WSR 17-18-075
PERMANENT RULES
DEPARTMENT OF
LABOR AND INDUSTRIES
[Filed September 5, 2017, 10:43 a.m., effective October 6, 2017]
Effective Date of Rule: Thirty-one days after filing.
Purpose: The purpose of adopting eRules Phase 8 is to have a consistent format across all department of occupational safety and health (DOSH) rules. The updated format would provide easy access to rules from [for] smart phones and tablet users. It will also provide easy navigation in PDF documents, as well as easier referencing by replacing bullets and dashes with numbers and letters. No rule requirements were changed as a result of this rule-making adoption. References, formatting and minor housekeeping changes were made throughout the chapters in this rule making. See below for a list of changes being adopted as proposed:
WAC 296-65-005 through 296-65-050.
• | Changed bullets to letters or numbers where applicable. |
• | Changed "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
WAC 296-65-003 Definitions.
• | Removed quotation marks from all defined words. |
• | Removed the word "means" from all applicable definitions and replaced it with a period, making all definitions complete sentences. |
WAC 296-301-010 through 296-301-225.
• | Changed "The employer" to "You must" where applicable. |
• | Removed numbered subdivision "titles" throughout chapter that are repetitive. |
• | Changed "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
WAC 296-301-015 Definitions applicable to this chapter.
• | Removed quotation marks from all defined words. |
• | Removed numbers from all definitions. |
• | Removed the word "means" from all applicable definitions and replaced it with a period, making all definitions complete sentences. |
WAC 296-303-01001 through 296-303-040.
• | Changed "The employer" to "You must" where applicable. |
• | Changed "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
WAC 296-303-01003 Definitions.
• | Removed quotation marks from all defined words. |
• | Removed numbers from all definitions. |
• | Removed the word "means" from all applicable definitions and replaced it with a period, making all definitions complete sentences. |
WAC 296-303-02501 General.
• | Updated reference in subsection (4) from "WAC 296-62-110" to "chapter 296-62 WAC, Part L." |
WAC 296-304-01001 through 296-304-20025.
• | Changed "The employer" to "You must" where applicable. |
• | Changed bullets to letters or numbers where applicable. |
• | Removed subdivision titles throughout chapter and renumbered sections where applicable. |
• | Changed "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
• | Changed "shall be not" to "must not be" where applicable. |
WAC 296-304-01001 Definitions.
• | Removed quotation marks from all defined words. |
• | Removed the word "means" from all applicable definitions in subsection and replaced it with a period, making all definitions complete sentences. |
WAC 296-304-01021 Competent person.
• | Changed lower case letters to numbers in the exception in the middle of subsection (2). |
WAC 296-304-020 Confined and enclosed spaces and other dangerous atmospheres in ship yard employment.
• | Removed the word "means" from all applicable definitions in subsection (2) and replaced it with a period, making all definitions complete sentences. |
WAC 296-304-03009 Flammable liquids.
• | Removed number (1) from opening paragraph and changed letters to numbers in the rest of the subsection. There wasn't a "(2)" to go with the (1) in the original language. |
WAC 296-803-100 through 296-803-70015.
• | Removed bold "you must" from the beginning of section and incorporated it into the language of applicable sections. |
• | Changed bullets/dashes/boxes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumbered/relettered the rest of the section. |
• | Changed uppercase "and" and "or" to lowercase where applicable. |
WAC 296-803-200, 296-803-300, 296-803-400, 296-803-500, 296-803-600, and 296-803-700.
• | Updated listed chapters into a "You must meet the requirements" table. |
WAC 296-803-50050 Protect employees working in a group.
• | Removed definition of "Primary authorized employee" from the end of this section – it is already located in the definition[s] section WAC 296-803-099. |
WAC 296-811-100 through 296-811-50005.
• | Removed bold "You must" and bullet and add "You must" to the applicable requirements listed below it. |
• | Changed bullets/dashes/boxes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumbered/relettered the rest of the section. |
WAC 296-811-100 Scope.
• | Removed definition of "Fire brigade" from this section – it's already in the definitions section WAC 296-811-099. |
WAC 296-811-200, 296-811-300, 296-811-400, and 296-811-500.
• | Updated listed chapters into a "You must meet the requirements" table. |
WAC 296-818-100 through 296-818-40015.
• | Removed bold "You must" and bullet and added "You must" to the applicable requirements listed below it. |
• | Changed bullets/dashes/boxes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumbered/relettered the rest of the section. |
• | Changed uppercase "and" and "or" to lowercase where applicable. |
WAC 296-818-200, 296-818-300, and 296-818-400.
• | Updated listed chapters into a "You must meet the requirements" table. |
WAC 296-824-100 and 296-824-20005 through 296-824-70005.
• | Removed bold "You must" and bullet and added "You must" to the applicable requirements listed below it. |
• | Changed bullets/dashes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumbered/relettered the rest of the section. |
• | Changed uppercase "and" and "or" to lowercase where applicable. |
• | Changed diamonds/boxes to letters/numbers where applicable. |
WAC 296-824-400, 296-824-500, and 296-824-600.
• | Updated listed chapters into a "You must meet the requirements" table. |
WAC 296-835-100 through 296-835-13030.
• | Removed bold "You must" and bullet and added "You must" to the applicable requirements listed below it. |
• | Changed bullets/dashes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumbered/relettered the rest of the section. |
• | Changed uppercase "and" and "or" to lowercase where applicable. |
• | Changed diamonds/boxes to letters/numbers where applicable. |
WAC 296-835-110, 296-835-120, and 296-835-130.
• | Updated listed chapters into a "You must meet the requirements" table. |
WAC 296-841-100 through 296-841-20025.
• | Changed bullets/dashes/boxes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumbered/relettered the rest of the section. |
• | Changed uppercase "and" and "or" to lowercase where applicable. |
WAC 296-841-100 Scope.
• | Removed definition of "Exposed or exposure" from the bottom of this section – it's already in the definitions section WAC 296-841-099. |
WAC 296-842-10200 through 296-842-22020.
• | Changed "The employer" to "You" where applicable. |
• | Changed "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
• | Changed bullets/dashes/boxes/diamonds to letters or numbers where applicable and renumbered/relettered the rest of the section. |
• | Changed uppercase "and" and "or" to lowercase where applicable. |
WAC 296-842-10200 Definitions.
• | Removed all numbers from definitions. |
• | Removed the word "means" from all applicable definitions and replace it with a period, making all definitions complete sentences. |
WAC 296-863-100 through 296-863-60015.
• | Removed bold "You must" and bullet and add "You must" to the applicable requirements listed below it. |
• | Changed "The employer" to "You must" where applicable. |
• | Changed "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
• | Changed bullets/dashes/boxes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumbered/relettered the rest of the section. |
• | Changed uppercase "and" and "or" to lowercase where applicable. |
WAC 296-863-100 Scope.
• | Removed the definition of "Powered industrial truck (PIT)" from the end of this section – it's already in the definition[s] section WAC 296-863-099. |
WAC 296-863-200, 296-863-300, 296-863-400, 296-863-500, and 296-863-600.
• | Updated listed chapters into a "You must meet the requirements" table. |
WAC 296-900-100 through 296-900-17505.
• | Removed bold "You must" and bullet and added "You must" to the applicable requirements listed below it. |
• | Changed "The employer" to "You must" where applicable. |
• | Changed "shall" to "must" where applicable. |
• | Changed bullets/dashes/boxes to letters or numbers where applicable and renumbered/relettered the rest of the section. |
• | Changed uppercase "and" and "or" to lowercase where applicable. |
WAC 296-900-110, 296-900-120, 296-900-130, 296-900-150, 296-900-160, and 296-900-170.
• | Updated listed chapters into a "You must meet the requirements" table. |
Citation of Rules Affected by this Order: New WAC 296-803-099 Definitions, 296-811-099 Definitions, 296-818-099 Definitions, 296-824-099 Definitions, 296-835-099 Definitions, 296-841-099 Definitions, 296-863-099 Definitions and 296-900-099 Definitions; repealing WAC 296-803-800 Definitions, 296-811-600 Definitions, 296-818-500 Definitions, 296-824-800 Definitions, 296-835-140 Definitions, 296-841-300 Definitions, 296-863-700 Definitions, 296-900-17510 Definitions and 296-900-180 Definitions; and amending WAC 296-65-003 Definitions, 296-65-005 Asbestos worker training course content, 296-65-007 Asbestos supervisor training course content, 296-65-010 Asbestos worker certification, 296-65-015 Training course approval, 296-65-017 Contractor certification, 296-65-020 Notification requirements, 296-65-030 Methods of compliance, 296-65-050 Denial, suspension, and revocation of certificates, 296-301-010 Textiles—Application requirements, 296-301-015 Definitions applicable to this chapter, 296-301-020 General safety requirements, 296-301-025 Openers and pickers, 296-301-030 Cotton cards, 296-301-035 Garnett machines, 296-301-040 Spinning mules, 296-301-04501 Cylinder dryers, 296-301-04503 Enclosed hot air dryers, 296-301-050 Warpers, 296-301-055 Drawing frames, slubbers, roving parts, cotton combers, ring spinning frames, twisters, 296-301-060 Gill boxes, 296-301-065 Heavy draw boxes, finishers, and speeders used in worsted drawing, 296-301-070 Silver and ribbon lappers (cotton), 296-301-075 Looms, 296-301-080 Shearing machines, 296-301-085 Continuous bleach range (cotton and rayon), 296-301-090 Kiers, 296-301-095 Gray and white bins, 296-301-100 Mercerizing range (piece goods), 296-301-105 Tenter frames, 296-301-110 Dyeing jigs, 296-301-115 Padders—Nip guards, 296-301-120 Drying cans, 296-301-125 Ironer, 296-301-130 Extractors, 296-301-135 Nip guards, 296-301-140 Sanforizing and palmer machine, 296-301-145 Rope washers, 296-301-150 Laundry washer tumbler or shaker, 296-301-155 Printing machine (roller type), 296-301-160 Calenders, 296-301-165 Rotary staple cutters, 296-301-170 Clothing folding machine, 296-301-175 Hand bailing machine, 296-301-180 Roll bench, 296-301-185 Cuttle or swing folder (overhead type), 296-301-190 Color mixing room, 296-301-195 Open tanks and vats for mixing and storage of hot or corrosive liquids, 296-301-200 Dye kettles and vats, 296-301-205 Acid carboys, 296-301-210 Handling caustic soda and caustic potash, 296-301-220 Personal protective equipment, 296-301-225 Workroom ventilation, 296-303-01001 General industrial safety standards, 296-303-01003 Definitions, 296-303-02001 Washroom machines, 296-303-02003 Starching and drying machines, 296-303-02005 Finishing machines, 296-303-02007 Miscellaneous machines and equipment, 296-303-02501 General, 296-303-02503 Mechanical, 296-303-030 Moving parts, 296-303-040 Starting and stopping devices, 296-304-01001 Definitions, 296-304-01006 Fire protection in shipyards, 296-304-01007 Fire safety plan, 296-304-01009 Precautions for hot work, 296-304-01011 Fire watches, 296-304-01013 Fire response, 296-304-01015 Hazards of fixed extinguishing systems on board vessels and vessel sections, 296-304-01017 Land-side fire protection systems, 296-304-01019 Training, 296-304-01021 Competent person, 296-304-020 Confined and enclosed spaces and other dangerous atmospheres in shipyard employment, 296-304-02003 Precautions and the order of testing before entering confined and enclosed spaces and other dangerous atmospheres, 296-304-02005 Cleaning and other cold work, 296-304-02007 Hot work, 296-304-02009 Maintenance of safe conditions, 296-304-02011 Warning signs and labels, 296-304-03001 Toxic cleaning solvents, 296-304-03003 Chemical paint and preservative removers, 296-304-03005 Mechanical paint removers, 296-304-03007 Painting, 296-304-03009 Flammable liquids, 296-304-04001 Ventilation and protection in welding, cutting and heating, 296-304-04005 Welding, cutting and heating in way of preservative coatings, 296-304-04007 Welding, cutting and heating of hollow metal containers and structures not covered by WAC 296-304-02003, 296-304-04009 Gas welding and cutting, 296-304-04011 Arc welding and cutting, 296-304-04013 Uses of fissionable material in ship-breaking, shipbuilding and ship repairing, 296-304-05001 Scaffolds or staging, 296-304-05003 Ladders, 296-304-05005 Guarding of deck openings and edges, 296-304-05007 Access to vessels, 296-304-05009 Access to and guarding of dry docks and marine railways, 296-304-05011 Access to cargo spaces and confined spaces, 296-304-05013 Working surfaces, 296-304-06001 Housekeeping, 296-304-06002 Sanitation, 296-304-06003 Illumination, 296-304-06005 Utilities, 296-304-06007 Work in confined or isolated spaces, 296-304-06009 Work on or in the vicinity of radar and radio, 296-304-06011 Work in or on lifeboats, 296-304-06013 Hazardous materials, 296-304-06015 First aid, 296-304-06016 Control of hazardous energy (lockout/tag-plus), 296-304-06017 Retention of DOT marking, placards, and labels, 296-304-06018 Motor vehicle safety equipment, operation and maintenance, 296-304-07001 Inspection, 296-304-07003 Ropes, chains and slings, 296-304-07005 Shackles and hooks, 296-304-07007 Chain falls and pull-lifts, 296-304-07009 Hoisting and hauling equipment, 296-304-07011 Use of gear, 296-304-07013 Qualifications of operators, 296-304-08001 General precautions, 296-304-08003 Portable electric tools, 296-304-08005 Hand tools, 296-304-08007 Abrasive wheels, 296-304-08009 Powder-actuated fastening tools, 296-304-08011 Internal combustion engines, other than ship's equipment, 296-304-090 Personal protective equipment (PPE)—General requirements, 296-304-09001 Hazard assessment and equipment selection, 296-304-09003 Training, 296-304-09005 Eye and face protection, 296-304-09007 Respiratory protection, 296-304-09009 Hearing protection, 296-304-09011 Head protection, 296-304-09013 Foot protection, 296-304-09015 Hand and body protection, 296-304-09017 Lifesaving equipment, 296-304-09019 Fall protection—General requirement, 296-304-09021 Personal fall arrest systems (PFAS), 296-304-09023 Positioning device systems, 296-304-10001 Ship's boilers, 296-304-10003 Ship's piping systems, 296-304-10005 Ship's propulsion machinery, 296-304-10007 Ship's deck machinery, 296-304-11001 Portable air receivers and other unfired pressure vessels, 296-304-11003 Drums and containers, 296-304-120 Electrical machinery—Electrical circuits and distribution boards, 296-304-13001 Purpose and scope, 296-304-13003 Definitions of terms, 296-304-14001 Application for accreditation, 296-304-14003 Action upon application, 296-304-14005 Duration and renewal of accreditation, 296-304-14007 Criteria governing accreditation to certificate vessels' cargo gear, 296-304-14011 Suspension or revocation of accreditation, 296-304-14013 Reconsideration and review, 296-304-15001 General duties—Exemptions, 296-304-15003 Recordkeeping and related procedures concerning records in custody of accredited persons, 296-304-15005 Recordkeeping and related procedures concerning records in custody of the vessel, 296-304-16001 General, 296-304-16003 Initial tests of cargo gear and tests after alterations, renewals or repairs, 296-304-16005 Periodic tests, examinations and inspections, 296-304-16007 Heat treatment, 296-304-16009 Exemptions from heat treatment, 296-304-16011 Grace periods, 296-304-16013 Gear requiring welding, 296-304-16015 Damaged components, 296-304-16017 Marking and posting of safe working loads, 296-304-16019 Requirements governing braking devices and power sources, 296-304-16021 Means of derrick attachment, 296-304-16023 Limitations on use of wire rope, 296-304-16025 Limitations on use of chains, 296-304-17001 Visual inspection before tests, 296-304-17003 Unit proof test—Winches, derricks and gear accessory thereto, 296-304-17005 Unit proof tests—Cranes and gear accessory thereto, 296-304-17007 Limitations on safe working loads and proof loads, 296-304-17009 Examinations subsequent to unit tests, 296-304-17011 Proof tests—Loose gear, 296-304-17013 Specially designed blocks and components, 296-304-17015 Proof tests—Wire rope, 296-304-17017 Proof tests after repairs or alterations, 296-304-17021 Heat treatment, 296-304-17023 Competent persons, 296-304-18001 Eligibility for accreditation to certificate shore-based material handling devices covered by chapter 296-56 WAC of the safety and health regulations for longshoring, 296-304-18003 Provisions respecting application for accreditation, action upon the application and related matters, 296-304-190 Duties of persons accredited to certificate shore-based material handling devices—General duties, exemptions, 296-304-20001 General provisions, 296-304-20003 Unit proof test and examination of cranes, 296-304-20005 Annual examination of cranes, 296-304-20007 Unit proof test and examination of derricks, 296-304-20009 Annual examination of cranes, 296-304-20011 Determination of crane or derrick safe working loads and limitations in absence of manufacturer's data, 296-304-20013 Safe working load reduction, 296-304-20015 Safe working load increase, 296-304-20017 Nondestructive examination, 296-304-20019 Wire rope, 296-304-20021 Heat treatment, 296-304-20023 Examination of bulk cargo loading or discharging spouts or suckers, 296-304-20025 Documentation, 296-803-100 Scope, 296-803-200 Summary, 296-803-20005 Establish a written energy control program, 296-803-300 Summary, 296-803-30005 Make sure new or modified machines and equipment can accept lockout devices, 296-803-400 Summary, 296-803-40005 Provide appropriate means to control energy, 296-803-40010 Make sure lockout and tagout devices meet these requirements, 296-803-40015 Make sure lockout devices meet these additional requirements, 296-803-40020 Make sure tagout devices meet these additional requirements, 296-803-500 Summary, 296-803-50005 Use energy control procedures, 296-803-50010 Meet these requirements when applying lockout or tagout devices, 296-803-50015 Meet these additional requirements when applying lockout devices, 296-803-50020 Meet these additional requirements when applying tagout devices, 296-803-50025 Protect employees from the hazards of stored and residual energy, 296-803-50030 Verify that the machine or equipment is safe before starting work, 296-803-50035 Meet these requirements when removing lockout or tagout devices and energizing the machine or equipment, 296-803-50040 Meet these requirements if it's necessary to temporarily energize a machine, equipment or component for testing or positioning, 296-803-50045 Protect employees during shift or personnel changes, 296-803-50050 Protect employees working in a group, 296-803-50055 Meet these additional requirements if more than one group is used, 296-803-50060 Coordinate with outside employers servicing or maintaining your machines or equipment, 296-803-600 Summary, 296-803-60005 Provide and document employee training on the energy control program, 296-803-60010 Provide additional training if you use tagout devices, 296-803-60015 Retrain Employees when necessary, 296-803-700 Summary, 296-803-70005 Perform and document periodic reviews to verify employees know and follow the energy control procedures, 296-803-70010 Do periodic reviews of procedures using lockout devices, 296-803-70015 Do periodic reviews of procedures using tagout devices, 296-811-100 Scope, 296-811-200 Establishing a fire brigade—Section contents, 296-811-20005 Organizing statement, 296-811-20010 Physical capability of brigade members, 296-811-300 Training—Section contents, 296-811-30005 Special hazards, 296-811-30010 Firefighting training, 296-811-400 Equipment—Section contents, 296-811-40005 Firefighting equipment, 296-811-40010 Protective clothing, 296-811-40015 Self-contained breathing apparatus' (SCBAs), 296-811-500 Requirements during firefighting—Section contents, 296-811-50005 Brigade members in interior structural fires, 296-818-100 Scope, 296-818-200 General safety—Summary contents, 296-818-20005 Dust hazards, 296-818-20010 Personal protective equipment (PPE), 296-818-20015 Housekeeping, 296-818-300 Operations—Summary contents, 296-818-30005 Combustible organic abrasive, 296-818-30010 Blast cleaning enclosures, 296-818-30015 Blast cleaning nozzles, 296-818-400 Exhaust ventilation systems—Summary contents, 296-818-40005 Construction, 296-818-40010 Explosion venting and wiring, 296-818-40015 Inspection and maintenance, 296-824-100 Scope, 296-824-20005 Develop an emergency response plan, 296-824-30005 Train your employees, 296-824-400 Medical surveillance, 296-824-40005 Provide medical surveillance to employees, 296-824-40010 Keep records, 296-824-500 Incident requirements, 296-824-50005 Recognize emergencies and initiate a response, 296-824-50010 Implement and maintain an incident command system (ICS), 296-824-50015 Prepare skilled support personnel, 296-824-50020 Make sure the incident commander oversees activities during the response, 296-824-50025 Use the buddy system in danger areas, 296-824-50030 Provide rescue and medical assistance, 296-824-600 Personal protective equipment, 296-824-60005 Personal protective equipment, 296-824-60010 Control hazards created by personal protective equipment, 296-824-60015 Use personal protective equipment (PPE) properly, 296-824-70005 Follow the appropriate postemergency response requirements, 296-835-100 Scope, 296-835-110 General requirements, 296-835-11005 Construct safe dip tanks, 296-835-11010 Provide proper ventilation for the vapor area, 296-835-11015 Take additional precautions if you recirculate ventilation system exhaust air into the workplace, 296-835-11020 Take additional precautions when using an exhaust hood, 296-835-11025 Periodically inspect your dip tanks and associated equipment and correct any deficiencies, 296-835-11030 Make sure employees working near dip tanks know appropriate first-aid procedures, 296-835-11035 Prepare dip tanks before cleaning, 296-835-11040 Safeguard cyanide tanks, 296-835-11045 Protect employees during welding, burning or other work using open flames, 296-835-11050 Protect employees that use liquids that may burn, irritate or otherwise harm the skin, 296-835-120 Additional requirements for dip tanks using flammable liquids or liquids with flashpoints greater than 199.4°F (93°C), 296-835-12005 Include additional safeguards when constructing dip tanks, 296-835-12010 Provide overflow pipes, 296-835-12015 Provide bottom drains, 296-835-12020 Provide fire protection in the vapor area, 296-835-12025 Provide additional fire protection for large dip tanks, 296-835-12035 Prevent static electricity sparks or arcs when adding liquids to a dip tank, 296-835-12040 Control ignition sources, 296-835-12045 Provide safe electrical wiring and equipment where the liquid can drip or splash, 296-835-12050 Keep the area around dip tanks clear of combustible material and properly dispose of waste, 296-835-12055 Make sure heating the liquid in your dip tanks does not cause a fire, 296-835-12060 Make sure a heating system used for drying objects does not cause a fire, 296-835-12065 Make sure conveyor systems are safe, 296-835-130 Additional requirements for dip tanks used for specific processes, 296-835-13005 Meet specific requirements if you use a hardening or tempering tank, 296-835-13010 Meet specific requirements if you use electrostatic equipment, 296-835-13015 Meet specific requirements if you use a flow coating process, 296-835-13020 Take additional precautions if your roll coating operation used a liquid that has a flashpoint below 140°F (60°C), 296-835-13025 Provide additional safeguards for vapor degreasing tanks, 296-835-13030 Control liquid spray over an open surface cleaning or degreasing tank, 296-841-100 Scope, 296-841-20005 Exposure evaluations, 296-841-20010 Exposure controls, 296-841-20015 Respirators, 296-841-20020 Notification, 296-841-20025 Permissible exposure limits (PELs), 296-842-10200 Definitions, 296-842-11005 Make sure voluntary use of respirators is safe, 296-842-12005 Develop and maintain a written program, 296-842-12010 Keep respirator program records, 296-842-13005 Select and provide appropriate respirators, 296-842-14005 Provide medical evaluations, 296-842-15005 Conduct fit testing, 296-842-16005 Provide effective training, 296-842-17005 Maintain respirators in a clean and reliable condition, 296-842-17015 Inspect and repair respirators, 296-842-18010 Make sure employees leave the use area before removing respirators, 296-842-19005 Provide standby assistance in immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) conditions, 296-842-20010 Prevent conditions that could create a hazardous breathing air supply, 296-842-20015 Make sure compressors do not create a hazardous breathing air supply, 296-842-22005 Use this medical questionnaire for medical evaluations, 296-842-22010 Follow these fit-testing procedures for tight-fitting respirators, 296-842-22015 Follow procedures established for cleaning and disinfecting respirators, 296-842-22020 Follow procedures established for seal checking respirators, 296-863-100 Scope, 296-863-200 Design, construction and equipment, 296-863-20005 Make sure PITs meet design and construction requirements, 296-863-20010 Meet these requirements when modifying or altering PITs, 296-863-20015 Make sure PITs are properly labeled, 296-863-20020 Protect operators from falling objects, 296-863-20025 Provide fall protection on order pickers, 296-863-20030 Provide directional lights on PITs when required, 296-863-20035 Make sure liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs meet these requirements, 296-863-20040 Meet these requirements when converting gasoline fuel PITs to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fuel, 296-863-300 Inspection, repair, maintenance and servicing, 296-863-30005 Make sure PITs are in safe working condition, 296-863-30010 Inspect your PITs, 296-863-30015 Meet these requirements when repairing PITs, 296-863-30020 Maintain your PITs properly, 296-863-30025 Service gasoline fueled PITs safely, 296-863-30030 Service liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs safely, 296-863-30035 Make sure battery charging areas are safe, 296-863-30040 Service batteries for electric PITs safely, 296-863-400 Operations, 296-863-40005 Protect employees around PITs, 296-863-40010 Operate PITs safely, 296-863-40015 Make sure PIT loads are carried safely, 296-863-40020 Meet these requirements when the operator leaves the normal operating position, 296-863-40025 Meet these requirements when operating near railroad tracks, 296-863-40030 Meet this requirement when using motorized hand trucks, 296-863-40035 Meet these requirements when using elevators, 296-863-40040 Meet these requirements when using dockboards (bridge plates), 296-863-40045 Meet these requirements when loading or unloading railroad cars with a PIT, 296-863-40050 Meet these requirements when loading or unloading highway trucks with PITs, 296-863-40055 Meet these additional requirements when operating liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs, 296-863-40060 Make sure work platforms and PITs used to lift people meet these requirements, 296-863-40065 Operate PITs using elevated work platforms safely, 296-863-500 Hazardous (classified) locations, 296-863-50005 Use the appropriate PITs in hazardous (classified) locations, 296-863-600 Training, 296-863-60005 Make sure PIT operators are trained, 296-863-60010 Retrain PIT operators as required, 296-863-60015 Evaluate PIT operator's performance, 296-900-100 Scope, 296-900-110 Variance, 296-900-11005 Applying for a variance, 296-900-11010 Interim orders, 296-900-11015 Renewing a temporary variance, 296-900-11020 Changing a variance, 296-900-11025 Variance hearings, 296-900-120 Inspections, 296-900-12005 WISHA inspections, 296-900-12010 Inspection techniques, 296-900-12015 Complaints, 296-900-130 Citation and notice, 296-900-13005 Citation and notice, 296-900-13010 Copies of future citation and notices, 296-900-13015 Posting citation and notices, 296-900-150 Certifying violation corrections, 296-900-15005 Certifying violation correction, 296-900-15010 Violation correction action plans, 296-900-15015 Progress reports, 296-900-15020 Timelines of violation correction documents, 296-900-15025 Inform employees about violation correction, 296-900-15030 Tag moveable equipment, 296-900-160 More time to comply, 296-900-16005 Requesting more time to comply, 296-900-16010 Post WISHA's Response to requests for more time, 296-900-16015 Correction date hearing requests, 296-900-16020 Post WISHA's violation correction hearing notice, 296-900-16025 Violation correction hearing procedures, 296-900-16030 Post the violation correction hearing decision, 296-900-170 Appeals, 296-900-17010 Appealing a corrective notice of redetermination (CNR), 296-900-17015 Posting appeals, and 296-900-17505 Scope and purpose.
Adopted under notice filed as WSR 17-11-119 on May 23, 2017.
Number of Sections Adopted in Order to Comply with Federal Statute: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0; Federal Rules or Standards: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0; or Recently Enacted State Statutes: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0.
Number of Sections Adopted at the Request of a Nongovernmental Entity: New 8, Amended 396, Repealed 9.
Number of Sections Adopted on the Agency's own Initiative: New 8, Amended 396, Repealed 9.
Number of Sections Adopted in Order to Clarify, Streamline, or Reform Agency Procedures: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0.
Number of Sections Adopted using Negotiated Rule Making: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0; Pilot Rule Making: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0; or Other Alternative Rule Making: New 0, Amended 0, Repealed 0.
Date Adopted: September 5, 2017.
Joel Sacks
Director
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 00-06-075, filed 3/1/00, effective 4/10/00)
WAC 296-65-003 Definitions.
Unless the context clearly requires otherwise, the definitions in this section apply throughout this standard.
(("))Approved((" means)). Approved by the department.
(("))Asbestos((")). Includes chrysotile, amosite, crocidolite, tremolite asbestos, anthophyllite asbestos, and actinolite asbestos, and any of these minerals that have been chemically treated and/or altered.
(("))Asbestos abatement project. An asbestos project involving three square feet or three linear feet, or more, of asbestos containing material.
Asbestos fiber((" means)). Asbestos fiber as defined in WAC 296-62-07703 as "fiber."
(("Asbestos abatement project" means an asbestos project involving three square feet or three linear feet, or more, of asbestos containing material.))
(("))Asbestos project((")). Includes the construction, demolition, repair, remodeling, maintenance or renovation of any public or private building or structure, mechanical piping equipment or system involving the demolition, removal, encapsulation, salvage, or disposal of material or outdoor activity releasing or likely to release asbestos fibers into the air.
(("))Certificate. A certificate issued by the department that must include the name of person awarded the certificate, certificate number, the discipline for which certification was conferred, training and examination dates, the course provider's name and address, and the course provider's telephone number, expiration date, and a statement that the person receiving the certificate has completed the training for asbestos accreditation under TSCA Title II.
Certified asbestos contractor((" means)). Any partnership, firm, association, corporation or sole proprietorship, registered under chapter 18.27 RCW, that submits a bid, or contracts to remove or encapsulate asbestos for another and is certified by the department to remove or encapsulate asbestos.
(("Certificate" means a certificate issued by the department that shall include the name of person awarded the certificate, certificate number, the discipline for which certification was conferred, training and examination dates, the course provider's name and address, and the course provider's telephone number, expiration date, and a statement that the person receiving the certificate has completed the training for asbestos accreditation under TSCA Title II.
"))Certified asbestos supervisor((" means)). An individual who is certified by the department under WAC 296-65-012.
(("))Certified asbestos worker((" means)). An individual certified by the department under WAC 296-65-010.
(("Department" means the department of labor and industries.
"))Demolition((" means)). The activity of razing a structure which includes the wrecking, removal, or dismantling of any load-supporting structural member of any facility including any related handling operations.
(("))Department. The department of labor and industries.
Director((" means)). The director of the department of labor and industries or the director's designee.
(("))Emergency project((" means)). A project that was not planned but results from a sudden, unexpected event and does not include operations that are necessitated by nonroutine failures of equipment or systems.
(("))Encapsulation((" means)). The application of an encapsulant to asbestos containing materials to control the release of asbestos fibers into the air. The encapsulation process either creates a membrane over the surface (bridging encapsulant) or penetrates the material and binds its components together (penetrating encapsulant).
(("))EPA MAP((" means)). The environmental protection agency model accreditation plan for asbestos requirements in 40 C.F.R. Part 763.
(("))HEPA filtration((" means)). High-efficiency particulate air filtration found in respirators and vacuum systems capable of filtering 0.3 micron particles with 99.97% efficiency.
(("))Intact((" means)). That the asbestos containing material has not crumbled, been pulverized, or otherwise deteriorated so that it is no longer likely to be bound with its matrix.
(("))NESHAP((" means)). The National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants.
(("))Owner((" means)). The person who owns any public or private building, structure, facility, or mechanical system, or the remnants thereof, or the agent of such person, but does not include individuals who work on asbestos projects in their own single-family residences, no part of which is used for commercial purposes.
(("))Person((" means)). Any individual, partnership, firm, association, corporation, sole proprietorship, or the state of Washington or its political subdivisions.
(("))Revocation((" means)). A permanent withdrawal of a certification issued by the department.
(("))Suspension((" means)). A temporary withdrawal of a certification issued by the department. No suspension ((shall)) must be less than six months or longer than one year.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-65-005 Asbestos worker training course content.
An approved asbestos worker training course ((shall)) must consist of four days of training with a minimum of thirty-two hours. This initial training course ((shall)) must provide, at a minimum, information on the following topics:
(1) The physical characteristics of asbestos including types, fiber size, aerodynamic characteristics and physical appearance.
(2) Examples of different types of asbestos and asbestos-containing materials. Real asbestos ((shall)) must be used only for observation by trainees and ((shall)) must be enclosed in sealed unbreakable containers.
(3) The health hazards of asbestos including the nature of asbestos related diseases, routes of exposure, dose-response relationships, synergism between cigarette smoking and asbestos exposure, latency period of diseases, hazards to immediate family, and the health basis for asbestos standards.
(4) Employee personal protective equipment including the classes and characteristics of respirator types, limitations of respirators, proper selection, inspection, donning, use, maintenance and storage procedure, methods for field checking of the facepiece-to-face seal (positive and negative-pressure checks), qualitative and quantitative fit testing procedures, variability between field and laboratory protection factors, factors that alter respirator fit (e.g., eye glasses and facial hair), the components of a proper respiratory protection program, respirator program administrator, requirements on oil lubricated reciprocating piston compressors for breathing air, and selection and use of personal protective clothing. Qualitative or quantitative fit testing ((shall)) must be performed on at least one student for demonstration purposes and in accordance with WAC 296-62-07715 and 296-62-07739.
(5) Use, storage and handling of launderable clothing, nonslip footwear, gloves, eye protection and hard hats.
(6) Medical monitoring procedures and requirements, including the provisions of chapter 296-842 WAC, any additional recommended procedures and tests, benefits of medical monitoring and employee access to records.
(7) Air monitoring procedures and requirements specified in WAC 296-62-07709, including a description of equipment, sampling methods and strategies, reasons for air monitoring, types of samples, including area, personal and clearance samples, current standards with proposed changes if any, employee observation and notification, recordkeeping and employee access to records, interpretation of air monitoring results, and analytical methods for bulk and air samples.
(8) State-of-the-art work practices for asbestos removal and encapsulation activities including purpose, proper construction and maintenance of barriers and decontamination enclosure systems, posting of warning signs, electrical and ventilation system lock-out, proper working techniques and tools with vacuum attachments for minimizing fiber release, use of wet methods and surfactants, use of negative-pressure ventilation equipment for minimizing employee exposure to asbestos fibers and contamination prevention, scoring and breaking techniques for rigid asbestos products, glove bag techniques, recommended and prohibited work practices, potential exposure situations, emergency procedures for sudden releases, use of HEPA vacuums and proper clean-up and disposal procedures. Work practice requirements for removal, encapsulation, enclosure, repair, and waste transportation ((shall)) must be discussed individually. Appropriate work practices for both indoor and outdoor asbestos projects ((shall)) must be included.
(9) Personal hygiene including entry and exit procedures for the work area, use of showers and prohibition of eating, drinking, smoking and chewing (gum or tobacco) in the work area. Potential exposures, such as family exposure ((shall)) must also be included.
(10) Additional safety hazards that may be encountered during asbestos removal and encapsulation activities and hazard abatement, including electrical hazards, scaffold and ladder hazards, slips, trips and falls, confined spaces, noise, and heat stress.
(11) The requirements, procedures and standards established by:
(a) The Environmental Protection Agency, 40 C.F.R. Part 61, Subparts A and M, and 40 C.F.R. Part 763.
(b) Washington state department of ecology.
(c) Local air pollution control agencies.
(d) Washington state department of labor and industries, division of industrial safety and health, chapter 49.17 RCW (Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act), chapter 49.26 RCW (Health and safety—Asbestos), and ensuing regulations.
(12) Actual worksite considerations.
(13) The instruction required by this section ((shall)) must include, at a minimum fourteen hours of hands-on training for the following:
(a) Glove bag techniques;
(b) The opportunity to don respirators including half facepiece and full facepiece air purifying respirators, powered air purifying respirators (PAPR), and Type-C supplied-air respirators;
(c) Removal of sprayed-on or troweled-on material, and pipe lagging;
(d) Basic construction of a decontamination unit, and proper entry and exit;
(e) Suit-up in protective clothing consisting of coveralls, foot coverings and head coverings.
(14) Course review, a review of the key aspects of the training course.
(15) Asbestos-containing materials ((shall)) must not be used for hands-on training.
(16) In recognition that asbestos abatement is an evolving industry, the department reserves the right to require additional subjects to be taught and to specify the amount of time which ((shall)) must be allotted to adequately cover required subjects. To ((assure)) ensure adequate coverage of required material, each sponsor ((shall)) must be provided and required to incorporate into the training course, a detailed outline of subject matter developed by the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-65-007 Asbestos supervisor training course content.
An approved asbestos supervisor training course ((shall)) must consist of at least five days of training. This initial training course ((shall)) must include lectures, demonstrations, at least fourteen hours of hands-on training, course review and a written examination. Audio-visual materials, where appropriate, are recommended to complement lectures. The training course ((shall)) must provide, at a minimum, information on the following topics:
(1) The physical characteristics of asbestos and asbestos-containing materials including identification of asbestos, aerodynamic characteristics, typical uses, physical appearance, hazard assessment considerations, and a summary of abatement control options.
(2) Health effects related to asbestos exposure including the nature of asbestos related diseases, routes of exposure, dose-response relationships and the lack of a safe level of exposure, synergism between asbestos exposure and cigarette smoking, latency period, hazards to the immediate family and the health basis for the standard.
(3) Employee personal protective equipment including the classes and characteristics of respirator types, limitations of respirators, proper selection, inspection, donning, use, maintenance, and storage procedures, methods for field checking of the facepiece-to-face seal (positive and negative pressure checks), variability between field and laboratory protection factors, quantitative and qualitative fit test requirements, factors that alter respirator fit (facial hair, scars, etc.), the components of a proper respirator program, requirements for oil lubricated reciprocating compressors, maintenance of Type-C systems, standards for breathing air, selection and use of personal protective clothing, use, storage, and handling of nondisposable clothing, and regulations covering personal protective equipment.
(4) State-of-the-art work practices for asbestos removal and encapsulation activities including purpose, proper construction and maintenance of barriers and decontamination enclosure systems, posting of warning signs, electrical and ventilation system lock-out, proper working techniques and tools with vacuum attachments for minimizing fiber release, use of wet methods and surfactants, use of negative-pressure ventilation equipment for minimizing employee exposure to asbestos fibers and contamination prevention, scoring and breaking techniques for rigid asbestos products, glove bag techniques, recommended and prohibited work practices, potential exposure situations, emergency procedures for sudden releases, use of HEPA vacuums and proper clean-up and disposal procedures. Work practice requirements for removal, encapsulation, and repair ((shall)) must be discussed separately. Appropriate work practices for both indoor and outdoor asbestos projects ((shall)) must be included.
(5) Personal hygiene including entry and exit procedures for the work area, use of showers and prohibition of eating, drinking, smoking, and chewing (gum and tobacco) in the work area. Potential exposures, such as family exposure ((shall)) must also be included.
(6) Additional safety hazards that may be encountered during asbestos abatement activities and how to deal with them, including electrical hazards, heat stress, air contaminants other than asbestos, fire and explosion hazards, scaffold and ladder hazards, slips, trips, and falls, confined space entry requirements, and noise hazards.
(7) Medical monitoring procedures and requirements, including the provisions of chapter 296-842 WAC, any additional recommended procedures and tests, benefits of medical monitoring and recordkeeping requirements.
(8) Air monitoring procedures and requirements specified in WAC 296-62-07709, including a description of equipment, sampling methods and strategies, reasons for air monitoring, types of samples, including area, personal and clearance samples, a description of aggressive sampling, current standards with proposed changes if any, employee observation and notification, recordkeeping, interpretation of air monitoring results, specifically from analyses performed by polarized light, phase contrast, and electron microscopy.
(9) The requirements, procedures, and standards established by:
(a) The Environmental Protection Agency, 40 C.F.R. Part 61, Subparts A and M, and 40 C.F.R. Part 763.
(b) The Washington state department of ecology.
(c) Local air pollution control agencies.
(d) Washington state department of labor and industries, division of industrial safety and health, chapter 49.17 RCW (Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act), chapter 49.26 RCW (Health and safety—Asbestos), and ensuing regulations.
(10) Actual worksite considerations.
(11) Insurance and liability issues including contractor issues, industrial insurance coverage and exclusions, third party liabilities and defenses, private insurance coverage and exclusions, recordkeeping recommended for legal and insurance purposes.
(12) Supervisory techniques for asbestos abatement projects including supervisory practices to enforce and reinforce the required work practices and discourage unsafe work practices.
(13) Contract specifications including a discussion of the key elements to be included in contract specifications.
(14) A minimum of fourteen hours of hands-on training for the following:
(a) Calibration of air-sampling equipment;
(b) Routine maintenance of air-purifying and air-supplied respirators;
(c) Setup of a decontamination unit including calculating the number of negative air machines needed as well as proper placement of the machines within the enclosure; and
(d) Quantitative and qualitative fit-testing protocols.
(15) Course review, a review of the key aspects of the training course.
(16) In recognition that asbestos abatement is an evolving industry, the department reserves the right to require additional subjects to be taught and to specify the amount of time which ((shall)) must be allotted to adequately cover required subjects. To ((assure)) ensure adequate coverage of required material, each sponsor ((shall)) must be provided and required to incorporate into their training course, a detailed outline of subject matter developed by the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-65-010 Asbestos worker certification.
(1) For the purposes of this section "individual" means any natural person.
(2) To qualify for an asbestos worker certificate, an individual must do the following:
(a) Successfully complete an approved asbestos worker training course;
(b) Achieve a score of at least seventy percent on a one hundred question multiple choice closed book examination approved by the department but administered by the training course sponsor. If an individual does not pass the examination, then another examination (meeting the above criteria) may be given after a sufficient period of study. The new examination must not duplicate more than fifty percent of the questions used on prior examinations;
(c) Submit to the department a timely application validated by an approved training course sponsor. To be considered timely, an application must be received by the department no later than sixty days after the completion of the course. In the event that an application is not timely, the individual will be required to pass, with a score of at least seventy percent, an examination administered by the department. A nonrefundable fifty-dollar fee will be assessed when the application is submitted to the department; and
(d) Pay the fee prescribed in WAC 296-65-025.
(3) Individuals must not perform any asbestos project work prior to issuance of the certificate.
(4) Certificates will be issued and mailed to the individual applicants and will be valid for one year from the date of issuance.
(5) Certified asbestos workers ((shall)) must attend an eight-hour worker refresher course prior to certificate renewal.
(a) The course ((shall)) must, at a minimum, adequately review the subjects required by WAC 296-65-005, update information on state-of-the-art procedures and equipment, and review regulatory changes and interpretations. The department may require specific subjects.
(b) An application for renewal of the certificate must be validated by the refresher training course instructor.
(c) The refresher course must be taken prior to expiration of the certificate.
(d) The department must receive the certificate renewal application no later than the expiration date of the current certificate. Applicants missing this renewal deadline will be required to pass, with a score of seventy percent, an examination administered by the department. A nonrefundable fifty-dollar fee will be charged to take this examination.
(e) Individuals whose certificates have been expired for more than six months will be required to retake the entire basic worker course.
(6) The initial TSCA Title II worker accreditation certificate and the current worker certificate must be available for inspection at all times at the location of the asbestos project.
(7) The department may suspend or revoke a certificate as provided in WAC 296-65-050 and chapter 296-900 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 97-01-079, filed 12/17/96, effective 3/1/97)
WAC 296-65-015 Training course approval.
(1) Basic and refresher asbestos training courses may be sponsored by any individual, person, or other entity having department approval. Approval ((shall)) must be contingent on the sponsor's compliance, as applicable, with licensing requirements established by the state board of vocational education.
(2) Prior to receiving department approval, each course ((shall)) must be evaluated by the department for the breadth of knowledge and experience required to properly train asbestos workers or supervisors. Course content ((shall)) must be carefully scrutinized for adequacy and accuracy. Training techniques will be evaluated by the department.
(3) Sponsors of basic and refresher training courses proposed for approval must submit:
(a) Background information about course sponsors;
(b) Course locations and fees;
(c) Copies of course handouts;
(d) A detailed description of course content and the amount of time allotted to each major topic;
(e) A description of teaching methods to be utilized and a list of all audio-visual materials; the department may, in its discretion, request that copies of the materials be provided for review. Any audio-visual materials provided to the department will be returned to the applicant;
(f) A list of all personnel involved in course preparation and presentation and a description of the background, special training and qualifications of each. Instructors ((shall)) must have academic and/or field experience in asbestos abatement. The department may, in its discretion, require proposed instructors to pass an examination on subjects related to their respective topics of instruction;
(g) A description of student evaluation methods and a copy of the required written examination including the scoring methodology to be used in grading the examination;
(h) A description of course evaluation methods;
(i) Any restrictions on attendance (language, class size, affiliation, etc.);
(j) A list of any other states that currently approve the training course;
(k) A letter from the course provider that clearly indicates how the course provider meets the EPA MAP requirements; and
(l) The amount and type of hands-on training for initial training courses.
(4) Application for training course approval and course materials ((shall)) must be submitted to the department at least sixty days prior to the requested approval date. Materials may be mailed to:
Asbestos Certification Program
Department of Labor and Industries
P.O. Box 44614
Olympia, Washington 98504-4614
(5) The decision to grant or renew approval of a basic or refresher asbestos training course ((shall)) must be in the sole discretion of the department.
Following approval of a basic or refresher asbestos training course, the department will issue the course sponsor an approval which is valid for one year from the date of issuance. Application for renewal must follow the procedures described in subsections (3) and (4) of this section.
Following approval of a basic or refresher asbestos training course, in recognition that asbestos abatement is an evolving industry, the department reserves the right to require additional subjects to be taught and to specify the amount of time which ((shall)) must be allotted to adequately cover required subjects. To ((assure)) ensure adequate coverage of required material, each sponsor ((shall)) must be provided and required to incorporate into their training course, a detailed outline of subject matter developed by the department.
(6) To be considered timely, the training course approval renewal must be received by the department no later than thirty days before the certificate expiration date.
(7) Any changes to a training course must be approved by the department in advance.
(8) The course sponsor ((shall)) must provide the department with a list of all persons who have completed a basic or refresher training course. The list must be provided no later than ten days after a course is completed and must include the name and address of each trainee.
(9) The course sponsor must notify the department, in writing, at least fourteen days before a training course is scheduled to begin. The notification must include the date, time and address where the training will be conducted.
(10) A representative of the department may, at the department's discretion, attend a training course as an observer to verify that the training course is conducted in accordance with the program approved by the department.
(11) Course sponsors conducting training outside the state of Washington ((shall)) must reimburse the department for reasonable travel expenses associated with department audits of the training courses. Reasonable travel expenses are defined as current state of Washington per diem and travel allowance rates including airfare and/or surface transportation rates. Such reimbursement ((shall)) must be paid within thirty days of receipt of the billing notice.
(12) The training course sponsor ((shall)) must limit each class to a maximum of thirty participants.
(13) The instructor to student ratio ((shall)) must not exceed one-to-ten for any of the training required by WAC 296-65-005(13) and 296-65-007(14).
(14) The department may terminate the training course approval, if in the department's judgment the sponsor fails to maintain the course content and quality as initially approved, or fails to make changes to a course as required by WAC 296-65-015(5). The minimum criteria for withdrawal of training course approval ((shall)) must include:
(a) Misrepresentation of the extent of training courses approval by a state or EPA;
(b) Failure to submit required information or notification in a timely manner;
(c) Failure to maintain requisite records;
(d) Falsification of accreditation records, instructor qualifications, or other accreditation information; or
(e) Failure to adhere to the training standards and accreditation requirements of chapter 296-65 WAC.
(15) Any "notice of termination of training course approval" issued by the department may act as an order of immediate restraint as described by RCW 49.17.130.
(16) Recordkeeping requirements for training providers: All approved providers of accredited asbestos training courses must comply with the following minimum recordkeeping requirements:
(a) Training course materials. A training provider must retain copies of all instructional materials used in delivery of the classroom training such as student manuals, instructor notebooks and handouts.
(b) Instructor qualifications. A training provider must retain copies of all instructors' resumes, and the documents approving each instructor issued by either EPA or the department. Instructors must be approved by the department before teaching courses for accreditation purposes. A training provider must notify the department in advance whenever it changes course instructors. Records must accurately identify the instructors that taught each particular course for each date that a course is offered.
(c) Examinations. A training provider must document that each person who receives an accreditation certificate for an initial training course has achieved a passing score on the examination. These records must clearly indicate the date upon which the exam was administered, the training course and discipline for which the exam was given, the name of the person who proctored the exam, a copy of the exam, and the name and test score of each person taking the exam. The topic and dates of the training course must correspond to those listed on that person's accreditation certificate.
(d) Accreditation certificates. The training providers ((shall)) must maintain records that document the names of all persons who have been awarded certificates, their certificate numbers, the disciplines for which accreditation was conferred, training and expiration dates, and the training location. The training provider ((shall)) must maintain the records in a manner that allows verification by telephone of the required information.
(e) Verification of certificate information. Training providers of refresher training courses ((shall)) must confirm that their students possess valid accreditation before granting course admission.
(f) Records retention and access.
(i) The training provider ((shall)) must maintain all required records for a minimum of three years. The training provider, however, may find it advantageous to retain these records for a longer period of time.
(ii) The training provider must allow reasonable access to all of the records required by the MAP, and to any other records which may be required by the department for the approval of asbestos training providers or the accreditation of asbestos training courses, to both EPA and to the department, on request.
(iii) If a training provider ceases to conduct training, the training provider ((shall)) must notify the department and give it the opportunity to take possession of that provider's asbestos training records.
(17) A representative of the department may, at the department's discretion, provide an examination as a substitution to the examination administered by the training course provider. The examination replacement will be used to verify that the training course is conducted in accordance with the program approved by the department.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-65-017 Contractor certification.
(1) In order to obtain certification, an asbestos contractor must submit an application to the department. The application ((shall)) must provide the following information:
(a) A list of asbestos projects conducted by the contractor during the previous twelve months. Such list ((shall)) must include for each project:
(i) Project name;
(ii) Location;
(iii) Brief description;
(iv) Identity of any citations or enforcement actions issued for violations of asbestos regulations by any local, state, or federal jurisdiction relative to each individual project; and
(v) Name of the on-site project manager or supervisor.
(b) A list of asbestos supervisors (include certification number) working for the company.
(c) A statement certifying that the contractor has read and understands all applicable Washington state rules and regulations regarding asbestos abatement and will comply with them.
(d) A statement certifying that the applicant contractor's asbestos license or accreditation issued by any other state or jurisdiction has not been revoked, suspended, or denied by that state or jurisdiction.
(2) Upon approval, the department will issue the contractor a certificate. Denial of approval ((shall)) must be in writing.
(3) Certificates ((shall)) must be valid for a period of twelve months. Certificates may be extended during department review of a renewal application.
Note: | In circumstances where it is necessary to coordinate an expiration date with the date of expiration of a contractor registration issued under chapter 18.27 RCW, certificates may be valid for less than one year. In such circumstances, the certificate fee prescribed in WAC 296-65-025 shall be prorated accordingly for the initial application only. |
(4) The application for certificate renewal ((shall)) must contain the information specified in subsection (1) of this section.
(5) Applications for renewal must be received by the department not less than sixty days before the certificate expires.
(6) The department may suspend or revoke the certificate as provided in WAC 296-65-050 and chapter 296-900 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-17-026, filed 8/10/99, effective 11/10/99)
WAC 296-65-020 Notification requirements.
(1) Before any person or individual begins an asbestos project as defined in WAC 296-62-07722 and 296-65-003 involving more than forty-eight square feet or ten linear feet, unless the surface area of the pipe is greater than forty-eight square feet, of asbestos containing material, written notification must be provided to the department. Notices must include:
(a) Name and address of the owner and contractor.
(b) Description of the facility including size, age, and prior use of the facility.
(c) Amount of asbestos-containing material to be removed or encapsulated.
(d) Location of the facility.
(e) Exact starting and completion dates of the asbestos project, including shifts during which abatement work will be accomplished. These dates must correspond to the dates specified for asbestos removal in the contract. Any change in these dates or work shifts must be communicated to the department by an amended notice filed at the office where the original notice was filed.
((•)) (i) When the starting date or time changes, the amended notice must be filed no later than 5:00 p.m. on the business day prior to the starting date in the original notice and prior to the new starting date.
((•)) (ii) When the completion date or time changes, the amended notice must be filed before completion of the project, and within eight hours from when the person learns that the change will occur.
(iii) Notice may be filed by facsimile (fax).
(f) Nature of the project and methods used to remove or encapsulate the material.
(2) Notices must be received by the department no later than ten days prior to the start of the project. Notices must be sent directly to the department of labor and industries regional office having jurisdiction on the project.
(3) The director may waive the prenotification requirement upon written request of an owner for large-scale, on-going projects. In granting such a waiver, the director will require the owner to provide prenotification if significant changes in personnel, methodologies, equipment, work site, or work procedures occur or are likely to occur. The director will further require annual resubmittal of such notification.
(4) The director, upon review of an owner's reports, work practices, or other data available as a result of inspections, audits, or other authorized activities, may reduce the size threshold for prenotification required by this section. Such a change will be based on the director's determination that significant problems in personnel, methodologies, equipment, work site, or work procedures are creating the potential for violations of this chapter.
(5) Emergency projects which disturb or release asbestos into the air must be reported to the department within three working days after commencement of the project in the manner otherwise required under this chapter. The employees, the employees' collective bargaining representative or employee representative, if any, and other persons at the project area must be notified of the emergency as soon as possible by the person undertaking the emergency project. A notice describing the nature of the emergency project must be clearly posted adjacent to the work area.
(6) Incremental phasing in the conduct or design of asbestos projects or otherwise conducting or designing asbestos projects of a size less than the threshold exemption specified in subsection (1) of this section, with the intent of avoiding the notification requirements, is a violation of this chapter.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-17-026, filed 8/10/99, effective 11/10/99)
WAC 296-65-030 Methods of compliance.
(1) Before submitting a bid or working on an asbestos abatement project, any person or individual must obtain an asbestos contractor certificate as provided in WAC 296-65-017 and must have in its employ at least one certified asbestos supervisor responsible for supervising all asbestos projects undertaken by the contractor.
(2) A certified asbestos supervisor will not be required on asbestos projects involving less than three square feet or three linear feet of asbestos-containing material unless the surface area of the pipe is greater than three square feet. A certified asbestos supervisor is required for all Class I and II asbestos work in accordance with WAC 296-62-07728(4).
(3) No employee or other individual is eligible to do work or supervise an asbestos project without being issued a certificate by the department.
(a) Employees performing Class I or Class II asbestos work must be certified asbestos workers as specified in WAC 296-62-07722.
(b) Employees performing Class III or Class IV asbestos work specified by WAC 296-62-07722 as an asbestos project ((shall)) must be certified asbestos workers.
(4) No person may assign any employee, contract with, or permit any individual, to work on an asbestos project as specified in WAC 296-62-07722 in any facility without the project being performed by a certified asbestos worker.
(5) A certified asbestos supervisor must provide direct, on-site supervision for an asbestos project. When an employer conducts an asbestos abatement project in its own facility by its own certified employees, supervision may be performed in the regular course of a certified asbestos supervisor's duties. Asbestos workers must have access to and be under the control of certified asbestos supervisors throughout the duration of the project.
(6) Any construction, renovation, remodeling, maintenance, repair, or demolition which was started without meeting the requirements of this section must be halted immediately and cannot be resumed before meeting such requirements.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 96-05-056, filed 2/16/96, effective 4/1/96)
WAC 296-65-050 Denial, suspension, and revocation of certificates.
(1) The department may deny, suspend, or revoke a certificate for failure of the holder to comply with any requirement of this chapter or any applicable health and safety standards and regulations.
(2) The criteria for decertification for asbestos workers, supervisors, and contractors ((shall)) must include:
(a) Performing work requiring accreditation at a job site without being in physical possession of initial and current accreditation certificates;
(b) Permitting the duplication or use of one's own accreditation certificate by another;
(c) Performing work for which accreditation has not been received; or
(d) Obtaining accreditation from a training provider that does not have approval to offer training for the particular discipline from either EPA or from a state that has a contractor accreditation plan at least as stringent as the EPA MAP.
(3) The following persons are not certified for the purposes of this chapter and their respective certificate(s) ((shall)) must be revoked by the department:
(a) Any person who obtains accreditation through fraudulent representation of training or examination documents;
(b) Any person who obtains training documentation through fraudulent means;
(c) Any person who gains admission to and completes refresher training through fraudulent representation of initial or previous refresher training documentation; or
(d) Any person who obtains accreditation through fraudulent representation of accreditation requirements such as education, training, professional registration, or experience.
(4) Before any certificate may be denied, suspended, or revoked, the holder thereof ((shall)) must be given written notice of the department's intention to do so, mailed by registered mail, return receipt requested, to the holder's last known address. The notice ((shall)) must enumerate the allegations against such holder and ((shall)) must give him or her the opportunity to request a conference before the department. At such conference, the department and the holder ((shall)) must have opportunity to produce witnesses and give testimony.
(5) A denial, suspension, or revocation order may be appealed to the board of industrial insurance appeals within fifteen working days after the denial, suspension, or revocation order is entered. The notice of appeal may be filed with the department or the board of industrial insurance appeals. The board of industrial insurance appeals ((shall)) must hold the hearing in accordance with procedures established in RCW 49.17.140. Any party aggrieved by an order of the board of industrial insurance appeals may obtain superior court review in the manner provided in RCW 49.17.150.
(6) The department may suspend or revoke any certificate issued under this chapter for a period of not less than six months upon the following grounds:
(a) The certificate was obtained through error or fraud; or
(b) The holder thereof is judged to be incompetent to carry out the work for which the certificate was issued.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 01-11-038, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01)
WAC 296-301-010 Textiles—Application requirements.
(1) Application. The requirements of this chapter for textile safety apply to the design, installation, processes, operation, and maintenance of textile machinery, equipment, and other plant facilities in all plants engaged in the manufacture and processing of textiles, except those processes used exclusively in the manufacture of synthetic fibers.
(2) These standards ((shall)) must be augmented by the Washington state general safety and health standards, and any other regulations of general application which are or will be made applicable to all industries.
(3) The provisions of this chapter ((shall)) must prevail in the event of conflict with or duplication of, provisions contained in chapter 296-24 WAC, the general safety and health standards, chapter 296-62 WAC, the general occupational health standards, and chapter 296-800 WAC, the safety and health core rule book.
(4) WAC 296-24-012 and 296-800-360 ((shall)) must apply where applicable to this industry.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-015 Definitions applicable to this chapter.
(((1) "))Belt shifter((" means)). A device for mechanically shifting a belt from one pulley to another.
(((2) "))Belt shifter lock((" means)). A device for positively locking the belt shifter in position while the machine is stopped and the belt is idling on the loose pulleys.
(((3) "))Calendar((" means)). A machine consisting of a set of heavy rollers mounted on vertical side frames and arranged to pass cloth between them. Calendars may have two to ten rollers, or bowls, some of which can be heated.
(((4) "Embossing calender" means a calender with two or more rolls, one of which is engraved for producing figured effects of various kinds on a fabric.
(5) "))Cans (drying)((" means)). Hollow cylindrical drums mounted in a frame so they can rotate. They are heated with steam and are used to dry fabrics or yarn as it passes around the perimeter of the can.
(((6) "))Carbonizing((" means)). The removing of vegetable matter such as burns, straws, etc., from wool by treatment with acid, followed by heat. The undesired matter is reduced to a carbon-like form which may be removed by dusting or shaking.
(((7) "Card" machine means a machine consisting of cylinders of various sizes—and in certain cases flats—covered with card clothing and set in relation to each other so that fibers in staple form may be separated into individual relationship. The speed of the cylinders and their direction of rotation varies. The finished product is delivered as a sliver. Cards of different types are: The revolving flat card, the roller-and-clearer card, etc.
(8) "))Card clothing((" means)). The material with which many of the surfaces of a card are covered; e.g., the cylinder, doffer, etc. It consists of a thick foundation material, usually made of textile fabrics, through which are pressed many fine, closely spaced, specially bent wires.
(((9) "))Card machine. A machine consisting of cylinders of various sizes—and in certain cases flats—covered with card clothing and set in relation to each other so that fibers in staple form may be separated into individual relationship. The speed of the cylinders and their direction of rotation varies. The finished product is delivered as a sliver. Cards of different types are: The revolving flat card, the roller-and-clearer card, etc.
Comber((" means)). A machine for combing fibers of cotton, wool, etc. The essential parts are a device for feeding forward a fringe of fibers at regular intervals and an arrangement of combs or pins which, at the right time, pass through the fringe. All tangled fibers, short fibers, and neps are removed and the long fibers are laid parallel.
(((10) "))Combing machinery((" means)). A general classification, including combers, sliver lap machines, ribbon lap machines, and gill boxes, but excluding cards.
(((11) "))Continuous bleaching ranges. Ranges of several types and may be made for cloth in rope or open-width form. The goods, after wetting out, pass through a squeeze roll into a saturator containing a solution of caustic soda and then to an enclosed J-box. A V-shaped arrangement is attached to the front part of the J-box for uniform and rapid saturation of the cloth with steam before it is packed down in the J-box. The cloth, in a single strand rope form, passes over a guide roll down the first arm of the "V" and up the second. Steam is injected into the "V" at the upper end of the second arm so that the cloth is rapidly saturated with steam at this point. The J-box capacity is such that cloth will remain hot for a sufficient time to complete the scouring action. It then passes a series of washers with a squeeze roll in between. The cloth then passes through a second set of saturator, J-box, and washer, where it is treated with the peroxide solution. By slight modification of the form of the unit, the same process can be applied to open-width cloth.
Cutter (rotary staple)((" means)). A machine consisting of one or more rotary blades used for the purpose of cutting textile fibers into staple lengths.
(((12) "))Embossing calender. A calender with two or more rolls, one of which is engraved for producing figured effects of various kinds on a fabric.
Exposed to contact((" means that)). The location of an object, material, nip point, or point of operation is such that a person is liable to come in contact with it in his normal course of employment.
(((13) "))Garnett machine((" means)). Any of a number of types of machines for opening hard twisted waste of wool, cotton, silk, etc. Essentially, such machines consist of a lickerin; one or more cylinders, each having a complement worker and stripper rolls; and a fancy roll and doffer. The action of such machines is somewhat like that of a wool card, but it is much more severe in that the various rolls are covered with garnett wire instead of card clothing.
(((14) "))Gill box((" means)). A machine used in the worsted system of manufacturing yarns. Its function is to arrange the fibers in parallel order. Essentially, it consists of a pair of feed rolls and a series of followers where the followers move at a faster surface speed and perform a combing action.
(((15) "))Industrial organic solvent. Any organic volatile liquid or compound, or any combination of these substances which are used to dissolve or suspend a nonvolatile or slightly volatile substance for industrial utilization. It shall also apply to such substances when used as detergents or cleansing agents. It shall not apply to petroleum products when such products are used as fuel.
Interlock((" means)). A device that operates to prevent the operation of machine while the cover or door of the machine is open or unlocked, and which will also hold the cover or door closed and locked while the machine is in motion.
(((16) "))Jig (dye)((" means)). A machine for dyeing piece goods. The cloth, at full width, passes from a roller through the dye liquor in an open vat and is then wound on another roller. The operation is repeated until the desired shade is obtained.
(((17) "))Kier((" means)). A large metal vat, usually a pressure type, in which fabrics may be boiled out, bleached, etc.
(((18) "))Lapper (ribbon)((" means)). A machine used to prepare laps for feeding a cotton comb; its purpose is to provide a uniform lap in which the fibers have been straightened as much as possible.
(((19) "))Lapper (sliver)((" means)). A machine in which a number of parallel card slivers are drafted slightly, laid side by side in a compact sheet, and wound into a cylindrical package.
(((20) "))Loom((" means)). A machine for effecting the interlacing of two series of yarns crossing one another at right angles. The warp yarns are wound on a warp beam and pass through heddles and reed. The filling is shot across in a shuttle and settled in place by reed and lay, and the fabric is wound on a cloth beam.
(((21) "Starch mangle" means a mangle that is used specifically for starching cotton goods. It commonly consists of two large rolls and a shallow open vat with several immersion rolls. The vat contains the starch solution.
(22) "Water mangle" means a calender having two or more rolls used for squeezing water from fabrics before drying. Water mangles also may be used in other ways during the finishing of various fabrics.
(23) "))Mule((" means)). A type of spinning frame having a head stock and a carriage as its two main sections. The head stock is stationary. The carriage is movable and it carries the spindles which draft and spin the roving into the yarn. The carriage extends over the whole width of the machine and moves slowly toward and away from the head stock during the spinning operation.
(((24) "))Nip((" means)). The point of contact between two in-running rolls.
(((25) "))Openers and pickers((" means)). A general classification which includes breaker pickers, intermediate pickers, finisher pickers, single process pickers, multiple process pickers, willow machines, card and picker waste cleaners, thread extractors, shredding machines, roving waste openers, shoddy pickers, bale breakers, feeders, vertical openers, lattice cleaners, horizontal cleaners, and any similar machinery equipped with either cylinders, screen section, calender section, rolls, or beaters used for the preparation of stock for further processing.
(((26) "))Paddler((" means)). Equipment consisting of a trough for a solution and two or more squeeze rolls between which cloth passes after being passed through a mordant or dye bath.
(((27) "))Point of operation((" means)). That part of the machine where the work of cutting, shearing, squeezing, drawing, or manipulating the stock in any other way is done.
(((28) "))Roller printing machine((" means)). A machine consisting of a large central cylinder, or pressure bowl, around the lower part of the perimeter of which is placed a series of engraved color rollers (each having a color trough), a furnisher roller, doctor blades, etc. The machine is used for printing fabrics.
(((29) "Continuous bleaching ranges" means ranges of several types and may be made for cloth in rope or open-width form. The goods, after wetting out, pass through a squeeze roll into a saturator containing a solution of caustic soda and then to an enclosed J-box. A V-shaped arrangement is attached to the front part of the J-box for uniform and rapid saturation of the cloth with steam before it is packed down in the J-box. The cloth, in a single strand rope form, passes over a guide roll down the first arm of the "V" and up the second. Steam is injected into the "V" at the upper end of the second arm so that the cloth is rapidly saturated with steam at this point. The J-box capacity is such that cloth will remain hot for a sufficient time to complete the scouring action. It then passes a series of washers with a squeeze roll in between. The cloth then passes through a second set of saturator, J-box, and washer, where it is treated with the peroxide solution. By slight modification of the form of the unit, the same process can be applied to open-width cloth.
(30) "))Mercerizing range((" generally means)). A 3-bowl mangle, a tenter frame, and a number of boxes for washing and scouring. The whole setup is in a straight line and all parts operate continuously. The combination is used to saturate the cloth with sodium hydroxide, stretch it while saturated, and washing out most of the caustic before releasing tension.
(((31) "))Sanforizing machine((" means)). A machine consisting of a large steam-heated cylinder, an endless, thick, woolen felt blanket which is in close contact with the cylinder for most of its perimeter, and an electrically heated shoe which presses the cloth against the blanket while the latter is in a stretched condition as it curves around feed-in roll.
(((32) "))Shearing machine((" means)). A machine used in shearing cloth. Cutting action is provided by a number of steel blades spirally mounted on a roller. The roller rotates in close contact with a fixed ledger blade. There may be from one to six such rollers on a machine.
(((33) "))Singeing machine((" means)). A machine used particularly with cotton, comprised of a heated roller, plate, or an open gas flame. The material is rapidly passed over the roller or the plate or through the open gas flame to remove fuzz or hairiness on yarn or cloth by burning.
(((34) "))Slasher((" means)). A machine used for applying a size mixture to warp yarns. Essentially, it consists of a stand for holding section beams, a size box, one or more cylindrical dryers or an enclosed hot air dryer, and a beaming end for finding the yarn on the loom beams.
(((35) "Industrial organic solvent" means any organic volatile liquid or compound, or any combination of these substances which are used to dissolve or suspend a nonvolatile or slightly volatile substance for industrial utilization. It shall also apply to such substances when used as detergents or cleansing agents. It shall not apply to petroleum products when such products are used as fuel.
(36) "))Starch mangle. A mangle that is used specifically for starching cotton goods. It commonly consists of two large rolls and a shallow open vat with several immersion rolls. The vat contains the starch solution.
Tenter frame((" means)). A machine for drying cloth under tension. It essentially consists of a pair of endless traveling chains fitted with clips of fine pins and carried on tracks. The cloth is firmly held at the selvages by the two chains which diverge as they move forward so that the cloth is brought to the desired width.
(((37) "))Warper((" means)). Any machine for preparing and arranging the yarns intended for the warp of a fabric, specifically, a beam warper.
Water mangle. A calender having two or more rolls used for squeezing water from fabrics before drying. Water mangles also may be used in other ways during the finishing of various fabrics.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-18-080, filed 8/31/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-301-020 General safety requirements.
(1) Means of stopping machines. Every textile machine ((shall)) must be provided with individual mechanical or electrical means for stopping such machines. On machines driven by belts and shafting a locking-type shifter or an equivalent positive device ((shall)) must be used. On operations where injury to the operator might result if motors were to restart after power failures, provision ((shall)) must be made to prevent machines from automatically restarting upon restoration of power.
(2) Handles. Stopping and starting handles ((shall)) must be designed to the proper length to prevent the worker's hand or fingers from striking against any revolving part, gear guard, or any other part of the machine.
(3) Machine guarding. ((An employer)) You must ensure that power transmission parts are guarded according to the requirements of WAC 296-24-205 through 296-24-20527.
(4) Housekeeping. Aisles and working spaces ((shall)) must be kept in good order in accordance with requirements of WAC 296-24-735 through 296-24-73505 and WAC 296-800-220.
(5) Inspection and maintenance. All guards and other safety devices, including starting and stopping devices, ((shall)) must be properly maintained.
(6) ((Lighting and illumination.)) Lighting and illumination ((shall)) must conform to the safety and health core rule book, WAC 296-800-210.
(7) ((Identification of piping systems.)) Identification of piping systems ((shall)) must conform to American National Standard A13.1-1956.
(8) Steam pipes. All pipes carrying steam or hot water for process or servicing machinery, when exposed to contact and located within seven feet of the floor or working platform ((shall)) must be covered with a heat-insulating material, or guarded with equivalent protection.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-025 Openers and pickers.
(1) Beater guards. When any opening or picker machinery is equipped with a beater, such beater ((shall)) must be provided with metal covers which will prevent contact with the beater. Such covers ((shall)) must be provided with an interlock which will prevent the cover from being raised while the machine is in motion and prevent the operation of the machine while the cover is open.
(2) ((Cleanout holes.)) Cleanout holes within reaching distance of the fan or picker beater ((shall)) must have their covers securely fastened and they ((shall)) must not be opened while the machine is in motion.
(3) Feed rolls. The feed rolls on all opening and picking machinery ((shall)) must be covered with a guard designed to prevent the operator from reaching the nip while the machinery is in operation.
(4) Removal of foreign ferrous material. All textile opener lines ((shall)) must be equipped with magnetic separators, tramp iron separators, or other means for the removal of foreign ferrous material.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-030 Cotton cards.
(1) Enclosures. Cylinder and lickerins ((shall)) must be equipped with guards and the doffers should be enclosed.
(2) Enclosure fastenings. The enclosures or covers ((shall)) must be kept in place while the machine is in operation, except when stripping or grinding.
(3) Stripping rolls. On operations calling for flat strippings which are allowed to fall on the doffer cover, where such strippings are removed by hand, the doffer cover ((shall)) must be kept closed and securely fastened to prevent the opening of the cover while the machine is in operation. When it becomes necessary to clean the cards while they are in motion, a long-handled brush or dust mop ((shall)) must be used.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-035 Garnett machines.
(1) Lickerin. Garnett lickerins ((shall)) must be enclosed.
(2) Fancy rolls. Garnett fancy rolls ((shall)) must be enclosed by covers. These ((shall)) must be installed in a way that keeps worker rolls reasonably accessible for removal or adjustment.
(3) Underside of machine. The underside of the garnett ((shall)) must be guarded by a screen mesh or other form of enclosure to prevent access while machine is running.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-040 Spinning mules.
A substantial fender of metal or hardwood ((shall)) must be installed in front of the carriage wheels, the fender to extend to within one-fourth inch of the rail.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-04501 Cylinder dryers.
(1) ((Reducing valves, safety valves, and pressure gages.)) Reducing valves, safety valves, and pressure gages ((shall)) must conform to the ASME Pressure Vessel Code, section VIII, Unfired Pressure Vessels, 1968.
(2) ((Vacuum relief valves.)) Vacuum relief valves ((shall)) must conform to the ASME Code for Pressure Vessels, section VIII, Unfired Pressure Vessels, 1968.
(3) Lever control. When slashers are operated by control levers, these levers ((shall)) must be connected to a horizontal bar or treadle located not more than 69 inches above the floor to control the operation from any point.
(4) Pushbutton control. Slashers operated by pushbutton control ((shall)) must have stop and start buttons located at each end of the machine, and additional buttons located on both sides of the machine, at the size box and the delivery end. If calender rolls are used, additional buttons ((shall)) must be provided at both sides of the machine at points near the nips, except when slashers are equipped with an enclosed dryer.
(5) Nip guards. All nip guards ((shall)) must comply with the requirements of WAC 296-301-04503(4).
(6) Cylinder enclosure. When enclosures or hoods are used over cylinder drying rolls, such enclosures or hoods ((shall)) must be provided with an exhaust system which will effectively prevent wet air and steam from escaping into the workroom.
(7) Expansion chambers. Slasher kettles and cookers ((shall)) must be provided with expansion chambers in the covers, or drains, to prevent surging over. Steam-control valves ((shall)) must be so located that they can be operated without exposing the worker to moving parts, hot surfaces, or steam.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-04503 Enclosed hot air dryers.
(1) Lever control. When slashers are operated by control levers, these levers ((shall)) must be connected to a horizontal bar or treadle located not more than 69 inches above the floor to control the operation from any point.
(2) Push-button control. Slashers operated by push-button control ((shall)) must have one start button at each end of the machine and stop buttons ((shall)) must be located on both sides of the machines at intervals spaced not more than 6 feet on centers.
Note: | Inching buttons should be installed. |
(3) Dryer enclosure. The dryer enclosure ((shall)) must be provided with an exhaust system which will effectively prevent wet air and steam from escaping into the workroom.
(4) Nip guards. All nip guards ((shall)) must comply with Table R-1.
TABLE R-1
GUARD OPENINGS
Openings in the guard or between the guard and working surface ((shall)) must not be greater than the following:
Distance of opening from nip point |
Maximum width of opening |
|||||
0 to 1 1/2 |
1/4 |
|||||
1 1/2 to 2 1/2 |
3/8 |
|||||
2 1/2 to 3 1/2 |
1/2 |
|||||
3 1/2 to 5 1/2 |
5/8 |
|||||
5 1/2 to 6 1/2 |
3/4 |
|||||
6 1/2 to 7 1/2 |
7/8 |
|||||
7 1/2 to 8 1/2 |
1 |
1/4 |
||||
The measurements in Table R-1 are all in inches.
(5) Expansion chambers. Slasher kettles and cookers ((shall)) must be provided with expansion chambers in the covers, or drains, to prevent surging over. Steam control valves ((shall)) must be so located that they can be operated without exposing the worker to moving parts, hot surfaces, or steam.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-050 Warpers.
(1) ((Swiveled double-bar gates.)) Swiveled double-bar gates ((shall)) must be installed on all warpers operating in excess of 450 yards per minute. These gates ((shall)) must be so interlocked that the machine cannot be operated until the gate is in the "closed position," except for the purpose of inching or jogging.
(2) ((Closed position.)) "Closed position" ((shall)) must mean that the top bar of the gate ((shall)) must be at least 42 inches from the floor or working platform; and the lower bar ((shall)) must be at least 21 inches from the floor or working platform; and the gate ((shall)) must be located 15 inches from the vertical tangent to the beam head.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-055 Drawing frames, slubbers, roving parts, cotton combers, ring spinning frames, twisters.
Gear housing covers on all installations of drawing frames, slubbers, roving frames, cotton combers, ring spinning frames, and twisters ((shall)) must be equipped with interlocks.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-060 Gill boxes.
(1) Pin guard. A pin guard ((shall)) must be placed ahead of the feed end and ((shall)) must be so designed that it will prevent the worker's fingers from being caught in the pins of the intersecting fallers.
(2) Nip guards. All nip guards ((shall)) must comply with the requirements of WAC 296-301-04503(4).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-065 Heavy draw boxes, finishers, and speeders used in worsted drawing.
(1) Band pulley covers. Covers for band pulleys ((shall)) must be closed when the machine is in motion.
(2) ((Benches or working platforms.)) Benches or working platforms approximately 10 inches in height and 8 inches in width should be installed along the entire running length of the machine for the worker to stand on while creeling the machine. Such benches or platforms ((shall)) must be covered with an abrasive or nonslip material.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-070 Silver and ribbon lappers (cotton).
Cover guard. An interlocking cover guard ((shall)) must be installed over the large calender drums and the lap spool, designed to prevent the operator from coming in contact with the nip.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-075 Looms.
(1) Shuttle guard. Each loom ((shall)) must be equipped with a guard designed to minimize the danger of the shuttle flying out of the shed.
(2) Protection for loom fixer. Provisions ((shall)) must be made so that every loom fixer can prevent the loom from being started while he is at work on the loom. This may be accomplished by means of a lock, the key to which is retained in the possession of the loom fixer, or by some other effective means to prevent starting the loom.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-080 Shearing machines.
All revolving blades on shearing machines ((shall)) must be guarded so that the opening between the cloth surface and the bottom of the guard will not exceed three-eighths inch.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-085 Continuous bleach range (cotton and rayon).
(1) J-box protection. Each valve controlling the flow of steam, injurious gases, or liquids into a J-box ((shall)) must be equipped with a chain, lock, and key, so that any worker who enters the J-box can lock the valve and retain the key in his possession. Any other method which will prevent steam, injurious gases, or liquids from entering the J-box while the worker is in it will comply with this provision.
(2) Open-width bleaching. The nip of all in-running rolls on open-width bleaching machine rolls ((shall)) must be protected with a guard to prevent the worker from being caught at the nip. The guard ((shall)) must extend across the entire length of the nip.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-090 Kiers.
(1) ((Reducing valves, safety valves, and pressure gages.)) Reducing valves, safety valves, and pressure gages ((shall)) must conform to the ASME Code for Unfired Pressure Vessels, section VIII, Unfired Pressure Vessels, 1968.
(2) Kier valve protection. Each valve controlling the flow of steam, injurious gases, or liquids into a kier ((shall)) must be equipped with a chain, lock, and key, so that any worker who enters the kier can lock the valve and retains the key. Any other method which will prevent steam, injurious gases, or liquids from entering the kier while the worker is in it will be acceptable.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-095 Gray and white bins.
Guard rails conforming to WAC 296-24-750 through 296-24-75011, of the general safety and health standards, ((shall)) must be provided where workers are required to plait by hand from the top of the bin so as to protect the worker from falling to a lower level.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-100 Mercerizing range (piece goods).
(1) Stopping devices. A stopping device ((shall)) must be provided at each end of the machine.
(2) Frame ends. A guard ((shall)) must be installed at each end of the frame between the in-running chain and the clip opener, to prevent the worker's fingers from being caught.
(3) Mangle and washers. The nip at the in-running rolls ((shall)) must conform to WAC 296-301-04503(4).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-105 Tenter frames.
(1) Stopping devices. A stopping device ((shall)) must be provided at each end of the machine.
(2) Frame ends. A guard ((shall)) must be installed at each end of the frame at the in-running chain and clip opener.
(3) ((Oil cups.)) Oil cups ((shall)) must be located to permit safe and easy access. They ((shall)) must be of the extension type to permit oiling while machines are operating.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-110 Dyeing jigs.
(1) Stopping devices. Each dye jig ((shall)) must be equipped with individual mechanical or electrical means for stopping the machine.
(2) ((Roll arms.)) Roll arms on jigs ((shall)) must be built to allow for extra large batches, and to prevent the center bar from being forced off, causing the batch to fall.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-115 Padders—Nip guards.
All nip guards ((shall)) must comply with the requirements of WAC 296-301-04503(4).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-120 Drying cans.
(1) ((Pressure reducing valves and pressure gages.)) Pressure reducing valves and pressure gages ((shall)) must conform to the ASME Code for Pressure Vessels, section VIII, 1968, Unfired Pressure Vessels.
(2) Vacuum collapse. If cans are not designed to prevent vacuum collapse, each can ((shall)) must be equipped with one or more vacuum relief valves with openings of such a size as to prevent the collapse of the can if vacuum occurs.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-125 Ironer.
(((1))) Each flat-work or collar ironer ((shall)) must be equipped with a safety bar or other guard across the entire front of the feed or first pressure rolls, so arranged that the striking of the bar or guard by the hand of the operator or other person will stop the machine. The pressure rolls ((shall)) must be covered or guarded so that the operator or other person cannot reach into the rolls without removing the guard. This may be either a vertical guard on all sides or a complete cover. If a vertical guard is used, the distance from the floor or working platform to the top of guard ((shall be)) must not be less than 6 feet.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-301-130 Extractors.
(1) Centrifugal extractor.
(a) Cover. Each extractor ((shall)) must be equipped with a metal cover.
(b) Interlocking device. Each extractor ((shall)) must be equipped with an interlocking device that will prevent the cover from being opened while the basket is in motion, and also prevent the power operation of the basket while the cover is open.
(c) Brakes. Each extractor ((shall)) must be equipped with a mechanically or electrically operated brake to quickly stop the basket when the power driving the basket is shut off.
(d) Maximum allowable speed. Each centrifugal extractor ((shall)) must be effectively secured in position on the floor or foundation so as to eliminate unnecessary vibration, and ((shall)) must not be operated at a speed greater than the manufacturer's rating, which ((shall)) must be stamped where easily visible in letters not less than one-quarter inch in height. The maximum allowable speed ((shall)) must be given in revolutions per minute (rpm).
