be displayed at one or both ends of an engine, car(s), or train, to indicate that workers are under or about the railway equipment.
((•)) (b) When such warning devices are displayed, the equipment must not be coupled to or moved.
((•)) (c) On a dead end spur, a blue signal may be displayed adjacent to the switch opening while cars are being loaded or unloaded.
(2) Blue signals and derails.
((•)) (a) Work being carried on which subjects employees to the hazard of moving railroad equipment must be protected by blue signals and locked derails set a minimum of 50 feet from one or both ends of the worksite.
((•)) (b) Where the spur track switch is less than 50 feet from the work location, the switch padlocked in the open position will take the place of the derail and the blue signal must be placed at that point.
(3) Signals unobscured. Equipment which would obscure the blue signal must not be placed on the track.
(4) Signals displayed by each maintenance crew. Each maintenance crew must display and remove its own set of blue signals.
(5) Warning device.
((•)) (a) A flashing warning light or other device must be installed near any opening which leads to a passageway crossing railroad tracks adjacent to the building.
((•)) (b) Such light or device must be activated prior to any switching or movement of railroad equipment to warn workers of the dangerous condition in the area.
(6) Cars to be immobilized. Spotted cars must either have brakes set, wheels blocked, or must be coupled to other immobilized cars to prevent each car from rolling.
(7) Crawling under or between coupled cars prohibited. Workers must not crawl under or pass between coupled railroad cars to cross tracks.
(8) Warning at road crossing. An audible whistle, horn or bell must be sounded by the locomotive engineer to give adequate warning prior to switching across any road crossing.
(9) Flying switches. When switching railroad equipment in congested areas or across roadways or walkways "flying switches" must be prohibited.
(10) Car opening devices. All box car doors and associated mechanisms must be carefully inspected before workers attempt to open or close them. If the door is not free and cannot be opened safely by hand, equipment must be provided, where necessary, and a safe method must be used to open or close the door.
(11) Clearance from railroad tracks. Materials must not be stacked or piled closer than 8 1/2' from the center line of a standard gauge railroad track.
(12) Operating under limited visibility conditions.
Unless trains are operated in a manner to allow the operator to see a safe stopping distance in the direction of travel, a ((flagperson(s))) flag person(s) must be positioned in such a manner to safely direct movement of the train.
((Flagperson)) (13) A flag person must:
((•)) (a) Remain within sight of the operator((,)); or
((•)) (b) Be equipped to maintain visual or voice communication with the operator as conditions dictate.
(((13) A flagperson)) (14) A flag person must direct the movement of trains being moved across main roads or thoroughfares which do not have adequate traffic warning lights, bells or barricades.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-190 Loading and unloading materials from railway cars or trucks.
(1) Safe access to top of railroad cars or trucks. Platforms with ladders or stairways must be installed or made available when needed so that workers may safely gain access to and perform work on the top of railroad cars or trucks when ladders are not installed on such equipment.
(2) Nets not to cover ladders. Rolled chip nets must not be positioned where they cover the ladders on railroad cars or trucks.
(3) Tipple type unloading device. When a tipple type unloading device is used for removing chips from cars, the cars must be properly secured in place and all employees must be in the clear before dumping operation is started.
(4) Handling pulp chips and hog fuel from trucks and trailers.
(a) Elevating platform-type or cable-lift type unloading devices must have adequate back bumper stops.
(b) Side rails or other positive means to prevent the trailer from falling must be used while unloading single trailer units.
(c) The truck or tractor must be secured when elevating platform lifts are used to elevate both the tractor and trailer or single unit trucks.
(d) All personnel must be clear of all hoisting or elevating mechanisms before dumping commences.
(e) No person is allowed in any truck while the truck is being elevated.
(5) Taking chip samples. A safe area and suitable device must be provided for the chip tester to use while taking chip samples.
(6) Derail required for hazardous materials. To protect tank cars from being moved while loading or unloading hazardous materials by use of pipes or hoses, a derail and blue flag must be set between the spotted tank cars and any moving railroad equipment.
(7) Moving cars by tugger or powered drums. When rail cars are moved by a tugger or powered drums with cables, a means should be provided or the area barricaded in such a manner that the moving cables do not endanger the workers.
(8) Handling pulpwood from flatcars and all other railway cars.
(a) Railroad flatcars for the conveyance of pulpwood loaded parallel to the length of the car must be equipped with safety-stake pockets.
(b) Where pulpwood is loaded crosswise on a flatcar sufficient stakes of sizes not smaller than 4 by 4 inches must be used to prevent the load from shifting.
(c) Cutting stakes on log bundles. When it is necessary to cut stakes:
((•)) (i) Those on the unloading side should be partially cut through first, and then the binder wires cut on the opposite side((.));
((•)) (ii) Wire cutters equipped with long extension handles must be used((.)); and
((•)) (iii) No person is permitted along the dumping side of the car after the stakes have been cut.
(d) Cutting bands on log bundles. When cutting bands on bundled logs, workers must:
((•)) (i) Position themselves in a safe location;
((•)) (ii) Not use double bitted axes for cutting bands;
((•)) (iii) Use caution to prevent being struck by ends of bands being cut; and((;
•)) (iv) If needed, wear personal protective equipment.
(e) Flatcars and all other cars must be:
((•)) (i) Chocked during unloading; and((,
•)) (ii) Rail clamping chocks must be used when equipment is not provided with hand brakes.
(9) Handling pulpwood from trucks.
(a) Cutting of stakes and binder wires must be done in accordance with (8)(c) of this section.
(b) Binders or stakes must not be loosened or removed:
((•)) (i) Until the logs are secured and held by equipment which will prevent them from rolling off the truck((,)); or
((•)) (ii) Barricades will prevent logs from striking the person removing the binders or stakes.
(c) Where binder chains and crane slings are used:
((•)) (i) The crane slings must be attached and taut before the binder chains are released; and((,
•)) (ii) The hooker must see that the helper is clear before signaling for the movement of the load.
(d) The truck driver must:
((•)) (i) Leave the truck cab and remain in the clear, preferably in a designated area((,)); and
((•)) (ii) Be in clear view of the unloading equipment operator while the unloader is approaching the loaded truck.
((•)) (e) After a complete load is lifted as a unit and held stationary, the truck driver may enter the cab and drive forward from under the suspended load.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-200 Bridge and dock plates.
Properly constructed bridge or dock plates must be furnished and used to bridge the area between a dock and truck or railroad car. The following requirements must be complied with for construction and use of such bridge or dock plates:
(1) Strength. The plate must be capable of supporting three times the maximum load to which it will be subjected.
(2) Stops. The plates must be provided with positive stops to prevent the plates from shifting or moving.
(3) Plates.
((•)) (a) The plates must bear solidly on the dock and on the floor of the car or truck.
((•)) (b) Plates with excessive teeter or rock must be repaired or replaced.
(4) Upturn or lip on plates. The sides of bridge or dock plates must have an upturn or lip of at least 4 inches covering the area between the edge of the loading dock and edge of car or truck floor whenever this distance exceeds 18 inches to prevent wheeled equipment from running off the sides.
(5) Bearing surface. Bridge or dock plates must have at least 6 inches bearing surface on the loading dock.
(6) Suitable fittings to be used. Bridge or dock plates intended to be moved by mechanized equipment must be designed for this purpose or appropriate fittings or attachments must be used.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-210 For conveyors, maintenance and inspection.
See ((chapter 296-24 WAC, Part D)) WAC 296-806-420 Conveyors.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-79-220 Deactivating and lockout requirements.
(1) Control requirement. Whenever the unexpected startup of machinery, the energizing of electrical circuits, the flow of material in piping systems or the removal of guards would endanger workers, such exposure must be prevented by deactivating and locking out the controls as required by chapter 296-803 WAC, Lockout/tagout (control of hazardous energy).
EXCEPTION: | In instances where any machine must be in motion for proper adjustment, for removal or replacement of materials from the machine, for machine clothing changes or for roping up, the following precautions must be observed((:)). |
((•)) (a) The machine must be operated at thread or jog speed;
((•)) (b) Extension tools which minimize personnel exposure must be used where possible;
((•)) (c) The operating controls must at all times be under the control of a qualified operator or craftsman;
((•)) (d) All personnel must remain in view of the operator or other means of communication shall be established; and
((•)) (e) All personnel must be beyond the reach of other machine section(s) or element(s) which offer potential exposure. In any instance where such potential exposure exists, such other section(s) or element(s) must be separately locked out.
(2) Group lockout or tagout devices. Procedures must meet the minimum requirements of chapter 296-803 WAC, Lockout/tagout (control of hazardous energy). ((The employer)) You must develop a specific written group lockout or tagout procedure and review it with the local plant labor/management safety committee before it can be utilized.