(2) Engine drum extractor—Over-speed governor. Each engine individually driving an extractor ((shall)) must be provided with an approved engine stop and a speed limit governor.
(3) Squeezer or wringer extractor—Nip guards. All nip guards ((shall)) must comply with the requirements of WAC 296-301-04503(4).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-135 Nip guards.
All nip guards for water mangle, starch mangle, backwasher (worsted yarn) crabbing machines, decating machines, ((shall)) must comply with the requirements of WAC 296-301-04503(4).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-140 Sanforizing and palmer machine.
A safety trip rod, cable, or wire center cord ((shall)) must be provided across the front and back of all palmer cylinders extending the length of the face of the cylinder. It ((shall)) must operate readily whether pushed or pulled. This safety trip ((shall)) must be not more than 72 inches above the level on which the operator stands and ((shall)) must be readily accessible.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-145 Rope washers.
(1) ((Splash guard.)) Splash guards ((shall)) must be installed on all rope washers unless the machine is so designed as to prevent the water or liquid from splashing the operator, the floor, or working surface.
(2) Safety stop bar. A safety trip rod, cable or wire center cord ((shall)) must be provided across the front and back of all rope washers extending the length of the face of the washer. It ((shall)) must operate readily whether pushed or pulled. This safety trip ((shall be)) must not be more than 72 inches above the level on which the operator stands and ((shall)) must be readily accessible.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-150 Laundry washer tumbler or shaker.
(1) Interlocking device. Each drying tumbler, each double cylinder shaker or clothes tumbler, and each washing machine ((shall)) must be equipped with an interlock device which will prevent the power operation of the inside cylinder when the outer door on the case or shell is open, and which will also prevent the outer door on the case or shell from being opened without shutting off the power. This should not prevent the movement of the inner cylinder by means of a hand operated mechanism or an "inching device."
(2) Means of holding covers or doors in open position. Each enclosed barrel ((shall)) must also be equipped with adequate means for holding open the doors or covers of the inner and outer cylinders or shells while it is being loaded or unloaded.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-155 Printing machine (roller type).
(1) Nip guards. All nip guards ((shall)) must comply with the requirements of WAC 296-301-04503(4).
(2) Crown wheel and roller gear nip protection. The engraved roller gears and the large crown wheel ((shall)) must be provided with a protective disc which will enclose the nips of the in-running gears. Individual discs for each nip will be deemed to be in compliance with the provisions of WAC 296-301-04503(4).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-160 Calenders.
The nip at the in-running side of the rolls ((shall)) must be provided with a guard extending across the entire length of the nip and arranged to prevent the fingers of the workers from being pulled in between the rolls or between the guard and the rolls, and constructed so that the cloth can be fed into the rolls safely.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-165 Rotary staple cutters.
A guard ((shall)) must be installed completely enclosing the cutters to prevent the hands of the operator from reaching the cutting zone.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-301-170 Clothing folding machine.
Cloth-folding machines ((shall)) must meet the requirements of chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-175 Hand bailing machine.
An angle-iron-handle stop guard ((shall)) must be installed at the right angle to the frame of the machine. The stop guard ((shall)) must be so designed and so located that it will prevent the handle from traveling beyond the vertical position should the handle slip from the operator's hand when the pawl has been released from the teeth of the takeup gear.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-180 Roll bench.
Cleats ((shall)) must be installed on the ends of roll benches.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-185 Cuttle or swing folder (overhead type).
The bottom of the overhead folders ((shall)) must be located not less than 7 feet from the floor or working surface.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-190 Color-mixing room.
Floors in color-mixing rooms ((shall)) must be constructed to drain easily.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 99-17-094, filed 8/17/99, effective 12/1/99)
WAC 296-301-195 Open tanks and vats for mixing and storage of hot or corrosive liquids.
(1) Guardrails ((shall)) must be provided for open tanks and vats which conform to the requirements of WAC 296-24-750 through 296-24-75011.
(2) Shutoff valves. Boiling tanks, caustic tanks, and hot liquid containers, so located that the operator cannot see the contents from the floor or working area, ((shall)) must have emergency shutoff valves controlled from a point not subject to danger of splash. Valves ((shall)) must conform to the ASME Pressure Vessel Code, section VIII, Unfired Pressure Vessels, 1968.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-200 Dye kettles and vats.
Pipes or drains of sufficient capacity to carry the contents safely away from the working area ((shall)) must be installed where there are dye kettles and vats which may at any time contain hot or corrosive liquids. These ((shall)) must not empty directly onto the floor.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-205 Acid carboys.
Carboys ((shall)) must be provided with inclinators, or the acid ((shall)) must be withdrawn from the carboys by means of pumping without pressure in the carboy, or by means of hand operated siphons.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-19, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-301-210 Handling caustic soda and caustic potash.
Means ((shall)) must be provided for handling and emptying caustic soda and caustic potash containers to prevent workers from coming in contact with the caustic (see WAC 296-301-220).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-03-093, filed 1/18/05, effective 3/1/05)
WAC 296-301-220 Personal protective equipment.
(1) Personal protective equipment. Workers engaged in handling acids or caustics in bulk, repairing pipe lines containing acids or caustics, etc., ((shall)) must be provided with personal protective equipment to conform to the requirements of WAC 296-800-160.
(2) Respiratory protection. ((Employers)) You must provide respiratory protection as required in chapter 296-842 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-301-225 Workroom ventilation.
In all workrooms in which potentially toxic substances are used, the maximum allowable concentrations listed in chapter 296-841 WAC, airborne contaminants, ((shall)) must be maintained. Open surface tanks ((shall)) must conform to the requirements of WAC 296-62-11021.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-303-01001 General industrial safety standards.
(1) General. These standards ((shall)) must be augmented by the Washington state general safety and health standards, and any other regulations of general application which are or will be made applicable to all industries.
(2) Additional requirements. ((The employer shall)) You must comply with the provisions of the standards referenced in this section. In the event of any conflict between this section and WAC 296-303-015 through 296-303-040, the requirements of WAC 296-303-015 through 296-303-040 ((shall)) must apply. The provisions of this chapter ((shall)) must prevail in the event of conflict with, or duplication of, provisions contained in chapters 296-24, 296-62, and 296-800 WAC.
(a) Industrial lighting. American National Standard Practice for Industrial Lighting, ANSI A11.1-1965 (R-1970).
(b) Floor and wall openings, railings, and toeboards. American National Standard Safety Requirements for Floor and Wall Openings, Railings, and Toeboards, ANSI 12.1-1956.
(c) Identification of piping systems. American National Standard Scheme for the Identification of Piping Systems, ANSI A13.1-1956.
(d) Mechanical power transmission apparatus. American National Standard Safety Standard for Mechanical Power Transmission Apparatus, ANSI B15.1-1971.
(e) Pressure piping—Power piping. American National Standard Code for Pressure Piping—Power Piping, ANSI B31.1.0-1967. Addenda to the American National Standard Code for Pressure Piping—Power Piping, ANSI B31.1.0a-1969.
(f) Sanitation. American National Standard Requirements for Sanitation in Places of Employment, ANSI Z4.1-1968.
(g) Local exhaust systems. American National Standard Fundamentals Governing the Design and Operation of Local Exhaust Systems, ANSI Z9.2-1960.
(h) Gas appliances and gas piping. American National Standard for the Installation of Gas Appliances and Gas Piping, ANSI Z21.30-1964.
(3) WAC 296-24-012 and 296-800-360 ((shall)) must apply where applicable to this industry.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-18, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-303-01003 Definitions.
(((1) "Laundry" means an establishment wherein the washing, ironing, or other finishing of clothes, or any other textiles is done, but excluding printing, bleaching, dry cleaning, or dyeing of clothes or other textiles.
(2) "Marking machine" means a power-driven machine used for marking clothes or other textiles.
(3) "Washing machine" means a power-driven machine used for washing clothes or other textiles. It generally consists of a stationary case or shell inside of which is a revolving perforated cylinder.
(4) "Extractor" means a power-driven centrifugal machine used for removing surplus moisture from clothes or other textiles by centrifugal action.
(5) "Wringer" means one or more power-driven rolls used for removing surplus moisture from clothes or other textiles.
(6) "Starch mixer" means a power-driven machine used for mixing or processing starch.
(7) "Starching machine" means a power-driven machine used for the starching of clothes or other textiles.
(8) "Drying tumbler" means a machine within which clothes or other textiles are dried by air, and which usually consists of an enclosure inside of which is a revolving cylinder.
(9) "Shaker" (clothes tumbler) means a revolving cylinder used for shaking out clothes or other textiles.
(10) "Drying room" means an enclosure used for drying clothes or other textiles, and containing any power-driven mechanism.
(11) "Dampening machine" means a machine used for dampening clothes or other textiles.
(12) "Ironer" means a hand- or power-operated machine, with one or more rolls or heated surfaces in contact, used for ironing or smoothing clothes or other textiles.
(13) "Shaping machine" means a power-driven machine used to shape, mold, or otherwise finish clothes or other textiles; this term shall also include shaping tables, stands, or shelves upon which the machine may be mounted.
(14) "Sewing machine" means a machine used for sewing or stitching clothes or other textiles.
(15) "Guarded" means covered, shielded, fenced, enclosed, or otherwise protected by means of suitable covers or casings, barrier rails, safety bars, or screens, to eliminate the possibility of accidental contact with, or dangerous approach by, persons or objects.
(16) "Enclosed" means that the object or equipment or part thereof is so guarded that accidental contact at the point of danger, during the regular operation of the equipment, is not possible.
(17) "Safety interlock" means a device that will prevent the operation of the machine while the cover or door is open or unlocked and will hold the cover or door closed and locked while the basket or cylinder is in motion.
(18) "Moving parts" means gears, sprockets, revolving shafts, clutches, belts, pulleys, or other revolving or reciprocating parts that are attached to, or form an integral part of, a machine.
(19) "Power transmission" pertains to equipment such as shafting, gears, belts, pulleys, or other parts used for transmitting power to the machine, and shall include prime movers.
(20) "Prime movers" includes steam, gas, oil, and air engines or motors, and steam and hydraulic turbines.
(21) "Point of operation" means the point or points at which clothes or other textiles are inserted or manipulated in the operation of the machine.)) Dampening machine. A machine used for dampening clothes or other textiles.
Drying room. An enclosure used for drying clothes or other textiles, and containing any power-driven mechanism.
Drying tumbler. A machine within which clothes or other textiles are dried by air, and which usually consists of an enclosure inside of which is a revolving cylinder.
Enclosed. The object or equipment or part thereof is so guarded that accidental contact at the point of danger, during the regular operation of the equipment, is not possible.
Extractor. A power-driven centrifugal machine used for removing surplus moisture from clothes or other textiles by centrifugal action.
Guarded. Covered, shielded, fenced, enclosed, or otherwise protected by means of suitable covers or casings, barrier rails, safety bars, or screens, to eliminate the possibility of accidental contact with, or dangerous approach by, persons or objects.
Ironer. A hand- or power-operated machine, with one or more rolls or heated surfaces in contact, used for ironing or smoothing clothes or other textiles.
Laundry. An establishment wherein the washing, ironing, or other finishing of clothes, or any other textiles is done, but excluding printing, bleaching, dry cleaning, or dyeing of clothes or other textiles.
Marking machine. A power-driven machine used for marking clothes or other textiles.
Moving parts. Gears, sprockets, revolving shafts, clutches, belts, pulleys, or other revolving or reciprocating parts that are attached to, or form an integral part of, a machine.
Point of operation. The point or points at which clothes or other textiles are inserted or manipulated in the operation of the machine.
Power transmission. Pertains to equipment such as shafting, gears, belts, pulleys, or other parts used for transmitting power to the machine, and shall include prime movers.
Prime movers. Includes steam, gas, oil, and air engines or motors, and steam and hydraulic turbines.
Safety interlock. A device that will prevent the operation of the machine while the cover or door is open or unlocked and will hold the cover or door closed and locked while the basket or cylinder is in motion.
Sewing machine. A machine used for sewing or stitching clothes or other textiles.
Shaker (clothes tumbler). A revolving cylinder used for shaking out clothes or other textiles.
Shaping machine. A power-driven machine used to shape, mold, or otherwise finish clothes or other textiles; this term shall also include shaping tables, stands, or shelves upon which the machine may be mounted.
Starch mixer. A power-driven machine used for mixing or processing starch.
Starching machine. A power-driven machine used for the starching of clothes or other textiles.
Washing machine. A power-driven machine used for washing clothes or other textiles. It generally consists of a stationary case or shell inside of which is a revolving perforated cylinder.
Wringer. One or more power-driven rolls used for removing surplus moisture from clothes or other textiles.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-303-02001 Washroom machines.
(1) Marking machine. Each power marking machine ((shall)) must be equipped with a spring-compression device of such design as to prevent injury to fingers, should they be caught between the marking plunger and platen; or the marking machine ((shall)) must be equipped with a control mechanism that will require the simultaneous action of both hands to operate the machine; or there ((shall)) must be a guard that will act as a barrier in front of, and which will prevent the operator's fingers from coming into contact with the marking plunger.
(2) Washing machine.
(a) Each washing machine ((shall)) must be equipped with an interlocking device that will prevent the inside cylinder from moving under power when the outer door on the case or shell is open, and will also prevent the door from being opened while the inside cylinder is in motion. This device should not prevent the movement of the inner cylinder under the action of a hand-operated mechanism or under the operation of an "inching device."
(b) Each washing machine ((shall)) must be provided with means for holding open the doors or covers of inner and outer cylinders or shells while being loaded or unloaded. Spring loaded devices are an acceptable means.
(3) Extractor.
(a) Each extractor ((shall)) must be equipped with a metal cover.
(b) Each extractor ((shall)) must be equipped with an interlocking device that will prevent the cover from being opened while the basket is in motion, and will also prevent the power operation of the basket while the cover is not fully closed and secured. This device should not prevent the movement of the basket by hand to ensure an even loading.
(c) Each extractor ((shall)) must also be effectively secured in position on the floor or foundation so as to eliminate unnecessary vibrations, and ((shall)) must not be operated at a speed greater than that given in the manufacturer's rating, which ((shall)) must be stamped on the inside of the basket where it is easily visible, in letters not less than one-fourth inch in height. The maximum permissible speed ((shall)) must be given in revolutions per minute.
(d) Each engine individually driving an extractor ((shall)) must be provided with an approved engine stop and a speed-limit governor. It is suggested that where an extractor is driven by a direct-current motor a "no field" release be installed to prevent overspeed, which may result from an open or broken field.
(4) Power wringer. Each power wringer ((shall)) must be equipped with a safety bar or other guard across the entire front of the feed or first pressure rolls, so arranged that the striking of the bar or guard by the hand of the operator or other person will stop the machine.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-18, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-303-02003 Starching and drying machines.
(1) Starching machine (cylinder or box type). Each starching machine, cylinder or box type, ((shall)) must be enclosed or guarded so as to prevent the operator or other person from coming into accidental contact with the cylinder or box while the machine is in motion.
(2) Drying-room fan. Each drying-room fan, any part of which is within 7 feet of the floor or working platform, ((shall)) must be guarded with wire mesh or screen of not less than No. 16 gauge, the openings of which will reject a ball one-half inch in diameter.
(3) Drying tumbler.
(a) Each drying tumbler ((shall)) must be equipped with an interlocking device that will prevent the inside cylinder from moving under power when the outer door on the case or shell is open, and also prevent the door from being opened while the inside cylinder is in motion. This device should not prevent the movement of the inner cylinder under the action of a hand-operated mechanism or under the operation of an inching device.
(b) Each drying tumbler ((shall)) must be provided with means for holding open the doors or covers of inner and outer cylinders or shells while being loaded or unloaded.
(4) Shaker (clothes tumbler).
(a) Each shaker or clothes tumbler of the single-cylinder type ((shall)) must be equipped with a device that will automatically prevent the tumbler from moving while the door is open.
(b) The tumbler ((shall)) must also be enclosed or guarded so as to prevent accidental contact by the operator or other person while the machine is in motion.
(c) Each shaker or clothes tumbler of the double-cylinder type ((shall)) must be equipped with an interlocking device that will prevent the inside cylinder from moving when the outer door on the case or shell is open and will also prevent the door from being opened while the inside cylinder is in motion. This device should not prevent the movement of the inner cylinder under the action of a hand-operated mechanism or under the operation of an inching device.
(d) Each shaker or clothes tumbler of the double-cylinder type ((shall)) must be provided with means for holding open the doors or covers of inner and outer cylinders or shells while being loaded or unloaded.
(5) Exception. Provisions of (3), (4)(a), (c) and (d) of this section ((shall)) must not apply to shakeout or conditioning tumblers where the clothes are loaded into the open end of the revolving cylinder and are automatically discharged out of the opposite end.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-18, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-303-02005 Finishing machines.
(1) Dampening machine. Each roll-dampening machine ((shall)) must be so equipped that the rolls will be entirely enclosed and so arranged as to prevent the fingers of the operator or other person from being caught between the rolls. This may be accomplished by:
(a) A slot or hopper;
(b) A rod or strip located directly in front of the feed and extending the full length of the rolls.
(2) Ironer.
(a) Each flat-work or collar ironer ((shall)) must be equipped with a safety bar or other guard across the entire front of the feed or first pressure rolls, so arranged that the striking of the bar or guard by the hand of the operator or other person will stop the machine. The pressure rolls ((shall)) must be covered or guarded so that the operator or other person cannot reach into the rolls without removing the guard. This may be either a vertical guard on all sides or a complete cover. If a vertical guard is used, the distance from the floor or working platform to the top of guard ((shall be)) must not be less than six feet.
(b) Each body-type ironer, roll or shoe type, including sleeve and band ironers, ((shall)) must be equipped with a safety bar or other guard across the entire length of the feed roll or shoe, so arranged that the striking of the bar or guard by the hand of the operator or other person will stop the machine. The hot roll or shoe ((shall)) must also be covered in such a way that the operator or other person cannot come into contact with the heated surfaces.
(c) Each combined rotary-bosom and coat ironer ((shall)) must be equipped with a safety bar or other guard across the entire length of the feed roll or shoe, so arranged that the striking of the bar or guard by the hand of the operator or other person will stop the machine. The hot roll or shoe ((shall)) must also be covered in such a way that the operator or other person cannot come into contact with the heated surfaces.
(d) Each ironing press (excluding hand or foot powered ones) ((shall)) must be equipped with a guard or means that will prevent the fingers of the operator or other person from being caught between the ironing surfaces.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 89-11-035, filed 5/15/89, effective 6/30/89)
WAC 296-303-02007 Miscellaneous machines and equipment.
(1) Sewing machine. Each sewing machine ((shall)) must be equipped with a guard permanently attached to the machine, so that the operator's fingers cannot pass under the needle. It ((shall)) must be of such form that the needle can be conveniently threaded without removing the guard. This requirement will not apply to domestic-type sewing machines having a presser-foot which is in the "down" position during operation of the machine.
(2) Exhaust or ventilating fans. Each exhaust or ventilating fan within seven feet of the floor or working platform ((shall)) must be completely covered with wire mesh of not less than No. 16 gauge, and with openings that will reject a ball one-half inch in diameter.
(3) Steam pipes.
(a) All steam pipes that are within seven feet of the floor or working platform, and with which the worker may come into contact, ((shall)) must be insulated or covered with a heat-resistive material or ((shall)) must be guarded to prevent direct contact with the worker.
(b) Where pressure-reducing valves are used, one or more relief or safety valves ((shall)) must be provided on the low-pressure side of the reducing valve, in case the piping or equipment on the low-pressure side does not meet the requirements for full initial pressure. The relief or safety valve ((shall)) must be located adjacent to, or as close as possible to, the reducing valve. Relief and safety valves vented to the atmosphere ((shall)) must be so constructed as to prevent injury or damage caused by fluid escaping from relief or safety valves. The vents ((shall)) must be of ample size and as short and direct as possible. The combined discharge capacity of the relief valves ((shall)) must be such that the pressure rating of the lower-pressure piping and equipment will not be exceeded if the reducing valve sticks or fails to open.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-18, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-303-02501 General.
(1) Floors.
(a) The floors of every room in a laundry that are used for washing purposes ((shall)) must be properly constructed of cement, tile, or similar material. The floors ((shall)) must be watertight, free from projections, crevices, or dangerous gradients. They ((shall)) must be maintained in good repair and ((so)) drained so that no water may accumulate.
(b) The floors of every room except washrooms ((shall)) must be constructed of hardwood or any impervious material, free from protruding nails, splinters, or loose boards, and ((shall)) must be so maintained.
(2) Table tops, shelves, and machine woodwork. Table tops, shelves, and machine woodwork ((shall)) must be constructed of materials properly surfaced, finished free from splinters, and so maintained.
(3) Markers. Markers and others handling soiled clothes ((shall)) must be warned against touching the eyes, mouth, or any part of the body on which the skin has been broken by a scratch or abrasion; and they ((shall)) must be cautioned not to touch or eat food until their hands have been thoroughly washed.
(4) Ventilation. Where artificial ventilation is necessary to the maintenance of comfortable working conditions, an adequate ventilating system ((shall)) must be installed as specified in ((WAC 296-62-110)) chapter 296-62 WAC, Part L of the general occupational health standards.
(5) Instruction of employees. Employees ((shall)) must be properly instructed as to the hazards of their work and be instructed in safe practices, by bulletins, printed rules, and verbal instructions.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-18, filed 5/6/74)
WAC 296-303-02503 Mechanical.
(1) Safety guards.
(a) No safeguard, safety appliance, or device attached to, or forming an integral part of any machinery ((shall)) must be removed or made ineffective except for the purpose of making immediate repairs or adjustments. Any such safeguard, safety appliance, or device removed or made ineffective during the repair or adjustment of such machinery ((shall)) must be replaced immediately upon the completion of such repairs or adjustments.
(b) No machine ((shall)) must be operated until such repairs and adjustments have been made and the machine is in good working condition.
(2) Steam-pressure apparatus. Steam machines ((shall)) must not be operated at a pressure above that given by the manufacturer's pressure rating as shown on name plate. If the steam source is at a pressure higher than that given by the manufacturer's rating, a stop valve, reducing valve, pressure gauge, and safety valve ((shall)) must be installed, in the order named, from the source. The safety valve ((shall)) must be located in a nonhazardous place.
(3) Machine adjustments. No moving parts of any machine ((shall)) must be oiled, cleaned, adjusted, or repaired while said machine is in operation or in motion except that the rolls of adjusting machines not equipped with hand-power means ((shall)) must be operated at the slowest speed possible with an operator constantly at the starting mechanism.
(4) Extractors. Each extractor ((shall)) must be dismantled and inspected at least once a year and, if necessary, repaired. Overdriven extractors, if provided with handholes through which basket and rings can be inspected, need not be dismantled.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-14-028, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05)
WAC 296-303-030 Moving parts.
(1) Machine guarding (other than point of operation). Moving parts of machines, such as gears, sprockets, belts, pulleys, and shafts, ((shall)) must be guarded in accordance with the requirements of chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
(2) Prime-mover guarding. Moving parts of prime movers such as fly-wheels, cranks and connecting rods, tail rods or extension piston rods, and governor balls, ((shall)) must be guarded in accordance with the requirements of chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 89-11-035, filed 5/15/89, effective 6/30/89)
WAC 296-303-040 Starting and stopping devices.
(1) Each power-driven machine ((shall)) must be provided with means for disconnecting from the source of power. Starting and stopping devices for machines ((shall)) must be ((so)) located so as to be operable from the front of the machine, and ((so)) constructed ((as)) to allow proper guarding of belts and pulleys.
(2) Doors of washing machines, extractors, and tumbler/shaker dryer machines, ((shall)) must have a cut-off micro switch or other method to shut off power when loading doors are opened, making inner cylinder, tumbler, or shaker mechanisms inoperative while the door is open. In those situations where the cylinder or mechanism continues to rotate/move, and present a hazard after the power is off, an interlocking device, breaking switch, or a time-delay switch is additionally required to prevent injury.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-304-01001 Definitions.
(("))Additional safety measure((" -)). A component of the tags-plus system that provides an impediment (in addition to the energy-isolating device) to the release of energy or the generalization or start-up of the machinery, equipment, or system being serviced. Examples of additional safety measures include, but are not limited to, removing an isolating circuit element; blocking a controlling switch; blocking, blanking, or bleeding lines; removing a valve handle or wiring it in place; opening an extra disconnecting device.
(("))Affected employee((" -)). An employee who normally operates or uses the machinery, equipment, or system that is going to be serviced under lockout/tags-plus or who is working in the area where servicing is being performed under lockout/tags-plus. An affected employee becomes an authorized employee when the employer assigns the employee to service any machine, equipment, or system under a lockout/tags-plus application.
(("))Alarm((" -)). A signal or message from a person or device that indicates that there is a fire, medical emergency, or other situation that requires emergency response or evacuation. At some shipyards, this may be called an "incident" or a "call for service."
(("))Alarm system((" -)). A system that warns employees at the worksite of danger.
(("))Anchorage((" -)). A secure point to attach lifelines, lanyards, or deceleration devices.
(("))Authorized employee((")):
(1) An employee who performs one or more of the following lockout/tags-plus responsibilities:
(a) Executes the lockout/tags-plus procedures;
(b) Installs a lock or tags-plus system on machinery, equipment, or systems; or
(c) Services any machine, equipment, or system under lockout/tags-plus application.
(2) An affected employee becomes an authorized employee when the employer assigns the employee to service any machine, equipment, or system under a lockout/tags-plus application.
(("))Body belt((" -)). A strap with means to both secure it around the waist and to attach it to a lanyard, lifeline, or deceleration device. Body belts may be used only in fall restraint or positioning device systems and may not be used for fall arrest. Body belts must be at least one and five-eighths inches (4.13 cm) wide.
(("))Body harness((" -)). Straps to secure around an employee so that fall arrest forces are distributed over at least the thighs, shoulders, chest and pelvis with means to attach it to other components of a personal fall arrest system.
(("))Capable of being locked out((" -)). An energy-isolating device is capable of being locked out if it has a locking mechanism built into it, or it has a hasp or other means of attachment to which, or through which, a lock can be affixed. Other energy-isolating devices are capable of being locked out if lockout can be achieved without the need to dismantle, rebuild, or replace the energy-isolating device or permanently alter its energy-control capability.
(("))Class II standpipe system((" -)). A one and one-half inch (3.8 cm) hose system which provides a means for the control or extinguishment of incipient stage fires.
(("))Cold work((" -)). Work that does not involve riveting, welding, burning, or other fire-producing or spark-producing operations.
(("))Contract employer((" -)). An employer, such as a painter, joiner, carpenter, or scaffolding subcontractor, who performs work under contract to the host employer or to another employer under contract to the host employer at the host employer's worksite. This excludes employers who provide incidental services that are not directly related to shipyard employment (such as mail delivery or office supply and food vending services).
(("))Competent person((" -)). A person who can recognize and evaluate employee exposure to hazardous substances or to other unsafe conditions and can specify the necessary protection and precautions necessary to ensure the safety of employees as required by these standards.
(("))Confined space((" -)). A small compartment with limited access such as a double bottom tank, cofferdam, or other small, confined space that can readily create or aggravate a hazardous exposure.
(("))Connector((" -)). A device used to connect parts of a personal fall arrest system or parts of a positioning device system together. It may be:
((•)) (a) An independent component of the system (such as a carabiner); or
((•)) (b) An integral component of part of the system (such as a buckle or D-ring sewn into a body belt or body harness or a snaphook spliced or sewn to a lanyard or self-retracting lanyard).
(("))Dangerous atmosphere((" -)). An atmosphere that may expose employees to the risk of death, incapacitation, injury, acute illness, or impairment of ability to self-rescue (i.e., escape unaided from a confined or enclosed space).
(("))Deceleration device((" -)). A mechanism, such as a rope grab, rip stitch lanyard, specially woven lanyard, tearing or deforming lanyard, or automatic self-retracting lifeline/lanyard, that serves to dissipate a substantial amount of energy during a fall arrest, or to limit the energy imposed on an employee during fall arrest.
(("))Deceleration distance((" -)). The additional vertical distance a falling employee travels, excluding lifeline elongation and free fall distance, before stopping, from the point at which the deceleration device begins to operate. It is measured from the location of an employee's body belt or body harness attachment point at the moment of activation (at the onset of fall arrest forces) of the deceleration device during a fall, to the location of that attachment point after the employee comes to a full stop.
(("))Designated area((" -)). An area established for hot work after an inspection that is free of fire hazards.
(("))Director((" -)). The director of the department of labor and industries or a designated representative.
(("))Drop test((" -)). A method utilizing gauges to ensure the integrity of an oxygen fuel gas burning system. The method requires that the burning torch is installed to one end of the oxygen and fuel gas lines and then the gauges are attached to the other end of the hoses. The manifold or cylinder supply valve is opened and the system is pressurized. The manifold or cylinder supply valve is then closed and the gauges are watched for at least sixty seconds. Any drop in pressure indicates a leak.
(("))Dummy load((" -)). A device used in place of an antenna to aid in the testing of a radio transmitter that converts transmitted energy into heat to minimize energy radiating outward or reflecting back to its source during testing.
(("))Emergency operations((" -)). Activities performed by fire response organizations that are related to: Rescue, fire suppression, emergency medical care, and special operations or activities that include responding to the scene of an incident and all activities performed at that scene.
(("))Employee((" -)). Any person engaged in ship repairing, ship building, or ship breaking or related employment as defined in these standards.
(("))Employer((" -)). An employer with employees who are employed, in whole or in part, in ship repair, ship building and ship breaking, or related employment as defined in these standards.
(("))Enclosed space((" -)). A space, other than a confined space, that is enclosed by bulkheads and overhead. It includes cargo holds, tanks, quarters, and machinery and boiler spaces.
(("))Energy-isolating device((" -)). A mechanical device that, when utilized or activated, physically prevents the release or transmission of energy. Energy-isolating devices include, but are not limited to, manually operated electrical circuit breakers; disconnect switches; line valves; blocks; and any similar device used to block or isolate energy. Control-circuit devices (for example, push buttons, selector switches) are not considered energy isolating devices.
(("))Equivalent((" -)). Alternative designs, materials, or methods to protect against a hazard which the employer can demonstrate will provide an equal or greater degree of safety for employees than the method or item specified in the standard.
(("))Fire hazard((" -)). A condition or material that may start or contribute to the spread of fire.
(("))Fire protection((" -)). Methods of providing fire prevention, response, detection, control, extinguishment, and engineering.
(("))Fire response((" -)). The activity taken by the employer at the time of an emergency incident involving a fire at the worksite, including fire suppression activities carried out by internal or external resources or a combination of both, or total or partial employee evacuation of the area exposed to the fire.
(("))Fire response employee((" -)). A shipyard employee who carries out the duties and responsibilities of shipyard firefighting in accordance with the fire safety plan.
(("))Fire response organization((" -)). An organized group knowledgeable, trained, and skilled in shipyard firefighting operations that responds to shipyard fire emergencies, including: Fire brigades, shipyard fire departments, private or contractual fire departments, and municipal fire departments.
(("))Fire suppression((" -)). The activities involved in controlling and extinguishing fires.
(("))Fire watch((" -)). The activity of observing and responding to the fire hazards associated with hot work in shipyard employment and the employees designated to do so.
(("))Fixed extinguishing system((" -)). A permanently installed fire protection system that either extinguishes or controls fire occurring in the space it protects.
(("))Flammable liquid((" -)). Means any liquid having a flashpoint at or below 199.4°F (93°C). Flammable liquids are divided into four categories as follows:
(a) Category 1 shall include liquids having flashpoints below 73.4°F (23°C) and having a boiling point at or below 95°F (35°C).
(b) Category 2 shall include liquids having flashpoints below 73.4°F (23°C) and having a boiling point above 95°F (35°C).
(c) Category 3 shall include liquids having flashpoints at or above 73.4°F (23°C) and at or below 140°F (60°C). When a Category 3 liquid with a flashpoint at or above 100°F (37.8°C) is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it shall be handled in accordance with the requirements for a Category 3 liquid with a flashpoint below 100°F (37.8°C).
(d) Category 4 shall include liquids having flashpoints above 140°F (60°C) and at or below 199.4°F (93°C). When a Category 4 flammable liquid is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it shall be handled in accordance with the requirements for a Category 3 liquid with a flashpoint at or above 100°F (37.8°C).
(e) When liquid with a flashpoint greater than 199.4°F (93°C) is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it shall be handled in accordance with the requirements for a Category 4 flammable liquid.
(("))Free fall((" -)). To fall before a personal fall arrest system begins to apply force to arrest the fall.
(("))Free fall distance((" -)). The vertical displacement of the fall arrest attachment point on the employee's body harness between onset of the fall and just before the system begins to apply force to arrest the fall. This distance excludes deceleration distance, and lifeline/lanyard elongation, but includes any deceleration device slide distance or self-retracting lifeline/lanyard extension before the device operates and fall arrest forces occur.
(("))Gangway((" -)). A ramp-like or stair-like means to board or leave a vessel including accommodation ladders, gangplanks and brows.
(("))Hazardous energy((" -)). Any energy source, including mechanical (for example, power transmission apparatus, counterbalances, springs, pressure, gravity), pneumatic, hydraulic, electrical, chemical, and thermal (for example, high or low temperature) energies, that could cause injury to employees.
(("))Hazardous substance((" -)). A substance likely to cause injury, illness or disease, or otherwise harm an employee because it is explosive, flammable, poisonous, corrosive, oxidizing, irritating, or otherwise harmful.
(("))Health care professional((" -)). A physician or any other health care professional whose legally permitted scope of practice allows the provider to independently provide, or be delegated the responsibility to provide, some or all of the advice or consultation this subpart requires.
(("))Hose systems((" -)). Fire protection systems consisting of a water supply, approved fire hose, and a means to control the flow of water at the output end of the hose.
(("))Host employer((" -)). An employer who is in charge of coordinating work or who hires other employers to perform work at a multiemployer workplace.
(("))Hot work((" -)). Riveting, welding, burning or other fire or spark producing operations.
(("))Incident management system((" -)). A system that defines the roles and responsibilities to be assumed by personnel and the operating procedures to be used in the management and direction of emergency operations; the system is also referred to as an "incident command system (ICS)."
(("))Incipient stage fire((" -)). A fire, in the initial or beginning stage, which can be controlled or extinguished by portable fire extinguishers, Class II standpipe or small hose systems without the need for protective clothing or breathing apparatus.
(("))Inerting((" -)). The displacement of the atmosphere in a permit space by noncombustible gas (such as nitrogen) to such an extent that the resulting atmosphere is noncombustible. This procedure produces an IDLH oxygen-deficient atmosphere.
(("))Interior structural firefighting operations((" -)). The physical activity of fire response, rescue, or both involving a fire beyond the incipient stage inside of buildings, enclosed structures, vessels, and vessel sections.
(("))Isolated location((" -)). An area in which employees are working alone or with little assistance from others due to the type, time, or location of their work. Such locations include remote locations or other work areas where employees are not in close proximity to others.
(("))Lanyard((" -)). A flexible line of rope, wire rope, or strap which generally has a connector at each end for connecting the body belt or body harness to a deceleration device, lifeline, or anchorage.
(("))Lifeline((" -)). A component consisting of a flexible line to connect to an anchorage at one end to hang vertically (vertical lifeline), or to connect to anchorages at both ends to stretch horizontally (horizontal lifeline), and which serves as a means for connecting other components of a personal fall arrest system to the anchorage.
(("))Lock((" -)). A device that utilizes a positive means, either a key or combination lock, to hold an energy isolating device in a "safe" position that prevents the release of energy and the start-up or energization of the machinery, equipment, or system to be serviced.
(("))Lockout((" -)). The placement of a lock on an energy-isolating device in accordance with an established procedure, thereby ensuring that the energy-isolating device and the equipment being controlled cannot be operated until the lock is removed.
(("))Lockout/tags-plus coordinator((" -)). An employee whom the employer designates to coordinate and oversee all lockout and tags-plus applications on vessels or vessel sections and at landside work areas when employees are performing multiple servicing operations on the same machinery, equipment, or systems at the same time, and when employees are servicing multiple machinery, equipment, or systems on the same vessel or vessel section at the same time. The lockout/tags-plus coordinator also maintains the lockout/tags-plus log.
(("))Lockout/tags-plus materials and hardware((" -)). Locks, chains, wedges, blanks, key blocks, adapter pins, self-locking fasteners, or other hardware used for isolating, blocking, or securing machinery, equipment, or systems to prevent the release of energy or the start-up or energization of machinery, equipment, or systems to be serviced.
(("))Lower levels((" -)). Those areas or surfaces to which an employee can fall. Such areas or surfaces include but are not limited to ground levels, floors, ramps, tanks, materials, water, excavations, pits, vessels, structures, or portions thereof.
(("))Motor vehicle((" -)). Any motor-driven vehicle operated by an employee that is used to transport employees, material, or property. For the purposes of this subpart, motor vehicles include passenger cars, light trucks, vans, motorcycles, all-terrain vehicles, small utility trucks, powered industrial trucks, and other similar vehicles. Motor vehicles do not include boats, or vehicles operated exclusively on a rail or rails.
(("))Motor vehicle safety equipment((" -)). Systems and devices integral to or installed on a motor vehicle for the purpose of effecting the safe operation of the vehicle, and consisting of such systems or devices as safety belts, airbags, headlights, tail lights, emergency/hazard lights, windshield wipers, defogging or defrosting devices, brakes, horns, mirrors, windshields and other windows, and locks.
(("))Multiemployer workplace((" -)). A workplace where there is a host employer and at least one contract employer.
(("))Normal production operations((" -)). The use of machinery or equipment, including, but not limited to, punch presses, bending presses, shears, lathes, keel press rollers, and automated burning machines, to perform a shipyard-employment production process.
(("))Personal alert safety system (PASS)((" -)). A device that sounds a loud signal if the wearer becomes immobilized or is motionless for thirty seconds or more.
(("))Personal fall arrest system((" -)). A system used to arrest an employee in a fall from a working level. It consists of an anchorage, connectors, body harness and may include a lanyard, a deceleration device, a lifeline, or a suitable combination.
(("))Physical isolation((" -)). The elimination of a fire hazard by removing the hazard from the work area (at least thirty-five feet for combustibles), by covering or shielding the hazard with a fire-resistant material, or physically preventing the hazard from entering the work area.
(("))Physically isolated((" -)). Positive isolation of the supply from the distribution piping of a fixed extinguishing system. Examples of ways to physically isolate include: Removing a spool piece and installing a blank flange; providing a double block and bleed valve system; or completely disconnecting valves and piping from all cylinders or other pressure vessels containing extinguishing agents.
(("))Portable toilet((" -)). A nonsewered portable facility for collecting and containing urine and feces. A portable toilet may be either flushable or nonflushable. For purposes of this section, portable toilets do not include privies.
(("))Portable unfired pressure vessel((" -)). A pressure container or vessel used aboard ship, other than the ship's equipment, containing liquids or gases under pressure. This does not include pressure vessels built to Department of Transportation regulations under 49 C.F.R. Part 178, Subparts C and H.
(("))Positioning device system((" -)). A body belt or body harness system rigged to allow an employee to be supported at an elevated vertical surface, such as a wall or window, and to be able to work with both hands free while leaning.
(("))Potable water((" -)). Water that meets the standards for drinking purposes of the state or local authority having jurisdiction, or water that meets the quality standards prescribed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's National Primary Water Regulations (40 C.F.R. part 141).
(("))Powder actuated fastening tool((" -)). A tool or machine that drives a stud, pin, or fastener by means of an explosive charge.
(("))Protected space((" -)). Any space into which a fixed extinguishing system can discharge.
(("))Proximity firefighting((" -)). Specialized firefighting operations that require specialized thermal protection and may include the activities of rescue, fire suppression, and property conservation at incidents involving fires producing very high levels of conductive, convective, and radiant heat such as aircraft fires, bulk flammable gas fires, and bulk flammable liquid fires. Proximity firefighting operations usually are exterior operations but may be combined with structural firefighting operations. Proximity firefighting is not entry firefighting.
(("))Qualified instructor((" -)). A person with specific knowledge, training, and experience in fire response or fire watch activities to cover the material found in WAC 296-304-01019 (2) or (3).
(("))Qualified person((" -)). A person who has successfully demonstrated the ability to solve or resolve problems related to the subject matter and work by possessing a recognized degree or certificate of professional standing or by extensive knowledge, training, and experience.
(("))Readily accessible/available((" -)). Capable of being reached quickly enough to ensure, for example, that emergency medical services and first-aid intervention are appropriate or that employees can reach sanitation facilities in time to meet their health and personal needs.
(("))Related employment((" -)). Any employment related to or performed in conjunction with ship repairing, ship building or ship breaking work, including, but not limited to, inspecting, testing, and serving as a watchman.
(("))Rescue((" -)). Locating endangered persons at an emergency incident, removing those persons from danger, treating the injured, and transporting the injured to an appropriate health care facility.
(("))Restraint (tether) line((" -)). A line from an anchorage, or between anchorages, to which the employee is secured so as to prevent the employee from walking or falling off an elevated work surface.
Note: | A restraint line is not necessarily designed to withstand forces resulting from a fall. |
(("))Rope grab((" -)). A deceleration device that travels on a lifeline and automatically, by friction, engages the lifeline and locks to arrest the fall of an employee. A rope grab usually uses the principle of inertial locking, cam/level locking or both.
(("))Sanitation facilities((" -)). Facilities, including supplies, maintained for employee personal and health needs such as potable drinking water, toilet facilities, hand-washing and hand-drying facilities, showers (including quick-drenching or flushing) and changing rooms, eating and drinking areas, first-aid stations, and on-site medical-service areas. Sanitation supplies include soap, waterless cleaning agents, single-use drinking cups, drinking water containers, toilet paper, and towels.
(("))Serviceable condition((" -)). The state or ability of supplies or goods, or of a tool, machine, vehicle, or other device, to be used or to operate in the manner prescribed by the manufacturer.
(("))Servicing((" -)). Workplace activities that involve the construction, installation, adjustment, inspection, modification, testing, or repair of machinery, equipment, or systems. Servicing also includes maintaining machines, equipment, or systems when performing these activities would expose the employee to harm from the start-up or energization of the system being serviced, or the release of hazardous energy.
(("))Sewered toilet((" -)). A fixture maintained for the purpose of urination and defecation that is connected to a sanitary sewer, septic tank, holding tank (bilge), or on-site sewage-disposal treatment facility, and that is flushed with water.
(("))Shall((")) or (("))must((" -)). Mandatory.
(("))Shield((" -)). To install a covering, protective layer, or other effective measure on or around steam hoses or temporary steam-piping systems, including metal fittings and couplings, to protect employees from contacting hot surfaces or elements.
(("))Ship breaking((" -)). Breaking down a vessel's structure to scrap the vessel, including the removal of gear, equipment or any component part of a vessel.
(("))Ship building((" -)). Construction of a vessel, including the installation of machinery and equipment.
(("))Ship repairing((" -)). Repair of a vessel including, but not limited to, alterations, conversions, installations, cleaning, painting, and maintenance.
(("))Shipyard firefighting((" -)). The activity of rescue, fire suppression, and property conservation involving buildings, enclosed structures, vehicles, vessels, aircraft, or similar properties involved in a fire or emergency situation.
(("))Short bight((" -)). A loop created in a line or rope that is used to tie back or fasten objects such as hoses, wiring, and fittings.
(("))Small hose system((" -)). A system of hoses ranging in diameter from 5/8" (1.6 cm) up to 1 1/2" (3.8 cm) which is for the use of employees and which provides a means for the control and extinguishment of incipient stage fires.
(("))Standpipe((" -)). A fixed fire protection system consisting of piping and hose connections used to supply water to approved hose lines or sprinkler systems. The hose may or may not be connected to the system.
(("))Tag((" -)). A prominent warning device that includes a means of attachment that can be securely fastened to an energy-isolating device in accordance with an established procedure to indicate that the energy-isolating device and the equipment being controlled must not be operated until the tag is removed by an authorized employee.
(("))Tags-plus system((" -)). A system to control hazardous energy that consists of an energy-isolating device with a tag affixed to it, and at least one additional safety measure.
(("))Verification of isolation((" -)). The means necessary to detect the presence of hazardous energy, which may involve the use of a test instrument (for example, a voltmeter), and, for other than electric shock protection, a visual inspection, or a deliberate attempt to start-up the machinery, equipment, or system.
(("))Vermin((" -)). Insects, birds, and other animals, such as rodents, that may create safety and health hazards for employees.
(("))Vessel((" -)). Every watercraft for use as a means of transportation on water, including special purpose floating structures not primarily designed for or used as a means of transportation on water.
(("))Vessel section((" -)). A subassembly, module, or other component of a vessel being built or repaired.
(("))Walkway((" -)). Any surface, whether vertical, slanted, or horizontal, on which employees walk, including areas that employees pass through, to perform their job tasks. Walkways include, but are not limited to, access ways, designated walkways, aisles, exits, gangways, ladders, ramps, stairs, steps, passageways, and scaffolding. If an area is, or could be, used to gain access to other locations, it is to be considered a walkway.
(("))Work area((" -)). A specific area, such as a machine shop, engineering space, or fabrication area, where one or more employees are performing job tasks.
(("))Working surface((" -)). Any surface where work is occurring, or areas where tools, materials, and equipment are being staged for performing work.
(("))Worksite((" -)). A general work location where one or more employees are performing work, such as a shipyard, pier, barge, vessel, or vessel section.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-08-003, filed 3/23/06, effective 4/23/06)
WAC 296-304-01006 Fire protection in shipyards.
(1) Purpose. The purpose of this section is to require ((employers)) you to protect all employees from fire hazards in shipyard employment, including employees engaged in fire response activities.
(2) Scope. This section covers employers with employees engaged in shipyard employment aboard vessels and vessel sections, and on land-side operations regardless of geographic location.
(3) Employee participation. ((The employer)) You must provide ways for employees or employee representatives, or both to participate in developing and periodically reviewing programs and policies adopted to comply with this section.
(4) Multiemployer worksites.
(a) Host employer responsibilities. The host employer's responsibilities are to:
(i) Inform all employers at the worksite about the content of the fire safety plan including hazards, controls, fire safety and health rules, and emergency procedures;
(ii) Make sure the safety and health responsibilities for fire protection are assigned as appropriate to other employers at the worksite; and
(iii) If there is more than one host employer, each host employer must communicate relevant information about fire-related hazards to other host employers. When a vessel owner or operator (temporarily) becomes a host shipyard employer by directing the work of ships' crews on repair or modification of the vessel or by hiring other contractors directly, the vessel owner or operator must also comply with these provisions for host employers.
(b) Contract employer responsibilities. The contract employer's responsibilities are to:
(i) Make sure that the host employer knows about the fire-related hazards associated with the contract employer's work and what the contract employer is doing to address them; and
(ii) Advise the host employer of any previously unidentified fire-related hazards that the contract employer identifies at the worksite.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-17-034, filed 8/7/07, effective 12/1/07)
WAC 296-304-01007 Fire safety plan.
(1) Employer responsibilities. ((The employer)) You must develop and implement a written fire safety plan that covers all the actions that employers and employees must take to ensure employee safety in the event of a fire. (See Appendix A to this section for a model fire safety plan.)
(2) Plan elements. ((The employer)) You must include the following information in the fire safety plan:
(a) Identification of the significant fire hazards;
(b) Procedures for recognizing and reporting unsafe conditions;
(c) Alarm procedures;
(d) Procedures for notifying employees of a fire emergency;
(e) Procedures for notifying fire response organizations of a fire emergency;
(f) Procedures for evacuation;
(g) Procedures to account for all employees after an evacuation; and
(h) Names, job titles, or departments for individuals who can be contacted for further information about the plan.
(3) Reviewing the plan with employees. ((The employer)) You must review the plan with each employee at the following times:
(a) By March 1, 2006, for employees who are currently working;
(b) Upon initial assignment for new employees; and
(c) When the actions the employee must take under the plan change because of a change in duties or a change in the plan.
(4) Additional employer requirements. ((The employer also)) You must also:
(a) Keep the plan accessible to employees, employee representatives, and WISHA;
(b) Review and update the plan whenever necessary, but at least annually;
(c) Document that affected employees have been informed about the plan as required by this subsection; and
(d) Ensure any outside fire response organization that the employer expects to respond to fires at the employer's worksite has been given a copy of the current plan.
(5) Contract employers. Contract employers in shipyard employment must have a fire safety plan for their employees, and this plan must comply with the host employer's fire safety plan.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-304-01009 Precautions for hot work.
(1) General requirements.
(a) Designated areas. ((The employer)) You may designate areas for hot work in sites such as vessels, vessel sections, fabricating shops, and subassembly areas that are free of fire hazards.
(b) Nondesignated areas.
(i) Before authorizing hot work in a nondesignated area, ((the employer)) you must visually inspect the area where hot work is to be performed, including adjacent spaces, to ensure the area is free of fire hazards, unless a marine chemist's certificate or shipyard competent person's log is used for authorization.
(ii) ((The employer shall)) You must authorize employees to perform hot work only in areas that are free of fire hazards, or that have been controlled by physical isolation, fire watches, or other positive means.
Note: | The requirements of (b) of this subsection apply to all hot work operations in shipyard employment except those covered by WAC 296-304-02007. |
(2) Specific requirements.
(a) Maintaining fire hazard-free conditions. ((The employer)) You must keep all hot work areas free of new hazards that may cause or contribute to the spread of fire. Unexpected energizing and energy release are covered by WAC 296-304-120. Exposure to toxic and hazardous substances is covered in chapter 296-841 WAC, Airborne contaminants; chapter 296-802 WAC, Employee medical and exposure records; and WAC 296-901-140, Hazard communication.
(b) Fuel gas and oxygen supply lines and torches. ((The employer)) You must make sure that:
(i) No unattended fuel gas and oxygen hose lines or torches are in confined spaces;
(ii) No unattended charged fuel gas and oxygen hose lines or torches are in enclosed spaces for more than fifteen minutes;
(iii) All fuel gas and oxygen hose lines are disconnected at the supply manifold at the end of each shift; and
(iv) All disconnected fuel gas and oxygen hose lines are rolled back to the supply manifold or to open air to disconnect the torch; or extended fuel gas and oxygen hose lines are not reconnected at the supply manifold unless the lines are given a positive means of identification when they were first connected and the lines are tested using a drop test or other positive means to ensure the integrity of fuel gas and oxygen burning system.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-19-086, filed 9/20/05, effective 12/1/05)
WAC 296-304-01011 Fire watches.
(1) Written fire watch policy. ((The employer)) You must create and keep current a written policy that specifies the following requirements for employees performing fire watch in the workplace:
(a) The training employees must be given (WAC 296-304-01019(3) contains detailed fire watch training requirements);
(b) The duties employees are to perform;
(c) The equipment employees must be given; and
(d) The personal protective equipment (PPE) that must be made available and worn as required by WAC 296-304-090.
(2) Posting fire watches. ((The employer)) You must post a fire watch if during hot work any of the following conditions are present:
(a) Slag, weld splatter, or sparks might pass through an opening and cause a fire;
(b) Fire-resistant guards or curtains are not used to prevent ignition of combustible materials on or near decks, bulkheads, partitions, or overheads;
(c) Combustible material closer than thirty-five feet (10.7 m) to the hot work in either the horizontal or vertical direction cannot be removed, protected with flame-proof covers, or otherwise shielded with metal or fire-resistant guards or curtains;
(d) The hot work is carried out on or near insulation, combustible coatings, or sandwich-type construction that cannot be shielded, cut back, or removed, or in a space within a sandwich-type construction that cannot be inerted;
(e) Combustible materials adjacent to the opposite sides of bulkheads, decks, overheads, metal partitions, or sandwich-type construction may be ignited by conduction or radiation;
(f) The hot work is close enough to cause ignition through heat radiation or conduction on the following:
(i) Insulated pipes, bulkheads, decks, partitions, or overheads; or
(ii) Combustible materials and/or coatings;
(g) The work is close enough to unprotected combustible pipe or cable runs to cause ignition; or
(h) A marine chemist, a Coast Guard-authorized person, or a shipyard competent person, as defined in WAC 296-304-020, requires that a fire watch be posted.
(3) Assigning employees to fire watch duty.
(a) ((The employer)) You must not assign other duties to a fire watch while the hot work is in progress.
(b) ((Employers)) You must ensure that employees assigned to fire watch duty:
(i) Have a clear view of and immediate access to all areas included in the fire watch;
(ii) Are able to communicate with workers exposed to hot work;
(iii) Are authorized to stop work if necessary and restore safe conditions within the hot work area;
(iv) Remain in the hot work area for at least thirty minutes after completion of the hot work, unless the employer or its representative surveys the exposed area and makes a determination that there is no further fire hazard;
(v) Are trained to detect fires that occur in areas exposed to the hot work;
(vi) Attempt to extinguish any incipient stage fires in the hot work area that are within the capability of available equipment and within the fire watch's training qualifications, as defined in WAC 296-304-01019;
(vii) Alert employees of any fire beyond the incipient stage; and
(viii) If unable to extinguish fire in the areas exposed to the hot work, activate the alarm.
(c) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees assigned to fire watch are physically capable of performing these duties.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-17-034, filed 8/7/07, effective 12/1/07)
WAC 296-304-01013 Fire response.
(1) Employer responsibilities. ((The employer)) You must:
(a) Decide what type of response will be provided and who will provide it; and
(b) Create, maintain, and update a written policy that:
(i) Describes the internal and outside fire response organizations that ((the employer)) you will use; and
(ii) Defines what evacuation procedures employees must follow, if ((the employer)) you choose((s)) to require a total or partial evacuation of the worksite at the time of a fire.
(2) Required written policy information.
(a) Internal fire response. If an internal fire response is to be used, ((the employer)) you must include the following information in ((the employer's)) your written policy:
(i) The basic structure of the fire response organization;
(ii) The number of trained fire response employees;
(iii) The fire response functions that may need to be carried out;
(iv) The minimum number of fire response employees necessary, the number and types of apparatuses, and a description of the fire suppression operations established by written standard operating procedures for each type of fire response at the employer's facility;
(v) The type, amount, and frequency of training that must be given to fire response employees; and
(vi) The procedures for using protective clothing and equipment.
(b) Outside fire response. If an outside fire response organization is used, ((the employer)) you must include the following information in the written policy:
(i) The types of fire suppression incidents to which the fire response organization is expected to respond at ((the employer's)) your facility or worksite;
(ii) The liaisons between ((the employer)) you and the outside fire response organizations; and
(iii) A plan for fire response functions that:
(A) Addresses procedures for obtaining assistance from the outside fire response organization;
(B) Familiarizes the outside fire response organization with the layout of ((the employer's)) your facility or worksite, including access routes to controlled areas, and site-specific operations, occupancies, vessels or vessel sections, and hazards; and
(C) Sets forth how hose and coupling connection threads are to be made compatible and includes where the adapter couplings are kept; or
(D) States that ((the employer)) you will not allow the use of incompatible hose connections.
(c) A combination of internal and outside fire response. If a combination of internal and outside fire response is to be used, ((the employer)) you must include the following information, in addition to the requirements in (a) and (b) of this subsection, in the written policy:
(i) The basic organizational structure of the combined fire response;
(ii) The number of combined trained fire responders;
(iii) The fire response functions that may need to be carried out;
(iv) The minimum number of fire response employees necessary, the number and types of apparatuses, and a description of the fire suppression operations established by written standard operating procedures for each particular type of fire response at the worksite; and
(v) The type, amount, and frequency of joint training with outside fire response organizations if given to fire response employees.
(d) Employee evacuation. ((The employer)) You must include the following information in ((the employer's)) your written policy:
(i) Emergency escape procedures;
(ii) Procedures to be followed by employees who may remain longer at the worksite to perform critical shipyard employment operations during the evacuation;
(iii) Procedures to account for all employees after emergency evacuation is completed;
(iv) The preferred means of reporting fires and other emergencies; and
(v) Names or job titles of the employees or departments to be contacted for further information or explanation of duties.
(e) Rescue and emergency response. ((The employer)) You must include the following information in ((the employer's)) your written policy:
(i) A description of the emergency rescue procedures; and
(ii) Names or job titles of the employees who are assigned to perform them.
(3) Medical requirements for shipyard fire response employees. ((The employer)) You must ensure that:
(a) All fire response employees receive medical examinations to assure that they are physically and medically fit for the duties they are expected to perform;
(b) Fire response employees, who are required to wear respirators in performing their duties, meet the medical requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators;
(c) Each fire response employee has an annual medical examination; and
(d) The medical records of fire response employees are kept in accordance with chapter 296-802 WAC, Employee medical and exposure records.
(4) Organization of internal fire response functions. ((The employer)) You must:
(a) Organize fire response functions to ensure enough resources to conduct emergency operations safely;
(b) Establish lines of authority and assign responsibilities to ensure that the components of the internal fire response are accomplished;
(c) Set up an incident management system to coordinate and direct fire response functions, including:
(i) Specific fire emergency responsibilities;
(ii) Accountability for all fire response employees participating in an emergency operation; and
(iii) Resources offered by outside organizations; and
(d) Provide the information required in this subsection to the outside fire response organization to be used.
(5) Personal protective clothing and equipment for fire response employees.
(a) General requirements. ((The employer)) You must:
(i) Supply to all fire response employees, at no cost, the appropriate personal protective clothing and equipment they may need to perform expected duties; and
(ii) Ensure that fire response employees wear the appropriate personal protective clothing and use the equipment, when necessary, to protect them from hazardous exposures.
(b) Thermal stability and flame resistance. ((The employer)) You must:
(i) Ensure that each fire response employee exposed to the hazards of flame does not wear clothing that could increase the extent of injury that could be sustained; and
(ii) Prohibit wearing clothing made from acetate, nylon, or polyester, either alone or in blends, unless it can be shown that:
(A) The fabric will withstand the flammability hazard that may be encountered; or
(B) The clothing will be worn in such a way to eliminate the flammability hazard that may be encountered.
(c) Respiratory protection. ((The employer)) You must:
(i) Provide self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) to all fire response employees involved in an emergency operation in an atmosphere that is immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH), potentially IDLH, or unknown;
(ii) Provide SCBA to fire response employees performing emergency operations during hazardous chemical emergencies that will expose them to known hazardous chemicals in vapor form or to unknown chemicals;
(iii) Provide fire response employees who perform or support emergency operations that will expose them to hazardous chemicals in liquid form either:
(A) SCBA; or
(B) Respiratory protective devices certified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) under 42 C.F.R. Part 84 as suitable for the specific chemical environment;
(iv) Ensure that additional outside air supplies used in conjunction with SCBA result in positive pressure systems that are certified by NIOSH under 42 C.F.R. Part 84;
(v) Provide only SCBA that meet the requirements of NFPA 1981-2002 Standard on Open-Circuit Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus for the Fire Service (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003); and
(vi) Ensure that the respiratory protection program and all respiratory protection equipment comply with chapter 296-842 WAC, Respiratory protection.
(d) Interior structural firefighting operations. ((The employer)) You must:
(i) Supply at no cost to all fire response employees exposed to the hazards of shipyard fire response, a helmet, gloves, footwear, and protective hoods, and either a protective coat and trousers or a protective coverall; and
(ii) Ensure that this equipment meets the applicable recommendations in NFPA 1971-2000 Standard on Protective Ensemble for Structural Firefighting (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003).
(e) Proximity firefighting operations. ((The employer)) You must provide, at no cost, to all fire response employees who are exposed to the hazards of proximity firefighting, appropriate protective proximity clothing that meets the applicable recommendations in NFPA 1976-2000 Standard on Protective Ensemble for Proximity Firefighting (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003).
(f) Personal alert safety system (PASS) devices. ((The employer)) You must:
(i) Provide each fire response employee involved in firefighting operations with a PASS device; and
(ii) Ensure that each PASS device meets the recommendations in NFPA 1982-1998 Standard on Personal Alert Safety Systems (PASS) (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003).
(g) Life safety ropes, body harnesses, and hardware. ((The employer)) You must ensure that:
(i) All life safety ropes, body harnesses, and hardware used by fire response employees for emergency operations meet the applicable recommendations in NFPA 1983-2001, Standard on Fire Service Life Safety Rope and System Components (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003);
(ii) Fire response employees use only Class I body harnesses to attach to ladders and aerial devices; and
(iii) Fire response employees use only Class II and Class III body harnesses for fall arrest and rappelling operations.
(6) Equipment maintenance.
(a) Personal protective equipment. ((The employer)) You must inspect and maintain personal protective equipment used to protect fire response employees to ensure that it provides the intended protection.
(b) Fire response equipment. ((The employer)) You must:
(i) Keep fire response equipment in a state of readiness;
(ii) Standardize all fire hose coupling and connection threads throughout the facility and on vessels and vessel sections by providing the same type of hose coupling and connection threads for hoses of the same or similar diameter; and
(iii) Ensure that either all fire hoses and coupling connection threads are the same within a facility or vessel or vessel section as those used by the outside fire response organization, or supply suitable adapter couplings if such an organization is expected to use the fire response equipment within a facility or vessel or vessel section.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-19-086, filed 9/20/05, effective 12/1/05)
WAC 296-304-01015 Hazards of fixed extinguishing systems on board vessels and vessel sections.
(1) Employer responsibilities. ((The employer)) You must comply with the provisions of this section whenever employees are exposed to fixed extinguishing systems that could create a dangerous atmosphere when activated in vessels and vessel sections, regardless of geographic location.
(2) Requirements for automatic and manual systems. Before any work is done in a space equipped with fixed extinguishing systems, ((the employer)) you must either:
(a) Physically isolate the systems or use other positive means to prevent the systems' discharge; or
(b) Ensure employees are trained to recognize:
(i) Systems' discharge and evacuation alarms and the appropriate escape routes; and
(ii) Hazards associated with the extinguishing systems and agents including the dangers of disturbing system components and equipment such as piping, cables, linkages, detection devices, activation devices, and alarm devices.
(3) Sea and dock trials. During trials, ((the employer)) you must ensure that all systems shall remain operational.
(4) Doors and hatches. ((The employer)) You must:
(a) Take protective measures to ensure that all doors, hatches, scuttles, and other exit openings remain working and accessible for escape in the event the systems are activated; and
(b) Ensure that all inward opening doors, hatches, scuttles, and other potential barriers to safe exit are removed, locked open, braced, or otherwise secured so that they remain open and accessible for escape if the systems' activation could result in a positive pressure in the protected spaces sufficient to impede escape.
(5) Testing the system.
(a) When testing a fixed extinguishing system involves a total discharge of extinguishing medium into a space, ((the employer)) you must evacuate all employees from the space and assure that no employees remain in the space during the discharge. ((The employer)) You must retest the atmosphere in accordance with WAC 296-304-02003 to ensure that the oxygen levels are safe for employees to enter.
(b) When testing a fixed extinguishing system does not involve a total discharge of the system's extinguishing medium, ((the employer)) you must make sure that the system's extinguishing medium is physically isolated and that all employees not directly involved in the testing are evacuated from the protected space.
(6) Conducting system maintenance. Before conducting maintenance on a fixed extinguishing system, ((the employer)) you must ensure that the system is physically isolated.
(7) Using fixed manual extinguishing systems for fire protection. If fixed manual extinguishing systems are used to provide fire protection for spaces in which the employees are working, ((the employer)) you must ensure that:
(a) Only authorized employees are allowed to activate the system;
(b) Authorized employees are trained to operate and activate the systems; and
(c) All employees are evacuated from the protected spaces, and accounted for, before the fixed manual extinguishing system is activated.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-17-034, filed 8/7/07, effective 12/1/07)
WAC 296-304-01017 Land-side fire protection systems.
(1) Employer responsibilities. ((The employer)) You must ensure all fixed and portable fire protection systems needed to meet WISHA standards for employee safety or employee protection from fire hazards in land-side facilities, including, but not limited to, buildings, structures, and equipment, meet the requirements of this section.
(2) Portable fire extinguishers and hose systems.
(a) ((The employer)) You must select, install, inspect, maintain, and test all portable fire extinguishers according to NFPA 10-2002 Standard for Portable Fire Extinguishers (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003).
(b) ((The employer is)) You are permitted to use Class II or Class III hose systems, in accordance with NFPA 10-2002, as portable fire extinguishers if ((the employer)) you select((s)), install((s)), inspect((s)), maintain((s)), and test((s)) those systems according to the specific recommendations in NFPA 14-2003 Standard for the Installation of Standpipe, Private Hydrant, and Hose Systems (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003).
(3) General requirements for fixed extinguishing systems. ((The employer)) You must:
(a) Ensure that any fixed extinguishing system component or extinguishing agent is approved by an OSHA nationally recognized testing laboratory for use on the specific hazards the employer expects it to control or extinguish;
(b) Notify employees and take the necessary precautions to ensure employees are safe from fire if for any reason a fire extinguishing system stops working, until the system is working again;
(c) Ensure all repairs to fire extinguishing systems and equipment are done by a qualified technician or mechanic;
(d) Provide and ensure employees use proper personal protective equipment when entering discharge areas in which the atmosphere remains hazardous to employee safety or health, or provide safeguards to prevent employees from entering those areas. See WAC 296-304-02003 for additional requirements applicable to safe entry into spaces containing dangerous atmospheres;
(e) Post hazard warning or caution signs at both the entrance to and inside of areas protected by fixed extinguishing systems that use extinguishing agents in concentrations known to be hazardous to employee safety or health; and
(f) Select, install, inspect, maintain, and test all automatic fire detection systems and emergency alarms according to NFPA 72-2002 National Fire Alarm Code (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003).
(4) Fixed extinguishing systems. ((The employer)) You must select, install, maintain, inspect, and test all fixed systems required by WISHA as follows:
(a) Standpipe and hose systems according to NFPA 14-2003 Standard for the Installation of Standpipe, Private Hydrant, and Hose Systems (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003);
(b) Automatic sprinkler systems according to NFPA 25-2002 Standard for the Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance of Water-based Fire Protection Systems, and either NFPA 13-2002 Standard for the Installation of Sprinkler Systems or NFPA 750-2003 Standard on Water Mist Fire Protection Systems (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003);
(c) Fixed extinguishing systems that use water or foam as the extinguishing agent according to NFPA 15-2001 Standard for Water Spray Fixed Systems for Fire Protection; NFPA 11-2005 Standard for Low, Medium, and High-Expansion Foam Systems; (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003);
(d) Fixed extinguishing systems using dry chemical as the extinguishing agent according to NFPA 17-2002 Standard for Dry Chemical Extinguishing Systems (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003); and
(e) Fixed extinguishing systems using gas as the extinguishing agent according to NFPA 12-2005 Standard on Carbon Dioxide Extinguishing Systems; NFPA 12A-2004 Standard on Halon 1301 Fire Extinguishing Systems; and NFPA 2001-2004 Standard on Clean Agent Fire Extinguishing Systems (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-19-086, filed 9/20/05, effective 12/1/05)
WAC 296-304-01019 Training.
(1) ((The employer)) You must train employees in the applicable requirements of this section:
(a) By March 1, 2006, for employees currently working;
(b) Upon initial assignment for new employees; and
(c) When necessary to maintain proficiency for employees previously trained.
(2) Employee training. ((The employer)) You must ensure that all employees are trained on:
(a) The emergency alarm signals, including system discharge alarms and employee evacuation alarms; and
(b) The primary and secondary evacuation routes that employees must use in the event of a fire in the workplace. While all vessels and vessel sections must have a primary evacuation route, a secondary evacuation route is not required when impracticable.
(3) Additional training requirements for employees expected to fight incipient stage fires. ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees expected to fight incipient stage fires are trained on the following:
(a) The general principles of using fire extinguishers or hose lines, the hazards involved with incipient firefighting, and the procedures used to reduce these hazards;
(b) The hazards associated with fixed and portable fire protection systems that employees may use or to which they may be exposed during discharge of those systems; and
(c) The activation and operation of fixed and portable fire protection systems that the employer expects employees to use in the workplace.
(4) Additional training requirements for shipyard employees designated for fire response. ((The employer)) You must:
(a) Have a written training policy stating that fire response employees must be trained and capable of carrying out their duties and responsibilities at all times;
(b) Keep written standard operating procedures that address anticipated emergency operations and update these procedures as necessary;
(c) Review fire response employee training programs and hands-on sessions before they are used in fire response training to make sure that fire response employees are protected from hazards associated with fire response training;
(d) Provide training for fire response employees that ensures they are capable of carrying out their duties and responsibilities under ((the employer's)) your standard operating procedures;
(e) Train new fire response employees before they engage in emergency operations;
(f) At least quarterly, provide training on the written operating procedures to fire response employees who are expected to fight fires;
(g) Use qualified instructors to conduct the training;
(h) Conduct any training that involves live fire response exercises in accordance with NFPA 1403-2002 Standard on Live Fire Training Evolutions (incorporated by reference, see WAC 296-304-01003);
(i) Conduct semiannual drills according to ((the employer's)) your written procedures for fire response employees that cover site-specific operations, occupancies, buildings, vessels and vessel sections, and fire-related hazards; and
(j) Prohibit the use of smoke generating devices that create a dangerous atmosphere in training exercises.
(5) Additional training requirements for fire watch duty.
(a) ((The employer)) You must ensure that each fire watch is trained by an instructor with adequate fire watch knowledge and experience to cover the items as follows:
(i) Before being assigned to fire watch duty;
(ii) Whenever there is a change in operations that presents a new or different hazard;
(iii) Whenever ((the employer has)) you have reason to believe that the fire watch's knowledge, skills, or understanding of the training previously provided is inadequate; and
(iv) Annually.
(b) ((The employer)) You must ensure that each employee who stands fire watch duty is trained in:
(i) The basics of fire behavior, the different classes of fire and of extinguishing agents, the stages of fire, and methods for extinguishing fires;
(ii) Extinguishing live fire scenarios whenever allowed by local and federal law;
(iii) The recognition of the adverse health effects that may be caused by exposure to fire;
(iv) The physical characteristics of the hot work area;
(v) The hazards associated with fire watch duties;
(vi) The personal protective equipment (PPE) needed to perform fire watch duties safely;
(vii) The use of PPE;
(viii) The selection and use of any fire extinguishers and fire hoses likely to be used by a fire watch in the work area;
(ix) The location and use of barriers;
(x) The means of communication designated by ((the employer)) you for fire watches;
(xi) When and how to start fire alarm procedures; and
(xii) ((The employer's)) Your evacuation plan.
(c) ((The employer)) You must ensure that each fire watch is trained to alert others to exit the space whenever:
(i) The fire watch perceives an unsafe condition;
(ii) The fire watch perceives that a worker performing hot work is in danger;
(iii) ((The employer)) You or a representative of ((the employer)) yours orders an evacuation; or
(iv) An evacuation signal, such as an alarm, is activated.
(6) Records. ((The employer)) You must keep records that demonstrate that employees have been trained as required by subsections (1) through (5) of this section.
(a) ((The employer)) You must ensure that the records include the employee's name; the trainer's name; the type of training; and the date(s) on which the training took place.
(b) ((The employer)) You must keep each training record for one year from the time it was made or until it is replaced with a new training record, whichever is shorter, and make it available for inspection and copying by WISHA on request.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-19-086, filed 9/20/05, effective 12/1/05)
WAC 296-304-01021 Competent person.
(1) Application. This section applies to shipyard employment.
(2) Designation.
(a) One or more competent persons ((shall)) must be designated by ((the employer)) you in accordance with the applicable requirements of this section, unless the requirements of WAC 296-304-020 through 296-304-02011, WAC 296-304-030 through 296-304-03009, WAC 296-304-040 through 296-304-04013, and WAC 296-304-080 through 296-304-08011, are always carried out by a marine chemist.
Exception: | The employer may designate any person who meets the applicable portions of the criteria set forth in subsection (3) of this section as a competent person who is limited to performing testing to the following situations: |
(((i))) 1. Repair work on small craft in boat yards where only combustible gas indicator tests are required for fuel tank leaks or when using flammable paints below decks; | |
(((ii))) 2. Building of wooden vessels where only knowledge of the precautions to be taken when using flammable paints is required; | |
(((iii))) 3. The breaking of vessels where there is no fuel oil or other flammable hazard; and | |
(((iv))) 4. Tests and inspections performed to comply with WAC 296-304-03007 (2)(h) and 296-304-03009 (1)(e). |
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must maintain either a roster of designated competent persons or a statement that a marine chemist will perform the tests or inspections which require a competent person.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must make the roster of designated persons or the statement available to employees, the employee's representative, or the director upon request.
(d) The roster ((shall)) must contain, as a minimum, the following:
(i) The employer's name;
(ii) The designated competent person's name(s); and
(iii) The date the employee was trained as a competent person.
(3) Criteria. ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each designated competent person has the following skills and knowledge:
(a) Ability to understand and carry out written or oral information or instructions left by marine chemists, Coast Guard-authorized persons and certified industrial hygienists;
(b) Knowledge of WAC 296-304-020 through 296-304-02011, WAC 296-304-030 through 296-304-03009, WAC 296-304-040 through 296-304-04013, and WAC 296-304-080 through 296-304-08011;
(c) Knowledge of the structure, location, and designation of spaces where work is done;
(d) Ability to calibrate and use testing equipment including, but not limited to, oxygen indicators, combustible gas indicators, carbon monoxide indicators, and carbon dioxide indicators, and to interpret accurately the test results of that equipment;
(e) Ability to perform all required tests and inspections which are or may be performed by a competent person as set forth in WAC 296-304-020 through 296-304-02011, WAC 296-304-030 through 296-304-03009, WAC 296-304-040 through 296-304-04013, and WAC 296-304-080 through 296-304-08011;
(f) Ability to inspect, test, and evaluate spaces to determine the need for further testing by a marine chemist or a certified industrial hygienist; and
(g) Ability to maintain records required by this section.
(4) Recordkeeping.
(a) When tests and inspections are performed by a competent person, marine chemist, or certified industrial hygienist as required by any provisions of WAC 296-304-020 through 296-304-02011, WAC 296-304-030 through 296-304-03009, WAC 296-304-040 through 296-304-04013, or WAC 296-304-080 through 296-304-08011, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the person performing the test and inspection records the location, time, date, location of inspected spaces, and the operations performed, as well as the test results and any instructions.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the records are posted in the immediate vicinity of the affected operations while work in the spaces is in progress. The records ((shall)) must be kept on file for a period of at least three months from the completion date of the specific job for which they were generated.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the records are available for inspection by the director, and employees and their representatives.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-17-034, filed 8/7/07, effective 12/1/07)
WAC 296-304-020 Confined and enclosed spaces and other dangerous atmospheres in shipyard employment.
Scope, application and definitions applicable to this subsection:
(1) Scope and application. This section applies to work in confined and enclosed spaces and other dangerous atmospheres in shipyard employment, including vessels, vessel sections, and on land-side operations regardless of geographic location.
(2) Definitions applicable to this section:
Adjacent spaces ((means)). Those spaces bordering a subject space in all directions, including all points of contact, corners, diagonals, decks, tank tops, and bulkheads.
Certified industrial hygienist (CIH) ((means)). An industrial hygienist who is certified by the American Board of Industrial Hygiene.
Coast Guard authorized person ((means)). An individual who meets the requirement of WAC 296-304-02015, Appendix C, for tank vessels, for passenger vessels, and for cargo and miscellaneous vessels.
Dangerous atmosphere ((means)). An atmosphere that may expose employees to the risk of death, incapacitation, impairment of ability to self-rescue (i.e., escape unaided from a confined or enclosed space), injury, or acute illness.
Director ((means)). The director of the department of labor and industries or his/her designated representative.
Enter with restrictions. Denotes a space where entry for work is permitted only if engineering controls, personal protective equipment, clothing, and time limitations are as specified by the marine chemist, certified industrial hygienist, or the shipyard competent person.
Entry ((means)). The action by which a person passes through an opening into a space. Entry includes ensuing work activities in that space and is considered to have occurred as soon as any part of the entrant's body breaks the plane of an opening into the space.
Hot work ((means)). Any activity involving riveting, welding, burning, the use of powder-actuated tools or similar fire-producing operations. Grinding, drilling, abrasive blasting, or similar spark-producing operations are also considered hot work except when such operations are isolated physically from any atmosphere containing more than 10 percent of the lower explosive limit of a flammable or combustible substance.
Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) ((means)). An atmosphere that poses an immediate threat to life or that is likely to result in acute or immediate severe health effects.
Inert or inerted atmosphere ((means)). An atmospheric condition where:
(a) The oxygen content of the atmosphere in the space is maintained at a level equal to or less than 8.0 percent by volume or at a level at or below 50 percent of the amount required to support combustion, whichever is less; or
(b) The space is flooded with water and the vapor concentration of flammable or combustible materials in the free space atmosphere above the water line is less than 10 percent of the lower explosive limit for the flammable or combustible material.
Labeled ((means)). Identified with a sign, placard, or other form of written communication, including pictograms, that provides information on the status or condition of the work space to which it is attached.
Lower explosive limit (LEL) ((means)). The minimum concentration of vapor in air below which propagation of a flame does not occur in the presence of an ignition source.
Marine chemist ((means)). An individual who possesses a current marine chemist certificate issued by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA).
NFPA ((means)). National Fire Protection Association.
Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) ((means)). An organization recognized by OSHA, in accordance with Appendix A of 29 C.F.R. 1910.7, which tests for safety and lists or labels or accepts equipment and materials that meet all the criteria found in Section 1910.7 (b)(1) through (b)(4)(ii).
Not safe for hot work ((denotes)). A space where hot work may not be performed because the conditions do not meet the criteria for "safe for hot work."
Not safe for workers ((denotes)). A space where an employee may not enter because the conditions do not meet the criteria for "safe for workers."
Oxygen-deficient atmosphere ((means)). An atmosphere having an oxygen concentration of less than 19.5 percent by volume.
Oxygen-enriched atmosphere ((means)). An atmosphere that contains 22.0 percent or more oxygen by volume.
Safe for hot work ((denotes)). A space that meets all of the following criteria:
(a) The oxygen content of the atmosphere does not exceed 22.0 percent by volume;
(b) The concentration of flammable vapors in the atmosphere is less than 10 percent of the lower explosive limit;
(c) The residues or materials in the space are not capable of producing a higher concentration than permitted in (a) or (b) of the above, under existing atmospheric conditions in the presence of hot work and while maintained as directed by the marine chemist or competent person; and
(d) All adjacent spaces have been cleaned, or inerted, or treated sufficiently to prevent the spread of fire.
Safe for workers ((denotes)). A space that meets the following criteria:
(a) The oxygen content of the atmosphere is at least 19.5 percent and below 22.0 percent by volume;
(b) The concentration of flammable vapors is below 10 percent of the lower explosive limit (LEL);
(c) Any toxic materials in the atmosphere associated with cargo, fuel, tank coatings, or inerting media are within permissible concentrations at the time of the inspection; and
(d) Any residues or materials associated with the work authorized by the marine chemist, certified industrial hygienist, or competent person will not produce uncontrolled release of toxic materials under existing atmospheric conditions while maintained as directed.
Space ((means)). An area on a vessel or vessel section or within a shipyard such as, but not limited to: Cargo tanks or holds; pump or engine rooms; storage lockers; tanks containing flammable or combustible liquids, gases, or solids; rooms within buildings; crawl spaces; tunnels; or accessways. The atmosphere within a space is the entire area within its bounds.
Upper explosive limit (UEL) ((means)). The maximum concentration of flammable vapor in air above which propagation of flame does not occur on contact with a source of ignition.
Vessel section ((means)). A subassembly, module, or other component of a vessel being built, repaired, or broken.
Visual inspection ((means)). The physical survey of the space, its surroundings and contents to identify hazards such as, but not limited to, restricted accessibility, residues, unguarded machinery, and piping or electrical systems.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-03-093, filed 1/18/05, effective 3/1/05)
WAC 296-304-02003 Precautions and the order of testing before entering confined and enclosed spaces and other dangerous atmospheres.
((The employer shall)) You must ensure that atmospheric testing is performed in the following sequence: Oxygen content, flammability, toxicity.
(1) Oxygen content.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the following spaces are visually inspected and tested by a competent person to determine the atmosphere's oxygen content prior to initial entry into the space by an employee:
(i) Spaces that have been sealed, such as, but not limited to, spaces that have been coated and closed up, and nonventilated spaces that have been freshly painted;
(ii) Spaces and adjacent spaces that contain or have contained combustible or flammable liquids or gases;
(iii) Spaces and adjacent spaces that contain or have contained liquids, gases, or solids that are toxic, corrosive, or irritant;
(iv) Spaces and adjacent spaces that have been fumigated; and
(v) Spaces containing materials or residues of materials that create an oxygen-deficient atmosphere.
(b) If the space to be entered contains an oxygen deficient atmosphere, the space ((shall)) must be labeled "not safe for workers" or, if oxygen-enriched, "not safe for workers—not safe for hot work." If an oxygen-deficient or oxygen-enriched atmosphere is found, ventilation ((shall)) must be provided at volumes and flow rates sufficient to ensure that the oxygen content is maintained at or above 19.5 percent and below 22.0 percent by volume. The warning label may be removed when the oxygen content is equal to or greater than 19.5 and less than 22.0 percent by volume.
(c) An employee may not enter a space where the oxygen content, by volume, is below 19.5 percent or above 22.0 percent.
Exception: An employee may enter for emergency rescue or for a short duration for installation of ventilation equipment necessary to start work in the space provided:
(i) The atmosphere in the space is monitored for oxygen content, by volume, continuously; and
(ii) Respiratory protection and other appropriate personal protective equipment and clothing are provided in accordance with WAC 296-304-090 through 296-304-09007.
Note to (a): | Other provisions for work in IDLH atmospheres are located in WAC 296-304-090 through 296-304-09007. |
(2) Flammable atmospheres.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that spaces and adjacent spaces that contain or have contained combustible or flammable liquids or gases are:
(i) Inspected visually by the competent person to determine the presence of combustible or flammable liquids; and
(ii) Tested by a competent person prior to entry by an employee to determine the concentration of flammable vapors and gases within the space.
(b) If the concentration of flammable vapors or gases in the space to be entered is equal to or greater than 10 percent of the lower explosive limit, the space shall be labeled "not safe for workers" and "not safe for hot work." Ventilation ((shall)) must be provided at volumes and flow rates sufficient to ensure that the concentration of flammable vapors is maintained below 10 percent of the lower explosive limit. The warning labels may be removed when the concentration of flammable vapors is below 10 percent of the lower explosive limit.