(3) Temporary or alternate power.
((•)) (a) Whenever possible, temporary or alternate sources of power to the equipment being worked on must be avoided.
((•)) (b) If the use of such power is necessary, all affected employees must be informed and the source of temporary or alternate power must be identified.
(4) Deactivating piping systems.
(a) Nonhazardous systems must be deactivated by at least locking out either the pump or a single valve.
(b) Lockout of the following hazardous material piping systems must isolate to the worksite and must provide protection against backflow where such potential exists:
((•)) (i) Gaseous systems that are operated at more than 200 psig;
((•)) (ii) Systems containing any liquid at more than 500 psig;
((•)) (iii) Systems containing any material at more than 130°F;
((•)) (iv) Any cryogenic system((,));
((•)) (v) Systems containing material which is chemically hazardous as defined by NFPA 704 1996 Class 3 and 4; and
((•)) (vi) Systems containing material classified as flammable or explosive as defined in NFPA Class I.
(c) Such systems must be deactivated by one of the following:
((•)) (i) Locking out both the pump and one valve between the pump and the worksite;
((•)) (ii) Locking out two valves between the hazard source and the worksite;
((•)) (iii) Installing and locking out a blank flange between the hazard source and worksite. When a blank flange (blind) is used to separate off portions of hazardous material systems from a portion which is in operation, ((the employer)) you must develop and implement a procedure for installation and removal of the blank flange that will ensure all hazards have been eliminated;
((•)) (iv) Line breaking between the hazard and the worksite;
((•)) (v) On hazardous chemical systems where the methods already listed are not feasible, or by themselves create a hazard, single valve closure isolation may be used provided that potentially exposed employees are adequately protected by other means such as personal protective equipment((.));
((•)) (vi) On all steam systems where the methods already listed are not feasible, single valve closure isolation may be used provided that the system is equipped with valves meeting all requirements of ANSI B16.5-1996 and ANSI B16.34-1996. Where single valve isolation is used, the steamline must also be equipped with a bleed valve downstream from the valve closure to prove isolation of the worksite.
Note: | Bleeder valves are recommended behind all primary valve closures on hazardous material systems. Consideration should be given to the nature of the material in the system when installing bleeder valves. To assist in preventing plugging, bleeder valves should generally be installed in the top one-third of the pipe. Short exhaust pipes should be installed on bleeder valves to direct the flow of possible escapement away from the position where an employee would normally be when using the bleeder valve. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-230 Confined spaces.
(1) Entry into confined spaces must be in accordance with chapter ((296-62 WAC, Part M)) 296-809 WAC.
(2) All equipment necessary to perform the work, including safety equipment, must be at the confined space and must be inspected or tested to assure that it functions properly.
(3) Protective equipment that will afford proper protection to the employee from any condition which may arise based on the hazard assessment, must be available either at the entrance or within the confined space.
(4) Electrical circuits leading into confined spaces where electrical conductive hazards exist must be protected by a ground fault interrupter or the voltage must not exceed 24 volts.
(5) Battery operated flashlights or lantern must be readily available for use by persons working in areas where escape would be difficult if normal lighting system should fail. Only explosion-proof type lights may be taken into any atmosphere which may contain an explosive concentration.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-250 Safety procedure for handling sulfur.
(1) Sulfur burners. Sulfur-burner houses must:
((•)) (a) Be safely and adequately ventilated((,)); and
((•)) (b) Have every precaution taken to guard against dust, explosion hazards and fires, in accordance with American National Standards Z9.2-1979 (R1991).
(2) Handling/storage of dry sulfur.
(a) Nonsparking tools and equipment must be used in handling dry sulfur.
(b) Sulfur storage bins must be kept free of sulfur dust accumulation, and buildings should be designed with explosion relief, in accordance with the latest revision of American National Standard Z9.2-1979 (R1991).
(c) Sulfur-melting equipment must not be located in the burner room.
(3) Handling/storage of liquid sulfur.
(a) Each facility utilizing liquid sulfur must:
((•)) (i) Carefully examine its own handling system; and
((•)) (ii) Formulate a written procedure for maintenance, receiving, storing and using this product.
(b) A minimum of two trained employees must be assigned when a tank car is first opened in preparation for venting and unloading.
(c) Approved respiratory protective equipment for H2S exposure, chemical splash goggles and gloves must be worn when performing this work.
(d) Spark producing or electric operated tools must not be used to unplug railroad car vents.
(e) Where venting can cause harmful exposure to other unprotected workers in the area:
((•)) (i) A venting system must be installed which adequately contains any gas escapement from a tank car while venting((.));
((•)) (ii) The vented gas must be carried to a safe location for discharge or circulated through a scrubbing system((.));
((•)) (iii) The venting system must be connected before valves which would allow escapement are opened.
(f) Smoking, open burning or welding must be prohibited while unloading is in process or danger of gas escapement exists.
(4) Acid plant - Protection for employees.
(a) Where lime slaking takes place, employees must be provided with rubber boots, rubber gloves, protective aprons, and eye protection. A deluge shower and eyewash must be provided to flush the skin and eyes to counteract lime and acid burns.
(b) Hoops for acid storage tanks must be:
(i) Made of round rods rather than flat strips((,)); and
(ii) Regularly inspected and safety maintained.
(c) Sulphur burner ignitors must have a means to automatically shut off the fuel to the ignitor when the flame has been extinguished.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-260 Pulpwood storage and handling.
(1) Piling of logs.
((•)) (a) Logs must be piled or removed in an orderly manner((.));
((•)) (b) The piles must be stable and individual logs properly placed to prevent them from rolling or falling((.));
((•)) (c) The ends must not project into walkways, roadways or areas reserved for other purposes; and
((•)) (d) Sufficient clearance must be maintained for safe travel of all vehicles and loads.
(2) Wire rope doglines used for towing or rafting must not be used when:
((•)) (a) They acquire jaggers to the extent that they present a hazard to the employees handling them; or
((• When)) (b) They are weakened to the extent that they are hazardous.
(3) Boom sticks must be capable of safely supporting the weight imposed upon them.
(4) Stiff booms must be:
((•)) (a) Made by fastening not less than two boom sticks together((.));
((•)) (b) Not less than 36 inches in width measured from outside to outside of the outer logs((.)); and
((•)) (c) Fastened together with not less than 4 inch by 6 inch cross ties or cable lashing properly recessed into notches in the boom sticks and secured.
(5) Pike poles must be kept in good repair. Conductive pike poles must not be used when it is possible that they may come in contact with electrical conductors.
(6) Logs must not be lifted over employees and employees must stay clear of the hazardous area near where logs are being lifted or swung.
(7) Storing or sorting on water or any boom work other than boom boat operations, must require a minimum of two persons.
(8) All mobile equipment used to handle logs, blocks or cants must be provided with adequate overhead protection.
(9) Unloading lines must be so arranged that it is not necessary for the worker to attach them on the pond or dump side of the load.
(10) Unauthorized vehicles and unauthorized foot traffic must not be allowed in any active sorting, storing, loading, or unloading areas.
(11) Log unloaders must not be moved about the premises with loads raised higher than absolutely necessary.
(12) Jackets or vests of fluorescent or other high visibility material must be worn by persons working on dry land log storage.
(13) All log dumps must be periodically cleared of bark and other debris.
(14) Handles of wood hooks must be locked to the shank to prevent them from rotating.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-270 Pulpwood preparation.
(1) Barker feeding devices must be designed in such a manner that the operator will not be required to hold or make any physical contact with any log or bolt during the barking operations.
(2) A dog or locking device in addition to the motor switch, clutch, belt shifter or other power disconnecting device must be installed on all intermittent barking drums to prevent the drum from moving while it is being filled or emptied.
(3) Hydraulic barkers.
(a) The inlet and outlet areas of hydraulic barkers must be equipped with baffles or devices that will reasonably prevent material from flying out while the machine is in operation.
(b) The operator must be protected by at least five-ply laminated glass or material of equivalent strength.
(4) The high pressure hoses of hydraulic barkers must be secured in such a manner that the hose connection ends will be restrained if a hose connection fails.
(5) The feed operator's station must not be in direct line with the chipper blades. Suitable safeguards must be installed to prevent chips or chunks from being thrown out and striking the person feeding the machine.
(6) When the operator cannot readily observe the material being fed into the chipper, a mirror or other device must be installed in such a position that the ingoing material can be monitored.
(7) Metal bars or other nonchippable devices must not be used to clear jams or plug-up at the feed entrance to a chipper or hog while the machine is running.
(8) Water wheel speed governor.