(c) An employee may not enter a space where the concentration of flammable vapors or gases is equal to or greater than 10 percent of the lower explosive limit.
Exception: An employee may enter for emergency rescue or for a short duration for installation of ventilation equipment necessary to start work in the space, provided:
(i) No ignition sources are present;
(ii) The atmosphere in the space is monitored continuously;
(iii) Atmospheres at or above the upper explosive limit are maintained; and
(iv) Respiratory protection and other appropriate personal protective equipment and clothing are provided in accordance with WAC 296-304-090 through 296-304-09007.
Note 1 to (2): | Additional provisions for work in IDLH atmospheres are located in WAC 296-304-090 through 296-304-09007. |
Note 2 to (2): | Additional provisions for work in spaces containing a flammable substance which also has a permissible exposure limit, are located in subsection (3) of this section and chapter 296-841 WAC. |
(3) Toxic, corrosive, irritant or fumigated atmospheres and residues.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that spaces or adjacent spaces that contain or have contained liquids, gases, or solids that are toxic, corrosive or irritant are:
(i) Inspected visually by the competent person to determine the presence of toxic, corrosive, or irritant residue contaminants; and
(ii) Tested by a competent person prior to initial entry by an employee to determine the air concentration of toxics, corrosives, or irritants within the space.
(b) If a space contains an air concentration of a material which exceeds a chapter 296-841 WAC, permissible exposure limit (PEL) or is IDLH, the space shall be labeled "not safe for workers." Ventilation ((shall)) must be provided at volumes and flow rates which will ensure that air concentrations are maintained within the PEL or, in the case of contaminants for which there is no established PEL, below the IDLH. The warning label may be removed when the concentration of contaminants is maintained within the PEL or below IDLH level.
(c) If a space cannot be ventilated to within the PELs or is IDLH, a marine chemist or CIH must retest until the space can be certified "enter with restrictions" or "safe for workers."
(d) An employee may not enter a space whose atmosphere exceeds a PEL or is IDLH.
Exception: An employee may enter for emergency rescue, or for a short duration for installation of ventilation equipment provided:
(i) The atmosphere in the space is monitored continuously;
(ii) Respiratory protection and other necessary and appropriate personal protective equipment and clothing are provided in accordance with WAC 296-304-090 through 296-304-09007.
Note to (3): | Other provisions for work in IDLH atmospheres are located in WAC 296-304-090 through 296-304-9007. |
(4) Training of employees entering confined and enclosed spaces or other dangerous atmospheres.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each employee that enters a confined or enclosed space and other areas with dangerous atmospheres is trained to perform all required duties safely.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each employee who enters a confined space, enclosed space, or other areas with dangerous atmospheres is trained to:
(i) Recognize the characteristics of the confined space;
(ii) Anticipate and be aware of the hazards that may be faced during entry;
(iii) Recognize the adverse health effects that may be caused by the exposure to a hazard;
(iv) Understand the physical signs and reactions related to exposures to such hazards;
(v) Know what personal protective equipment is needed for safe entry into and exit from the space;
(vi) Use personal protective equipment; and
(vii) Where necessary, be aware of the presence and proper use of barriers that may be needed to protect an entrant from hazards.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each entrant into confined or enclosed spaces or other dangerous atmospheres is trained to exit the space or dangerous atmosphere whenever:
(i) ((The employer)) You or his or her representative orders evacuation;
(ii) An evacuation signal such as an alarm is activated; or
(iii) The entrant perceives that he or she is in danger.
(d) ((The employer shall)) You must provide each employee with training:
(i) Before the entrant begins work addressed by this chapter; and
(ii) Whenever there is a change in operations or in an employee's duties that presents a hazard about which the employee has not previously been trained.
(e) ((The employer shall)) You must certify that the training required by (a) through (d) of this subsection has been accomplished.
(i) The certification ((shall)) must contain the employee's name, the name of the certifier, and the date(s) of the certification.
(ii) The certification ((shall)) must be available for inspection by the director, employees, and their representatives.
(5) Rescue teams. ((The employer shall)) You must either establish a shipyard rescue team or arrange for an outside rescue team which will respond promptly to a request for rescue service.
(a) Shipyard rescue teams ((shall)) must meet the following criteria:
(i) Each employee assigned to the shipyard team ((shall)) must be provided with and trained to use the personal protective equipment he or she will need, including respirators and any rescue equipment necessary for making rescues from confined and enclosed spaces and other dangerous atmospheres.
(ii) Each employee assigned to the shipyard rescue team ((shall)) must be trained to perform his or her rescue functions including confined and enclosed and other dangerous atmosphere entry.
(iii) Shipyard rescue teams ((shall)) must practice their skills at least once every 12 months. Practice drills ((shall)) must include the use of mannequins and rescue equipment during simulated rescue operations involving physical facilities that approximate closely those facilities from which rescue may be needed.
Note to (5)(a)(iii): | If the team performs an actual rescue during the 12 month period, an additional practice drill for that type of rescue is not required. |
(iv) At least one person on each rescue team ((shall)) must maintain current certification in basic first aid which includes maintenance of an airway, control of bleeding, maintenance of circulation and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) skills.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must inform outside rescue teams of the hazards that the team may encounter when called to perform confined and enclosed space or other dangerous atmosphere rescue at ((the employer's)) your facility so that the rescue team can be trained and equipped.
Note to (5): | The criteria for in-house rescue, listed in (5)(a) can be used by the employer in evaluating outside rescue services. |
(6) Exchanging hazard information between employers. Each employer whose employees work in confined and enclosed spaces or other dangerous atmospheres ((shall)) must ensure that all available information on the hazards, safety rules, and emergency procedures concerning those spaces and atmospheres is exchanged with any other employer whose employees may enter the same spaces.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-17-034, filed 8/7/07, effective 12/1/07)
WAC 296-304-02005 Cleaning and other cold work.
(1) Locations covered by this section. ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that manual cleaning and other cold work are not performed in the following spaces unless the conditions of subsection (2) of this section have been met:
(a) Spaces containing or having last contained bulk quantities of combustible or flammable liquids or gases; and
(b) Spaces containing or having last contained bulk quantities of liquids, gases or solids that are toxic, corrosive or irritating.
(2) Requirements for performing cleaning or cold work.
(a) Liquid residues of hazardous materials ((shall)) must be removed from work spaces as thoroughly as practicable before employees start cleaning operations or cold work in a space. Special care ((shall)) must be taken to prevent the spilling or the draining of these materials into the water surrounding the vessel, or for shore-side operations, onto the surrounding work area.
(b) Testing ((shall)) must be conducted by a competent person to determine the concentration of flammable, combustible, toxic, corrosive, or irritant vapors within the space prior to the beginning of cleaning or cold work.
(c) Continuous ventilation ((shall)) must be provided at volumes and flow rates sufficient to ensure that the concentration(s) of:
(i) Flammable vapor is maintained below 10 percent of the lower explosive limit; and
Note to (2)(c)(i): | Spaces containing highly volatile residues may require additional ventilation to keep the concentration of flammable vapors below 10 percent of the lower explosive limit and within the permissible exposure limit. |
(ii) Toxic, corrosive, or irritant vapors are maintained within the permissible exposure limits and below IDLH levels.
(d) Testing ((shall)) must be conducted by the competent person as often as necessary during cleaning or cold work to assure that air concentrations are below 10 percent of the lower explosive limit and within the PELs and below IDLH levels. Factors such as, but not limited to, temperature, volatility of the residues and other existing conditions in and about the spaces are to be considered in determining the frequency of testing necessary to assure a safe atmosphere.
Note to (2)(d): | See WAC 296-304-02013—Appendix B, for additional information on frequency of testing. |
(e) Spills or other releases of flammable, combustible, toxic, corrosive, and irritant materials ((shall)) must be cleaned up as work progresses.
(f) An employee may not enter a confined or enclosed space or other dangerous atmosphere if the concentration of flammable or combustible vapors in work spaces exceeds 10 percent of the lower explosive limit.
Exception: An employee may enter for emergency rescue or for a short duration for installation of ventilation equipment provided:
(i) No ignition sources are present;
(ii) The atmosphere in the space is monitored continuously;
(iii) The atmosphere in the space is maintained above the upper explosive limit; and
(iv) Respiratory protection, personal protective equipment, and clothing are provided in accordance with WAC 206-304-090 through 296-304-09007.
Note to (2)(f): | Other provisions for work in IDLH and other dangerous atmospheres are located in WAC 296-304-090 through 296-304-09007. |
(g) A competent person ((shall)) must test ventilation discharge areas and other areas where discharged vapors may collect to determine if vapors discharged from the spaces being ventilated are accumulating in concentrations hazardous to employees.
(h) If the tests required in (g) of this subsection indicate that concentrations of exhaust vapors that are hazardous to employees are accumulating, all work in the contaminated area ((shall)) must be stopped until the vapors have dissipated or been removed.
(i) Only explosion-proof, self-contained portable lamps, or other electric equipment approved by a National Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) for the hazardous location ((shall)) must be used in spaces described in subsection (1) of this section, until such spaces have been certified as "safe for workers."
Note to (2)(i): | Battery-fed, portable lamps or other electric equipment bearing the approval of a NRTL for the class, and division of the location in which they are used are deemed to meet the requirements of (i) of this subsection. |
(j) ((The employer shall)) You must prominently post signs that prohibit sources of ignition within or near a space that has contained flammable or combustible liquids or gases in bulk quantities:
(i) At the entrance to those spaces;
(ii) In adjacent spaces; and
(iii) In the open area adjacent to those spaces.
(k) All air moving equipment and its component parts, including duct work, capable of generating a static electric discharge of sufficient energy to create a source of ignition, ((shall)) must be bonded electrically to the structure of a vessel or vessel section or, in the case of land-side spaces, grounded to prevent an electric discharge in the space.
(l) Fans ((shall)) must have nonsparking blades, and portable air ducts shall be of nonsparking materials.
Note to (2): | See WAC 296-304-02003(3) and applicable requirements of chapter 296-62 WAC, general occupational health standards, for other provisions affecting cleaning and cold work. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-17-034, filed 8/7/07, effective 12/1/07)
WAC 296-304-02007 Hot work.
(1) Hot work requiring testing by a marine chemist or Coast Guard authorized person.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that hot work is not performed in or on any of the following confined and enclosed spaces and other dangerous atmospheres, boundaries of spaces or pipelines until the work area has been tested and certified by a marine chemist or a U.S. Coast Guard authorized person as "safe for hot work":
(i) Within, on, or immediately adjacent to spaces that contain or have contained combustible or flammable liquids or gases.
(ii) Within, on, or immediately adjacent to fuel tanks that contain or have last contained fuel; and
(iii) On pipelines, heating coils, pump fittings or other accessories connected to spaces that contain or have last contained fuel.
(iv) Exception: On dry cargo, miscellaneous and passenger vessels and in the landside operations within spaces which meet the standards for oxygen, flammability and toxicity in WAC 296-304-02003, but are adjacent to spaces containing flammable gases or liquids, as long as the gases or liquids with a flash point below 150 deg. F (65.6 deg. C) when the distance between such spaces and the work is 25 feet (7.62 m) or greater.
Note: | For flammable liquids with flash points above 150 deg. F (65.6 deg. C), see subsection (2) of this section. |
Note to (1)(a): | The criteria for "safe for hot work" is located in the definition section, WAC 296-304-020(2). |
(b) The certificate issued by the marine chemist or Coast Guard authorized person ((shall)) must be posted in the immediate vicinity of the affected operations while they are in progress and kept on file for a period of at least three months from the date of the completion of the operation for which the certificate was generated.
(2) Hot work requiring testing by a competent person.
(a) Hot work is not permitted in or on the following spaces or adjacent spaces or other dangerous atmospheres until they have been tested by a competent person and determined to contain no concentrations of flammable vapors equal to or greater than 10 percent of the lower explosive limit:
(i) Dry cargo holds;
(ii) The bilges;
(iii) The engine room and boiler spaces for which a marine chemist or a Coast Guard authorized person certificate is not required under subsection (1)(a)(i) of this section; and
(iv) Vessels and vessel sections for which a marine chemist or Coast Guard authorized person certificate is not required under subsection (1)(a)(i) of this section; and
(v) Land-side confined and enclosed spaces or other dangerous atmospheres not covered by subsection (1)(a) of this section.
(b) If the concentration of flammable vapors or gases is equal to or greater than 10 percent of the lower explosive limit in the space or an adjacent space where the hot work is to be done, then the space ((shall)) must be labeled "not safe for hot work" and ventilation ((shall)) must be provided at volumes and flow rates sufficient to ensure that the concentration of flammable vapors or gases is below 10 percent by volume of the lower explosive limit. The warning label may be removed when the concentration of flammable vapors and gases are below 10 percent of the lower explosive limit.
Note to WAC 296-304-02007: | See WAC 296-304-02013—Appendix B, for additional information relevant to performing hot work safely. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-02009 Maintenance of safe conditions.
(1) Preventing hazardous materials from entering. Pipelines that could carry hazardous materials into spaces that have been certified "safe for workers" or "safe for hot work" ((shall)) must be disconnected, blanked off, or otherwise blocked by a positive method to prevent hazardous materials from being discharged into the space.
(2) Alteration of existing conditions. When a change that could alter conditions within a tested confined or enclosed space or other dangerous atmosphere occurs, work in the affected space or area ((shall)) must be stopped. Work may not be resumed until the affected space or area is visually inspected and retested and found to comply with WAC 296-304-02003, 296-304-02005, and 296-304-02007, as applicable.
Note to (2): | Examples of changes that would warrant the stoppage of work include: The opening of manholes or other closures or the adjusting of a valve regulating the flow of hazardous materials. |
(3) Tests to maintain the conditions of a marine chemist's or Coast Guard authorized person's certificates. A competent person ((shall)) must visually inspect and test each space certified as "safe for workers" or "safe for hot work," as often as necessary to ensure that atmospheric conditions within that space are maintained within the conditions established by the certificate after the certificate has been issued.
(4) Change in the conditions of a marine chemist's or Coast Guard authorized person's certificate. If a competent person finds that the atmospheric conditions within a certified space fail to meet the applicable requirements of WAC 296-304-02003, 296-304-02005, and 296-304-02007, work in the certified space ((shall)) must be stopped and may not be resumed until the space has been retested by a marine chemist or Coast Guard authorized person and a new certificate issued in accordance with WAC 296-304-02007(1).
(5) Tests to maintain a competent person's findings. After a competent person has conducted a visual inspection and tests required in WAC 296-304-02003, 296-304-02005, and 296-304-02007 and determined a space to be safe for an employee to enter, he or she ((shall)) must continue to test and visually inspect spaces as often as necessary to ensure that the required atmospheric conditions within the tested space are maintained.
(6) Changes in conditions determined by competent person's findings. After the competent person has determined initially that a space is safe for an employee to enter and he or she finds subsequently that the conditions within the tested space fail to meet the requirements of WAC 296-304-02003, 296-304-02005, and 296-304-02007, as applicable, work ((shall)) must be stopped until the conditions in the tested space are corrected to comply with WAC 296-304-02003, 296-304-02005, and 296-304-02007, as applicable.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 95-04-006, filed 1/18/95, effective 3/10/95)
WAC 296-304-02011 Warning signs and labels.
(1) Employee comprehension of signs and labels. ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each sign or label posted to comply with the requirements of this section is presented in a manner that can be perceived and understood by all employees.
(2) Posting of large work areas. A warning sign or label required by subsection (1) of this section need not be posted at an individual tank, compartment or work space within a work area if the entire work area has been tested and certified: "Not safe for workers," "not safe for hot work," and if the sign or label to this effect is posted conspicuously at each means of access to the work area.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-03-093, filed 1/18/05, effective 3/1/05)
WAC 296-304-03001 Toxic cleaning solvents.
(1) When toxic solvents are used, ((the employer shall)) you must employ one or more of the following measures to safeguard the health of employees exposed to these solvents.
(a) The cleaning operation ((shall)) must be completely enclosed to prevent the escape of vapor into the working space.
(b) Either natural ventilation or mechanical exhaust ventilation ((shall)) must be used to remove the vapor at the source and to dilute the concentration of vapors in the working space to a concentration which is safe for the entire work period.
(c) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees are protected against:
((•)) (i) Toxic vapors by suitable respiratory protective equipment that meets the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC; and
((•)) (ii) Exposure of skin and eyes to contact with toxic solvents and their vapors by suitable clothing and equipment.
(2) The principles in the threshold limit values to which attention is directed in WAC 296-304-02005 and applicable sections in chapters 296-62 and 296-841 WAC will be used by the department of labor and industries in enforcement proceedings in defining a safe concentration of air contaminants.
(3) When flammable solvents are used, precautions ((shall)) must be taken in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-304-03009.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 98-02-006, filed 12/26/97, effective 3/1/98)
WAC 296-304-03003 Chemical paint and preservative removers.
(1) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees are protected against:
((•)) (a) Skin contact during the handling and application of chemical paint and preservative removers; and
((•)) (b) Eye injury by goggles or face shields that meet the requirements of WAC 296-304-09005 (1) and (2).
(2) When using flammable paint and preservative removers precautions ((shall)) must be taken in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-304-03009.
(3) When using chemical paint and preservative removers which contain volatile and toxic solvents, such as benzol, acetone and amyl acetate, the provisions of WAC 296-304-03001 ((shall)) must be applicable.
(4) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees using paint and rust removers containing strong acids or alkalies are protected by suitable face shields to prevent chemical burns on the face and neck according to the requirements of WAC 296-304-09005 (1) and (2).
(5) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all employees working within range of a steam gun blast are protected by suitable face shields according to the requirements of WAC 296-304-09005 (1) and (2). Metal parts of the steam gun itself must be insulated to protect the operator against heat burns.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-304-03005 Mechanical paint removers.
(1) Power tools.
(a) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees engaged in the removal of paints, preservatives, rusts or other coatings by means of power tools are protected against eye injury by goggles or face shields that meets the requirements of WAC 296-304-09005 (1) and (2).
(b) All portable rotating tools used for the removal of paints, preservatives, rusts or other coatings ((shall)) must be adequately guarded to protect both the operator and nearby workers from flying missiles.
(c) Portable electric tools ((shall)) must be grounded in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-304-08003 (1) and (2).
(d) In a confined space, ((the employer)) you must provide mechanical exhaust ventilation sufficient to keep the dust concentration to a minimum, or must protect employees by respiratory protective equipment that meets the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC.
(2) Flame removal.
(a) ((The employer)) You must ensure that when hardened preservative coatings are removed by flame in enclosed spaces, the employees exposed to fumes are protected by air line respirators that meet the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC. Employees performing this operation in the open air, and those exposed to the resulting fumes, must be protected by a fume filter respirator that meets the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC.
(b) Flame or heat ((shall)) must not be used to remove soft and greasy preservative coatings.
(3) Abrasive blasting.
(a) Equipment. Hoses and fittings used for abrasive blasting ((shall)) must meet the following requirements:
(i) Hoses((. Hose)) of a type to prevent shocks from static electricity ((shall)) must be used.
(ii) Hose couplings. Hose lengths ((shall)) must be joined by metal couplings secured to the outside of the hose to avoid erosion and weakening of the couplings.
(iii) Nozzles((. Nozzles shall)) must be attached to the hose by fittings that will prevent the nozzle from unintentionally becoming disengaged. Nozzle attachments shall be of metal and ((shall)) must fit onto the hose externally.
(iv) Dead man control. A dead man control device ((shall)) must be provided at the nozzle end of the blasting hose either to provide direct cutoff or to signal the pot tender by means of a visual and audible signal to cut off the flow, in the event the blaster loses control of the hose. The pot tender ((shall)) must be available at all times to respond immediately to the signal.
(b) Replacement. Hoses and all fittings used for abrasive blasting ((shall)) must be inspected frequently to ((insure)) ensure timely replacement before an unsafe amount of wear has occurred.
(c) Personal protective equipment.
(i) ((The employer)) You must ensure that abrasive blasters working in enclosed spaces are protected by abrasive blasting respirators that meet the requirements of chapter 296-818 WAC, Abrasive blasting and chapter 296-842 WAC.
(ii) ((The employer)) You must ensure that abrasive blasters working in the open are protected as required in subsection (1) of this section.
Exception: | When synthetic abrasives containing less than one percent free silica are used, the employer may substitute particulate or dust filter respirators that are approved by the National Institute of Safety and Health (NIOSH) and used according to chapter 296-842 WAC. |
(iii) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees, including machine tenders and abrasive recovery workers, working in areas where unsafe concentrations of abrasive materials and dusts are present are protected by eye and respiratory protective equipment that meets the requirements of WAC 296-304-09005 (1) and (2) and chapter 296-842 WAC.
Exception: | This requirement does not apply to blasters. |
(iv) ((The employer)) You must ensure that a blaster is protected against injury from exposure to the blast by appropriate protective clothing, including gloves that meet the requirements of WAC 296-304-09015(1).
(v) A surge from a drop in pressure in the hose line can throw a blaster off the staging. To protect against this hazard, ((the employer)) you must ensure that a blaster is protected by a personal fall arrest system, that meets the requirements of WAC 296-304-09021. The personal fall arrest system must be tied off to the ship or other structure during blasting from elevations where adequate fall protection cannot be provided by railings.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-03-093, filed 1/18/05, effective 3/1/05)
WAC 296-304-03007 Painting.
All respirators required by this section must meet the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC.
(1) Paints mixed with toxic vehicles or solvents.
(a) When employees spray paints mixed with toxic vehicles or solvents, ((the employer)) you must ensure that the following conditions are met:
(i) In confined spaces, employees continuously exposed to spraying are protected by air line respirators.
(ii) In tanks or compartments, employees continuously exposed to spraying are protected by air line respirators. Where mechanical ventilation is provided, employees are protected by respirators.
(iii) In large and well ventilated areas, employees exposed to spraying are protected by respirators.
(b) ((The employer)) You must ensure that where employees apply by brush paints with toxic solvents in confined spaces or other areas where lack of ventilation creates a hazard, the employees are protected by filter respirators.
(c) When flammable paints or vehicles are used, precautions ((shall)) must be taken in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-304-03009.
(d) The metallic parts of air moving devices, including fans, blowers, and jet-type air movers, and all duct work ((shall)) must be electrically bonded to the vessel's structure.
(2) Paints and tank coatings dissolved in highly volatile, toxic and flammable solvents. Several organic coatings, adhesives and resins are dissolved in highly toxic, flammable and explosive solvents with flash points below 80°F. Work involving such materials ((shall)) must be done only when all of the following special precautions have been taken:
(a) Sufficient exhaust ventilation ((shall)) must be provided to keep the concentration of solvent vapors below ten percent of the lower explosive limit. Frequent tests ((shall)) must be made by a competent person to ascertain the concentration.
(b) If the ventilation fails or if the concentration of solvent vapors reaches or exceeds ten percent of the lower explosive limit, painting ((shall)) must be stopped and the compartment ((shall)) must be evacuated until the concentration again falls below ten percent of the lower explosive limit. If the concentration does not fall when painting is stopped, additional ventilation to bring the concentration down to ten percent of the lower explosive limit ((shall)) must be provided.
(c) Ventilation ((shall)) must be continued after the completion of painting until the space or compartment is gas free. The final determination as to whether the space or compartment is gas free ((shall)) must be made after the ventilating equipment has been shut off for a least ten minutes.
(d) Exhaust ducts ((shall)) must discharge clear of working areas and away from sources of possible ignition. Periodic tests ((shall)) must be made to ensure that the exhausted vapors are not accumulating in other areas within or around the vessel or dry dock.
(e) All motors and control equipment ((shall)) must be of the explosion-proof type. Fans ((shall)) must have nonferrous blades. Portable air ducts ((shall)) must also be of nonferrous materials. All motors and associated control equipment ((shall)) must be properly maintained and grounded.
(f) Only nonsparking paint buckets, spray guns and tools ((shall)) must be used. Metal parts of paint brushes and rollers ((shall)) must be insulated. Staging ((shall)) must be erected in a manner which ensures that it is nonsparking.
(g) Only explosion proof lights, approved by the Underwriters' Laboratories for use in Class I, Group D atmospheres, or approved as permissible by the U.S. Bureau of Mines or the U.S. Coast Guard, ((shall)) must be used.
(h) A competent person ((shall)) must inspect all power and lighting cables to ensure that the insulation is in excellent condition, free of all cracks and worn spots, that there are no connections within fifty feet of the operation, that lines are not overloaded, and that they are suspended with sufficient slack to prevent undue stress or chafing.
(i) The face, eyes, head, hands and all other exposed parts of the bodies of employees handling highly volatile paints must be protected according to WAC 296-304-090. All footwear must be nonsparking, such as rubbers, rubber boots or rubber soled shoes without nails. Coveralls or other outer clothing must be made of cotton. Rubber gloves, instead of plastic gloves, must be used to protect against the danger of static sparks.
(j) No matches, lighted cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, and no cigarette lighters or ferrous articles ((shall)) must be taken into the area where work is being done.
(k) All solvent drums taken into the compartment ((shall)) must be placed on nonferrous surfaces and ((shall)) must be grounded to the vessel. Metallic contact ((shall)) must be maintained between containers and drums when materials are being transferred from one to another.
(l) Spray guns, paint pots, and metallic parts of connecting tubing ((shall)) must be electrically bonded, and the bonded assembly ((shall)) must be grounded to the vessel.
(m) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all employees continuously in a compartment in which such painting is performed, are protected by air line respirators and by suitable protective clothing. Employees entering such compartments for a limited time must be protected by filter cartridge type respirators.
(n) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all employees doing exterior paint spraying with such paints are protected by suitable filter cartridge type respirators and by suitable protective clothing.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-03009 Flammable liquids.
(((1))) In all cases when liquid solvents, paint and preservative removers, paints or vehicles, other than those covered by WAC 296-304-03007(2), are capable of producing a flammable atmosphere under the conditions of use the following precautions ((shall)) must be taken:
(((a))) (1) Smoking, open flames, arcs and spark-producing equipment ((shall)) must be prohibited in the area.
(((b))) (2) Ventilation ((shall)) must be provided in sufficient quantities to keep the concentration of vapors below ten percent of their lower explosive limit. Frequent tests ((shall)) must be made by a competent person to ascertain the concentration.
(((c))) (3) Scrapings and rags soaked with these materials ((shall)) must be kept in a covered metal container.
(((d))) (4) Only explosion proof lights, approved by the Underwriters' Laboratories for use in Class I, Group D atmospheres, or approved as permissible by the U.S. Bureau of Mines or the U.S. Coast Guard, ((shall)) must be used.
(((e))) (5) A competent person ((shall)) must inspect all power and lighting cables to ensure that the insulation is in excellent condition, free of all cracks and worn spots, that there are no connections within fifty feet of the operation, that lines are not overloaded, and that they are suspended with sufficient slack to prevent undue stress or chafing.
(((f))) (6) Suitable fire extinguishing equipment ((shall)) must be immediately available in the work area and shall be maintained in a state of readiness for instant use.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-03-093, filed 1/18/05, effective 3/1/05)
WAC 296-304-04001 Ventilation and protection in welding, cutting and heating.
(1) Mechanical ventilation requirements.
(a) For the purposes of this section, mechanical ventilation ((shall)) must meet the following requirements:
(i) Mechanical ventilation ((shall)) must consist of either general mechanical ventilation systems or local exhaust systems.
(ii) General mechanical ventilation ((shall)) must be of sufficient capacity and so arranged as to produce the number of air changes necessary to maintain welding fumes and smoke within safe limits.
(iii) Local exhaust ventilation ((shall)) must consist of freely movable hoods intended to be placed by the welder or burner as close as practicable to the work. This system ((shall)) must be of sufficient capacity and so arranged as to remove fumes and smoke at the source and keep the concentration of them in the breathing zone within safe limits.
(iv) Contaminated air exhausted from a working space ((shall)) must be discharged into the open air or otherwise clear of the source of intake air.
(v) All air replacing that withdrawn ((shall)) must be clean and respirable.
(vi) Oxygen ((shall)) must not be used for ventilation purposes, comfort cooling, blowing dust or dirt from clothing, or for cleaning the work area.
(2) Welding, cutting and heating in confined spaces.
(a) Except as provided in WAC 296-304-04001 (2)(c) and (3)(b), either general mechanical or local exhaust ventilation meeting the requirements of (1) of this section ((shall)) must be provided whenever welding, cutting or heating is performed in a confined space.
(b) The means of access ((shall)) must be provided to a confined space and ventilation ducts to this space ((shall)) must be arranged in accordance with WAC 296-304-05011 (2)(a) and (b).
(c) When sufficient ventilation cannot be obtained without blocking the means of access, employees in the confined space ((shall)) must be protected by air line respirators in accordance with the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC, and an employee on the outside of such a confined space ((shall)) must be assigned to maintain communication with those working within it and to aid them in an emergency.
(3) Welding, cutting or heating of metals of toxic significance.
(a) Welding, cutting or heating in any enclosed spaces aboard the vessel involving the metals specified in this subsection ((shall)) must be performed with either general mechanical or local exhaust ventilation meeting the requirements of (1) of this section.
(i) Zinc-bearing base or filler metals or metals coated with zinc-bearing materials.
(ii) Lead base metals.
(iii) Cadmium-bearing filler materials.
(iv) Chromium-bearing metals or metals coated with chromium-bearing materials.
(b) Welding, cutting, or heating in any enclosed spaces aboard the vessel involving the metals specified in this subsection ((shall)) must be performed with local exhaust ventilation in accordance with the requirements of (1) of this section or employees ((shall)) must be protected by air line respirators in accordance with the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC.
(i) Metals containing lead, other than as an impurity, or metals coated with lead-bearing materials.
(ii) Cadmium-bearing or cadmium coated base metals.
(iii) Metals coated with mercury-bearing metals.
(iv) Beryllium-containing base or filler metals. Because of its high toxicity, work involving beryllium ((shall)) must be done with both local exhaust ventilation and air line respirators.
(c) Employees performing such operations in the open air ((shall)) must be protected by filter type respirators in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-304-09003, except that employees performing such operations on beryllium-containing base or filler metals ((shall)) must be protected by air line respirators in accordance with the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC.
(d) Other employees exposed to the same atmosphere as the welders or burners ((shall)) must be protected in the same manner as the welder or burner.
(4) Inert-gas metal-arc welding.
(a) Since the inert-gas metal-arc welding process involves the production of ultraviolet radiation of intensities of 5 to 30 times that produced during shielded metal-arc welding, the decomposition of chlorinated solvents by ultraviolet rays, and the liberation of toxic fumes and gases, employees ((shall)) must not be permitted to engage in, or be exposed to the process until the following special precautions have been taken:
(i) The use of chlorinated solvents ((shall)) must be kept at least two hundred feet from the exposed arc, and surfaces prepared with chlorinated solvents ((shall)) must be thoroughly dry before welding is permitted on such surfaces.
(ii) Helpers and other employees in the area not protected from the arc by screening as provided in WAC ((206-304-04011(5) shall)) 296-304-04011(5) must be protected by filter lenses meeting the requirements of Tables I-1A and B (see below). When two or more welders are exposed to each other's arc, filter lens goggles of a suitable type meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-09001 (1) and (3) ((shall)) must be worn under welding helmets or hand shields to protect the welder against flashes and radiant energy when either the helmet is lifted or the shield is removed.
(iii) Welders and other employees who are exposed to radiation ((shall)) must be suitably protected so that the skin is covered completely to prevent burns and other damage by ultraviolet rays. Welding helmets and hand shields ((shall)) must be free of leaks and openings, and free of highly reflective surfaces.
(iv) When inert-gas metal-arc welding is being performed on stainless steel, the requirements of (3)(b) of this section ((shall)) must be met to protect against dangerous concentrations of nitrogen dioxide.
(5) General welding, cutting and heating.
(a) Welding, cutting and heating not involving conditions or materials described in (2), (3) or (4) of this section may normally be done without mechanical ventilation or respiratory protective equipment, but where, because of unusual physical or atmospheric conditions, an unsafe accumulation of contaminants exists, suitable mechanical ventilation or respiratory protective equipment ((shall)) must be provided.
(b) Employees performing any type of welding, cutting or heating ((shall)) must be protected by suitable eye protective equipment in accordance with the requirements of Tables I-1A and B (see below).
(6) ((Residues and cargos of metallic ores.)) Residues and cargos of metallic ores of toxic significance ((shall)) must be removed from the area or protected from the heat before welding, cutting or heating is begun.
TABLE I-1A
FILTER LENSES FOR PROTECTION AGAINST
RADIANT ENERGY
OPERATIONS |
ELECTRODE SIZE 1/32 IN |
ARC CURRENT |
MINIMUM PROTECTIVE SHADE |
|
Shielded metal arc welding |
Less than 3 3-5 5-8 More than 8 |
Less than 60 60-160 160-250 250-550 |
7 8 10 11 |
|
Gas metal arc welding and flux cored arc welding |
Less than 60 60-160 160-250 250-550 |
7 10 10 10 |
||
Gas Tungsten arc welding |
Less than 50 50-150 150-500 |
8 8 10 |
||
Air carbon arc cutting |
(Light) (Heavy) |
Less than 500 500-1000 |
10 11 |
|
Plasma arc welding |
Less than 20 20-100 100-400 400-800 |
6 8 10 11 |
||
Plasma arc cutting |
(Light)** (Medium)** (Heavy)** |
Less than 300 300-400 400-800 |
8 9 10 |
|
Torch brazing |
— |
— |
3 |
|
Torch soldering |
— |
— |
2 |
|
Carbon Arc welding |
— |
— |
14 |
|
** | These values apply where the actual arc is clearly seen. Lighter filters may be used when the arc is hidden by the workplace. |
TABLE I-1B
FILTER LENSES FOR PROTECTION AGAINST
RADIANT ENERGY
OPERATIONS |
PLATE THICKNESS... INCHES |
PLATE THICKNESS... MM |
MINIMUM* PROTECTIVE SHADE |
Gas welding |
|||
Light Medium Heavy |
Under 1/8 1/8 - 1/2 Over 1/2 |
Under 3.2 3.2 - 12.7 Over 12.7 |
4 5 6 |
Oxygen cutting |
|||
Light Medium Heavy |
Under 1 1 - 6 Over 6 |
Under 25 25 - 100 Over 150 |
3 4 5 |
* | As rule of thumb, start with a shade that is too dark to see the weld zone. Then go to a lighter shade which gives sufficient view of the weld zone without going below the minimum. In oxyfuel gas welding or cutting where the torch produces a high yellow light, it is desirable to use a filter lens that absorbs the yellow or sodium line in the viable light of the (spectrum) operation. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-04005 Welding, cutting and heating in way of preservative coatings.
(1) Before welding, cutting or heating is commenced on any surface covered by a preservative coating whose flammability is not known, a test ((shall)) must be made by a competent person to determine its flammability. Preservative coatings ((shall)) must be considered to be highly flammable when scrapings burn with extreme rapidity.
(2) Precautions ((shall)) must be taken to prevent ignition of highly flammable hardened preservative coatings. When coatings are determined to be highly flammable they ((shall)) must be stripped from the area to be heated to prevent ignition. A 1 1/2-inch or larger fire hose with fog nozzle, which has been uncoiled and placed under pressure, ((shall)) must be immediately available for instant use in the immediate vicinity, consistent with avoiding freezing of the hose.
(3) Protection against toxic preservative coatings.
(a) In enclosed spaces all surfaces covered with toxic preservatives shall be stripped of all toxic coatings for a distance of at least 4 inches from the area of heat application or the employees ((shall)) must be protected by air line respirators meeting the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators.
(b) In the open air employees ((shall)) must be protected by a filter type respirator in accordance with the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators.
(4) Before welding, cutting or heating is commenced in enclosed spaces on metals covered by soft and greasy preservatives, the following precautions ((shall)) must be taken:
(a) A competent person ((shall)) must test the atmosphere in the space to ensure that it does not contain explosive vapors, since there is a possibility that some soft and greasy preservatives may have flash points below temperatures which may be expected to occur naturally. If such vapors are determined to be present, no hot work ((shall)) must be commenced until such precautions have been taken ((as)) that will ensure ((that)) the welding, cutting or heating can be performed in safety.
(b) The preservative coatings ((shall)) must be removed for a sufficient distance from the area to be heated to ensure that the temperature of the unstripped metal will not be appreciably raised. Artificial cooling of the metal surrounding the heated area may be used to limit the size of the area required to be cleaned. The prohibition contained in WAC 296-304-03005 (2)(b) ((shall)) must apply.
(5) Immediately after welding, cutting or heating is commenced in enclosed spaces on metal covered by soft and greasy preservatives, and at frequent intervals thereafter, a competent person ((shall)) must make tests to ensure that no flammable vapors are being produced by the coatings. If such vapors are determined to be present, the operation ((shall)) must be stopped immediately and ((shall)) must not be resumed until such additional precautions have been taken as are necessary to ensure that the operation can be resumed safely.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 76-7, filed 3/1/76)
WAC 296-304-04007 Welding, cutting and heating of hollow metal containers and structures not covered by WAC 296-304-02003.
(1) Drums, containers, or hollow structures which have contained toxic or flammable substances ((shall)) must, before welding, cutting, or heating is undertaken on them, either be filled with water or thoroughly cleaned of such substances and ventilated and tested.
(2) Before heat is applied to a drum, container, or hollow structure, a vent or opening ((shall)) must be provided for the release of any built-up pressure during the application of heat.
(3) Before welding, cutting, heating or brazing is begun on structural voids such as skegs, bilge keels, fair waters, masts, booms, support stanchions, pipe stanchions or railings, a competent person ((shall)) must inspect the object and, if necessary, test it for the presence of flammable liquids or vapors. If flammable liquids or vapors are present, the object ((shall)) must be made safe.
(4) Objects such as those listed in (3) of this section ((shall)) must also be inspected to determine whether water or other nonflammable liquids are present which, when heated, would build up excessive pressure. If such liquids are determined to be present, the object ((shall)) must be vented, cooled, or otherwise made safe during the application of heat.
(5) Jacketed vessels ((shall)) must be vented before and during welding, cutting or heating operations in order to release any pressure which may build up during the application of heat.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-04009 Gas welding and cutting.
(1) Transporting, moving and storing compressed gas cylinders.
(a) Valve protection caps ((shall)) must be in place and secure. Oil ((shall)) must not be used to lubricate protection caps.
(b) When cylinders are hoisted, they ((shall)) must be secured on a cradle, slingboard or pallet. They ((shall)) must not be hoisted by means of magnets or choker slings.
(c) Cylinders ((shall)) must be moved by tilting and rolling them on their bottom edges. They ((shall)) must not be intentionally dropped, struck, or permitted to strike each other violently.
(d) When cylinders are transported by vehicle, they ((shall)) must be secured in position.
(e) Valve protection caps ((shall)) must not be used for lifting cylinders from one vertical position to another. Bars ((shall)) must not be used under valves or valve protection caps to pry cylinders loose when frozen. Warm, not boiling, water ((shall)) must be used to thaw cylinders loose.
(f) Unless cylinders are firmly secured on a special carrier intended for this purpose, regulators ((shall)) must be removed and valve protection caps put in place before cylinders are moved.
(g) A suitable cylinder truck, chain, or other steadying device ((shall)) must be used to keep cylinders from being knocked over while in use.
(h) When work is finished, when cylinders are empty or when cylinders are moved at any time, the cylinder valves ((shall)) must be closed.
(i) Acetylene cylinders ((shall)) must be secured in an upright position at all times except, if necessary, for short periods of time while cylinders are actually being hoisted or carried.
(2) Placing cylinders.
(a) Cylinders ((shall)) must be kept far enough away from the actual welding or cutting operation so that sparks, hot slag or flame will not reach them. When this is impractical, fire resistant shields ((shall)) must be provided.
(b) Cylinders ((shall)) must be placed where they cannot become part of an electrical circuit. Electrodes ((shall)) must not be struck against a cylinder to strike an arc.
(c) Fuel gas cylinders ((shall)) must be placed with valve end up whenever they are in use. They ((shall)) must not be placed in a location where they would be subject to open flame, hot metal, or other sources of artificial heat.
(d) Cylinders containing oxygen or acetylene or other fuel gas ((shall)) must not be taken into confined spaces.
(3) Treatment of cylinders.
(a) Cylinders, whether full or empty, ((shall)) must not be used as rollers or supports.
(b) No person other than the gas supplier ((shall)) must attempt to mix gases in a cylinder. No one except the owner of the cylinder or person authorized by ((him shall)) them must refill a cylinder. No one ((shall)) must use a cylinder's contents for purposes other than those intended by the supplier. Only cylinders bearing Interstate Commerce Commission identification and inspection markings ((shall)) must be used.
(c) No damaged or defective cylinder ((shall)) must be used.
(4) Use of fuel gas. ((The employer shall)) You must thoroughly instruct employees in the safe use of fuel gas, as follows:
(a) Before connecting a regulator to a cylinder valve, the valve ((shall)) must be opened slightly and closed immediately. (This action is generally termed "cracking" and is intended to clear the valve of dust or dirt that might otherwise enter the regulator.) The person cracking the valve ((shall)) must stand to one side of the outlet, not in front of it. The valve of a fuel gas cylinder ((shall)) must not be cracked where the gas would reach welding work, sparks, flame or other possible sources of ignition.
(b) The cylinder valve ((shall)) must always be opened slowly to prevent damage to the regulator. To permit quick closing, valves on fuel gas cylinders ((shall)) must not be opened more than 1 1/2 turns. When a special wrench is required, it ((shall)) must be left in position on the stem of the valve while the cylinder is in use so that the fuel gas flow can be shut off quickly in case of emergency. In the case of a manifolded or coupled cylinders, at least one such wrench ((shall)) must always be available for immediate use. Nothing ((shall)) must be placed on top of a fuel gas cylinder, when in use, which may damage the safety device or interfere with the quick closing of the valve.
(c) Fuel gas ((shall)) must not be used from cylinders through torches or other devices which are equipped with shut-off valves without reducing the pressure through a suitable regulator attached to the cylinder valve or manifold.
(d) Before a regulator is removed from a cylinder valve, the cylinder valve ((shall)) must always be closed and the gas released from the regulator.
(e) If, when the valve on a fuel gas cylinder is opened, there is found to be a leak around the valve stem, the valve ((shall)) must be closed and the gland nut tightened. If this action does not stop the leak, the use of the cylinder ((shall)) must be discontinued, and it ((shall)) must be properly tagged and removed from the vessel. In the event that fuel gas should leak from the cylinder valve rather than from the valve stem and the gas cannot be shut off, the cylinder ((shall)) must be properly tagged and removed from the vessel. If a regulator attached to a cylinder valve will effectively stop a leak through the valve seat the cylinder need not be removed from the vessel.
(f) If a leak should develop at a fuse plug or other safety device, the cylinder ((shall)) must be removed from the vessel.
(5) Fuel gas and oxygen manifolds.
(a) Fuel gas and oxygen manifolds ((shall)) must bear the name of the substance they contain in letters at least one (1) inch high which ((shall be)) must either be painted on the manifold or on a sign permanently attached to it.
(b) Fuel gas and oxygen manifolds ((shall)) must be placed in safe and accessible locations in the open air. They ((shall)) must not be located within enclosed spaces.
(c) Manifold hose connections, including both ends of the supply hose that lead to the manifold, ((shall)) must be such that the hose cannot be interchanged between fuel gas and oxygen manifolds and supply header connections. Adapters ((shall)) must not be used to permit the interchange of hose. Hose connections ((shall)) must be kept free of grease and oil.
(d) When not in use, manifold and header hose connections ((shall)) must be capped.
(e) Nothing ((shall)) must be placed on top of a manifold, when in use, which will damage the manifold or interfere with the quick closing of the valves.
(6) Hose.
(a) Fuel gas hose and oxygen hose ((shall)) must be easily distinguishable from each other. The contrast may be made by different colors or by surface characteristics readily distinguishable by the sense of touch. Oxygen and fuel gas hoses ((shall)) must not be interchangeable. A single hose having more than one gas passage, a wall failure of which would permit the flow of one gas into the other gas passage, ((shall)) must not be used.
(b) When parallel sections of oxygen and fuel gas hose are taped together, not more than 4 inches out of 8 inches ((shall)) must be covered by tape.
(c) All hose carrying acetylene, oxygen, natural or manufactured fuel gas, or any gas or substance which may ignite or enter into combustion or be in any way harmful to employees, ((shall)) must be inspected at the beginning of each shift. Defective hoses ((shall)) must be removed from service.
(d) Hose which has been subjected to flashback or which shows evidence of severe wear or damage ((shall)) must be tested to twice the normal pressure to which it is subject, but in no case less than two hundred psi. Defective hose or hose in doubtful condition ((shall)) must not be used.
(e) Hose couplings ((shall)) must be of the type that cannot be unlocked or disconnected by means of a straight pull without rotary motion.
(f) Boxes used for the stowage of gas hose ((shall)) must be ventilated.
(7) Torches.
(a) Clogged torch tip openings ((shall)) must be cleaned with suitable cleaning wires, drills or other devices designed for such purpose.
(b) Torches ((shall)) must be inspected at the beginning of each shift for leaking shut-off valves, hose couplings, and tip connections. Defective torches ((shall)) must not be used.
(c) Torches ((shall)) must be lighted by friction lighters or other approved devices, and not by matches or from hot work.
(8) Pressure regulators. Oxygen and fuel gas pressure regulators including their related gauges ((shall)) must be in proper working order while in use.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-04011 Arc welding and cutting.
(1) Manual electrode holders.
(a) Only manual electrode holders which are specifically designed for arc welding and cutting and are of a capacity capable of safely handling the maximum rated current required by the electrodes ((shall)) must be used.
(b) Any current carrying parts passing through the portion of the holder which the arc welder or cutter grips in his hand, and the outer surfaces of the jaws of the holder, ((shall)) must be fully insulated against the maximum voltage encountered to ground.
(2) Welding cables and connectors.
(a) All arc welding and cutting cables ((shall)) must be of the completely insulated, flexible type, capable of handling the maximum current requirements of the work in progress, taking into account the duty cycle under which the arc welder or cutter is working.
(b) Only cable free from repair or splices for a minimum distance of ten feet from the cable end to which the electrode holder is connected ((shall)) must be used, except that cables with standard insulated connectors or with splices whose insulating quality is equal to that of the cable are permitted.
(c) When it becomes necessary to connect or splice lengths of cable one to another, substantial insulated connectors of a capacity at least equivalent to that of the cable ((shall)) must be used. If connections are effected by means of cable lugs, they ((shall)) must be securely fastened together to give good electrical contact, and the exposed metal parts of the lugs ((shall)) must be completely insulated.
(d) Cables in poor repair ((shall)) must not be used. When a cable, other than the cable lead referred to in (b), becomes worn to the extent of exposing bare conductors, the portion thus exposed ((shall)) must be protected by means of rubber and friction tapes or other equivalent insulation.
(3) Ground returns and machine grounding.
(a) A ground return cable ((shall)) must have a safe current carrying capacity equal to or exceeding the specified maximum output capacity of the arc welding or cutting unit which it services. When a single ground return cable services more than one unit, its safe current carrying capacity ((shall)) must equal or exceed the total specified maximum output capacities of all the units which it services.
(b) Structures or pipe lines, except pipelines containing gases or flammable liquids or conduits containing electrical circuits, may be used as part of the ground return circuit, provided that the pipe or structure has a current carrying capacity equal to that required by (2).
(c) When a structure or pipe line is employed as a ground return circuit, it ((shall)) must be determined that the required electrical contact exists at all joints. The generation of an arc, sparks or heat at any point ((shall)) must cause rejection of the structure as a ground circuit.
(d) When a structure or pipe line is continuously employed as a ground return circuit, all joints ((shall)) must be bonded, and periodic inspections ((shall)) must be conducted to ensure that no condition of electrolysis or fire hazard exists by virtue of such use.
(e) The frames of all arc welding and cutting machines ((shall)) must be grounded either through a third wire in the cable containing the circuit conductor or through a separate wire which is grounded at the source of the current. Grounding circuits, other than by means of the vessel's structure, ((shall)) must be checked to ensure that the circuit between the ground and the grounded power conductor has resistance low enough to permit sufficient current to flow to cause the fuse or circuit breaker to interrupt the current.
(f) All ground connections ((shall)) must be inspected to ensure that they are mechanically strong and electrically adequate for the required current.
(4) Operating instructions. ((Employers shall)) You must instruct employees in the safe means of arc welding and cutting as follows:
(a) When electrode holders are to be left unattended, the electrodes ((shall)) must be removed and the holders ((shall)) must be so placed or protected that they cannot make electrical contact with employees or conducting objects.
(b) Hot electrode holders ((shall)) must not be dipped in water, since to do so may expose the arc welder or cutter to electric shock.
(c) When the arc welder or cutter has occasion to leave his work or to stop work for any appreciable length of time, or when the arc welding or cutting machine is to be moved, the power supply switch to the equipment ((shall)) must be opened.
(d) Any faulty or defective equipment ((shall)) must be reported to the supervisor.
(5) Shielding. Whenever practicable, all arc welding and cutting operations ((shall)) must be shielded by noncombustible or flame-proof screens which will protect employees and other persons working in the vicinity from the direct rays of the arc.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 76-7, filed 3/1/76)
WAC 296-304-04013 Uses of fissionable material in ship-breaking, shipbuilding and ship repairing.
(1) In ship-breaking, shipbuilding and ship repairing and related activities involving the use of and exposure to sources of ionizing radiation not only on conventionally powered but also on nuclear powered vessels, the applicable provisions of the Atomic Energy Commission's Standards for Protection Against Radiation (10 C.F.R. Part 20), relating to protection against occupational radiation exposure, ((shall)) must apply.
(2) Any activity which involves the use of radioactive material, whether or not under license from the Atomic Energy Commission, ((shall)) must be performed by competent persons specially trained in the proper and safe operation of such equipment. In the case of materials used under commission license, only persons actually licensed, or competent persons under direction and supervision of the licensee, ((shall)) must perform such work.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-05001 Scaffolds or staging.
(1) General requirements.
(a) All scaffolds and their supports whether of lumber, steel or other material, ((shall)) must be capable of supporting the load they are designed to carry with a safety factor of not less than four.
(b) All lumber used in the construction of scaffolds ((shall)) must be spruce, fir, long leaf yellow pine, Oregon pine or wood of equal strength. The use of hemlock, short leaf yellow pine, or short fiber lumber is prohibited.
(c) Lumber dimensions as given are nominal except where given in fractions of an inch.
(d) All lumber used in the construction of scaffolds ((shall)) must be sound, straight-grained, free from cross grain, shakes and large, loose or dead knots. It ((shall)) must also be free from dry rot, large checks, worm holes or other defects which impair its strength or durability.
(e) Scaffolds ((shall)) must be maintained in a safe and secure condition. Any component of the scaffold which is broken, burned or otherwise defective ((shall)) must be replaced.
(f) Barrels, boxes, cans, loose bricks, or other unstable objects ((shall)) must not be used as working platforms or for the support of planking intended as scaffolds or working platforms.
(g) No scaffold ((shall)) must be erected, moved, dismantled or altered except under the supervision of competent persons.
(h) No welding, burning, riveting or open flame work ((shall)) must be performed on any staging suspended by means of fiber rope.
(i) Lifting bridles on working platforms suspended from cranes ((shall)) must consist of four legs so attached that the stability of the platform is assured.
(j) Unless the crane hook has a safety latch or is moused, the lifting bridles on working platforms suspended from cranes ((shall)) must be attached by shackles to the lower lifting block or other positive means ((shall)) must be taken to prevent them from becoming accidentally disengaged from the crane hook.
(2) Independent pole wood scaffolds.
(a) All pole uprights ((shall)) must be set plumb. Poles ((shall)) must rest on a foundation of sufficient size and strength to distribute the load and to prevent displacement.
(b) In light-duty scaffolds not more than 24 feet in height, poles may be spliced by overlapping the ends not less than 4 feet and securely nailing them together. A substantial cleat ((shall)) must be nailed to the lower section to form a support for the upper section except when bolted connections are used.
(c) All other poles to be spliced ((shall)) must be squared at the ends of each splice, abutted, and rigidly fastened together by not less than two cleats securely nailed or bolted thereto. Each cleat ((shall)) must overlap each pole end by at least 24 inches and ((shall)) must have a width equal to the face of the pole to which it is attached. The combined cross sectional area of the cleats ((shall)) must be not less than the cross sectional area of the pole.
(d) Ledgers ((shall)) must extend over two consecutive pole spaces and ((shall)) must overlap the poles at each end by not less than 4 inches. They ((shall)) must be left in position to brace the poles as the platform is raised with the progress of the work. Ledgers ((shall)) must be level and ((shall)) must be securely nailed or bolted to each pole and ((shall)) must be placed against the inside face of each pole.
(e) All bearers ((shall)) must be set with their greater dimension vertical and ((shall)) must extend beyond the ledgers upon which they rest.
(f) Diagonal bracing ((shall)) must be provided between the parallel poles, and cross bracing ((shall)) must be provided between the inner and outer poles or from the outer poles to the ground.
(g) Minimum dimensions and spacing of members ((shall)) must be in accordance with Table E-1 in WAC 296-304-07011.
(h) Platform planking ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of (8) of this section.
(i) Backrails and toeboards ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of (9) of this section.
(3) Independent pole metal scaffolds.
(a) Metal scaffold members ((shall)) must be maintained in good repair and free of corrosion.
(b) All vertical and horizontal members ((shall)) must be fastened together with a coupler or locking device which will form a positive connection. The locking device ((shall)) must be of a type which has no loose parts.
(c) Posts ((shall)) must be kept plumb during erection and the scaffold ((shall)) must be subsequently kept plumb and rigid by means of adequate bracing.
(d) Posts ((shall)) must be fitted with bases supported on a firm foundation to distribute the load. When wooden sills are used, the bases ((shall)) must be fastened thereto.
(e) Bearers ((shall)) must be located at each set of posts, at each level, and at each intermediate level where working platforms are installed.
(f) Tubular bracing ((shall)) must be applied both lengthwise and crosswise as required.
(g) Platform planking ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of (8) of this section.
(h) Backrails and toeboards ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of (9) of this section.
(4) Wood trestle and extension trestle ladders.
(a) The use of trestle ladders, or extension sections or base sections of extension trestle ladders longer than 20 feet is prohibited. The total height of base and extension may, however, be more than 20 feet.
(b) The minimum dimensions of the side rails of the trestle ladder, or the base sections of the extension trestle ladder, ((shall)) must be as follows:
(i) Ladders up to and including those 16 feet long ((shall)) must have side rails of not less than 1 5/16 x 2 3/4 inch lumber.
(ii) Ladders over 16 feet long and up to and including those 20 feet long ((shall)) must have side rails of not less than 1 5/16 x 3 inch lumber.
(c) The side rails of the extension section of the extension trestle ladder ((shall)) must be parallel and ((shall)) must have minimum dimensions as follows:
(i) Ladders up to and including 12 feet long ((shall)) must have side rails of not less than 1 5/16 x 2 1/4 inch lumber.
(ii) Ladders over 12 feet long and up to and including those 16 feet long ((shall)) must have side rails of not less than 1 5/16 x 2 1/2 inch lumber.
(iii) Ladders over 16 feet long and up to and including those 20 feet long ((shall)) must have side rails of not less than 1 5/16 x 3 inch lumber. (Rev. 2-17-76)
(d) Trestle ladders and base sections of extension trestle ladders ((shall)) must be so spread that when in an open position the spread of the trestle at the bottom, inside to inside, ((shall be not)) must not be less than 5 1/2 inches per foot of the length of the ladder.
(e) The width between the side rails at the bottom of the trestle ladder or of the base section of the extension trestle ladder ((shall be not)) must not be less than 21 inches for all ladders and sections 6 feet or less in length. For longer lengths of ladder the width ((shall)) must be increased at least 1 inch for each additional foot of length. The width between the side rails of the extension section of the trestle ladder ((shall)) must be not less than 12 inches.
(f) In order to limit spreading, the top ends of the side rails of both the trestle ladder and of the base section of the extension trestle ladder ((shall)) must be beveled, or of equivalent construction, and ((shall)) must be provided with a metal hinge.
(g) A metal spreader or locking device to hold the front and back sections in an open position, and to hold the extension section securely in the elevated position, ((shall)) must be a component of each trestle ladder or extension trestle ladder.
(h) Rungs ((shall)) must be parallel and level. On the trestle ladder, or on the base section of the extension trestle ladder, rungs ((shall)) must be spaced not less than 8 inches nor more than 18 inches apart; on the extension section of the extension trestle ladder, rungs ((shall)) must be spaced not less than 6 inches nor more than 12 inches apart.
(i) Platform planking ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of (8) of this section, except that the width of the platform planking ((shall)) must not exceed the distance between the side rails.
(j) Backrails and toeboards ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of (9) of this section.
(5) Painters' suspended scaffolds.
(a) The supporting hooks of swinging scaffolds ((shall)) must be constructed to be equivalent in strength to mild steel or wrought iron, ((shall)) must be forged with care, ((shall be not)) must not be less than 7/8 inch in diameter, and ((shall)) must be secured to a safe anchorage at all times.
(b) The ropes supporting a swinging scaffold ((shall)) must be equivalent in strength to first-grade 3/4 inch diameter manila rope properly rigged into a set of standard 6 inch blocks consisting of at least one double and one single block.
(c) Manila and wire ropes ((shall)) must be carefully examined before each operation and thereafter as frequently as may be necessary to ensure their safe condition.
(d) Each end of the scaffold platform ((shall)) must be supported by a wrought iron or mild steel stirrup or hanger, which in turn is supported by the suspension ropes.
(e) Stirrups ((shall)) must be constructed so as to be equivalent in strength to wrought iron 3/4 inch in diameter.
(f) The stirrups ((shall)) must be formed with a horizontal bottom member to support the platform, ((shall)) must be provided with means to support the guardrail and midrail and ((shall)) must have a loop or eye at the top for securing the supporting hook on the block.
(g) Two or more swinging scaffolds ((shall)) must not at any time be combined into one by bridging the distance between them with planks or any other form of platform.
(h) No more than two persons ((shall)) must be permitted to work at one time on a swinging scaffold built to the minimum specifications contained in this section. Where heavier construction is used, the number of persons permitted to work on the scaffold ((shall)) must be determined by the size and the safe working load of the scaffold.
(i) Backrails and toeboards ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of (9) of this section.
(j) The swinging scaffold platform ((shall)) must be one of the three types described in (k), (l), and (m) of this section.
(k) The ladder-type platform consists of boards upon a horizontal ladder-like structure, referred to herein as the ladder, the side rails of which are parallel. If this type of platform is used the following requirements ((shall)) must be met:
(i) The width between the side rails ((shall)) must be no more than 20 inches.
(ii) The side rails of ladders in ladder-type platforms ((shall)) must be equivalent in strength to a beam of clear straight-grained spruce of the dimensions contained in Table E-2 in WAC 296-304-07011.
(iii) The side rails ((shall)) must be tied together with tie rods. The tie rods ((shall be not)) must not be less than 5/16 inch in diameter, located no more than 5 feet apart, pass through the rails, and be riveted up tight against washers at both ends.
(iv) The rungs ((shall)) must be of straight-grained oak, ash, or hickory, not less than 1 1/8 inches diameter, with 7/8 inch tenons mortised into the side rails not less than 7/8 inch and ((shall)) must be spaced no more than 18 inches on centers.
(v) Flooring strips ((shall)) must be spaced no more than 5/8 inch apart except at the side rails, where 1 inch spacing is permissible.
(vi) Flooring strips ((shall)) must be cleated on their undersides.
(l) The plank-type platform consists of planks supported on the stirrups or hangers. If this type of platform is used, the following requirements ((shall)) must be met:
(i) The planks of plank-type platforms ((shall be not)) must not be less than 2 x 10 inch lumber.
(ii) The platform ((shall be no)) must not be more than 24 inches in width.
(iii) The planks ((shall)) must be tied together by cleats of not less than 1 x 6 inch lumber, nailed on their undersides at intervals of not more than 4 feet.
(iv) The planks ((shall)) must extend not less than 6 inches nor more than 18 inches beyond the supporting stirrups.
(v) A cleat ((shall)) must be nailed across the platform on the underside at each end outside the stirrup to prevent the platform from slipping off the stirrup.
(vi) Stirrup supports ((shall be not)) must not be more than 10 feet apart.
(m) The beam-type platform consists of longitudinal side stringers with cross beams set on edge and spaced not more than 4 feet apart on which longitudinal platform planks are laid. If this type platform is used the following requirements ((shall)) must be met:
(i) The side stringers ((shall)) must be of sound, straight-grained lumber, free from knots, and of not less than 2 x 6 inch lumber, set on edge.
(ii) The stringers ((shall)) must be supported on the stirrups with a clear span between stirrups of not more than 16 feet.
(iii) The stringers ((shall)) must be bolted to the stirrups by U-bolts passing around the stirrups and bolted through the stringers with nuts drawn up tight on the inside face.
(iv) The ends of the stringers ((shall)) must extend beyond the stirrups not less than 6 inches nor more than 12 inches at each end of the platform.
(v) The platform ((shall)) must be supported on cross beams of 2 x 6 inch lumber between the side stringers securely nailed thereto and spaced not more than 4 feet on centers.
(vi) The platform ((shall be not)) must not be more than 24 inches wide.
(vii) The platform ((shall)) must be formed of boards 7/8 inch in thickness by not less than 6 inches in width, nailed tightly together, and extending to the outside face of the stringers.
(viii) The ends of all platform boards ((shall)) must rest on the top of the cross beams, ((shall)) must be securely nailed, and at no intermediate points in the length of the platform ((shall)) must there by any cantilever ends.
(6) Horse scaffolds.
(a) The minimum dimensions of lumber used in the construction of horses ((shall)) must be in accordance with Table E-3 in WAC 296-304-07011.
(b) Horses constructed of materials other than lumber ((shall)) must provide the strength, rigidity and security required of horses constructed of lumber.
(c) The lateral spread of the legs ((shall)) must be equal to not less than one-third of the height of the horse.
(d) All horses ((shall)) must be kept in good repair, and ((shall)) must be properly secured when used in staging or in locations where they may be insecure.
(e) Platform planking ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of (8) of this section.
(f) Backrails and toeboards ((shall)) must be in accordance with (9) of this section.
(7) Other types of scaffolds.
(a) Scaffolds of a type for which specifications are not contained in this section ((shall)) must meet the general requirements of (1), (8) and (9) of this section, ((shall)) must be in accordance with recognized principles of design and ((shall)) must be constructed in accordance with accepted standards covering such equipment.
(8) Scaffold or platform planking.
(a) Except as otherwise provided in (5)(k) and (m), platform planking ((shall be of not)) must not be less than 2 x 10 inch lumber. Platform planking ((shall)) must be straight-grained and free from large or loose knots and may be either rough or dressed.
(b) Platforms of staging ((shall be not)) must not be less than two 10 inch planks in width except in such cases as the structure of the vessel or the width of the trestle ladders make it impossible to provide such a width.
(c) Platform planking ((shall)) must project beyond the supporting members at either end by at least 6 inches but in no case ((shall)) must it project more than 12 inches unless the planks are fastened to the supporting members.
(d) Table E-4 in WAC 296-304-07011 ((shall)) must be used as a guide in determining safe loads for scaffold planks.
(9) Backrails and toeboards.
(a) Scaffolding, staging, runways, or working platforms which are supported or suspended more than 5 feet above a solid surface, or at any distance above the water, ((shall)) must be provided with a railing which has a top rail whose upper surface is from 42 to 45 inches above the upper surface of the staging, platform, or runway and a midrail located halfway between the upper rail and the staging, platform, or runway.
(b) Rails ((shall)) must be of 2 x 4 inch lumber, flat bar or pipe. When used with rigid supports, taut wire or fiber rope of adequate strength may be used. If the distance between supports is more than 8 feet, rails ((shall)) must be equivalent in strength to 2 x 4 inch lumber. Rails ((shall)) must be firmly secured. Where exposed to hot work or chemicals, fiber rope rails ((shall)) must not be used.
(c) Rails may be omitted where the structure of the vessel prevents their use. When rails are omitted employees working more than 5 feet above solid surfaces ((shall)) must be protected by safety belts and life lines meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-09021(2), and employees working over water ((shall)) must be protected by personal flotation devices meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-09017(1).
(d) Employees working from swinging scaffolds which are triced out of a vertical line below their supports or from scaffolds on paint floats subject to surging, ((shall)) must be protected against falling toward the vessel by a railing or a safety belt and line attached to the backrail.
(e) When necessary, to prevent tools and materials from falling on men below, toeboards of not less than 1 x 4 inch lumber ((shall)) must be provided.
(10) Access to staging.
(a) Access from below to staging more than 5 feet above a floor, deck or the ground ((shall)) must consist of well secured stairways, cleated ramps, fixed or portable ladders meeting the applicable requirements of WAC 296-304-05003 or rigid type noncollapsible trestles with parallel and level rungs.
(b) Ramps and stairways ((shall)) must be provided with 36-inch handrails with midrails.
(c) Ladders ((shall)) must be so located or other means ((shall)) must be taken so that it is not necessary for employees to step more than one foot from the ladder to any intermediate landing or platform.
(d) Ladders forming integral parts of prefabricated staging are deemed to meet the requirements of these regulations.
(e) Access from above to staging more than 3 feet below the point of access ((shall)) must consist of a straight, portable ladder meeting the applicable requirements of WAC 296-304-05003 or a Jacob's ladder properly secured, meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-05007(4).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-05003 Ladders.
(1) General requirements.
(a) The use of ladders with broken or missing rungs or steps, broken or split side rails, or other faulty or defective construction is prohibited. When ladders with such defects are discovered, they ((shall be)) must immediately be withdrawn from service. Inspection of metal ladders ((shall)) must include checking for corrosion of interiors of open end, hollow rungs.
(b) When sections of ladders are spliced, the ends ((shall)) must be abutted, and not fewer than 2 cleats ((shall)) must be securely nailed or bolted to each rail. The combined cross sectional area of the cleats ((shall be not)) must not be less than the cross sectional area of the side rail. The dimensions of side rails for their total length ((shall)) must be those specified in (2) or (3) of this section.
(c) Portable ladders ((shall)) must be lashed, blocked or otherwise secured to prevent their being displaced. The side rails of ladders used for access to any level ((shall)) must extend not less than 36 inches above that level. When this is not practical, grab rails which will provide a secure grip for an employee moving to or from the point of access ((shall)) must be installed.
(d) Portable metal ladders ((shall)) must be of strength equivalent to that of wood ladders. Manufactured portable metal ladders provided by ((the employer shall)) you must be in accordance with the provisions of the United States of America Standard Safety Code for Portable Metal Ladders, A14.2-1972.
(e) Portable metal ladders ((shall)) must not be used near electrical conductors nor for electric arc welding operations.
(f) Manufactured portable wood ladders provided by the employer ((shall)) must be in accordance with the provisions of the United States of America Standard Safety Code for Portable Wood Ladders, A-14.1-1968.
(2) Construction of portable wood cleated ladders up to 30 feet in length.
(a) Wood side rails ((shall)) must be made from west coast hemlock, eastern spruce, Sitka spruce, or wood of equivalent strength. Material ((shall)) must be seasoned, straight-grained wood, and free from shakes, checks, decay or other defects which will impair its strength. The use of low density woods is prohibited.
(b) Side rails ((shall)) must be dressed on all sides, and kept free of splinters.
(c) All knots ((shall)) must be sound and hard. The use of material containing loose knots is prohibited. Knots ((shall)) must not appear on the narrow face of the rail and, when in the side face, ((shall)) must be not more than 1/2 inch in diameter or within 1/2 inch of the edge of the rail or nearer than 3 inches to a tread or rung.
(d) Pitch pockets not exceeding 1/8 inch in width, 2 inches in length and 1/2 inch in depth are permissible in wood side rails, provided that not more than one such pocket appears in each 4 feet of length.
(e) The width between side rails at the base ((shall be not)) must not be less than 11 1/2 inches for ladders 10 feet or less in length. For longer ladders, this width ((shall)) must be increased at least 1/4 inch for each additional 2 feet in length.
(f) Side rails ((shall)) must be at least 1 5/8 x 3 5/8 inches in cross section.
(g) Cleats (meaning rungs rectangular in cross section with the wide dimension parallel to the rails) ((shall)) must be of the material used for side rails, straight-grained and free from knots. Cleats ((shall)) must be mortised into the edges of the side rails 1/2 inch, or filler blocks ((shall)) must be used on the rails between the cleats. The cleats ((shall)) must be secured to each rail with three 10d common wire nails or fastened with through bolts or other fasteners of equivalent strength. Cleats ((shall)) must be uniformly spaced not more than 12 inches apart.
(h) Cleats 20 inches or less in length ((shall)) must be at least 25/32 x 3 inches in cross section. Cleats over 20 inches but not more than 30 inches in length ((shall)) must be at least 25/32 x 3 3/4 inches in cross section.
(3) Construction of portable wood cleated ladders from 30 to 60 feet in length.
(a) Ladders from 30 to 60 feet in length ((shall)) must be in accordance with the specifications of (2) of this section with the following exceptions:
(i) Rails ((shall be of not)) must not be less than 2 x 6 inch lumber.
(ii) Cleats ((shall be of not)) must not be less than 1 x 4 inch lumber.
(iii) Cleats ((shall)) must be nailed to each rail with five 10d common wire nails or fastened with through bolts or other fastenings of equivalent strength.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-05005 Guarding of deck openings and edges.
(1) When employees are working in the vicinity of flush manholes and other small openings of comparable size in the deck and other working surfaces, such openings ((shall)) must be suitably covered or guarded to a height of not less than 30 inches, except where the use of such guards is made impracticable by the work actually in progress.
(2) When employees are working around open hatches not protected by coamings to a height of 24 inches or around other large openings, the edge of the opening ((shall)) must be guarded in the working area to a height of 36 to 42 inches, except where the use of such guards is made impracticable by the work actually in progress.
(3) When employees are exposed to unguarded edges of decks, platforms, flats, and similar flat surfaces, more than 5 feet above a solid surface, the edges ((shall)) must be guarded by adequate guardrails meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-05001 (9)(a) and (b), unless the nature of the work in progress or the physical conditions prohibit the use or installation of such guardrails.
(4) When employees are working near the unguarded edges of decks of vessels afloat, they ((shall)) must be protected by buoyant personal flotation devices, meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-09017(1).
(5) Sections of bilges from which floor plates or gratings have been removed ((shall)) must be guarded by guardrails except where they would interfere with work in progress. If these open sections are in a walkway at least two 10-inch planks placed side by side, or equivalent, ((shall)) must be laid across the opening to provide a safe walking surface.
(6) Gratings, walkways, and catwalks, from which sections or ladders have been removed, ((shall)) must be barricaded with adequate guardrails.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 98-02-006, filed 12/26/97, effective 3/1/98)
WAC 296-304-05007 Access to vessels.
(("))Barge((" -)). An unpowered, flat bottom, shallow draft vessel including scows, carfloats and lighters, but not ship-shaped or deep-draft barges.
(("))River towboat((" -)). A shallow draft, low free board, self-propelled vessel designed to tow river barges by pushing ahead.
(1) Access to vessels afloat. ((The employer shall)) You must not permit employees to board or leave any vessel, except a barge or river towboat, until the following requirements have been met:
(a) Whenever practicable, a gangway of not less than 20 inches walking surface, of adequate strength, maintained in safe repair and safely secured ((shall)) must be used. If a gangway is not practicable, a substantial straight ladder, extending at least 36 inches above the upper landing surface and adequately secured against shifting or slipping ((shall)) must be provided. When conditions are such that neither a gangway nor a straight ladder can be used, a Jacob's ladder meeting the requirements of (4)(a) and (b) of this section may be used.
(b) Each side of such gangway, and the turntable if used, ((shall)) must have a railing with a minimum height of approximately 33 inches measured perpendicularly from rail to walking surface at the stanchion, with a midrail. Rails ((shall)) must be of wood, pipe, chain, wire or rope and shall be kept taut at all times.
(c) Gangways on vessels inspected and certificated by the U.S. Coast Guard are deemed to meet the foregoing requirements, except in cases where the vessel's regular gangway is not being used.
(d) The gangway ((shall)) must be kept properly trimmed at all times.
(e) When a fixed tread accommodation ladder is used, and the angle is low enough to require employees to walk on the edge of the treads, cleated duckboards ((shall)) must be laid over and secured to the ladder.
(f) When the lower end of a gangway overhangs the water between the ship and the dock in such a manner that there is danger of employees falling between the ship and the dock, a net or other suitable protection ((shall)) must be rigged at the foot of the gangway in such a manner as to prevent employees from falling from the end of the gangway.
(g) If the foot of the gangway is more than one foot away from the edge of the apron, the space between them ((shall)) must be bridged by a firm walkway equipped with railings, with a minimum height of approximately 33 inches with midrails on both sides.
(h) Supporting bridles ((shall)) must be kept clear so as to permit unobstructed passage for employees using the gangway.
(i) When the upper end of the means of access rests on or flush with the top of the bulwark, substantial steps properly secured and equipped with at least one substantial handrail approximately 33 inches in height ((shall)) must be provided between the top of the bulwark and the deck.
(j) Obstructions ((shall)) must not be laid on or across the gangway.
(k) The means of access ((shall)) must be adequately illuminated for its full length.
(l) Unless the construction of the vessel makes it impossible, the means of access ((shall be so)) must be located so that drafts of cargo do not pass over it. In any event loads ((shall)) must not be passed over the means of access while employees are on it.
(2) Access to vessels in drydock or between vessels. Gangways meeting the requirements of (1)(a), (b), (i), (j) and (l) of this section ((shall)) must be provided for access from wing wall to vessel or, when two or more vessels, other than barges or river towboats, are lying abreast, from one vessel to another.
(3) Access to barges and river towboats.
(a) Ramps for access of vehicles to or between barges ((shall)) must be of adequate strength, provided with side boards, well maintained and properly secured.
(b) Unless employees can step safely to or from the wharf, float, barge, or river towboat, either a ramp in accordance with the requirements of (a) of this section or a safe walkway in accordance with the requirements of (1)(g) of this section ((shall)) must be provided. When a walkway is impracticable, a substantial straight ladder, extending at least 36 inches above the upper landing surface and adequately secured against shifting or slipping ((shall)) must be provided. When conditions are such that neither a walkway nor a straight ladder can be used, a Jacob's ladder in accordance with the requirements of (4) of this section may be used.
(c) The means of access ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of (1)(i), (j) and (k) of this section.
(4) Jacob's ladders.
(a) Jacob's ladders ((shall)) must be of the double rung or flat tread type. They ((shall)) must be well maintained and properly secured.
(b) A Jacob's ladder ((shall)) must either hang without slack from its lashings or be pulled up entirely.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-05009 Access to and guarding of dry docks and marine railways.
(1) A gangway, ramp or permanent stairway of not less than 20 inches walking surface, of adequate strength, maintained in safe repair and securely fastened, ((shall)) must be provided between a floating dry dock and the pier or bulkhead.
(2) Each side of such gangway, ramp or permanent stairway, including those which are used for access to wing walls from dry dock floors, ((shall)) must have a railing with a midrail. Such railings on gangways or ramps ((shall)) must be approximately 42 inches in height; and railings on permanent stairways ((shall be not)) must not be less than approximately 30 or more than approximately 34 inches in height. Rails ((shall)) must be of wood, pipe, chain, wire, or rope and ((shall)) must be kept taut at all times.
(3) Railings meeting the requirements of (2) of this section ((shall)) must be provided on the means of access to and from the floors of graving docks.
(4) Railings approximately 42 inches in height, with a midrail, ((shall)) must be provided on the edges of wing walls of floating dry docks and on the edges of graving docks. Sections of the railings may be temporarily removed where necessary to permit line handling while a vessel is entering or leaving the dock.
(5) When employees are working on the floor of a floating dry dock where they are exposed to the hazard of falling into the water, the end of the dry dock ((shall)) must be equipped with portable stanchions and 42 inch railings with a midrail. When such a railing would be impracticable or ineffective, other effective means ((shall)) must be provided to prevent employees from falling into the water.
(6) Access to wingwalls from floors of dry docks ((shall)) must be by ramps, permanent stairways or ladders meeting the applicable requirements of WAC 296-304-05003.
(7) Catwalks on stiles of marine railways ((shall)) must be no less than 20 inches wide and ((shall)) must have on at least one side a guardrail and midrail meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-05001 (9)(a) and (b).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-05011 Access to cargo spaces and confined spaces.
(1) Cargo spaces.
(a) There ((shall)) must be at least one safe and accessible ladder in any cargo space which employees must enter.
(b) When any fixed ladder is visibly unsafe, ((the employer shall)) you must prohibit its use by employees.
(c) Straight ladders of adequate strength and suitably secured against shifting or slipping ((shall)) must be provided as necessary when fixed ladders in cargo spaces do not meet the requirements of (a) of this section. When conditions are such that a straight ladder cannot be used, a Jacob's ladder meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-05007(4) may be used.
(d) When cargo is stowed within 4 inches of the back of ladder rungs, the ladder ((shall)) must be deemed "unsafe" for the purpose of this section.
(e) Fixed ladders or straight ladders provided for access to cargo spaces ((shall)) must not be used at the same time that cargo drafts or other loads are entering or leaving the hold. Before using these ladders to enter or leave the hold, the employee ((shall)) must be required to inform the winchman or crane signalman of his intention.
(2) Confined spaces.
(a) More than one means of access ((shall)) must be provided to a confined space in which employees are working and in which the work may generate a hazardous atmosphere in the space except where the structure or arrangement of the vessel makes this provision impractical.
(b) When the ventilation ducts required by these regulations must pass through these means of access, the ducts ((shall)) must be of such a type and so arranged as to permit free passage of an employee through at least two of these means of access.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-05013 Working surfaces.
(1) When firebox floors present tripping hazards of exposed tubing or of missing or removed refractory, sufficient planking to afford safe footing ((shall)) must be laid while work is being carried on within the boiler.
(2) ((The employer)) You must provide and ensure the use of fall protection when employees work aloft or elsewhere at elevations more than 5 feet above a solid surface.
(a) Employees must be protected by the use of scaffolds, ladders, or personal protection equipment according to WAC 296-304-09021, or 296-304-09023.
(b) Employees must work from scaffolds when visually restricted by:
((•)) (i) Blasting hoods;
((•)) (ii) Welding helmets; and
((•)) (iii) Burning goggles; except:
((•)) (A) For the initial and final welding or burning operation to start or complete a job such as the erection and dismantling of hung scaffolding; or
((•)) (B) Other similar, nonrepetitive jobs of brief duration.
(3) For work performed in restricted quarters, such as behind boilers and in between congested machinery units and piping, work platforms at least 20 inches wide meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-05001 (8)(b) ((shall)) must be used. Backrails may be omitted if bulkheading, boilers, machinery units, or piping afford proper protection against falling.
(4) When employees are boarding, leaving, or working from small boats or floats, they ((shall)) must be protected by personal flotation devices meeting the requirements of WAC 296-304-09017(1).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06001 Housekeeping.
(1) Good housekeeping conditions ((shall)) must be maintained at all times. Adequate aisles and passageways ((shall)) must be maintained in all work areas. All staging platforms, ramps, stairways, walkways, aisles, and passageways on vessels or dry docks ((shall)) must be kept clear of all tools, materials, and equipment except that which is in use, and all debris such as welding rod tips, bolts, nuts, and similar material. Hose and electric conductors ((shall)) must be elevated over or placed under the walkway or working surfaces or covered by adequate crossover planks. While a walkway is being used as a working surface, that portion ((shall)) must be cordoned off to prevent it from being used as a walkway.
(2) All working areas on vessels and dry docks ((shall)) must be:
(a) Cleared of tools, materials, and equipment that are not necessary to perform the job in progress;
(b) Cleared of debris, including solid and liquid wastes, at the end of each workshift or job, whichever occurs first;
(c) Maintained, so far as practicable, in a dry condition. When a wet process is used, the employer shall maintain drainage and provide false floors, platforms, mats, or other dry standing places. When the employer demonstrates that this procedure is not practicable, the employer ((shall)) must provide each employee working in the wet process with protective footgear, in accordance with WAC 296-304-09013.
(3) Slippery conditions on walkways or working surfaces ((shall)) must be eliminated as they occur. If it is not practicable for ((the employer)) you to remove slippery conditions, ((the employer either shall)) you must either:
(a) Restrict employees to designated walkways and working surfaces where ((the employer has)) you have eliminated slippery conditions; or
(b) Provide slip-resistant footwear in accordance with WAC 296-304-09013.
(4) Free access ((shall)) must be maintained at all times to all exits and to all fire-alarm boxes or fire-extinguishing equipment.
(5) All oils, paints, thinners, solvents waste, rags, or other flammable substances ((shall)) must be disposed of or kept in fire resistant covered containers when not in use.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06002 Sanitation.
(1) General requirements.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must provide adequate and readily accessible sanitation facilities.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must establish and implement a schedule for servicing, cleaning, and supplying each facility to ensure it is maintained in a clean, sanitary, and serviceable condition.
(2) Potable water. ((The employer shall)) You must provide potable water for all employee health and personal needs and ensure that only potable water is used for these purposes.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must provide potable drinking water in amounts that are adequate to meet the health and personal needs of each employee.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must dispense drinking water from a fountain, a covered container with single-use drinking cups stored in a sanitary receptacle, or single-use bottles. ((The employer shall)) You must prohibit the use of shared drinking cups, dippers, and water bottles.
(3) Nonpotable water.
(a) ((The employer)) You may use nonpotable water for other purposes such as firefighting and cleaning outdoor premises so long as it does not contain chemicals, fecal matter, coliform, or other substances at levels that may create a hazard for employees.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must clearly mark nonpotable water supplies and outlets as "not safe for health or personal use."
(4) Toilets.