((•)) (a) Water wheels, when directly connected to marker disks or grinders, must be provided with speed governors, if operated with gate wide open((.)); and
((•)) (b) Water wheels directly connected to pulp grinders must be provided with speed governors limiting the peripheral speed of the grinder to that recommended by the manufacturer.
(9) Knot cleaners of the woodpecker type.
((•)) (a) The operators of knot cleaners of the woodpecker type must wear eye protection equipment((.)); and
((•)) (b) Such knot cleaners should be enclosed to protect passersby from flying chips.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-27003 Log hauls, slips, and carriages.
(1) Controls must be:
((•)) (a) Arranged to operate from a position where the operator will at all times be in the clear of logs, machinery, lines, and rigging((.)); and
((•)) (b) Marked to indicate their function.
(2) Log decks must be provided with effective means to prevent logs from accidentally rolling down the deck and onto the carriage or its runway.
(3) When needed for protection of personnel, an automatic stop or interlocking device must be installed on log hauls or slips. These devices are not a substitute for lockout.
(4) A barricade or other positive stop of adequate strength must be provided to protect the sawyer from rolling logs.
(5) Canting gear or other equipment must not hang over the log deck in such a manner as to endanger employees.
(6) The sawyer ((shall)) must be primarily responsible for the safety of the carriage crew and offbearers and must exercise due care in the operation of the carriage and log turning devices.
(7) Feed works and log turning control levers must be so arranged that they may be secured when not in use and must be adequately guarded against accidental activation.
(8) A control device must be provided so that the sawyer may stop the head rig section of the mill without leaving the stand.
(9) An effective method of disengaging the head rig saws from the power unit must be installed on all head rigs where the power unit is not directly controlled by the sawyer.
(10) The sawyer must be safeguarded either by location or by use of substantial screens or approved safety glass.
(11) Carriages upon which employees are required to work must be solidly decked over and the employees properly protected.
(12) The feed control lever of friction or belt-driven carriage feed works must be designed to operate away from the saws or carriage track.
(13) A substantial stop or bumper must be installed at each end of the carriage run.
(14) Substantial sweeps must be installed in front of each carriage wheel. Such sweeps must extend to within 1/4 inch of the rails.
(15) Where power-operated log turners are used, carriage knees must be provided with goosenecks or other substantial means of protecting the carriage crew.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-27005 Band saws.
(1) Band saws must be given a thorough daily inspection and any deficiency reported and corrected.
(2) Any band saw found to have developed a crack greater than one-tenth the width of the saw must ((be)):
((•)) (a) Be removed from service until the width of the saw is reduced to eliminate the crack((,));
((•)) (b) Have the cracked section ((is)) removed((,)); or
((•)) (c) Have the development of the crack ((is)) arrested by welding.
(3) Band saws must not be continued in use on the head rig for which they have been designed after they have been reduced 40% in width.
(4) Band saw guides must be maintained in good condition and proper alignment at all times.
(5) All head band saw wheels must have a minimum rim thickness of 5/8 inches, except for a distance not to exceed one inch from the front edge of the wheel.
(6) Band saws must not be run at a speed in excess of the manufacturer's recommendations.
(7) A band wheel that has developed a crack in the rim must be immediately removed from service. If a crack has developed in a spoke, the wheel must be removed from service until properly repaired.
(8) All band wheel guards must be constructed of not lighter than ten U.S. Gauge metal, or not less than two-inch wood material or equivalent, attached to substantial frames. Necessary ventilating ports, not larger than two by four inches, and suitable doors or gates for the lubrication and repair of the saw will be permitted.
(9) Every band mill must be equipped with a saw catcher, rest or guard of substantial construction.
(10) Each gang ripper of band or straight saw type must have the cutting edges of the saw guarded by a hood or screen substantially secured to the framework of the machine.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-27015 Construction and use of pulpwood splitters.
(1) The activating control unit for a splitter must be of the clutch or positive acting type and must be so arranged and designed that it will not repeat without additional activation before starting a second cycle.
(2) The base or rest upon which the wood ((seats)) sits while being split must have a corrugated surface or other means ((shall)) must be provided which will prevent the wood block or log from shifting as the pressure is applied.
(3) The splitter base or rest and wood to be split must be free of ice, snow, and chips.
(4) The splitter machine operator must have a clear, unobstructed view of the work area adjacent to the splitting operation when other workers must be in such area while blocks are being split.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-280 Chip and hog fuel storage.
(1) ((Entry into bins and silos.
(a))) Entry into chip bins and silos((,)) must be in compliance with the requirements of confined space entry, WAC 296-79-230, of this chapter.
(((b))) (a) Chip and sawdust bins. Steam or compressed air lances, or other safe methods, must be used for breaking bridges and hangups.
(((c))) (b) Employees must be prohibited from working under or on top overhangs or bridges. Extreme care must be taken to prevent chips or hog fuel from creating an overhang or bridging.
(((d))) (c) Hog fuel bins must be provided with an approved railed platform or walkways near the top or other approved means must be provided for use of employees engaged in dislodging hog fuel.
(2) Exterior chip and hog fuel storage.
(a) When mobile equipment is used on top of hog fuel or chip piles, a roll-over protection system must be installed on the equipment.
(b) If the cab is of the enclosed type, windshield wipers must be installed.
(c) If used during hours of darkness the area must be adequately illuminated or the equipment must have adequate lights to provide the operator sufficient illumination to safely perform the work.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-29003 Warning of digester being blown.
(1) Procedures must be developed to ensure that digester operators are aware of personnel entering hazardous areas.
((•)) (a) Audible warning signals and red warning lights must be installed in areas which may be hazardous to personnel while digesters are being blown.
((•)) (b) Such devices must be activated prior to blowing a digester and the warning lights must remain lighted as long as the hazard exists.
(2) Blowing digester. Blow-off valves must be opened slowly.
(3) After the digester has started to be blown, the blow-off valve must be left open, and the hand plate must not be removed until the person responsible signals the blow-pit person that the blow is completed. Whenever it becomes necessary to remove the hand plate to clear stock, operators must wear eye protection equipment and protective clothing to guard against burns from hot stock.
(4) Blow-pit hoops must be maintained in a safe condition.
(5) Where the processes of the sulfate and soda operations are similar to those of the sulfite processes, the standard of WAC 296-79-29001 and 296-79-29003, of this chapter, applies to both processes.
(6) Means must be provided so the digester cook can signal the employee in the chip bin before starting to load the digester.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-29013 Pulping device procedures.
Each company must develop a safe procedure which ((shall)) must be followed for feeding, clearing jams, or removing foreign objects from any pulping device. These procedures must comply with applicable provisions of this standard.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-29015 Off machine repulping devices.
(1) When fed manually from the floor above, conveniently located emergency stop devices must be provided at the top level.
(2) When fed from floor above:
((•)) (a) The chute opening, if less than standard guardrail height from the feed platform or floor, must be provided with a complete guardrail or other enclosure to standard guardrail height((.)); and
((•)) (b) Openings for manual feeding must be sufficient only for entry of stock and must be provided with at least two permanently secured crossrails, in accordance with, the general safety and health standards, WAC 296-24-75003.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-29021 Shredders and blowers.
(1) On manually fed broke shredders, the feed table must be of a height and distance from the knives as to prevent the operator from reaching or falling into the knives or the operator must be safeguarded by other acceptable means.
(2) A smooth-pivoted idler roll resting on the stock or feed table must be provided in front of feed rolls except when arrangements prevent the operator from standing closer than 36 inches to any part of the feed rolls.
(3) Any manually fed cutter, shredder, or duster must be provided with an idler roll as specified in (2) of this section or the operator ((shall)) must use special hand-feeding tools.
(4) Blowers used for transporting materials must be provided with feed hoppers having outer edges located not less than 48 inches from the fan.
(5) The blower discharge outlets and work areas must be arranged to prevent material from falling on workers.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-29027 Guillotine type roll splitters.
(1) The engaging control for activating the guillotine blade must be a "deadman type" switch that demands continuous operator activation and must be:
((•)) (a) A positive two-hand operating control((,)); or
((•)) (b) Located far enough from the cutting location so that the operator cannot reach the blade during the cutting process.
(2) Personnel must not position any part of the body under the blade.
(3) Rolls must be in the horizontal position while being split.
(4) Rolls must be centered directly below the blade.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-29029 Broke hole.
(1) An alarm bell or flashing light must be actuated or other suitable warning must be given before dropping material through a broke hole when persons working below may be endangered.
(2) Broke holes must be guarded to the fullest extent possible consistent with operational necessities. The degree of guarding provided by standard height and strength guardrails will be considered as a minimum acceptable level of protection.
(3) When repulping devices or feed conveyor systems for repulping devices are located beneath broke holes, special precautions must be used((.)):
((•)) (a) The broke hole opening must be reduced to the smallest practical dimension((.));
((•)) (b) If the broke hole opening is large enough to permit a worker to fall through and is not guarded at least to the equivalent degree of protection provided by standard guardrails, any employee pushing broke down the broke hole must wear a safety belt or harness attached to a lanyard((,)); and
((•)) (c) The lanyard must be fastened in such a manner that it is impossible for the person to fall into the repulping device.
(4) Guarding to the equivalent degree of protection provided by standard guardrails and meeting the requirements of subsections (2) and (3), may be achieved by the use of guard bars separated no more than 15-1/2 inches in a vertical plane and 12 inches in a horizontal plane, or any other location within that segment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-29031 Industrial kiln guns and ammunition.
((The employer)) You must ensure that there are written instructions, including safety procedures, for storing and operating industrial kiln guns and ammunition. All personnel working with this equipment must be instructed in these procedures and must follow them.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-29033 Chlorine dioxide system.
See chapter 296-62 WAC, Part P and chapter 296-67 WAC, process safety management.
(1) Sodium chlorate.
(a) Personnel handling and working with sodium chlorate must be thoroughly instructed in precautions to be used in handling and special work habits.
(b) Facilities for storage and handling of sodium chlorate must be constructed so as to eliminate possible contact of dry or evaporated sodium chlorate with wood or other material which could cause a fire or explosion.
(c) Sodium chlorate facilities should be constructed with a minimum of packing glands, stuffing boxes, etc.
(2) Chlorine dioxide.
Chlorine dioxide generating and storage facilities must be placed in areas which are adequately ventilated and are easily kept clean of wood, paper, pulp, etc., to avoid contamination which might cause a reaction. This can be accomplished by placing these facilities in a separate room or in a designated outside space.
(3) General.
(a) Facilities handling sodium chlorate and chlorine dioxide must be declared "no smoking" areas and must have signs posted accordingly.
(b) Management ((shall)) must be responsible for developing written instructions including safety procedures for operating and maintaining the generator and associated equipment. All personnel working on this equipment must be thoroughly trained in these procedures and must follow them. A periodic review of these procedures is recommended.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-79-300 Machine room equipment and procedures.
(1) Pulp and paper machines must be equipped with emergency stopping control(s) which can be actuated quickly from all normal operating stations. If useful for the safety of personnel, the stopping control(s) must be interlocked with adequate retarding or braking action to stop the machine as quickly as is practical. The devices must consist of push buttons for electric motive power (or electrically operated engine stops), pull cords connected directly to the prime mover, control clutches, or other devices.
(2) Steps and footwalks along the fourdrinier/forming and press section must have nonslip surfacing and be complete with standard handrails, when practical.
(3) If a machine must be lubricated while in operation an automatic lubricating device must be provided or oil cups and grease fittings must be provided which can be serviced safely without exposing the worker to any hazards.
(4) All levers carrying weights must be so constructed that weights will not slip or fall off.
(5) Guarding inrunning nip points. (((a))) The drums on pulp and paper machine winders((.
(i) These drums)) must be provided with suitable guards to prevent a person from being caught between the roll and the front drum on the winder when the pinch point is on the operator's side.
(((ii))) (a) Such guards must be interlocked with the drive mechanism to prevent the winder from running while the guard is not in place. Except that the winder may be wired to allow it to run at thread or jog speed only for adjustment and start up purposes while the guard is not in position.
(((iii))) (b) A zero speed switch or locking device must be installed to prevent the guard from being removed while the roll is turning above thread or jog speed.
(((b))) (c) Rewinders.
When rewinding large rolls and the nip point is adjacent to the normal work area((.)):
((•)) (i) The nip point must be protected by a barrier guard ((and));
((•)) (ii) Such guard must be interlocked with the drive mechanism to prevent operating the machine above thread or jog speed without the guard in place; and
((•)) (iii) A zero speed switch must be installed to prevent the guard from being raised while the roll is turning.
(((c))) (d) Inrunning nips where paper is not being fed into a calender must be guarded.
(6) An audible alarm must be sounded prior to starting up any section of a pulp or paper machine. Sufficient time must be allowed between activation of the alarm system and start up of the equipment to allow any persons to clear the hazardous area.
(7) When starting up a dryer section, steam to heat the drums must be introduced slowly and while the drums are revolving.
(8) A safe method must be used when starting paper into the nip of drum type reels or calender stacks. This may be accomplished by the use of feeder belts, carrier ropes, air carriage or other device or instrument.
((•)) (a) A rope carrying system should be used wherever possible at points of transfer((,)); or
((•)) (b) Sheaves should be spaced so that they do not create a nip point with each other and the sheave and its support should be capable of withstanding the speed and breaking strength of the rope for which they are intended.
(9) Employees must not feed a stack with any hand held device which is capable of going through the nip.
(10) Employees must not attempt to remove a broken carrier rope from a dryer while the section is running at operating speed.
(11) Employees must stop the dryer to remove a wrap except in cases where it can be safely removed by using air or other safe means.
(12) To remove deposits from rolls, a specially designed scraper or tool ((shall)) must be used. Scraping of rolls must be performed on the outgoing nip side.
(13) Doctor blades.
(a) Cleaning. Employees must not place their hands between the sharp edge of an unloaded doctor blade and the roll while cleaning the doctor blade.
(b) Doctor blades must have the sharp edges properly guarded during transportation and storage.
(c) Special protective gloves must be provided and must be worn by employees when filing or handling sharp edged doctor blades.
(14) Handling reels.
(a) Reels must stop rotating before being lifted away from reel frame.
(b) Crane hooks must not be used to stop a turning reel.
(((b))) (c) Exposed rotating reel shafts with square block ends must be guarded.
(((c))) (d) The crane operator must ascertain that reels are properly seated at winder stand or at reel arms before they disengage the hooks.
(((d))) (e) On stored reels, a clearance of at least 8 inches between the reels of paper must be maintained.
(15) All winder shafts must be equipped with a winder collar guide. The winder must have a guide rail to align the shaft for easy entrance into the opened rewind shaft bearing housing. If winder shafts are too heavy for manual handling, mechanical equipment must be used.
(16) Shaftless winders must be provided with a barrier guard of sufficient strength and size to confine the rolls in the event they become dislodged while running.
(17) All calender stacks and spreader bars must be grounded according to chapter 296-24 WAC, Part L, and WAC 296-800-280 as protection against shock induced by static electricity.
(18) Nonskid type surface required.
(a) All exposed sole plates between dryers, calenders, reels, and rewinders must have a nonskid type surface.
(b) A nonskid type surface must be provided in the work areas around the winders or rewinders.
(19) If a powered roll ejector is used it should be interlocked to prevent accidental actuation until the receiving platform or roll lowering table is in position to receive the roll.
(20) Employees must keep clear of hazardous areas around the lowerator, especially all lowerator openings in a floor and where roll is being discharged.
(21) Provision must be made to hold the rider roll when in a raised position unless counterbalancing eliminates the hazard.
(22) Drain openings in pits. Flush floor drain openings larger than 3 inches in diameter in the bottom of pits must be guarded to prevent workers from stepping through, while working in this area.
(23) Employees must not enter into or climb on any paper machine roll that is subject to free turning unless a positive locking device has been installed to prevent the roll from turning.
(24) ((The employer)) You must ensure sufficient inspection and nondestructive examination of reel spool and calender roll journals. The type and frequency of testing must be adequate to detect indications of failure. Any reel spool or calender roll journal found to have an indication of failure must be removed from service. Nondestructive examination personnel must be qualified in accordance with SNT-TC 1A.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-31003 Corrugator.
(1) Every recessed floor conveyor system must be identified by standard color coding, and so designed and installed to minimize tripping hazards.
(2) All areas subject to wet processes must be provided with drains.
((•)) (a) Drain trenches must be provided with gratings flush with the adjoining floor.
((•)) (b) Use of curbing in work areas should be avoided in new installations. If the use of curbing cannot be avoided, the design must be such that the curbs do not constitute a tripping hazard in normal working areas. When curbing exists and constitutes a hazard, it must be color coded.
(3) Rails of rail mounted devices such as roll stands must be flush with the adjacent floor, and so installed to provide a minimum of 18 inches clearance between the equipment and walls or other fixed objects.
(4) All corrugating and pressure rolls must be equipped with appropriately designed and installed threading guides so as to prevent contact with the infeed nip of the various rolls by the operator.
(5) A minimum of 4 inches clearance or effective nip guarding must be maintained between heated drums, idler rolls, and cross shafting on all preheaters and preconditioners.
(6) Lower elevating conveyor belt rolls on the single facer bridge must have a minimum nip clearance of 4 inches or effective nip guarding.