(a) General requirements. ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that sewered and portable toilets:
(i) Provide privacy at all times. When a toilet facility contains more than one toilet, each toilet ((shall)) must occupy a separate compartment with a door and walls or partitions that are sufficiently high to ensure privacy; and
(ii) Are separate for each sex, except as provided in (a)(ii)(B) of this subsection;
(A) The number of toilets provided for each sex ((shall)) must be based on the maximum number of employees of that sex present at the worksite at any one time during a workshift. A single occupancy toilet room ((shall)) must be counted as one toilet regardless of the number of toilets it contains; and
(B) ((The employer does)) You do not have to provide separate toilet facilities for each sex when they will not be occupied by more than one employee at a time, can be locked from the inside, and contain at least one toilet.
(iii) ((The employer shall)) You must establish and implement a schedule to ensure that each sewered and portable toilet is maintained in a clean, sanitary, and serviceable condition.
(b) Minimum number of toilets. ((The employer shall)) You must provide at least the following number of toilets for each sex. Portable toilets that meet the requirements in (c) of this subsection may be included in the minimum number of toilets.
Table F-1
Minimum Number of Toilets
Number of employees of each sex |
Minimum number of toilets per sex |
|
1 to 15 |
1 |
|
16 to 35 |
2 |
|
36 to 55 |
3 |
|
56 to 80 |
4 |
|
81 to 110 |
5 |
|
111 to 150 |
6 |
|
Over 150 |
1 additional toilet for each additional 40 employees |
|
Note to Table F-1: When toilets will only be used by men, urinals may be provided instead of toilets, except that the number of toilets in such cases ((shall)) must not be reduced to less than two-thirds of the minimum specified.
(c) Portable toilets.
(i) ((The employer shall)) You must provide portable toilets, pursuant to paragraph (4)(b) of this section and Table F-1, only when ((the employer)) you demonstrate((s)) that it is not feasible to provide sewered toilets, or when there is a temporary increase in the number of employees for a short duration of time.
(ii) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each portable toilet is vented and equipped, as necessary, with lighting.
(d) Exception for normally unattended worksites and mobile work crews. The requirement to provide toilets does not apply to normally unattended worksites and mobile work crews, provided that ((the employer)) you ensure((s)) that employees have immediately available transportation to readily accessible sanitation facilities that are maintained in a clean, sanitary, and serviceable condition and meet the other requirements of this section.
(5) Handwashing facilities.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must provide handwashing facilities at or adjacent to each toilet facility.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each handwashing facility:
(i) Is equipped with either hot and cold or lukewarm running water and soap, or with waterless skin-cleansing agents that are capable of disinfecting the skin or neutralizing the contaminants to which the employee may be exposed; and
(ii) If the facility uses soap and water, it is supplied with clean, single-use hand towels stored in a sanitary container and a sanitary means for disposing of them, clean individual sections of continuous cloth toweling, or a hand-drying air blower.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must inform each employee engaged in the application of paints or coatings or in other operations in which hazardous or toxic substances can be ingested or absorbed about the need for removing surface contaminants from their skin's surface by thoroughly washing their hands and face at the end of the workshift and prior to eating, drinking, or smoking.
(6) Showers.
(a) When showers are required by an OSHA standard, ((the employer shall)) you must provide one shower for each ten, or fraction of ten, employees of each sex who are required to shower during the same workshift.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each shower is equipped with soap, hot and cold water, and clean towels for each employee who uses the shower.
(7) Changing rooms. When ((an employer)) you provide((s)) protective clothing to prevent employee exposure to hazardous or toxic substances, ((the employer shall)) you must provide the following:
(a) Changing rooms that provide privacy for each sex; and
(b) Storage facilities for street clothes, as well as separate storage facilities for protective clothing.
(8) Eating, drinking, and break areas. ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that food, beverages, and tobacco products are not consumed or stored in any area where employees may be exposed to hazardous or toxic substances.
(9) Waste disposal.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must provide waste receptacles that meet the following requirements:
(i) Each receptacle is constructed of materials that are corrosion resistant, leak-proof, and easily cleaned or disposable;
(ii) Each receptacle is equipped with a solid tight-fitting cover, unless it can be kept in clean, sanitary, and serviceable condition without the use of a cover;
(iii) Receptacles are provided in numbers, sizes, and locations that encourage their use; and
(iv) Each receptacle is emptied as often as necessary to prevent it from overfilling and in a manner that does not create a hazard for employees. Waste receptacles for food ((shall)) must be emptied at least every day, unless unused.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must not permit employees to work in the immediate vicinity of uncovered garbage that could endanger their safety and health.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that employees working beneath or on the outboard side of a vessel are not contaminated by drainage or waste from overboard discharges.
(10) Vermin control.
(a) To the extent reasonably practicable, ((the employer shall)) you must clean and maintain the workplace in a manner that prevents vermin infestation.
(b) Where vermin are detected, ((the employer shall)) you must implement and maintain an effective vermin-control program.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06003 Illumination.
(1) All means of access and walkways leading to working areas as well as the working areas themselves ((shall)) must be adequately illuminated.
(a) For landside areas, ((the employer shall)) you must provide illumination that meets the levels set forth in Table F-2.
Table F-2
Minimum Lighting Intensities in Foot-Candles
Lumens (foot-candles) |
Area or operation |
|
3 |
General areas on vessels and vessel sections such as accessways, exits, gangways, stairs, and walkways. |
|
5 |
General landside areas such as corridors, exits, stairs, and walkways. |
|
5 |
All assigned work areas on any vessel or vessel section. |
|
5 |
Landside tunnels, shafts, vaults, pumping stations, and underground work areas. |
|
10 |
Landside work areas such as machine shops, electrical equipment rooms, carpenter shops, lofts, tool rooms, warehouses, and outdoor work areas. |
|
10 |
Changing rooms, showers, sewered toilets, and eating, drinking, and break areas. |
|
30 |
First-aid stations, infirmaries, and offices. |
|
Note to Table F-2: The required illumination levels in this table do not apply to emergency or portable lights.
(b) For vessels and vessel sections, ((the employer shall)) you must provide illumination that meets the levels set forth in the table to (a) of this subsection or meet ANSI/IESNA RP-7-01.
(c) When adequate illumination is not obtainable by permanent lighting sources, temporary lighting may be used as supplementation.
(d) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that neither matches nor open-flame devices are used for lighting.
(2) Temporary lights ((shall)) must meet the following requirements:
(a) Temporary lights ((shall)) must be equipped with guards to prevent accidental contact with the bulb, except that guards are not required when the construction of the reflector is such that the bulb is deeply recessed;
(b) Temporary lights ((shall)) must be equipped with heavy duty electric cords with connections and insulation maintained in safe condition. Temporary lights ((shall)) must not be suspended by their electric cords unless cords and lights are designed for this means of suspension. Splices must have insulation with a capacity that exceeds that of the original insulation of the cord; and
(c) Cords ((shall)) must be kept clear of working spaces and walkways or other locations in which they are readily exposed to damage.
(3) Exposed noncurrent-carrying metal parts of temporary lights furnished by ((the employer shall)) you must be grounded either through a third wire in the cable containing the circuit conductors or through a separate wire which is grounded at the source of the current. Grounding ((shall)) must be in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-304-08003(2).
(4) Where temporary lighting from sources outside the vessel is the only means of illumination, portable emergency lighting equipment ((shall)) must be available to provide illumination for safe movement of employees. If natural sunlight provides sufficient illumination, portable or emergency lights are not required.
(5) Employees ((shall)) must not be permitted to enter dark spaces without a suitable portable light. The use of matches and open flame lights is prohibited. In nongas free spaces, portable lights ((shall)) must meet the requirements of WAC 296-304-02005 (2)(i).
(6) Temporary lighting stringers or streamers ((shall)) must be so arranged as to avoid overloading of branch circuits. Each branch circuit ((shall)) must be equipped with overcurrent protection of capacity not exceeding the rated current carrying capacity of the cord used.
(7) Explosion-proof, self-contained lights. ((The employer shall)) You must provide and ensure that each employee uses only explosion-proof, self-contained temporary and portable lights, approved for hazardous conditions by a nationally recognized testing laboratory (NRTL), in any area that the atmosphere is determined to contain a concentration of flammable vapors that are at or above ten percent of the lower explosive limit (LEL).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06005 Utilities.
(1) Steam supply and hoses.
(a) Prior to supplying a vessel with steam from a source outside the vessel, ((the employer shall)) you must ascertain from responsible vessel's representatives, having knowledge of the condition of the plant, the safe working pressure of the vessel's steam system. ((The employer shall)) You must install a pressure gauge and a relief valve of proper size and capacity at the point where the temporary steam hose joins the vessel's steam piping system or systems. The relief valve ((shall)) must be set and capable of relieving at a pressure not exceeding the safe working pressure of the vessel's system in its present condition, and there ((shall be no)) must not be any means of isolating the relief valve from the system which it protects. The pressure gauge and relief valve ((shall)) must be located so as to be visible and readily accessible, and each relief valve is to be positioned so it is not likely to cause injury if steam is released.
(b) Steam hose and fittings ((shall)) must have a safety factor of not less than five, and ((shall)) must be used in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications.
(c) When steam hose is hung in a bight or bights, the weight ((shall)) must be relieved by appropriate lines to reduce tension on the hose and its fittings. The hose ((shall)) must be protected against chafing.
(d) Steam hose ((shall)) must be protected from damage and hose and temporary piping ((shall)) must be ((so)) shielded where passing through normal work areas as to prevent accidental contact by employees.
(2) Electric power. When the vessel is supplied with electric power from a source outside the vessel, the following precautions ((shall)) must be taken prior to energizing the vessel's circuits:
(a) If in dry dock, the vessel ((shall)) must be adequately grounded.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ascertain from responsible vessel's representatives, having a knowledge of the condition of the vessel's electrical system, that all circuits to be energized are in a safe condition.
(c) All circuits to be energized ((shall)) must be equipped with overcurrent protection of capacity not exceeding the rated current carrying capacity of the cord used.
(3) Infrared electrical heat lamps. All infrared electrical heat lamps ((shall)) must be equipped with guards that surround the lamps with the exception of the face, to minimize accidental contact with the lamps.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06007 Work in confined or isolated spaces.
When any work is performed in a confined space, except as provided in WAC 296-304-04001 (2)(c), or when an employee is working alone in an isolated location, the employee ((shall)) must be checked, by sight or verbal communication:
(1) Throughout each workshift at regular intervals appropriate to the job assignment to ensure the employee's safety and health; and
(2) At the end of the job assignment or at the end of the workshift, whichever occurs first.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06009 Work on or in the vicinity of radar and radio.
(1) ((The employer shall)) You must service each vessel's radar and communication systems in accordance with WAC 296-304-06016, Control of hazardous energy.
(2) ((The employer shall)) You must secure each vessel's radar and communication system so it is incapable of energizing or emitting radiation before any employee begins work:
(a) On or in the vicinity of the system;
(b) On or in the vicinity of a system equipped with a dummy load; or
(c) Aloft, such as on a mast or king post.
(3) When a vessel's radar or communication system is operated, serviced, repaired, or tested, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that:
(a) There is no other work in progress aloft; and
(b) No employee is closer to the system's antenna or transmitter than the manufacturer's specified safe minimum distance for the type, model, and power of the equipment.
(4) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that no employee enters an area designated as hazardous by manufacturers' specifications while a radar or communication system is capable of emitting radiation.
(5) The requirements of this section do not apply when a radar or communication system is incapable of emitting radiation at levels that could injure workers in the vicinity of the system, or if the radar or communication system is incapable of energizing in a manner than could injure workers working on or in the vicinity of the system.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06011 Work in or on lifeboats.
(1) Before employees are permitted to work in or on a lifeboat, either stowed or in a suspended position, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the boat is secured independently of the releasing gear to prevent the boat from falling due to accidental tripping of the releasing gear and movement of the davits or capsizing of a boat in chocks.
(2) Employees ((shall)) must not be permitted to remain in boats while the boats are being hoisted or lowered, except when ((the employer)) you demonstrate((s)) that it is necessary to conduct operational tests or drills over water, or in the event of an emergency.
(3) Employees ((shall)) must not be permitted to work on the outboard side of lifeboats stowed on their chocks unless the boats are secured by gripes or otherwise secured to prevent them from swinging outboard.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-304-06013 Hazardous materials.
((")) (1) Hazardous material((" -)). A material with one or more of the following characteristics:
((•)) (a) Has a flash point below 140°F, closed cup, or is subject to spontaneous heating;
((•)) (b) Has a threshold limit value below 500 p.p.m. in the case of a gas or vapor, below 500 mg./m.3 for fumes, and below 25 m.p.p.c.f. in case of a dust;
((•)) (c) Has a single dose oral LD50 below 500 mg./kg.;
((•)) (d) Is subject to polymerization with the release of large amounts of energy;
((•)) (e) Is a strong oxidizing or reducing agent;
((•)) (f) Causes first degree burns to skin in short time exposure, or is systematically toxic by skin contact; or
((•)) (g) In the course of normal operations, may produce dusts, gases, fumes, vapors, mists, or smokes that have one or more of the above characteristics.
(((1))) (2) No chemical product, such as a solvent or preservative; no structural material, such as cadmium or zinc coated steel, or plastic material; and no process material, such as welding filler metal; which is a hazardous material may be used until ((the employer has)) you have ascertained the potential fire, toxic, or reactivity hazards which are likely to be encountered in the handling, application, or utilization of such a material.
(((2))) (3) In order to ascertain the hazards, as required by subsection (1) of this section, ((the employer shall)) you must obtain the following items of information which are applicable to a specific product or material to be used:
(a) The name, address, and telephone number of the source of the information specified in this section preferably those of the manufacturer of the product or material.
(b) The trade name and synonyms for a mixture of chemicals, a basic structural material, or for a process material; and the chemical name and synonyms, chemical family, and formula for a single chemical.
(c) Chemical names of hazardous ingredients, including, but not limited to, those in mixtures, such as those in: (i) Paints, preservatives, and solvents; (ii) alloys, metallic coatings, filler metals and their coatings or core fluxes; and (iii) other liquids, solids, or gases (e.g., abrasive materials).
(d) An indication of the percentage, by weight or volume, which each ingredient of a mixture bears to the whole mixture, and of the threshold limit value of each ingredient, in appropriate units.
(e) Physical data about a single chemical or a mixture of chemicals, including boiling point, in degrees Fahrenheit; vapor pressure, in millimeters of mercury; vapor density of gas or vapor (air=1); solubility in water, in percent by weight; specific gravity of material (water=1); percentage volatile, by volume, at 70°F.; evaporation rate for liquids (either butyl acetate or ether may be taken as 1); and appearance and odor.
(f) Fire and explosion hazard data about a single chemical or a mixture of chemicals, including flashpoint, in degrees Fahrenheit; flammable limits, in percent by volume in air; suitable extinguishing media or agents; special firefighting procedures; and unusual fire and explosion hazard information.
(g) Health hazard data, including threshold limit value, in appropriate units, for a single hazardous chemical or for the individual hazardous ingredients of a mixture as appropriate, effects of overexposure; and emergency and first-aid procedures.
(h) Reactivity data, including stability, incompatibility, hazardous decomposition products, and hazardous polymerization.
(i) Procedures to be followed and precautions to be taken in cleaning up and disposing of materials leaked or spilled.
(j) Special protection information, including use of personal protective equipment, such as respirators, eye protection, and protective clothing, and of ventilation, such as local exhaust, general, special, or other types.
(k) Special precautionary information about handling and storing.
(l) Any other general precautionary information.
(((3))) (4) The pertinent information required by subsection (2) of this section ((shall)) must be recorded either on United States Department of Labor Form LSB 00S-4, Material Safety Data Sheet, or on an essentially similar form which has been approved by the department of labor and industries. Copies of Form LSB 00S-4 may be obtained at any of the following regional offices of the occupational safety and health administration:
(a) Pacific region. (Arizona, California, Hawaii, and Nevada.)
10353 Federal Building, 450 Golden Gate Avenue, Box 36017, San Francisco, Calif. 94102.
(b) Region X, OSHA, (Alaska, Washington, Idaho, and Oregon), 300 Fifth Avenue, Suite 1280, Seattle, Washington 98104-2397.
A completed SDS form ((shall)) must be preserved and available for inspection for each hazardous chemical on the worksite.
(((4) The employer shall)) (5) You must instruct employees who will be exposed to the hazardous materials as to the nature of the hazards and the means of avoiding them.
(((5) The employer shall)) (6) You must provide all necessary controls, and the employees ((shall)) must be protected by suitable personal protective equipment against the hazards identified under subsection (1) of this section and those hazards for which specific precautions are required in WAC 296-304-020 through 296-304-04013.
(((6) The employer shall)) (7) You must provide adequate washing facilities for employees engaged in the application of paints or coatings or in other operations where contaminants can, by ingestion or absorption, be detrimental to the health of the employees. ((The employer shall)) You must encourage good personal hygiene practices by informing the employees of the need for removing surface contaminants by thorough washing of hands and face prior to eating or smoking.
(((7) The employer shall)) (8) You must not permit eating or smoking in areas undergoing surface preparation or preservation or where shiprepairing, shipbuilding, or shipbreaking operations produce atmospheric contamination.
(((8) The employer shall)) (9) You must not permit employees to work in the immediate vicinity of uncovered garbage and ((shall)) must ensure that employees working beneath or on the outboard side of a vessel are not subject to contamination by drainage or waste from overboard discharges.
(((9))) (10) Requirements of WAC 296-901-140, Hazard communication, will apply to shiprepairing, shipbuilding, and shipbreaking when potential hazards of chemicals and communicating information concerning hazards and appropriate protective equipment is applicable to an operation.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06015 First aid.
(1) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that emergency medical services and first aid are readily accessible.
(2) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that health care professionals are readily available for advice and consultation on matters of workplace health.
(3) First-aid providers.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that there is an adequate number of employees trained as first-aid providers at each worksite during each workshift unless:
(i) There is an on-site clinic or infirmary with first-aid providers during each workshift; or
(ii) ((The employer)) You can demonstrate that outside first-aid providers (i.e., emergency medical services) can reach the worksite within five minutes of a report of injury or illness. ((The employer)) You must take appropriate steps to ascertain that emergency medical assistance will be readily available promptly if an injury or illness occurs.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that a first-aid provider is able to reach an injured/ill employee within five minutes of a report of a serious injury, illness, or accident such as one involving cardiac arrest, acute breathing problems, uncontrolled bleeding, suffocation, electrocution, or amputation.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must use the following factors in determining the number and location of employees who must have first-aid training:
(i) Size and location of each worksite;
(ii) The number of employees at each worksite;
(iii) The hazards present at each worksite; and
(iv) The distance of each worksite from hospitals, clinics, and rescue squads.
(d) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that first-aid providers are trained to render first aid, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
(e) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each first-aid provider maintains current first aid and CPR certifications, such as issued by the Red Cross, American Heart Association, or other equivalent organization.
(4) First-aid supplies.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must provide and maintain adequate first-aid supplies that are readily accessible to each worksite. ((An employer's)) Your on-site infirmary or clinic containing first-aid supplies that are readily accessible to each worksite complies with this requirement.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the placement, content, and amount of first-aid supplies are adequate for the size and location of each worksite, the number of employees at each worksite, the hazards present at each worksite, and the distance of each worksite from hospitals, clinics, and rescue squads.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that first-aid supplies are placed in a weatherproof container.
(d) ((The employer shall)) You must maintain first-aid supplies in a dry, sterile, and serviceable condition.
(e) ((The employer shall)) You must replenish first-aid supplies as necessary to ensure that there is an adequate supply when needed.
(f) ((The employer shall)) You must inspect first-aid supplies at sufficient intervals to ensure that they are adequate and in a serviceable condition.
(5) Quick-drenching and flushing facilities. Where the potential exists for an employee to be splashed with a substance that may result in an acute or serious injury, ((the employer shall)) you must provide facilities for quick-drenching or flushing the eyes and body. ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that such a facility is located for immediate emergency use within close proximity to operations where such substances are being used.
(6) Basket stretchers.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must provide an adequate number of basket stretchers, or the equivalent, readily accessible to where work is being performed on a vessel or vessel section. ((The employer is)) You are not required to provide basket stretchers or the equivalent where emergency response services have basket stretchers or the equivalent that meet the requirements of this subsection (6)(a).
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure each basket stretcher, or the equivalent, is equipped with:
(i) Permanent lifting bridles that enable the basket stretcher, or the equivalent, to be attached to hoisting gear capable of lifting at least five thousand pounds (2,270 kg);
(ii) Restraints that are capable of securely holding the injured/ill employee while the basket stretcher, or the equivalent, is lifted or moved; and
(iii) A blanket or other suitable covering for the injured/ill employee.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must store basket stretchers, or the equivalent, and related equipment (i.e., restraints, blankets) in a clearly marked location in a manner that prevents damage and protects the equipment from environmental conditions.
(d) ((The employer shall)) You must inspect stretchers, or the equivalent, and related equipment at intervals that ensure the equipment remains in a safe and serviceable condition, but at least once a year.
Appendix A to WAC 296-304-06015 - First-aid kits and automated external defibrillators (nonmandatory)
1. First-aid supplies are required to be adequate and readily accessible under WAC 296-304-06015 (1) and (4). An example of the minimal contents of a generic first-aid kit for workplace settings is described in ANSI/ISEA Z308.1-2009, "Minimum Requirements for Workplace First Aid Kits and Supplies." The contents of the kit listed in this ANSI standard should be adequate for small worksites. When larger operations or multiple operations are being conducted at the same worksite, employers should determine the need for additional first-aid kits, additional types of first-aid equipment and supplies, and additional quantities and types of supplies and equipment in the first-aid kits.
2. In a similar fashion, employers that have unique or changing first-aid needs at their worksite may need to enhance their first-aid kits. The employer can use the OSHA 300 Log, OSHA 301 Incident Report form, or other reports to identify these unique problems. Consultation from the local fire or rescue department, appropriate health care professional or local emergency room may be helpful to employers in these circumstances. By assessing the specific needs of their worksite, employers can ensure that reasonably anticipated supplies are available. Employers should assess the specific needs of their worksite periodically, and augment first-aid kits appropriately.
3. If it is reasonably anticipated that employees will be exposed to blood or other potentially infectious materials while using first-aid supplies, employers must provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) in compliance with the provisions of chapter 296-823 WAC, bloodborne pathogens. This standard lists appropriate PPE for this type of exposure, such as gloves, gowns, face shields, masks, and eye protection.
4. Employers who provide automated external defibrillators (AEDs) at their workplaces should designate who will use AEDs and train those employees so they know how to correctly use the AEDs. Although a growing number of AEDs are now designed to be used by any person, even without training, training reinforces proper use and promotes the usefulness of AEDs as part of an effective cardiopulmonary resuscitation plan. For AEDs to be effective, employers should:
a. Ensure that AEDs are located so they can be utilized within three to five minutes of a report of an accident or injury;
b. Ensure that employees use AEDs in accordance with manufacturers' specifications; and
c. Inspect, test, and maintain AEDs in accordance with manufacturers' specifications.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06016 Control of hazardous energy (lockout/tags-plus).
Definition: (("))Tags-plus system((" -)). A system to control hazardous energy that consists of an energy-isolating device with a tag affixed to it, and at least one additional safety measure.
(1) Scope, application, and effective dates.
(a) Scope. This section covers the servicing of machinery, equipment, and systems when the energization or start-up of machinery, equipment, or systems, or the release of hazardous energy, could endanger an employee.
(b) Application.
(i) This section applies to the servicing of any machinery, equipment, or system that employees use in the course of shipyard employment work and that is conducted:
(A) In any landside facility that performs shipyard employment work; and
(B) On any vessel or vessel section.
(ii) This section applies to such servicing conducted on a vessel by any employee including, but not limited to, the ship's officers and crew unless such application is preempted by the regulations of another agency.
(c) When other standards in this chapter require the use of a lock or tag, ((the employer shall)) you must use and supplement them with the procedural and training requirements specified in this section.
(d) Exceptions. This section does not apply to:
(i) Work on cord- and plug-connected machinery, equipment, or system, provided the employer ensures that the machinery, equipment, or system is unplugged and the plug is under the exclusive control of the employee performing the servicing;
(ii) Minor servicing activities performed during normal production operations, including minor tool changes and adjustments, that are routine, repetitive, and integral to the use of the machinery, equipment, or system, provided ((the employer)) you ensure((s)) that the work is performed using measures that provide effective protection from energization, start-up, or the release of hazardous energy.
(2) Lockout/tags-plus program. ((The employer shall)) You must establish and implement a written program and procedures for lockout and tags-plus systems to control hazardous energy during the servicing of any machinery, equipment, or system in shipyard employment. The program ((shall)) must cover:
(a) Procedures for lockout/tags-plus systems while servicing machinery, equipment, or systems in accordance with subsection (3) of this section;
(b) Procedures for protecting employees involved in servicing any machinery, equipment, or system in accordance with subsections (4) through (13) of this section;
(c) Specifications for locks and tags-plus hardware in accordance with subsection (14) of this section;
(d) Employee information and training in accordance with subsection (15) of this section;
(e) Incident investigations in accordance with subsection (16) of this section; and
(f) Program audits in accordance with subsection (17) of this section.
(3) General requirements.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that, before any authorized employee performs servicing when energization or start-up, or the release of hazardous energy, may occur, all energy sources are identified and isolated, and the machinery, equipment, or system is rendered inoperative.
(b) If an energy-isolating device is capable of being locked, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure the use of a lock to prevent energization or start-up, or the release of hazardous energy, before any servicing is started, unless ((the employer)) you can demonstrate that the utilization of a tags-plus system will provide full employee protection as set forth in (f) of this subsection.
(c) If an energy-isolating device is not capable of being locked, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure the use of a tags-plus system to prevent energization or start-up, or the release of hazardous energy, before any servicing is started.
(d) Each tags-plus system shall consist of:
(i) At least one energy-isolating device with a tag affixed to it; and
(ii) At least one additional safety measure that, along with the energy isolating device and tag required in (d)(i) of this subsection, will provide the equivalent safety available from the use of a lock.
(e) After the effective date of this section, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that each energy-isolating device for any machinery, equipment, or system is designed to accept a lock whenever the machinery, equipment, or system is extensively repaired, renovated, modified, or replaced, or whenever new machinery, equipment, or systems are installed. This requirement does not apply when a shipyard employer:
(i) Does not own the machinery, equipment, or system; or
(ii) Builds or services a vessel or vessel section according to customer specifications.
(f) Full employee protection.
(i) When a tag is used on an energy-isolating device that is capable of being locked out, the tag ((shall)) must be attached at the same location that the lock would have been attached; and
(ii) ((The employer shall)) You must demonstrate that the use of a tags-plus system will provide a level of safety equivalent to that obtained by using a lock. In demonstrating that an equivalent level of safety is achieved, ((the employer shall)) you must:
(A) Demonstrate full compliance with all tags-plus related provisions of this standard; and
(B) Implement such additional safety measures as are necessary to provide the equivalent safety available from the use of a lock.
(g) Lockout/tags-plus coordination.
(i) ((The employer shall)) You must establish and implement lockout/tags-plus coordination when:
(A) Employees on vessels and in vessel sections are servicing multiple machinery, equipment, or systems at the same time; or
(B) Employees on vessels, in vessel sections, and at landside facilities are performing multiple servicing operations on the same machinery, equipment, or system at the same time.
(ii) The coordination process ((shall)) must include a lockout/tags-plus coordinator and a lockout/tags-plus log. Each log ((shall)) must be specific to each vessel, vessel section, and landside work area.
(iii) ((The employer shall)) You must designate a lockout/tags-plus coordinator who is responsible for overseeing and approving:
(A) The application of each lockout and tags-plus system;
(B) The verification of hazardous energy isolation before the servicing of any machinery, equipment, or system begins; and
(C) The removal of each lockout and tags-plus system.
(iv) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the lockout/tags-plus coordinator maintains and administers a continuous log of each lockout and tags-plus system. The log ((shall)) must contain:
(A) Location of machinery, equipment, or system to be serviced;
(B) Type of machinery, equipment, or system to be serviced;
(C) Name of the authorized employee applying the lockout/tags-plus system;
(D) Date that the lockout/tags-plus system is applied;
(E) Name of authorized employee removing the lock or tags-plus system; and
(F) Date that lockout/tags-plus system is removed.
(4) Lockout/tags-plus written procedures.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must establish and implement written procedures to prevent energization or start-up, or the release of hazardous energy, during the servicing of any machinery, equipment, or system. Each procedure ((shall)) must include:
(i) A clear and specific outline of the scope and purpose of the lockout/tags-plus procedure;
(ii) The means ((the employer)) you will use to enforce compliance with the lockout/tags-plus program and procedures; and
(iii) The steps that must be followed for:
(A) Preparing for shutting down and isolating of the machinery, equipment, or system to be serviced, in accordance with subsection (5) of this section;
(B) Applying the lockout/tags-plus system, in accordance with subsection (6) of this section;
(C) Verifying isolation, in accordance with subsection (7) of this section;
(D) Testing the machinery, equipment, or system, in accordance with subsection (8) of this section;
(E) Removing lockout/tags-plus systems, in accordance with subsection (9) of this section;
(F) Starting up the machinery, equipment, or system that is being serviced, in accordance with subsection (10) of this section;
(G) Applying lockout/tags-plus systems in group servicing operations, in accordance with subsection (11) of this section;
(H) Addressing multiemployer worksites involved in servicing any machinery, equipment, or system, in accordance with subsection (12) of this section; and
(I) Addressing shift or personnel changes during servicing operations, in accordance with subsection (13) of this section.
Note to (a) of this subsection: ((The employer)) You need only develop a single procedure for a group of similar machines, equipment, or systems if the machines, equipment, or systems have the same type and magnitude of energy and the same or similar types of controls, and if a single procedure can satisfactorily address the hazards and the steps to be taken to control these hazards.
(b) ((The employer's)) Your lockout procedures do not have to be in writing for servicing machinery, equipment, or systems, provided that all of the following conditions are met:
(i) There is no potential for hazardous energy to be released (or to reaccumulate) after shutting down, or restoring energy to, the machinery, equipment, or system;
(ii) The machinery, equipment, or system has a single energy source that can be readily identified and isolated;
(iii) The isolation and lock out of that energy source will result in complete deenergization and deactivation of the machinery, equipment, or system, and there is no potential for reaccumulation of energy;
(iv) The energy source is isolated and secured from the machinery, equipment, or system during servicing;
(v) Only one lock is necessary for isolating the energy source;
(vi) The lock is under the exclusive control of the authorized employee performing the servicing;
(vii) The servicing does not create a hazard for any other employee; and
(viii) ((The employer)) You, in utilizing this exception, ((has)) have not had any accidents or incidents involving the activation or reenergization of this type of machinery, equipment, or system during servicing.
(5) Procedures for shutdown and isolation.
(a) Before an authorized employee shuts down any machinery, equipment, or system, ((the employer shall)) you must:
(i) Ensure that the authorized employee has knowledge of:
(A) The source, type, and magnitude of the hazards associated with energization or start-up of the machine, equipment, or system;
(B) The hazards associated with the release of hazardous energy; and
(C) The means to control these hazards; and
(ii) Notify each affected employee that the machinery, equipment, or system will be shutdown and deenergized prior to servicing, and that a lockout/tags-plus system will be implemented.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the machinery, equipment, or system is shutdown according to the written procedures the employer established.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must use an orderly shutdown to prevent exposing any employee to risks associated with hazardous energy.
(d) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the authorized employee relieves, disconnects, restrains, or otherwise renders safe all potentially hazardous energy that is connected to the machinery, equipment, or system.
(6) Procedures for applying lockout/tags-plus systems.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that only an authorized employee applies a lockout/tags-plus system.
(b) When using lockout systems, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the authorized employee affixes each lock in a manner that will hold the energy isolating device in a safe or off position.
(c) When using tags-plus systems, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the authorized employee affixes a tag directly to the energy-isolating device that clearly indicates that the removal of the device from a safe or off position is prohibited.
(d) When the tag cannot be affixed directly to the energy-isolating device ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the authorized employee locates it as close as safely possible to the device, in a safe and immediately obvious position.
(e) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each energy-isolating device that controls energy to the machinery, equipment, or system is effective in isolating the machinery, equipment, or system from all potentially hazardous energy source(s).
(7) Procedures for verification of deenergization and isolation.
(a) Before servicing machinery, equipment, or a system that has a lockout/tags-plus system, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the authorized employee, or the primary authorized employee in a group lockout/tags-plus application, verifies that the machinery, equipment, or system is deenergized and all energy sources isolated.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the authorized employee, or the primary authorized employee in a group lockout/tags-plus application, continues verifying deenergization and isolation while servicing the machinery, equipment, or system.
(c) Each authorized employee in a group lockout/tags-plus application who will be servicing the machinery, equipment, or system must be given the option to verify that the machinery, equipment, or system is deenergized and all energy sources isolated, even when verification is performed by the primary authorized employee.
(8) ((Procedures for testing.)) In each situation in which a lockout/tags-plus system must be removed temporarily and the machinery, equipment, or system restarted to test it or to position a component, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the authorized employee does the following in sequence:
(a) Clears tools and materials from the work area;
(b) Removes nonessential employees from the work area;
(c) Removes each lockout/tags-plus system in accordance with subsection (9) of this section;
(d) Restarts the machinery, equipment, or system and then proceeds with testing or positioning; and
(e) After completing testing or positioning, deenergizes and shuts down the machinery, equipment, or system and reapplies all lockout/tags-plus systems in accordance with subsections (5) through (7) of this section to continue servicing.
(9) Procedures for removal of lockout and tags-plus systems.
(a) Before removing any lockout/tags-plus system and restoring the machinery, equipment, or system to use, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the authorized employee does the following:
(i) Notifies all other authorized and affected employees that the lockout/tags-plus system will be removed;
(ii) Ensures that all employees in the work area have been safely positioned or removed; and
(iii) Inspects the work area to ensure that nonessential items have been removed and machinery, equipment, or system components are operationally intact.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each lock or tags-plus system is removed by the authorized employee who applied it.
(c) When the authorized employee who applied the lockout/tags-plus system is not available to remove it, ((the employer)) you may direct removal by another authorized employee, provided ((the employer developed and incorporated)) you develop and incorporate into the lockout/tags-plus program the specific procedures and training that address such removal, and demonstrate((s)) that the specific procedures used provide a level of employee safety that is at least as effective in protecting employees as removal of the system by the authorized employee who applied it. After meeting these requirements, ((the employer shall)) you must do the following in sequence:
(i) Verify that the authorized employee who applied the lockout/tags-plus system is not in the facility;
(ii) Make all reasonable efforts to contact the authorized employee to inform him/her that the lockout/tags-plus system has been removed; and
(iii) Ensure that the authorized employee who applied the lock or tags-plus system has knowledge of the removal before resuming work on the affected machinery, equipment, or system.
(10) Procedures for start-up.
(a) Before an authorized employee turns on any machinery, equipment, or system after servicing is completed, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the authorized employee has knowledge of the source, type, and magnitude of the hazards associated with energization or start-up, and the means to control these hazards.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must execute an orderly start-up to prevent or minimize any additional or increased hazard(s) to employees. ((The employer shall)) You must perform the following tasks before starting up the machinery, equipment, or system:
(i) Clear tools and materials from the work area;
(ii) Remove any nonessential employees from the work area; and
(iii) Start-up the machinery, equipment, or system according to the detailed procedures ((the employer)) you established for that machinery, equipment, or system.
(11) Procedures for group lockout/tags-plus. When more than one authorized employee services the same machinery, equipment, or system at the same time, the following procedures ((shall)) must be implemented:
(a) Primary authorized employee. ((The employer shall)) You must:
(i) Assign responsibility to one primary authorized employee for each group of authorized employees performing servicing on the same machinery, equipment, or system;
(ii) Ensure that the primary authorized employee determines the safe exposure status of each authorized employee in the group with regard to the lockout/tags-plus system;
(iii) Ensure that the primary authorized employee obtains approval from the lockout/tags-plus coordinator to apply and remove the lockout/tags-plus system; and
(iv) Ensure that the primary authorized employee coordinates the servicing operation with the coordinator when required by subsection (3)(g)(i) of this section.
(b) Authorized employees. ((The employer shall)) You must either:
(i) Have each authorized employee apply a personal lockout/tags-plus system; or
(ii) Use a procedure that ((the employer)) you can demonstrate affords each authorized employee a level of protection equivalent to the protection provided by having each authorized employee apply a personal lockout/tags-plus system. Such procedures ((shall)) must incorporate a means for each authorized employee to have personal control of, and accountability for, his or her protection such as, but not limited to, having each authorized employee:
(A) Sign a group tag (or a group tag equivalent), attach a personal identification device to a group lockout device, or performs a comparable action before servicing is started; and
(B) Sign off the group tag (or the group tag equivalent), remove the personal identification device, or perform a comparable action when servicing is finished.
(12) Procedures for multiemployer worksites.
(a) The host employer ((shall)) must establish and implement procedures to protect employees from hazardous energy in multiemployer worksites. The procedures ((shall)) must specify the responsibilities for host and contract employers.
(b) Host employer responsibilities. The host employer ((shall)) must carry out the following responsibilities in multiemployer worksites:
(i) Inform each contract employer about the content of the host employer's lockout/tags-plus program and procedures;
(ii) Instruct each contract employer to follow the host employer's lockout/tags-plus program and procedures; and
(iii) Ensure that the lockout/tags-plus coordinator knows about all servicing operations and communicates with each contract employer who performs servicing or works in an area where servicing is being conducted.
(c) Contract employer responsibilities. Each contract employer ((shall)) must perform the following duties when working in a multiemployer worksite:
(i) Follow the host employer's lockout/tags-plus program and procedures;
(ii) Ensure that the host employer knows about the lockout/tags-plus hazards associated with the contract employer's work and what the contract employer is doing to address these hazards; and
(iii) Inform the host employer of any previously unidentified lockout/tags-plus hazards that the contract employer identifies at the multiemployer worksite.
Note to subsection (12) of this section: The host employer may include provisions in its contract with the contract employer for the contract employer to have more control over the lockout/tags-plus program if such provisions will provide an equivalent level of protection for the host employer's and contract employer's employees as provided by subsection (l) of this section.
(13) Procedures for shift or personnel changes.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must establish and implement specific procedures for shift or personnel changes to ensure the continuity of lockout/tags-plus protection.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must establish and implement provisions for the orderly transfer of lockout/tags-plus systems between authorized employees when they are starting and ending their workshifts, or when personnel changes occur during a workshift, to prevent energization or start-up of the machinery, equipment, or system being serviced or the release of hazardous energy.
(14) Lockout/tags-plus materials and hardware.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must provide locks and tags-plus system hardware used for isolating, securing, or blocking machinery, equipment, or systems from all hazardous energy sources.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each lock and tag is uniquely identified for the purpose of controlling hazardous energy and is not used for any other purpose.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each lock and tag meets the following requirements:
(i) Durable.
(A) Each lock and tag is capable of withstanding the existing environmental conditions for the maximum period of time that servicing is expected to last;
(B) Each tag is made so that weather conditions, wet or damp conditions, corrosive substances, or other conditions in the work area where the tag is used or stored will not cause it to deteriorate or become illegible;
(ii) Standardized.
(A) Each lock and tag is standardized in at least one of the following areas: Color, shape, or size; and
(B) Each tag is standardized in print and format;
(iii) Substantial.
(A) Each lock is sturdy enough to prevent removal without the use of extra force or unusual techniques, such as bolt cutters or other metal-cutting tools;
(B) Each tag and tag attachment is sturdy enough to prevent inadvertent or accidental removal;
(C) Each tag attachment has the general design and basic safety characteristics of a one-piece, all environment-tolerant nylon tie;
(D) Each tag attachment is nonreusable, attachable by hand, self-locking, and nonreleasable, and has a minimum unlocking strength of fifty pounds;
(iv) Identifiable. Each lock and tag indicates the identity of the authorized employee applying it; and
(v) Each tag warns of hazardous conditions that could arise if the machinery, equipment, or system is energized and includes a legend such as one of the following: "Do Not Start," "Do Not Open," "Do Not Close," "Do Not Energize," or "Do Not Operate."
(15) Information and training.
(a) Initial training. ((The employer shall)) You must train each employee in the applicable requirements of this section no later than the effective date of this section.
(b) General training content. ((The employer shall)) You must train each employee who is, or may be, in an area where lockout/tags-plus systems are being used so they know:
(i) The purpose and function of ((the employer's)) your lockout/tags-plus program and procedures;
(ii) The unique identity of the locks and tags to be used in the lockout/tags-plus system, as well as the standardized color, shape or size of these devices;
(iii) The basic components of the tags-plus system: An energy-isolating device with a tag affixed to it and an additional safety measure;
(iv) The prohibition against tampering with or removing any lockout/tags-plus system; and
(v) The prohibition against restarting or reenergizing any machinery, equipment, or system being serviced under a lockout/tags-plus system.
(c) Additional training requirements for affected employees. In addition to training affected employees in the requirements in (b) of this subsection, ((the employer also shall)) you must also train each affected employee so he/she knows:
(i) The use of ((the employer's)) your lockout/tags-plus program and procedures;
(ii) That affected employees are not to apply or remove any lockout/tags-plus system; and
(iii) That affected employees are not to bypass, ignore, or otherwise defeat any lockout/tags-plus system.
(d) Additional training requirements for authorized employees. In addition to training authorized employees in the requirements in (b) and (c) of this subsection, ((the employer also shall)) you must also train each authorized employee so he/she knows:
(i) The steps necessary for the safe application, use, and removal of lockout/tags-plus systems to prevent energization or start-up or the release of hazardous energy during servicing of machinery, equipment, or systems;
(ii) The type of energy sources and the magnitude of the energy available at the worksite;
(iii) The means and methods necessary for effective isolation and control of hazardous energy;
(iv) The means for determining the safe exposure status of other employees in a group when the authorized employee is working as a group's primary authorized employee;
(v) The requirement for tags to be written so they are legible and understandable to all employees;
(vi) The requirement that tags and their means of attachment be made of materials that will withstand the environmental conditions encountered in the workplace;
(vii) The requirement that tags be securely attached to energy-isolating devices so they cannot be accidentally removed while servicing machinery, equipment, or systems;
(viii) That tags are warning devices, and alone do not provide physical barriers against energization or start-up, or the release of hazardous energy, provided by locks, and energy-isolating devices; and
(ix) That tags must be used in conjunction with an energy-isolating device to prevent energization or start-up or the release of hazardous energy.
(e) Additional training for lockout/tags-plus coordinator. In addition to training lockout/tags-plus coordinators in the requirements in (b), (c), and (d) of this subsection, ((the employer shall)) you must train each lockout/tags-plus coordinator so he/she knows:
(i) How to identify and isolate any machinery, equipment, or system that is being serviced; and
(ii) How to accurately document lockout/tags-plus systems and maintain the lockout/tags-plus log.
(f) Employee retraining.
(i) ((The employer shall)) You must retrain each employee, as applicable, whenever:
(A) There is a change in his/her job assignment that presents new hazards or requires a greater degree of knowledge about ((the employer's)) your lockout/tags-plus program or procedures;
(B) There is a change in machinery, equipment, or systems to be serviced that presents a new energy-control hazard;
(C) There is a change in ((the employer's)) your lockout/tags-plus program or procedures; or
(D) It is necessary to maintain the employee's proficiency.
(ii) ((The employer also shall)) You must also retrain each employee, as applicable, whenever an incident investigation or program audit indicates that there are:
(A) Deviations from, or deficiencies in, the employer's lockout/tags-plus program or procedures; or
(B) Inadequacies in an employee's knowledge or use of the lockout/tags-plus program or procedures.
(iii) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that retraining establishes the required employee knowledge and proficiency in ((the employer's)) your lockout/tags-plus program and procedures and in any new or revised energy-control procedures.
(g) Upon completion of employee training, ((the employer shall)) you must keep a record that the employee accomplished the training, and that this training is current. The training record ((shall)) must contain at least the employee's name, date of training, and the subject of the training.
(16) Incident investigation.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must investigate each incident that resulted in, or could reasonably have resulted in, energization or start-up, or the release of hazardous energy, while servicing machinery, equipment, or systems.
(b) Promptly but not later than twenty-four hours following the incident, ((the employer shall)) you must initiate an incident investigation and notify each employee who was, or could reasonably have been, affected by the incident.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the incident investigation is conducted by at least one employee who has the knowledge of, and experience in, ((the employer's)) your lockout/tags-plus program and procedures, and in investigating and analyzing incidents involving the release of hazardous energy. ((The employer)) You may also use additional individuals to participate in investigating the incident.
(d) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the individual(s) conducting the investigation prepare(s) a written report of the investigation that includes:
(i) The date and time of the incident;
(ii) The date and time the incident investigation began;
(iii) Location of the incident;
(iv) A description of the incident;
(v) The factors that contributed to the incident;
(vi) A copy of any lockout/tags-plus log that was current at the time of the incident; and
(vii) Any corrective actions that need to be taken as a result of the incident.
(e) ((The employer shall)) You must review the written incident report with each employee whose job tasks are relevant to the incident investigation findings, including contract employees when applicable.
(f) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the incident investigation and written report are completed, and all corrective actions implemented, within thirty days following the incident.
(g) If ((the employer)) you demonstrate((s)) that it is infeasible to implement all of the corrective actions within thirty days, ((the employer shall)) you must prepare a written abatement plan that contains an explanation of the circumstances causing the delay, a proposed timetable for the abatement, and a summary of the steps ((the employer is)) you are taking in the interim to protect employees from hazardous energy while servicing machinery, equipment, or systems.
(17) Program audits.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must conduct an audit of the lockout/tags-plus program and procedures currently in use at least annually to ensure that the procedures and the requirements of this section are being followed and to correct any deficiencies.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the audit is performed by:
(i) An authorized employee other than the one(s) currently using the energy control procedure being reviewed; or
(ii) Individuals other than an authorized employee who are knowledgeable about ((the employer's)) your lockout/tags-plus program and procedures and the machinery, equipment, or systems being audited.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that the audit includes:
(i) A review of the written lockout/tags-plus program and procedures;
(ii) A review of the current lockout/tags-plus log;
(iii) Verification of the accuracy of the lockout/tags-plus log;
(iv) A review of incident reports since the last audit;
(v) A review conducted between the auditor and authorized employees regarding the authorized employees' responsibilities under the lockout systems being audited; and
(vi) A review conducted between the auditor and affected and authorized employees regarding their responsibilities under the tags-plus systems being audited.
(d) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that, within fifteen days after completion of the audit, the individual(s) who conducted the audit prepare and deliver to ((the employer)) you a written audit report that includes at least:
(i) The date of the audit;
(ii) The identity of the individual(s) who performed the audit;
(iii) The identity of the procedure and machinery, equipment, or system that were audited;
(iv) The findings of the program audit and recommendations for correcting deviations or deficiencies identified during the audit;
(v) Any incident investigation reports since the previous audit; and
(vi) Descriptions of corrective actions ((the employer has)) you have taken in response to the findings and recommendations of any incident investigation reports prepared since the previous audit.
(e) ((The employer shall)) You must promptly communicate the findings and recommendations in the written audit report to each employee having a job task that may be affected by such findings and recommendations.
(f) ((The employer shall)) You must correct the deviations or inadequacies in the lockout/tags-plus program within fifteen days after receiving the written audit report.
(18) Recordkeeping.
(a) Table R-1 specifies what records ((the employer)) you must retain and how long ((the employer)) you must retain them:
Table R-1
Retention of Records Required by WAC 296-304-06016
The employer must keep the following records |
For at least |
Current lockout/tags-plus program and procedures |
Until replaced by updated program and procedures |
Training records |
Until replaced by updated records for each type of training |
Incident investigation reports |
Until the next program audit is completed |
Program audit report |
12 months after being replaced by the next audit report |
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must make all records required by this section available to employees, their representatives, and the director.
(19) Appendices. Nonmandatory Appendix A to this section is a guideline to assist employers and employees in complying with the requirements of this section, and to provide them with other useful information. The information in Appendix A does not add to, or in any way revise, the requirements of this section.
Appendix A to WAC 296-304-06016 (Nonmandatory) - Typical minimal lockout/tags-plus procedures general lockout/tags-plus procedure.
Lockout/tags-plus procedure for (name of company for single procedure or identification of machinery, equipment, or system if multiple procedures used).
Purpose
This procedure establishes the minimum requirements for the lockout/tags-plus application of energy-isolating devices on vessels and vessel sections, and for landside facilities whenever servicing is done on machinery, equipment, or systems in shipyards. This procedure shall be used to ensure that all potentially hazardous energy sources have been isolated and the machinery, equipment, or system to be serviced has been rendered inoperative through the use of lockout or tags-plus procedures before employees perform any servicing when the energization or start-up of the machinery, equipment, or system, or the release of hazardous energy could cause injury.
Compliance with this program
All employees are required to comply with the restrictions and limitations imposed on them during the use of lockout or tags-plus applications. Authorized employees are required to perform each lockout or tags-plus application in accordance with this procedure. No employee, upon observing that machinery, equipment, or systems are secured using lockout or tags-plus applications, shall attempt to start, open, close, energize, or operate that machinery, equipment, or system.
Procedures for lockout/tags-plus systems
(1) Notify each affected employee that servicing is required on the machinery, equipment, or system, and that it must be isolated and rendered inoperative using a lockout or tags-plus system.
(2) The authorized employee shall refer to shipyard employer's procedures to identify the type and magnitude of the energy source(s) that the machinery, equipment, or system uses, shall understand the hazards of the energy, and shall know the methods to control the energy source(s).
(3) If the machinery, equipment, or system is operating, shut it down in accordance with the written procedures (depress the stop button, open switch, close valve, etc.) established by the employer.
(4) Secure each energy-isolating device(s) through the use of a lockout or tags-plus system (for instance, disconnecting, blanking, and affixing tags) so that the energy source is isolated and the machinery, equipment, or system is rendered inoperative.
(5) Lockout system. Affix a lock to each energy-isolating device(s) with assigned individual lock(s) that will hold the energy isolating device(s) in a safe or off position. Potentially hazardous energy (such as that found in capacitors, springs, elevated machine members, rotating flywheels, hydraulic systems, and air, gas, steam, or water pressure, etc.) must be controlled by methods such as grounding, repositioning, blocking, bleeding down, etc.
(6) Tags-plus system. Affix a tag to each energy-isolating device and provide at least one additional safety measure that clearly indicates that removal of the device from the safe or off position is prohibited. Potentially hazardous energy (such as that found in capacitors, springs, elevated machine members, rotating flywheels, hydraulic systems and air, gas, steam, or water pressure, etc.) must be controlled by methods such as grounding, repositioning, blocking, bleeding down, etc.
(7) Ensure that the machinery, equipment, or system is relieved, disconnected, restrained, or rendered safe from the release of all potentially hazardous energy by checking that no personnel are exposed, and then verifying the isolation of energy to the machine, equipment, or system by operating the push button or other normal operating control(s), or by testing to make certain it will not operate.
CAUTION: | Return operating control(s) to the safe or off position after verifying the isolation of the machinery, equipment, or system. |
(8) The machinery, equipment, or system is now secured by a lockout or tags-plus system, and servicing by the authorized person may be performed.
Procedures for removal of lockout/tags-plus systems
When servicing is complete and the machinery, equipment, or system is ready to return to normal operating condition, the following steps shall be taken:
(1) Notify each authorized and affected employee(s) that the lockout/tags-plus system will be removed and the machinery, equipment, or system reenergized.
(2) Inspect the work area to ensure that all employees have been safely positioned or removed.
(3) Inspect the machinery, equipment, or system and the immediate area around the machinery, equipment, or system to ensure that nonessential items have been removed and that the machinery, equipment, or system components are operationally intact.
(4) Reconnect the necessary components, remove the lockout/tags-plus material and hardware, and reenergize the machinery, equipment, or system through the established detailed procedures determined by the employer.
(5) Notify all affected employees that servicing is complete and the machinery, equipment, or system is ready for testing or use.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-304-06017 Retention of DOT markings, placards, and labels.
(1) Any employer who receives a package of hazardous material that is required to be marked, labeled, or placarded in accordance with the U.S. Department of Transportation Hazardous Materials Regulations (49 C.F.R. parts 171 through 180) ((shall)) must retain those markings, labels, and placards on the package until the packaging is sufficiently cleaned of residue and purged of vapors to remove any potential hazards.
(2) Any employer who receives a freight container, rail freight car, motor vehicle, or transport vehicle that is required to be marked or placarded in accordance with the U.S. Department of Transportation Hazardous Materials Regulations ((shall)) must retain those markings and placards on the freight container, rail freight car, motor vehicle, or transport vehicle until the hazardous materials are sufficiently removed to prevent any potential hazards.
(3) ((The employer shall)) You must maintain markings, placards, and labels in a manner that ensures that they are readily visible.
(4) For nonbulk packages that will not be reshipped, the requirements of this section are met if a label or other acceptable marking is affixed in accordance with WAC 296-901-14012, Labels and other forms of warning and WAC 296-901-14014, Safety data sheets.
(5) For the purposes of this section, the term "hazardous material" and any other terms not defined in this section have the same definition as specified in the U.S. Department of Transportation Hazardous Materials Regulations.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-06018 Motor vehicle safety equipment, operation, and maintenance.
(1) Application.
(a) This section applies to any motor vehicle used to transport employees, materials, or property at worksites engaged in shipyard employment. This section does not apply to motor vehicle operation on public streets and highways.
(b) The requirements of this section apply to employer-provided motor vehicles. The requirements of subsections (2)(b) and (d) and (3)(b) of this section also apply to employee-provided motor vehicles.
(c) Only the requirements of subsection (2)(a) through (c) of this section apply to powered industrial trucks, as defined in chapter 296-863 WAC. The maintenance, inspection, operation, and training requirements in chapter 296-863 WAC continue to apply to powered industrial trucks used for shipyard employment.
(2) Motor vehicle safety equipment.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each motor vehicle acquired or initially used after the effective date of this rule is equipped with a safety belt for each employee operating or riding in the motor vehicle. This requirement does not apply to any motor vehicle that was not equipped with safety belts at the time of manufacture.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each employee uses a safety belt, securely and tightly fastened, at all times while operating or riding in a motor vehicle.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that vehicle safety equipment is not removed from any employer-provided vehicle. ((The employer shall)) You must replace safety equipment that is removed.
(d) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each motor vehicle used to transport an employee has firmly secured seats for each employee being transported and that all employees being transported are using such seats.
(3) Motor vehicle maintenance and operation.
(a) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that each motor vehicle is maintained in a serviceable and safe operating condition, and removed from service if it is not in such condition.
(b) ((The employer shall)) You must ensure that, before a motor vehicle is operated, any tools and materials being transported are secured if their movements may create a hazard for employees.
(c) ((The employer shall)) You must implement measures to ensure that motor vehicle operators are able to see, and avoid harming, pedestrians and bicyclists at shipyards. Measures that ((employers)) you may implement to comply with this requirement include:
(i) Establishing dedicated travel lanes for motor vehicles, bicyclists, and pedestrians;
(ii) Installing crosswalks and traffic control devices such as stop signs, mirrors at blind spots, or physical barriers to separate travel lanes;
(iii) Establishing appropriate speed limits for all motor vehicles;
(iv) Establishing "no drive" times to allow for safe movement of pedestrians;
(v) Providing reflective vests or other gear so pedestrians and bicyclists are clearly visible to motor vehicle operators;
(vi) Ensuring that bicycles have reflectors, lights, or other equipment to maximize visibility of the bicyclist; or
(vii) Other measures that ((the employer)) you can demonstrate are as effective in protecting pedestrians and bicyclists as those measures specified in this section.
Reference: | See chapter 296-864 WAC, Split (multipiece) rim and single-piece rim wheels, for requirements relating to servicing multipiece and single-piece rim wheels. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-07001 Inspection.
(1) All gear and equipment provided by ((the employer)) you for rigging and materials handling ((shall)) must be inspected before each shift and, when necessary, at intervals during its use to ensure that is safe. Defective gear ((shall)) must be removed and repaired or replaced before further use.
(2) The safe working load of gear as specified in WAC 296-304-07003 and 296-304-07005 ((shall)) must not be exceeded.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-24-071, filed 12/4/12, effective 1/4/13)
WAC 296-304-07003 Ropes, chains and slings.
(1) Manila rope and manila rope slings. ((Employers)) You must ensure that manila rope and manila-rope slings:
(a) Have permanently affixed and legible identification markings as prescribed by the manufacturer that indicate the recommended safe working load for the type(s) of hitch(es) used, the angle upon which it is based, and the number of legs if more than one;
(b) Not be loaded in excess of its recommended safe working load as prescribed on the identification markings by the manufacturer; and
(c) Not be used without affixed and legible identification markings as required by (a) of this subsection.
(2) Wire rope and wire rope slings.
(a) ((Employers)) You must ensure that wire rope and wire rope slings:
(i) Have permanently affixed and legible identification markings as prescribed by the manufacturer that indicate the recommended safe working load for the type(s) of hitch(es) used, the angle upon which it is based, and the number of legs if more than one;
(ii) Not be loaded in excess of its recommended safe working load as prescribed on the identification markings by the manufacturer; and
(iii) Not be used without affixed and legible identification markings as required by (a)(i) of this subsection.
(b) Protruding ends of strands in splices on slings and bridles ((shall)) must be covered or blunted.
(c) Where U-bolt wire rope clips are used to form eyes, ((employers)) you must use Table G-1 in WAC 296-304-07011 to determine the number and spacing of clips. ((Employers)) You must apply the U-bolt so that the "U" section is in contact with the dead end of the rope.
(d) Wire rope ((shall)) must not be secured by knots.
(3) Chains and chain slings.
(a) ((Employers)) You must ensure that chain and chain slings:
(i) Have permanently affixed and legible identification markings as prescribed by the manufacturer that indicate the recommended safe working load for the type(s) of hitch(es) used, the angle upon which it is based, and the number of legs if more than one;
(ii) Not be loaded in excess of its recommended safe working load as prescribed on the identification markings by the manufacturer; and
(iii) Not be used without affixed and legible identification markings as required by (a)(i) of this subsection.
(b) All sling chains, including end fastenings, ((shall)) must be given a visual inspection before being used on the job. A thorough inspection of all chains in use ((shall)) must be made every 3 months. Each chain ((shall)) must bear an indication of the month in which it was thoroughly inspected. The thorough inspection ((shall)) must include inspection for wear, defective welds, deformation and increase in length or stretch.
(c) ((Employers)) You must note interlink wear, not accompanied by stretch in excess of 5 percent, and remove the chain from service when maximum allowable wear at any point of link, as indicated in Table G-2 in WAC 296-304-07011, has been reached.
(d) Chain slings ((shall)) must be removed from service when, due to stretch, the increase in length of a measured section exceeds five percent; when a link is bent, twisted or otherwise damaged; or when raised scarfs or defective welds appear.
(e) All repairs to chains ((shall)) must be made under qualified supervision. Links or portions of the chain found to be defective as described in (d) of this section ((shall)) must be replaced by links having proper dimensions and made of material similar to that of the chain. Before repaired chains are returned to service, they ((shall)) must be proof tested to the proof test load recommended by the manufacturer.
(f) Wrought iron chains in constant use ((shall)) must be annealed or normalized at intervals not exceeding six months when recommended by the manufacturer. The chain manufacturer ((shall)) must be consulted for recommended procedures for annealing or normalizing. Alloy chains ((shall)) must never be annealed.
(g) A load ((shall)) must not be lifted with a chain having a kink or knot in it. A chain ((shall)) must not be shortened by bolting, wiring or knotting.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-24-071, filed 12/4/12, effective 1/4/13)
WAC 296-304-07005 Shackles and hooks.
(1) Shackles. ((Employers)) You must ensure that shackles:
(a) Have permanently affixed and legible identification markings as prescribed by the manufacturer that indicate the recommended safe working load;
(b) Not be loaded in excess of its recommended safe working load as prescribed on the identification markings by the manufacturer; and
(c) Not be used without affixed and legible identification markings as required by (a) of this subsection.
(2) Hooks.
(a) The manufacturer's recommendations ((shall)) must be followed in determining the safe working loads of the various sizes and types of specific and identifiable hooks. All hooks for which no applicable manufacturer's recommendations are available ((shall)) must be tested to twice the intended safe working load before they are initially put into use. ((The employer shall)) You must maintain a record of the dates and results of such tests.
(b) Loads ((shall)) must be applied to the throat of the hook since loading the point overstresses and bends or springs the hook.
(c) Hooks ((shall)) must be inspected periodically to see that they have not been bent by overloading. Bent or sprung hooks ((shall)) must not be used.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-07007 Chain falls and pull-lifts.
(1) Chain falls and pull-lifts ((shall)) must be clearly marked to show the capacity and the capacity ((shall)) must not be exceeded.
(2) Chain falls ((shall)) must be regularly inspected to ensure that they are safe, particular attention being given to the lift chain, pinion, sheaves and hooks for distortion and wear. Pull-lifts ((shall)) must be regularly inspected to ensure that they are safe, particular attention being given to the ratchet, pawl, chain and hooks for distortion and wear.
(3) Straps, shackles, and the beam or overhead structure to which a chain fall or pull-lift is secured ((shall)) must be of adequate strength to support the weight of load plus gear. The upper hook ((shall)) must be moused or otherwise secured against coming free of its support.
(4) Scaffolding ((shall)) must not be used as a point of attachment for lifting devices, such as tackles, chain falls, and pull-lifts unless the scaffolding is specifically designed for that purpose.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-07009 Hoisting and hauling equipment.
(1) Derrick and crane certification:
(a) Derricks and cranes which are part of, or regularly placed aboard barges, other vessels, or on wingwalls of floating drydocks, and are used to transfer materials or equipment from or to a vessel or drydock, ((shall)) must be tested and certificated in accordance with the standards provided in WAC 296-304-130 gear certification, by persons accredited for that purpose.
(b) Subsection (a) of this section ((shall)) must take effect 180 days after the effective date of the amendment.
(2) The moving parts of hoisting and hauling equipment ((shall)) must be guarded.
(3) Mobile crawler or truck cranes used on a vessel:
(a) The maximum manufacturer's rated safe working loads for the various working radii of the boom and the maximum and minimum radii at which the boom may be safely used with and without outriggers ((shall)) must be conspicuously posted near the controls and ((shall)) must be visible to the operator. A radius indicator ((shall)) must be provided.
(b) The posted safe working loads of mobile crawler or truck cranes under the conditions of use ((shall)) must not be exceeded.
(4) Accessible areas within the swing radius of the outermost part of the body of a revolving derrick or crane whether permanently or temporarily mounted, ((shall)) must be guarded in such a manner as to prevent an employee from being in such a position as to be struck by the crane or caught between the crane and fixed parts of the vessel or of the crane itself.
(5) Marine railways((:
(a))). The cradle or carriage on the marine railway ((shall)) must be positively blocked or secured when in the hauled position to prevent it from being accidentally released.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-24-071, filed 12/4/12, effective 1/4/13)
WAC 296-304-07011 Use of gear.
(1) Loads ((shall)) must be safely rigged before being hoisted.
(2) Plates ((shall)) must be handled on and off hulls by means of shackles whenever possible. Clips or pads of ample size ((shall)) must be welded to the plate to receive the shackle pins whenever there are no holes in the plate. When it is not possible to make holes in or to weld pads to the plate, alligator tongs, grab hooks, grab clamps or screw clamps may be used. In such cases special precautions ((shall)) must be taken to keep employees from under such lifts.
(3) Tag lines ((shall)) must be provided on loads likely to swing or to need guidance.
(4) When slings are secured to eyebolts, the slings ((shall)) must be so arranged, using spreaders if necessary, that the pull is within 20 degrees of the axis of the bolt.
(5) Slings ((shall)) must be padded by means of wood blocks or other suitable material where they pass over sharp edges or corners of loads so as to prevent cutting or kinking.
(6) Skips ((shall)) must be rigged to be handled by not less than 3 legged bridles, and all legs ((shall)) must always be used. When open end skips are used, means ((shall)) must be taken to prevent the contents from falling.
(7) Loose ends of idle legs of slings in use ((shall)) must be hung on the hook.
(8) Employees ((shall)) must not be permitted to ride the hook or the load.
(9) Loads (tools, equipment or other materials) ((shall)) must not be swung or suspended over the heads of employees.
(10) Pieces of equipment or structure susceptible to falling or dislodgement ((shall)) must be secured or removed as early as possible.
(11) An individual who is familiar with the signal code in use ((shall)) must be assigned to act as a signalman when the hoist operator cannot see the load being handled. Communications ((shall)) must be made by means of clear and distinct visual or auditory signals except that verbal signals ((shall)) must not be permitted.
(12) Pallets, when used, ((shall)) must be of such material and construction and so maintained as to safely support and carry the loads being handled on them.
(13) A section of hatch through which materials or equipment are being raised, lowered, moved, or otherwise shifted manually or by a crane, winch, hoist, or derrick, ((shall)) must be completely opened. The beam or pontoon left in place adjacent to an opening ((shall)) must be sufficiently lashed, locked or otherwise secured to prevent it from moving so that it cannot be displaced by accident.
(14) Hatches ((shall)) must not be opened or closed while employees are in the square of the hatch below.
(15) Before loads or empty lifting gear are raised, lowered, or swung, clear and sufficient advance warning ((shall)) must be given to employees in the vicinity of such operations.
(16) At no time ((shall)) will an employee be permitted to place himself or herself in a hazardous position between a swinging load and a fixed object.
TABLE E-1
DIMENSIONS AND SPACING OF WOOD
INDEPENDENT-POLE SCAFFOLD MEMBERS
Structural Members |
Light duty (Up to 25 pounds per square foot) |
Heavy duty (25 to 75 pounds per square foot) |
||||||
Height in feet |
Height in feet |
|||||||
< 24 |
˃24<40 |
40<60 |
<24 |
˃24<40 |
40<60 |
|||
Poles or uprights (in inches) . . . . |
2x4 |
3x4 or 2x6 |
4x4 |
3x4 |
4x4 |
4x6 |
||
Bearers (in inches) . . . . |
2x4 |
2x6 |
2x6 |
2x8 |
2x8 |
2x10 |
||
Ledgers (in inches) . . . . |
2x6 |
2x6 |
2x6 |
2x8 |
2x8 |
2x8 |
||
Stringer (not supporting bearers) (in inches) . . . . |
1x6 |
1x6 |
1x6 |
1x6 |
1x6 |
1x6 |
||
Braces (in inches) . . . . |
1x4 |
1x6 |
1x6 |
1x6 |
1x6 |
1x6 |
||
Pole spacing— longitudinally (in feet) . . . . |
7 1/2 |
7 1/2 |
7 1/2 |
7 |
7 |
7 |
||
Pole spacing— transversely (in feet) . . . . |
6 1/2 min |
7 1/2 min |
8 1/2 min |
6 1/2 |
10 |
10 |
||
Ledger spacing— vertically (in feet) . . . . |
7 |
7 |
7 |
4 1/2 |
4 1/2 |
4 1/2 |
||
TABLE E-2
SPECIFICATIONS FOR SIDE RAILS OF LADDERS
Length (in feet) |
Cross section (in inches) |
|||
At ends |
At center |
|||
15 . . . . |
1 7/8 x 2 3/4 |
1 7/8 x 3 3/4 |
||
16 . . . . |
1 7/8 x 2 3/4 |
1 7/8 x 3 3/4 |
||
17 . . . . |
1 7/8 x 3 |
1 7/8 x 4 |
||
18 . . . . |
1 7/8 x 3 |
1 7/8 x 4 |
||
20 . . . . |
1 7/8 x 3 |
1 7/8 x 4 1/2 |
||
24 . . . . |
1 7/8 x 3 |
1 7/8 x 4 1/2 |
||
TABLE E-3
SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE CONSTRUCTION OF HORSES
Structural |
Height in feet |
||
Members |
<10 |
˃10<16 |
16<20 |
Inches |
Inches |
Inches |
|
Legs . . . . |
2x4 |
3x4 |
4x6 |
Bearers or headers |
2x6 |
2x8 |
4x6 |
Crossbraces . . . . |
2x4 or 1x8 |
2x4 |
2x6 |
Longitudinal braces . . . . |
2x4 |
2x6 |
2x6 |
TABLE E-4
SAFE CENTER LOADS FOR SCAFFOLD PLANK
OF 1,100 POUNDS FIBRE STRESS
[Codification note: The graphic presentation of this table has been varied in order that it would fall within the printing specifications for the Washington Administrative Code. The following table had lumber dimensions in the table heading typed in vertically across the page while the remainder of the table was typed horizontally on the page. The "Span in Feet" materials (6 through 16) which ran top to bottom has been switched to run left to right on the page. The "Lumber dimensions in inches" which ran left to right on the page has been switched to run top to bottom on the page.]
Lumber dimensions in inches |
Span in Feet |
|||||
6 |
8 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
16 |
|
A-2 x 10 |
||||||
B-1 5/8 x 9 1/2 |
256 |
192 |
153 |
128 |
110 |
... |
A-2 x 12 |
||||||
B-1 5/8 x 11 1/2 |
309 |
232 |
186 |
155 |
133 |
116 |
A-3 x 8 |
||||||
B-2 5/8 x 7 1/2 |
526 |
395 |
316 |
263 |
225 |
197 |
A-3 x 10 |
||||||
B-2 5/8 x 9 1/2 |
667 |
600 |
400 |
333 |
286 |
250 |
A-3 x 12 |
||||||
B-2 5/8 x 11 1/2 |
807 |
605 |
484 |
404 |
346 |
303 |
(A)—Rough lumber. |
||||||
(B)—Dressed lumber. |
||||||
TABLE G-1
NUMBER AND SPACING OF U-BOLT WIRE
ROPE CLIPS
Number of Clips |
||||||||
Improved plow steel rope diameter inches |
Drop forged |
Other material |
Minimum spacing (inches) |
|||||
* |
. . . . |
... |
... |
|||||
1/2 |
. . . . |
3 |
4 |
3 |
||||
5/8 |
. . . . |
3 |
4 |
3 3/4 |
||||
3/4 |
. . . . |
4 |
5 |
4 1/2 |
||||
7/8 |
. . . . |
4 |
5 |
5 1/4 |
||||
1 |
. . . . |
4 |
6 |
6 |
||||
1 1/8 |
. . . . |
5 |
6 |
6 3/4 |
||||
1 1/4 |
. . . . |
5 |
7 |
7 1/2 |
||||
1 3/8 |
. . . . |
6 |
7 |
8 1/4 |
||||
1 1/2 |
. . . . |
6 |
8 |
9 |
||||
*Three clips shall be used on wire size less than 1/2-inch diameter. |
||||||||
TABLE G-2
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE WEAR AT
ANY POINT OF LINK
Chain size in inches |
Maximum allowable wear in fraction of inches |
||
1/4 (9/32). . . . |
3/64 |
||
3/8. . . . |
5/64 |
||
1/2. . . . |
7/64 |
||
5/8. . . . |
9/64 |
||
3/4. . . . |
5/32 |
||
7/8. . . . |
1/64 |
||
1. . . . |
3/16 |
||
1 1/8. . . . |
7/32 |
||
1 1/4. . . . |
1/4 |
||
1 3/8. . . . |
9/32 |
||
1 1/2. . . . |
5/16 |
||
1 3/4. . . . |
1/32 |
||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-07013 Qualifications of operators.
(1) When ship's gear is used to hoist materials aboard, a competent person ((shall)) must determine that the gear is properly rigged, that it is in safe condition, and that it will not be overloaded by the size and weight of the lift.
(2) Only those employees who understand the signs, notices, and operating instructions, and are familiar with the signal code in use, ((shall)) must be permitted to operate a crane, winch, or other power operated hoisting apparatus.
(3) No employee known to have defective uncorrected eyesight or hearing, or to be suffering from heart disease, epilepsy, or similar ailments which may suddenly incapacitate him, ((shall)) must be permitted to operate a crane, winch or other power operated hoisting apparatus.
(4) No minor under eighteen years of age ((shall)) must be employed in occupations involving the operation of any power-driven hoisting apparatus or assisting in such operations by work such as hooking on, loading slings, rigging gear, etc.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-08001 General precautions.
(1) Hand lines, slings, tackles of adequate strength, or carriers such as tool bags with shoulder straps ((shall)) must be provided and used to handle tools, materials, and equipment so that employees will have their hands free when using ship's ladders and access ladders. The use of hose or electric cords for this purpose is prohibited.
(2) When air tools of the reciprocating type are not in use, the discs and tools ((shall)) must be removed.
(3) All portable, power-driven circular saws ((shall)) must be equipped with guards above and below the base plate or shoe. The upper guard ((shall)) must cover the saw to the depth of the teeth, except for the minimum arc required to permit the base to be tilted for bevel cuts. The lower guard ((shall)) must cover the saw to the depth of the teeth, except for the minimum arc required to allow proper retraction and contact with the work. When the tool is withdrawn from the work, the lower guard ((shall)) must automatically and instantly return to the covering position.
(4) The moving parts of machinery on dry docks ((shall)) must be guarded.
(5) Before use, pneumatic tools ((shall)) must be secured to the extension hose or whip by some positive means to prevent the tool from becoming accidentally disconnected from the whip.
(6) The moving parts of drive mechanisms, such as gearing and belting on large portable tools, ((shall)) must be adequately guarded.
(7) Headers, manifolds, and widely spaced hose connections on compressed air lines ((shall)) must bear the word "air" in letters at least 1 inch high, which ((shall)) must be painted either on the manifolds or separate hose connections, or on signs permanently attached to the manifolds or connections. Grouped air connections may be marked in one location.
(8) Before use, compressed air hose ((shall)) must be examined. Visibly damaged and unsafe hose ((shall)) must not be used.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-08003 Portable electric tools.
(1) The frames of portable electric tools and appliances, except double insulated tools approved by Underwriters' Laboratories, ((shall)) must be grounded either through a third wire in the cable containing the circuit conductors or through a separate wire which is grounded at the source of the current.
(2) Grounding circuits, other than by means of the structure of the vessel on which the tool is being used, ((shall)) must be checked to ensure that the circuit between the ground and the grounded power conductor has resistance which is low enough to permit sufficient current to flow to cause the fuse or circuit breaker to interrupt the current.
(3) Portable electric tools which are held in the hand ((shall)) must be equipped with switches of a type which must be manually held in the closed position.
(4) Worn or frayed electric cables ((shall)) must not be used.
(5) ((The employer shall)) You must notify the officer in charge of the vessel before using electric power tools operated with the vessel's current.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-08005 Hand tools.
(1) ((Employers shall)) You must not issue or permit the use of unsafe hand tools.
(2) Wrenches, including crescent, pipe, end and socket wrenches, ((shall)) must not be used when jaws are sprung to the point that slippage occurs.
(3) Impact tools, such as drift pins, wedges, and chisels, ((shall)) must be kept free of mushroomed heads.
(4) The wooden handles of tools ((shall)) must be kept free of splinters or cracks and ((shall)) must be kept tight in the tool.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 98-02-006, filed 12/26/97, effective 3/1/98)
WAC 296-304-08007 Abrasive wheels.
(1) Floor stand and bench mounted abrasive wheels used for external grinding ((shall)) must be provided with safety guards (protection hoods). The maximum angular exposure of the grinding wheel periphery and sides ((shall)) must be not more than 90 degrees, except that when work requires contact with the wheel below the horizontal plane of the spindle, the angular exposure ((shall)) must not exceed 125 degrees. In either case the exposure ((shall)) must begin not more than 65 degrees above the horizontal plane of the spindle. Safety guards ((shall)) must be strong enough to withstand the effect of a bursting wheel.
(2) Floor and bench mounted grinders ((shall)) must be provided with work rests which are rigidly supported and readily adjustable. Such work rests ((shall)) must be kept a distance not to exceed 1/8 inch from the surface of the wheel.
(3) Cup type wheels ((use)) used for external grinding ((shall)) must be protected by either a revolving cup guard or a band type guard in accordance with the provisions of the United States of American Standard Safety Code for the Use, Care, and Protection of Abrasive Wheels, B7.1.1970. All other portable abrasive wheels used for external grinding ((shall)) must be provided with safety guards (protection hoods) meeting the requirements of (5) of this section, except as follows:
(a) When the work location makes it impossible, in which case a wheel equipped with safety flanges as described in (6) of this section ((shall)) must be used.
(b) When wheels 2 inches or less in diameter which are securely mounted on the end of a steel mandrel are used.
(4) Portable abrasive wheels used for internal grinding ((shall)) must be provided with safety flanges (protection flanges) meeting the requirements of (6) of this section, except as follows:
(a) When wheels 2 inches or less in diameter which are securely mounted on the end of a steel mandrel are used.
(b) If the wheel is entirely within the work being ground while in use.
(5) When safety guards are required, they ((shall)) must be ((so)) mounted so as to maintain proper alignment with the wheel, and the guard and its fastenings ((shall)) must be of sufficient strength to retain fragments of the wheel in case of accidental breakage. The maximum angular exposure of the grinding wheel periphery and sides ((shall)) must not exceed 180 degrees.
(6) When safety flanges are required, they ((shall)) must be used only with wheels designed to fit the flanges. Only safety flanges of a type and design and properly assembled so as to insure that the pieces of the wheel will be retained in case of accidental breakage ((shall)) must be used.
(7) All abrasive wheels ((shall)) must be closely inspected and ring tested before mounting to ensure that they are free from cracks or defects.
(8) Grinding wheels ((shall)) must fit freely on the spindle and ((shall)) must not be forced on. The spindle nut ((shall)) must be tightened only enough to hold the wheel in place.
(9) The power supply ((shall)) must be sufficient to maintain the rated spindle speed under all conditions of normal grinding. The rated maximum speed of the wheel ((shall)) must not be exceeded.
(10) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all employees using abrasive wheels are protected by eye protection equipment that meets the requirements of WAC 296-304-09005 (1) and (2), except when adequate eye protection is provided by eye shields permanently attached to the bench or floor stand.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-08009 Powder-actuated fastening tools.
(1) ((The employer)) You must ensure powder-actuated fastening tools are used, designed, constructed, and maintained according to the requirements of WAC 296-807-150, Powder actuated fastening systems.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees using powder-actuated fastening tools are protected by personal protective equipment that meets the requirements of WAC 296-304-09005 (1) and (2). ((The employer)) You must also meet the requirements of chapter 296-817 WAC, Hearing loss prevention (noise).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-08011 Internal combustion engines, other than ship's equipment.
(1) When internal combustion engines, furnished by ((the employer)) you are used in a fixed position below decks, for such purposes as driving pumps, generators, and blowers, the exhaust ((shall)) must be led to the open air, clear of any ventilation intakes and openings through which it might enter the vessel
(2) All exhaust line joints and connections ((shall)) must be checked for tightness immediately upon starting the engine, and any leaks ((shall)) must be corrected at once.
(3) When internal combustion engines on vehicles, such as forklifts and mobile cranes, or on portable equipment such as fans, generators, and pumps exhaust into the atmosphere below decks, the competent person ((shall)) must make tests of the carbon monoxide content of the atmosphere as frequently as conditions require to ensure that dangerous concentrations do not develop. Employees ((shall)) must be removed from the compartment involved when the carbon monoxide concentration exceeds 50 parts per million (0.005%). ((The employer shall)) You must use blowers sufficient in size and number and so arranged as to maintain the concentration below this allowable limit before work is resumed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 98-02-006, filed 12/26/97, effective 3/1/98)
WAC 296-304-090 Personal protective equipment (PPE)—General requirements.
((The employer)) (1) You must provide and ensure that each affected employee uses the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for the eyes, face, head, extremities, torso, and respiratory system, including protective clothing, protective shields, hearing protection, protective barriers, personal fall protection equipment, and life saving equipment, wherever the employee is exposed to hazards that require the use of PPE. ((The employer)) You must furnish the personal protective equipment at no cost to employees if:
((•)) (a) The intended purpose is to protect against hazardous materials (the PPE may be contaminated by hazardous materials in the course of employment); or
((•)) (b) The PPE is of such a nature that it would not reasonably be worn outside the worksite.
(2) The provision of personal protective equipment which may reasonably be worn outside of the workplace is subject to labor-management negotiations, but ((the employer)) you must ensure that exposed employees are wearing the appropriate PPE.
(3) Examples of PPE that must be provided at no cost to employees include, but are not limited to:
((•)) (a) Boots worn to protect against chemicals;
((•)) (b) Nonprescription protective eye wear;
((•)) (c) Goggles to fit over prescription eye wear;
((•)) (d) Metatarsal protection; and
((•)) (e) Full body harnesses and lanyards.
(4) Examples of PPE that provision is subject to labor-management negotiation include, but are not limited to:
((•)) (a) Leather boots with or without steel toes;
((•)) (b) Coats to protect against inclement weather; and
((•)) (c) Prescription protective eye wear (except as part of a full facepiece or hooded respirator).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 98-02-006, filed 12/26/97, effective 3/1/98)
WAC 296-304-09001 Hazard assessment and equipment selection.
(1) ((The employer)) You must assess its work activity to determine if hazards that require the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) are present, or are likely to be present.
(((a))) If such hazards are present, or likely to be present, ((the employer)) you must:
(((i))) (a) Select, and require each affected employee to use, PPE that will protect the employee from the hazards identified in the hazard assessment;
(((ii))) (b) Inform the affected employee what types of PPE to use;
(((iii))) (c) Select PPE that properly fits the affected employee; and
(((iv))) (d) Verify that the hazard assessment has been performed through a document that contains the following information:
((•)) (i) Work activity evaluated;
((•)) (ii) Occupation;
((•)) (iii) Date(s) of the hazard assessment; and
((•)) (iv) The name of the person performing the hazard assessment.
Note: | A hazard assessment conducted according to the trade or occupation of affected employees will be considered to comply with this requirement if it addresses all PPE-related hazards to which employees are exposed in the course of their work activities. |
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that employees do not use defective or damaged PPE.
(3) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all unsanitary PPE, including all previously used PPE, is cleaned and disinfected before it is reissued.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 98-02-006, filed 12/26/97, effective 3/1/98)
WAC 296-304-09003 Training.
((The employer)) You must provide training to each employee for whom PPE is required by this section.
(1) Each employee whose work activities require the use of PPE must be trained to know at least the following:
(a) When PPE is necessary;
(b) What PPE is necessary;
(c) How to properly put on, take off, adjust, and wear PPE;
(d) The limitations of the PPE; and
(e) The proper care, maintenance, useful life and disposal of the PPE.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that each affected employee demonstrates the ability to use PPE properly before being allowed to perform work where its use is required.