(7) Web shears at the discharge end of the double facer must be equipped with barrier type guards.
(8) Slitter stations not in use must be disconnected from the power source by positive means.
(9) Elevating type conveyors must have the floor area color-coded.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99)
WAC 296-79-320 Sulfite recovery furnace area requirements.
(1) ((The employer)) You must have a program to train all personnel associated with recovery boiler operations in safe operating procedures and emergency shutdown procedures.
(2) An audible warning system must be installed in kraft and soda base sulfite recovery furnace areas and must be actuated whenever an emergency exists.
(3) All personnel who enter the recovery furnace area must understand the emergency evacuation procedure.
(4) Warning system maintenance. Emergency warning systems in the recovery furnace areas must be kept in proper working condition and must be tested or checked weekly.
(5) Personnel must stand to the side while opening a furnace or boiler firebox door.
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-99-005 What definitions apply to this chapter?
Choked leg. Excess material buildup that stops the movement of grain and of the bucket elevator. A bucket elevator is not considered choked if it moves and the boot and discharge are clear.
Flat storage structure. A grain storage structure that:
(a) Cannot empty by gravity alone;
(b) Can be entered through an opening at ground level; and
(c) Must be entered to remove leftover grain.
Fugitive grain dust. Combustible grain dust particles, accumulated inside storage structures, that are small enough to pass through a U.S. standard 40 mesh sieve (425 microns or less).
Grain. Raw and processed grain of cereal grass seeds and grain products handled in facilities within the scope of WAC 296-99-015(1).
Grain elevator. A facility in which bulk raw grains are stored by means of elevating machinery for later shipment.
Hot work. Work that involves electric or gas welding, cutting, brazing or similar heat-producing tasks that could be a source of ignition.
Inside bucket elevator. A bucket elevator with the boot and more than twenty percent of the total leg height (above grade or ground level) inside a grain elevator structure. Bucket elevators used inside of rail or truck dump sheds are not considered inside bucket elevators.
Jogging. To start and stop drive motors repeatedly over short intervals.
Lagging. A covering on drive pulleys used to increase the driving friction between the pulley and the belt.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-99-010 What safety hazards does this chapter require the employer to control?
This chapter directs ((the employer)) you to control dust fires, explosions and other safety hazards in grain handling facilities including the waterfront dock areas at marine terminals (chapter 296-56 WAC will not apply).
All provisions from chapters 296-24, 296-62, and 296-800 WAC also apply. If rules in either of these chapters conflict with rules in chapter 296-99 WAC, chapter 296-99 WAC will prevail.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-015 What grain-handling operations does this chapter cover?
(1) WAC 296-99-010 through 296-99-070 apply to:
((•)) (a) Dry grinding operations of soycake;
((•)) (b) Dry corn mills;
((•)) (c) Dust pelletizing plants;
((•)) (d) Feed mills;
((•)) (e) Flour mills;
((•)) (f) Flat storage structures;
((•)) (g) Grain elevators;
((•)) (h) Rice mills; and
((•)) (i) Soybean flaking operations.
(2) WAC 296-99-075, 296-99-080, and 296-99-085 apply only to grain elevators.
(3) Chapter 296-99 WAC does not apply to alfalfa storage or processing operations if they do not use grain products.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-025 What are the requirements for an emergency action plan?
((The employer)) You must develop and implement an emergency action plan that meets the requirements of WAC 296-24-567.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-99-030 What training must an employer provide for employees?
(1) ((The employer)) You must train employees:
(a) Annually; and
(b) Whenever a new job assignment exposes an employee to a new hazard.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees are trained in the following:
(a) General safety precautions against fires and explosions, including how to recognize and prevent the hazards of excess dust accumulation and ignition sources.
(b) Specific procedures and safety practices for job tasks including, but not limited to:
((•)) (i) Cleaning grinding equipment;
((•)) (ii) Clearing choked legs;
((•)) (iii) Housekeeping;
((•)) (iv) Hot work; and
((•)) (v) Preventive maintenance.
(3) ((The employer)) You must provide additional training for employees who are assigned special tasks, including but not limited to:
(a) Procedures for grain storage entry according to chapter 296-809 WAC, Confined spaces, and how to:
((•)) (i) Control hazardous energy (lockout/tagout) according to chapter 296-803 WAC, Lockout/tagout (control of hazardous energy);
((•)) (ii) Avoid getting buried by moving grain (engulfment);
((•)) (iii) Avoid falling from heights; and
((•)) (iv) Prevent mechanical hazards.
(b) How to handle flammable or toxic substances.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-035 When must an employer issue a hot work permit?
(1) Before allowing an employee to start any hot work, ((the employer)) you must:
(a) Issue to the employee a permit that states that all safety precautions required by WAC 296-24-695 are in place; and
(b) Keep the permit on file until the hot work is complete.
(2) ((The employer)) You may allow an employee to perform hot work without a permit if:
(a) ((The employer's)) Your representative personally monitors the hot work to prevent employee exposure to injury from either fire or explosion during the entire operation; or
(b) The hot work is done in welding shops authorized by ((the employer)) you; or
(c) The hot work is done in hot work areas authorized by the employer which are located outside of the grain handling structure.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-01-086, filed 12/20/11, effective 2/1/12)
WAC 296-99-040 What practices must an employer follow for entry into grain storage structures?
This section applies to employee entry into all grain storage structures.
(1) ((The employer)) You must ensure that the practice of walking down grain is prohibited. "Walking down grain" means an employee walks on grain to make it flow within or out from a grain storage structure, or an employee is on moving grain.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that during the entry and occupation of a storage structure the employee uses:
((•)) (a) A body harness with a lifeline; or
((•)) (b) A boatswain's chair that meets the requirements of chapter 296-874 WAC, Scaffolds:
(((a))) (i) The employee is exposed to a fall hazard such as when entering from the top or above the level of the stored grain; or
(((b))) (ii) The employee is exposed to an engulfment hazard such as when entering at the level of the stored grain, or while walking or standing on the grain. The lifeline must be rigged so that its position and length will prevent the employee from sinking below waist level.
(3) ((The employer)) You must ensure that during the occupation of storage structures, including walking or standing on grain, employees are protected from hazards related to:
((•)) (a) Mechanical;
((•)) (b) Electrical;
((•)) (c) Hydraulic; and
((•)) (d) Pneumatic equipment.
By using safeguards, lockout-tagout, or other equally effective means. All provisions for the control of hazardous energy (lockout/tagout) from chapter 296-803 WAC apply to this chapter.
(4) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees are prohibited from entering any storage structure where a build-up of grain overhead (bridging) or on the sides could fall and bury them.
(5) ((The employer)) You must ensure, as minimum precautions, that employee entry and occupation of all grain storage structures including flat storage structures is done according to all applicable requirements of chapter 296-809 WAC, Confined spaces, when the storage structure:
((•)) (a) Has limited or restricted means of entry and exit; and
((•)) (b) Is not designed for continuous employee occupancy.
(6) ((The employer)) You may allow an employee to perform confined space entry work in grain storage structures without a permit if the employer's representative personally monitors the work to prevent employee exposure to illness or injury from atmospheric hazards during the entire operation.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-045 What information must an employer provide to contractors?
(1) ((The employer)) You must inform contractors working at the grain handling facility of:
(a) General safety rules; and
(b) Specific fire and explosion hazards related to the contractor's work and work area.
(2) ((The employer)) You must explain the emergency action plan to each contractor.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-050 What elements must an employer include in the housekeeping program?
(1) ((The employer)) You must develop and enforce a written housekeeping program that:
(a) Establishes frequency and methods for reducing and cleaning up hazardous accumulations of fugitive grain dust;
(b) Identifies priority areas for clean up of hazardous accumulations of fugitive grain dust, including floor areas:
((•)) (i) Within thirty-five feet (10.7 m) of inside bucket elevators;
((•)) (ii) Of enclosed grinding equipment; and
((•)) (iii) Of enclosed grain dryers located inside the facility((; and)).
(c) Requires that fugitive grain dust is cleaned up immediately whenever accumulations exceed one-eighth inch (.32 cm) at priority housekeeping areas, or provide protection against fire and explosion that is equal to the required clean up.
(2) ((The employer)) You must prohibit the use of compressed air to blow dust from ledges, walls, and other areas unless all machinery that provides an ignition source in the area is shut down, and all other known potential ignition sources in the area are removed or controlled.
(3) ((The employer)) You must also ensure that the housekeeping program addresses procedures for removing grain and product spills from work areas. Spills are not considered fugitive grain dust accumulations.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-055 What is the maximum allowable grate opening size?
((The employer)) You must ensure that receiving-pit feed openings, such as truck or railcar receiving-pits, are covered by grates with maximum openings of two and one-half inches (6.35 cm).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-060 How must filter collectors be installed?