(3) ((The employer)) You must retrain any employee who does not understand or display the skills required by subsection (2) of this section. Circumstances where retraining is required include, but are not limited to, situations where:
(a) Changes in occupation or work make previous training obsolete; or
(b) Changes in the types of PPE to be used make previous training obsolete; or
(c) Inadequacies in an affected employee's knowledge or use of assigned PPE indicate that the employee has not retained the understanding or skill.
(4) ((The employer)) You must verify that each affected employee has received the required training through a document that contains the following information:
((•)) (a) Name of each employee trained;
((•)) (b) Date(s) of training; and
((•)) (c) Type of training the employee received.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 10-09-088, filed 4/20/10, effective 6/1/10)
WAC 296-304-09005 Eye and face protection.
(1) ((The employer)) You must provide each affected employee with eye and face protection according to the following requirements:
(a) Each affected employee must use appropriate eye or face protection when exposed to eye or face hazards caused by flying particles, molten metal, liquid chemicals, acid or caustic liquids, chemical gases or vapors, or potentially injurious light radiation.
(b) Each affected employee must use eye or face protection that provides side protection when there is a hazard from flying objects. A detachable side protector (e.g., a clip-on or slide-on side shield) that meets the requirements of this section is acceptable.
(c) Each affected employee who wears prescription lenses must:
((•)) (i) Use eye protection that incorporates the prescription in its design; or
((•)) (ii) Be protected by eye protection that can be worn over prescription lenses without disturbing the proper position of either the PPE or the prescription lenses.
(d) Each affected employee must use equipment with filter lenses of a shade that provides appropriate protection from injurious light radiation. Tables I-1A and I-1B lists the appropriate shade numbers for various operations. If filter lenses are used in goggles worn under a helmet with a lens, the shade number of the lens in the helmet may be reduced so that the shade numbers of the two lenses will equal the value shown in the Tables I-1A and I-1B.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all protective eye and face devices comply with ANSI Z87.1, American National Standard Practice for Occupational and Educational Eye and Face Protection, edition 1989, revision 1998, or edition 2003.
((Employers)) (3) You may use alternate eye and face protection if they can demonstrate such devices are at least as effective as those constructed in accordance with one of the above consensus standards.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-20-055, filed 10/3/05, effective 12/1/05)
WAC 296-304-09007 Respiratory protection.
((The employer)) You must provide respiratory protection that meets the requirements of chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-11-060, filed 5/19/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-09009 Hearing protection.
((The employer)) You must meet the requirements of chapter 296-817 WAC, Hearing loss prevention (noise).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-03-013, filed 1/7/14, effective 2/10/14)
WAC 296-304-09011 Head protection.
(1) ((The employer)) You must provide each affected employee with head protection according to the following requirements:
(a) Each affected employee wears a protective helmet when working in areas where there is a potential for injury to the head.
(b) Each affected employee wears a protective helmet designed to reduce electrical shock hazards where there is potential for electric shock or burns from contact with exposed electrical conductors that could contact the head.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all protective helmets comply with any of the following consensus standards:
((•)) (a) ANSI Z89.1-2009, American National Standard for Industrial Head Protection.
((•)) (b) ANSI Z89.1-2003, American National Standard for Industrial Head Protection.
((•)) (c) ANSI Z89.1-1997, American National Standard for Industrial Head Protection.
((•)) (d) ANSI Z89.1-1986, American National Standard for Personnel Protection—Protective Headwear for Industrial Workers—Requirements.
((Employers)) (3) You may use alternate head protection if they can demonstrate such devices are at least as effective as those constructed in accordance with one of the above consensus standards.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 10-09-088, filed 4/20/10, effective 6/1/10)
WAC 296-304-09013 Foot protection.
(1) ((The employer)) You must ensure that each affected employee wears protective footwear when working in areas where:
((•)) (a) There is a danger of foot injuries from falling or rolling objects;
((•)) (b) There is a danger of foot injuries from objects piercing the sole; or
((•)) (c) Where an employee's feet are exposed to electrical hazards.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that all protective footwear complies with one of the following consensus standards:
((•)) (a) ASTM F-2412-2005, Standard Test Methods for Foot Protection, and ASTM F-2413-2005, Standard Specification for Performance Requirements for Protective Footwear.
((•)) (b) ANSI Z41-1999, American National Standard for Personal Protection—Protective Footwear.
((•)) (c) ANSI Z41-1991, American National Standard for Personal Protection—Protective Footwear.
((Employers)) (3) You may use alternate footwear if they can demonstrate it is at least as effective as those constructed in accordance with one of the above consensus standards.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 98-02-006, filed 12/26/97, effective 3/1/98)
WAC 296-304-09015 Hand and body protection.
((The employer)) (1) You must ensure that each affected employee uses appropriate hand protection and other protective clothing where there is exposure to hazards such as:
((•)) (a) Skin absorption of harmful substances;
((•)) (b) Severe cuts or lacerations;
((•)) (c) Severe abrasions;
((•)) (d) Punctures;
((•)) (e) Chemical burns;
((•)) (f) Thermal burns;
((•)) (g) Harmful temperature extremes; and
((•)) (h) Sharp objects.
(((1))) (2) Hot work operations. ((The employer)) You must ensure that an employee's clothing is free from flammable or combustible materials (such as grease or oil) while engaged in hot work operations or working near an ignition or oxygen source.
(((2))) (3) Electrical protective devices. ((The employer)) You must ensure that each affected employee wears protective electrical insulating gloves and sleeves or other electrical protective equipment, if that employee is exposed to electrical shock hazards while working on electrical equipment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-09017 Lifesaving equipment.
(1) Personal flotation devices (PFD).
((•)) You must provide your employees with PFDs approved by the United States Coast Guard for use on commercial or merchant vessels. The following are appropriate or allowable United States Coast Guard approved PFDs:
Type of PFD |
General Description |
Type I |
Off-shore life jacket - effective for all waters or where rescue may be delayed. |
Type II |
Near-shore buoyant vest - intended for calm, inland water or where there is a good chance of quick rescue. |
Type III |
Flotation aid - good for calm, inland water, or where there is a good chance of rescue. |
Type V |
Flotation aids such as boardsailing vests, deck suits, work vests and inflatable PFDs marked for commercial use. |
Note: | ((•)) 1. Commercially available PFDs are marked or imprinted with the Type of PFD. |
((•)) 2. Type IV PFDs are throwable devices. They are used to aid persons who have fallen into the water. | |
((•)) 3. The requirements for USCG approval are in 46 C.F.R. Part 160, Coast Guard Lifesaving Equipment Specifications. |
((The employer)) You must ensure that each personal flotation device is inspected before use for dry rot, chemical damage, or other defects that may affect its strength and buoyancy. Defective personal ((floatation)) flotation devices ((shall)) must not be used.
(2) Ring life buoys and ladders.
(a) ((The employer)) You must ensure that when work is performed on a floating vessel 200 feet (61 m) or more in length, at least three 30-inch (0.76 m) U.S. Coast Guard approved ring life buoys with lines attached are located in readily visible and accessible places. Ring life buoys must be located one forward, one aft, and one at the access to the gangway.
(b) On floating vessels under 200 feet (61 m) in length, at least one 30-inch (0.76 m) U.S. Coast Guard approved ring life buoy with line attached must be located at the gangway.
(c) At least one 30-inch (0.76 m) U.S. Coast Guard approved ring life buoy with a line attached must be located on each staging alongside of a floating vessel on which work is performed.
(d) At least 90 feet (27.43 m) of line must be attached to each ring life buoy.
(e) There must be at least one portable or permanent ladder near each floating vessel on which work is performed. The ladder must be long enough to help an employee reach safety in the event of a fall into the water.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 98-02-006, filed 12/26/97, effective 3/1/98)
WAC 296-304-09019 Fall protection—General requirement.
((The employer)) You must provide and ensure the use of fall protection when employees work aloft or elsewhere at elevations more than 5 feet above a solid surface.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-09021 Personal fall arrest systems (PFAS).
Personal fall arrest systems must meet the requirements of this section.
(1) ((The employer)) You must ensure that connectors and anchorages meet the following criteria:
(a) Connectors are made of drop forged, pressed, or formed steel or of materials with equivalent strength.
(b) Connectors have a corrosion-resistant finish, and all surfaces and edges are smooth to prevent damage to the interfacing parts of the system.
(c) D-rings and snaphooks can sustain a minimum tensile load of 5,000 pounds (22.24 Kn).
(d) D-rings and snaphooks are proof-tested to a minimum tensile load of 3,600 pounds (16 Kn) without cracking, breaking, or being permanently deformed.
(e) Snaphooks lock and are designed and used to prevent disengagement of the snaphook by contact of the snaphook keeper with the connected part.
(f) On suspended scaffolds or similar work platforms with horizontal lifelines that may become vertical lifelines, the devices used for connection to the horizontal lifeline can lock in any direction on the lifeline.
(g) Anchorages used for attachment of personal fall arrest equipment are independent of any anchorage used to support or suspend platforms.
(h) Anchorages can support at least 5,000 pounds (22.24 Kn) per employee attached, or are designed, installed, and used as follows:
(i) As part of a complete personal fall arrest system that maintains a safety factor of at least two; and
(ii) Under the direction and supervision of a qualified person.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that lifelines, lanyards, and personal fall arrest systems meet the following criteria:
(a) When vertical lifelines are used, each employee has a separate lifeline.
(b) Vertical lifelines and lanyards have a minimum tensile strength of 5,000 pounds (22.24 Kn).
(c) Self-retracting lifelines and lanyards that automatically limit free fall distances to 2 feet (0.61 m) or less can sustain a minimum tensile load of 3000 pounds (13.34 Kn) applied to a self-retracting lifeline or lanyard with the lifeline or lanyard in the fully extended position.
(d) Self-retracting lifelines and lanyards which do not limit free fall distance to 2 feet (0.61 m) or less, ripstitch lanyards and tearing and deforming lanyards can sustain a minimum static tensile load of 5,000 pounds (22.24 Kn) applied to the device when they are in the fully extended position.
(e) Horizontal lifelines are designed, installed, and used under the supervision of a qualified person, and only used as part of a complete personal fall arrest system that maintains a safety factor of at least two.
Note: | The system strength needs below are based on a maximum combined weight of employee and tools of 310 pounds. If combined weight is more than 310 pounds (140.62 kg), appropriate allowances must be made or the system will not be in compliance. |
(f) Effective April 20, 1998, ((the employer)) you must ensure that personal fall arrest systems:
(i) Limit the maximum arresting force on a falling employee to 1,800 pounds (8 Kn) when used with a body harness;
(ii) Bring a falling employee to a complete stop and limit the maximum deceleration distance an employee travels to 3.5 feet (1.07 m); and
(iii) Are strong enough to withstand twice the potential impact energy of an employee free falling a distance of 6 feet (1.8 m), or the free fall distance permitted by the system, whichever is less.
(g) ((The employer)) You must ensure that personal fall arrest systems are rigged so that an employee can neither free fall more than 6 feet (1.83 m) nor contact any lower level.
(3) ((The employer)) You must select, use, and care for systems and system components according to the following requirements:
(a) Lanyards are attached to employees using personal fall arrest systems, as follows:
The attachment point of a body harness is in the center of the wearer's back near the shoulder level, or above the wearer's head. If the maximum free fall distance is less than 20 inches, the attachment point may be located in the chest position.
(b) Ropes and straps (webbing) used in lanyards, lifelines and strength components of body harnesses are made from synthetic fibers or wire rope.
(c) Ropes, harnesses, and lanyards are compatible with their hardware.
(d) Lifelines and lanyards are protected against cuts, abrasions, burns from hot work operations and deterioration by acids, solvents, and other chemicals.
(e) Personal fall arrest systems are inspected before each use for mildew, wear, damage, and other deterioration. Defective components are removed from service.
(f) Personal fall arrest systems and components subjected to impact loading are immediately removed from service and not used again for employee protection until inspected and determined by a qualified persons to be undamaged and suitable for reuse.
(g) ((The employer)) You must provide for prompt rescue of employees in the event of a fall or must ensure that employees are able to rescue themselves.
(h) Personal fall arrest systems and components are used only for employee fall protection and not to hoist materials.
(4) Training. Before using personal fall arrest equipment, ((the employer)) you must ensure that each affected employee is trained to understand the application limits of the equipment and proper hook-up, anchoring, and tie-off techniques. Affected employees must also be trained to demonstrate the proper use, inspection, and storage of their equipment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-09023 Positioning device systems.
((The employer)) You must ensure that positioning device systems and their use meet the requirements of this section.
(1) ((The employer)) You must ensure that connectors and anchorages meet the following criteria:
(a) Connectors have a corrosion-resistant finish, and all surfaces and edges are smooth to prevent damage to interfacing parts of this system.
(b) Connecting assemblies have a minimum tensile strength of 5,000 pounds (22.24 Kn).
(c) Positioning device systems are secured to an anchorage that can support at least twice the potential impact load of an employee's fall.
(d) Only locking type snaphooks are used in positioning device systems.
(2) ((The employer)) You must ensure that positioning device systems meet the following criteria:
(a) Restraint (tether) lines have a minimum breaking strength of 3,000 pounds (13.34 Kn).
(b) Beginning April 20, 1998, the following system performance criteria for positioning device systems are met:
(i) A window cleaner's positioning system can withstand without failure, a drop test consisting of a 6-foot (1.83 m) drop of a 250-pound (113.34 kg) weight. The system limits the initial arresting force to a maximum of 2,000 pounds (8.89 Kn), with a maximum duration of 2 milliseconds. The system limits any subsequent arresting forces imposed on the falling employee to a maximum of 1,000 pounds (4.45 Kn);
(ii) All other positioning device systems can withstand without failure a drop test consisting of a 4-foot (1.22 m) drop of a 250-pound (113.34 kg) weight.
(3) ((The employer)) You must ensure that a positioning device system is used and cared for according to the following requirements:
(a) Positioning device systems are inspected before each use for mildew, wear, damage, and other deterioration. Defective components are removed from service.
(b) A positioning device system or component subjected to impact loading is immediately removed from service and not used again for employee protection, unless inspected and determined by a qualified person to be undamaged and suitable for reuse.
(4) Training. Before using a positioning device system, ((the employer)) you must ensure that employees are trained in the application limits, proper hook-up, anchoring and tie-off techniques, methods of use, inspection, and storage of positioning device systems.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-10001 Ship's boilers.
Before work is performed in the fire, steam, or water spaces of a boiler where employees may be subject to injury from the direct escape of a high temperature medium, such as steam, or water, oil, or other medium at a high temperature entering from an interconnecting system, ((the employer shall insure)) you must ensure that the following steps are taken:
(1) The isolation and shutoff valves connecting the dead boiler with the live system or systems ((shall)) must be secured, blanked, and locked or tagged, in accordance with WAC 296-304-06016, indicating that employees are working in the boiler. This tag ((shall)) must not be removed nor the valves unblanked until it is determined that this may be done without creating a hazard to the employees working in the boiler, or until the work in the boiler is completed. Where valves are welded instead of bolted at least two isolation and shutoff valves connecting the dead boiler with the live system or systems ((shall)) must be secured, locked and tagged.
(2) Drain connections to atmosphere on all of the dead interconnecting systems ((shall)) must be opened for visual observation of drainage.
(3) A warning sign calling attention to the fact that employees are working in the boilers ((shall)) must be hung in a conspicuous location in the engine room. This sign ((shall)) must not be removed until it is determined that the work is completed and all employees are out of the boilers.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-10003 Ship's piping systems.
Before work is performed on a valve, fitting, or section of piping in a piping system where employees may be subject to injury from the direct escape of steam, or water, oil, or other medium at a high temperature, ((the employer shall insure)) you must ensure that the following steps are taken:
(1) The isolation and shutoff valves connecting the dead system with the live system or systems shall be secured, blanked, and locked or tagged, in accordance with WAC 296-304-06016, indicating that employees are working on the systems. This tag ((shall)) must not be removed nor the valves unblanked until it is determined that this may be done without creating a hazard to the employees working on the system, or until the work on the system is completed. Where valves are welded instead of bolted at least two isolation and shutoff valves connecting the dead system with the live system or systems ((shall)) must be secured, locked, and tagged.
(2) Drain connections to the atmosphere on all of the dead interconnecting systems ((shall)) must be opened for visual observation of drainage.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-10005 Ship's propulsion machinery.
(1) Before work is performed on the main engine, reduction gear, or connecting accessories, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the following steps are taken:
(a) The jacking gear ((shall)) must be engaged to prevent the main engine from turning over. A sign ((shall)) must be posted at the throttle indicating that the jacking gear is engaged. This sign ((shall)) must not be removed until the jacking gear can be safely disengaged.
(b) If the jacking gear is steam driven, the stop valves to the jacking gear ((shall)) must be secured, locked, and tagged in accordance with WAC 296-304-06016, indicating that employees are working on the main engine.
(c) If the jacking gear is electrically driven, the circuit controlling the jacking gear ((shall)) must be deenergized by tripping the circuit breaker, opening the switch or removing the fuse, whichever is appropriate. The breaker, switch, or fuse location ((shall)) must be tagged indicating that employees are working on the main engine.
(2) Before the jacking engine is operated, the following precautions ((shall)) must be taken:
(a) A check ((shall)) must be made to ensure that all employees, equipment, and tools are clear of the engine, reduction gear, and its connecting accessories.
(b) A check ((shall)) must be made to ensure that all employees, equipment and tools are free of the propeller.
(3) Before work is started on or in the immediate vicinity of the propeller, a warning sign calling attention to the fact that employees are working in that area ((shall)) must be hung in a conspicuous location in the engine room. This sign ((shall)) must not be removed until it is determined that the work is completed and all employees are free of the propeller.
(4) Before the main engine is turned over (e.g., when warming up before departure or testing after an overhaul) a check ((shall)) must be made to ensure that all employees, equipment, and tools are free of the propeller.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-04-099, filed 2/4/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-304-10007 Ship's deck machinery.
(((1))) Before work is performed on the anchor windlass or any of its attached accessories, ((the employer shall)) you must ensure that the following steps are taken:
(((a))) (1) The devil claws (also known as chain toppers) ((shall)) must be made fast to the anchor chains.
(((b))) (2) The riding pawls ((shall)) must be in the engaged position.
(((c))) (3) In the absence of devil claws and riding pawls, the anchor chains ((shall)) must be secured to a suitable fixed structure of the vessel.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-11001 Portable air receivers and other unfired pressure vessels.
(1) Portable, unfired pressure vessels, built after the effective date of this regulation, ((shall)) must be marked and reported indicating that they have been designed and constructed to meet the standards of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section VIII, Rules for Construction of Unfired Pressure Vessels, 1963. They ((shall)) must be subjected to a hydrostatic pressure test of one and one-half times the working pressure of the vessels.
(2) Portable, unfired pressure vessels, not built to the code requirements of (1) of this section, and built prior to the effective date of this regulation, ((shall)) must be examined quarterly by a competent person, and approved by the state boiler inspecting division. They ((shall)) must be subjected yearly to a hydrostatic pressure test of one and one-half times the working pressure of the vessels.
(3) The relief valves on the portable, unfired pressure vessels in (1) and (2) of this section ((shall)) must be set to the safe working pressure of the vessels, or set to the lowest safe working pressure of the systems, whichever is lower.
(4) A record of such examinations and tests made in compliance with the requirements of (1) and (2) of this section ((shall)) must be maintained.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-11003 Drums and containers.
(1) Shipping drums and containers ((shall)) must not be pressurized to remove their contents.
(2) A temporarily assembled pressurized piping system conveying hazardous liquids or gases ((shall)) must be provided with a relief valve and by-pass to prevent rupture of the system and the escape of such hazardous liquids or gases.
(3) Pressure vessels, drums and containers containing toxic or flammable liquids or gases ((shall)) must not be stored or used where they are subject to open flame, hot metal, or other sources of artificial heat.
(4) Unless pressure vessels, drums and containers of 30 gallon capacity or over containing flammable or toxic liquids or gases are placed in an out-of-the-way area where they will not be subject to physical injury from an outside source, barriers or guards ((shall)) must be erected to protect them from such physical injury.
(5) Containers of 55 gallons or more capacity containing flammable or toxic liquid ((shall)) must be surrounded by dikes or pans which enclose a volume equal to at least 35 percent of the total volume of the containers.
(6) Fire extinguishers adequate in number and suitable for the hazard ((shall)) must be provided. These extinguishers ((shall)) must be located in the immediate area where pressure vessels, drums and containers containing flammable liquids or gases are stored or in use. Such extinguishers ((shall)) must be ready for use at all times.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-12-060, filed 6/5/12, effective 8/1/12)
WAC 296-304-120 Electrical machinery—Electrical circuits and distribution boards.
(1) Before an employee is permitted to work on an electrical circuit, except when the circuit must remain energized for testing and adjusting, the circuit ((shall)) must be deenergized and checked at the point at which the work is to be done to ((insure that)) ensure it is actually deenergized. When testing or adjusting an energized circuit a rubber mat, duck board, or other suitable insulation ((shall)) must be used underfoot where an insulated deck does not exist.
(2) Deenergizing the circuit ((shall)) must be accomplished by opening the circuit breaker, opening the switch, or removing the fuse, whichever method is appropriate. The circuit breaker, switch, or fuse location ((shall)) must be locked out or tagged, in accordance with WAC 296-304-06016, to indicate that an employee is working on the circuit. Such tags ((shall)) must not be removed nor the circuit energized until it is definitely determined that the work on the circuit has been completed.
(3) When work is performed immediately adjacent to an open-front energized board or in back of an energized board, the board ((shall)) must be covered or some other equally safe means ((shall)) must be used to prevent contact with any of the energized parts.
Note: | WAC 296-304-120 is applicable only to shipbuilding and ship repairing. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-13001 Purpose and scope.
(1) The regulations in this part implement WAC 296-304-07001 through 296-304-07013. They provide procedures and standards governing accreditation of persons by the department of labor and industries, for the purpose of certificating shore-based material handling devices, and the manner in which such certification ((shall)) must be performed.
(2) Accreditation is not required, and the regulations of this part are not applicable, under the following circumstances:
(a) Persons not required to be accredited for gear certification purposes, may, nevertheless, apply for and receive accreditation by the department of labor and industries.
(b) The appropriate portions of this section ((shall)) must apply to persons accredited except insofar as exemptions may be granted.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-13003 Definitions of terms.
(1) (("))Vessel((" means)). Every description of watercraft or other artificial contrivance used or capable of being used, as a means of transportation on water, including special-purpose floating structures not primarily designed for or used as a means of transportation on water.
(2) Except as otherwise noted, "cargo gear," as used in WAC 296-304-140 through 296-304-17023, includes that gear forming a part of a vessel's equipment which is used for the handling of cargo other than bulk liquids, but does not include gear which is used only for handling or holding hoses, handling ships' stores, handling the gangway, or boom conveyor belt systems for the self-unloading of bulk cargo vessels.
(3) With reference to equipment covered by this section.
(a) (("))Derrick((" means—)):
(i) When applied to vessels' cargo handling gear, a mechanical device for lifting, including a boom which is suspended at its head by a topping lift from a mast, king post, or similar structure, controlled in the horizontal plane by vangs, and used either singly or in pairs with married falls;
(ii) When applied to shore-based material handling devices, a mechanical device intended for lifting, with or without a boom supported at its head by a topping lift from a mast, fixed A frame, or similar structure. The mast or equivalent member may or may not be supported by guys or braces. The boom, where fitted, may or may not be controlled in the horizontal plane by guys (vangs). The term includes shear legs.
(b) (("))Crane((" means)). A mechanical device intended for lifting or lowering a load and moving it horizontally, in which the hoisting mechanism is an integral part of the machine. A crane may be a fixed or mobile machine.
(c) (("))Bulk cargo spout((" means)). A spout, which may or may not be telescopic and may or may not have removable sections, but is suspended over the vessel from some overhead structure by wire rope or other means. Such a spout is often used with a "thrower" or "trimming machine." A grain loading spout is an example of those covered by this definition.
(d) (("))Bulk cargo sucker((" means)). A pneumatic conveyor which utilizes a spout-like device, which may be adjustable vertically and/or laterally, and which is suspended over a vessel from some overhead structure by wire rope or other means. An example of an installation of this nature is the "grain sucker" used to discharge grain from barges.
(4) (("))Director((" means)). The director of the department of labor and industries, or his authorized representative.
(5) (("))Bureau((" means)). The Bureau of Labor Standards, U.S. Department of Labor.
(6) (("))Person((" includes)). Any individual, partnership, corporation, agency, association, or organization.
(7) (("))Competent person((" means)):
(a) An individual qualified to perform gear certification functions with respect to vessels' cargo handling gear, as specifically set forth in WAC 296-304-17023.
(b) An individual qualified under the provisions of WAC 296-304-180 through 296-304-18003 and 296-304-190 through 296-304-19001 to perform gear certification functions with respect to shore-based material handling devices.
(8) (("))Ton((" means)). A ton of 2,240 pounds when applied to vessels' cargo handling gear, and a ton of 2,000 pounds when applied to shore-based material handling devices or to shore-type cranes permanently mounted aboard barges or other vessels employed in domestic trade and designed on the basis of the 2,000-pound ton. Capacity ratings may be stated in pounds.
(9) (("))Nondestructive((")) examination ((means)). Examination of structure or parts by electronic, ultrasonic, or other nondestructive examination suitable for the purpose.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-14001 Application for accreditation.
(1) Application. Any person seeking accreditation ((shall)) must file an original and duplicate copy of an application for accreditation with the director of the department of labor and industries, on a form provided by the department of labor and industries, for this purpose. Each application ((shall)) must be signed and certified by the applicant and, if the applicant is an agency or organization, by a responsible officer of such agency or organization.
(2) Contents of application. The application form ((shall)) must include the following information:
(a) A statement detailing the applicable types of work performed by the applicant in the past, noting the amount and extent of such work performed within the previous three years, listing representative vessels involved, and including representative job orders if available, or equivalent evidence;
(b) Descriptive details concerning any testing instruments and heat treatment furnaces which are to be used in conducting required tests or heat treatments. Test reports indicating that instruments meet the accuracy standards set forth in this section ((shall)) must be included;
(c) A list setting forth the ports in which applicant currently conducts his business as well as those in which he proposes to conduct gear certification activities;
(d) A list of the applicant's responsible qualified personnel, both supervisory and managerial and including any surveyors, with resumes of their individual experience in the testing, examination, inspection and heat treatment of cargo gear. Such list ((shall)) must include any branch office personnel or surveyors appointed to act in the applicant's behalf in any of the ports of the United States: Provided, however, That where the submission of individual resumes would be unduly burdensome because of the large number of persons engaged in the applicant's behalf, the applicant, after stating this fact, need only submit a list of its personnel together with a detailed statement of the qualifications upon which the appointment of surveyors is bases;
(e) Names of at least three business references who will furnish information regarding work performed by the applicant;
(f) Any additional information the applicant deems to be pertinent.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-14003 Action upon application.
(1) Upon receipt of an application for accreditation, the director ((shall)) must approve or deny the application. The director may conduct an investigation, which may include a hearing, prior to approving or denying an application. To the extent he deems appropriate, the director may provide an opportunity to other interested persons to present data and views on the application prior to approval or denial.
(2) Any application which fails to present the information required by the prescribed form may be returned to the applicant with a notation of deficiencies and without prejudice to submission of a new or revised application.
(3) If the application is approved, notice of approval ((shall)) must be mailed to the applicant. If the application is denied, notice of such denial ((shall)) must be mailed to the applicant and such denial ((shall)) must be without prejudice to any subsequent application except where such action is deemed to be in the public interest. In the event an application is denied with prejudice, the provisions of WAC 296-304-14013 ((shall)) must be applicable.
(4) A copy of the notice of accreditation ((shall)) must be kept on file by applicant at the applicant's place of business.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-14005 Duration and renewal of accreditation.
The period of accreditation ((shall)) must not exceed three years. Applications for renewal of accreditation ((shall)) must be made on the same form as described in WAC 296-304-14001. No accreditation ((shall)) must expire until action on an application for renewal ((shall)) must have been finally determined: Provided, That such application has been properly executed in accordance with WAC 296-304-14001 and filed with and received by the director not less than 15 nor more than 60 days prior to the expiration date. A final determination means either the approval or initial denial of the application for renewal. The procedure specified in WAC 296-304-14003 ((shall)) must be applicable to all applications for renewal.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-14007 Criteria governing accreditation to certificate vessels' cargo gear.
(1) A person applying for accreditation to issue registers and pertinent certificates, to maintain registers and appropriate records, and to conduct initial, annual and quadrennial surveys, ((shall)) must not be accredited unless ((he is)) they are engaged in one or more of the following activities:
(a) Classification of vessels;
(b) Certification of vessels' cargo gear;
(c) Shipbuilding or ship repairing, or both insofar as related to work on vessels' cargo handling gear;
(d) Unit and loose gear testing of vessels' cargo handling gear.
(2) Applicants for accreditation under WAC 296-304-14007(1) for operations in coastal or Great Lakes ports who come within WAC 296-304-14007 (1)(b) or (d) ((shall)) must not be accredited unless they conduct at least 1,500 hours of cargo gear certification work per year.
(3) A person applying for accreditation to carry out tests of loose gear or wire rope, or both, or to carry out heat treatments, and to issue the related certificates, ((shall)) must be engaged in one or both of the following activities:
(a) Testing of loose gear or wire rope, or both;
(b) Heat treatment of chains and loose cargo gear.
(4) A person applying for accreditation ((shall)) must be staffed by individuals technically qualified to conduct the inspections and examinations and to conduct or supervise tests and heat treatments prescribed in this part. Any representatives, agents or surveyors acting on behalf of a person applying for accreditation in ports in which such operations are conducted ((shall)) must be similarly qualified.
(((a))) Accreditation to conduct such nondestructive examination as may be a part of any certification activity may be granted to applicants found competent and equipped to carry out this activity.
(5) Except as noted in WAC 296-304-13001 (2)(a), and unless exemptions are granted under WAC 296-304-15001(8), a person applying for accreditation as specified in WAC 296-304-14007(1) ((shall)) must be prepared to carry out all of the requirements of WAC 296-304-150 through 296-304-15005, 296-304-160 through 296-304-16025, and 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023 except that loose gear and wire rope tests and heat treatments may be carried out by the manufacturer of the gear concerned or by another person accredited specifically for this purpose.
(6) A person applying for accreditation ((shall)) must have a satisfactory record of performance.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-14011 Suspension or revocation of accreditation.
The director may suspend or revoke an accreditation of any person for cause. Except in cases of willfulness or cases in which the public interest requires otherwise, before any accreditation is suspended or revoked facts or conduct which may warrant such action ((shall)) must be called to the attention of the person involved in writing and that person ((shall)) must be afforded an opportunity to achieve or demonstrate appropriate compliance.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-14013 Reconsideration and review.
(1) Any person aggrieved by the action of the director or his authorized representative in denying, granting, suspending or revoking an accreditation under this section may within 15 days after such action, (a) file a written request for reconsideration thereof by the director or the authorized representative of the director who made the decision in the first instance, or (b) file a written request for review of the decision by the director or an authorized representative of the director, who has taken no part in the action which is the subject for review.
(2) A request for reconsideration ((shall)) must be granted where the applicant shows that there is additional evidence which may materially affect the decision and that there were reasonable grounds for failure to adduce such evidence in the original proceedings.
(3) Any person aggrieved by the action of the director or authorized representative of the director in denying a request for reconsideration may, within 15 days after the denial of such request, file with the director or his authorized representative a written request for review.
(4) Any person aggrieved by the reconsidered determination of the director or authorized representative of the director, may within 15 days after such determination, file with the director a written request for review.
(5) A request for review ((shall)) must be granted where reasonable grounds for the review are set forth in the request.
(6) If a request for reconsideration or review is granted, all interested persons ((shall)) must be afforded an opportunity to present their views.
(7) No cargo gear certification function ((shall)) must be performed by any person seeking reconsideration or review under this section pending the final decision with respect to such reconsideration or review.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-15001 General duties—Exemptions.
(1) Except as noted in WAC 296-304-13001 and 296-304-15001(8), the requirements set forth in WAC 296-304-160 through 296-304-16025 and 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023 ((shall)) must be strictly adhered to in all testing, examinations, inspections and heat treatments.
(2) Supervision of all testing, examinations, inspections, and heat treatments ((shall)) must be carried out only by such persons as are listed in the application for accreditation or subsequent supplements thereto, submitted pursuant to this section.
(3) The certificates issued by an accredited person ((shall)) must be signed and all register entries made only by an authorized agent of such accredited person. No certification ((shall)) must be issued until any deficiencies considered by the accredited person to constitute a currently unsatisfactory condition have been corrected. Replacement parts ((shall)) must be of equal or better quality as original equipment and suitable for the purpose. In the event deficiencies remain uncorrected and no certification may therefore be issued, the accredited person ((shall)) must inform the nearest district office of the department of labor and industries of the circumstances.
(4) Dynamometers or other recording test equipment owned by an accredited person ((shall)) must have been tested for accuracy within the six months next preceding application for accreditation or renewal of same. Such test ((shall)) must be performed with calibrating equipment which has been checked in turn so that indications are traceable to the U.S. Bureau of Standards. A copy of test reports ((shall)) must accompany the application. Where test equipment is not the property of the accredited person, that person ((shall)) must not issue any certificate based upon the use of such equipment unless its owner has made available a certificate of accuracy based on the requirements of this section, obtained within 1 year prior to such use, and stating the errors of the equipment. Reasonable standards of accuracy ((shall)) must be met and proof loads adjusted as necessary.
(5) An accredited person ((shall)) must, upon request, provide the nearest local office of the department of labor and industries with advance information as to scheduled testing or of such other functions as are performed and facilitate the department of labor and industries observation of any such activities as it may desire to witness: Provided, however, That tests need not be delayed, except when specifically requested by the department of labor and industries under unusual circumstances.
(6) All cargo gear registers or certificates issued by an accredited person ((shall)) must be made on forms prescribed or approved by the department of labor and industries.
(7) Unless otherwise instructed by the director in specific instances, any person accredited under WAC 296-304-14007(1) ((shall)) must accept certificates relating to loose gear or wire rope tests or to heat treatments which are issued by the manufacturer of the gear concerned, by another person accredited specifically by the director for this purpose, or by any other person whose certificates are acceptable to the department of labor and industries. Such certificates ((shall)) must either be attached as a part of the vessel's certification or ((shall)) must be used as the basis for the issuance of the accredited person's own loose gear, wire rope, or heat treatment certificates. In the latter case, the original certificates ((shall)) must be kept on file by the accredited person as part of the permanent record of the vessel concerned.
(8) In case of practical difficulties or unnecessary hardships, the director in his discretion may grant exemptions from any provision of WAC 296-304-150 through 296-304-15005, 296-304-160 through 296-304-16025 and 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-15003 Recordkeeping and related procedures concerning records in custody of accredited persons.
(1) An accredited person ((shall)) must maintain records of all work performed under WAC 296-304-160 through 296-304-16025 and 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023.
(2) An accredited person ((shall)) must maintain a continuous record of the status of the certification of each vessel issued a register by such person.
(3) The records required in (1) and (2) of this section ((shall)) must be available for examination by the director.
(4) When annual or quadrennial tests, inspections, examinations, or heat treatments are performed by an accredited person, other than the person who originally issued the vessel's register, such accredited person ((shall)) must furnish copies of any certificates issued and information as to register entries to the person originally issuing the register.
(5) An accredited person ((shall)) must inform the nearest local office of the department of labor and industries whenever a vessel is initially certificated under these regulations and a register in the prescribed form has been issued.
(6) A copy of each certificate relating to unit tests or thorough examinations, except those issued by the manufacturer and those issued by accredited persons outside of the United States, ((shall)) must be sent to the nearest local office of the department of labor and industries within 10 days after issuance. Such records ((shall)) must form a part of the department of labor and industries file on the accredited person.
(7) An accredited person ((shall)) must promptly notify the nearest local office of the department of labor and industries with respect to any changes in technical personnel, in fee schedules in geographical areas in which operations are conducted, or other pertinent substantial changes in its organization or operations.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-15005 Recordkeeping and related procedures concerning records in custody of the vessel.
(1) A fully completed and up-to-date register ((shall)) must be kept in the form prescribed or approved by the department of labor and industries, giving the particulars required with respect to:
(a) The inspections and thorough examinations required by WAC 296-304-16005 (1) and (2).
(b) The thorough examinations required by WAC 296-304-16005(3).
(c) The thorough examinations required by WAC 296-304-16009.
(d) The heat treatment required by WAC 296-304-16007 (1) and (2), and 296-304-16013.
(2) Certificates in the form prescribed or approved by the department of labor and industries ((shall)) must be kept up-to-date, be attached to the register, and ((shall)) must contain the particulars required with respect to:
(a) The testing and examinations required by WAC 296-304-16003, 296-304-16005(1) and 296-304-16013.
(b) The heat treatment required by WAC 296-304-16007 and 296-304-16013.
(3) The certificates and entries in the register ((shall)) must be signed by a person qualified under WAC 296-304-17023.
(4) Adequate means ((shall)) must be provided to enable persons examining the register, or any certificate attached thereto, to identify items of cargo gear referred to therein. Small items of gear, such as shackles, ((shall)) must bear a mark to indicate that they have been initially tested.
(5) Records ((shall)) must be kept aboard vessels identifying wire rope or articles of loose gear obtained from time to time and required to be certificated under the regulations of this section.
(6) An accredited person ((shall)) must instruct the vessel's officers or the vessel's operator if the vessel is unmanned, that the vessel's register and certificates ((shall)) must be preserved for at least 4 years after the date of the latest entry except in the case of nonrecurring test certificates concerning gear which is kept in use for a longer period, in which event the pertinent certificates ((shall)) must be retained so long as that gear is continued in use.
(7) In cases where derricks, spouts, suckers, or cranes are mounted permanently aboard barges which remain in domestic inland waters service, the certification documentation ((shall)) must comply with the provisions of WAC 296-304-20025.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-16001 General.
(1) Except as noted in WAC 296-304-13001 and as provided in exemptions under WAC 296-304-15001(9), certification performed by accredited persons ((shall)) must conform to the requirements contained in this section.
(2) Safe working loads assigned to assembled units of gear ((shall)) must be based on applicable design criteria acceptable to the accredited person. Where no design data on which to base a rating is obtainable, the safe working load ratings assigned ((shall)) must be based on the owner's information and warranty that those so assigned are correct. Unit test certificates ((shall)) must state the basis for any such safe working load assignment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16003 Initial tests of cargo gear and tests after alterations, renewals or repairs.
(1) Before being taken into use, hoisting machines, fixed gear aboard vessels accessory thereto, and loose gear and wire rope used in connection therewith, ((shall)) must be tested and examined and the safe working load thereof certified in the manner set forth in WAC 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023.
(2) Replacement or additional loose gear and wire rope obtained from time to time ((shall)) must also be tested and examined in the manner set forth in WAC 296-304-16003(1). However, the replacement of a component part of an article of loose gear, such as a sheave, pin, or bushing does not require a new test certificate so long as the new component at least equals in all particulars the part replaced.
(3) In the case of untested gear which has been in use, an initial test in conformance with WAC 296-304-16003(1) ((shall)) must be carried out: Provided, however, That existing standing rigging and wire rope will not be required to be tested but ((shall)) must be thoroughly examined to ascertain its fitness for continued use in conformance with the requirements of WAC 296-304-16023 and 296-304-16025.
(4) In the case of important alterations or renewals of the machinery and gear and also after repairs due to failure of or damage to other than loose components, a test as required in WAC 296-304-16003(1) ((shall)) must be carried out.
(5) If the operation in which cargo gear is engaged never utilizes more than a fraction of the safe working load rating, the owner may, at his option, have said gear certificated for, and limited in operation to, a lesser maximum safe working load: Provided, however, That the gear concerned is physically capable of operation at the original load rating and the load reduction is not for the purpose of avoiding correction of any deficiency.
(6) In no case ((shall)) must safe working loads be increased beyond the original design limitations unless such increase is based on engineering calculations by or acceptable to the accredited certification agency, and all necessary structural changes are carried out.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16005 Periodic tests, examinations and inspections.
After being taken into use, every hoisting machine, all fixed gear aboard vessels accessory thereto and loose gear used in connection therewith, ((shall)) must be tested, thoroughly examined or inspected as follows:
(1) Derricks with their winches and accessory gear, including the attachments, as a unit; and cranes and other hoisting machines with their accessory gear, as a unit, ((shall)) must be tested and thoroughly examined every four years in the manner set forth in WAC 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023.
(2) Derricks, their permanent attachments and any other fixed gear the dismantling of which is especially difficult ((shall)) must be visually inspected every twelve months. In order to facilitate such inspection all derricks ((shall)) must be lowered.
(3) All hoisting machines (e.g., cranes, winches), blocks, shackles, and all other accessory gear not included in WAC 296-304-16005(2), ((shall)) must be thoroughly examined every twelve months by means of a visual examination, supplemented as necessary by other means, such as a hammer test or with electronic, ultrasonic, or other nondestructive methods, carried out as carefully as conditions permit in order to arrive at a reliable conclusion as to the safety of the parts examined. Particular attention ((shall)) must be paid to the suitability for continued use of all swivels and the pins and bushing of blocks. If necessary, parts of the machines or gear ((shall)) must be dismantled. If blocks are disassembled, all shell bolt nuts ((shall)) must be securely locked upon reassembly.
(4) Where a derrick or crane is mounted on a barge hull and ballast tanks within the hull are used to facilitate use of the derrick or crane, or uncontrolled free surface may be a factor, each annual inspection or examination, as required, ((shall)) must include such inspection as is necessary for the purpose of determining the integrity of any internals contributing to stability under conditions of use. The owner ((shall)) must provide the accredited person with necessary information on any ballasting arrangements required.
(5) Annual inspection or examination, as required, ((shall)) must include, among other things, examination of the following:
(a) Derrick heel attachment points. Heel pins may, if possible, be examined by nondestructive examination.
(b) Shrouds and stays necessary in the use of the gear, together with attachment points.
(c) Deck fittings for the securing of vangs, topping lifts, and/or preventers.
(d) Means of attachment to the hull of "A" frame or other fixed derrick or crane structure and of mobile types of equipment permanently placed aboard the barge or vessel.
(e) Clamshell buckets or other similar equipment, such as magnets, etc., used in conjunction with a derrick or crane mounted aboard a vessel, with particular attention to closing line wires and sheaves. The accredited person may supplement such examination by requesting any operational tests he may deem appropriate.
(f) Winch and other operating drums for excessive wear or defect.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16007 Heat treatment.
(1) All chains (other than bridle chains attached to derricks or masts), rings, hooks, shackles, and swivels made of wrought iron, which are used in hoisting or lowering, ((shall)) must be annealed in accordance with WAC 296-304-17021 at the following intervals:
(a) Half inch and smaller chains, rings, hooks, shackles, and swivels in general use, at least once every six months; and
(b) All other chains, rings, hooks, shackles, and swivels in general use, at least once every twelve months.
(c) In the case of gear used solely on lifting machinery worked by hand, twelve months ((shall)) must be substituted for six months in WAC 296-304-16007 (1)(a) and two years for twelve months in WAC 296-304-16007 (1)(b).
(d) When used in this paragraph, the term "in general use" means used on fifty-two or more days in a year. In any case, however, the period between annealings ((shall)) must not exceed two years.
(2) Chains, rings, hooks, shackles, and swivels made of material other than wrought iron or steel ((shall)) must be heat treated when necessary in accordance with WAC 296-304-17021(2).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16009 Exemptions from heat treatment.
Gear made of steel, or gear which contains (as in ball bearing swivels), or is permanently attached to (as with blocks), equipment made of materials which cannot be subjected to heat treatment, ((shall)) must be exempt from the requirements of WAC 296-304-16007. Such gear, however, ((shall)) must be thoroughly examined in the manner described in WAC 296-304-16005(3).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16011 Grace periods.
Grace periods allowed in connection with the requirements of this section are as follows:
(1) Annual or six-month requirements - By the end of the voyage during which they become due;
(2) Quadrennial requirements - Within six months after the date when due;
(3) Grace periods ((shall)) must not be deemed to extend subsequent due dates.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16013 Gear requiring welding.
Chains or other gear which have been lengthened, altered or repaired by welding, ((shall)) must be properly heat treated where necessary, and, before again being put into use, ((shall)) must be tested and reexamined in the manner set forth in WAC 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16015 Damaged components.
(1) Pursuant to WAC 296-304-18003, any derrick or associated permanent fitting which is deformed in service between surveys ((shall)) must be subjected to proof test to determine its suitability for continued service. If a proof test indicates that the derrick or associated permanent fitting may be continued in service without repair, a note of the existing deformity shall be made on the test certificate. When, in the opinion of the accredited person, it is unsafe to conduct a proof test with an existing deformity, the derrick or associated permanent fitting ((shall)) must be replaced or repaired and then subjected to proof test in accordance with WAC 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023.
(2) Any loose gear components which are injured or deformed by a proof load ((shall)) must be replaced before a certificate is issued.
(3) Any derrick, other fixed installation, or associated permanent fitting, which is injured or deformed by a proof load ((shall)) must be replaced or repaired and another proof load test ((shall)) must be conducted without damage before a certificate is issued.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16017 Marking and posting of safe working loads.
(1) The safe working load of the assembled gear and the minimum angle to the horizontal at which this load may be applied ((shall)) must be plainly marked at the heels of all booms along with the date of the test. Where gear is certificated for use in union purchase, the union purchase safe working load ((shall)) must also be plainly marked. Any limitations ((shall)) must be noted in the vessel's papers.
(2) The safe working load ((shall)) must be marked on all blocks used in hoisting or lowering.
(3) When the capacity of the boom of a crane or derrick has been or will be rated in accordance with the variance of its radius, the maximum safe working loads for the various working angles of the boom and the maximum and minimum radius at which the boom may be safely used, ((shall)) must be conspicuously posted near the controls and visible to the crane operator. Ratings may be stated in pounds. When they are stated in tons of 2,000 pounds, this fact ((shall)) must be indicated.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16019 Requirements governing braking devices and power sources.
All types of winches and cranes ((shall)) must be provided with means to stop and hold the proof load in any position, and the efficiency of such means ((shall)) must be demonstrated. Electric winches, electrohydraulic winches fitted with electromagnetic or hydraulic brakes at the winch, or electric cranes, ((shall)) must be equipped so that a failure of the electric power ((shall)) must stop the motion and set the brakes without any action on the part of the operator. Current for operation of electric winches and cranes during the tests ((shall)) must be taken from the vessel's circuits. Shore current may be used if it passes through the vessel's main switchboard.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16021 Means of derrick attachment.
Appropriate measure ((shall)) must be taken to prevent the foot of a derrick from being ((accidently)) accidentally lifted from its socket or support during the test.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16023 Limitations on use of wire rope.
(1) An eye splice made in any wire rope ((shall)) must have at least three tucks with a whole strand of rope and two tucks with one-half of the wires cut out of each strand. However, this requirement ((shall)) must not operate to preclude the use of another form of splice or connection which can be shown to be as efficient.
(2) Except for eye splices in the ends of wires, each wire rope used in hoisting or lowering, in guying derricks, or as a topping lift, preventer or pendant, ((shall)) must consist of one continuous piece without knot or splice.
(3) Eyes in the ends of wire rope cargo falls ((shall)) must not be formed by knots and, in single part falls, ((shall)) must not be formed by wire rope clips.
(4) The ends of falls ((shall)) must be secured to the winch drums by clamps, U-bolts, shackles or some other equally strong method. Fiber rope fastenings ((shall)) must not be used.
(5) Wire rope ((shall)) must not be used for the vessel's cargo gear if in any length of eight diameters, the total number of visible broken wires exceeds 10 percent of the total number of wires, or if the rope shows other signs of excessive wear, corrosion, or defect. Particular attention ((shall)) must be given to the condition of those sections of wire rope adjacent to any terminal connections, those sections exposed to abnormal wear, and those sections not normally exposed for examination.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-16025 Limitations on use of chains.
Chains forming a part of vessel's cargo gear ((shall)) must not be used when, due to stretch, the increase of length of a measured section exceeds five percent, when a link is damaged, or when other external defects are evident. Chains ((shall)) must not be shortened by bolting, wiring, or knotting.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17001 Visual inspection before tests.
Before any test under this WAC 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023 is carried out, a visual inspection of the gear involved ((shall)) must be conducted and any visibly defective gear ((shall)) must be replaced or repaired. The provisions of WAC 296-304-16005(4) ((shall)) must be adhered to.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17003 Unit proof test—Winches, derricks and gear accessory thereto.
(1) Winches, with the whole of the gear accessory thereto (including derricks, goosenecks, eye plates, eye bolts, or other attachments), ((shall)) must be tested with a proof load which ((shall)) must exceed the safe working load as follows:
Safe working load |
Proof load |
Up to 20 tons. . . . |
25 percent in excess. |
20-50 tons. . . . |
5 tons in excess. |
Over 50 tons. . . . |
10 percent in excess. |
(2) The proof load ((shall)) must be lifted with the vessel's normal tackle with the derrick at an angle not more than 15 degrees to the horizontal, or, at the designed minimum angle when this is greater, or, when this is impracticable, at the lowest practicable angle. The angle at which the test was made ((shall)) must be stated in the certificate of test. After the proof load has been lifted, it ((shall)) must be swung as far as possible in both directions. In applying the proof load, the design factors of the gear concerned will determine whether the load is applied with a single part fall or with a purchase and the certificate of test shall state the means used. Where winches are fitted with mechanical brakes for manual operation they ((shall)) must be demonstrated to be in satisfactory operating condition.
(3) In the case of heavy lift derrick barges, proof loads ((shall)) must be applied, except as limited by design and stability considerations, at the maximum and minimum radius for which designed, as well as at any intermediate radius which the surveyor may deem necessary, and ((shall)) must be swung as far as possible in both directions. Data with respect to each proof load applied ((shall)) must be entered in the test certificate.
(4) No items of cargo gear furnished by outside sources ((shall)) must be used as a part of the vessel's gear for the purpose of accomplishing the proof test.
(5) All tests prescribed by this section should in general be carried out by dead load, except that in the case of quadrennial tests, replacements, or renewals, spring or hydraulic balances may be used where dead loads are not reasonably available. However, no exception ((shall)) must be allowed in the case of gear on new vessels.
(6) The test ((shall)) must not be regarded as satisfactory unless the indicator remains constant under the proof load for a period of at least 5 minutes.
(7) The safe working load, determined pursuant to the requirements of this section, ((shall)) must be applicable only to a swinging derrick. When using two fixed derricks in "union purchase" rigs, the safe working load should generally be reduced. It is recommended that owners obtain union purchase safe working load certification based upon design study and analysis by, or acceptable to, a qualified technical office of an accredited gear certification agency, with the recognition that such determinations are valid only for the conditions contemplated in the analysis.
(((a))) Where both guys and preventers are fitted, union purchase certification ((shall)) must state whether the guy or the preventer is the working strength member, when the guy is for slewing only, and when the guy and preventor should share working loads as far as practicable.
(8) When necessary in the proof testing of heavy derricks, the appropriate shrouds and stays ((shall)) must be rigged.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17005 Unit proof tests—Cranes and gear accessory thereto.
(1) Except as noted in WAC 296-304-17005(5), cranes and other hoisting machines, together with gear accessory thereto, ((shall)) must be tested with a proof load which ((shall)) must exceed the safe working load as follows:
Safe working load |
Proof load |
Up to 20 tons. . . . |
25 percent in excess. |
20-50 tons. . . . |
5 tons in excess. |
Over 50 tons. . . . |
10 percent in excess. |
(2) The proof load ((shall)) must be lifted and swung as far as possible in both directions. If the jib or boom of the crane has a variable radius, it ((shall)) must be tested with proof loads, as specified in WAC 296-304-17005(1), at the maximum and minimum radius. In the case of hydraulic cranes, when owing to the limitation of pressure it is impossible to lift a load 25 percent in excess of the safe working load, it will be sufficient to lift the greatest possible load.
(3) Initial proof tests of new cranes ((shall)) must be made only with a dead load as specified in WAC 296-304-17005(2).
(4) Initial tests of cranes which have been in service, quadrennial tests, or tests associated with replacements or renewals, may be made with spring or hydraulic balances where dead loads are not reasonably available, under the following conditions:
(a) Tests ((shall)) must be conducted at maximum, minimum, and intermediate radius points, as well as such points in the arc of rotation as meet with the approval of the accredited person.
(b) An additional test ((shall)) must be conducted with partial load and ((shall)) must include all functions and movements contemplated in the use of the crane.
(5) In cases where shore-type cranes are mounted permanently aboard barges, the requirements of WAC 296-304-170 through 296-304-17023 with respect to unit proof tests and examinations ((shall)) must not apply and the applicable requirements of WAC 296-304-200 through 296-304-20025 ((shall)) must be adhered to with respect to unit proof tests and examinations.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17007 Limitations on safe working loads and proof loads.
The proof loads specified in WAC 296-304-17003 and 296-304-17005 ((shall)) must be adjusted as necessary to meet any pertinent limitations based on stability and/or on structural competence at particular radii. Safe working loads ((shall)) must be reduced accordingly.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17009 Examinations subsequent to unit tests.
(1) After satisfactory completion of the unit proof load tests required by WAC 296-304-17003 and 296-304-17005, the cargo gear and all component parts thereof ((shall)) must be given a thorough visual examination, supplemented as necessary by other means, such as a hammer test or with electronic, ultrasonic, or other nondestructive methods, to determine if any of the parts were damaged, deformed, or otherwise rendered unsafe for further use.
(2) When the test of gear referred to in WAC 296-304-17008(1) is being conducted for the first time on a vessel, accessory gear ((shall)) must be dismantled or disassembled for examination after the test. The sheaves and pins of the blocks included in this test need not be removed unless there is evidence of deformation or failure.
(3) For subsequent tests such parts of the gear ((shall)) must be dismantled or disassembled after the test as necessary to determine their suitability for continued service.
(4) When blocks are disassembled all shell bolt nuts ((shall)) must be securely locked upon reassembly.
(5) In carrying out the requirements of this section, replacement ((shall)) must be required of:
(a) Any swivel found to have excessive tolerance as a result of wear on any bearing surface.
(b) Pins of blocks found to be shouldered, notched, or grooved from wear, in which case, in addition to replacing the pin, sheave bushings ((shall)) must be examined for suitability for continued use.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-17011 Proof tests—Loose gear.
(1) Chains, rings, shackles and other loose gear (whether accessory to a machine or not) ((shall)) must be tested with a proof load equal to that shown against the article in the following table:
Article of gear |
Proof load |
|
Chain, ring, hook, shackle or swivel. . . . |
100 percent in excess of the safe working load. |
|
Blocks: Single sheave block. . . . |
300 percent in excess of the safe working load.1 |
|
Multiple sheave block with safe working load up to and including 20 tons. . . . |
100 percent in excess of the safe working load. |
|
Multiple sheave block with safe working load over 20 tons up to and including 40 tons. . . . |
20 tons in excess of the safe working load. |
|
Multiple sheave block with safe working load over 40 tons. . . . |
50 percent in excess of the safe working load. |
|
Pitched chains used with hand-operated blocks and rings, hooks, shackles or swivels permanently attached thereto. . . . |
50 percent in excess of the safe working load. |
|
Hand-operated blocks used with pitched chains and rings, hooks, shackles or swivels permanently attached thereto . . . . |
50 percent in excess of the safe working load. |
1 | The proof load applied to the block is equivalent to twice the maximum resultant load on the eye or pin of the block when lifting the nominal safe working load defined in WAC 296-304-17011 (1)(a) below. The proof load is, therefore, equal to four times the safe working load as defined in WAC 296-304-17011 (1)(a) below or twice the safe working load as defined in WAC 296-304-17011 (1)(b) below. |
(a) The nominal safe working load of a single-sheave block should be the maximum load which can be safely lifted by the block when the load is attached to a rope which passes around the sheave of the block.
(b) In the case of a single-sheave block where the load is attached directly to the block instead of to a rope passing around the sheave, it is permissible to lift a load equal to twice the nominal safe working load of the block as defined in WAC 296-304-17011 (1)(a) above.
(c) In the case of a lead block so situated that an acute angle cannot be formed by the two parts of the rope passing over it (i.e., the angle is always 90° or more), the block need not have a greater nominal safe working load than one-half the maximum resultant load which can be placed upon it.
(2) In cases where persons accredited to carry out loose gear tests may be retained to conduct tests of special stevedoring gear as described in WAC 296-56-60098 (8)(e), which does not form part of a vessel's equipment, such tests ((shall)) must adhere to the requirements set forth in WAC 296-56-60098 (8)(e).
(3) After being tested as required by WAC 296-304-17011(1), and before being taken into use, all chains, rings, hooks, shackles, blocks or other loose gear, except as noted in WAC 296-304-17013, ((shall)) must be thoroughly examined, the sheaves and pins of the blocks being removed for this purpose, to determine whether any part has been injured or permanently deformed by the test. Shell bolt nuts ((shall)) must be securely locked upon reassembly. Defective loose gear components ((shall)) must be replaced before the certificate is issued.
(4) Any certificate relating to shackles, swivels or strength members of single-sheave blocks which have been restored to original dimensions by welding ((shall)) must state this fact.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17013 Specially designed blocks and components.
(1) Blocks and connecting components of an unusual nature which are specially designed and constructed as an integral part of a particular lifting unit and are either permanently affixed or of such design that two or more components must be tested together need not be considered as loose gear for purposes of WAC 296-304-17011.
(2) In lieu of the loose gear proof test required by WAC 296-304-17011(1), design data ((shall)) must be submitted to an accredited certification agency indicating design and material specifications and analysis whereby the designed strength of such gear may be determined.
(3) Subsequent to the test of the lifting unit as a whole, a thorough visual examination ((shall)) must be made of disassembled parts and an electronic, ultrasonic, or other equally efficient nondestructive examination ((shall)) must be made of those parts not dismantled to ensure the safe condition of such parts.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17015 Proof tests—Wire rope.
Wire rope, except as provided in WAC 296-304-16003(2), ((shall)) must be tested by sample, a piece being tested to destruction, and the safe working load of running ropes, unless otherwise acceptable to the department of labor and industries on the basis of design, ((shall)) must not exceed one-fifth of the breaking load of the sample tested. In the case of running ropes used in gear with a safe working load exceeding 10 tons, the safe working load ((shall)) must not exceed one-fourth of the breaking load of the sample tested.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17017 Proof tests after repairs or alterations.
When proof loads are applied after repairs or alterations, all parts of the assembled gear ((shall)) must be examined as required in WAC 296-304-17009, 296-304-17011(3), or 296-304-17013(c), whichever is applicable.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17021 Heat treatment.
(1) The annealing of wrought iron gear required by this section ((shall)) must be accomplished at a temperature between 1100° and 1200°F. and the exposure ((shall)) must be of between thirty and sixty minutes duration. After being annealed, the gear ((shall)) must be allowed to cool slowly and ((shall)) must then be carefully inspected. All annealing ((shall)) must be carried out in a closed furnace.
(2) When heat treatment of loose gear made of other than wrought iron or steel is recommended by the manufacturer, it ((shall)) must be carried out in accordance with the specifications of the manufacturer.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-17023 Competent persons.
All gear certification functions ((shall)) must be performed by competent persons as set forth in the following table:
Functions |
Competent person |
Any testing, examination, inspection, or heat treatment required in United States ports. |
Responsible individual, surveyor or other authorized agent of a person accredited by the department of labor and industries under the regulations contained in this part. |
Any testing, examination, inspection, or heat treatment required to be performed while the vessel is in other than United States ports. |
Responsible individual, surveyor or other authorized agent of persons recognized by the Commandant of the United States Coast Guard or by a foreign nation whose certification is accepted by the department of labor and industries as being in substantial accordance with WAC 296-304-15005(1). |
Testing, examination and inspection of loose gear or wire rope; heat treatment of loose gear. |
Employees or authorized agents of persons accredited specifically by the department of labor and industries for this purpose under the regulations contained in this section, or the manufacturer of the gear concerned unless disapproved by the director. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-18001 Eligibility for accreditation to certificate shore-based material handling devices covered by chapter 296-56 WAC of the safety and health regulations for longshoring.
(1) A person applying for accreditation to carry out certification activities and to issue and maintain the requisite records must be:
(a) A manufacturer of cranes or derricks or of specialized equipment of the type for which accreditation application is made, or a person or organization representing such a manufacturer in a technical capacity; or
(b) Technically experienced and qualified to carry out examinations and/or testing, as applicable, of vessels or shore-based equipment or gear of the type for which accreditation application is made.
(2) The owner of shore-based equipment affected may designate a member of his organization to carry out certification functions respecting the owner's equipment, on the following conditions:
(a) The designee is technically experienced and qualified in the inspection and maintenance or design of the type of equipment involved, aside from employment as an operator only.
(b) The designee has applied to an accredited, nationally operating certification agency and has been granted appointment or equivalent recognition by that agency as a surveyor for the purpose intended.
(c) Certification activities carried out by the designee are cleared through the offices, and are subject to the approval, of the accredited certificating agency. When equipment is found satisfactory for use upon any survey, said equipment may be used pending receipt of notification of such approval or any disapproval.
(d) In cases where equipment is certificated by a person designated by the equipment owner, the cognizant accredited certification agency retains the right to inspect such equipment as desired and convenient, in order to ascertain the adequacy of the certification activity performed.
(3) Accreditation to conduct such nondestructive examination as may be a part of any certification activity may be granted to applicants found competent and equipped to carry out this activity.
(4) Unless exemptions are granted at the discretion of the director in cases of practical difficulties or unnecessary hardship, applicants for accreditation as specified in this section ((shall)) must be prepared to carry out all necessary functions, except that any requisite wire rope tests, nondestructive examinations, and heat treatments may be carried out by the manufacturer of the gear concerned or by another person accredited specifically for these purposes.
(5) A person applying for accreditation ((shall)) must have a satisfactory record of relevant experience and performance.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-18003 Provisions respecting application for accreditation, action upon the application, and related matters.
The provisions of WAC 296-304-14001, 296-304-14003, 296-304-14005, 296-304-14009, 296-304-14011 and 296-304-14013 ((shall)) must govern accreditation to certificate shore-based material handling devices, to the extent applicable.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-190 Duties of persons accredited to certificate shore-based material handling devices—General duties, exemptions.
The requirements of WAC 296-304-200 through 296-304-20025 ((shall)) must be strictly observed: Provided, however, that in cases of practical difficulties or unnecessary hardship, the director in his discretion may grant exemptions or variations from any provision in that section.
(1) Except as otherwise noted in this section, all functions required by WAC 296-304-200 through 296-304-20025 ((shall)) must be carried out by or under the supervision of a person accredited for the purpose or by his authorized representative.
(2) All required unit proof load tests ((shall)) must be carried out by the use of weights as a dead load. Only where this is not possible may dynamometers or other recording test equipment be used. Any such recording test equipment owned by an accredited person ((shall)) must have been tested for accuracy within the 6 months next preceding application for accreditation or renewal thereof. Such test ((shall)) must be performed with calibrating equipment which has been checked in turn so that indications are traceable to the U.S. Bureau of Standards. A copy of test reports ((shall)) must accompany the accreditation application. Where test equipment is not the property of the accredited person, that person ((shall)) must not issue any certificate based upon the use of such equipment unless its owner has made available a certificate of accuracy based on the requirements of this section, obtained within the year prior to such use, and stating the errors of the equipment. In any event reasonable standards of accuracy ((shall)) must be met and proof loads adjusted as necessary.
(3) The qualifications of any person appointed or recognized by any accredited person for the purpose of carrying out certification functions ((shall)) must meet with the approval of the director.
(4) WAC 296-304-15001 (5) and (7) and 296-304-15003 ((shall)) must govern, to the extent applicable, persons accredited under WAC 296-304-180 through 296-304-18003.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-304-20001 General provisions.
(1) Certification of shore-based material handling devices ((shall)) must conform to the requirements contained in this section, except in cases for which exemptions or variations have been granted by the director as provided in WAC 296-304-18001(4) and 296-304-190.
(2) Any replacements or repairs deemed necessary by the accredited person ((shall)) must be carried out before application of a proof test.
(3) "Ton" in this section means a ton of 2,000 pounds.
(4) When applied to shore-based material handling devices, ratings may be stated in pounds rather than tons. When stated in tons of 2,000 pounds, this fact ((shall)) must be indicated.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20003 Unit proof test and examination of cranes.
(1) Unit proof tests of cranes ((shall)) must be carried out at the following times:
(a) In the cases of new cranes, before initial use and every 4 years thereafter.
(b) In the cases of uncertificated cranes which have been in use, at the time of initial certification and every 4 years thereafter.
(c) After important alterations and renewals, and after repairs due to failure of, or damage to, major components.
(2) Unit proof load tests of cranes ((shall)) must be carried out where applicable with the boom in the least stable direction relative to the mounting, based on the manufacturer's specifications.
(3) Unit proof load tests ((shall)) must be based on the manufacturer's load ratings for the conditions of use and ((shall)) must, except in the case of bridge type cranes utilizing a trolley, consist of application of a proof load of 10 percent in excess of the load ratings at maximum and minimum radius, and at such intermediate radii as the certificating authority may deem necessary in the circumstances.1 Trolley equipped cranes ((shall)) must be subject to a proof load of 25 percent in excess of the manufacturer's load rating. In cases of foreign manufacture, the manufacturer's specifications ((shall)) must be subject to approval by the certificating authority as being equivalent to U.S. practice.
1 | The manufacturer's load ratings are usually based upon percentage of tipping loads under some conditions and upon limitations of structural competence at others, as well as on other criteria such as type of crane mounting, whether or not outriggers are used, etc. Some cranes utilizing a trolley may have only one load rating assigned and applicable at any outreach. It is important that the manufacturer's ratings be used. |
The weight of all auxiliary handling devices such as, but not limited to, magnets, hooks, slings, and clamshell buckets ((shall)) must be considered part of the load.
(4) An examination ((shall)) must be carried out in conjunction with each unit proof load test. The accredited person, or his authorized representative, ((shall)) must make a determination as to correction of deficiencies found. The examination ((shall)) must cover the following points as applicable:
(a) All functional operating mechanisms ((shall)) must be examined for improper function, maladjustment, and excessive component wear, with particular attention to sheaves, pins, and drums. The examination ((shall)) must include operation with partial load, in which all functions and movements, including, where applicable, maximum possible rotation in both directions, are performed.
(b) All safety devices ((shall)) must be examined for malfunction.
(c) Lines, tanks, valves, drains, pumps, and other parts of air or hydraulic systems ((shall)) must be examined for deterioration or leakage.
(d) Loose gear components, such as hooks, including wire rope and wire rope terminals and connections, ((shall)) must be checked with particular attention to sections of wire rope exposed to abnormal wear and to sections not normally exposed for examination. The provisions of WAC 296-304-16023 shall apply in wire rope examinations. Cracked or deformed hooks ((shall)) must be discarded and not reused on any equipment subject to the provisions of chapter 296-56 WAC longshoring and WAC 296-304-130 through 296-304-13503.
(e) Rope reeving ((shall)) must comply with manufacturer's recommendations.
(f) Deformed, cracked, or excessively corroded members in crane structure and boom ((shall)) must be repaired or replaced as necessary.
(g) Loose bolts, rivets, or other connections ((shall)) must be corrected.
(h) Worn, cracked, or distorted parts affecting safe operation ((shall)) must be corrected.
(i) Brake and clutch system parts, linings, pawls, and ratchets ((shall)) must be examined for excessive wear and free operation.
(j) Load, boom angle, or other indicators ((shall)) must be checked over their full range for any significant inaccuracy. A boom angle or radius indicator ((shall)) must be fitted.
(k) It ((shall)) must be ascertained that there is a durable rating chart visible to the operator, covering the complete range of the manufacturer's capacity ratings at all operating radii, for all permissible boom lengths and jib lengths, with alternate ratings for optional equipment affecting such ratings. Necessary precautions or warnings ((shall)) must be included. Operating controls ((shall)) must be marked or an explanation of controls ((shall)) must be posted at the operator's position to indicate function.
(l) Where used, clamshell buckets or other similar equipment such as magnets, etc., ((shall)) must be carefully examined in all respects, with particular attention to closing line wires and sheaves. The accredited person may supplement such examination by requesting any operational tests as may be appropriate.
(m) Careful examination of the junction areas of removable boom sections, particularly for proper seating, cracks, deformities, or other defects in securing bolts and in the vicinity of such bolts.
(n) It ((shall)) must be ascertained that no counterweights in excess of the manufacturer's specifications are fitted.
(o) Such other examination or supplemental functional tests ((shall)) must be made as may be deemed necessary by the accredited person under the circumstances.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20005 Annual examination of cranes.
(((1))) In any year in which no quadrennial unit proof test is required, an examination ((shall)) must be carried out by an accredited person or his authorized representative. Such examination ((shall)) must be made not later than the anniversary date of the quadrennial certification and ((shall)) must conform with the requirements of WAC 296-304-20003(4).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20007 Unit proof test and examination of derricks.
(1) Unit proof tests of derricks ((shall)) must be carried out at the same times as are specified in WAC 296-304-20003(1) for cranes.
(2) Unit proof load tests and safe working load ratings ((shall)) must be based on the design load ratings at the ranges of boom angles or operating radii. Unit proof loads ((shall)) must exceed the safe working load as follows:
Safe working load |
Proof load |
Up to 20 tons . . . . |
25 percent in excess. |
20-50 tons . . . . |
5 tons in excess. |
Over 50 tons . . . . |
10 percent in excess. |
Proof loads ((shall)) must be applied at the designed maximum and minimum boom angles or radii, or, if this is impracticable, as close to these as practicable. The angles or radii of test ((shall)) must be stated in the certificate of test. Proof loads ((shall)) must be swung as far as possible in both directions. The weight of all auxiliary handling devices ((shall)) must be considered a part of the load.
(3) After satisfactory completion of a unit proof load test the derrick and all component parts thereof ((shall)) must be carefully examined in accordance with the requirements of WAC 296-304-20003(4), as far as applicable.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20009 Annual examination of derricks.
(((1))) In any year in which no quadrennial unit proof test is required, an examination ((shall)) must be carried out by an accredited person or his authorized representative. Such annual examination ((shall)) must be made not later than the anniversary date of the quadrennial certification and ((shall)) must conform in all applicable respects with WAC 296-304-20003(4).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20011 Determination of crane or derrick safe working loads and limitations in absence of manufacturer's data.
(((1))) In the event neither manufacturer's data nor design data on safe working loads (including any applicable limitations) are obtainable, the safe working load ratings assigned ((shall)) must be based on the owner's information and warranty that those so assigned are correct. Unit test certificates ((shall)) must state the basis for any such safe working load assignment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20013 Safe working load reduction.
(((1))) If the operation in which equipment is engaged never utilizes more than a fraction of the safe working load rating, the owner of such equipment may, at his option, have the crane or derrick certificated for and operated at a lesser maximum safe working load in keeping with the use and based on radius and other pertinent factors: Provided, however, That the equipment concerned is physically capable of operation at the original load rating and the load reduction is not for the purpose of avoiding correction of any deficiency.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20015 Safe working load increase.
(((1))) In no case ((shall)) must safe working loads be increased beyond the manufacturer's ratings or original design limitations unless such increase meets with the manufacturer's approval. Where the manufacturer's services are not available, or where the equipment is of foreign manufacture, engineering design analysis by, or acceptable to, the accredited certification agency is required. All necessary structural changes ((shall)) must be carried out.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20017 Nondestructive examination.
(((1))) Wherever it is considered necessary by the accredited person or his authorized representative and wherever it is practical and advisable to avoid disassembly of equipment, removal of pins, etc., examination of structure or parts by electronic ultrasonic or other nondestructive methods may be carried out, provided that the procedure followed is acceptable to the director and the person carrying out such examination is accredited or acceptable to the director for the purpose.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20019 Wire rope.
(1) Wire rope and replacement wire rope ((shall)) must be of the same size, same or better grade, and same construction as originally furnished by the equipment manufacturer or contemplated in the design, unless otherwise recommended by the equipment or the wire rope manufacturer due to actual working condition requirements. In the absence of specific requirements as noted, wire rope ((shall)) must be of a size and construction suitable for the purpose, and a safety factor of 4 ((shall)) must be adhered to, and verified by wire rope test certificate.
(2) Wire rope in use on equipment previously constructed and prior to initial certification of said equipment ((shall)) must not be required to be tested but ((shall)) must be subject to thorough examination at the time of initial certification of the equipment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20021 Heat treatment.
(((1))) Wherever heat treatment of any loose gear is recommended by the manufacturer, it ((shall)) must be carried out in accordance with the specifications of the manufacturer.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20023 Examination of bulk cargo loading or discharging spouts or suckers.
(((1))) Those portions of bulk cargo loading or discharging spouts or suckers which extend over vessels, together with any portable extensions, rigging components, outriggers, and attachment points, supporting them or any of their components vertically, ((shall)) must be examined annually. The examination ((shall)) must be carried out with particular attention to the condition of wire rope and accessories. The equipment ((shall)) must not be considered satisfactory unless, in the opinion of the accredited person or his authorized representative, it is deemed fit to serve its intended function.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending Order 74-25, filed 5/7/74)
WAC 296-304-20025 Documentation.
(1) Documents issued respecting a certification function by an accredited person ((shall)) must be on forms approved for such use by the director and ((shall)) must so state.
(2) Such documents ((shall)) must be issued by the accredited person to the owners of affected equipment, attesting to satisfactory compliance with applicable requirements. The forms used ((shall)) must contain the following information:
(a) Unit proof tests where required—
(i) Identification of crane or derrick including manufacturer, model number, serial number, and ownership.
(ii) Basis for assignment of safe working load ratings, with the ratings assigned (i.e., whether based on manufacturer's ratings, whether for any specific service, etc.).
(iii) Proof test details noting radii and proof loads, how applied, and, where applicable, direction relative to mounting.
(iv) A statement that the test and associated examination were conducted and all applicable requirements of this section are met.
(v) Any necessary remarks or supplementary data, including limitations imposed and the reason therefor.
(vi) Name of accredited person and identification of authorized representative actually conducting test and/or examination.
(vii) Authorized signature of accredited person, date and place of test and/or examination.
(b) Annual examination of cranes or derricks—
(i) Information specified in WAC 296-304-20025 (2)(a)(i), (v), (vi) and (vii).
(ii) A statement that the required examination has been carried out and that, in the opinion of the accredited person or his authorized representative, the equipment has been found in compliance in all applicable respects with the requirements of this section.
(c) Annual examination of bulk cargo loadings or discharging spouts or suckers—
(i) Specific identification of equipment.
(ii) A statement that examination has been completed and that, in the opinion of the accredited person or his authorized representative, the equipment meets the criteria of WAC 296-304-20023(1).
(iii) Information specified in WAC 296-304-20025 (2)(a)(i), (v), (vi) and (vii).
(3) Certificates relating to wire rope, whether tested by or under the supervision of the accredited person or by its manufacturer and whether or not issued on the basis of the manufacturer's certificates, ((shall)) must follow the general format of a wire rope test form approved by the director.
(4) Accredited persons ((shall)) must advise owners of affected equipment of the necessity for maintaining required documentation or acceptable copies thereof available for inspection at or near the worksite of the equipment involved.
(a) Where initial and periodic tests as well as annual examinations are required, documentation available for inspection ((shall)) must include the latest unit test certificate and any subsequent annual examination certificates, together with wire rope test certificates relating to any replacements since the last unit test or annual examination.
(b) Where only annual examination is required, documentation available for inspection ((shall)) must include the latest annual examination certificate and wire rope test certificates relating to any wire replaced since the last annual examination.
(c) In the event that heat treatment of any loose gear is recommended by its manufacturer, the latest heat treatment certificate, attesting to compliance with the manufacturer's specifications, ((shall)) must be part of the available documentation.
(5) No certification ((shall)) must be issued until any deficiencies considered by the accredited person to constitute a currently unsatisfactory condition have been corrected. Replacement parts shall be of equal or better quality as original equipment and suitable for the purpose. In the event deficiencies remain uncorrected and no certification therefore is issued, the accredited person ((shall)) must inform of the circumstances the nearest district office of the department of labor and industries.
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-803-099 Definitions.
Affected employee. An employee who is required to operate, use, or be in the area where a machine or equipment could be locked or tagged out for service or maintenance.
Authorized employee. An employee who locks or tags out a machine or equipment to do service or maintenance.
Can be locked out. An energy-isolating device that can be locked in the "off" or "safe" position.
Employer. Based on chapter 49.17 RCW, an employer is any person, firm, corporation, partnership, business trust, legal representative, or other business entity which engages in any business, industry, profession, or activity in this state and employs one or more employees or who contracts with one or more persons, the essence of which is the personal labor of such person or persons and includes the state, counties, cities, and all municipal corporations, public corporations, political subdivisions of the state, and charitable organizations: Provided, That any persons, partnership, or business entity not having employees, and who is covered by the Industrial Insurance Act must be considered both an employer and an employee.
Energized. Connected to an energy source or containing residual or stored energy.
Energy-isolating device. A mechanical device that physically prevents transmitting or releasing energy. This includes, but is not limited to:
(a) Manually operated electrical circuit breakers.
(b) Disconnect switches.
(c) Manually operated switches that disconnect the conductors of a circuit from all ungrounded supply conductors if no pole of the switch can be operated independently.
(d) Line valves.
(e) Blocks.
(f) Similar devices used to block or isolate energy.
Push buttons, selector switches and other control circuit type devices are not energy isolating devices.
Energy source. Any source of electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical, thermal or other energy, including gravity.
Hot tap. A procedure which involves welding on pressurized pipelines, vessels, or tanks to install connections or accessories. It is commonly used to replace or add sections of pipeline used in air, gas, water, steam, and petrochemical distribution systems without interrupting service.
Lockout. Placing a lockout device on an energy-isolating device using an established procedure to make sure the machine or equipment cannot be operated until the lockout device is removed.
Lockout device. A device that uses a positive means, such as a key or combination lock, to hold an energy-isolating device in the "safe" or "off" position. This includes blank flanges and bolted slip blinds.
Normal production operations. Using a machine or equipment for its intended production function.
Primary authorized employee. An authorized employee who has overall responsibility for meeting the requirements of the lockout/tagout procedures.
Service and maintenance. Activities such as constructing, installing, setting-up, adjusting, inspecting, modifying, maintaining, and servicing machines or equipment. It also includes lubricating, cleaning, unjamming, and making tool changes.
Setting-up. Work done to prepare a machine or equipment for normal production operations.
Tagout. Placing a tagout device on an energy-isolating device using an established procedure to indicate that the energy-isolating device and the machine or equipment being controlled may not be operated until the tagout device is removed.
Tagout device. A prominent warning device, such as a tag and a means of attachment. It can be securely fastened to an energy-isolating device to indicate that the energy-isolating device and the machine or equipment being controlled may not be operated until the tagout device is removed.
You. See definition of employer.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-100 Scope.
This chapter applies to the service and maintenance of machines and equipment, including piping systems, if employees could be injured by the:
((–)) (1) Unexpected energization or start up of the machine or equipment; or
((OR
–)) (2) Release of stored energy.
Energy sources include mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical, thermal, or other energy, including gravity.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Machines and equipment include those that produce high intensity electromagnetic fields. |
((•)) 2. When other Title 296 WAC standards require the use of lockout or tagout, they have to be used and supplemented by the procedural and training requirements of this chapter. |
Exemption: | This chapter does not apply to: |
((•)) 1. Construction activities covered by chapter 296-155 WAC, Safety standards for construction work. | |
((•)) 2. Agriculture activities covered by chapter 296-307 WAC, Safety standards for agriculture. | |
((•)) 3. Maritime activities covered by chapter 296-56 WAC, Safety standards—Longshore, stevedore and related waterfront operations and chapter 296-304 WAC, Safety standards for ship repairing, shipbuilding and shipbreaking. | |
((•)) 4. Oil and gas well drilling and servicing. | |
((•)) 5. Installations for generating, transmitting, and distributing electrical power (including related communication and metering equipment) that are controlled exclusively by electric utilities. | |
((•)) 6. Hot tap operations on pressurized pipelines used to transmit and distribute substances such as gas, steam, water, or petroleum products if the employer can demonstrate that all of the following apply: | |
((–)) a. Continuity of service is essential. | |
((–)) b. Shutdown of the system is impractical. | |
((–)) c. Proven effective employee protection is provided by following documented procedures and using special equipment. | |
((•)) 7. Service and maintenance of fire alarm and extinguishing systems and their components if: | |
((–)) a. Other employees depend on these systems for fire safety; and | |
((AND | |
–)) b. Employees working on fire extinguishing systems are protected from the unexpected release of hazardous energy by appropriate alternative measures. | |
((•)) 8. Work on electric equipment receiving power only through a cord and plug if: | |
((–)) a. Unplugging the equipment eliminates the possibility of unexpected energization, unexpected start up, or the release of stored energy; and | |
((AND | |
–)) b. The plug is kept under the exclusive control of the employee doing the service or maintenance. | |
((•)) 9. Exposure to electrical hazards from electrical work on, near, or with conductors or equipment that is covered by chapter 296-24 WAC, General safety and health standards, Part L, Electrical. | |
((•)) 10. Service and maintenance during normal production operations, if an employee is not required to: | |
((–)) a. Remove or bypass a guard or other safety device; or | |
((OR | |
–)) b. Place any body part into the point of operation or any other hazardous area created by machine operation. | |
((•)) 11. Minor tool changes, adjustments, and other minor service during normal production operations if: | |
((–)) a. They are routine, repetitive, and integral to the use of the equipment for production; and | |
((AND | |
–)) b. The work is done using measures which provide effective protection from hazards. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-200 Summary.
Your responsibility:
To establish an energy control program.
((You must:
WAC 296-803-20005 Establish a written energy control program.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Establish a written energy control program |
WAC 296-803-20005 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-20005 Establish a written energy control program.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must establish a written energy control program to protect employees that service or maintain a machine or equipment from injury caused by the:
((–)) (a) Unexpected energization or start up of the machine or equipment; or
((OR
–)) (b) Release of stored energy.
((•)) (2) You must make sure the program contains all of the following:
((–)) (a) Energy control procedures as described in WAC 296-803-500.
((–)) (b) Employee training as described in WAC 296-803-600.
((–)) (c) Periodic reviews as described in WAC 296-803-700.
((•)) (3) You must develop and document in writing energy control procedures to protect employees doing service or maintenance of a machine or equipment from potentially hazardous energy.
Exemption: | You do not have to have written energy control procedures for a particular machine or equipment if all of the following apply: |
((•)) 1. The machine or equipment has a single energy source that is easily identified and can be isolated. | |
((•)) 2. The machine or equipment is completely deenergized and deactivated by isolating and locking out the energy source. | |
((• There's)) 3. There is no stored or residual energy that could be a hazard to employees, and the machine or equipment cannot reaccumulate such energy after ((it's)) it has been shut down. | |
((•)) 4. The energy source can be locked out with a single lockout device. | |
((•)) 5. The machine or equipment is isolated from the energy source and locked out during service or maintenance. | |
((•)) 6. The authorized employee doing the service or maintenance has exclusive control of the lockout device. | |
((•)) 7. The service or maintenance does not create a hazard for other employees. | |
((•)) 8. The machine or equipment has never been unexpectedly energized or activated during service or maintenance. |
((You must:
•)) (4) You must make sure energy control procedures clearly and specifically outline:
((–)) (a) The scope, purpose, authorization, rules, and techniques to control hazardous energy; and
((AND
–)) (b) How ((you'll)) you will make sure employees follow the procedures.
((•)) (5) You must make sure energy control procedures specifically identify at least the following:
((–)) (a) When the procedure must be used.
((–)) (b) What the specific procedural steps are for:
((■)) (i) Shutting down, isolating, blocking, and securing the machine or equipment.
((■)) (ii) Placing, removing, and transferring lockout or tagout devices and who is responsible for them.
((–)) (c) How to test the machine or equipment to verify the effectiveness of lockout devices, tagout devices, and other energy control measures.
Note: | Similar machines and equipment may be covered by a single written procedure if all of the following apply: |
((•)) 1. They use the same type and magnitude of energy. | |
((•)) 2. They have the same or similar types of controls. | |
((•)) 3. The specific machines and equipment covered by the procedure are identified by at least type and location. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-300 Summary.
Your responsibility:
To make sure new or modified machines and equipment can accept lockout devices.
((You must:
WAC 296-803-30005 Make sure new or modified machines and equipment can accept lockout devices.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Make sure new or modified machines and equipment can accept lockout devices |
WAC 296-803-30005 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-16-108, filed 8/4/09, effective 11/1/09)
WAC 296-803-30005 Make sure new or modified machines and equipment can accept lockout devices.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure energy-isolating devices designed to accept a lockout device are provided on machines and equipment that:
((–)) (1) Are newly installed((.)); or
((OR
–)) (2) Have undergone major replacement, repair, renovation, or modification after July 2, 1990.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-400 Summary.
Your responsibility:
To provide appropriate lockout and tagout devices and means to control energy.
((You must:
WAC 296-803-40005 Provide appropriate means to control energy.
WAC 296-803-40010 Make sure lockout and tagout devices meet these requirements.
WAC 296-803-40015 Make sure lockout devices meet these additional requirements.
WAC 296-803-40020 Make sure tagout devices meet these additional requirements.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Provide appropriate means to control energy |
WAC 296-803-40005 |
Make sure lockout and tagout devices meet these requirements |
WAC 296-803-40010 |
Make sure lockout devices meet these additional requirements |
WAC 296-803-40015 |
Make sure tagout devices meet these additional requirements |
WAC 296-803-40020 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-16-108, filed 8/4/09, effective 11/1/09)
WAC 296-803-40005 Provide appropriate means to control energy.
((You must:
•)) You must provide the means necessary to isolate, secure, or block machines and equipment from energy sources.
Note: | Examples of means to control energy include: |
((•)) 1. Locks. | |
((•)) 2. Tags. | |
((•)) 3. Chains. | |
((•)) 4. Wedges. | |
((•)) 5. Key blocks. | |
((•)) 6. Adapter pins. | |
((•)) 7. Self-locking fasteners. | |
((•)) 8. Blank flanges. | |
((•)) 9. Cribbing. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-40010 Make sure lockout and tagout devices meet these requirements.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure lockout and tagout devices meet all of the following:
((–)) (1) Create no additional hazards.
((–)) (2) Have a distinctive design or appearance.
((–)) (3) Are the only devices used for controlling energy.
((–)) (4) Are not used for any other purpose.
((–)) (5) Are durable enough to withstand the environment ((they're)) they are used in for the maximum time ((they're)) they are expected to be used.
((–)) (6) Are standardized within the facility by color, shape, or size.
((–)) (7) Identify the person applying the device.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-40015 Make sure lockout devices meet these additional requirements.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure lockout devices are strong enough so that removing them by other than the normal unlocking method requires:
((–)) (1) Excessive force; or
((OR
–)) (2) Unusual techniques such as the use of bolt cutters or other metal-cutting tools.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-40020 Make sure tagout devices meet these additional requirements.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure all tags:
((–)) (a) Use the same print and format within a facility.
((–)) (b) Are constructed and printed so they will not deteriorate and the message on the tag remains legible when:
((■)) (i) Exposed to weather.
((■)) (ii) Used in wet or damp locations.
((■)) (iii) Used in corrosive environments such as areas where acid or alkali chemicals are handled or stored.
((–)) (c) Have a warning about not energizing the machine or equipment.
Note: | The warning on the tag should include wording such as: |
((•)) 1. Do not start. | |
((•)) 2. Do not open. | |
((•)) 3. Do not close. | |
((•)) 4. Do not energize. | |
((•)) 5. Do not operate. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must make sure tagout devices are strong enough to prevent unintentional or accidental removal.
((•)) (3) You must make sure the means used to attach the tag to the energy-isolating device meets all of the following:
((–)) (a) Is not reusable.
((–)) (b) Is self-locking.
((–)) (c) Can be attached by hand.
((–)) (d) Cannot be released with a force of less than fifty pounds.
((–)) (e) Is similar in design and basic characteristics to a one-piece, all-environment-tolerant, nylon cable tie.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-500 Summary.
Your responsibility:
To make sure energy control procedures are used and include these requirements.
((You must:
ENERGY CONTROL PROCEDURES
WAC 296-803-50005 Use energy control procedures.
APPLYING LOCKOUT OR TAGOUT DEVICES
WAC 296-803-50010 Meet these requirements when applying lockout or tagout devices.
WAC 296-803-50015 Meet these additional requirements when applying lockout devices.
WAC 296-803-50020 Meet these additional requirements when applying tagout devices.
STORED ENERGY
WAC 296-803-50025 Protect employees from the hazards of stored and residual energy.
VERIFYING MACHINE ISOLATION
WAC 296-803-50030 Verify that the machine or equipment is safe before starting work.
REMOVING ENERGY CONTROL DEVICES
WAC 296-803-50035 Meet these requirements when removing lockout or tagout devices and energizing the machine or equipment.
TEMPORARY ENERGIZATION
WAC 296-803-50040 Meet these requirements if it's necessary to temporarily energize a machine, equipment, or component for testing or positioning.
SHIFT OR PERSONNEL CHANGES
WAC 296-803-50045 Protect employees during shift or personnel changes.
GROUP LOCKOUT/TAGOUT
WAC 296-803-50050 Protect employees working in a group.
WAC 296-803-50055 Meet these additional requirements if more than one group is used.
OUTSIDE EMPLOYEES
WAC 296-803-50060 Coordinate with outside employers servicing or maintaining your machines or equipment.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Energy Control Procedures |
|
Use energy control procedures |
WAC 296-803-50005 |
Applying Lockout or Tagout Devices |
|
Meet these requirements when applying lockout or tagout devices |
WAC 296-803-50010 |
Meet these additional requirements when applying lockout devices |
WAC 296-803-50015 |
Meet these additional requirements when applying tagout devices |
WAC 296-803-50020 |
Stored Energy |
|
Protect employees from the hazards of stored and residual energy |
WAC 296-803-50025 |
Verifying Machine Isolation |
|
Verify that the machine or equipment is safe before starting work |
WAC 296-803-50030 |
Removing Energy Control Devices |
|
Meet these requirements when removing lockout or tagout devices and energizing the machine or equipment |
WAC 296-803-50035 |
Temporary Energization |
|
Meet these requirements if it is necessary to temporarily energize a machine, equipment, or component for testing or positioning |
WAC 296-803-50040 |
Shift or Personnel Changes |
|
Protect employees during shift or personnel changes. |
WAC 296-803-50045 |
Group Lockout/Tagout |
|
Protect employees working in a group |
WAC 296-803-50050 |
Meet these additional requirements if more than one group is used |
WAC 296-803-50055 |
Outside Employers |
|
Coordinate with outside employers servicing or maintaining your machines or equipment |
WAC 296-803-50060 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50005 Use energy control procedures.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must use energy control procedures to protect employees servicing or maintaining machines and equipment from potentially hazardous energy.
((•)) (2) You must use a lockout system if an energy-isolating device can be locked out.
Exemption: | A tagout system may be used instead of a lockout system if it meets all of the following: |
((•)) 1. The tagout device is attached where you would have put the lockout device. | |
((•)) 2. The tagout system provides the same level of employee protection as a lockout system. | |
((•)) 3. You can demonstrate that the tagout system: | |
((–)) a. Meets all tagout requirements of this chapter. | |
((–)) b. Includes additional safety measures to provide the same level of safety as a lockout system. |
Note: | Additional safety measures used with the tagout system to provide protection equal to a lockout system could include actions such as: |
((•)) 1. Removing part of the isolating circuit. | |
((•)) 2. Blocking a controlling switch. | |
((•)) 3. Opening an extra disconnecting device. | |
((•)) 4. Removing a valve handle. |
((You must:
•)) (3) You must use a tagout system if an energy-isolating device cannot be locked out.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-16-108, filed 8/4/09, effective 11/1/09)
WAC 296-803-50010 Meet these requirements when applying lockout or tagout devices.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure, before a machine or equipment is turned off, that the authorized employee knows all of the following:
((–)) (a) Type and magnitude of the energy.
((–)) (b) Hazards of the energy to be controlled.
((–)) (c) Method or means to control the energy.
((•)) (2) You must turn off or shut down the machine or equipment using established procedures. An orderly shut down is necessary to avoid any additional or increased hazard to employees as a result of the equipment stoppage.
((•)) (3) You must completely isolate the machine or equipment from its energy sources using the appropriate energy-isolating devices after the machine or equipment has been turned off.
((•)) (4) You must make sure you or the authorized employee notify affected employees that the machine or equipment is being locked or tagged out before the devices are applied.
((•)) (5) You must make sure a lockout or tagout device is applied:
((–)) (a) For each energy-isolating device.
((–)) (b) Only by the authorized employee doing the service or maintenance.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50015 Meet these additional requirements when applying lockout devices.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure lockout devices hold the energy-isolating device in a "safe" or "off" position.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50020 Meet these additional requirements when applying tagout devices.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure a tagout device is put on an energy-isolating device so it clearly shows that moving the energy-isolating device from the "safe" or "off" position is prohibited.
((•)) (2) You must make sure a tagout device, when used with an energy-isolating device that can be locked out, is fastened to the device at the same point a lock would have been attached.
((•)) (3) You must make sure a tagout device that cannot be attached directly to an energy-isolating device is located:
((–)) (a) As close as safely possible to the energy-isolating device; and
((AND
–)) (b) In a position that is immediately obvious to anyone attempting to operate the energy-isolating device.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50025 Protect employees from the hazards of stored and residual energy.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure all potentially hazardous stored and residual energy is relieved, disconnected, restrained, or otherwise rendered safe after the lockout or tagout devices have been put on the energy-isolating devices.
((•)) (2) You must continue to verify the isolation of machines and equipment that could reaccumulate stored energy to a hazardous level until:
((–)) (a) Service or maintenance is completed; or
((OR
–)) (b) The possibility of reaccumulating hazardous energy does not exist.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50030 Verify that the machine or equipment is safe before starting work.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure the authorized employee verifies that the machine or equipment ((that's)) that has been locked out or tagged out has been isolated from all energy sources and deenergized before starting work.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50035 Meet these requirements when removing lockout or tagout devices and energizing the machine or equipment.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure the authorized employee does the following before removing any lockout or tagout device:
((–)) (a) Inspects the work area to make sure nonessential items have been removed;
((–)) (b) Verifies the machine or equipment is in operating condition and ready to energize; and
((AND
–)) (c) Check that employees in the area are in positions that make it safe to energize the machine or ((equpiment)) equipment.
((•)) (2) You must make sure only the authorized employee who applied a lockout or tagout device removes it.
Exemption: | The employer may have the lockout or tagout device removed by someone other than the authorized employee who applied it if all of the following conditions are met: |
((•)) 1. The energy control program has documented, specific procedures and training for this situation. | |
((•)) 2. You can show that the specific procedures used are as safe as having the device removed by the authorized employee who applied it. | |
((•)) 3. The specific procedures include at least the following: | |
((–)) a. Verifying the authorized employee who applied the device is not at the facility. | |
((–)) b. Making all reasonable efforts to contact and inform the authorized employee that the lockout or tagout device is being removed. | |
((–)) c. Making sure the authorized employee is informed, before resuming work at the facility, that the lockout or tagout device has been removed. |
((You must:
• Do the following before energizing or starting the machine or equipment:
–)) (3) You must notify affected employees before energizing or starting the machine or equipment that the lockout or tagout devices have been removed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50040 Meet these requirements if ((it's)) it is necessary to temporarily energize a machine, equipment, or component for testing or positioning.
((You must:
•)) You must follow your normal energy control procedures to:
((–)) (1) Remove the lockout or tagout devices.
((–)) (2) Energize the machine, equipment, or component.
((–)) (3) Reapply the lockout or tagout devices when testing or positioning is completed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50045 Protect employees during shift or personnel changes.
((You must:
•)) You must use specific procedures for shift or personnel changes to:
((–)) (1) Make sure ((there's)) there is continuous lockout or tagout protection during the change; and
((AND
–)) (2) Provide for the orderly transfer of lockout or tagout device protection between employees.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50050 Protect employees working in a group.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure your energy control procedures provide each member of a crew, craft, department, or other group with the same level of protection as that provided by an individual lockout or tagout device.
((•)) (2) You must make sure each authorized employee:
((–)) (a) Puts a personal lockout or tagout device on the group lockout device, lockbox, or comparable mechanism before beginning work; and
((AND
–)) (b) Does not remove it until they have finished work on the machine or equipment.
((•)) (3) You must assign a primary authorized employee who:
((–)) (a) Has overall responsibility for the service or maintenance;
((–)) (b) Attaches their lockout or tagout device to the energy-isolating device when the equipment is deenergized and before any work begins; and
((AND
–)) (c) Is the last person to remove their lockout or tagout device when the job is completed.
((Definition:
The primary authorized employee is the authorized employee who has overall responsibility for meeting the requirements of the lockout/tagout procedures.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50055 Meet these additional requirements if more than one group is used.
((You must:
•)) You must do all of the following if more than one group works on a machine or equipment that has to be locked or tagged out:
((–)) (1) Assign an authorized employee as the group coordinator with overall responsibility to:
((■)) (a) Coordinate the different work groups; and
((AND
■)) (b) Maintain continuous lockout or tagout protection.
((–)) (2) Assign a primary authorized employee in each group who has:
((■)) (a) Responsibility for the group of employees who are protected by a group lockout or tagout device; and
((AND
■)) (b) A way to determine which employees of the group are exposed to the machine or equipment ((that's)) that is locked or tagged out.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-50060 Coordinate with outside employers servicing or maintaining your machines or equipment.
((You must:
•)) You must do the following before allowing another employer's personnel to service or maintain machines or equipment if your energy control procedures require they be locked or tagged out:
((–)) (1) Inform the outside employer of your lockout or tagout procedures.
((–)) (2) Make sure the outside employer informs you of their lockout or tagout procedures.
((–)) (3) Make sure you and the outside employer confirm that all employees understand and will follow the restrictions of the other employer's energy control program.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-600 Summary.
Your responsibility:
To train employees on your energy control program.
((You must:
WAC 296-803-60005 Provide and document employee training on the energy control program.
WAC 296-803-60010 Provide additional training if you use tagout devices.
WAC 296-803-60015 Retrain employees when necessary.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Provide and document employee training on the energy control program |
WAC 296-803-60005 |
Provide additional training if you use tagout devices |
WAC 296-803-60010 |
Retrain employees when necessary |
WAC 296-803-60015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-60005 Provide and document employee training on the energy control program.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must train employees to make sure that they:
((–)) (a) Understand the purpose and function of the energy control program; and
((AND
–)) (b) Have the knowledge and skills necessary to carry out their program responsibilities.
((•)) (2) You must train each authorized employee in:
((–)) (a) The type and magnitude of energy available in the workplace.
((–)) (b) Recognizing hazardous energy sources that apply.
((–)) (c) Methods and means to isolate and control energy.
((•)) (3) You must instruct each affected employee in the purpose and use of the energy control procedures.
((•)) (4) You must instruct all employees who work or may work where energy control procedures might be used about the:
((–)) (a) Procedures being used; and
((AND
–)) (b) Prohibition against attempting to restart or reenergize a machine or equipment ((that's)) that is locked out or tagged out.
((•)) (5) You must document that employee training has been done and kept up to date.
((–)) Include the employee's name and the training date.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-60010 Provide additional training if you use tagout devices.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure employees are trained in the following:
((–)) (1) Tags are warning devices and do not provide the same level of physical restraint as a lock.
((–)) (2) When attached to energy-isolating devices, tags are not to be:
((■)) (a) Removed without the approval of the authorized person responsible for it; or
((OR
■)) (b) Bypassed, ignored, or otherwise defeated.
((–)) (3) Tags need to be legible and understandable to be effective.
((–)) (4) Tags may evoke a false sense of security.
((–)) (5) The meaning of tags needs to be understood as part of the overall energy control program.
((–)) (6) Tags and their means of attachment must be:
((■)) (a) Securely attached to energy-isolating devices so they cannot be inadvertently or accidentally detached; and
((AND
■)) (b) Made of materials that will withstand the environmental conditions they will be exposed to.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-16-108, filed 8/4/09, effective 11/1/09)
WAC 296-803-60015 Retrain employees when necessary.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must retrain authorized and affected employees to introduce new or revised control methods and procedures when ((there's)) there is a change in any of the following:
((–)) (a) Job assignments.
((–)) (b) Machines, equipment, or processes that present a new hazard.
((–)) (c) Energy control procedures.
((•)) (2) You must retrain employees to reestablish proficiency when:
((–)) (a) A periodic review shows the employee deviates from, or has inadequate knowledge of, the energy control procedures; or
((OR
–)) (b) The employer has reason to believe retraining is necessary.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-700 Summary.
Your responsibility:
To do periodic reviews to make sure employees know and use your energy control procedures.
((You must:
WAC 296-803-70005 Perform and document periodic reviews to verify employees know and follow the energy control procedures.
WAC 296-803-70010 Do periodic reviews of procedures using lockout devices.
WAC 296-803-70015 Do periodic reviews of procedures using tagout devices.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Perform and document periodic reviews to verify employees know and follow the energy control procedures |
WAC 296-803-70005 |
Do periodic reviews of procedures using lockout devices |
WAC 296-803-70010 |
Do periodic reviews of procedures using tagout devices |
WAC 296-803-70015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-70005 Perform and document periodic reviews to verify employees know and follow the energy control procedures.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must do a periodic review at least annually to:
((–)) (a) Make sure employees know and can apply the energy control procedures.
((–)) (b) Correct any deviations or inadequacies identified.
Exemption: | Energy control procedures used less frequently than once a year only need to be reviewed before being used. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must have the periodic review done by an authorized employee other than the ones using the energy control procedure being reviewed.
((•)) (3) You must document that periodic reviews have been done.
((–)) Include all of the following:
((■)) (a) Machine or equipment the energy control procedure was used for.
((■)) (b) Date of the review.
((■)) (c) Employees included in the review.
((■)) (d) Person doing the review.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-70010 Do periodic reviews of procedures using lockout devices.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure, if a periodic review involves lockout devices, the reviewing employee reviews responsibilities with each authorized employee who uses the procedure.
Note: | Periodic reviews of authorized employees using energy control procedures involving only lockout devices can be done in a group meeting if desired. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-15-105, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04)
WAC 296-803-70015 Do periodic reviews of procedures using tagout devices.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure, if a periodic review involves tagout devices, the reviewing employee reviews with each authorized and affected employee the:
((–)) (1) Employee's responsibilities under the procedure; and
((AND
–)) (2) Limitations of tagout devices.
Note: | Periodic reviews of authorized and affected employees using energy control procedures involving tagout devices have to be done with each employee individually. |
Reference: | See WAC 296-803-60010, Provide additional training if you use tagout devices, in this chapter for the limitations of tagout devices. |
REPEALER
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
WAC 296-803-800 |
Definitions. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-811-099 Definitions.
Buddy-breathing device. An equipment accessory for self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) that permits a second person (a "buddy") to share the air supply used by the SCBA wearer.
Extinguisher classification. The letter classification given an extinguisher to designate the class or classes of fires on which that extinguisher will be effective. For example, use a Class A extinguisher on a Class A fire. See also fire classifications.
Portable fire extinguishers are classified for use on certain classes of fires and are rated within that class for relative extinguishing effectiveness at a temperature of plus 70°F by nationally recognized testing laboratories. This is based upon fire classifications and fire extinguishment potentials as determined by fire tests.
Note: | The classification and rating system described in this section is used by Underwriters' Laboratories, Inc., and Underwriters' Laboratories of Canada, and is based on extinguishing preplanned fires of determined size and description as follows: |
Extinguisher Class |
Fire Test for Classification and Rating |
Class A |
Wood and excelsior fires excluding deep-seated conditions. |
Class B |
Two-inch depth gasoline fires in square pans. |
Class C |
No fire test. Agent must be a nonconductor of electricity. |
Class D |
Special tests on specific combustible metal fires. |
Extinguisher rating (see also "extinguisher classification"). The numerical rating, such as 2A, given to an extinguisher that indicates the extinguishing potential of the unit based on standardized tests developed by Underwriters' Laboratories, Inc.
Fire brigade. An organized group of employees whose primary employment is other than firefighting but who are knowledgeable, trained, and skilled in specialized firefighting operations based on site-specific hazards present at a single commercial facility or facilities under the same management.
Fire classifications. Fires are classified based on the types of burning materials:
Fire Class |
Types of Burning Materials |
Class A |
Fires involving ordinary combustible materials such as paper, wood, cloth, and some rubber and plastic materials. |
Class B |
Fires involving flammable liquids, flammable gases, greases, and similar materials, and some rubber and plastic materials. |
Class C |
Fires involving energized (live) electrical equipment where it is important that the extinguishing agent not conduct electricity. (When electrical equipment is deenergized, it is safe to use an extinguisher for Class A or B fires on it, since electricity is not an issue then.) |
Class D |
Fire involving combustible metals such as magnesium, titanium, zirconium, sodium, lithium, and potassium. |
Incipient fire stage. A fire in the beginning stage that can be controlled or put out by portable fire extinguishers, or small hose systems, without the need for protective clothing or breathing apparatus.
Inspection. A visual check of fire protection systems and equipment to ensure they are in place, charged, and ready for use if there is a fire.
Interior structural firefighting. The physical activity of suppressing fire, rescuing people, or both, inside buildings or enclosed structures involved in a fire that is past the incipient stage.
Maintenance. Servicing fire protection equipment and systems to ensure they will perform as expected if there is a fire. Maintenance differs from inspection in that maintenance requires checking internal fittings, devices, and agent supplies, as well as correcting deficiencies found.
Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA). Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) in which the air pressure in the breathing zone is higher than that of the immediate environment during both inhaling and exhaling.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-100 Scope.
This chapter applies if you choose to establish a fire brigade.
((Definition:
A fire brigade is an organized group of employees whose primary employment is other than firefighting but who are knowledgeable, trained, and skilled in specialized firefighting operations based on site-specific hazards present at a single commercial facility or facilities under the same management.))
Note: | Nothing in this chapter requires you to establish an employee fire brigade. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-200 Establishing a fire brigade—Section contents.
Your responsibility:
To decide on brigade functions in the workplace and make sure brigade members are capable of doing them.
((Organizing statement
WAC 296-811-20005.
Physical capability of brigade members
WAC 296-811-20010.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Organizing statement |
WAC 296-811-20005 |
Physical capability of brigade members |
WAC 296-811-20010 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-20005 Organizing statement.
((You must:
•)) You must develop a written fire brigade policy that is available for inspection by employees or their designated representatives, that covers all of the following:
((–)) (1) The role and responsibilities of the fire brigade in the workplace.
((–)) (2) The basic organizational structure of the fire brigade.
((–)) (3) The number of brigade members.
((–)) (4) Type, amount, and frequency of training for brigade members according to the section Firefighting training, WAC 296-811-30010, in this chapter.
Note: | You may also want to include: |
((•)) 1. Descriptions of brigade member duties. | |
((•)) 2. Line authority of each brigade officer. | |
((•)) 3. Number of brigade officers. | |
((•)) 4. Number of training instructors. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-20010 Physical capability of brigade members.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure brigade members who are assigned to fight interior structural fires are physically capable of doing this activity.
((–)) Do not permit employees with known physical limitations that can be reasonably identified, such as heart disease or seizure disorder, to participate in structural firefighting activities unless the employee has been released by a physician to do so.
Note: | Not all brigade members need to be physically capable of fighting interior structural fires. Brigade members who are not physically capable of fighting interior structural fires may be assigned to other brigade duties that match their physical capabilities, such as pump operation or fire prevention inspection. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-300 Training—Section contents.
Your responsibility:
To inform brigade members of special hazards in the workplace and train them for their brigade functions.
((Special hazards
WAC 296-811-30005.
Firefighting training
WAC 296-811-30010.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Special hazards |
WAC 296-811-30005 |
Firefighting training |
WAC 296-811-30010 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-30005 Special hazards.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must develop, include in training, and make available to brigade members, written procedures that describe the following:
((–)) (a) The special hazards they may encounter in their workplace.
((–)) (b) The actions they need to take in situations that involve these hazards.
((•)) (2) You must inform brigade members of any changes to those hazards, or the actions to take, when changes happen.
((–)) Examples of special hazards include storing and using flammable liquids and gases, toxic chemicals, and radioactive substances.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-30010 Firefighting training.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure training that a brigade member receives elsewhere that meets one or more requirements in Table 1, Training for brigade members, has been:
((–)) (a) Received within the past year;
((–)) (b) Documented as having been received, such as with a completion certificate.
((•)) (2) You must provide training frequently enough to keep brigade members able to do their functions satisfactorily and safely.
Note: | You may choose to train more often, monthly or even weekly, for some equipment or techniques. Consult fire training resources, such as the International Fire Service Training Association, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), or the International Society of Fire Service Instructors, for recommendations about fire training schools or programs. |
((You must:
•)) (3) You must make sure brigade members are trained according to Table 1, Training for Brigade Members.
Table 1: Training for Brigade Members
For these brigade members |
Provide training that is |
At these times |
||
All brigade members, including leaders, trainers, and incident commanders. |
• |
Appropriate to their assigned duties and functions. |
• |
Initially before they do any fire brigade emergency activities; |
• |
Appropriate to special hazards in the workplace. |
AND |
||
• |
Similar to that of reputable fire training schools. |
• |
Every year after initial training. |
|
• |
A combination of hands-on and classroom experiences. |
|||
• |
Suited to the industry you are part of, such as oil refining or chemical processing. |
|||
Brigade members assigned to do interior structural firefighting. |
All of the above plus the following: |
At the above times plus the following: |
||
• |
Specific training in interior structural firefighting. |
• |
Every quarter. |
|
Brigade members assigned as leaders, training instructors, or both. |
All of the above plus the following: |
As needed to maintain their expertise at a higher level than that of other brigade members. |
||
• |
Additional training that is more comprehensive than that of other brigade members and appropriate to their assigned duties and functions. |
|||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-400 Equipment—Section contents.
Your responsibility:
To provide brigade members with equipment and protective clothing appropriate for their brigade functions.
((Firefighting equipment
WAC 296-811-40005.
Protective clothing
WAC 296-811-40010.
Respiratory protective devices
WAC 296-811-40015.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Firefighting equipment |
WAC 296-811-40005 |
Protective clothing |
WAC 296-811-40010 |
Self-contained breathing apparatus' (SCBAs) |
WAC 296-811-40015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-40005 Firefighting equipment.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must provide appropriate firefighting equipment for the fire brigade.
((•)) (2) You must inspect and maintain brigade firefighting equipment according to Table 2, Fire Brigade Equipment Inspection and Maintenance.
Table 2: Fire Brigade Equipment Inspection and Maintenance
For this equipment |
Do the following |
|
All brigade firefighting equipment. |
• |
Inspect at least every year. |
• |
Maintain in safe operating condition. |
|
• |
Replace if damaged or in unsafe condition. |
|
Brigade respirators and portable fire extinguishers. |
Inspect at least every month and after each use. |
|
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-40010 Protective clothing.
((You must:
•)) You must provide appropriate protective clothing for fire brigade members who do interior structural firefighting. Make sure protective clothing is:
((–)) (1) Provided at no cost.
((–)) (2) Meets the requirements for foot, body, hand, eye, face, and head protection found in another chapter, Safety standards for firefighters, chapter 296-305 WAC.
Exemption: | ((•)) Protective clothing requirements do not apply to the following fire brigade members: |
((–)) 1. Those who ((don't)) do not perform interior structural firefighting. | |
((–)) 2. Those who use only standpipe systems or portable fire extinguishers to control or put out fires that are in the incipient stage only. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-15-145, filed 7/21/09, effective 9/1/09)
WAC 296-811-40015 Self-contained breathing apparatus' (SCBAs).
((•)) (1) Provide SCBAs, other than escape self-contained breathing apparatus' (ESCBAs), and make sure they are used by each fire brigade member who does interior structural firefighting.
((•)) (2) Make sure SCBAs do the following:
((–)) (a) Meet the requirements found in chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators.
((–)) (b) Are positive-pressure or pressure-demand type.
((–)) (c) Use only compressed-air cylinders that((:
■)) meet department of transportation (DOT) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) requirements.
((–)) (d) Have a service life of at least thirty minutes, as required by 42 C.F.R., Part 84.
((–)) (e) Have an automatic alarm that can be heard when seventy-five to eighty percent of its service life has been used up.
Note: | ((•)) An SCBA can have a quick-disconnect valve or "buddy breathing" accessory only if the valve or accessory does not do any of the following: |
((–)) 1. Damage the SCBA. | |
((–)) 2. Restrict the SCBA's air flow. | |
((–)) 3. Interfere with the SCBA's normal operation. | |
((–)) 4. The "buddy breathing" accessory or quick-disconnect valve need not be certified by NIOSH. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-500 Requirements during firefighting—Section contents.
Your responsibility:
To make sure brigade members use safe practices during interior structural firefighting.
((Brigade members in interior structural fires
WAC 296-811-50005.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Brigade members in interior structural fires |
WAC 296-811-50005 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-01-073, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06)
WAC 296-811-50005 Brigade members in interior structural fires.
IMPORTANT:
Nothing in this section is meant to prevent fire brigade members assigned to respond to fires from rescue activities in an immediately dangerous to life and health (IDLH) atmosphere before the whole team assigned to respond to fires has arrived.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure at least two qualified fire brigade members go together into an IDLH atmosphere and remain in visual or voice contact with each other at all times.
((•)) (2) You must maintain standby assistance, with two people, as required by another section, Standby requirements for immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) conditions, WAC 296-842-19005.
Note: | One of the two brigade members providing standby assistance can be assigned another role, such as safety officer, as long as the safety or health of any firefighter working the incident will not be jeopardized if the brigade member becomes unavailable through giving assistance or rescue. |
Reference: | More information on interior structural fires is located in another section, WAC 296-305-05001, Emergency fireground operations—Structural. |
REPEALER
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
WAC 296-811-600 |
Definitions. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-818-099 Definitions.
Abrasive. A solid granular substance used in abrasive blasting operations.
Abrasive blasting. The forcible application of an abrasive to a surface using either:
(a) Pneumatic or hydraulic pressure; or
(b) Centrifugal force.
Abrasive-blasting respirator. A supplied air or a continuous flow respirator constructed with a shroud that covers and protects the head, neck, and shoulders.
Automatic blast cleaning systems. A unit that has a blast cleaning chamber which usually has both of the following to provide a timed cleaning cycle:
(a) An automatic timer; and
(b) An automatic shutoff control.
Baffles. Partial enclosures in and around the emission sources which improve or enhance airflow at the hood.
Blast cleaning barrel. A complete enclosure that rotates on an axis or an internal tread to tumble parts in order to expose various surfaces of the parts to an automatic blast spray.
Blast cleaning room. An enclosed room where blasting operations are performed by an operator who works from inside the room using a blasting nozzle to direct the flow of abrasive material.
Blasting cabinet. An enclosure where the operator stands outside using a blasting nozzle through an opening, or openings in the enclosure.
Dust collector. A device in an exhaust ventilation system used to remove dust from air.
Exhaust ventilation system. A system that removes contaminated air using the following:
(a) Enclosure or hood;
(b) Duct work;
(c) Dust collecting equipment;
(d) Exhauster; and
(e) Discharge stack.
Local exhaust ventilation. The mechanical removal of contaminated air from the point where the contaminant is being generated or liberated.
Make-up air systems. A ventilation system that controls the volume of outdoor air supplied to a building to replace air being exhausted.
Rotary blast cleaning table. An enclosure where the pieces to be cleaned are placed on a rotating table and passed automatically through a series of blast sprays.
Tempered make-up air. Air which has been conditioned by changing its heat content to get a specific desired temperature.
Ventilation. The provision, circulation or exhausting of air into or from an area or space.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-100 Scope.
This chapter applies to all abrasive blasting operations where an abrasive is forcibly applied to a surface using any of the following:
((•)) (1) Pneumatic pressure;
((•)) (2) Hydraulic pressure;
((•)) (3) Centrifugal force.
References: | Depending on your work processes, here are examples of other chapters you may need: |
Safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC; | |
Machine safety, chapter 296-806 WAC; | |
Respiratory hazards, chapter 296-841 WAC; | |
Respirators, chapter 296-842 WAC; | |
Lead, chapter 296-857 WAC; | |
Scaffolds, chapter 296-874 WAC; | |
Cadmium, chapter 296-62 WAC; | |
Part L, Electrical, chapter 296-24 WAC. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-200 General safety—Summary contents.
Your responsibility:
To protect employees from hazards associated with their work environment.
((Dust hazards
WAC 296-818-20005
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
WAC 296-818-20010
Housekeeping
WAC 296-818-20015))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Dust hazards |
WAC 296-818-20005 |
Personal protective equipment |
WAC 296-818-20010 |
Housekeeping |
WAC 296-818-20015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-20005 Dust hazards.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) 1. Abrasives and the surface coatings on materials blasted are shattered and pulverized during blasting operations. The dust formed will contain particles that could result in the following hazards:
((–)) a. Respiratory;
((–)) b. Fire;
((–)) c. Explosion.
((•)) 2. Wet blasting methods minimize dust exposure, but dispersed droplets, mists, and dried residues may become airborne and create potential exposures.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must evaluate the potential health hazards from abrasive blasting operations by considering the composition and toxicity of the abrasive material and the surface being abraded.
References: | ((•)) 1. For additional hazard assessment requirements, go to these separate chapters: |
((–)) a. Respirators, chapter 296-842 WAC; | |
((–)) b. The Safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC; | |
((–)) c. Personal protective equipment, WAC 296-800-16005. | |
((•)) 2. For requirements on the use of Combustible organic abrasive, go to WAC 296-818-30005. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must keep dust concentrations below the permissible exposure limits found in a separate chapter, Respiratory hazards, chapter 296-841 WAC.
Note: | When sampling for dust concentrations, place the sample collection device: |
((–)) 1. In the breathing zone of the operator; and | |
((AND | |
–)) 2. Outside the respiratory protection worn. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-05-071, filed 2/17/09, effective 4/1/09)
WAC 296-818-20010 Personal protective equipment (PPE).
((You must:
•)) (1) You must provide, at no cost to the employee, and make sure personal protective equipment is worn.
((•)) (2) You must follow the requirements in Table-1, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Table-1: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PROVIDE |
WHEN |
Abrasive Blasting Respirators |
Operators work in any of the following situations: |
- Inside blast cleaning rooms |
|
- Where silica sand is used in manual blasting operations |
|
- Where concentrations of toxic dust exceed the permissible exposure limits found in a separate chapter: |
|
■ Respiratory hazards, WAC 296-841-20020, Table-3 "Exposure Limits for Air Contaminants" |
|
Exemption: |
|
• An abrasive respirator does not need to be worn if the operator is physically separated from the nozzle and blast by an exhaust ventilated enclosure. |
|
Definition: |
|
Abrasive-blasting respirator |
|
A supplied air or a continuous flow respirator constructed to cover and protect the operator's head, neck and shoulders from rebounding abrasive. |
|
Eye and Face protection to both of the following: - Blasting operators |
Respirators worn during blasting operations do not provide eye and face protection |
- Personnel working near blasting operations |
|
Gloves and Aprons made of heavy canvas or leather; |
Operators are exposed to the impact of rebounding abrasives |
OR |
|
Equivalent protection |
Notes: | ((•)) 1. Use only respirators certified by NIOSH in 42 C.F.R. Part 84 for protecting employees from dusts, and other hazards produced during abrasive blasting operations, like((: |
–)) using a garnet sand to blast a concrete surface, resulting in crystalline silica dust. | |
((•)) 2. A filtering face piece may be used only for short, intermittent, or occasional dust exposures for any of the following tasks: | |
((–)) a. To protect the operator during abrasive blasting operations performed outside the enclosure or outdoors where nonsilica abrasives are used on materials with low toxicity; | |
((–)) b. Clean-up; | |
((–)) c. Dumping dust collectors; | |
((–)) d. Unloading shipments of sand at receiving areas when the following controls are not feasible: | |
((■)) i. Enclosures; | |
((■)) ii. Exhaust ventilation; or | |
((OR | |
■)) iii. Other means. |
Reference: | ((•)) For additional requirements to help you fully protect employees, go to the following separate chapters: |
((–)) 1. The Safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC((:)); | |
((■)) Personal protective equipment (PPE), WAC 296-800-160. | |
((–)) 2. Respiratory hazards, chapter 296-841 WAC; | |
((–)) 3. Respirators, chapter 296-842 WAC: | |
((■)) a. Respirator program, WAC 296-842-120; | |
((■)) b. Specifications for air quality, WAC 296-842-200. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-20015 Housekeeping.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must keep aisles and walkways clear of steel shot or similar abrasives that may create a slipping hazard.
((•)) (2) You must prohibit the accumulation of dust on the floors or ledges outside blasting enclosures.
((•)) (3) You must clean up dust spills promptly.
Note: | Removal of accumulated dust should be done: |
((•)) 1. With a high efficiency particulate air filter (HEPA), vacuum cleaner when the plant is not in operation; and | |
((AND | |
•)) 2. By a person wearing a respirator approved for the existing conditions. |
Reference: | ((•)) For additional housekeeping requirements, see the Safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC, Housekeeping, WAC 296-800-220. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-300 Operations—Summary contents.
Your responsibility:
To follow these operational requirements.
((Combustible organic abrasives
WAC 296-818-30005
Blast cleaning enclosures
WAC 296-818-30010
Blast cleaning nozzles
WAC 296-818-30015))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Combustible organic abrasives |
WAC 296-818-30005 |
Blast cleaning enclosures |
WAC 296-818-30010 |
Blast cleaning nozzles |
WAC 296-818-30015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-30005 Combustible organic abrasive.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) This section applies to blasting operations where flammable or explosive dust mixtures may be present.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must prohibit the use of combustible organic abrasives, except in automatic blast cleaning systems.
((•)) (2) You must bond and ground the blast nozzle to prevent the buildup of static charges.
Note: | Fine dust produced from combustible, organic abrasive is a fire and explosion hazard. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-30010 Blast cleaning enclosures.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must install adequate ventilation systems in blast cleaning enclosures that are able to do all of the following:
((–)) (a) Control concentrations of airborne contaminants below the permissible exposure limits that apply;
((–)) (b) Provide a continuous inward flow of air at all openings in the enclosure during blasting operations;
((–)) (c) Minimize the escape of dust into adjacent work areas;
((–)) (d) Maintain visibility in blast cleaning rooms and cabinets;
((–)) (e) Rapidly clear dust from the air after blasting stops;
((–)) (f) Discharge exhaust so contaminated air does not do either of the following:
((■)) (i) Present a health hazard to any worker; or
((■)) (ii) Reenter buildings in harmful amounts.
((•)) (2) You must make sure ventilation systems are designed and operated so employees are not exposed to excessive air velocities.
((•)) (3) You must make sure make-up air systems do not interfere with the effectiveness of the exhaust system, and are designed to do both of the following:
((–)) (a) Replace exhausted air in ample quantities;
((–)) (b) Temper make-up (supply) air when necessary.
((•)) (4) You must do both of the following before opening the blast cleaning enclosure:
((–)) (a) Turn the blast off;
((–)) (b) Run the exhaust system for a sufficient period of time to clear the air of dust particles.
((•)) (5) You must follow the requirements in Table-2, Blast Cleaning Enclosures.
Table-2: Blast Cleaning Enclosures
If you have |
Then make sure |
Air inlets and access openings |
They are either baffled or arranged so the combination of inward airflow and baffles minimizes both of the following: |
- The escape of abrasive or dust particles into adjacent work areas. |
|
- Visible spurts of dust |
|
Small access openings where dust might escape |
Slit resistant baffles are installed in multiple sets at all small access openings, and do both of the following: |
- Regularly inspect them |
|
- Replace them when needed |
|
An observation window in enclosures where hard, deep cutting abrasives are used |
The window is made of safety glass protected by screening |
Notes: |
|
• Hard, deep cutting abrasives may shatter normal glass. |
|
• If the safety glass shatters, the protective screening will help contain the glass and protect employees from cuts and lacerations. |
|
Small operator access doors |
They are flanged and tight when closed, and open from both inside and outside the enclosure. |
Note: |
|
If you have a small operator access door and a large work access door, the large work access door may open or close from the outside only. |
References: | For more information on: |
((•)) 1. Air velocities, refer to the following: | |
((–)) a. The latest edition of Recommended Industrial Ventilation Guidelines (ACGIH); | |
((–)) b. NIOSH 1976 Industrial Ventilation; | |
((•)) 2. Exit routes, go to the Safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-310. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-30015 Blast cleaning nozzles.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure nozzles are all of the following:
((–)) (1) Mounted on a support when not in use;
((–)) (2) Equipped with operating valves that are manually held open.
Note: | ((•)) To help prevent the buildup of static charges, pressurized tanks used to supply abrasive should be: |
((–)) 1. Connected to the manual control of the nozzle; and | |
((AND | |
–)) 2. Have the relief valve or opening located so it can safely vent. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-400 Exhaust ventilation systems—Summary contents.
Your responsibility:
To make sure exhaust ventilation systems meet these requirements.
((Construction
WAC 296-818-40005
Explosion venting and wiring
WAC 296-818-40010
Inspection and maintenance
WAC 296-818-40015))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Construction |
WAC 296-818-40005 |
Explosion venting and wiring |
WAC 296-818-40010 |
Inspection and maintenance |
WAC 296-818-40015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-40005 Construction.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure exhaust systems are constructed, installed, inspected, and maintained to meet both of the following:
((–)) (1) The American National Standards Institute (ANSI), Z9.2-2001 for((:
■)) Fundamentals Governing the Design and Operation of Local Exhaust Systems;
((–)) (2) The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 91-2004 for((:
■)) Exhaust Systems for Air Conveying of Vapors, Gases and Noncombustible Particulate Solids.
Reference: | ((•)) Refer to the American National Standards Institute, ANSI Z9.4-1997 for information on ((the following: |
–)) Exhaust Systems for Abrasive-blasting Operations, Ventilation, and Safe Practices for Fixed Location Enclosures. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-40010 Explosion venting and wiring.
((You must:
•)) You must follow the requirements in Table-3 for flammable or combustible dust mixtures.
Table-3: Explosion Venting and Wiring
If you have |
Then |
Flammable or explosive dust mixtures that may be present |
Make sure the construction of equipment, including the exhaust system and all electrical wiring, meets both of the following: |
• The American National Standard Installation (ANSI) of Blower and Exhaust Systems for Dust, Stock, and Vapor Removal or Conveying, NFPA 91. 2004. |
|
• The electrical requirements for Class II locations in WAC 296-24-95613, located in Part L of chapter 296-24 WAC. |
|
Make sure blast cleaning enclosures, the ducts, and the dust collector are constructed with either loose panels or explosion venting areas that meet all of the following: |
|
• Provides pressure relief in case of an explosion. |
|
• Are located away from occupied areas. |
|
• The Guide for Deflagations, NFPA 68. 2002. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-12-074, filed 6/6/06, effective 9/1/06)
WAC 296-818-40015 Inspection and maintenance.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure the exhaust ventilation system is fully operational by checking the static pressure drop at the exhaust ducts leading from the equipment at both of the following times:
((–)) (a) When installation is completed;
((–)) (b) Annually after installation.
((•)) (2) You must repair or clean exhaust systems when either of the following occur:
((–)) (a) Dust leaks are found; or
((–)) (b) The pressure drop gauge indicates a change exceeding 20 percent.
((•)) (3) You must use an abrasive separator to separate larger particles for reuse on installations where abrasive is recirculated.
((•)) (4) You must set up dust collecting equipment to do both of the following:
((–)) (a) Empty and remove accumulated dust without contaminating work areas;
((–)) (b) Discharge the air used in blast cleaning equipment.
Note: | Dispose fine dust from dry collectors by doing one of the following: |
((•)) 1. Emptying and transporting the fine dust in enclosed containers; | |
((•)) 2. Using a sluice with a wetting process to contain the dust. |
REPEALER
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
WAC 296-818-500 |
Definitions. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-824-099 Definitions.
The following definitions are specific to this chapter:
Annually. Any twelve-month cycle.
Buddy system. A system of organizing employees (who enter or stand by danger areas) into work groups, so each employee can be observed by at least one other member of the group. The purpose of this system is to provide rapid assistance to employees in an emergency.
Clean-up operation(s). An operation where hazardous substances are removed, contained, incinerated, neutralized, stabilized, cleared up or, in any other manner, processed or handled with the goal of making the site safer for people or the environment.
Danger area. Areas where conditions pose a serious danger to employees, such as areas where:
(a) Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) conditions could exist;
(b) High levels of exposure to toxic substances could exist; or
(c) There is a potential for exceeding the lower explosive limit (LEL), also known as the lower flammability limit (LFL), of a substance.
Decontamination. Removing hazardous substances from employees and their equipment so potential adverse health effects will not occur.
Emergency response. An organized response to an anticipated release of a hazardous substance that is, or could become an uncontrolled release.
Emergency response plan. A written plan that requires coordination between emergency response participants, and contains procedures, criteria, and other information that will be applied to emergency response operations. Each employer's plan should be compatible with local and state plans.
Engineering controls. Methods of controlling employee exposures by modifying the source or reducing the quantity of contaminants.
Hazardous materials team (HAZMAT team). A group of employees who are expected to perform responses to releases, or possible releases, of hazardous substances for the purpose of control and stabilization. As a result of their duties, HAZMAT team members may have close contact with hazardous substances.
Note: | A HAZMAT team may be a separate component of a fire brigade or fire department. |
Hazardous substance. Any of the following substances that could adversely affect an exposed employee's health or safety:
(a) Substances defined under section 101(14) of the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA) or "Superfund" Act (visit: http://www.epa.gov);
(b) Biological or other disease-causing agents released that could reasonably be expected to cause death, disease, behavioral abnormalities, cancer, genetic mutation, physiological malfunctions (including malfunctions in reproduction) or physical deformations in a person or their offspring when the person:
(i) Is directly exposed to the agent in the environment;
(ii) Directly ingests, inhales, or assimilates the agent from the environment;
(iii) Indirectly ingests the agent through a food chain.
(c) Substances listed by the United States Department of Transportation as hazardous materials under Title 49 (Transportation) in the Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.), Part 172, section 101 and appendices (visit: http://www.nara.gov and search for "List of C.F.R. subjects"); and
(d) Hazardous wastes as defined in this chapter.
Hazardous waste. A substance designated by chapter 173-303 WAC, Dangerous waste regulations, department of ecology, as a dangerous waste or an extremely hazardous waste and any waste fitting the definition of "health hazard" in this chapter.
Note: | For department of ecology regulations, visit: http://www.ecy.wa.gov. |
Health hazard. A chemical that is classified as posing one of the following hazardous effects: Acute toxicity (any route of exposure); skin corrosion or irritation; serious eye damage or eye irritation; respiratory or skin sensitization; germ cell mutagenicity; carcinogenity; reproductive toxicity; specific target organ toxicity (single or repeated exposure); aspiration hazard. The criteria for determining whether a chemical is classified as a health hazard are detailed in Appendix A of the Hazard Communication Standard WAC 296-901-140 and 296-901-14006 (definition of "simple asphyxiant").
Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH). Any atmospheric condition that would:
(a) Cause an immediate threat to life;
(b) Cause permanent or delayed adverse health effects;
(c) Interfere with an employee's ability to escape.
Incident command system (ICS). An organized approach to control and manage operations at an emergency response incident.
Incidental release. A release that can be safely controlled at the time of the release and does not have the potential to become an uncontrolled release.
Note: | Example of a situation that results in an incidental release: A tanker truck is receiving a load of hazardous liquid when a leak occurs. The driver knows the only hazard from the liquid is minor skin irritation. The employer has trained the driver on procedures and provided equipment to use for a release of this quantity. The driver puts on skin protection and stops the leak. A spill kit is used to contain, absorb, and pick up the spilled material for disposal. |
Limited action. Action necessary to:
(a) Secure an operation during emergency responses; or
(b) Prevent an incident from increasing in severity.
Examples include shutting down processes and closing emergency valves.
Lines of authority. A preestablished ranking of individuals, qualified to assume a commanding role during an emergency response, noted in an emergency response plan and implemented during a response. This is most important when responders from multiple employers could participate in an emergency response.
Lower explosive limit (LEL). See lower flammable limit (LFL).
Lower flammable limit (LFL). The lowest concentration of a material that will propagate a flame. The LFL is usually expressed as a percent (by volume) of the material in air (or other oxidant).
Must. Must means mandatory.
Permissible exposure limit (PEL). The established time-weighted-average (TWA) concentration or ceiling concentration of a contaminant that must not be exceeded. The exposure, inhalation, or dermal permissible limit specified in chapter 296-841 WAC, Airborne contaminants.
Personal protective equipment (PPE). Protective items designed to be worn by the user to protect them against airborne, skin contact and other hazards. This includes items such as respiratory protection, protective suits, gloves, eye protection, etc.
Postemergency response. The stage of the emergency response where the immediate threat from the release has been stabilized or eliminated, and cleanup of the site has started.
Published exposure level. Exposure limits published in "National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Recommendations for Occupational Safety and Health" (DHHS publication #92-100, 1992).
If an exposure limit is not published by NIOSH, then "published exposure level" means the exposure limits published by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) in "TLVs and BEIs-Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents" (1999 edition).
Note: | Additional exposure levels published by recognized organizations such as the American Industrial Hygiene Association are not required to be observed by this rule; however, they may be a useful resource when a hazardous substance is not covered by NIOSH and ACGIH publications. |
Release. A spill, leak, or other type of hazardous substance discharge.
Uncontrolled release. A release where significant safety and health risks could be created. Releases of hazardous substances that are either incidental or could not create a safety or health hazard (i.e., fire, explosion or chemical exposure) are not considered to be uncontrolled releases.
Examples of conditions that could create a significant safety and health risk:
(a) Large-quantity releases;
(b) Small releases that could be highly toxic;
(c) Potentially contaminated individuals arriving at hospitals; and
(d) Airborne exposures that could exceed a WISHA permissible exposure limit or a published exposure limit and employees are not adequately trained or equipped to control the release.
Example of an uncontrolled release:
A forklift driver knocks over a container of a solvent-based liquid, releasing the contents onto the warehouse floor. The driver has been trained to recognize the vapor is flammable and moderately toxic when inhaled. The driver has not been trained or provided appropriate equipment to address this type of spill. In this situation, it is not safe for the driver to attempt a response. The driver needs to notify someone of the release so an emergency response can be initiated.
Workplace.
(a) A fixed facility;
(b) A temporary location (such as a traffic corridor); or
(c) Locations where employees respond to emergencies.
You. The employer. For a complete definition of "employer" see Safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-824-100 Scope.
This chapter states the minimum requirements that help you protect the safety and health of your employees during a response to a hazardous substance releases in your workplace or any other location.
This chapter applies if your employees are, or could become, involved in responding to uncontrolled releases of hazardous substances in your workplace or any other location. Use the scope flow chart, and definitions that follow, to determine if this chapter applies to your workplace(s). Defined words are italicized in the flow chart.
EXEMPTION: | ((•)) 1. This chapter does not apply to you if your workplace is a hazardous waste site. If you are not sure about your site classification, see chapter 296-843 WAC, Hazardous waste operations. |
((•)) 2. If your workplace is a treatment, storage, and disposal site this chapter may apply. |
Note: | Requirements in other chapters may also apply to your workplace. You will find some safety and health requirements (for example, personal protective equipment) are addressed on a general level in the WISHA Safety and Health Core Rules, chapter 296-800 WAC, while being addressed for a specific application in this rule. When this happens, both requirements apply and should not conflict. |
If you are uncertain which requirements to follow, you must comply with the more protective requirement. Contact your local L&I office if you need assistance in making this determination. |
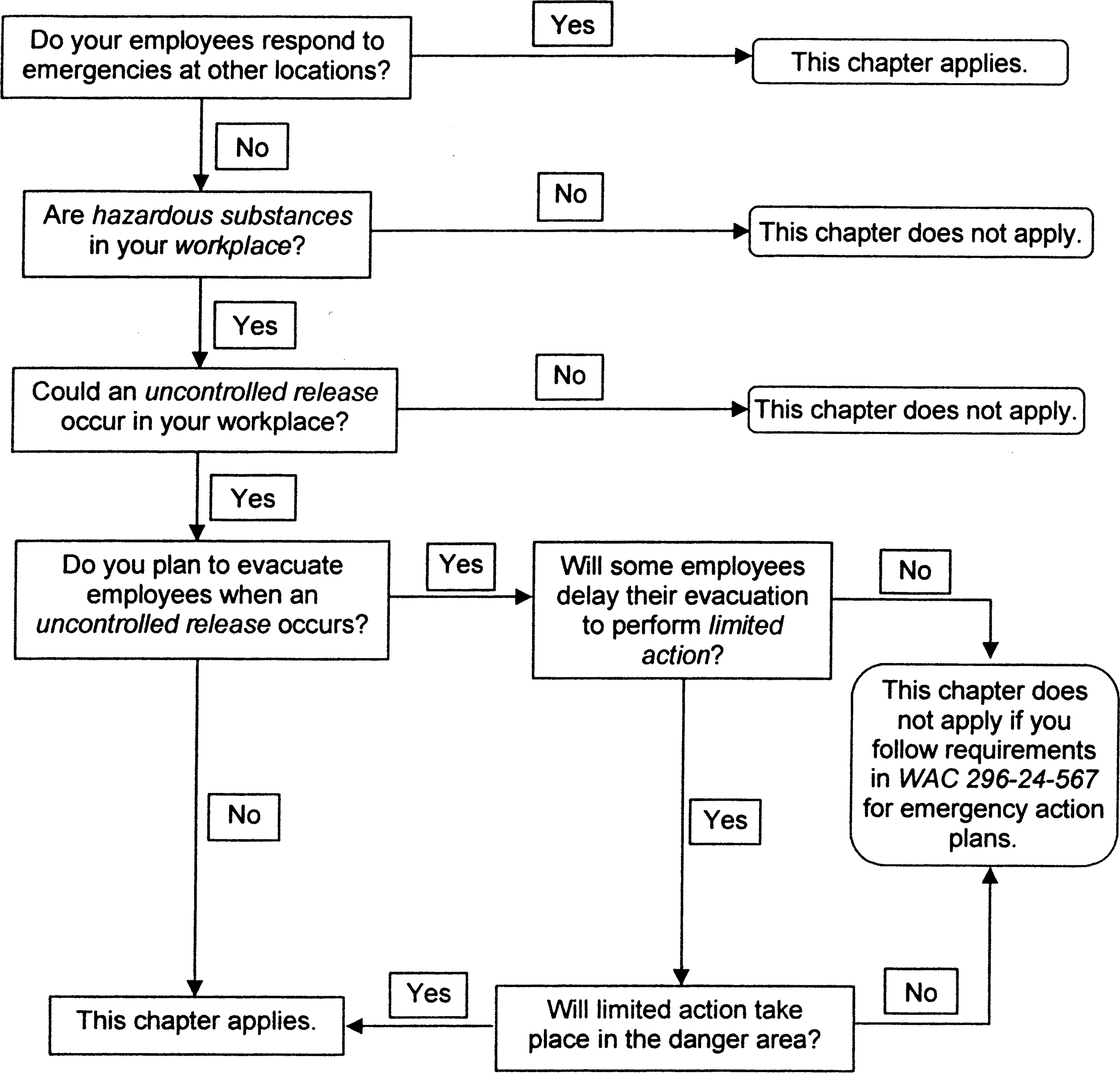 |
Definitions applicable to the flow chart. (See WAC 296-824-800 for additional definitions used in the chapter):
Danger area
Areas where conditions pose a serious danger to employees, such as areas where:
((•)) (a) Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) conditions could exist; or
((OR
•)) (b) High levels of exposure to toxic substances could exist; or
((OR
•)) (c) There is a potential for exceeding the lower explosive limit (LEL), also known as the lower flammability limit (LFL), of a substance.
Emergency response
A response to an anticipated release of a hazardous substance that is, or could become, an uncontrolled release.
Hazardous substance
Any biological, radiological, or chemical substance that can have adverse effects on humans. (See WAC 296-824-800 for a more specific definition.)
Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH)
Any atmospheric condition that would:
((•)) (a) Cause an immediate threat to life;
((•)) (b) Cause permanent or delayed adverse health effects;
((•)) (c) Interfere with an employee's ability to escape.
Incidental release
A release that can be safely controlled at the time of the release and does not have the potential to become an uncontrolled release.
Example of a situation that results in an incidental release:
A tanker truck is receiving a load of hazardous liquid when a leak occurs. The driver knows the only hazard from the liquid is minor skin irritation. The employer has trained the driver on procedures and provided equipment to use for a release of this quantity. The driver puts on skin protection and stops the leak. A spill kit is used to contain, absorb, and pick up the spilled material for disposal.
Limited action
Action necessary to:
((•)) (a) Secure an operation during emergency responses((,)); or
((OR
•)) (b) Prevent an incident from increasing in severity.
Examples include shutting down processes and closing emergency valves.
Release
A spill, leak, or other type of hazardous substance discharge.
Uncontrolled release
A release where significant safety and health risks could be created. Releases of hazardous substances that are either incidental or could not create a safety or health hazard (i.e., fire, explosion or chemical exposure) are not considered to be uncontrolled releases.
Examples of conditions that could create a significant safety and health risk:
((•)) (a) Large-quantity releases;
((•)) (b) Small-releases that could be highly toxic;
((•)) (c) Potentially contaminated individuals arriving at hospitals;
((•)) (d) Airborne exposures that could exceed a WISHA permissible exposure limit or a published exposure limit and employees are not adequately trained or equipped to control the release.
Example of an uncontrolled release:
A forklift driver knocks over a container of a solvent-based liquid, releasing the contents onto the warehouse floor. The driver has been trained to recognize the vapor is flammable and moderately toxic when inhaled. The driver has not been trained or provided appropriate equipment to address this type of spill. In this situation, it is not safe for the driver to attempt a response. The driver needs to notify someone of the release so an emergency response can be initiated.
Workplace
((•)) (a) A fixed facility; or
((OR
•)) (b) A temporary location (such as a traffic corridor); or
((OR
•)) (c) Locations where employees respond to emergencies.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-824-20005 Develop an emergency response plan.
Note: | ((•)) 1. You may already have an emergency response plan, such as required by chapter 296-843 WAC, Hazardous waste operations or by state and locally coordinated response efforts (Section 303 of Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act (SARA), Title III). You may use those plans to comply with this section, if they include the items listed below. |
((•)) 2. Before a written emergency response plan can be developed, you will need to anticipate the types of uncontrolled releases that employees could encounter in your workplace(s). |
((You must:))
(1) You must make sure your plan is written and adequately addresses, as a minimum, all of the following:
((•)) (a) Preemergency planning and coordination with additional responders (including personnel from other employers such as: Fire departments, law enforcement agencies, emergency medical services, and state or federal agencies)((.));
((•)) (b) Personnel roles, (See Table 1) and lines of authority and communications for all affected parties including responders;
((•)) (c) Employee training (see WAC 296-824-30005 for more detail):
Note: | ((•)) 1. Responders' level of training depends on the duties or roles the employer assigns. |
((•)) 2. Training for the employees' role should address the competencies specified in Tables 3 through 6. | |
((•)) 3. Training on specific substances may be appropriate depending on the number and characteristics of hazardous substances expected to be encountered. For example, if employees may only respond to one substance, you could provide training (covering the knowledge and skills specified in Tables 3 through 6) on that single substance. If employees might respond to a range of hazardous substances, training may be required to cover categories of hazardous substances. | |
((•)) 4. Videos and automated training methods (for example: Interactive computer-based programs) may be used in training; however, instructors must be readily available to: | |
((–)) a. Encourage and provide responses to questions for the benefit of the group. | |
((–)) b. Evaluate employee understanding of the material. | |
((–)) c. Provide other instructional interaction to the group. |
((•)) (i) Emergency recognition;
((•)) (ii) Immediate emergency procedures including:
((–)) (A) Methods of alerting employees (see WAC 296-800-310, exit routes and employee alarm systems) and outside responders;
((–)) (B) Procedures for limited action (emergency prevention);
Note: | Limited action includes shutting down processes, closing emergency valves and other critical actions to secure the operation, or prevent the incident from increasing in severity. |
Limited Action and Employee Roles |
|
If . . . |
Then employees involved would be: |
Limited action could be conducted in the danger area |
Considered emergency responders |
Limited action will not be conducted in the danger area |
Considered evacuees, not emergency responders |
((–)) (C) Details of who will evacuate immediately and who will remain behind for limited action;
((–)) (D) Evacuation routes and procedures;
((–)) (E) How to establish safe distances and places of refuge (for example, during emergency response the incident commander (IC) decides to make changes based on new developments, i.e., changes in the wind direction).
((•)) (d) Methods of securing and controlling access to the site;
((•)) (e) Emergency medical treatment and first aid;
((•)) (f) A complete personal protective equipment (PPE) program that addresses:
((–)) (i) Selection of PPE including selection criteria to be used and the identification, specified use and limitations of the PPE selected.
((–)) (ii) Training on proper use of PPE (including maintenance).
((–)) (iii) Hazards created by wearing PPE including heat stress during temperature extremes, and/or other appropriate medical considerations.
((–)) (iv) Criteria used for determining the proper fit of PPE.
((–)) (v) Procedures covering proper use of PPE including procedures for inspection, putting it on (donning) and removing it (doffing).
((–)) (vi) Maintenance of PPE including procedures for decontamination, disposal and storage.
((–)) (vii) Methods used to evaluate the effectiveness of your PPE program.
Note: | ((•)) 1. If a manufacturer's printed information or WISHA rule adequately addresses procedural requirements (such as donning or doffing for PPE), it is not necessary to rewrite this into your program; simply attach the printed information. |
((•)) 2. You may use written procedures provided by the equipment manufacturer when they meet the requirements of other chapters, including chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators. |
((•)) (g) Emergency equipment;
((•)) (h) Emergency response procedures;
((•)) (i) Decontamination procedures determined by a hazardous materials specialist or other qualified individual;
((•)) (j) Methods to critically assess the response and conduct appropriate follow-up.
((You must:))
(2) You must make your written emergency response plan available to employees, their representatives, and WISHA personnel for inspecting or copying.
Note: | In situations where multiple employers could respond to an incident, all plans should consistently address: |
((•)) 1. Who will be designated as the incident commander (IC); and | |
((AND | |
•)) 2. If, when, and how transfer of the incident commander (IC) position will take place. |
Table 1 Roles and Duties of Emergency Responders |
||
If the employee's role is: |
Then all of the following apply. They: |
|
First responder at the awareness level |
• |
Are likely to witness or discover a hazardous substance release |
• |
Are trained to initiate an emergency response by notifying the proper authorities of the release |
|
• |
Take no further action beyond notifying the authorities |
|
First responder at the operations level |
• |
Respond to actual or potential releases in order to protect nearby persons, property, and/or the environment from the effects of the release |
• |
Are trained to respond defensively, without trying to stop the release |
|
• |
May try to: |
|
- Confine the release from a safe distance |
||
- Keep it from spreading |
||
- Protect others from hazardous exposures |
||
Hazardous materials technician |
• |
Respond to releases or potential releases, with the intent of stopping the release |
• |
Are trained to approach the point of release offensively in order to, either: |
|
- Plug |
||
- Patch |
||
- Stop the release using other methods |
||
Hazardous materials specialist |
• |
Respond along with, and provide support to, hazardous materials technicians |
• |
Are required to have more specific knowledge of hazardous substances than a hazardous materials technician |
|
• |
Act as the site activity liaison when federal, state, local, and other government authorities participate |
|
Incident commander |
• |
Have ultimate responsibility for: |
- Direction |
||
- Control |
||
- Coordination of the response effort |
||
- Will assume control of the incident beyond the first responder awareness level |
||
Specialist employee |
• |
Are a technical, medical, environmental, or other type of expert |
• |
May represent a hazardous substance manufacturer, shipper, or a government agency |
|
• |
May be present at the scene or may assist from an ((offsite)) off-site location |
|
• |
Regularly work with specific hazardous substances |
|
• |
Are trained in the hazards of specific substances |
|
• |
Are expected to give technical advice or assistance to the incident commander or incident safety officer, when requested |
|
Skilled support personnel |
• |
Are needed to perform an immediate, specific emergency support task at the site |
• |
Are skilled in the operation of equipment including: |
|
- Earth moving equipment |
||
- Cranes |
||
- Hoisting equipment |
||
Incident safety officer |
• |
Are designated by the incident commander |
• |
Are knowledgeable in operations being implemented at the site |
|
• |
Have specific responsibility to: |
|
- Identify and evaluate hazards |
||
- Provide direction on employee safety matters |
||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-30005 Train your employees.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Use Tables 3 through 6 to identify your employees' training competencies. |
((•)) 2. You may conduct training internally, or use outside training services to comply with this section. | |
((–)) 3. When outside trainers are hired, you are still responsible for making sure the requirements of this section are met. For example, employers may compare the course outline to the competencies listed in Tables 3 through 6. |
((You must:
•)) You must make sure employees are appropriately trained for their assigned roles and duties as follows:
EXEMPTION: | Skilled support employees are not covered by the training requirements in this section. (See WAC 296-824-50015.) |
((-)) (1) Initial training:
((•)) (a) Provide initial training before the employee is allowed to participate in an actual emergency response operation.
Note: | When first responders at the awareness or operations level have sufficient experience to objectively demonstrate competencies specified in Table 3, you may accept experience instead of training. |
((•)) (b) Make sure initial training adequately addresses the competencies in Tables 3 through 6 and the minimum training durations in Table 2.
(c) Certify that employees objectively demonstrate competencies specified in Tables 3, 4 and 5 (except for employees trained as first responders at the awareness level).
((-)) (2) Retraining (refresher) training:
((•)) (a) Provide retraining annually;
((•)) (b) Make sure retraining covers necessary content;
((•)) (c) Document training or demonstrated competency.
Note: | Retraining is not required when employees demonstrate competencies annually and a record is kept of the demonstration methodology used. |
((-)) (3) Trainer qualifications:
((•)) (a) Verify trainers have satisfactorily completed an instructors' training course for the subjects they teach. For example, courses offered by the United States National Academy, or equivalent courses are acceptable((.)); or
((OR
•)) (b) Have the educational and instructional experience necessary for training.
((-)) (4) Specialist employees:
((•)) Specialist employees who have been sent to the scene to advise or assist must receive training or demonstrate competency in their specialty, annually.
Table 2 Minimum Training Durations for All Responders |
|
If you are a: |
Then: |
First responder at the awareness level |
Training duration needs to be sufficient to provide the required competencies |
First responder at the operations level |
You need a minimum of 8 hours training (see Table 3) |
Hazardous materials technician |
You need a minimum of 24 hours training (see Table 4) |
Hazardous materials specialist |
You need a minimum of 24 hours training (see Table 4) |
Incident commander |
You need a minimum of 24 hours training (see Table 5) |
Table 3 Competencies for First Responders at the Awareness Level and Operations Level |
||
Employees must be able to show they: |
When they are designated as First Responders at the: |
|
Awareness Level |
Operations Level |
|
Understand what hazardous substances are and their associated risks. |
X |
X |
Recognize the presence of hazardous substances in an emergency. |
X |
X |
Can identify the hazardous substances, when possible. |
X |
X |
Understand the potential consequences of hazardous substances in an emergency. |
X |
X |
Understand the role of a first responder at the awareness level as described in: • The employer's emergency response plan, including site security and control. • The United States Department of Transportation's Emergency Response Guidebook. (search at: http://www.dot.gov). |
X |
X |
Can use The United States Department of Transportation's Emergency Response Guidebook. |
X |
X |
Recognize the need for additional resources and the need to notify the incident's communication center accordingly. |
X |
X |
Know basic hazard and risk assessment techniques. |
X |
|
Can select and use personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriate for first responder operations level. |
X |
|
Understand basic hazardous materials terms. |
X |
|
Can perform basic control, containment, and/or confinement operations within the capabilities of the resources and PPE available. |
X |
|
Can implement decontamination procedures to their level training. |
X |
|
Understand relevant standard operating and termination procedures. |
X |
|
Table 4 Competencies for Hazardous Materials Technicians and Hazardous Materials Specialist |
||
Employees must be able to show they: |
When they are designated as a Hazardous Materials: |
|
Technician |
Specialist |
|
Have the competencies specified for the first responder operations level. (See Table 3) |
X |
X |
Can implement an employer's emergency response plan. |
X |
X |
Can function within their assigned role in the incident command system. |
X |
X |
Understand hazard and risk assessment techniques. |
X |
X |
Understand basic chemical and toxicological terminology and behavior. |
X |
X |
Can use field survey instruments and equipment to classify, identify, and verify materials at the incident. |
X |
X |
Can select and use personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriate for hazardous materials technicians. |
X |
X |
Can perform advance control, containment, and/or confinement operations within the capabilities of the resources and PPE available. |
X |
X |
Can implement decontamination procedures to their level of training. |
X |
X |
Understand termination procedures. |
X |
X |
Can implement the local emergency response plan. |
X |
|
Know of the state emergency response plan. |
X |
|
Can develop a site safety and control plan. |
X |
|
Understand chemical, radiological, and toxicological terminology and behavior. |
X |
|
Understand in-depth hazard and risk techniques. |
X |
|
Can use advanced survey instruments and equipment to classify, identify and verify materials at the incident. |
X |
|
Can select and use proper specialized chemical PPE given to hazardous materials specialists. |
X |
|
Can perform specialized control, containment, and/or confinement operations within the capabilities of the resources and PPE available. |
X |
|
Can determine decontamination procedures. |
X |
|
Table 5 Competencies for Incident Commanders |
|
Employees designated as Incident Commanders must be able to show they: |
|
• |
Have competencies specified for the First Responder Operations Level. (See Table 3.) |
• |
Know of the state emergency response plan and the Federal Regional Response Team. |
• |
Can implement the local emergency response plan. |
• |
Can implement the employer's emergency response plan. |
• |
Have knowledge of the incident command system (ICS) and understand how they relate to it. |
• |
Can implement the employer's ICS. |
• |
Understand the hazards and risks associated with employees working in chemical protective clothing. |
• |
Understand the importance of decontamination procedures. |
Note: |
If the first employee arriving at the scene is not trained as an IC, they may take control of the incident within their designated role and training level. |
Table 6 Competencies for Specialist Employees |
|
Employees designated as Specialist Employees must be able to show they: |
|
• |
Have current knowledge in their field regarding safety and health practices relating to the specific hazardous substances. |
• |
Have the knowledge of the ICS and understand how they relate to it. |
• |
Understand the care and use of personal protective equipment (PPE). |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-400 Medical surveillance.
Summary.
Your responsibility:
To provide and document medical surveillance for your employees.
((You must:
Provide medical surveillance to employees
WAC 296-824-40005
Keep records
WAC 296-824-40010.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Provide medical surveillance to employees |
WAC 296-824-40005 |
Keep records |
WAC 296-824-40010 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-03-093, filed 1/18/05, effective 3/1/05)
WAC 296-824-40005 Provide medical surveillance to employees.
((You must:))
(1) You must provide medical surveillance for employees to comply with Tables 7 and 8, and the following:
((•)) (a) Make medical surveillance available at:
((–)) (i) Reasonable times and places((.));
((–)) (ii) No cost to employees, including travel associated costs such as mileage, gas or bus fare if the employee is required to travel off-site; and
((AND
–)) (iii) Wages for additional time spent outside of employees normal work hours.
((•)) (b) Make sure a licensed physician performs or supervises exams and procedures((.));
((•)) (c) Give complete information to the examining physician including:
((–)) (i) A copy of this chapter.
((–)) (ii) A description of the employee's duties that relate to hazardous substance exposure.
((–)) (iii) The hazardous substance exposure levels anticipated for the employee.
((–)) (iv) A description of the personal protective equipment (PPE) the employee could use.
((–)) (v) Information available from previous medical examinations.
((–)) (vi) The medical evaluation information required by chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators.
((•)) (d) Medical exams must include, at a minimum:
((–)) (i) A medical history;
((–)) (ii) A work history (or updated history if on file);
((–)) (iii) A special emphasis on:
((■)) (A) Assessment of symptoms related to handling hazardous substances;
((■)) (B) Health hazards;
((■)) (C) Evaluation of fitness for duty (including the ability to wear any personal protective equipment (PPE) or other conditions that may be expected at the workplace).
((–)) (iv) Other content as determined by the examining physician.
Note: | The physician should consult the Occupational Safety and Health Guidance Manual for Hazardous Waste Site Activities and the Medical Management Guidelines for Acute Chemical Exposure (search OSHA web site: http://www.osha.gov). |
(2) You must obtain the physician's written opinion and give a copy to the employee that includes:
((•)) (a) A statement of whether or not medical conditions were found which would increase the employee's risk for impairment during emergency response work or respirator use.
((–)) Do not include specific findings or diagnoses unrelated to occupational exposures.
((•)) (b) Limitations recommended to the employee's assigned work, if any.
((•)) (c) Exam and test results if the employee requests this information.
((•)) (d) A statement that affirms the employee has been confidentially informed of medical exam results (including medical conditions requiring follow-up).
Table 7 Medical Surveillance for Employee Categories |
|
If the employee is covered by this chapter and is: |
Then you must: |
• Exposed for at least 30 days a year to health hazards or hazardous substances at or above the permissible exposure limit or published exposure levels (even when respirators are used), OR • Required to wear a respirator for at least 30 days a year.* |
• Offer standard medical surveillance as specified in Table 8.* |
• A hazardous materials (HAZMAT) team member • A hazardous materials specialist |
• Provide standard medical surveillance as specified in Table 8. |
• An emergency responder who shows immediate or delayed signs or symptoms possibly resulting from exposure to hazardous substances during an incident. |
• Provide incident-specific medical surveillance as specified in Table 8. |
• Not an emergency responder and: - May be injured - Shows immediate or delayed signs or symptoms possibly resulting from exposure to hazardous substances - May have been exposed to hazardous substances at concentrations above the permissible exposure limits (PELs) or the published exposure levels without appropriate PPE. |
• Offer incident-specific medical surveillance as specified in Table 8. |
*Note: | A medical evaluation for respirator use is required by chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators, for those employees who have not been cleared for respirator use during medical surveillance activities. |
Table 8 Frequency of Exams and Consultations |
|
If the employee is covered by: |
Then medical surveillance must include: |
• Standard medical surveillance |
• Exams and consultations: - Before assignment. Note: If the employee is a hazardous materials (HAZMAT) team member or a hazardous materials specialist, the employee must receive a baseline physical examination. - At least once every 12 months after their initial assignment unless the physician believes a shorter, or longer interval (but no more than 24 months) is appropriate. - Whenever employees are reassigned to an area where they will no longer be covered by medical surveillance and they have not been examined within the past 6 months. - As soon as possible after an employee reports: ♦ Signs or symptoms of possible overexposure to hazardous substances or health hazards ♦ Injury ♦ Exposure above the permissible exposure limits or published exposure levels - At the termination of their employment unless they were examined within the past 6 months. |
• Incident-specific medical surveillance |
• Medical consultations and exams: - As soon as possible following the incident or development of signs or symptoms. - At additional times, if the physician determines follow-up is medically necessary. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-40010 Keep records.
((You must:
•)) You must keep a record of:
((–)) (1) Name and Social Security number of the employee receiving medical surveillance;
((–)) (2) Physicians' written opinions, recommended limitations, and results of examinations and tests;
((–)) (3) Any employee medical complaints regarding hazardous substance exposures;
((–)) (4) A copy of all information given to the examining physician (except a copy of this chapter).
Note: | Keep records meeting the criteria specified in chapter 296-62 WAC, Part B, Access to records, for the length of time specified in that chapter. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-500 Incident requirements.
Summary.
Your responsibility:
To conduct and manage emergency response operations so employees are protected from hazardous substances and conditions.
((You must:
Recognize emergencies and initiate a response
WAC 296-824-50005
Implement and maintain an incident command system (ICS)
WAC 296-824-50010
Prepare skilled support personnel
WAC 296-824-50015
Make sure the incident commander oversees activities during the response
WAC 296-824-50020
Use the buddy system in danger areas
WAC 296-824-50025
Provide rescue and medical assistance
WAC 296-824-50030.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Recognize emergencies and initiate a response |
WAC 296-824-50005 |
Implement and maintain an incident command system (ICS) |
WAC 296-824-50010 |
Prepare skilled support personnel |
WAC 296-824-50015 |
Make sure the incident commander oversees activities during the response |
WAC 296-824-50020 |
Use the buddy system in danger areas |
WAC 296-824-50025 |
Provide rescue and medical assistance |
WAC 296-824-50030 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-50005 Recognize emergencies and initiate a response.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure employees follow procedures in your emergency response plan to:
((–)) (1) Recognize when an emergency response must be initiated;
((–)) (2) Notify employees, and others designated in your plan, of the release;
((–)) (3) Follow immediate emergency procedures; and
((–)) (4) Prevent the incident from increasing in severity or to secure the operation.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-50010 Implement and maintain an incident command system (ICS).
((You must:))
(1) You must make sure a single individual, acting as the incident commander (IC), is in charge of the site-specific incident command system (ICS) and acts within their designated role and training level.
Note: | ((•)) 1. For multiemployer worksites: |
((–)) a. The IC has responsibility for controlling emergency response operations at the site for all employers. | |
((–)) b. Emergency response plans should be consistent in designating who assumes the IC position. | |
((•)) 2. If the first employee arriving at the scene is not trained as an IC (see Table 5, Competencies for Incident Commanders, WAC 296-824-30005), they may take control of the incident within their designated role and training level. |
(2) You must make sure all employers' emergency responders and their communications are coordinated and controlled by the IC.
Note: | The IC may delegate tasks to subordinates (within their training level). |
(3) You must make sure each employer at the scene has designated a representative to assist the IC.
(4) You must establish security and control of the site as specified in your written emergency response plan.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-50015 Prepare skilled support personnel.
Note: | The duties of skilled support personnel are described in Table 1, Roles and Duties of Emergency Responders. |
((You must:))
(1) You must make sure that your skilled support personnel (including those employees who are not regularly employed by you) who could be exposed to on-scene hazards are given an initial briefing at the site before they participate in any emergency response. The initial briefing must include:
((•)) (a) What chemical hazards are involved;
((•)) (b) What duties are to be performed; and
((•)) (c) Instruction in the wearing of appropriate personal protective equipment.
Note: | Skilled support personnel do not need to comply with the other training requirements of this chapter. |
(2) You must make sure the safety and health precautions given to your employees are also given to skilled support personnel.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-50020 Make sure the incident commander oversees activities during the response.
The employer of the incident commander (IC) must:
(1) Identify all hazardous substances and conditions present, within their training level, using site analysis and maximum exposure limits, when appropriate.
(2) Implement emergency response procedures appropriate to the hazardous substances and conditions present, such as:
((•)) (a) Procedures that address the use of engineering controls, hazardous substance handling, and new technologies;
((•)) (b) Procedures that address decontamination;
((•)) (c) Procedures that address PPE; and
((•)) (d) Procedures that limit the number of personnel to those who are actively performing emergency response operations, in areas where exposure could exist.
(3) Designate an incident safety officer (ISO).
((•)) Make sure the ISO demonstrates knowledge about operations being implemented at the emergency response site. They must:
((–)) (a) Identify and evaluate hazards;
((–)) (b) Communicate with the IC about hazards, immediately informing the IC of corrective actions that must be taken when conditions are judged to be:
((♦)) (i) An imminent danger; or
((OR
♦)) (ii) Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH).
((–)) (c) Provide direction about the safety of operations.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-50025 Use the buddy system in danger areas.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure operations and tasks (including limited actions) in danger areas are conducted using the buddy system in teams of two or more.
Definition:
Danger areas are areas where conditions pose a serious danger to employees, such as areas where:
((•)) (a) Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) conditions could exist((.)); or
((OR
•)) (b) High levels of exposure to toxic substances could exist((.));
((OR
•)) (c) There is a potential for exceeding the lower explosive limit (LEL), also known as the lower flammability limit (LFL), of a hazardous substance.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 03-09-110, filed 4/22/03, effective 8/1/03)
WAC 296-824-50030 Provide rescue and medical assistance.