(1) ((The employer)) You must ensure that, on a pneumatic dust collection system, each fabric dust filter collector has a monitoring device that will show a pressure drop across the surface of its filter.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that each filter collector installed after March 30, 1988, is:
(a) Located outside the facility; or
(b) When located inside the facility, protected by an explosion suppression system; or
(c) Isolated by a structure with at least a one hour fire-resistance rating:
((•)) (i) Next to an exterior wall;
((•)) (ii) Vented to the outside; and
((•)) (iii) The vent and ductwork must resist rupture from intense heat.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-99-065 What preventive maintenance program must an employer implement?
(1) ((The employer)) You must implement a written program that covers the requirements of chapter 296-803 WAC, Lockout/tagout (control of hazardous energy).
(2) ((The employer)) You must implement preventive maintenance procedures that include the following:
(a) Conducting regularly scheduled inspections for specified machinery.
(b) Preparing written inspection reports kept on file that include:
((•)) (i) The date of each inspection;
((•)) (ii) The name of the inspector; and
((•)) (iii) The serial number, or other identification of the machinery as described next in (c) of this subsection.
(c) Conducting regularly scheduled inspections and completing immediate repairs of the mechanical equipment and safety controls of the following machinery:
((•)) (i) Grain dryers;
((•)) (ii) Grain stream processing equipment;
((•)) (iii) Dust collection systems including their filter collectors that malfunction or operate below designed efficiency;
((•)) (iv) Overheated bearings; and
((•)) (v) Slipping or misaligned belt drives for inside bucket elevators.
When immediate repairs are not feasible, then the affected machine must be taken out of service.
(d) Performing lubrication and other maintenance according to manufacturers' recommendations or more often when needed, such as when operating records indicate that a more stringent schedule is necessary.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-070 How must grain stream processing equipment be equipped?
((The employer)) You must ensure that the following grain stream processing equipment has an effective means of removing ferrous material from the incoming grain:
((•)) (1) Hammer mills;
((•)) (2) Grinders; and
((•)) (3) Pulverizers.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-075 How many means of emergency escape must an employer provide?
((The employer)) You must provide the following number of emergency escape means:
Structure |
Number of escape means |
|
Galleries (bin decks) |
Two |
|
Tunnels of grain elevators constructed after November 14, 1988 |
Two |
|
Tunnels of grain elevators constructed on or before November 14, 1988 |
One |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-080 How must continuous-flow bulk raw grain dryers be equipped and installed?
(1) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all direct-heat grain dryers have automatic controls that:
(a) Shut off the fuel supply in case of power, flame, or ventilation airflow shutoff; and
(b) Stop the grain flow into the dryer if the dryer exhaust gets too hot.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that each direct-heat grain dryer installed after March 30, 1988, is:
(a) Located outside the grain elevator; or
(b) When located inside the grain elevator, protected by a fire or explosion suppression system; or
(c) Isolated by a structure with at least a one hour fire-resistance rating.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-22-065, filed 11/3/97, effective 1/1/98)
WAC 296-99-085 What special requirements apply to inside bucket elevators?
(1) ((The employer)) You must prohibit jogging of a bucket elevator to free a choked leg.
(("Jogging" means to start and stop drive motors repeatedly over short intervals.
(2) The employer)) (2) You must ensure that all belts and lagging purchased after March 30, 1988, are conductive and have a maximum surface electrical resistance of 300 megohms.
(3) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all bucket elevators have safe access to the head pulley section for inspection of the head pulley, lagging, belt, and discharge throat. The boot section must also have safe access for its clean-out and inspection of the pulley and belt.
(4) ((The employer)) You must:
(a) Mount bearings externally to the leg casing; or
(b) Have vibration and temperature monitoring; or
(c) Have other means to monitor the condition of bearings mounted inside or partially inside the leg casing.
(5) ((The employer)) You must ensure that bucket elevators have a motion detection device that will stop the elevator if belt speed is reduced to less than eighty percent of normal operating speed.
(6) ((The employer)) You must:
(a) Ensure that bucket elevators have a belt alignment monitoring device that will initiate an alarm to employees when the belt is not tracking properly; or
(b) Use a system to keep the belt tracking properly.
(7) Subsections (5) and (6) of this section do not apply to grain elevators with a permanent storage capacity of less than one million bushels, if daily visual inspection is made of bucket movement and belt tracking.
(8) Subsections (4), (5), and (6) of this section do not apply to the following:
(a) Bucket elevators with an operational fire and explosion suppression system capable of protecting at least the head and boot section of the bucket elevator; or
(b) Bucket elevators with pneumatic or other dust control systems or methods that keep the dust concentration inside the bucket elevator at least twenty-five percent below the lower explosive limit at all times during operations.
REPEALER
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
WAC 296-99-020 |
What definitions apply to this chapter? |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 08-20-123, filed 10/1/08, effective 11/1/08)
WAC 296-115-015 Definitions.
(((1))) Approved ((means)). Approved by the assistant director or an authorized representative. However, if a provision of this chapter requires approval by an agency or organization other than the department, such as nationally recognized testing laboratories or the United States Coast Guard, then approval by the specified authority will be accepted.
(((2))) Assistant director ((means)). The assistant director of the division of occupational safety and health (DOSH) within the department of labor and industries.
(((3))) Authorized person ((means)). A person approved or assigned by the employer to perform a specific type of duty or duties or be at a specific location or locations at the workplace.
(((4))) Bare boat charter ((means)). The unconditional lease, rental, or charter of a boat by the owner, or owner's agent, to a person who by written agreement, or contract, assumes all responsibility and liability for the operation, navigation, and provisioning of the boat during the term of the agreement or contract, except when a captain or crew is required or provided by the owner or owner's agents to be hired by the charterer to operate the vessel.
(((5))) Carrying passengers or cargo ((means)). The transporting of any person or persons or cargo on a vessel for a fee or other consideration.
(((6))) C.F.R. ((means)) Code of Federal Regulations.
(((7))) Charter boat ((means)). A vessel or barge operating on waters of the state of Washington which is:
(a) Not inspected or licensed by the United States Coast Guard and over which the United States Coast Guard does not exercise jurisdiction; and
(b) Rented, leased, or chartered to carry seven or more persons, or cargo.
(((8))) Commercial ((means)). Any activity from which the operator, or the person chartering, renting, or leasing a vessel derives a profit, and/or which qualifies as a legitimate business expense under the Internal Revenue Statutes.
(((9))) Competent person ((means)). Someone who is capable of identifying existing and predictable hazards in the surroundings or working conditions that are unsanitary, hazardous, or dangerous to employees, and who has authorization to take prompt action to eliminate them.
(((10))) Confined space ((means)). A space that is all of the following:
(a) Large enough and arranged so that an employee could fully enter the space and perform work; and
(b) Has limited or restricted means for entry or exit. Examples of spaces with limited or restricted entry are tanks, vessels, silos, storage bins, hoppers, vaults, and pits; and
(c) Not primarily designed for human occupancy.
(((11))) Defect ((means)). Any characteristic or condition that tends to weaken or reduce the strength of the tool, object, or structure of which it is a part.
(((12))) Department ((means)). The department of labor and industries.
(((13))) Employee ((means)):
(a) Someone who is employed in the business of an employer; and
(b) Every person in this state who is working for an employer under an independent contract for personal labor.
(((14))) Employer ((means)). Any person, firm, corporation, partnership, business trust, legal representative, or other business entity that operates a passenger vessel for hire in this state and employs one or more employees or contracts with one or more persons for personal labor. Any person, partnership, or business entity that has no employees, and is covered by the Industrial Insurance Act is considered both an employer and an employee.
(((15))) Enclosed space ((means)). Any space, other than a confined space, which is enclosed by bulkheads and overhead. It includes cargo holds, tanks, quarters, and machinery and boiler spaces.
(((16))) Equipment ((means)). A system, part, or component of a vessel as originally manufactured, or a system, part, or component manufactured or sold for replacement, repair, or improvement of a system, part, or component of a vessel; an accessory or equipment for a vessel; or a marine safety article, accessory, or equipment, including radio equipment, intended for use by a person on board a vessel.
(((17))) Hazard ((means)). A condition, potential or inherent, that is likely to cause injury, death, or occupational disease.
(((18))) Hazardous substance ((means)). A substance that, because it is explosive, flammable, poisonous, corrosive, oxidizing, irritating, or otherwise harmful, is likely to cause death or injury, including all substances listed on the USCG hazardous materials list.
(((19))) Inspection ((means)). The examination of vessels by the assistant director or an authorized representative of the assistant director.
(((20))) Keel laid ((means)). The date a vessel's keel was laid or the vessel was at a similar stage of construction.
(((21))) Maritime safety specialist ((means)). A technical and operations specialist in maritime issues located in the department.
(((22))) Master ((means)). The individual having command of the vessel and who is the holder of a valid license that authorizes the individual to serve as master of a small passenger vessel.
(((23))) Passenger ((means)). A passenger who pays for carriage on a vessel, whether directly or indirectly to the owner, charterer, operator, agent, or any other person having an interest in the vessel.
(((24))) Should ((means)). Recommended.
(((25))) Standard safeguard ((means)). A device intended to remove a hazard incidental to the machine, appliance, tool, or equipment to which the device is attached. Standard safeguards must be constructed of either metal, wood, other suitable material, or a combination. The final determination of the sufficiency of any safeguard rests with the assistant director.
(((26))) State waters ((means)). All nonnavigable waters within the territorial limits of the state of Washington, and not subject to the jurisdiction of the United States Coast Guard.
(((27))) Substantial ((means)). An object is constructed of such strength, material, and workmanship that it will withstand all normal wear, shock, and usage.
(((28))) Suitable ((means)). That which fits, or has the qualities or qualifications to meet a given purpose, occasion, condition, function, or circumstance.
(((29))) Under way ((means)). A vessel is not at anchor, made fast to the shore, or aground.
(((30))) USCG ((means)). The United States Coast Guard.
(((31))) United States Coast Guard Navigation ((means)). Rules International/Inland, Commandants Instruction M16672.2D as now adopted, or legally amended by the United States Coast Guard.
(((32))) Vessel ((means)). Every description of motorized watercraft, other than a bare boat charter boat, seaplane, or sailboat, used or capable of being used to transport seven or more passengers, or cargo, on water for rent, lease, or hire.
(((33))) Working day ((means)). A calendar day, except Saturdays, Sundays, and legal holidays as described in RCW 1.16.050. The time within which an act must be done is computed by excluding the first working day and including the last working day.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 08-20-123, filed 10/1/08, effective 11/1/08)
WAC 296-115-025 Vessel inspection and certification.
(1) The department must inspect all vessels subject to this chapter to ensure they are safe and seaworthy at least once each year.
(2) The department may also inspect a vessel:
(a) If requested to do so by the owner, operator, or master of the vessel;
(b) After an explosion, fire, or any other accident involving the vessel;
(c) Upon receipt of a complaint from any person;
(d) At the discretion of the department.
(3) The department will charge the owner of a vessel a fee for each certification or recertification inspection. See WAC 296-115-120 for fee schedule.
(4) No person will operate a passenger vessel if the vessel does not have a valid certificate of inspection issued by the department.
(5) After inspecting a vessel and determining it is safe and seaworthy, the department will issue a certificate of inspection for that vessel. The certificate will be valid for one year after the date of inspection and contain:
(a) The certificate must set forth the date of the inspection;
(b) The names of the vessel and the owner;
(c) The number of lifeboats, if required;
(d) The number of life preservers required;
(e) The number of passengers allowed; and
(f) Any other information the department requires by rule.
(6) Any time a vessel is found to be not safe or seaworthy, or not in compliance with the provisions of this chapter:
(a) The department may refuse to issue a certificate of inspection until the deficiencies have been corrected and may cancel any certificate of inspection currently issued.
(b) The department must give the owner a written statement why the vessel was found to be unsafe, unseaworthy, or not in compliance with the provisions of this chapter, including a specific reference to the statute or rule.
(7) Department inspectors may, upon presenting their credentials to the owner, master, operator, or agent in charge of a vessel, board the vessel without delay to make an inspection.
(a) Inspectors must inform the owner, master, operator, or agent in charge that their intent is to inspect the vessel.
(b) During the inspection, inspectors must have access to all areas of the vessel. Inspectors may question privately the owner, master, operator, or agent in charge of the vessel, or any crew member of or passenger on the vessel.
(c) If any person refuses to allow inspectors to board a vessel for an inspection, or refuses to allow access to any areas of the vessel, the department may request a warrant from the superior court for the county in which the vessel is located. The court will grant the warrant if:
((•)) (i) There is evidence that the vessel has sustained a fire, explosion, unintentional grounding, or has been involved in any other accident;
((•)) (ii) There is evidence that the vessel is not safe or seaworthy; or
((•)) (iii) The department shows that the inspection furthers a general administrative plan for enforcing the safety requirements of chapter 88.04 RCW, the Charter Boat Safety Act.
(8) The owner or master of a vessel must post the certificate of inspection behind glass or other suitable transparent material in a conspicuous area of the vessel.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-115-050 General requirements.
(1) Where an existing charter vessel does not meet a particular requirement of this section, the assistant director may grant:
(a) A temporary variance to allow time for modifications to be made.
(b) A permanent variance if the degree of protection afforded is judged to be adequate for the service in which the vessel is used.
(2) Lifesaving equipment required by this section must be approved by the USCG.
(3) The following lifesaving equipment is required:
(a) All vessels carrying passengers must carry life floats or buoyant apparatus for all persons on board.
(i) All life floats or buoyant apparatus must be international orange in color.
(ii) Vessels operating not more than one mile from land are not required to carry life floats or buoyant apparatus.
(iii) Lifeboats, life rafts, dinghies, dories, skiffs, or similar type craft may be substituted for the required life floats or buoyant apparatus if the substitution is approved by the assistant director.
(iv) Life floats, buoyant apparatus, or any authorized substitute must be U.S. Coast Guard approved and have the following equipment:
((•)) (A) Two paddles or oars not less than four feet in length.
((•)) (B) A painter of at least one-half inch diameter and thirty feet in length.
(b) All vessels must have a USCG-approved adult life preserver for the number of people the vessel is certified to carry, with at least ten percent additional of a type suitable for children or greater number to provide a life jacket for each child-sized person on board.
(i) Life preservers must be stowed in readily accessible places in the upper part of the vessel; and
(ii) Each life preserver must be marked with the vessel's name.
(c) All vessels must carry in a readily accessible location at least one ring life buoy of an approved type with sixty feet of buoyant line attached. The ring life buoy must:
(i) Be ready to cast loose at any time; and
(ii) Have a floating water light, unless operation is limited to daytime.
(4) Fire protection general.
(a) The general construction of a vessel must minimize fire hazards.
(b) Internal combustion engine exhausts, boiler and galley uptakes, and similar sources of ignition must be kept clear of and suitably insulated from woodwork or other combustible material.
(c) Lamp, paint, and oil lockers and similar storage areas for flammable liquids must be constructed of metal or lined with metal.
(5) Fire protection equipment. Equipment required to be of an approved type must be approved by the USCG or other agency acceptable to the director.
(a) Fire pumps.
(i) All vessels carrying more than forty-nine passengers must carry an approved power fire pump capable of reaching any part of the vessel.
(ii) All other vessels must carry an approved hand fire pump. These pumps must be provided with a suitable suction and discharge hose, and may also serve as bilge pumps.
(b) Fixed fire extinguishing system.
(i) The following vessels must have a fixed fire extinguishing system to protect the machinery and fuel tank spaces:
((•)) (A) Those powered by internal combustion engines using gasoline or other fuel having a flashpoint of 110°F or lower; and
((•)) (B) Those with hulls constructed of fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) or wood.
(ii) This system must be an approved type and have a capacity sufficient to protect the space.
(iii) Controls for the fixed system must be installed in an accessible location outside the space protected.
(iv) A device must be provided to automatically shut down power ventilation serving the protected space and engines that draw intake air from the protected space prior to release of the extinguishing agent into the space.
(c) Fire axe. All vessels must have one fire axe located in or near the pilothouse.
(d) Portable fire extinguishers.
(i) All vessels must have a minimum number of portable fire extinguishers of an approved size and type. The number required will be determined by Table 1, Portable Fire Extinguishers.
(ii) Portable fire extinguishers must be inspected at least once a month. Extinguishers found defective must be serviced or replaced.
(iii) Portable fire extinguishers must be serviced at least once a year. The required service must consist of discharging and recharging foam and dry chemical extinguishers and weighing and inspecting carbon dioxide extinguishers.
(iv) Portable fire extinguishers must be hydrostatically tested at intervals not to exceed those specified in WAC 296-800-300 in the safety and health core rules.
(v) Portable fire extinguishers of the vaporizing liquid type such as carbon tetrachloride and other toxic vaporizing liquids are prohibited and must not be carried on any vessel.
(vi) Portable fire extinguishers must be mounted in brackets or hangers near the space protected. The location must be marked in a manner satisfactory to the assistant director.