((You must:))
(1) You must provide stand-by employees equipped with the same level of personal protective equipment (PPE) as the entrants, for assistance or rescue.
Note: | ((•)) 1. The buddy system applies to stand-by employees (see WAC 296-824-50025). |
((•)) 2. One of the two stand-by employees can be assigned to another task provided it does not interfere with the performance of the stand-by role. | |
((•)) 3. Rescue equipment should be selected and provided based on the types of rescue situations that could occur. |
((You must:))
(2) You must make sure employees trained in first aid are readily available with necessary medical equipment and have a way to transport the injured.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Employee training is covered by WAC 296-800-150, first aid. This rule requires training on the eighteen subjects listed in addition to any subjects that are specific to your workplace emergency hazards (for example: If exposure to corrosive substances could occur, training would need to include first-aid procedures for treating chemical burns). |
((•)) 2. Employers who designate and train their employees to provide first aid are covered by chapter 296-823 WAC, Occupational exposure to bloodborne pathogens. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-600 Personal protective equipment.
Summary.
Your responsibility:
To provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and make sure it is used properly.
((You must:
Use appropriate personal protective equipment
WAC 296-824-60005
Control hazards created by PPE
WAC 296-824-60010
Use PPE properly
WAC 296-824-60015.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Personal protective equipment |
WAC 296-824-60005 |
Control hazards created by personal protective equipment (PPE) |
WAC 296-824-60010 |
Use personal protective equipment (PPE) properly |
WAC 296-824-60015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-05-071, filed 2/17/09, effective 4/1/09)
WAC 296-824-60005 Personal protective equipment.
Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
Note: | ((•)) 1. Only properly trained employees should select PPE. Hazardous materials technicians and hazardous materials specialists can select PPE within the competencies specified in Table 4. |
((•)) 2. Selection requirements in other PPE rules also apply, including: | |
((–)) a. WAC 296-800-160((,)) Personal protective equipment. | |
((–)) b. Chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators. | |
((–)) c. WAC 296-24-58505((,)) Fire brigades. | |
((–)) d. Chapter 296-305 WAC, Safety standards for firefighting. |
((You must:
•)) (1) You must provide appropriate PPE at no cost to the employees and make sure it is used if hazards could be present.
((–)) (2) You must select PPE (such as respirators, gloves, protective suits and other PPE) based on:
((♦)) (a) An evaluation of the performance characteristics (such as breakthrough time and hazardous substance-specificity of the material or item) relevant to the requirements and limitations of the site.
((♦)) (b) Task-specific conditions and durations.
((♦)) (c) The hazards and potential hazards of the site (see Table 9, Selecting PPE for Specific Hazards).
((–)) (3) You must select totally encapsulating chemical protective (TECP) suits, as specified in Table 9, that:
((♦)) (a) Maintain positive air pressure.
((♦)) (b) Prevent inward test gas leakage of more than 0.5 percent.
Note: | Follow the manufacturer's recommended procedure for testing a TECP suit's ability to maintain positive air pressure and prevent inward gas leakage. Other established test protocols for these suits, for example NFPA 1991 and ASTM F1052-97, may also be used. |
Table 9 Selecting PPE for Specific Hazards |
|
If: |
Then: |
• Inhalation hazards could be present. |
• Positive-pressure (pressure-demand) self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) OR • A decreased level of respiratory protection only when the incident commander determines, from air monitoring results, that employees will be adequately protected. |
Chemical exposure levels will create a substantial possibility of: • Immediate death. • Immediate serious illness or injury. • Reduced ability to escape. |
Either positive-pressure (pressure-demand): • SCBA • Air-line respirators equipped with an escape air supply. |
Skin absorption of a hazardous substance may result in a substantial possibility of: • Immediate death. • Immediate serious illness or injury. • Reduced ability to escape. |
Protection equivalent to Level A including a totally encapsulating chemical protective (TECP) suit. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-60010 Control hazards created by personal protective equipment (PPE).
((You must:
•)) You must control hazards created by the use of PPE, including:
((–)) (1) Heat stress due to extremely high temperatures.
((–)) (2) Any other employee health hazard and consideration.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-20-034, filed 9/24/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-824-60015 Use personal protective equipment (PPE) properly.
((You must:))
(1) You must make sure employees inspect PPE before, during and after use, following your plan's procedures.
(2) You must make sure employees put on (don) and remove (doff) PPE following your plan's procedures.
(3) You must make sure employees do not interchange self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) air cylinders from different manufacturers, unless all of the following apply:
((•)) (a) There is a life-saving emergency;
((•)) (b) You need a supplemental air supply;
((•)) (c) The cylinders are of the same capacity and pressure rating.
(4) You must make sure compressed air cylinders used with SCBAs meet the testing and service life requirements of the United States Department of Transportation (USDOT). Search at: http://www.dot.gov.
Note: | You can also check with the cylinder manufacturers to obtain USDOT test and service life specifications. |
((You must:))
(5) You must make sure PPE is maintained in a safe and reliable condition using your plan's procedures.
PPE maintenance includes:
((•)) (a) Decontamination;
((•)) (b) Cleaning;
((•)) (c) Inspection;
((•)) (d) Identification of damage or defects;
((•)) (e) Parts repair or replacement;
((•)) (f) Storage or disposal.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-824-70005 Follow the appropriate postemergency response requirements.
Important:
((•)) 1. Postemergency response is the stage of the emergency response where the immediate threat from the release has been stabilized or eliminated, and cleanup of the site has started.
((•)) 2. When cleanup is done by the employees who were part of the initial emergency response, the employees are not covered by this section (however, training, PPE and other requirements in WAC 296-824-20005 through 296-824-60015 apply to these employees).
((You must:))
(1) You must follow Table 10 to determine which requirements apply to your postemergency response activities.
(2) You must maintain clean-up equipment as specified in Table 10.
Table 10 Rules that Apply to Postemergency Response Activities |
|
When response cleanup is performed by employees who were not part of the initial emergency response and: |
The following rules or requirements apply: |
It is necessary to remove hazardous substances, health hazards and contaminated materials (example: Soil) from the site |
Chapter 296-843 WAC, Hazardous waste operations. |
Cleanup is done on plant property using plant or workplace employees AND It is not necessary to remove hazardous substances, health hazards and contaminated materials from the site. |
For training: • WAC 296-24-567(1), Employee emergency action plans • Chapter 296-842 WAC, Respirators • WAC 296-901-140, Hazard communication • Other appropriate training requirements relevant to personal protective equipment (PPE) and decontamination For equipment: • Make sure that all equipment used for clean-up work is serviced and inspected before use. |
REPEALER
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
WAC 296-824-800 |
Definitions. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-835-099 Definitions.
ACGIH. American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists.
Adjacent area. Any area within twenty feet (6.1 m) of a vapor area that is not separated from the vapor area by tight partitions.
ANSI. American National Standards Institute.
Approved. Approved or listed by a nationally recognized testing laboratory. Refer to federal regulation 29 C.F.R. 1910.7, for definition of nationally recognized testing laboratory.
Autoignition temperature. The minimum temperature required to cause self-sustained combustion without any other source of heat.
Detearing. A process for removing excess wet coating material from the bottom edge of a dipped or coated object or material by passing it through an electrostatic field.
Dip tank. A container holding a liquid other than plain water that is used for dipping or coating. An object may be immersed (or partially immersed) in a dip tank or it may be suspended in a vapor coming from the tank.
Flammable liquid. Any liquid having a flashpoint at or below 199.4°F (93°C). Flammable liquids are divided into four categories as follows:
(a) Category 1 shall include liquids having flashpoints below 73.4°F (23°C) and having a boiling point at or below 95°F (35°C).
(b) Category 2 shall include liquids having flashpoints below 73.4°F (23°C) and having a boiling point above 95°F (35°C).
(c) Category 3 shall include liquids having flashpoints at or above 73.4°F (23°C) and at or below 140°F (60°C). When a Category 3 liquid with a flashpoint at or above 100°F (37.8°C) is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it shall be handled in accordance with the requirements for a Category 3 liquid with a flashpoint below 100°F (37.8°C).
(d) Category 4 shall include liquids having flashpoints above 140°F (60°C) and at or below 199.4°F (93°C). When a Category 4 flammable liquid is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it shall be handled in accordance with the requirements for a Category 3 liquid with a flashpoint at or above 100°F (37.8°C).
(e) When liquid with a flashpoint greater than 199.4°F (93°C) is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it shall be handled in accordance with the requirements for a Category 4 flammable liquid.
Flashpoint. The minimum temperature at which a liquid gives off a vapor within a test vessel in sufficient concentration to form an ignitable mixture with air near the surface of the liquid, and shall be determined as follows:
(a) The flashpoint of liquids having a viscosity less than 45 Saybolt universal second(s) at 100°F (37.8°C) and a flashpoint below 175°F (79.4°C) shall be determined in accordance with the Standard Method of Test for Flashpoint by the Tag Closed Tester, ASTM D-56-69 (incorporated by reference; WAC 296-901-14024, Appendix B—Physical hazard criteria).
(b) The flashpoints of liquids having a viscosity of 45 Saybolt universal second(s) or more at 175°F (79.4°C) or higher shall be determined in accordance with the Standard Method of Test for Flashpoint by the Pensky Martens Closed Tester, ASTM D-93-69 (incorporated by reference; WAC 296-901-14024, Appendix B—Physical hazard criteria).
Lower flammable limit. The lowest concentration of a material that will propagate a flame. The LFL is usually expressed as a percent by volume of the material in air (or other oxidant).
NFPA. National Fire Protection Association.
Vapor area. Any area in the vicinity of dip tanks, their drain boards or associated drying, conveying, or other equipment where the vapor concentration could exceed twenty-five percent of the lower flammable limit (LFL) for the liquid in the tank.
You. The employer. See the definition of employer in the safety and health core rules, WAC 296-800-370.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-100 Scope.
IMPORTANT:
A dip tank is a container holding a liquid other than plain water that is used for dipping or coating. An object may be completely or partially immersed (in a dip tank) or it may be suspended in a vapor coming from the tank.
Exemption: Dip tanks that use a molten material (molten metal, alloy, salt, etc.) are not covered by this chapter.
This chapter applies to:
((•)) (1) A dip tank that uses a liquid other than plain water, or the vapor of the liquid, to:
((–)) (a) Clean an object;
((–)) (b) Coat an object;
((–)) (c) Alter the surface of an object; or
((OR
–)) (d) Change the character of an object.
((•)) (2) Draining or drying an object that has been dipped or coated.
Examples of covered dipping and coating operations include, but are not limited to:
((–)) (a) Paint dipping;
((–)) (b) Electroplating;
((–)) (c) Anodizing;
((–)) (d) Pickling;
((–)) (e) Quenching;
((–)) (f) Tanning;
((–)) (g) Degreasing;
((–)) (h) Stripping;
((–)) (i) Cleaning;
((–)) (j) Dyeing;
((–)) (k) Flow coating;
((–)) (l) Roll coating.
Reference: You have to do a hazard assessment to identify hazards or potential hazards in your workplace and determine if PPE is necessary to protect your employees. See personal protective equipment (PPE), WAC 296-800-160, in the core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-110 General requirements.
Summary.
Your responsibility:
Safeguard employees working with dip tanks.
((You must:
CONSTRUCTION
Construct safe dip tanks
WAC 296-835-11005
VENTILATION
Provide proper ventilation for the vapor area
WAC 296-835-11010
Take additional precautions if you recirculate ventilation system exhaust air into the workplace
WAC 296-835-11015
Take additional precautions when using an exhaust hood
WAC 296-835-11020
INSPECTION
Periodically inspect your dip tanks and associated equipment and correct any deficiencies
WAC 296-835-11025
FIRST AID
Make sure employees working near dip tanks know appropriate first-aid procedures
WAC 296-835-11030
CLEANING
Prepare dip tanks before cleaning
WAC 296-835-11035
CYANIDE
Safeguard cyanide tanks
WAC 296-835-11040
WELDING
Protect employees during welding, burning or other work using open flames
WAC 296-835-11045
LIQUIDS HARMFUL TO SKIN
Provide additional protection for employees working near dip tanks that use liquid that may burn, irritate, or otherwise harm the skin
WAC 296-835-11050.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Construction |
|
Construct safe dip tanks |
WAC 296-835-11005 |
Ventilation |
|
Provide proper ventilation for the vapor area |
WAC 296-835-11010 |
Take additional precautions if you recirculate ventilation system exhaust air into the workplace |
WAC 296-835-11015 |
Take additional precautions when using an exhaust hood |
WAC 296-835-11020 |
Inspection |
|
Periodically inspect your dip tanks and associated equipment and correct any deficiencies |
WAC 296-835-11025 |
First Aid |
|
Make sure employees working near dip tanks know appropriate first-aid procedures |
WAC 296-835-11030 |
Cleaning |
|
Prepare dip tanks before cleaning |
WAC 296-835-11035 |
Cyanide |
|
Safeguard cyanide tanks |
WAC 296-835-11040 |
Welding |
|
Protect employees during welding, burning, or other work using open flames |
WAC 296-835-11045 |
Liquid Harmful to Skin |
|
Protect employees that use liquids that may burn, irritate, or otherwise harm the skin |
WAC 296-835-11050 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-11005 Construct safe dip tanks.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure dip tanks, including any drain boards, are strong enough to support the expected load.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-11010 Provide proper ventilation for the vapor area.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure mechanical ventilation meets the requirements of one or more of the following standards:
((–)) (a) NFPA 34-1995, Standard for Dipping and Coating Processes Using Flammable or Combustible Liquids;
((–)) (b) ACGIH's "Industrial Ventilation: A Manual of Recommended Practice" (22nd ed., 1995);
((–)) (c) ANSI Z9.1-1971, Practices for Ventilation and Operation of Open-Surface Tanks and ANSI Z9.2-1979, Fundamentals Governing the Design and Operation of Local Exhaust Systems.
Note: | Some, or all, of the consensus standards (such as ANSI and NFPA) may have been revised. If you comply with a later version of a consensus standard, you will be considered to have complied with any previous version of the same consensus standard. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must limit the vapor area to the smallest practical space by using mechanical ventilation.
((•)) (3) You must keep airborne concentration of any substance below twenty-five percent of its lower flammable limit (LFL).
((•)) (4) You must make sure mechanical ventilation draws the flow of air into a hood or exhaust duct.
((•)) (5) You must have a separate exhaust system for each dip tank if the combination of substances being removed could cause a:
((–)) (a) Fire;
((–)) (b) Explosion; or
((OR
–)) (c) Potentially hazardous chemical reaction.
Reference: You need to keep employee exposure within safe levels when the liquid in a dip tank creates an exposure hazard. See Air contaminants, WAC 296-62-075 through 296-62-07515.
Note: | You may use a tank cover or material that floats on the surface of the liquid to replace or assist ventilation. The method or combination of methods you choose has to maintain the airborne concentration of the hazardous material and the employee's exposure within safe limits. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-835-11015 Take additional precautions if you recirculate ventilation system exhaust air into the workplace.
IMPORTANT:
This section applies if exhaust air from dipping or coating operations that use flammable liquids, or liquids with flashpoints greater than 199.4°F (93°C) is recirculated back into the work environment.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must only recirculate air that contains no substance at a concentration that could pose a health or safety hazard to employees.
((•)) (2) You must make sure any exhaust system that recirculates air into the workplace:
((–)) (a) Passes the air through a device that removes contaminants;
((–)) (b) Sounds an alarm and automatically shuts down the dip tank operation, if the vapor concentration of any substance in the exhaust air exceeds twenty-five percent of its LFL;
((–)) (c) Monitors the concentration of vapor from flammable liquids or liquids with flashpoints greater than 199.4°F (93°C) with approved equipment.
Note: | ((•)) 1. The LFL concentration in the air must be determined after the air passes through the air-cleaning device and before the air reenters the workspace. |
((•)) 2. Most substances will pose a health hazard at a concentration far below twenty-five percent of its LFL. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-11020 Take additional precautions when using an exhaust hood.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure each room with an exhaust hood has a source of outside air that:
((–)) (1) Enters the room in a way that will not interfere with the function of the hood; and
((–)) (2) Replaces at least ninety percent of the air taken in through the hood.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-11025 Periodically inspect your dip tanks and associated equipment and correct any deficiencies.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must inspect or test your dip tanks and associated equipment periodically, including:
((–)) (a) Covers;
((–)) (b) Overflow pipes;
((–)) (c) Bottom drains and valves;
((–)) (d) Electrical wiring, equipment, and grounding connections;
((–)) (e) Ventilating systems;
((–)) (f) Fire extinguishing equipment.
((•)) (2) You must inspect the hoods and ductwork of the ventilation system for corrosion and damage and make sure the airflow is adequate:
((–)) (a) At least quarterly during operation;
((–)) (b) Prior to operation after a prolonged shutdown.
((•)) (3) You must promptly fix any deficiencies found.
Note: | ((•)) 1. To assist you in tracking your inspections and actions taken from those inspections, you may want to keep a written record. |
((•)) 2. It is recommended that inspections be at least quarterly even if the system is not operating. Depending on the chemicals in use more frequent inspection may be required. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 17-02-066, filed 1/3/17, effective 2/3/17)
WAC 296-835-11030 Make sure employees working near dip tanks know appropriate first-aid procedures.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure your employees know the appropriate first-aid procedures for the hazards of your dipping and coating operations.
Note: | ((•)) 1. First-aid procedures are contained in the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the chemicals used in the dip tank. |
((•)) 2. First-aid supplies appropriate for the hazards of the dipping or coating operation need to be located near the dip tank to be considered "readily available" as required by WAC 296-800-15020. |
Reference: There are additional requirements that may include providing emergency washing facilities and employee training. See first aid, WAC 296-800-150, and chapter 296-901 WAC, Globally harmonized system for hazard communication, in the safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-835-11035 Prepare dip tanks before cleaning.
((You must:)) (1) You must drain the contents of the tank and open any cleanout doors.
(2) You must ventilate the tank to clear any accumulated hazardous vapors.
Reference: There may be requirements that apply before an employee enters a dip tank. See chapter 296-809 WAC, Confined spaces.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-11040 Safeguard cyanide tanks.
((You must:
•)) You must provide a dike or other safeguard(s) to prevent cyanide from mixing with an acid if a dip tank fails.
Note: | This would also apply to spills or other means by which cyanide could come in contact with an acid in sufficient quantity to produce a hazardous gas. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 05-03-093, filed 1/18/05, effective 3/1/05)
WAC 296-835-11045 Protect employees during welding, burning, or other work using open flames.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure the dip tank and the area around it are thoroughly cleaned of solvents and vapors before performing work involving:
((–)) (1) Welding;
((–)) (2) Burning; or
((OR
–)) (3) Open flames.
Reference: There are additional requirements for this type of work. See Welding, cutting and brazing, chapter 296-24 WAC, Part I, and Respiratory protection, chapter 296-842 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-11050 Protect employees that use liquids that may burn, irritate, or otherwise harm the skin.
((You must:)) (1) You must make sure washing facilities, including hot water, are available for every ten employees that work with dip tank liquids.
(2) You must satisfy medical requirements:
((•)) (a) Make sure an employee with any small skin abrasion, cut, rash, or open sore receives treatment by a properly designated person.
((•)) (b) Make sure an employee with a sore, burn, or other skin lesion that needs medical treatment, has a physician's approval before they perform their regular work.
((•)) (c) Make sure employees who work with chromic acid receive periodic examinations of their exposed body parts, especially their nostrils.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Periodic means on a yearly basis unless otherwise indicated. |
((•)) 2. Any time chromic acid spills onto an employee's skin or their clothing is saturated, a physician should be responsible for evaluating and monitoring the area where chromic acid made contact with the skin. |
((You must:))
(3) You must provide lockers or other storage space to prevent contamination of street clothes.
Reference: You have to do a hazard assessment to identify hazards or potential hazards in your workplace and determine if PPE is necessary to protect your employees. See Personal protective equipment (PPE), WAC 296-800-160, in the safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-835-120 Additional requirements for dip tanks using flammable liquids or liquids with flashpoints greater than 199.4°F (93°C).
Summary.
IMPORTANT:
This section applies to((:
•)) flammable liquids or liquids with flashpoints greater than 199.4°F (93.3°C) or higher if you:
((–)) (1) Heat the liquid; and
((–)) (2) Dip a heated object in the tank.
Reference: Store flammable liquids or liquids with a flashpoint greater than 199.4°F (93°C) in accordance with WAC 296-24-330, in the general safety and health standards.
Your responsibility:
Safeguard employees working with dip tanks containing flammable liquids or liquids with a flashpoint greater than 199.4°F (93°C).
((You must:
CONSTRUCTION
Include additional safeguards when constructing dip tanks
WAC 296-835-12005
Provide overflow pipes
WAC 296-835-12010
Provide bottom drains
WAC 296-835-12015
FIRE PROTECTION
Provide fire protection in the vapor area
WAC 296-835-12020
Provide additional fire protection for large dip tanks
WAC 296-835-12025
ELECTRICAL WIRING AND EQUIPMENT AND SOURCES OF IGNITION
Prevent static electricity sparks or arcs when adding liquids to a dip tank
WAC 296-835-12035
Control ignition sources in the vapor area and adjacent area
WAC 296-835-12040
Provide safe wiring and electrical equipment where the liquid can drip or splash
WAC 296-835-12045
HOUSEKEEPING
Keep the area around dip tanks clear of combustible material and properly dispose of waste
WAC 296-835-12050
HEATING LIQUID
Make sure heating the liquid in your dip tanks does not cause a fire
WAC 296-835-12055
HEAT DRYING
Make sure a heating system used for drying objects does not cause a fire
WAC 296-835-12060
CONVEYORS
Make sure the conveyor system for dip tanks is safe
WAC 296-835-12065.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Construction |
|
Include additional safeguards when constructing dip tanks |
WAC 296-835-12005 |
Provide overflow pipes |
WAC 296-835-12010 |
Provide bottom drains |
WAC 296-835-12015 |
Fire Protection |
|
Provide fire protection in the vapor area |
WAC 296-835-12020 |
Provide additional fire protection for large dip tanks |
WAC 296-835-12025 |
Electrical Wiring and Equipment and Sources of Ignition |
|
Prevent static electricity sparks or arcs when adding liquids to a dip tank |
WAC 296-835-12035 |
Control ignition sources |
WAC 296-835-12040 |
Keep the area around dip tanks clear of combustible material and properly dispose of waste |
WAC 296-835-12050 |
Heating Liquid |
|
Make sure heating the liquid in your dip tanks does not cause a fire |
WAC 296-835-12055 |
Heat Drying |
|
Make sure a heating system used for drying objects does not cause a fire |
WAC 296-835-12060 |
Conveyors |
|
Make sure the conveyor systems are safe |
WAC 296-835-12065 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-12005 Include additional safeguards when constructing dip tanks.
((You must:)) (1) You must make sure the dip tank, drain boards (if provided), and supports, are made of noncombustible material.
(2) You must make sure piping connections on drains and overflow pipes allow easy access to the inside of the pipe for inspection and cleaning.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-12010 Provide overflow pipes.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must provide an overflow pipe on dip tanks that:
((–)) (a) Hold more than one hundred fifty gallons of liquid; or
((OR
–)) (b) Have more than ten square feet of liquid surface area.
((•)) (2) You must make sure the overflow pipe is:
((–)) (a) Properly trapped;
((–)) (b) Able to prevent the dip tank from overflowing;
((–)) (c) Three inches or more (7.6 cm) in diameter;
((–)) (d) Discharged to a safe location.
Note: | Discharged to a safe location could be a: |
((–)) 1. Safe location outside the building; or | |
((OR | |
–)) 2. Closed, properly vented salvage tank or tanks that can hold more than the dip tank. |
((You must:
•)) (3) You must make sure the bottom of the overflow pipe is at least six inches (15.2 cm) below the top of the tank.
Note: | The overflow pipe should be large enough to remove water applied to the liquid surface of the dip tank from automatic sprinklers or other sources in the event of fire. Smaller dip tanks should be equipped with overflow pipes, if practical. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-835-12015 Provide bottom drains.
Exemption: A bottom drain is not required if:
((–)) 1. The viscosity of the liquid makes it impractical to empty the tank by gravity or pumping; or
((OR
–)) 2. The dip tank has an automatic closing cover that meets the requirements of WAC 296-835-12025.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must provide a bottom drain on all dip tanks that hold more than five hundred gallons of liquid.
((•)) (2) You must make sure the bottom drain:
((–)) (a) Is properly trapped;
((–)) (b) Will empty the dip tank during a fire;
((–)) (c) Has pipes large enough to empty the tank within five minutes;
((–)) (d) Uses automatic pumps if gravity draining is not practical;
((–)) (e) Is capable of both manual and automatic operation;
((–)) (f) Discharges to a safe location.
Note: | Discharges to a safe location could be a: |
((–)) 1. Safe location outside the building; or | |
((OR | |
–)) 2. Closed, properly vented salvage tank or tanks that can hold more than the dip tank. |
((You must:
•)) (3) You must make sure manual operation of the bottom drain is performed from a safe and easily accessible location.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-835-12020 Provide fire protection in the vapor area.
((You must:
•)) You must provide a manual fire extinguisher near the tank that is suitable for putting out fires involving flammable liquids and liquids with flashpoints greater than 199.4°F (93°C).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-835-12025 Provide additional fire protection for large dip tanks.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must provide at least one automatic fire extinguishing system or an automatic dip tank cover if the tank:
((–)) (a) Holds one hundred fifty gallons or more of liquid; or
((OR
–)) (b) Has four square feet or more of liquid surface area.
((•)) (2) You must make sure automatic fire extinguishing systems or automatic dip tank covers meet the requirements of Table 1.
Exemption: An automatic fire extinguishing system or an automatic dip tank cover is not required for a hardening or tempering tank that:
((•)) 1. Holds less than five hundred gallons; or
((OR
•)) 2. Has less than twenty-five square feet of liquid surface area.
Table 1: Automatic Fire Protection System Requirements
IF YOU PROVIDE: |
THEN YOU MUST: |
An automatic fire extinguishing system |
• Use extinguishing materials suitable for a fire fueled by the liquid in the tank • Make sure the system protects the: – Tanks – Drain boards – Stock over drain boards. |
A dip tank cover |
• Make sure the cover is: – Closed by approved automatic devices in the event of fire – Able to be manually activated – Kept closed when the tank is not being used - Made of noncombustible material or tin-clad material with locked metal joints. |
Reference: Automatic fire extinguishing systems have specific requirements. See:
((–)) 1. WAC 296-24-622 for automatic dry chemical extinguishing system requirements.
((–)) 2. WAC 296-24-623 for automatic carbon dioxide extinguishing system requirements.
((–)) 3. WAC 296-24-627 for automatic water spray extinguishing system and automatic foam extinguishing system requirements.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-12035 Prevent static electricity sparks or arcs when adding liquids to a dip tank.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure any portable container used to add liquid to the tank is:
((–)) (1) Electrically bonded to the dip tank;
((–)) (2) Positively grounded.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-12040 Control ignition sources.
((You must:)) (1) You must make sure the vapor areas and adjacent areas do not have any:
((•)) (a) Open flames.
((•)) (b) Spark producing devices.
((•)) (c) Heated surfaces hot enough to ignite vapors.
(2) You must use explosion-proof wiring and equipment in the vapor area.
Reference: Electrical wiring and equipment has to meet the requirements of the applicable hazardous (classified) location. See Hazardous (classified) locations, WAC 296-24-95613. Electrostatic equipment has specific electrical requirements. See WAC 296-835-13010.
((You must:))
(3) You must prohibit smoking in any vapor area((:)).
((•)) Post an easily seen "NO SMOKING" sign near each dip tank.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-12045 Provide safe electrical wiring and equipment where the liquid can drip or splash.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure all electrical wiring and equipment in the vapor area is approved for areas that have:
((–)) (1) Deposits of easily ignited residue;
((–)) (2) Explosive vapor.
Exemption: This does not apply to wiring that is:
((–)) 1. In rigid conduit, threaded boxes or fittings;
((–)) 2. Has no taps, splices, or terminal connections.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-12050 Keep the area around dip tanks clear of combustible material and properly dispose of waste.
((You must:)) (1) You must make sure the area surrounding dip tanks is:
((–)) (a) Completely free of combustible debris;
((–)) (b) As free of combustible stock as possible.
(2) You must provide approved metal waste cans that are:
((–)) (a) Used for immediate disposal of rags and other material contaminated with liquids from dipping or coating operations;
((–)) (b) Emptied and the contents properly disposed of at the end of each shift.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-12055 Make sure heating the liquid in your dip tanks does not cause a fire.
((You must:
•)) You must keep the temperature of the liquid in the dip tank:
((–)) (1) Below the liquid's boiling point;
((–)) (2) At least 100°F below the liquid's autoignition temperature.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-12060 Make sure a heating system used for drying objects does not cause a fire.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure the heating system used in a drying operation that could cause ignition:
((–)) (1) Has adequate mechanical ventilation that operates before and during the drying operation;
((–)) (2) Shuts down automatically if a ventilating fan fails to maintain adequate ventilation;
((–)) (3) Is installed as required by NFPA 86-1999, Standard for Ovens and Furnaces.
Note: | Some, or all, of the consensus standards (such as ANSI and NFPA) may have been revised. If you comply with a later version of a consensus standard, you will be considered to have complied with any previous version of the same consensus standard. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-12065 Make sure conveyor systems are safe.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure the conveyor system shuts down automatically if:
((–)) (1) The ventilation system fails to maintain adequate ventilation; or
((OR
–)) (2) There is a fire.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-130 Additional requirements for dip tanks used for specific processes.
Summary.
Your responsibility: Safeguard employees working with dip tanks used for specific processes.
((You must:
HARDENING OR TEMPERING
Meet specific requirements if you use a hardening or tempering tank
WAC 296-835-13005
ELECTROSTATIC EQUIPMENT
Meet specific requirements if you use electrostatic equipment
WAC 296-835-13010
FLOW COATING
Meet specific requirements if you use flow coating
WAC 296-835-13015
ROLL COATING
Take additional precautions if your roll coating operation uses a liquid that has a flashpoint below 140°F (60°C)
WAC 296-835-13020
VAPOR DEGREASING
Provide additional safeguards for vapor degreasing tanks
WAC 296-835-13025
SPRAY CLEANING OR DEGREASING
Control liquid spray over an open surface cleaning or degreasing tank
WAC 296-835-13030.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Hardening or Tempering |
|
Meet specific requirements if you use a hardening or tempering tank |
WAC 296-835-13005 |
Electrostatic Equipment |
|
Meet specific requirements if you use electrostatic equipment |
WAC 296-835-13010 |
Flow Coating |
|
Meet specific requirements if you use a flow coating process |
WAC 296-835-13015 |
Roll Coating |
|
Take additional precautions if your roll coating operation uses a liquid that has a flashpoint below 140°F (60°C) |
WAC 296-835-13020 |
Vapor Degreasing |
|
Provide additional safeguards for vapor degreasing tanks |
WAC 296-835-13025 |
Spray Cleaning or Degreasing |
|
Control liquid spray over an open surface cleaning or degreasing tank |
WAC 296-835-13030 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-835-13005 Meet specific requirements if you use a hardening or tempering tank.
((You must:)) (1) You must provide an automatic fire extinguishing system or an automatic dip tank cover for any hardening and tempering tank that uses flammable liquids or liquids with flashpoints greater than 199.4°F (93°C) and:
((–)) (a) Holds five hundred gallons (1893 L) or more of liquid; or
((OR
–)) (b) Has twenty-five square feet (2.37 m2) or more of liquid surface area.
(2) Prevent fires.
((•)) (a) You must make sure hardening and tempering tanks are:
((–)) (i) Not located on or near combustible flooring.
((–)) (ii) Located as far away as practical from furnaces.
((–)) (iii) Equipped with noncombustible hoods and vents (or equally effective devices) for venting to the outside.
((•)) (b) You must treat vent ducts as flues and keep them away from combustible material, particularly roofs.
(3) You must make sure air under pressure is not used to:
((•)) (a) Fill the tank; or
((OR
•)) (b) Agitate the liquid in the tank.
(4) You must equip each tank with an alarm that will sound when the temperature is within 50°F (10°C) of the liquid's flashpoint (alarm set point).
(5) You must make sure a limit switch shuts down conveyors supplying work to the tank when the temperature reaches the alarm setpoint, if operationally practical.
(6) You must have a circulating cooling system if the temperature of the liquid can exceed the alarm set point.
Note: | The bottom drain of the tank may be combined with the oil circulating system if the requirements for bottom drains in WAC 296-835-12015 are satisfied. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-13010 Meet specific requirements if you use electrostatic equipment.
ELECTRICAL
((You must:))
(1) Provide safe electrical equipment.
((•)) (a) You must make sure electrodes in your equipment are:
((–)) (i) Substantial;
((–)) (ii) Rigidly supported;
((–)) (iii) Permanently located;
((–)) (iv) Effectively insulated from ground by insulators.
((•)) (b) You must make sure the insulators are:
((–)) (i) Nonporous;
((–)) (ii) Noncombustible;
((–)) (iii) Kept clean and dry.
((•)) (c) You must make sure high voltage leads to electrodes are effectively:
((–)) (i) Supported on permanent, suitable insulators;
((–)) (ii) Guarded against accidental contact or grounding.
(2) You must make sure transformers, powerpacks, control apparatus, and all other electrical parts of the equipment:
((–)) (a) Are located outside the vapor area; or
((OR
–)) (b) Meet the requirements of WAC 296-835-12040.
Exemption: High voltage grids and their connections may be located in the vapor area without meeting the requirements of WAC 296-835-12040.
PAINT DETEARING
((You must:))
(3) Safeguard paint detearing operations.
((•)) You must use approved electrostatic equipment in paint detearing operations.
(4) You must make sure goods being paint deteared are:
((–)) (a) Supported on conveyors;
((–)) (b) Not manually handled.
(5) You must keep a minimum safe distance (twice the sparking distance) between goods being paint deteared and the electrodes or conductors of the electrostatic equipment at all times by:
((–)) (a) Arranging the conveyors to provide the necessary distance;
((–)) (b) Supporting the goods to prevent swinging or movement, if necessary.
((•)) (6) You must post a sign that shows the minimum safe distance (twice the sparking distance) near the equipment, where it can be easily seen.
(((6))) (7) You must keep paint detearing operations separate from storage areas and people by using fences, rails or guards that are:
((–)) (a) Made of conducting material;
((–)) (b) Adequately grounded.
(((7))) (8) You must protect paint detearing operations from fire by installing:
((–)) (a) Automatic sprinklers; or
((OR
–)) (b) An approved automatic fire extinguishing system.
(((8))) (9) You must collect and remove paint deposits by:
((–)) (a) Providing removable drip plates and screens;
((–)) (b) Cleaning these plates and screens in a safe location.
AUTOMATIC DISCONNECT REQUIREMENT
((You must:
(9))) (10) You must make sure electrostatic equipment has automatic controls that immediately disconnect the power supply to the high-voltage transformer and signal the operator, if:
((•)) (a) Ventilating fans or equipment stop or fail for any reason;
((•)) (b) Conveyors do not work properly;
((•)) (c) A ground (or imminent ground) occurs anywhere in the high-voltage system; or
((OR
•)) (d) Goods being paint deteared come within twice the sparking distance of the electrodes or conductors of the equipment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-13015 Meet specific requirements if you use a flow coating process.
((You must:)) (1) You must make sure all piping is substantial and rigidly supported.
(2) You must make sure the paint is supplied by a:
((•)) (a) Gravity tank that does not hold more than ten gallons (38 L); or
((OR
•)) (b) Direct low-pressure pumping system.
(3) You must have an approved heat-actuated device that shuts down the pumping system if there is a fire.
Note: | The area of the sump, and any areas on which paint flows, should be included in the area of dip tank. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-13020 Take additional precautions if your roll coating operation uses a liquid that has a flashpoint below 140°F (60°C).
IMPORTANT:
This section applies to the processes of roll coating, roll spreading, or roll impregnating that use a liquid having a flashpoint below 140°F (60°C). Material may be passed directly through a tank or over the surface of a roller that revolves partially submerged in the liquid.
((You must:
•)) You must prevent sparks from static electricity by:
((–)) (1) Bonding and grounding all metallic parts (including rotating parts) and installing static collectors; or
((OR
–)) (2) Maintaining a conductive atmosphere (one with a high relative humidity, for example) in the vapor area.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-13025 Provide additional safeguards for vapor degreasing tanks.
((You must:)) (1) You must make sure, if the tank has a condenser or a vapor-level thermostat, that it keeps the vapor level at least:
((•)) (a) Thirty-six inches (91 cm) below the top of the tank if the width of the tank is seventy-two inches or more; or
((OR
•)) (b) One-half the tank width below the top of the tank if the tank is less than seventy-two inches wide.
(2) You must make sure, if you use gas as a fuel to heat the tank liquid, that the combustion chamber is airtight (except for the flue opening) to prevent solvent vapors from entering the air-fuel mixture.
(3) You must make sure the exhaust flue:
((•)) (a) Is made of corrosion-resistant material;
((•)) (b) Extends to the outside;
((•)) (c) Has a draft diverter if mechanical exhaust is used.
(4) You must take special precautions to keep solvent vapors from mixing with the combustion air of the heater if chlorinated or fluorinated hydrocarbon solvents (for example, trichloroethylene or freon) are used in the dip tank.
(5) You must keep the temperature of the heating element low enough to keep a solvent or mixture from:
((•)) (a) Decomposing; or
((OR
•)) (b) Generating excessive vapor.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 02-15-102, filed 7/17/02, effective 10/1/02)
WAC 296-835-13030 Control liquid spray over an open surface cleaning or degreasing tank.
((You must:
•)) You must control the spray to the greatest extent feasible by:
((–)) (1) Enclosing the spraying operation as completely as possible; and
((–)) (2) Using mechanical ventilation to provide enough inward air velocity to prevent the spray from leaving the vapor area.
Note: | Mechanical baffles may be used to help prevent the discharge of spray. |
Reference: Spray painting operations are covered in Spray finishing using flammable and combustible materials, WAC 296-24-370, and Spray-finishing operations, WAC 296-62-11019.
REPEALER
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
WAC 296-835-140 |
Definitions. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-841-099 Definitions.
Breathing zone. The space around and in front of an employee's nose and mouth, forming a hemisphere with a six to nine inch radius.
Ceiling limit. See Permissible exposure limits (PELs).
Dust. Solid particles suspended in air. Dusts are generated by handling, drilling, crushing, grinding, rapid impact, detonation, or decrepitation of organic or inorganic materials such as rock, ore, metal, coal, wood, grain, etc.
Exposed or exposure. The contact an employee has with a toxic substance, harmful physical agent or oxygen deficient condition, whether or not protection is provided by respirators or other personal protective equipment (PPE). Exposure can occur through various routes of entry, such as inhalation, ingestion, skin contact, or skin absorption.
Fume. Solid particles suspended in air, generated by condensation from the gaseous state, generally after volatilization from molten metals, etc.
Gas. A normally formless fluid which can be changed to the liquid or solid state by the effect of increased pressure or decreased temperature or both.
General exhaust ventilation. The general movement of air out of an area or permit-required confined space by mechanical or natural means.
Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH). An atmospheric condition that would:
(a) Cause an immediate threat to life;
(b) Cause permanent or delayed adverse health effects; or
(c) Interfere with an employee's ability to escape.
Mist. Liquid droplets suspended in air, generated by condensation from the gaseous to the liquid state or by breaking up a liquid into a dispersed state, such as by splashing, foaming, spraying or atomizing.
Nuisance dust (or inert dust). Dusts that, when inhaled, have little adverse effect on the lungs and do not produce significant organic disease or toxic effect when exposures are kept under reasonable control.
The biological reaction to these dusts in lung tissue has the following characteristics:
(a) The architecture of the air spaces remains intact;
(b) Scar tissue (collagen) is not formed to a significant extent; and
(c) The tissue reaction is potentially reversible.
Oxygen deficient. An atmosphere with an oxygen content below 19.5% by volume.
Permissible exposure limits (PEL). The amount of an airborne chemical, toxic substance, or other harmful agent that must not be exceeded during any part of the workday.
An airborne chemical or toxic substance can have 3 PEL values:
(a) TWA8. This is an 8-hour, time-weighted average limit.
(b) Short-term exposure limit (STEL). This is typically a 15-minute, time-weighted average limit.
(c) Ceiling limit (C). This is an instantaneous limit.
Short-term exposure limit (STEL). See Permissible exposure limits (PELs).
Temper. To condition air for a specific work environment by changing its temperature or moisture content.
Time weighted average (TWA8). See Permissible exposure limits (PELs).
Toxic substance. Any chemical substance or biological agent, such as bacteria, virus, and fungus, which is any of the following:
(a) Listed in the latest edition of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances (RTECS).
(b) Shows positive evidence of an acute or chronic health hazard in testing conducted by, or known to, the employer.
(c) The subject of a safety data sheet kept by or known to the employer showing the material may pose a hazard to human health.
Vapor. The gaseous form of a substance that is normally in the solid or liquid state.
Ventilation. Providing, circulating or exhausting air into or out of an area or space.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-841-100 Scope.
This chapter applies when your employees are, or could be, exposed to an airborne hazard.
((•)) (1) The following are examples of airborne contaminants that may become airborne hazards in some workplaces:
((–)) (a) Chemicals listed in Table 3, Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) for Airborne Contaminants;
((–)) (b) Any substance:
((■)) (i) Listed in the latest edition of the NIOSH Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances;
((■)) (ii) For which positive evidence of an acute or chronic health hazard exists through tests conducted by, or known to, the employer;
((■)) (iii) That may pose a hazard to human health as stated on a safety data sheet (SDS) kept by, or known to, the employer.
((–)) (c) Biological agents such as harmful bacteria, viruses or fungi.
((■)) Examples include:
(i) TB aerosols ((and));
(ii) Anthrax;
((–)) (iii) Pesticides;
((–)) (iv) Chemicals used as crowd control agents, such as pepper spray; and
((–)) (v) Chemicals present at clandestine drug labs.
((•)) (2) Airborne contaminants exist in a variety of physical forms such as dusts, fibers, fogs, fumes, mists, gases, smoke, sprays, vapors, or aerosols.
((Definition:
Exposed or exposure:
The contact an employee has with a toxic substance, harmful physical agent or oxygen-deficient condition, whether or not protection is provided by respirators or other personal protective equipment (PPE). Exposure can occur through various routes of entry, such as inhalation, ingestion, skin contact, or skin absorption.))
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-841-20005 Exposure evaluations.
(1) Conduct an exposure evaluation to determine or reasonably estimate whether an employee is or could be exposed to either of the following:
((–)) (a) An airborne contaminant above a permissible exposure limit (PEL) listed in Table 3; or
((OR
–)) (b) Other airborne hazards, such as biological hazards.
Note: | ((•)) 1. When evaluating air contaminants, keep in mind that oxygen deficient conditions may also occur due to: |
((–)) a. Processes such as fermentation, decomposition of organic matter, or combustion of fossil fuels. | |
((–)) b. Displacement by another gas such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide. | |
((•)) 2. Rules for specific substances may contain additional requirements for determining employee exposure. | |
((•)) 3. Samples from a representative group of employees may be used for other employees performing the same work activities, when the duration and level of exposure are similar. |
(2) Conclude that an atmosphere is immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) when you cannot determine or reasonably estimate employee exposure.
(3) Do all the following when you perform your evaluation:
(a) Determine the form of the airborne contaminant, such as dust, mist, gas, or biological agent.
(b) Make sure you ((don't)) do not use the amount of protection provided to employees by respirators as a factor in determining whether employees are exposed to an airborne hazard.
(c) Make sure any air monitoring results used to determine employee exposures are based on personal air samples taken from, or representative of, the employee's breathing zone.
((■)) You may use area sampling to screen for the presence of an airborne contaminant; however, results from area sampling ((can't)) cannot be used if they ((don't)) do not adequately represent exposure of affected employees.
(d) Include potential emergency and rescue situations that may occur, such as equipment or power failures, uncontrolled chemical reactions, fire, explosion, or human error.
(e) Include workplace conditions such as work processes, types of material, exposure control methods, work practices, and environmental conditions.
(f) Address extended work periods. For work shifts longer than eight hours, evaluate the continuous eight-hour portion of the shift expected to have the highest average exposure concentration.
(4) Use either of the following types of documentation to conclusively demonstrate that employee exposure cannot meet or exceed any PEL for the airborne contaminant during any reasonably anticipated conditions:
((–)) (a) Personal air samples that represent an employee's usual or worst-case exposure during the entire shift((.)); or
((OR
–)) (b) Specific information about products, materials, or activities that provides for an estimate of the level of employee exposure such as safety data sheets (SDSs), observations, previous air sampling results, other measurements, calculations, or pesticide labels.
Note: | ((•)) You should use methods of sampling and analysis that have been validated by the laboratory performing the analysis. |
(5) Use the following formula to evaluate employee exposure to two or more substances that have additive health effects:
Em |
= |
C1 |
+ |
C2 |
+ |
... |
+ |
Cn |
L1 |
L2 |
Ln |
The symbol |
Is the … |
E |
Equivalent exposure for the mixture. When the value of E is greater than 1, an airborne hazard is present. |
C |
Concentration of a specific airborne contaminant. |
L |
TWA8, STEL, or ceiling limit for that airborne contaminant, from Table 3, Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) for Airborne Contaminants. |
Note: | ((•)) 1. When results from your exposure evaluation indicate an airborne hazard, follow requirements in WAC 296-841-20010 through 296-841-20020 of this chapter. |
((•)) 2. When changes occur that increase the level of exposure to an airborne hazard, you may need to conduct a new exposure evaluation to make sure exposure controls and other protective measures are sufficient. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-05-062, filed 2/20/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-841-20010 Exposure controls.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) Respirators and other personal protective equipment are not exposure controls. Respirators may be used to protect employees while exposure controls are being installed or when ((it's)) it is not feasible to use exposure controls to remove or reduce the airborne hazard.
(1) Use feasible exposure controls to reduce employee exposure to one of the following:
((–)) (a) A level below the permissible exposure limits (PEL) in Table 3;
((–)) (b) A level that removes the airborne hazard, when no PEL is established;
((–)) (c) The lowest achievable level, when exposure cannot be reduced to below the PEL or the airborne hazard ((can't)) cannot be removed.
(2) Make sure exposure controls ((don't)) do not create or increase employee health hazards. For example, when ventilation systems are installed:
((–)) (a) Prevent contaminated exhaust air from either:
((■)) (i) Reentering the building in harmful amounts; or
((or
■)) (ii) Exposing any employee to a health hazard.
((–)) (b) Temper make-up air, when necessary.
((–)) (c) Prevent employee exposure to excessive air velocities.
(3) Use make-up air systems that will not interfere with the effectiveness of the exhaust air system.
((–)) For example, make sure enough make-up air is provided to replace the amount of air exhausted.
Note: | ((•)) Table 1 provides examples of possible exposure controls. |
Table 1
Examples of Possible Controls
Preferred exposure controls include: |
For example: |
Using a different chemical (this is also known as substitution) |
((•)) Choose a chemical with a lower evaporation rate or vapor pressure |
((•)) Choose a chemical ((that's)) that is not hazardous |
|
Changing a process to decrease emissions |
((•)) Use hand rolling or paint dipping instead of paint spraying |
((•)) Bolt items instead of welding them |
|
Separating employees from emissions areas and sources |
((•)) Use control rooms |
((•)) Build an enclosure around process machinery or other emissions sources |
|
((•)) Automate a process |
|
Using local exhaust ventilation to remove emissions at or near the source |
((•)) Install exhaust hoods or slots to capture emissions |
((•)) Use an exhausted enclosure (like a blasting cabinet or laboratory hood) |
|
Other exposure controls include: |
For example: |
Using general exhaust ventilation to dilute and remove emissions in the work area |
((•)) Allow natural air movement to create an adequate airflow through an area |
Note: |
((•)) Use mechanical fans |
This ((isn't)) is not recommended for control of highly toxic airborne contaminants such as carcinogens, where low exposures can still present a health hazard |
|
Modifying work practices |
((•)) Change the position of the employee relative to the work so fumes, vapors, or smoke ((aren't)) are not directed into the employee's face |
Limiting the amount of time employees can spend in a contaminated area. |
((•)) Establish a contaminant-free area for tasks such as prep work that ((don't)) do not need to be done in the exposure area |
Implementing an employee rotation schedule |
Have employees alternate working in the exposure area so that each employee gets less overall exposure |
Note: |
|
This control will increase the number of employees exposed to the airborne contaminant. Due to this risk, employee rotation is NOT recommended for highly toxic airborne contaminants such as carcinogens, where low exposures can still present a health hazard. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-05-062, filed 2/20/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-841-20015 Respirators.
Require employees to use respirators when airborne hazards have not been removed using feasible exposure controls. For example, use respirators at any of the following times:
((–)) (1) While exposure controls are being evaluated or put in place;
((–)) (2) When the airborne hazard is not completely removed;
((–)) (3) When exposure controls are NOT feasible.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-05-062, filed 2/20/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-841-20020 Notification.
Notify employees who are or may be exposed to airborne hazards, as specified in Table 2.
Note: | ((•)) The notification may be provided either individually, to a group, or by posting of results in an appropriate location that is accessible to affected employees. |
Table 2
Notification Requirements
Notify employees of: |
As follows: |
Any exposure result above a permissible exposure limit (PEL) |
Within five business days, after the employee's exposure result is known to the employer |
The corrective action being taken to reduce employee exposure to or below the PEL |
Within fifteen business days, after the employee's exposure result is known to the employer |
AND |
|
The schedule for completion of the corrective action and any reasons why exposures cannot be lowered to below the PEL |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-05-062, filed 2/20/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-841-20025 Permissible exposure limits (PELs).
IMPORTANT:
The following information applies to Table 3, Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) for Airborne Contaminants.
((•)) (1) Ppm refers to parts of vapor or gas per million parts of air by volume, at 25 degrees C and 760 mm Hg pressure.
((•)) (2) Mg/m3 refers to milligrams of an airborne contaminant per cubic meter of air.
((•)) (3) F/cc refers to fibers per cubic centimeter of air.
((•)) (4) For a metal that is measured as the metal itself, only the CAS number for the metal is given. The CAS numbers for individual compounds of the metal are not provided. For more information about CAS registry numbers see the web site: http://www.cas.org.
((•)) (5) Short-term exposure limits (STEL) pertain to fifteen-minute exposure periods, unless another time period is noted in Table 3.
((•)) (6) An "X" in the "skin" column indicates the contaminant can be absorbed through the skin, either by airborne or direct contact.
((–)) (a) Personal protective equipment (PPE) to prevent skin contact may be needed to minimize the risk for adverse health effects when employees are exposed to these chemicals.
((–)) (b) Requirements for the use of gloves, coveralls, goggles, and other personal protective equipment can be found in WAC 296-800-160, Personal protective equipment (PPE).
((•)) (7) Nuisance dusts (also known as inert dusts) are included in the Table 3 listing, particulates not otherwise regulated (PNOR).
((–)) The PNOR listing in Table 3 also applies to other particulate airborne contaminants for which a specific PEL is NOT listed unless the airborne contaminant is found to require a lower limit.
((•)) (8) The respirable fraction of a particulate airborne contaminant is measured by sampling with a size-selector having the following characteristics:
Mean aerodynamic diameter in micrometers |
Percent passing the selector |
1 |
97 |
2 |
91 |
3 |
74 |
4 |
50 |
5 |
30 |
6 |
17 |
7 |
9 |
8 |
5 |
10 |
1 |
Table 3 "Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) for Airborne Contaminants"
Airborne contaminant |
CAS |
TWA8 |
STEL |
Ceiling |
Skin |
Abate (Temephos) |
3383-96-8 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Acetaldehyde |
75-07-0 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Acetic acid |
64-19-7 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Acetic anhydride |
108-24-7 |
—— |
—— |
5 ppm |
—— |
Actinolite (asbestiform) (as asbestos) (see WAC 296-62-077 and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
Acetone |
67-64-1 |
750 ppm |
1,000 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Acetonitrile |
75-05-8 |
40 ppm |
60 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Acetylaminofluorene (see WAC 296-62-073) |
53-96-3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Acetylene |
74-86-2 |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Acetylene dichloride (1,2-Dichloroethylene) |
540-59-0 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Acetylene tetrabromide |
79-27-6 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) |
50-78-2 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Acrolein |
107-02-8 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Acrylamide |
79-06-1 |
0.03 mg/m3 |
0.09 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Acrylic acid |
79-10-7 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
Acrylonitrile (Vinyl cyanide) (see WAC 296-62-07336) |
107-13-1 |
2 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Aldrin |
309-00-2 |
0.25 mg/m3 |
0.75 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Allyl alcohol |
107-18-6 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Allyl chloride |
107-05-1 |
1 ppm |
2 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Allyl glycidyl ether (AGE) |
106-92-3 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Allyl propyl disulfide |
2179-59-1 |
2 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
alpha-Alumina (Aluminum oxide) |
1344-28-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Aluminum (as Al) |
7429-90-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Pyro powders |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Welding fumes |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Soluble salts |
—— |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Alkyls (NOC) |
—— |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Aluminum oxide (Alundum, Corundum) |
7429-90-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
4-Aminodiphenyl (see WAC 296-62-073) |
92-67-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
2-Aminoethanol (Ethanolamine) |
141-43-5 |
3 ppm |
6 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Aminopyridine |
504-29-0 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Amitrole |
61-82-5 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Ammonia |
7664-41-7 |
25 ppm |
35 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ammonium chloride, fume |
12125-02-9 |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Ammonium sulfamate (Ammate) |
7773-06-0 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5.0 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Amosite (as asbestos) (see WAC 296-62-077 and and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
n-Amyl acetate |
628-63-7 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
sec-Amyl acetate |
626-38-0 |
125 ppm |
156 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Aniline and homologues |
62-53-3 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Anisidine (o, p-isomers) |
29191-52-4 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Anthophyllite (asbestiform) (as asbestos) (see WAC 296-62-077 and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
Antimony and compounds (as Sb) |
7440-36-0 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
ANTU (alpha Naphthyl thiourea) |
86-88-4 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
0.9 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Argon |
7440-37-1 |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Arsenic, organic compounds (as As) |
7440-38-2 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Arsenic, inorganic compounds (as As) (when use is covered by chapter 296-848 WAC) |
7440-38-2 |
0.01 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Arsenic, inorganic compounds (as As) (when use is not covered by chapter 296-848 WAC) |
7440-38-2 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Arsine |
7784-42-1 |
0.05 ppm |
0.15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Asbestos (see WAC 296-62-077 and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
Asphalt (Petroleum fumes) |
8052-42-4 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Atrazine |
1912-24-9 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Azinphos methyl (Guthion) |
86-50-0 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Azodrin (Monocrotophos) |
6923-22-4 |
0.25 mg/m3 |
0.75 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Barium, soluble compounds (as Ba) |
7440-39-3 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Barium sulfate |
7727-43-7 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Baygon (Propoxur) |
114-26-1 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Benomyl |
17804-35-2 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Benzene (see chapter 296-849 WAC) |
71-43-2 |
1 ppm |
5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Benzidine (see WAC 296-62-073) |
92-87-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
p-Benzoquinone (Quinone) |
106-51-4 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Benzo(a) pyrene (Coal tar pitch volatiles) |
65996-93-2 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Benzoyl peroxide |
94-36-0 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Benzyl chloride |
100-44-7 |
1ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Beryllium and beryllium compounds (as Be) |
7440-41-7 |
0.002 mg/m3 |
0.005 mg/m3 (30 min.) |
0.025 mg/m3 |
—— |
Biphenyl (Diphenyl) |
92-52-4 |
0.2 ppm |
0.6 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Bismuth telluride, undoped |
1304-82-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Bismuth telluride, Se-doped |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Borates, tetra, sodium salts |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Anhydrous |
1330-43-4 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Decahydrate |
1303-96-4 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Pentahydrate |
12179-04-3 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Boron oxide |
1303-86-2 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Boron tribromide |
10294-33-4 |
—— |
—— |
1 ppm |
—— |
Boron trifluoride |
6737-07-2 |
—— |
—— |
1 ppm |
—— |
Bromacil |
314-40-9 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Bromine |
7726-95-6 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Bromine pentafluoride |
7789-30-2 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Bromochloromethane (Chlorobromomthane) |
74-97-5 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Bromoform |
15-25-2 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
X |
Butadiene (1,3-butadiene) (see WAC 296-62-07460) |
106-99-0 |
1 ppm |
5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Butane |
106-97-8 |
800 ppm |
1,000 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Butanethiol (Butyl mercaptan) |
109-79-5 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Butanone (Methyl ethyl ketone) |
78-93-3 |
200 ppm |
300 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Butoxy ethanol (Butyl cellosolve) |
111-76-2 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
X |
n-Butyl acetate |
123-86-4 |
150 ppm |
200 ppm |
—— |
—— |
sec-Butyl acetate |
105-46-4 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
tert-Butyl acetate |
540-88-5 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Butyl acrylate |
141-32-2 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
n-Butyl alcohol |
71-36-3 |
—— |
—— |
50 ppm |
X |
sec-Butyl alcohol |
78-92-2 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
tert-Butyl alcohol |
75-65-0 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Butylamine |
109-73-9 |
—— |
—— |
5 ppm |
X |
Butyl cellosolve (2-Butoxy ethanol) |
111-76-2 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
tert-Butyl chromate (as Cr) (see WAC 296-62-08003) |
1189-85-1 |
0.005 mg/m3 |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
X |
n-Butyl glycidyl ether (BGE) |
2426-08-6 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
n-Butyl lactate |
138-22-7 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—- |
—— |
Butyl mercaptan |
109-79-5 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
o-sec-Butylphenol |
89-72-5 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
p-tert-Butyl-toluene |
98-51-1 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Cadmium oxide fume (as Cd) (see WAC 296-62-074 and 296-155-174) |
1306-19-0 |
0.005 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Cadmium dust and salts (as Cd) (see WAC 296-62-074 and 296-155-174) |
7440-43-9 |
0.005 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Calcium arsenate (see chapter 296-848 WAC) |
—— |
0.01 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Calcium carbonate |
1317-65-3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Calcium cyanamide |
156-62-7 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Calcium hydroxide |
1305-62-0 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Calcium oxide |
1305-78-8 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Calcium silicate |
1344-95-2 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Calcium sulfate |
7778-18-9 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Camphor (synthetic) |
76-22-2 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Caprolactam |
105-60-2 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Dust |
—— |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Vapor |
—— |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Captafol (Difolatan) |
2425-06-1 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Captan |
133-06-2 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Carbaryl (Sevin) |
63-25-2 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Carbofuran (Furadon) |
1563-66-2 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Carbon black |
1333-86-4 |
3.5 mg/m3 |
7 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Carbon dioxide |
124-38-9 |
5,000 ppm |
30,000 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Carbon disulfide |
75-15-0 |
4 ppm |
12 ppm |
—— |
X |
Carbon monoxide |
630-08-0 |
35 ppm |
200 ppm (5 min.) |
1,500 ppm |
—— |
Carbon tetrabromide |
558-13-4 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Carbon tetrachloride (Tetrachloromethane) |
56-23-5 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Carbonyl chloride (Phosgene) |
7803-51-2 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Carbonyl fluoride |
353-50-4 |
2 ppm |
5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Catechol (Pyrocatechol) |
120-80-9 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Cellosolve acetate (2-Ethoxyethylacetate) |
111-15-9 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Cellulose (paper fiber) |
9004-34-6 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Cesium hydroxide |
21351-79-1 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Chlordane |
57-74-9 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Chlorinated camphene (Toxaphen) |
8001-35-2 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Chlorinated diphenyl oxide |
55720-99-5 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Chlorine |
7782-50-5 |
0.5 ppm |
—— |
1 ppm |
—— |
Chlorine dioxide |
10049-04-4 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Chlorine trifluoride |
7790-91-2 |
—— |
—— |
0.1 ppm |
—— |
Chloroacetaldehyde |
107-20-0 |
—— |
—— |
1 ppm |
—— |
a-Chloroacetophenone (Phenacyl chloride) |
532-21-4 |
0.05 ppm |
0.15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Chloroacetyl chloride |
79-04-9 |
0.05 ppm |
0.15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Chlorobenzene (Monochlorobenzene) |
108-90-7 |
75 ppm |
113 ppm |
—— |
—— |
o-Chlorobenzylidene malononitrile (OCBM) |
2698-41-1 |
—— |
—— |
0.05 ppm |
X |
Chlorobromomethane |
74-97-5 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Chloro-1, 3-butadiene (beta-Chloroprene) |
126-99-8 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
Chlorodifluoromethane |
75-45-6 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Chlorodiphenyl (42% Chlorine) (PCB) (Polychlorobiphenyls) |
53469-21-9 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Chlorodiphenyl (54% Chlorine) (Polychlorobiphenyls (PCB)) |
11097-69-1 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
1-Chloro-2, 3-epoxypropane (Epichlorhydrin) |
106-89-8 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
2-Chloroethanol (Ethylene chlorohydrin) |
107-07-3 |
—— |
—— |
1 ppm |
X |
Chloroethylene (vinyl chloride) (See WAC 296-62-07329) |
75-01-4 |
1 ppm |
5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Chloroform (Trichloromethane) |
67-66-3 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1-Chloro-1-nitropropane |
600-25-9 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
—— |
bis-Chloromethyl ether (see WAC 296-62-073) |
542-88-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Chloromethyl methyl ether (Methyl chloromethyl ether) (see WAC 296-62-073) |
107-30-2 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Chloropentafluoroethane |
76-15-3 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Chloropicrin (Nitrotrichloromethane) |
76-06-2 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
beta-Chloroprene (2-Chloro-1, 3-butadiene) |
126-99-8 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
o-Chlorostyrene |
2039-87-4 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
o-Chlorotoluene |
95-49-8 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Chloro-6-trichloromethyl pyridine (Nitrapyrin) |
1929-82-4 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Chlorpyrifos |
2921-88-2 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Chromic acid and chromates (as Cr) (when the compound is not covered by WAC 296-62-08003) |
Varies with compound |
—— |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
—— |
Chromium |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Chromium (VI) compounds (as Cr) (when the compound is covered by WAC 296-62-08003) |
—— |
0.005 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Chromium metal or Chromium (II) compounds Or Chromium (III) compounds |
7440-47-3 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Chromyl chloride (as Cr) (see WAC 296-62-08003) |
14977-61-8 |
0.005 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Chrysene (Coal tar pitch volatiles) |
65996-93-2 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Chrysotile (as asbestos) (see WAC 296-62-077 and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
Clopidol |
2971-90-6 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Coal dust (less than 5% SiO2) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Coal dust (greater than or equal to 5% SiO2) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Coal tar pitch volatiles (benzene soluble fraction) Acridine Anthracene Benzo (a) pyrene Chrysene Phenanthrene Pyrene |
65996-93-2 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Cobalt, metal fume & dust (as Co) |
7440-48-4 |
0.05 mg/m3 |
0.15 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Cobalt carbonyl (as Co) |
10210-68-1 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Cobalt hydrocarbonyl (as Co) |
16842-03-8 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Coke oven emissions (see WAC 296-62-200) |
—— |
0.15 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Copper (as Cu) |
7440-50-8 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Fume |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Dusts and mists |
—— |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Cotton dust (raw) (waste sorting, blending, cleaning, willowing and garetting) (see WAC 296-62-14533) |
—— |
1 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Corundum (Aluminum oxide) |
7429-90-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Crag herbicide (Sesone, Sodium-2, 4-dichloro-phenoxyethyl sulfate) |
136-78-7 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Cresol (all isomers) |
1319-77-3 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Crocidolite (as asbestos) (see WAC 296-62-077 and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
Crotonaldehyde |
123-73-9; 4170-30-3 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Crufomate |
299-86-5 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Cumene |
98-82-8 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
X |
Cyanamide |
420-04-2 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Cyanide (as CN) |
Varies with compound |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Cyanogen |
460-19-5 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Cyanogen chloride |
506-77-4 |
—— |
—— |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
Cyclohexane |
110-82-7 |
300 ppm |
375 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Cyclohexanol |
108-93-0 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
X |
Cyclohexanone |
108-94-1 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
X |
Cyclohexene |
110-83-8 |
300 ppm |
375 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Cyclohexylamine |
108-91-8 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Cyclonite (RDX) |
121-82-4 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
3.0 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Cyclopentadiene |
542-92-7 |
75 ppm |
113 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Cyclopentane |
287-92-3 |
600 ppm |
750 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Cyhexatin (Tricyclohexyltin hydroxide) |
13121-70-5 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
2,4-D (Dichlorophenoxy- acetic acid) |
94-75-7 |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
DBCP (1,2-Dibromo-3- chloropropane) (See WAC 296-62-07342) |
96-12-8 |
0.001 ppm |
—— |
0.005 ppm |
—— |
DDT (Dichlorodiphenyltri- chloroethane) |
50-29-3 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
DDVP, (Dichlorvos) |
62-73-7 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dasanit (Fensulfothion) |
115-90-2 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Decaborane |
17702-41-9 |
0.05 ppm |
0.15 ppm |
—— |
X |
Demeton |
8065-48-3 |
0.01 ppm |
0.03 ppm |
—— |
X |
Diacetone alcohol (4-hydroxy-4-methyl- 2-pentanone) |
123-42-2 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 2-Diaminoethane (Ethylenediamine) |
107-15-3 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Diazinon |
333-41-5 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Diazomethane |
334-88-3 |
0.2 ppm |
0.6 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Diborane |
19287-45-7 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dibrom (see Naled) |
300-76-5 |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
1, 2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane (DBCP) (see WAC 296-62-07342) |
96-12-8 |
0.001 ppm |
—— |
0.005 ppm |
—— |
2-N-Dibutylamino ethanol |
102-81-8 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dibutyl phosphate |
107-66-4 |
1 ppm |
2 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dibutyl phthalate |
84-74-2 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Dichloroacetylene |
7572-29-4 |
—— |
——- |
0.1 ppm |
—— |
o-Dichlorobenzene |
95-50-1 |
—— |
—— |
50 ppm |
—— |
p-Dichlorobenzene |
106-46-7 |
75 ppm |
110 ppm |
—— |
—— |
3, 3'-Dichlorobenzidine (see WAC 296-62-073) |
91-94-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Dichlorodiphenyltri- chloroethane (DDT) |
50-29-3 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Dichlorodifluoromethane |
75-71-8 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 3-Dichloro-5, 5-dimethyl hydantoin |
118-52-5 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
1, 1-Dichloroethane (Ethylidine chloride) |
75-34-3 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 2-Dichloroethane (Ethylene dichloride) |
107-06-2 |
1 ppm |
2 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 1-Dichloroethylene (Vinylidene chloride) |
75-35-4 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 2-Dichloroethylene (Acetylene dichloride) |
540-59-0 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dichloroethyl ether |
111-44-4 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dichlorofluoromethane |
75-43-4 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dichloromethane (Methylene chloride) (See chapter 296-859 WAC) |
75-09-2 |
25 ppm |
125 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 1-Dichloro-1-nitroethane |
594-72-9 |
2 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) |
94-75-7 |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
1, 2-Dichloropropane (Propylene dichloride) |
78-87-5 |
75 ppm |
110 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dichloropropene |
542-75-6 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
X |
2, 2-Dichloropropionic acid |
75-99-0 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dichlorotetrafluoroethane |
76-14-2 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dichlorvos (DDVP) |
62-73-7 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dicrotophos |
141-66-2 |
0.25 mg/m3 |
0.75 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Dicyclopentadiene |
77-73-6 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dicyclopentadienyl iron |
102-54-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Dieldrin |
60-57-1 |
0.25 mg/m3 |
0.75 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Diethanolamine |
111-42-2 |
3 ppm |
6 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Diethylamine |
109-89-7 |
10 ppm |
25 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Diethylaminoethanol |
100-37-8 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
Diethylene triamine |
111-40-0 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Diethyl ether (Ethyl ether) |
60-29-7 |
400 ppm |
500 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Diethyl ketone |
96-22-0 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Diethyl phthalate |
84-66-2 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Difluorodibromomethane |
75-61-6 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Difolatan (Captafol) |
2425-06-1 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Diglycidyl ether (DGE) |
2238-07-5 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dihydroxybenzene (Hydroquinone) |
123-31-9 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Diisobutyl ketone (2, 6- Dimethylheptanone) |
108-83-8 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Diisopropylamine |
108-18-9 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dimethoxymethane (Methylal) |
109-87-5 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dimethyl acetamide |
127-19-5 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dimethylamine |
124-40-3 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
4-Dimethylaminoazo benzene (see WAC 296-62-073) |
60-11-7 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Dimethylaminobenzene (Xylidene) |
1300-73-8 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dimethylaniline (N, N-Dimethylaniline) |
121-69-7 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dimethylbenzene (Xylene) |
1300-73-8 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Dimethyl-1, 2-dibromo-2, 2-dichloroethyl phosphate (Naled) |
300-76-5 |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Dimethylformamide |
68-12-2 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
2, 6-Dimethylheptanone (Diisobutyl ketone) |
108-83-8 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 1-Dimethylhydrazine |
57-14-7 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dimethyl phthalate |
131-11-3 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Dimethyl sulfate |
77-78-1 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dinitolmide (3, 5-Dinitro-o-toluamide) |
148-01-6 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Dinitrobenzene (all isomers - alpha, meta and para) |
528-29-0; 99-65-0; 100-25-4 |
0.15 ppm |
0.45 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dinitro-o-cresol |
534-52-1 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
3, 5-Dinitro-o-toluamide (Dinitolmide) |
148-01-6 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Dinitrotoluene |
25321-14-6 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Dioxane (Diethylene dioxide) |
123-91-1 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dioxathion |
78-34-2 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Diphenyl (Biphenyl) |
92-52-4 |
0.2 ppm |
0.6 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Diphenylamine |
122-39-4 |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Diphenylmethane diisocyanate (Methylene bisphenyl isocyanate (MDI)) |
101-68-8 |
—— |
—— |
0.02 ppm |
—— |
Dipropylene glycol methyl ether |
34590-94-8 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
X |
Dipropyl ketone |
123-19-3 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Diquat |
85-00-7 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Di-sec, Octyl phthalate (Di-2-ethylhexylphthalate) |
117-81-7 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Disulfram |
97-77-8 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Disulfoton |
298-04-4 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
2, 6-Di-tert-butyl-p-cresol |
128-37-0 |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Diuron |
330-54-1 |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Divinyl benzene |
1321-74-0 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Emery |
12415-34-8 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Endosulfan (Thiodan) |
115-29-7 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Endrin |
72-20-8 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Epichlorhydrin (1-Chloro-2, 3-epoxypropane) |
106-89-8 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
EPN |
2104-64-5 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
1, 2-Epoxypropane (Propylene oxide) |
75-56-9 |
20 ppm |
30 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2, 3-Epoxy-1-propanol (Glycidol) |
556-52-5 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethane |
—— |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Ethanethiol (Ethyl mercaptan) |
75-08-1 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethanol (Ethyl alcohol) |
64-17-5 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethanolamine (2-Aminoethanol) |
141-43-5 |
3 ppm |
6 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethion |
563-12-2 |
0.4 mg/m3 |
1.2 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
2-Ethoxyethanol (Glycol monoethyl ether) |
110-80-5 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
2-Ethoxyethyl acetate (Cellosolve acetate) |
111-15-9 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Ethyl acetate |
141-78-6 |
400 ppm |
500 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethyl acrylate |
140-88-5 |
5 ppm |
25 ppm |
—— |
X |
Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) |
64-17-5 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethylamine |
75-04-07 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethyl amyl ketone (5-Methyl-3-hepatone) |
541-85-5 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethyl benzene |
100-41-4 |
100 ppm |
125 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethyl bromide |
74-96-4 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethyl butyl ketone (3-Heptanone) |
106-35-4 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethyl chloride |
75-00-3 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethylene |
74-85-1 |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Ethylene chlorohydrin (2-Chloroethanol) |
107-07-3 |
—— |
—— |
1 ppm |
X |
Ethylenediamine (1,2- Diaminoethane) |
107-15-3 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
Ethylene dibromide |
106-93-4 |
0.1 ppm |
0.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethylene dichloride (1,2-Dichloroethane) |
107-06-2 |
1 ppm |
2 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethylene glycol |
107-21-1 |
—— |
—— |
50 ppm |
—— |
Ethylene glycol dinitrate |
628-96-6 |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate (Methyl cellosolve acetate) |
—— |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Ethyleneimine (see WAC 296-62-073) |
151-56-4 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
X |
Ethylene oxide (see chapter 296-855 WAC) |
75-21-8 |
1 ppm |
5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethyl ether (Diethyl ether) |
60-29-7 |
400 ppm |
500 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethyl formate |
109-94-4 |
100 ppm |
125 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethylidine chloride (1, 1-Dichloroethane) |
107-06-2 |
1 ppm |
2 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethylidene norbornene |
16219-75-3 |
—— |
—— |
5.0 ppm |
—— |
Ethyl mercaptan (Ethanethiol) |
75-08-1 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
n-Ethylmorpholine |
100-74-3 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Ethyl sec-amyl ketone (5-methyl-3-heptanone) |
541-85-5 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Ethyl silicate |
78-10-4 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Fenamiphos |
22224-92-6 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Fensulfothion (Dasanit) |
115-90-2 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Fenthion |
55-38-9 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Ferbam |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
14484-64-1 |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Ferrovanadium dust |
12604-58-9 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Fluorides (as F) |
Varies with compound |
2.5 mg/m3 |
5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Fluorine |
7782-41-4 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Fluorotrichloromethane (see Trichlorofluoro methane) |
75-69-4 |
—— |
—— |
1,000 ppm |
—— |
Fonofos |
944-22-9 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Formaldehyde (see chapter 296-856 WAC) |
50-00-0 |
0.75 ppm |
2 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Formamide |
75-12-7 |
20 ppm |
30 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Formic acid |
64-18-6 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Furadon (carbofuran) |
1563-66-2 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Furfural |
98-01-1 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Furfuryl alcohol |
98-00-0 |
10 ppm |
15 ppm |
—— |
X |
Gasoline |
8006-61-9 |
300 ppm |
500 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Germanium tetrahydride |
7782-65-2 |
0.2 ppm |
0.6 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Glass, fibrous or dust |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Glutaraldehyde |
111-30-8 |
—— |
—— |
0.2 ppm |
—— |
Glycerin mist |
56-81-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Glycidol (2, 3-Epoxy-1-propanol) |
556-52-5 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Glycol monoethyl ether (2-Ethoxyethanol) |
110-80-5 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Grain dust (oat, wheat, barley) |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Graphite, natural |
7782-42-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable particulate |
—— |
2.5 mg/m3 |
5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Graphite, synthetic |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Guthion (Azinphosmethyl) |
86-50-0 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Gypsum |
13397-24-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Hafnium |
7440-58-6 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Helium |
—— |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Heptachlor |
76-44-8 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Heptane (n-heptane) |
142-82-5 |
400 ppm |
500 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Heptanone (Methyl n-amyl ketone) |
110-43-0 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
3-Heptanone (Ethyl butyl ketone) |
106-35-4 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Hexachlorobutadiene |
87-68-3 |
0.02 ppm |
0.06 ppm |
—— |
X |
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene |
77-47-4 |
0.01 ppm |
0.03 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Hexachloroethane |
67-72-1 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Hexachloronaphthalene |
1335-87-1 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Hexafluoroacetone |
684-16-2 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Hexane |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
n-hexane |
110-54-3 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
other isomers |
Varies with compound |
500 ppm |
1,000 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Hexanone (Methyl-n-butyl ketone) |
591-78-6 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Hexone (Methyl isobutyl ketone) |
108-10-1 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
sec-Hexyl acetate |
108-84-9 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Hexylene glycol |
107-41-5 |
—— |
—— |
25 ppm |
—— |
Hydrazine |
302-01-2 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Hydrogen |
—— |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Hydrogenated terphenyls |
61788-32-7 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Hydrogen bromide |
10035-10-6 |
—— |
—— |
3.0 ppm |
—— |
Hydrogen chloride |
7647-01-0 |
—— |
—— |
5.0 ppm |
—— |
Hydrogen cyanide |
74-90-8 |
—— |
4.7 ppm |
—— |
X |
Hydrogen fluoride |
7664-39-3 |
—— |
—— |
3 ppm |
—— |
Hydrogen peroxide |
7722-84-1 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Hydrogen selenide (as Se) |
7783-07-5 |
0.05 ppm |
0.15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Hydrogen sulfide |
7783-06-4 |
10 ppm |
15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Hydroquinone (Dihydroxybenzene) |
123-31-9 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
4-Hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pentanone (Diacetone alcohol) |
123-42-2 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Hydroxypropyl acrylate |
99-61-1 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
X |
Indene |
95-13-6 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Indium and compounds (as In) |
7440-74-6 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Iodine |
7553-56-2 |
—— |
—— |
0.1 ppm |
—— |
Iodoform |
75-47-8 |
0.6 ppm |
1.8 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Iron oxide dust and fume (as Fe) |
1309-37-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Iron pentacarbonyl (as Fe) |
13463-40-6 |
0.1 ppm |
0.2 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Iron salts, soluble (as Fe) |
Varies with compound |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Isoamyl acetate |
123-92-2 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Isoamyl alcohol (primary and secondary) |
123-51-3 |
100 ppm |
125 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Isobutyl acetate |
110-19-0 |
150 ppm |
188 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Isobutyl alcohol |
78-83-1 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Isooctyl alcohol |
26952-21-6 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
X |
Isophorone |
78-59-1 |
4 ppm |
—— |
5 ppm |
—— |
Isophorone diisocyanate |
4098-71-9 |
0.005 ppm |
0.02 ppm |
—— |
X |
Isopropoxyethanol |
109-59-1 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Isopropyl acetate |
108-21-4 |
250 ppm |
310 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Isopropyl alcohol |
67-63-0 |
400 ppm |
500 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Isopropylamine |
75-31-0 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
N-Isopropylaniline |
768-52-5 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Isopropyl ether |
108-20-3 |
250 ppm |
313 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Isopropyl glycidyl ether (IGE) |
4016-14-2 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
——- |
—— |
Kaolin |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Ketene |
463-51-4 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Lannate (Methomyl) |
16752-77-5 |
2.5 mg/m3 |
5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Lead, inorganic (as Pb) (see WAC 296-62-07521 and 296-155-176) |
7439-92-1 |
0.05 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Lead arsenate (as Pb) (see WAC 296-62-07521, 296-155-176, and chapter 296-848 WAC) |
3687-31-8 |
0.05 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Lead chromate (as Pb) (see WAC 296-62-08003, 296-62-07521, and 296-155-176) |
7758-97-6 |
0.05 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Limestone |
1317-65-3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Lindane |
58-89-9 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Lithium hydride |
7580-67-8 |
0.025 mg/m3 |
0.075 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
L.P.G. (liquified petroleum gas) |
68476-85-7 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Magnesite |
546-93-0 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Magnesium oxide fume |
1309-48-4 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Malathion |
121-75-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Maleic anhydride |
108-31-6 |
0.25 ppm |
0.75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Manganese and compounds (as Mn) |
7439-96-5 |
—— |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
—— |
Manganese cyclopentadienyl tricarbonyl (as Mn) |
12079-65-1 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Manganese tetroxide and fume (as Mn) |
7439-96-5 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Marble |
1317-65-3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
MBOCA (4, 4'-Methylene bis (2-chloro-aniline)) (see WAC 296-62-073) |
101-14-4 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
X |
MDA (4, 4-Methylene dianiline) (see WAC 296-62-076 and 296-155-173) |
101-77-9 |
0.01 ppm |
0.1 ppm |
—— |
X |
MDI (Methylene bisphenyl isocyanate) (Diphenylmethane diisocyanate) |
101-68-8 |
—— |
—— |
0.02 ppm |
—— |
MEK (Methyl ethyl ketone) (2-Butanone) |
78-93-3 |
200 ppm |
300 ppm |
—— |
—— |
MEKP (Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide) |
1338-23-4 |
—— |
—— |
0.2 ppm |
—— |
Mercury (as Hg) |
7439-97-6 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Aryl and inorganic |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Organo-alkyl compounds |
—— |
0.01 mg/m3 |
0.03 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Vapor |
—— |
0.05 mg/m3 |
0.15 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Mesityl oxide |
141-79-7 |
15 ppm |
25 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methacrylic acid |
79-41-4 |
20 ppm |
30 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methane |
—— |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Methanethiol (Methyl mercaptan) |
74-93-1 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methanol (Methyl alcohol) |
67-56-1 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methomyl (lannate) |
16752-77-5 |
2.5 mg/m3 |
5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Methoxychlor |
72-43-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
2-Methoxyethanol (Methyl cellosolve) |
109-86-4 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
2-Methoxyethyl acetate (Methyl cellosolve acetate) |
110-49-6 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
4-Methoxyphenol |
150-76-5 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Methyl acetate |
79-20-9 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl acetylene (propyne) |
74-99-7 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl acetylene-propadiene mixture (MAPP) |
—— |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl acrylate |
96-33-3 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methylacrylonitrile |
126-98-7 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methylal (Dimethoxy-methane) |
109-87-5 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl alcohol (methanol) |
67-56-1 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methylamine |
74-89-5 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl amyl alcohol (Methyl isobutyl carbinol) |
108-11-2 |
25 ppm |
40 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methyl n-amyl ketone (2-Heptanone) |
110-43-0 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
N-Methyl aniline (Monomethyl aniline) |
100-61-8 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methyl bromide |
74-83-9 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methyl-n-butyl ketone (2-Hexanone) |
591-78-6 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl cellosolve (2-Methoxyethanol) |
109-86-4 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methyl cellosolve acetate (2-Methoxyethyl acetate) |
110-49-6 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methyl chloride |
74-87-3 |
50 ppm |
100 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl chloroform (1, 1, 1-trichlorethane) |
71-55-6 |
350 ppm |
450 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl chloromethyl ether (chloromethyl methyl ether) (see WAC 296-62-073) |
107-30-2 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Methyl 2-cyanoacrylate |
137-05-3 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methylcyclohexane |
108-87-2 |
400 ppm |
500 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methylcyclohexanol |
25639-42-3 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methylcyclohexanone |
583-60-8 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl (as Mn) |
12108-13-3 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Methyl demeton |
8022-00-2 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Methylene bisphenyl isocyanate (MDI) (Diphenylmethane diisocyanate) |
101-68-8 |
—— |
—— |
0.02 ppm |
—— |
4, 4'-Methylene bis (2-chloro-aniline) (MBOCA) (see WAC 296-62-073) |
101-14-4 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
X |
Methylene bis (4-cyclohexylisocyanate) |
5124-30-1 |
—— |
—— |
0.01 ppm |
—— |
Methylene chloride (Dichloromethane) (see chapter 296-859 WAC) |
75-09-2 |
25 ppm |
125 ppm |
—— |
—— |
4, 4-Methylene dianiline (MDA) (see WAC 296-62-076 and 296-155-173) |
101-77-9 |
0.01 ppm |
0.1 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) (2-Butanone) |
78-93-3 |
200 ppm |
300 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP) |
1338-23-4 |
—— |
—— |
0.2 ppm |
—— |
Methyl formate |
107-31-3 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
5-Methyl-3-heptanone (Ethyl amyl ketone) |
541-85-5 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl hydrazine (Monomethyl hydrazine) |
60-34-4 |
—— |
—— |
0.2 ppm |
X |
Methyl iodide |
74-88-4 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methyl isoamyl ketone |
110-12-3 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl isobutyl carbinol (Methyl amyl alcohol) |
108-11-2 |
25 ppm |
40 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methyl isobutyl ketone (Hexone) |
108-10-1 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl isocyanate |
624-83-9 |
0.02 ppm |
0.06 ppm |
—— |
X |
Methyl isopropyl ketone |
563-80-4 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl mercaptan (Methanethiol) |
74-93-1 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl methacrylate |
80-62-6 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl parathion |
298-00-0 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Methyl propyl ketone (2-Pentanone) |
107-87-9 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Methyl silicate |
684-84-5 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
alpha-Methyl styrene |
98-83-9 |
50 ppm |
100 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Mevinphos (Phosdrin) |
7786-34-7 |
0.01 ppm |
0.03 ppm |
—— |
X |
Metribuzin |
21087-64-9 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Mica (Silicates) Respirable fraction |
12001-26-2 |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Molybdenum (as Mo) |
7439-98-7 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Soluble compounds |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Insoluble compounds |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Monochlorobenzene (Chlorobenzene) |
108-90-7 |
75 ppm |
113 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Monocrotophos (Azodrin) |
6923-22-4 |
0.25 mg/m3 |
0.75 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Monomethyl aniline (N-Methyl aniline) |
100-61-8 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
X |
Monomethyl hydrazine |
—— |
—— |
—— |
0.2 ppm |
—— |
Morpholine |
110-91-8 |
20 ppm |
30 ppm |
—— |
X |
Naled (Dibrom) |
300-76-5 |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Naphtha |
8030-30-6 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
X |
Naphthalene |
91-20-3 |
10 ppm |
15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
alpha-Naphthylamine (see WAC 296-62-073) |
134-32-7 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
beta-Naphthylamine (see WAC 296-62-073) |
91-59-8 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Neon |
7440-01-9 |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Nickel carbonyl (as Ni) |
13463-39-3 |
0.001 ppm |
0.003 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Nickel (as Ni) |
7440-02-0 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Metal and insoluble compounds |
—— |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Soluble compounds |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Nicotine |
54-11-5 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Nitrapyrin (2-Chloro-6 trichloromethyl pyridine) |
1929-82-4 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Nitric acid |
7697-37-2 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Nitric oxide |
10102-43-9 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
p-Nitroaniline |
100-01-6 |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Nitrobenzene |
98-95-3 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
X |
4-Nitrobiphenyl (see WAC 296-62-073) |
92-93-3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
p-Nitrochlorobenzene |
100-00-5 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
4-Nitrodiphenyl (see WAC 296-62-073) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Nitroethane |
79-24-3 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Nitrogen |
7727-37-9 |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Nitrogen dioxide |
10102-44-0 |
—— |
1 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Nitrogen oxide (Nitrous oxide) |
10024-97-2 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Nitrogen trifluoride |
7783-54-2 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Nitroglycerin |
55-63-0 |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Nitromethane |
75-52-5 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1-Nitropropane |
108-03-2 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Nitropropane |
79-46-9 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
N-Nitrosodimethylamine (see WAC 296-62-073) |
62-75-9 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Nitrotoluene |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
o-isomer |
88-72-2 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
m-isomer |
98-08-2 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
p-isomer |
99-99-0 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Nitrotrichloromethane (Chloropicrin) |
76-06-2 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Nitrous oxide (Nitrogen oxide) |
10024-97-2 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Nonane |
111-84-2 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Nuisance dusts (see Particulates not otherwise regulated) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Octachloronaphthalene |
2234-13-1 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Octane |
111-65-9 |
300 ppm |
375 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Oil mist mineral (particulate) |
8012-95-1 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Osmium tetroxide (as Os) |
20816-12-0 |
0.0002 ppm |
0.0006 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Oxalic acid |
144-62-7 |
1 mg/m3 |
2 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Oxygen See requirements in other chapters such as: Chapter 296-809 WAC, Confined spaces; chapter 296-843 WAC, Hazardous waste operations; chapter 296-824 WAC, Emergency response; WAC 296-62-100, Oxygen deficient atmospheres |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Oxygen difluoride |
7783-41-7 |
—— |
—— |
0.05 ppm |
—— |
Ozone |
10028-15-6 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Paper fiber (Cellulose) |
9004-34-6 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Paraffin wax fume |
8002-74-2 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Paraquat |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
4685-14-7 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
1910-42-5 |
|||||
2074-50-2 |
|||||
Parathion |
56-38-2 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (see coal tar pitch volatiles) |
—— |
—— |
|||
Particulates not otherwise regulated |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Pentaborane |
19624-22-7 |
0.005 ppm |
0.015 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Pentachloronaphthalene |
1321-64-8 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Pentachlorophenol |
87-86-5 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Pentaerythritol |
115-77-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Pentane |
109-66-0 |
600 ppm |
750 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2-Pentanone (methyl propyl ketone) |
107-87-9 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Perchloroethylene (tetrachloroethylene) |
127-18-4 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Perchloromethyl mercaptan |
594-42-3 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Perchloryl fluoride |
7616-94-6 |
3 ppm |
6 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Perlite |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Petroleum distillates (Naptha, rubber solvent) |
—— |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phenacyl chloride (a-Chloroacetophenone) |
532-21-4 |
0.05 ppm |
0.15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phenol |
108-95-2 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Phenothiazine |
92-84-2 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
p-Phenylene diamine |
106-50-3 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Phenyl ether (vapor) |
101-84-8 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phenyl ether-diphenyl mixture (vapor) |
—— |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phenylethylene (Styrene) |
100-42-5 |
50 ppm |
100 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phenyl glycidyl ether (PGE) |
122-60-1 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phenylhydrazine |
100-63-0 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Phenyl mercaptan |
108-98-5 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phenylphosphine |
638-21-1 |
—— |
—— |
0.05 ppm |
—— |
Phorate |
298-02-2 |
0.05 mg/m3 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Phosdrin (Mevinphos) |
7786-34-7 |
0.01 ppm |
0.03 ppm |
—— |
X |
Phosgene (carbonyl chloride) |
75-44-5 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phosphine |
7803-51-2 |
0.3 ppm |
1 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phosphoric acid |
7664-38-2 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Phosphorus (yellow) |
7723-14-0 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Phosphorous oxychloride |
10025-87-3 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phosphorus pentachloride |
10026-13-8 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phosphorus pentasulfide |
1314-80-3 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Phosphorus trichloride |
12-2-19 |
0.2 ppm |
0.5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Phthalic anhydride |
85-44-9 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
m-Phthalodinitrile |
626-17-5 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Picloram |
1918-02-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Picric acid (2, 4, 6- Trinitrophenol) |
88-89-1 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Pindone (2-Pivalyl-1, 3-indandione, Pival) |
83-26-1 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Piperazine dihydrochloride |
142-64-3 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Pival (Pindone) |
83-26-1 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Plaster of Paris |
26499-65-0 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Platinum (as Pt) |
7440-06-4 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Metal |
—— |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Soluble salts |
—— |
0.002 mg/m3 |
0.006 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Polychlorobiphenyls (Chlorodiphenyls) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
42% Chlorine (PCB) |
53469-21-9 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
54% Chlorine (PCB) |
11097-69-1 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Portland cement |
65997-15-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Potassium hydroxide |
1310-58-3 |
—— |
—— |
2 mg/m3 |
—— |
Propane |
74-98-6 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Propargyl alcohol |
107-19-7 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
X |
beta-Propiolactone (see WAC 296-62-073) |
57-57-8 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Propionic acid |
79-09-4 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Propoxur (Baygon) |
114-26-1 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
n-Propyl acetate |
109-60-4 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
n-Propyl alcohol |
71-23-8 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
X |
n-Propyl nitrate |
627-13-4 |
25 ppm |
40 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Propylene |
—— |
Simple asphyxiant |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Propylene dichloride (1, 2-Dichloropropane) |
78-87-5 |
75 ppm |
110 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Propylene glycol dinitrate |
6423-43-4 |
0.05 ppm |
0.15 ppm |
—— |
X |
Propylene glycol monomethyl ether |
107-98-2 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Propylene imine |
75-55-8 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Propylene oxide (1,2- Epoxypropane) |
75-56-9 |
20 ppm |
30 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Propyne (Methyl acetylene) |
74-99-7 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Pyrethrum |
8003-34-7 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Pyridine |
110-86-1 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Pyrocatachol (Catechol) |
120-80-9 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
X |
Quinone (p-Benzoquinone) |
106-51-4 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
RDX (Cyclonite) |
—— |
1.5 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Resorcinol |
108-46-3 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Rhodium (as Rh) |
7440-16-6 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Insoluble compounds, metal fumes and dusts |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Soluble compounds, salts |
—— |
0.001 mg/m3 |
0.003 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Ronnel |
299-84-3 |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Rosin core solder, pyrolysis products (as formaldehyde) |
8050-09-7 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Rotenone |
83-79-4 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Rouge |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Rubber solvent (naphtha) |
8030-30-6 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Selenium compounds (as Se) |
7782-49-2 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Selenium hexafluoride (as Se) |
7783-79-1 |
0.05 ppm |
0.15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Sesone (Crag herbicide) |
136-78-7 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Sevin (Carbaryl) |
63-25-2 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silane (see Silicon tetrahydride) |
7803-62-5 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Silica, amorphous, precipitated and gel |
112926-00-8 |
6 mg/m3 |
12 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silica, amorphous, diatomaceous earth, containing less than 1% crystalline silica |
61790-53-2 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
6 mg/m3 |
12 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silica, crystalline cristobalite |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
14464-46-1 |
0.05 mg/m3 |
0.15 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silica, crystalline quartz |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
14808-60-7 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silica, crystalline tripoli (as quartz) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
1317-95-9 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silica, crystalline tridymite |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
15468-32-3 |
0.05 mg/m3 |
0.15 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silica, fused |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
60676-86-0 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silicates (less than 1% crystalline silica) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Mica |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
12001-26-2 |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Soapstone |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
6 mg/m3 |
12 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Talc (containing asbestos) (as asbestos) (see WAC 296-62-07705 and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
Talc (containing no asbestos) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
14807-96-6 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Tremolite (asbestiform) (as asbestos) (see WAC 296-62-07705 and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
Silicon |
7440-21-3 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silicon carbide |
409-21-2 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Silicon tetrahydride (Silane) |
7803-62-5 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Silver, metal dust and soluble compounds (as Ag) |
7440-22-4 |
0.01 mg/m3 |
0.03 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Soapstone |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
6 mg/m3 |
12 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Sodium azide (as HN3 or NaN3) |
26628-22-8 |
—— |
—— |
0.1 ppm |
X |
Sodium bisulfite |
7631-90-5 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Sodium-2, 4-dichloro- phenoxyethyl sulfate (Crag herbicide) |
136-78-7 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Sodium fluoroacetate |
62-74-8 |
0.05 mg/m3 |
0.15 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Sodium hydroxide |
1310-73-2 |
—— |
—— |
2 mg/m3 |
—— |
Sodium metabisulfite |
7681-57-4 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Starch |
9005-25-8 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Stibine |
7803-52-3 |
0.1 ppm |
0.3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Stoddard solvent |
8052-41-3 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Strychnine |
57-24-9 |
0.15 mg/m3 |
0.45 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Styrene (Phenylethylene, Vinyl benzene) |
100-42-5 |
50 ppm |
100 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Subtilisins |
9014-01-1 |
—— |
0.00006 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
(60 min.) |
|||||
Sucrose |
57-50-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Sulfotep (TEDP) |
3689-24-5 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Sulfur dioxide |
7446-09-5 |
2 ppm |
5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Sulfur hexafluoride |
2551-62-4 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Sulfuric acid |
7664-93-9 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Sulfur monochloride |
10025-67-9 |
—— |
—— |
1 ppm |
—— |
Sulfur pentafluoride |
5714-22-1 |
—— |
—— |
0.01 ppm |
—— |
Sulfur tetrafluoride |
7783-60-0 |
—— |
—— |
0.1 ppm |
—— |
Sulfuryl fluoride |
2699-79-8 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Sulprofos |
35400-43-2 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Systox (Demeton) |
8065-48-3 |
0.01 ppm |
0.03 ppm |
—— |
X |
2, 4, 5-T (2, 4, 5- tri- chlorophenoxyacetic acid) |
93-76-5 |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Talc (containing asbestos) (as asbestos) (see WAC 296-62-07705 and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
Talc (containing no asbestos) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
14807-96-6 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Tantalum |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Metal and oxide dusts |
7440-25-7 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
TDI (Toluene-2, 4-diisocyanate) |
584-84-9 |
0.005 ppm |
0.02 ppm |
—— |
—— |
TEDP (Sulfotep) |
3689-24-5 |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Tellurium and compounds (as Te) |
13494-80-9 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Tellurium hexafluoride (as Te) |
7783-80-4 |
0.02 ppm |
0.06 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Temephos (Abate) |
3383-96-8 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
TEPP |
107-49-3 |
0.004 ppm |
0.012 ppm |
—— |
X |
Terphenyls |
26140-60-3 |
—— |
—— |
0.5 ppm |
—— |
1, 1, 1, 2-Tetrachloro-2, 2-difluoroethane |
76-11-0 |
500 ppm |
625 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 1, 2, 2-Tetrachloro-1, 2-difluoroethane |
76-12-0 |
500 ppm |
625 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 1, 2, 2-Tetrachloroethane |
79-34-5 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
X |
Tetrachloroethylene (Perchloroethylene) |
127-18-4 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Tetrachloromethane (Carbon tetrachloride) |
56-23-5 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Tetrachloronaphthalene |
1335-88-2 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Tetraethyl lead (as Pb) |
78-00-2 |
0.075 mg/m3 |
0.225 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Tetrahydrofuran |
109-99-9 |
200 ppm |
250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Tetramethyl lead (as Pb) |
75-74-1 |
0.075 mg/m3 |
0.225 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Tetramethyl succinonitrile |
3333-52-6 |
0.5 ppm |
1.5 ppm |
—— |
X |
Tetranitromethane |
509-14-8 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Tetrasodium pyrophosphate |
7722-88-5 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Tetryl (2, 4, 6-trinitrophenyl- methylnitramine) |
479-45-8 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Thallium (soluble compounds) (as Tl) |
7440-28-0 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
4, 4-Thiobis (6-tert-butyl-m-cresol) |
96-69-5 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Thiodan (Endosulfan) |
115-29-7 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Thioglycolic acid |
68-11-1 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
——- |
X |
Thionyl chloride |
7719-09-7 |
—— |
—— |
1 ppm |
—— |
Thiram (see WAC 296-62-07519) |
137-26-8 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Tin (as Sn) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Inorganic compounds |
7440-31-5 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Tin (as Sn) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Organic compounds |
7440-31-5 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Tin oxide (as Sn) |
21651-19-4 |
2 mg/m3 |
4 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Titanium dioxide |
13463-67-7 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
TNT (2, 4, 6-Trinitrotoluene) |
118-96-7 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Toluene |
108-88-3 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Toluene-2, 4-diisocyanate (TDI) |
584-84-9 |
0.005 ppm |
0.02 ppm |
——- |
—— |
m-Toluidine |
108-44-1 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
o-Toluidine |
95-53-4 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
p-Toluidine |
106-49-0 |
2.0 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Toxaphene (Chlorinated camphene) |
8001-35-2 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Tremolite (asbestiform) (as asbestos) (see WAC 296-62-07705 and chapter 296-65 WAC) |
—— |
0.1 f/cc |
1.0 f/cc (30 minutes) |
—— |
—— |
Tributyl phosphate |
126-73-8 |
0.2 ppm |
0.6 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Trichloroacetic acid |
76-03-9 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 2, 4-Trichlorobenzene |
120-82-1 |
—— |
—— |
5 ppm |
—— |
1, 1, 1-Trichloroethane (Methyl chloroform) |
71-55-6 |
350 ppm |
450 ppm |
—— |
—— |
1, 1, 2-Trichloroethane |
79-00-5 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Trichloroethylene |
79-01-6 |
50 ppm |
200 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Trichlorofluoromethane (Fluorotrichloromethane) |
75-69-4 |
—— |
—— |
1,000 ppm |
—— |
Trichloromethane (Chloroform) |
67-66-3 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Trichloronaphthalene |
1321-65-9 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
1, 2, 3-Trichloropropane |
96-18-4 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
1, 1, 2-Trichloro-1, 2, 2-trifluoroethane |
76-13-1 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Tricyclohexyltin hydroxide (Cyhexatin) |
13121-70-5 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Triethylamine |
121-44-8 |
10 ppm |
15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Trifluorobromomethane |
75-63-8 |
1,000 ppm |
1,250 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Trimellitic anhydride |
552-30-7 |
0.005 ppm |
0.015 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Trimethylamine |
75-50-3 |
10 ppm |
15 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Trimethyl benzene |
25551-13-7 |
25 ppm |
38 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Trimethyl phosphite |
121-45-9 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
—— |
2, 4, 6-Trinitrophenol (Picric acid) |
88-89-1 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
2, 4, 6-Trinitrophenyl- methylnitramine (Tetryl) |
479-45-8 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
——- |
X |
2, 4, 6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) |
118-96-7 |
0.5 mg/m3 |
1.5 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Triorthocresyl phosphate |
78-30-8 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
X |
Triphenyl amine |
603-34-9 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Triphenyl phosphate |
115-86-6 |
3 mg/m3 |
6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Tungsten (as W) |
7440-33-7 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Soluble compounds |
—— |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Insoluble compounds |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Turpentine |
8006-64-2 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Uranium (as U) |
7440-61-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Soluble compounds |
—— |
0.05 mg/m3 |
0.15 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Insoluble compounds |
—— |
0.2 mg/m3 |
0.6 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
n-Valeraldehyde |
110-62-3 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Vanadium (as V2O5) |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
1314-62-1 |
0.05 mg/m3 |
0.15 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Vegetable oil mist |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Vinyl acetate |
108-05-1 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Vinyl benzene (Styrene) |
100-42-5 |
50 ppm |
100 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Vinyl bromide |
593-60-2 |
5 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Vinyl chloride (Chloroethylene) (see WAC 296-62-07329) |
75-01-4 |
1 ppm |
5 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Vinyl cyanide (Acrylonitrile) (see WAC 296-62-07336) |
107-13-1 |
2 ppm |
10 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Vinyl cyclohexene dioxide |
106-87-6 |
10 ppm |
20 ppm |
—— |
X |
Vinyl toluene |
25013-15-4 |
50 ppm |
75 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Vinylidene chloride (1, 1-Dichloroethylene) |
75-35-4 |
1 ppm |
3 ppm |
—— |
—— |
VM & P Naphtha |
8032-32-4 |
300 ppm |
400 ppm |
—— |
—— |
Warfarin |
81-81-2 |
0.1 mg/m3 |
0.3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Welding fumes (total particulate) |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Wood dust |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Nonallergenic; (All woods except allergenics) |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Allergenics (e.g. cedar, mahogany and teak) |
—— |
2.5 mg/m3 |
5 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Xylenes (ortho, meta, and para isomers) (Dimethylbenzene) |
1330-20-7 |
100 ppm |
150 ppm |
—— |
—— |
m-Xylene alpha, alpha-diamine |
1477-55-0 |
—— |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
X |
Xylidine (Dimethylaminobenzene) |
1300-73-8 |
2 ppm |
4 ppm |
—— |
X |
Yttrium |
7440-65-5 |
1 mg/m3 |
3 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Zinc chloride fume |
7646-85-7 |
1 mg/m3 |
2 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Zinc chromate (as Cr) (see WAC 296-62-08003) |
Varies with compound |
0.005 mg/m3 |
—— |
0.1 mg/m3 |
—— |
Zinc oxide |
1314-13-2 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m |
—— |
—— |
Zinc oxide fume |
1314-13-2 |
5 mg/g3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Zinc stearate |
557-05-1 |
—— |
—— |
—— |
—— |
Total particulate |
—— |
10 mg/m3 |
20 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Respirable fraction |
—— |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Zirconium compounds (as Zr) |
7440-67-2 |
5 mg/m3 |
10 mg/m3 |
—— |
—— |
Reviser's note: The spelling errors in the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
Reviser's note: The typographical error in the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appears in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040.