Table 1
Portable Fire Extinguishers
Type Extinguisher Permitted |
||||
Space Protected |
Minimum # Required |
CG Class |
Medium |
Minimum Size |
Operating station |
1 |
B-I, C-I |
Halon CO2 Dry chemical |
2.5 lb. 4 lb. 2 lb. |
Machinery space |
1 Located just outside exit |
B-II, C-II |
CO2 Dry chemical |
15 lb. 10 lb. |
Open vehicle deck |
1 for every 10 vehicles |
B-II |
Foam Halon CO2 Dry chemical |
2.5 gal. 10 lb. 15 lb. 10 lb. |
Accommodation space |
1 for each 2,500 sq. ft. or fraction thereof |
A-II |
Foam Dry chemical |
2.5 gal. 10 lb. |
Galley, pantry, concession stand |
1 |
A-II, B-II |
Foam Dry chemical |
2.5 gal. 10 lb. |
(6) Means of escape.
(a) All vessels must have at least two avenues of escape from all general areas accessible to the passengers or where the crew may be quartered or normally employed. The avenues must be located so that if one is not available the other may be. At least one of the avenues should be independent of watertight doors.
(b) One vertical means of escape is acceptable where the length of the compartment is less than twelve feet under the following conditions:
(i) There is no source of fire in the space, such as a galley stove or heater and the vertical escape is remote from the engine and fuel tank space; or
(ii) The arrangement is such that the installation of two means of escape does not materially improve the safety of the vessel or those aboard.
(7) Ventilation.
(a) All enclosed spaces within the vessel must be properly vented or ventilated. Where such openings would endanger the vessel under adverse weather conditions, means must be provided to close them.
(b) All crew and passenger space must be adequately ventilated in a manner suitable to the purpose of the space.
(8) Crew and passenger accommodations.
(a) Vessels with crew members living aboard must have suitable accommodations.
(b) Vessels carrying passengers must have fixed seating for the maximum number of passengers permitted, installed as follows:
(i) Spacing that provides for ready escape in case of fire or other casualty.
(ii) Aisles not over fifteen feet long must be not less than twenty-four inches wide.
(iii) Aisles over fifteen feet long must be not less than thirty inches wide.
(iv) Where seats are in rows the distance from seat front to seat front must be not less than thirty inches.
(v) The assistant director may grant special exception to fixed seating spacing requirements if escape over the side can be readily accomplished through windows or other openings in the way of the seats.
(c) Portable or temporary seating may be installed but must be arranged as provided for fixed seating.
(9) Toilet facilities and drinking water.
(a) Vessels must be provided with toilets and wash basins as specified in WAC 296-800-230 unless vessels are used exclusively on short runs of approximately thirty minutes or less.
(b) All toilets and wash basins must be fitted with adequate plumbing. Facilities for men and women must be in separate compartments, except in the case of vessels carrying forty-nine passengers and less, the assistant director may approve other arrangements.
(c) Potable drinking water must be provided for all passengers and crew according to WAC 296-800-23005.
(d) Covered trash containers must be provided in passenger areas.
(10) Rails and guards.
(a) Rails or equivalent protection must be installed near the periphery of all weather decks accessible to passengers and crews. Where space limitations make deck rails impractical for areas designed for crew only, such as at narrow catwalks in the way of deckhouse sides, hand grabs may be substituted.
(b) Rails must consist of evenly spaced courses. The spacing must not be greater than four inches except as provided in WAC 296-115-050 (10)(d). Lower rail courses may not be required if all or part of the space below the upper rail course is fitted with a bulwark, chain link fencing, wire mesh or the equivalent.
(c) On passenger decks of vessels engaged in ferry or excursion type operation, rails must be at least forty-two inches high. The top rail must be pipe, wire, chain, or wood and must withstand at least two hundred pounds of side loading. The space below the top rail must be fitted with bulwarks, chain link fencing, wire mesh, or the equivalent.
(d) On vessels engaged in other than passenger service, the rails must be not less than thirty-six inches high. Where vessels are used in special service, the assistant director may approve other arrangements, but in no case less than thirty inches high.
(e) Suitable storm rails or hand grabs must be installed where necessary in all passageways, at deckhouse sides, and at ladders and hatches where passengers or crew might have normal access.
(f) Suitable covers, guards, or rails must be installed in the way of all exposed and hazardous places such as gears or machinery. (See chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety for detailed requirements.)
(11) Machinery installation.
(a) Propulsion machinery.
(i) Propulsion machinery must be suitable in type and design for the propulsion requirements of the hull of the vessel in which it is installed. Installations meeting the requirements of the USCG or USCG-recognized classification society are considered acceptable to the assistant director.
(ii) Installations using gasoline or diesel as a fuel must meet the requirements of applicable USCG standards.
(b) Auxiliary machinery and bilge systems.
(i) All vessels must be provided with a suitable bilge pump, piping, and valves for removing water from the vessel.
(ii) Vessels carrying more than forty-nine passengers must have a power operated bilge pump. The source of power must be independent of the propulsion machinery. Other vessels must have a hand operated bilge pump, but may have a power operated pump if it is operated by an independent power source.
(c) Steering apparatus and miscellaneous systems.
(i) All vessels must be provided with a suitable steering apparatus.
(ii) All vessels must be provided with navigation lights and shapes, whistles, fog horns, and fog bells as required by the USCG rules of navigation.
(iii) All vessels must be equipped with a suitable number of portable battery lights for emergency purposes. There should be at least two, one located at the operating station and the other at the access to the propulsion machinery.
(d) Electrical installations. The electrical installations of all vessels must be at least equal to applicable USCG standards, or as approved by the assistant director.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 15-11-066, filed 5/19/15, effective 7/1/15)
WAC 296-115-060 Operations.
(1) No person will rent, lease, or hire out a charter boat, carry, advertise for carrying, or arrange for carrying, more than six passengers on a vessel for a fee or other consideration on state waters unless the vessel meets the requirements of this chapter.
(2) Notice of casualty.
(a) The owner or person in charge of any vessel involved in a marine accident or casualty involving any of the following must report the incident immediately to the department:
(i) Damage to property in excess of one thousand five hundred dollars.
(ii) Major damage affecting the seaworthiness or safety of the vessel.
(iii) Loss of life or an injury to a person that requires medical treatment beyond first aid.
(iv) Fire on board the vessel.
(b) The report must be in writing to the assistant director. Upon receipt of the report the assistant director may request an investigation by a marine dock inspector.
(c) For work-related injuries and illness involving any employee that resulted in death, inpatient hospitalization, amputation or loss of an eye, ((the employer)) you must comply with the recordkeeping and reporting regulations in chapter 296-27 WAC.
(3) Miscellaneous operations.
(a) In the case of collision, accident, or other casualty involving a vessel, the operator((,)) must:
(i) So far as possible without serious danger to the vessel or persons aboard, render any necessary assistance to other persons affected by the collision, accident, or casualty to save them from danger.
(ii) Provide the name and address of the vessel owner and the name of the vessel to any person injured and to the owner of any property damaged.
(b) The person in charge of the vessel must see that the provisions of the certificate of inspection are strictly adhered to. This will not limit the person in charge from taking any action in an emergency judged necessary to help vessels in distress or to prevent loss of life.
(c) The operator of a vessel must comply with the provisions of the USCG Navigation Rules International/Inland, Commandants Instruction M16672.2D.
(d) The operator of a vessel must test the vessel's steering gear, signaling whistle, controls, and communication system before getting under way for the day's operation.
(e) Vessels using fuel with a flashpoint of 110°F or lower must not take on fuel when passengers are on board.
(f) All vessels must enforce "no smoking" provisions when fueling. Locations on the vessel where flammable liquids are stored must be posted "no smoking."
(g) All vessels must prepare and post emergency check-off lists in a conspicuous place accessible to crew and passengers, covering the following:
(i) Man overboard.
(ii) Fire.
(h) The persons in charge must conduct emergency drills to ensure that the crew is familiar with their duties in an emergency and must document the drills.
(i) Carrying hazardous substances is prohibited on vessels. However, the assistant director may authorize a vessel to carry specific types and quantities of hazardous substances if the assistant director approves the type, quantity, and manner in which it is carried.
(j) All areas accessible to passengers or crew must be kept in a clean and sanitary condition. All walking surfaces must be free of slipping or tripping hazards and in good repair.
(4) First aid.
(a) All passenger vessels at all times must have a person holding a valid certificate of first-aid/CPR training.
(b) A first-aid kit or first-aid room must be provided on all vessels. The size and quantity of first-aid supplies or equipment required must be determined by the number of persons normally dependent upon each kit or equipment. The first-aid kit or supplies must be in a weatherproof container with individually sealed packages for each type of item. The location of the first-aid station or kit must be posted or marked "first aid" on the container.