REPEALER
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
WAC 296-841-300 |
Definitions. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-10200 Definitions.
(((1))) Air-line respirator. An atmosphere-supplying respirator for which breathing air is drawn from a source separate from and not worn by the user, such as:
(a) A cylinder or a tank;
(b) A compressor;
(c) An uncontaminated environment.
Air-purifying respirator (APR) ((means)). A respirator equipped with an air-purifying element such as a filter, cartridge, or canister, OR having a filtering facepiece, for example, a dust mask. The element or filtering facepiece is designed to remove specific contaminants, such as particles, vapors, or gases, from air that passes through it.
(((2) Air-line respirator means an atmosphere-supplying respirator for which breathing air is drawn from a source separate from and not worn by the user, such as:
• A cylinder or a tank;
• A compressor;
• An uncontaminated environment.
(3))) Air supplied respirator (see air-line respirator).
(((4))) Assigned protection factor (APF) ((indicates)). The workplace level of respiratory protection that a respirator or class of respirators is expected to provide to employees when you implement a continuing, effective respiratory protection program as specified by this chapter. For example, an effective program makes sure the respirator is:
((•)) (a) Functioning properly;
((•)) (b) Fitted to the user;
((•)) (c) Worn by trained individuals; and
((•)) (d) Used with the limitations specified on the NIOSH-approval label.
(((5))) Atmosphere-supplying respirator ((means)). A respirator that supplies the user with breathing air from sources, such as:
((•)) (a) A cylinder or a tank;
((•)) (b) A compressor;
((•)) (c) An uncontaminated environment.
(((6))) Breathing air ((means)). Air supplied to an atmosphere-supplying respirator. This air meets the specifications found in WAC 296-842-20005.
(((7))) Canister or cartridge (air-purifying) ((is)). Part of an air-purifying respirator that consists of a container holding materials such as fiber, treated charcoal, or a combination of the two, that removes contaminants from the air passing through the cartridge or canister.
(((8))) Cartridge respirator (see also air-purifying respirator) ((means)). An air-purifying respirator equipped with one or more cartridges. These respirators have a facepiece made from silicone, rubber OR other plastic-like materials.
(((9))) Demand respirator ((means)). An atmosphere-supplying respirator that sends breathing air to the facepiece only when suction (negative pressure) is created inside the facepiece by inhalation. Demand respirators are "negative pressure" respirators.
(((10))) DOSH ((means)). The division of occupational safety and health, located in the department of labor and industries.
(((11))) Dust mask ((is)). A name used to refer to filtering-facepiece respirators. Dust masks may or may not be NIOSH certified. See filtering facepiece.
(((12))) Emergency respirator ((means)). A respirator suitable for rescue, escape, or other activities during emergency situations.
(((13))) Emergency situation ((means)). Any occurrence that could or does result in a significant uncontrolled release of an airborne contaminant. Causes of emergency situations include, but are not limited to, equipment failure, rupture of containers, or failure of control equipment.
(((14))) End-of-service-life indicator (ESLI) ((is)). A system that warns the air-purifying respirator user that cartridges or canisters must be changed. An example of an ESLI is a dot on the respirator cartridge that changes color.
(((15))) Escape-only respirator ((is)). A respirator that can only be used to exit during emergencies. Look for this use limitation on the respirator's NIOSH approval label.
(((16))) Exposed, or exposure ((means)). The contact an employee has with a toxic substance, harmful physical agent, or oxygen deficient condition. Exposure can occur through various routes of entry, such as inhalation, ingestion, skin contact, or skin absorption.
(((17))) Filter ((means)). Fibrous material that removes dust, spray, mist, fume, fog, smoke particles, OR other aerosols from the air.
(((18))) Filtering-facepiece respirator ((means)). A tight-fitting, half-facepiece, negative-pressure, particulate air-purifying respirator with the facepiece mainly composed of filter material. These respirators do not use cartridges or canisters and may have sealing surfaces composed of rubber, silicone or other plastic-like materials. They are sometimes referred to as "dust masks."
(((19))) Fit factor ((is)). A number providing an estimate of fit for a particular respiratory inlet covering to a specific individual during quantitative fit testing.
(((20))) Fit test (see also qualitative fit test and quantitative fit test) ((is)). An activity where the facepiece seal of a respirator is challenged, using a DOSH accepted procedure, to determine if the respirator provides an adequate seal.
(((21))) Full-facepiece respirator ((means)). A tight-fitting respirator that covers the wearer's nose, mouth, and eyes.
(((22))) Gas mask ((means)). An air-purifying respirator equipped with one or more canisters. These respirators have a facepiece made from silicone, rubber OR other plastic-like materials.
(((23))) Half-facepiece respirator ((is)). A tight-fitting respirator that only covers the wearer's nose and mouth.
(((24))) Helmet ((means)). The rigid part of a respirator that covers the wearer's head AND also provides head protection against impact or penetration.
(((25))) High-efficiency particulate air filter (HEPA) ((is)). A powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) filter that removes at least 99.97% of monodisperse dioctyl phthalate (DOP) particles with a mean particle diameter of 0.3 micrometer from contaminated air.
Note: | Filters designated, under 42 C.F.R. Part 84, as an "N100," "R100," or "P100" provide the same filter efficiency (99.97%) as HEPA filters. |
(((26))) Hood ((is)). The part of a respirator that completely covers the wearer's head and neck AND may also cover some or all of the shoulders and torso.
(((27))) Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) ((means)). An atmospheric condition that would:
((•)) (a) Cause an immediate threat to life; ((or
•)) (b) Cause permanent or delayed adverse health effects; or
((•)) (c) Interfere with an employee's ability to escape.
(((28))) Licensed health care professional (LHCP) ((means)). An individual whose legally permitted scope of medical practice allows him or her to provide some or all of the health care services required for respirator users' medical evaluations.
(((29))) Loose-fitting facepiece ((is)). A respiratory inlet covering that is designed to form a partial seal with the face.
(((30))) Negative-pressure respirator ((means)). Any tight-fitting respirator in which the air pressure inside the facepiece is less than the air pressure outside the respirator during inhalation.
(((31))) NIOSH ((is)). The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. NIOSH is the federal agency that certifies respirators for occupational use.
(((32))) Oxygen deficient ((is)). An atmosphere with an oxygen content below 19.5% by volume.
(((33))) Permissible exposure limits (PELs) ((are)). Employee exposures to toxic substances or harmful agents that must not be exceeded. PELs are specified in applicable DOSH chapters.
(((34))) Positive-pressure respirator ((means)). A respirator in which the air pressure inside the respiratory inlet covering is greater than the air pressure outside the respirator.
(((35))) Powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) ((means)). An air-purifying respirator equipped with a blower that draws ambient air through cartridges or canisters. These respirators, as a group, are not classified as positive pressure respirators and must not be used as such.
(((36))) Pressure-demand respirator ((means)). A positive-pressure atmosphere-supplying respirator that sends breathing air to the respiratory inlet covering when the positive pressure is reduced inside the facepiece by inhalation or leakage.
(((37))) Qualitative fit test (QLFT) ((is)). A test that determines the adequacy of respirator fit for an individual. The test relies on the employee's ability to detect a test substance. Test results are either "pass" or "fail."
(((38))) Quantitative fit test (QNFT) ((is)). A test that determines the adequacy of respirator fit for an individual. The test relies on specialized equipment that performs numeric measurements of leakage into the respiratory inlet covering. Test results are used to calculate a "fit factor."
(((39))) Required use ((is)). Respirator use that:
((•)) (a) Is necessary to protect employees from respiratory hazards; or
((•)) (b) The employer decides to require for his or her own reasons. For example, the employer decides to follow more rigorous exposure limits.
(((40))) Respirator ((is)). A type of personal protective equipment designed to protect the wearer from airborne contaminants, oxygen deficiency, or both.
(((41))) Respiratory hazard ((means)). Airborne hazards and oxygen deficiency that are addressed in chapter 296-841 WAC, Airborne contaminants.
(((42))) Respiratory inlet covering ((is)). The part of a respirator that forms the protective barrier between the user's respiratory tract and an air-purifying device or breathing air source or both. The respiratory inlet covering may be a facepiece, helmet, hood, suit, or mouthpiece respirator with nose clamp.
(((43))) Seal check ((means)). Actions conducted by the respirator user each time the respirator is put on, to determine if the respirator is properly seated on the face.
(((44))) Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) ((is)). An atmosphere-supplying respirator designed for the breathing air source, to be carried by the user.
(((45))) Service-life ((means)). The period of time that a respirator, filter or sorbent, or other respiratory equipment provides adequate protection to the wearer. For example, the period of time that sorbent cartridge is effective for removing a harmful substance from the air.
(((46))) Sorbent ((means)). Rigid, porous material, such as charcoal, used to remove vapor or gas from the air.
(((47))) Supplied-air respirator (see air-line respirator).
(((48))) Tight-fitting facepiece ((is)). A respiratory inlet covering forming a complete seal with the face OR neck. Mouthpiece respirators are not tight-fitting facepieces.
(((49))) Voluntary use ((means)). Respirator use that is requested by the employee and permitted by the employer when no respiratory hazard exists.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-11005 Make sure voluntary use of respirators is safe.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) Respirator use is not voluntary, and the required use sections of this chapter apply, if:
((– An employer)) 1. You choose((s)) to require respirator use.
((–)) 2. A respiratory hazard, such as exposure to a substance over the permissible exposure limit (PEL) or hazardous exposure to an airborne biological hazard, is present. To evaluate respiratory hazards in your workplace, see chapter 296-841 WAC, Airborne contaminants.
((–)) 3. Some requirements in this section do not apply if only filtering-facepiece respirators are used voluntarily.
((–)) 4. Some filtering-facepiece respirators are equipped with a sorbent layer for absorbing "nuisance" organic vapors. These can be used for voluntary use, but are not NIOSH certified for protection against hazardous concentrations of organic vapor.
(1) Make sure voluntary respirator use does NOT:
(a) Interfere with an employee's ability to work safely, such as restricting necessary vision or radio communication; or
((OR))
(b) Create health hazards.
Note: | Examples of health hazards include: |
((•)) 1. Skin irritation, dermatitis, or other health effects caused by using a dirty respirator. | |
((•)) 2. Illness created by sharing contaminated respirators. | |
((•)) 3. Health effects caused by use of an unsafe air supply, such as carbon monoxide poisoning. |
(2) Provide all voluntary respirator users with the advisory information in Table 2 at no cost to them.
(3) Develop and maintain a written program that includes the following:
(a) Medical evaluation provisions as specified in WAC 296-842-14005.
(b) Procedures to properly clean and disinfect respirators, according to WAC 296-842-22015, if they are reused.
(c) How to properly store respirators, according to WAC 296-842-17010, so that using them does not create hazards.
(d) Procedures to make sure there is a safe air supply, according to WAC 296-842-20010, when using air-line respirators and SCBAs.
(e) Effective training to ensure respirator use does NOT create a hazard.
Exemption: | If employees use only filtering-facepiece respirators and do so only voluntarily, you do not need to develop and maintain a written program. |
(4) Use Table 2 to provide information to employees who voluntarily use any type of respirator.
Table 2
Advisory Information for Employees Who Voluntarily Use Respirators |
|||
• Respirators protect against airborne hazards when properly selected and used. Respirator usage that is required by DOSH or your employer is not voluntary use. With required use, your employer will need to provide further training and meet additional requirements in this chapter. DOSH recommends voluntary use of respirators when exposure to substances is below DOSH permissible exposure limits (PELs) because respirators can provide you an additional level of comfort and protection. |
|||
• If you choose to voluntarily use a respirator (whether it is provided by you or your employer) be aware that respirators can create hazards for you, the user. You can avoid these hazards if you know how to use your respirator properly AND how to keep it clean. Take these steps: |
|||
– Read and follow all instructions provided by the manufacturer about use, maintenance (cleaning and care), and warnings regarding the respirator's limitations. |
|||
– Choose respirators that have been certified for use to protect against the substance of concern. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) certifies respirators. If a respirator is not certified by NIOSH, you have no guarantee that it meets minimum design and performance standards for workplace use. |
|||
■ A NIOSH approval label will appear on or in the respirator packaging. It will tell you what protection the respirator provides. |
|||
– Keep track of your respirator so you do not mistakenly use someone else's. |
|||
– DO NOT wear your respirator into: |
|||
■ Required use situations when you are only allowed voluntary use. |
|||
■ Atmospheres containing hazards that your respirator is not designed to protect against. |
|||
For example, a respirator designed to filter dust particles will not protect you against solvent vapor, smoke or oxygen deficiency. |
|||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 14-07-086, filed 3/18/14, effective 5/1/14)
WAC 296-842-12005 Develop and maintain a written program.
Exemption: | This section does NOT apply to respirator use that is voluntary. See WAC 296-842-11005 for voluntary use program requirements. |
(1) Develop a complete worksite-specific written respiratory protection program that includes the applicable elements listed in Table 3. The program ((shall)) must cover each employee required by this section to use a respirator.
Note: | Pay for respirators, medical evaluations, fit testing, training, maintenance, travel costs, and wages. |
(2) Keep your program current and effective by evaluating it and making corrections. Do ALL of the following:
(a) Make sure procedures and program specifications are followed and appropriate.
(b) Make sure selected respirators continue to be effective in protecting employees. For example, if changes in work area conditions, level of employee exposure, or employee physical stress have occurred, you need to reevaluate your respirator selection.
(c) Have supervisors periodically monitor employee respirator use to make sure employees are using them properly.
(d) Regularly ask employees required to use respirators about their views concerning program effectiveness and whether they have problems with:
((–)) (i) Respirator fit during use;
((–)) (ii) Any effects of respirator use on work performance;
((–)) (iii) Respirators being appropriate for the hazards encountered;
((–)) (iv) Proper use under current worksite conditions;
((–)) (v) Proper maintenance.
(e) When developing your written program include applicable elements listed in Table 3.
Table 3
Required Elements for Required-Use Respirator Programs |
||
• Selection: |
||
– Procedures for respirator selection |
||
– A list specifying the appropriate respirator for each respiratory hazard in your workplace |
||
– Procedures for issuing the proper type of respirator, if appropriate |
||
• Medical evaluation provisions |
||
• Fit-test provisions and procedures, if tight-fitting respirators are selected |
||
• Training provisions that address: |
||
– Respiratory hazards encountered during: |
||
■ Routine activities |
||
■ Infrequent activities, for example, bimonthly cleaning of equipment |
||
■ Reasonably foreseeable emergencies, for example, rescue, spill response, or escape situations |
||
– Proper use of respirators, for example, how to put on or remove respirators, and use limitations. |
||
Note: |
You do NOT need to repeat training on respiratory hazards if employees have been trained on this in compliance with other rules such as WAC 296-901-140, Hazard communication. |
|
• Respirator use procedures for: |
||
– Routine activities |
||
– Infrequent activities |
||
– Reasonably foreseeable emergencies |
||
• Maintenance: |
||
– Procedures and schedules for respirator maintenance covering: |
||
■ Cleaning and disinfecting |
||
■ Storage |
||
■ Inspection and repair |
||
■ When to discard respirators |
||
– A cartridge or canister change schedule IF air-purifying respirators are selected for use against gas or vapor contaminants AND an end-of-service-life-indicator (ESLI) is not available. In addition, provide: |
||
■ The data and other information you relied on to calculate change schedule values (for example, highest contaminant concentration estimates, duration of employee respirator use, expected maximum humidity levels, user breathing rates, and safety factors) |
||
• Procedures to ensure a safe air quantity and quality IF atmosphere-supplying respirators (air-line or SCBA) are selected |
||
• Procedures for evaluating program effectiveness on a regular basis |
||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-12010 Keep respirator program records.
(1) A written copy of the current respirator program must be kept by the employer.
(2) Keep each employee's current fit test record, if fit testing is conducted, until the next fit test is administered. Fit test records must include:
(a) Employee name;
(b) Test date;
(c) Type of fit-test performed;
(d) Description (type, manufacturer, model, style, and size) of the respirator tested;
(e) Results of fit tests, for example, for quantitative fit tests include the overall fit factor AND a print out, or other recording of the test.
(3) Keep training records that include employees' names and the dates trained.
(4) Keep written recommendations from the LHCP.
Reference: | See chapter 296-802 WAC, Employee medical and exposure records, for additional requirements that apply to medical records. |
(5) ((Employers)) You must allow affected employees and their representatives to examine and copy records required by this section.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-24-071, filed 12/4/12, effective 1/4/13)
WAC 296-842-13005 Select and provide appropriate respirators.
Exemption: | This section does NOT apply to respirator use that is voluntary. See WAC 296-842-11005 for voluntary use program requirements. |
IMPORTANT:
See chapter 296-841 WAC, Airborne contaminants, for:
((•)) 1. Hazard evaluation requirements. Evaluation results are necessary for respirator selection.
((•)) 2. References to substance-specific rules that may also apply to you and have additional respirator selection requirements. These references are found in the permissible exposure limit (PEL) table.
A respirator ((shall)) must be provided to each employee when such equipment is necessary to protect the health of the employee. Select and provide, at no cost to employees, appropriate respirators for routine use, infrequent use, and reasonably foreseeable emergencies (such as escape, emergency, and spill response situations) by completing the following process:
Respirator Selection Process
Step 1: If your only respirator use is for escape, skip to Step 8 to select appropriate respirators.
Step 2: If the respiratory hazard is a biological aerosol, such as TB (tuberculosis), anthrax, psittacosis (parrot fever), or hanta virus, select a respirator appropriate for nonemergency activities recognized to present a health risk to workers AND skip to Step 8.
((•)) (a) If respirator use will occur during emergencies, skip to Step 8 and document the analysis used to select the appropriate respirator.
((•)) (b) Use Centers for Disease Control (CDC) selection guidance for exposures to specific biological agents when this guidance exists. Visit http://www.cdc.gov.
Step 3: If the respiratory hazard is a pesticide, follow the respirator specification on the pesticide label AND skip to Step 9.
Step 4: Determine the expected exposure concentration for each respiratory hazard of concern. Use the results from the evaluation required by chapter 296-841 WAC, Airborne contaminants.
Step 5: Determine if the respiratory hazard is classified as IDLH; if it is NOT IDLH skip to Step 7.
((•)) The respiratory hazard IS classified as IDLH if:
((–)) (a) The atmosphere is oxygen deficient or oxygen enriched;
((OR
–)) (b) You CANNOT measure or estimate your expected exposure concentration; or
((OR
–)) (c) Your measured or estimated expected exposure concentration is greater or equal to the IDLH value in the NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards.
Note: | DOSH uses the IDLH values in the 1990 edition of the NIOSH Pocket Guide to Hazardous Chemicals to determine the existence of IDLH conditions. You may use more recent editions of this guide. Visit www.cdc.gov/niosh for more information. |
Step 6: Select an appropriate respirator from one of the following respirators for IDLH conditions and skip to Step 8:
((•)) (a) Full-facepiece, pressure demand, self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) certified by NIOSH for a minimum service life of thirty minutes; or
((OR
•)) (b) Full-facepiece, pressure demand air-line respirator equipped with an auxiliary self-contained air supply.
Exception: | If the respiratory hazard is oxygen deficiency AND you can show oxygen concentrations can be controlled within the ranges listed in Table 4 under ALL foreseeable conditions, you are allowed to select ANY type of SCBA or air-line respirator: |
Table 4
Concentration Ranges for Oxygen Deficiency
Altitude (as ft. above sea level) |
Oxygen Concentration Range (as percent oxygen) |
Below 3,001 |
16.0 - 19.5 |
3,001 - 4,000 |
16.4 - 19.5 |
4,001 - 5,000 |
17.1 - 19.5 |
5,001 - 6,000 |
17.8 - 19.5 |
6,001 - 7,000 |
18.5 - 19.5 |
7,001 - 8,000 |
19.3 - 19.5 |
Above 8,000 feet the exception does not apply. Oxygen-enriched breathing air must be supplied above 14,000 feet. |
|
Step 7: Select respirator types with assigned protection factors (APFs) from Table 5 that are appropriate to protect employees from the expected exposure concentration.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Appendix B, using assigned protection factors (APFs) for respirator selection, found in this chapter, uses the hazard-ratio approach established by ANSI Z88.2-1992 to determine which respirator types can provide a sufficient level of protection. |
((•)) 2. If no permissible exposure limit (PEL) is established for an airborne contaminant, use relevant available information and informed professional judgment to determine an acceptable exposure limit value to use for calculating hazard ratios. For example, you may use exposure limit values established by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH). |
Step 8: Consider hazards that could require selection of specific respirator types. For example, select full-facepiece respirators to prevent eye irritation or abrasive blasting helmets to provide particle rebound protection.
Note: | Rules for specific substances have additional selection specifications that apply to escape and other types of respirators. Make sure you follow those additional requirements before finalizing your selection. |
Step 9: Evaluate user and workplace factors that might compromise respirator performance, reliability or safety.
Examples:
((•)) (a) High humidity or temperature extremes in the workplace.
((•)) (b) Necessary voice communication.
((•)) (c) High traffic areas and moving machinery.
((•)) (d) If respirator use is for escape only, follow this step and then skip to Step 11.
((•)) (e) If the respiratory hazard is a pesticide, follow the requirements on the pesticide label and skip to Step 11.
((•)) (f) Time or distance for escape.
Step 10: Follow Table 6 requirements to select an air-purifying respirator.
((•)) If Table 6 requirements cannot be met, you must select an appropriate air-line respirator or an SCBA.
Step 11: Make sure respirators you select are certified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
((•)) (a) Respirators provided exclusively for escape from IDLH atmospheres must be NIOSH-certified for escape from the atmosphere in which they will be used.
((•)) (b) To maintain certification, make sure the respirator is used according to cautions and limitations specified on the NIOSH approval label. This includes manufacturer restrictions on cartridges and canisters.
For SCBAs, use only the respirator manufacturer's NIOSH-approved breathing gas containers, marked and maintained in accordance with the Quality Assurance 68 provisions of the NIOSH approval for the SCBA as issued in accordance with the NIOSH respirator certification standard at 42 C.F.R. Part 84.
Note: | While selecting respirators, you will need to select a sufficient number of types, models or sizes to provide for fit testing. You can also consider other respirator use issues, such as accommodating facial hair with a loose fitting respirator. |
Use Table 5 to identify the assigned protection factor for different types of respirators.
((•)) (c) These assigned protection factors are only effective when the employer implements a continuing, effective respirator program as required by this chapter, including training, fit testing, maintenance, and use requirements.
((•)) (d) You may select respirators assigned for use in higher workplace concentrations of a hazardous substance for use at lower concentrations of that substance, or when required use is independent of concentration.
Table 5
Assigned Protection Factors (APF) for Respirator Types
If the respirator is a(n) … |
Then the APF is … |
Air-purifying respirator with a: |
|
• Quarter-mask. . . . |
5 |
• Half-facepiece. This category includes filtering facepiece and elastomeric facepiece models . . . . |
10 |
• Full-facepiece . . . . |
50 |
Powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) with a: |
|
• Loose-fitting facepiece . . . . |
25 |
• Half-facepiece . . . . |
50 |
• Full-facepiece . . . . |
1000 |
• Hood or helmet . . . . |
25/1000 (see note) |
Note: PAPRs with helmets/hoods may receive an APF of 1000 only when you have evidence that testing of these respirators demonstrates performance at a level of protection of 1,000 or greater. Such evidence must be provided by the respirator manufacturer. This level of performance can best be demonstrated by performing a workplace protection factor (WPF) or simulated workplace protection factor (SWPF) study or equivalent testing. |
|
Air-line respirator with a: |
|
• Half-facepiece and designed to operate in demand mode . . . . |
10 |
• Loose-fitting facepiece and designed to operate in continuous flow mode . . . . |
25 |
• Half-facepiece and designed to operate in continuous-flow mode . . . . |
50 |
• Half-facepiece and designed to operate in pressure-demand or other positive-pressure mode. . . . |
50 |
• Full-facepiece and designed to operate in demand mode . . . . |
50 |
• Full-facepiece and designed to operate in continuous-flow mode . . . . |
1000 |
• Full-facepiece and designed to operate in pressure-demand or other positive-pressure mode. . . . |
1000 |
• Helmet or hood and designed to operate in continuous-flow mode . . . . |
25/1000 (see note) |
Note: Air-line respirators with helmets/hoods designed to operate in continuous-flow mode may receive an APF of 1000 when you have evidence that testing of these respirators demonstrates performance at a level of protection of 1,000 or greater. Such evidence must be provided by the respirator manufacturer. This level of performance can best be demonstrated by performing a workplace protection factor (WPF) or simulated workplace protection factor (SWPF) study or equivalent testing. |
|
Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) with a tight fitting: |
|
• Half-facepiece and designed to operate in demand mode . . . . |
10 |
• Full-facepiece and designed to operate in demand mode . . . . |
50 |
• Full-facepiece and designed to operate in pressure-demand or other positive pressure mode (e.g., open/closed circuit) . . . . |
10,000 |
• Helmet or hood and designed to operate in demand mode. . . . |
50 |
• Helmet or hood and designed to operate in pressure-demand or other positive-pressure mode (e.g., open/closed circuit). . . . |
10,000 |
Combination respirators: |
|
• When using a combination respirator, such as an air-line respirator with an air-purifying filter, you must make sure the APF is appropriate to the mode of operation in which the respirator is used . . . . |
|
Escape respirators: |
|
• APFs in this table do not apply to respirators used solely for escape. To select escape respirators, go to Step 8 of this section . . . . |
|
Use Table 6 to select air-purifying respirators for particle, vapor, or gas contaminants.
Table 6
Requirements for Selecting Any Air-purifying Respirator
If the contaminant is a … |
Then … |
|
• Gas OR vapor |
• Provide a respirator with canisters or cartridges equipped with a NIOSH-certified, end-of-service-life indicator (ESLI) |
|
OR |
||
• If a canister or cartridge with an ESLI is NOT available, develop a cartridge change schedule to make sure the canisters or cartridges are replaced before they are no longer effective |
||
OR |
||
• Select an atmosphere-supplying respirator |
||
• Particle, such as a dust, spray, mist, fog, fume, or aerosol |
• Select respirators with filters certified to be at least 95% efficient by NIOSH |
|
– For example, N95s, R99s, P100s, or High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters |
||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-14005 Provide medical evaluations.
Exemption: | This section does not apply to employees who only use: |
((•)) 1. Filtering-facepiece respirators voluntarily. See WAC 296-842-11005 for voluntary use requirements; or | |
((•)) 2. Escape-only respirators that are mouthpiece, loose-fitting, or hooded respirators. |
IMPORTANT:
((•)) 1. If an employee has been provided with a medical evaluation addressing respirator use, as required by another chapter, that evaluation will meet the requirements of this section.
((•)) 2. Using a respirator can create physical risks for an employee each time it is worn. The extent of these risks depends on these factors:
((–)) a. Type of respirator;
((–)) b. Environmental conditions at the worksite;
((–)) c. Physical demands of the work;
((–)) d. Use of the protective clothing;
((–)) e. Employee's health status.
Follow the medical evaluation process, Steps 1 through 7 in this section, to provide medical evaluations for employees at no cost to them.
Medical Evaluation Process
Step 1: Identify employees who need medical evaluations AND determine the frequency of evaluations from Table 7. Include employees who:
((•)) (a) Are required to use respirators; or
((OR
•)) (b) Voluntarily use respirators that are not filtering-facepiece respirators.
Note: | You may use a previous employer's medical evaluation for an employee if you can: |
((•)) 1. Show the employee's previous work and use conditions were substantially similar to yours; and | |
((AND | |
•)) 2. Obtain a copy of the licensed health care professional's (LHCP's) written recommendation approving the employee's use of the respirator chosen by you. |
Step 2: Identify a licensed health care professional (LHCP) to perform your medical evaluations.
Note: | If you select a different LHCP, you do not need to have new medical evaluations done. |
Step 3: Make sure your LHCP has the following information before the evaluation is completed:
((•)) (a) Information describing the respirators employees may use, including the weight and type.
((•)) (b) How the respirators will be used, including:
((–)) (i) How often the respirator will be used, for example, daily, or once a month;
((–)) (ii) The duration of respirator use, for example, a minimum of one hour, or up to twelve hours;
((–)) (iii) The employee's expected physical work effort;
((–)) (iv) Additional personal protective clothing and equipment to be worn;
((–)) (v) Temperature and humidity extremes expected during use((;)).
((•)) (c) A copy of your written respiratory protection program and this chapter.
Note: | ((•)) 1. You may choose to send the questionnaire to the LHCP ahead of time, giving time to review it and add any necessary questions. |
((•)) 2. The LHCP determines what questions to add to the questionnaire, if any; however, questions in Parts 1-3 may not be deleted or substantially altered. |
Step 4: Administer the medical questionnaire in WAC 296-842-22005 to employees, OR provide them a medical exam that obtains the same information.
Note: | You may use online questionnaires if the questions are the same and requirements of this section are met. |
((•)) (a) Administer the examination or questionnaire at no cost to employees:
((–)) (i) During the employee's normal working hours; or
((OR
–)) (ii) At a time and place convenient to the employee.
((•)) (b) Maintain employee confidentiality during examination or questionnaire administration:
((–)) (i) Do not view employee's answers on the questionnaire;
((–)) (ii) Do not act in a manner that may be considered a breach of confidentiality.
Note: | Providing confidentiality is important for securing successful medical evaluations. It helps make sure the LHCP gets complete and dependable answers on the questionnaire. |
((•)) (c) Make sure employees understand the content of the questionnaire.
((•)) (d) Provide the employee with an opportunity to discuss the questionnaire or exam results with the LHCP.
Step 5: Provide follow-up evaluation for employees when:
((•)) (a) The LHCP needs more information to make a final recommendation; or
((OR
•)) (b) An employee gives any positive response to questions 1-8 in Part 2 OR to questions 1-6 in Part 3 of the DOSH medical evaluation questionnaire in WAC 296-842-22005.
Note: | Follow-up may include: |
((•)) 1. Employee consultation with the LHCP such as a telephone conversation to evaluate positive questionnaire responses; | |
((•)) 2. Medical exams; | |
((•)) 3. Medical tests or other diagnostic procedures. |
Step 6: Obtain a written recommendation from the LHCP that contains only the following medical information:
((•)) (a) Whether or not the employee is medically able to use the respirator;
((•)) (b) Any limitations of respirator use for the employee;
((•)) (c) What future medical evaluations, if any, are needed;
((•)) (d) A statement that the employee has been provided a copy of the written recommendation.
Step 7: Provide a powered, air-purifying respirator (PAPR) when the LHCP determines the employee should not wear a negative-pressure air-purifying respirator AND is able to wear a PAPR.
Reference: | See WAC 296-842-13005 for requirements regarding selection of air-purifying respirators. |
Note: | ((•)) 1. You may discontinue medical evaluations for an employee when the employee no longer uses a respirator. |
((•)) 2. If you have staff conducting your medical evaluations, they may keep completed questionnaires and findings as confidential medical records, if they are maintained separately from other records. |
Use Table 7 to determine medical evaluation frequency.
Table 7
Evaluation Frequency
Type of Evaluation: |
When required: |
||
Initial medical evaluations |
• Before respirators are fit-tested or used in the workplace. |
||
Subsequent medical evaluations |
• If any of these occur: |
||
– Your licensed health care professional (LHCP) recommends them; for example, periodic evaluations at specified intervals. |
|||
– A respirator program administrator or supervisor informs you that an employee needs reevaluation. |
|||
– Medical signs or symptoms (such as breathing difficulties) are: |
|||
■ Observed during fit testing or program evaluation; or |
|||
((OR)) |
|||
■ Reported by the employee. |
|||
– Changes in worksite conditions such as physical work effort, personal protective clothing, or temperature that could substantially increase the employee's physiological stress. |
|||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-15005 Conduct fit testing.
Exemption: | This section does not apply to any respirators that are: |
((•)) 1. Voluntarily used. See WAC 296-842-11005 for voluntary use requirements. | |
((•)) 2. Mouthpiece respirators and other escape-only respirators. | |
((•)) 3. Loose-fitting respirators. |
IMPORTANT:
((•)) 1. Fit testing is an activity where the seal of a respirator is tested to determine if it's adequate.
((•)) 2. This section covers general requirements for fit testing. Specific fit testing procedures are covered in WAC 296-842-22010.
(1) Provide, at no cost to the employee, fit tests for ALL tight fitting respirators on the following schedule:
(a) Before employees are assigned duties that may require the use of respirators;
(b) At least every twelve months after initial testing;
(c) Whenever any of the following occurs:
((■)) (i) A different respirator facepiece is chosen such as a different type, model, style, or size;
((■)) (ii) You become aware of a physical change in an employee that could affect respirator fit. For example, you may observe, or be told about, facial scarring, dental changes, cosmetic surgery, or obvious weight changes;
((■)) (iii) An employee notifies you, or your LHCP, that the respirator fit is unacceptable. During the retest, you must give an employee reasonable opportunity to select a different respirator facepiece (size, model, etc.).
Note: | You may accept a fit test completed by a previous employer IF: |
((•)) 1. You obtain written documentation of the fit test; | |
((AND | |
•)) 2. The results of the fit test are not more than twelve months old; | |
((AND | |
•)) 3. The employee will use the same respirator (the same type, model, style, and size); and | |
((AND | |
•)) 4. The fit test was conducted in a way that meets the requirements of WAC 296-842-15005 and 296-842-22010. |
(2) Select and use an appropriate fit-testing procedure from WAC 296-842-22010 of this chapter.
(3) Use quantitative fit-test methods when a negative pressure respirator will be used in concentrations requiring a protection factor greater than 10. This includes:
((■)) (a) Full facepiece air-purifying respirators;
((■)) (b) SCBAs operated in demand (negative pressure) mode;
((■)) (c) Air-line respirators operated in demand mode.
(4) Make sure tight-fitting PAPRs, SCBAs, or air-line respirators are fit tested in negative-pressure mode. This must be done by either:
(a) Temporarily converting the respirator user's actual facepiece into a negative pressure respirator using the appropriate filters; or
((OR))
(b) Using an identical negative pressure air-purifying respirator facepiece as a surrogate for the SCBA, air-line or PAPR. The surrogate facepiece must have the same sealing surfaces as the SCBA, air-line, or PAPR.
Remove any modifications made to the respirator facepiece for fit testing and return the facepiece to the NIOSH approved configuration before the facepiece is used in the workplace.
(5) Make sure the person conducting fit testing is able to do ALL of the following:
(a) Prepare test solutions if required;
(b) Make sure equipment works properly;
(c) Perform tests properly;
(d) Recognize invalid tests;
(e) Calculate fit factors properly if required.
Note: | ((•)) 1. No specific training program or certification is required for those who conduct fit tests. |
((•)) 2. You should consider evaluating these individuals to determine their proficiency in the fit-testing method to be used. | |
((•)) 3. You can use an evaluation form such as the form included in the American National Standard for Respirator Fit Testing Methods, ANSI/AIHA Z88.10-2001 to determine if the individual meets these requirements. Visit www.ansi.org or www.aiha.org. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-16005 Provide effective training.
Exemption: | This section does not apply to respirators that are voluntarily used. See WAC 296-842-11005 for voluntary use requirements. |
(1) Train employees, based on their duties, if they do any of the following:
(a) Use respirators;
(b) Supervise respirator users;
(c) Issue, repair, or adjust respirators.
(2) Present effective training in a way that employees understand.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Training may be provided using audiovisuals, slide presentations, formal classroom instruction, informal discussions during safety meetings, training programs conducted by outside sources, or a combination of these methods. |
((•)) 2. You may want to have instructors available when using video or automated training methods to: | |
((–)) a. Encourage and provide responses to questions for the benefit of employees. | |
((–)) b. Evaluate employees' understanding of the material. | |
((–)) c. Provide other instructional interaction to employees. |
(3) Make sure a qualified instructor provides training.
(4) Provide training, at no cost to the employee, at these times:
(a) Initially, before worksite respirator use begins;
(b) Periodically, within twelve months of the previous training;
(c) Additionally, when the following occur:
((■)) (i) The employee has not retained knowledge or skills; or
((OR
■)) (ii) Changes in the worksite, or type of respirator make previous training incomplete or obsolete.
Note: | ((•)) 1. You may accept an employee's previous training, such as training provided by another employer, to satisfy the initial training requirement if: |
((–)) a. You can demonstrate the employee received training within the past twelve months; and | |
((AND | |
–)) b. The employee can demonstrate the knowledge and skills to use required respirators effectively. | |
((•)) 2. If you accept an employee's previous training to satisfy the initial training requirement, you are still responsible for providing periodic, and additional training when needed. Periodic training would need to be provided within twelve months of the employee's previous training. |
(5) Make sure employees can demonstrate the following knowledge and skills as required by their duties:
(a) Why the respirator is necessary. Include, for example, information identifying respiratory hazards such as hazardous chemicals, the extent of the employee's exposure, and potential health effects and symptoms;
(b) The respirator's capabilities and limitations. Include, for example, how the respirator provides protection and why air-purifying respirators cannot be used in oxygen-deficient conditions;
(c) How improper fit, use, or maintenance can compromise the respirator's effectiveness and reliability;
(d) How to properly inspect, put on, seal check, use, and remove the respirator;
(e) How to clean, disinfect, repair, and store the respirator, or how to get this done by someone else;
(f) How to use the respirator effectively in emergency situations; including what to do when a respirator fails and where emergency respirators are stored;
(g) Medical signs and symptoms that may limit or prevent the effective use of respirators such as shortness of breath or dizziness;
(h) ((The employer's)) Your general obligations under this chapter. For example, developing a written program, selecting appropriate respirators, and providing medical evaluations.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-17005 Maintain respirators in a clean and reliable condition.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) This section applies to employees who voluntarily use respirators only when maintenance is necessary to prevent the respirator from creating a hazard. See WAC 296-842-11005 for voluntary use requirements.
(1) Make sure respirators are kept, at no cost to the employee, clean, sanitary and in good working order.
(2) Clean and disinfect respirators as often as specified in Table 8 of this section.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Use required cleaning and disinfecting procedures in WAC 296-842-22015, or the manufacturer's procedures that: |
((–)) a. Result in a clean and sanitary respirator; | |
((–)) b. Do not damage the respirator; | |
((–)) c. Do not harm the user. | |
((•)) 2. Automated cleaning and disinfecting are permitted. | |
((•)) 3. Cleaning and disinfecting may be done by a central facility as long as you make sure respirators provided are clean, sanitary, and function properly. |
(3) Make sure respirators are assembled properly after cleaning or disinfecting.
Table 8
Required Frequencies for Cleaning and Disinfecting Respirators
If the respirator will be … |
Then clean and disinfect the respirator … |
|
• Used exclusively by one employee |
• As often as needed to: |
|
– Keep it clean and functional; and |
||
((AND)) |
||
– To prevent health hazards such as skin irritation |
||
• Shared for nonemergency use; or |
• Before it is worn by another employee |
|
((OR)) |
||
• Used for fit-testing or training |
||
• Shared for emergency use |
• After each use so the respirator is immediately ready for use at all times |
|
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-05-072, filed 2/20/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-842-17015 Inspect and repair respirators.
(1) Conduct respirator inspections as often as specified in Table 9.
(2) Make sure respirator inspections cover all of the following:
(a) Respirator function;
(b) Tightness of connections;
(c) The condition of the facepiece, head straps, valves, connecting tubes, and cartridge, canisters or filters;
(d) Pliability and deterioration of elastomeric parts;
(e) Maintenance of air or oxygen cylinders;
(f) Making sure SCBA air cylinders are at ninety percent of the manufacturer's recommended pressure level;
(g) Proper functioning of SCBA regulators when air-flow is activated; and
(h) Proper functioning of SCBA low-pressure warning devices when activated.
(3) Certify inspections for emergency respirators by documenting the following:
(a) Inspection date;
(b) Serial number of each respirator or other identifying information;
(c) Inspector's name or signature;
(d) Inspection findings; and
(e) Required action, if problems are found.
Note: | ((•)) When documenting inspections you may either: |
((–)) 1. Provide the information on a tag or label and attach it to the respirator compartment; or | |
((OR | |
–)) 2. Include the information in an inspection report stored in paper or electronic files accessible to employees. |
(4) Repair or replace any respirator that is not functioning properly before the employee returns to a situation where respirators are required.
If respirators fail inspection or are not functioning properly during use due to problems such as leakage, vapor or gas breakthrough, or increased breathing resistance, ALL of the following apply:
(a) Do NOT permit such respirators to be used until properly repaired or adjusted;
(b) Use only NIOSH-certified parts;
(c) Make sure repairs and adjustments are made by appropriately trained individuals;
Use the manufacturer or a technician trained by the manufacturer to repair or adjust reducing and admission valves, regulators, and warning devices on SCBAs or air-line respirators.
(d) Follow the manufacturer's recommendations and specifications for the type and extent of repairs.
(5) Use Table 9 to determine how often to inspect respirators.
Table 9
Required Frequencies for Respirator Inspections
If the respirator is … |
Then inspect … |
A SCBA in any use |
• Before each use; and |
((AND)) |
|
• During cleaning; or |
|
((OR)) |
|
• Monthly if NOT used |
|
Used for nonemergencies, including day-to-day or infrequent use |
• Inspect before each use; and |
((AND)) |
|
• During cleaning |
|
Used only for emergencies |
• Check for proper function before and after each use; and |
((AND)) |
|
• Inspect at least monthly as instructed by the manufacturer |
|
Used for escape-only purposes |
• Before carrying into a work place for use |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-05-072, filed 2/20/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-842-18010 Make sure employees leave the use area before removing respirators.
Make sure employees leave the use area for any of these reasons:
((–)) (1) To replace air-purifying filters, cartridges, or canisters;
((–)) (2) When they smell or taste (detect) vapor or gas leakage from, for example, cartridges, canister, or the facepiece seal;
((–)) (3) When they detect changes in breathing resistance;
((–)) (4) To readjust their respirators;
((–)) (5) To wash their faces and respirators as necessary to prevent skin or eye irritation;
((–)) (6) If they become ill;
((–)) (7) If they experience sensations of dizziness, nausea, weakness, breathing difficulty, coughing, sneezing, vomiting, fever, or chills.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-19005 Provide standby assistance in immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) conditions.
IMPORTANT:
DOSH currently uses the IDLH values in the 1990 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards to determine the existence of IDLH conditions. You may use more recent editions of this guide. Visit www.cdc.gov/niosh for more information.
(1) Provide at least two standby employees outside the IDLH area.
Note: | You need only one standby employee if the IDLH condition is well characterized, will remain stable AND you can show one employee can adequately do ALL of the following: |
((•)) 1. Monitor employees in the IDLH area; | |
((•)) 2. Implement communication; and | |
((•)) 3. Initiate rescue duties. |
(2) Train and equip standby employees to provide effective emergency rescue. Equip them with:
(a) A pressure-demand SCBA or a pressure-demand air-line respirator with an auxiliary SCBA, for each standby employee;
(b) Appropriate retrieval equipment, when it would help with the effective rescue of the entrant, or an equivalent means of rescue.
(3) Make sure standby employees maintain visual, voice, or signal line communication with employees in the IDLH area.
(4) Make sure that in the event of an emergency:
(a) Standby employees notify you or your designee before they enter the IDLH area to provide emergency rescue;
(b) You provide necessary assistance when notified.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-24-071, filed 12/4/12, effective 1/4/13)
WAC 296-842-20010 Prevent conditions that could create a hazardous breathing air supply.
(1) Use SCBA and air-line respirators safely:
((–)) DO NOT supply compressed oxygen to SCBAs or air-line respirators that previously used compressed air.
Note: | Compressed air leaves residues containing hydrocarbons such as oil or grease. Fire or explosion can occur if compressed oxygen makes contact with these residues. |
(2) Use breathing air couplings on air-line respirators that are NOT compatible with couplings for nonrespirable air or other gas systems, for example, utility air used for manufacturing purposes.
(3) DO NOT allow asphyxiating substances to enter breathing air lines; for example, do not flush nitrogen through worksite air lines also used for breathing air.
(4) Use equipment specifically designed for oxygen service or distribution IF oxygen concentrations greater than 23.5% are used.
Note: | Respiratory equipment NOT designed for oxygen service or distribution can create fire or explosion hazards in oxygen concentrations higher than 23.5%. |
(5) Make sure cylinders used to supply breathing air for SCBAs or air-line respirators are tested and maintained as described in the federal Department of Transportation's (DOT) Shipping Container Specification Regulations, Title 49 C.F.R. Part 180.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Use only cylinders marked (with serial number, cylinder pressure, DOT exemption number, and test dates) according to these DOT regulations. |
((•)) 2. To find any Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.) visit: www.access.gpo.gov. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-05-072, filed 2/20/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-842-20015 Make sure compressors do not create a hazardous breathing air supply.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) 1. Ambient-air movers (or pumps) used to supply air to respirators must be used according to the manufacturer's instructions.
((•)) 2. Respirators used with ambient-air movers must be approved by NIOSH to operate within the pressure ranges of the air mover.
(1) Locate or modify compressor intakes so they will not pick up contaminated air OR exhaust gases such as carbon monoxide (CO) from:
((•)) (a) Fuel-powered vehicles;
((OR
•)) (b) The internal combustion motor of the compressor; or
((OR
•)) (c) Other contaminant sources in the area, for example, a ventilation system discharge.
Note: | ((•)) 1. You may need to reposition or extend the compressor's intake or engine exhaust pipe or outlet, especially if they are located near each other. |
((•)) 2. Be aware that exhaust gases may not adequately disperse when the compressor is operated in: | |
((–)) a. An enclosed space such as a small room, a corner, or near a wall; or | |
((OR | |
–)) b. In turbulent wind conditions. |
(2) Equip compressors with suitable air-purifying filters, water traps, and sorbents (such as charcoal beds) and maintain them as follows:
(a) Periodically change or clean them according to the manufacturer or supplier's instructions
(b) Keep a tag at the compressor with the following information:
((–)) (i) When the sorbent and filters were last replaced or cleaned;
((–)) (ii) The date of the most recent changes or cleaning;
((–)) (iii) The signature of the person authorized by the employer to perform changes or cleaning.
Note: | To be sure you are providing the recommended operating pressure for respirators, you may need to install a delivery pressure gauge where the respirator's airline hose attaches to the manifold or other air outlet. |
(3) Make sure the carbon monoxide (CO) level in breathing air from compressors does NOT exceed ten parts per million (ppm).
Maintain CO levels below ten ppm in oil lubricated compressors by using at least one of the following:
(a) An effective CO alarm
(b) An effective high temperature alarm AND testing the air supply often enough to prevent CO levels from exceeding ten ppm.
Note: | ((•)) 1. If you do not have a reliable CO-free area available for locating your compressor intake, consider these examples of methods to prevent CO contamination of the air supply: |
((–)) a. Use of continuous and effective carbon monoxide alarms and filters; | |
((–)) b. Conduct frequent monitoring of air quality; | |
((–)) c. Use a CO converter (converts CO to carbon dioxide). | |
((•)) 2. How often to test depends on a number of considerations, for example: | |
((–)) a. Compressor age; | |
((–)) b. Maintenance history of the compressor; | |
((–)) c. Stability of CO readings. | |
((•)) 3. If the CO or high temperature alarm cannot be heard by the employee, a flashing light or other effective alternative to an audio alarm needs to be used. | |
((•)) 4. Safeguards, such as alarms, are necessary to prevent CO contamination resulting from compressor overheating. When alarms are provided, proper maintenance practices such as periodic inspections and calibration will help make sure alarms remain effective. | |
((•)) 5. Any type of oil-lubricated compressor, such as screw or piston types, may produce dangerous levels of CO if overheating occurs. | |
((–)) Old compressors are known to leak oil due to worn parts, increasing the possibility for overheating. Newer compressors may also overheat if maintenance practices are poor. For example, poor maintenance practices may lead to disconnected or incorrectly set alarms, inoperative shut-offs, or an impaired cooling system. | |
((•)) 6. You need to instruct employees to move to a safe area when the alarm sounds AND to stop using respirators. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-22005 Use this medical questionnaire for medical evaluations.
Use the medical questionnaire in Table 10 when conducting medical evaluations.
Note: | ((•)) 1. You may use a physical exam instead of this questionnaire if the exam covers the same information as the questionnaire. |
((•)) 2. You may use online questionnaires if the questions are the same and the requirements in WAC 296-842-14005 of this chapter are met. | |
((•)) 3. You may choose to send the questionnaire to the LHCP ahead of time, giving time to review it and add any necessary questions. | |
((•)) 4. The LHCP determines what questions to add to the questionnaire, if any; however, questions in Parts 1-3 may not be deleted or substantially altered. |
Table 10
DOSH Medical Evaluation Questionnaire |
|
Employer instructions: |
|
• You may use online questionnaires if the requirements in WAC 296-842-14005 are met. |
|
• You must tell your employee how to deliver or send the completed questionnaire to the health care provider you have selected. |
|
• You must NOT review employees' questionnaires. |
|
Health care provider's instructions: |
|
• Review the information in this questionnaire and any additional information provided to you by the employer. |
|
• You may add questions to this questionnaire at your discretion; HOWEVER, questions in Parts 1-3 may not be deleted or substantially altered. |
|
• Follow-up evaluation is required for any positive response to questions 1-8 in Part 2, or questions 1-6 in Part 3. This might include: Phone consultations to evaluate positive responses, medical tests, and diagnostic procedures. |
|
• When your evaluation is complete, send a copy of your written recommendation to the employer AND employee. |
|
Employee information and instructions: |
|
• Your employer must allow you to answer this questionnaire during normal working hours, or at a time and place that is convenient to you. |
|
• Your employer or supervisor must not look at or review your answers at any time. |
|
Part 1 - Employee Background Information |
|||
ALL employees must complete this part |
|||
Please print |
|||
1. Today's date: |
|||
2. Your name: |
|||
3. Your age (to nearest year): |
|||
4. Sex (circle one): Male / Female |
|||
5. Your height: ft. in. |
|||
6. Your weight: lbs. |
|||
7. Your job title: |
|||
8. A phone number where you can be reached by the health care professional who reviews this questionnaire (include Area Code): |
|||
9. The best time to call you at this number: |
|||
10. Has your employer told you how to contact the health care professional who will review this questionnaire? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
11. Check the type of respirator(s) you will be using: |
|||
a. N, R, or P filtering-facepiece respirator (for example, a dust mask, OR an N95 filtering-facepiece respirator). |
|||
b. Check all that apply. |
|||
□ Half mask □ Full facepiece mask □ Helmet hood □ Escape |
|||
□ Nonpowered cartridge or canister □ Powered air-purifying cartridge respirator (PAPR) |
|||
□ Supplied-air or Air-line |
|||
Self contained breathing apparatus (SCBA): □ Demand or □ Pressure demand |
|||
Other: |
|||
12. Have you previously worn a respirator? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," describe what type(s): |
|||
Part 2 - General Health Information |
|||
ALL employees must complete this part |
|||
Please circle "Yes" or "No" |
|||
1. Do you currently smoke tobacco, or have you smoked tobacco in the last month? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
2. Have you ever had any of the following conditions? |
|||
a. Seizures (fits): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Diabetes (sugar disease): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Allergic reactions that interfere with your breathing: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. Claustrophobia (fear of closed-in places): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
e. Trouble smelling odors: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
3. Have you ever had any of the following pulmonary or lung problems? |
|||
a. Asbestosis: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Asthma: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Chronic bronchitis: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. Emphysema: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
e. Pneumonia: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
f. Tuberculosis: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
g. Silicosis: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
h. Pneumothorax (collapsed lung): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
i. Lung cancer: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
j. Broken ribs: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
k. Any chest injuries or surgeries: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
l. Any other lung problem that you have been told about: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
4. Do you currently have any of the following symptoms of pulmonary or lung illness? |
|||
a. Shortness of breath: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Shortness of breath when walking fast on level ground or walking up a slight hill or incline: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Shortness of breath when walking with other people at an ordinary pace on level ground: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. Have to stop for breath when walking at your own pace on level ground: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
e. Shortness of breath when washing or dressing yourself: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
f. Shortness of breath that interferes with your job: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
g. Coughing that produces phlegm (thick sputum): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
h. Coughing that wakes you early in the morning: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
i. Coughing that occurs mostly when you are lying down: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
j. Coughing up blood in the last month: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
k. Wheezing: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
l. Wheezing that interferes with your job: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
m. Chest pain when you breathe deeply: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
n. Any other symptoms that you think may be related to lung problems: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
5. Have you ever had any of the following cardiovascular or heart problems? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
a. Heart attack: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Stroke: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Angina: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. Heart failure: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
e. Swelling in your legs or feet (not caused by walking): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
f. Heart arrhythmia (heart beating irregularly): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
g. High blood pressure: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
h. Any other heart problem that you have been told about: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
6. Have you ever had any of the following cardiovascular or heart symptoms? |
|||
a. Frequent pain or tightness in your chest: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Pain or tightness in your chest during physical activity: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Pain or tightness in your chest that interferes with your job: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. In the past 2 years, have you noticed your heart skipping or missing a beat: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
e. Heartburn or indigestion that is not related to eating: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
f. Any other symptoms that you think may be related to heart or circulation problems: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
7. Do you currently take medication for any of the following problems? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
a. Breathing or lung problems: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Heart trouble: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Blood pressure: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. Seizures (fits): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
8. If you have used a respirator, have you ever had any of the following problems? (If you have never used a respirator, check the following space and go to question 9:) |
|||
a. Eye irritation: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Skin allergies or rashes: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Anxiety: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. General weakness or fatigue: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
e. Any other problem that interferes with your use of a respirator? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
9. Would you like to talk to the health care professional who will review this questionnaire about your answers? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
Part 3 - Additional Questions for Users of Full-Facepiece Respirators or SCBAs |
|||
Please circle "Yes" or "No" |
|||
1. Have you ever lost vision in either eye (temporarily or permanently)? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
2. Do you currently have any of these vision problems? |
|||
a. Need to wear contact lenses: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Need to wear glasses: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Color blindness: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. Any other eye or vision problem: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
3. Have you ever had an injury to your ears, including a broken ear drum? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
4. Do you currently have any of these hearing problems? |
|||
a. Difficulty hearing: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Need to wear a hearing aid: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Any other hearing or ear problem: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
5. Have you ever had a back injury? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
6. Do you currently have any of the following musculoskeletal problems? |
|||
a. Weakness in any of your arms, hands, legs, or feet: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Back pain: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Difficulty fully moving your arms and legs: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. Pain or stiffness when you lean forward or backward at the waist: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
e. Difficulty fully moving your head up or down: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
f. Difficulty fully moving your head side to side: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
g. Difficulty bending at your knees: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
h. Difficulty squatting to the ground: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
i. Climbing a flight of stairs or a ladder carrying more than 25 lbs: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
j. Any other muscle or skeletal problem that interferes with using a respirator: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
Part 4 - Discretionary Questions |
|||
Complete questions in this part ONLY IF your employer's health care provider says they are necessary |
|||
1. In your present job, are you working at high altitudes (over 5,000 feet) or in a place that has lower than normal amounts of oxygen? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," do you have feelings of dizziness, shortness of breath, pounding in your chest, or other symptoms when you are working under these conditions: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
2. Have you ever been exposed (at work or home) to hazardous solvents, hazardous airborne chemicals (such as gases, fumes, or dust), OR have you come into skin contact with hazardous chemicals? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," name the chemicals, if you know them: |
|||
3. Have you ever worked with any of the materials, or under any of the conditions, listed below: |
|||
a. Asbestos? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Silica (for example, in sandblasting)? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Tungsten/cobalt (for example, grinding or welding this material)? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. Beryllium? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
e. Aluminum? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
f. Coal (for example, mining)? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
g. Iron? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
h. Tin? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
i. Dusty environments? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
j. Any other hazardous exposures? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," describe these exposures: |
|||
4. List any second jobs or side businesses you have: |
|||
5. List your previous occupations: |
|||
6. List your current and previous hobbies: |
|||
7. Have you been in the military services? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," were you exposed to biological or chemical agents (either in training or combat)? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
8. Have you ever worked on a HAZMAT team? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
9. Other than medications for breathing and lung problems, heart trouble, blood pressure, and seizures mentioned earlier in this questionnaire, are you taking any other medications for any reason (including over-the-counter medications)? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," name the medications if you know them: |
|||
10. Will you be using any of the following items with your respirator(s)? |
|||
a. HEPA filters: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Canisters (for example, gas masks): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Cartridges: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
11. How often are you expected to use the respirator(s)? |
|||
a. Escape-only (no rescue): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
b. Emergency rescue only: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
c. Less than 5 hours per week: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
d. Less than 2 hours per day: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
e. 2 to 4 hours per day: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
f. Over 4 hours per day: |
|||
12. During the period you are using the respirator(s), is your work effort: |
|||
a. Light (less than 200 kcal per hour): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," how long does this period last during the average shift: hrs. mins. |
|||
Examples of a light work effort are sitting while writing, typing, drafting, or performing light assembly work; or standing while operating a drill press (1-3 lbs.) or controlling machines. |
|||
b. Moderate (200 to 350 kcal per hour): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," how long does this period last during the average shift: hrs. mins. |
|||
Examples of moderate work effort are sitting while nailing or filing; driving a truck or bus in urban traffic; standing while drilling, nailing, performing assembly work, or transferring a moderate load (about 35 lbs.) at trunk level; walking on a level surface about 2 mph or down a 5-degree grade about 3 mph; or pushing a wheelbarrow with a heavy load (about 100 lbs.) on a level surface. |
|||
c. Heavy (above 350 kcal per hour): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," how long does this period last during the average shift: hrs. mins. |
|||
Examples of heavy work are lifting a heavy load (about 50 lbs.) from the floor to your waist or shoulder; working on a loading dock; shoveling; standing while bricklaying or chipping castings; walking up an 8-degree grade about 2 mph; climbing stairs with a heavy load (about 50 lbs.). |
|||
13. Will you be wearing protective clothing and/or equipment (other than the respirator) when you are using your respirator? |
Yes |
/ |
No |
If "yes," describe this protective clothing and/or equipment: |
|||
14. Will you be working under hot conditions (temperature exceeding 77°F): |
Yes |
/ |
No |
15. Will you be working under humid conditions: |
Yes |
/ |
No |
16. Describe the work you will be doing while using your respirator(s): |
|||
17. Describe any special or hazardous conditions you might encounter when you are using your respirator(s) (for example, confined spaces, life-threatening gases): |
|||
18. Provide the following information, if you know it, for each toxic substance that you will be exposed to when you are using your respirator(s): |
|||
Name of the first toxic substance: |
|||
Estimated maximum exposure level per shift: |
|||
Duration of exposure per shift: |
|||
Name of the second toxic substance: |
|||
Estimated maximum exposure level per shift: |
|||
Duration of exposure per shift: |
|||
Name of the third toxic substance: |
|||
Estimated maximum exposure level per shift: |
|||
Duration of exposure per shift: |
|||
The name of any other toxic substances that you will be exposed to while using your respirator: |
|||
19. Describe any special responsibilities you will have while using your respirator(s) that may affect the safety and well being of others (for example, rescue, security). |
|||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-22010 Follow these fit-testing procedures for tight-fitting respirators.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) 1. This section contains procedural requirements that apply during actual fit testing.
((•)) 2. See WAC 296-842-15005 of this chapter for fit-testing requirements that apply to your overall program.
Exemptions: | This section does NOT apply to employees who: |
((•)) 1. Voluntarily use respirators; or | |
((OR | |
•)) 2. Are required to use mouthpiece respirators. |
(1) Follow the procedure in Table 11 to choose a respirator for fit testing:
(a) Prior to conducting fit tests; and
((AND))
(b) Any time your employee must select a different respirator such as when a previously selected respirator fails a test.
(2) Select and follow at least one of the following fit test procedures:
(a) Qualitative fit-test procedures:
((♦)) (i) Isoamyl acetate vapor (IAA, banana oil) in Table 12;
((♦)) (ii) Saccharine aerosol in Table 13;
((♦)) (iii) Bitrex™ aerosol in Table 14;
((♦)) (iv) Irritant smoke in Table 15.
(b) Quantitative fit-test procedures:
((♦)) (i) Ambient aerosol condensation nuclei counter such as the Portacount™, in Table 16;
((♦)) (ii) Controlled negative pressure (CNP) such as the FitTester 3000™, in Table 17;
((♦)) (iii) Generated aerosol in Table 18.
(3) Make sure employees perform the appropriate fit-test exercises listed in Table 19.
(4) Clean and maintain equipment according to the manufacturer's instructions.
(5) Make sure during fit testing employees wear any safety equipment that could:
(a) Interfere with respirator fit; and
((AND))
(b) Be worn in the workplace. For example, chemical splash goggles.
(6) Check, prior to fit testing, for conditions that may interfere with the respirator seal or valve functions. If you find such conditions, do NOT conduct fit testing for that individual.
Note: | Examples of conditions that may interfere with the respirator seal or valve functions include: |
((•)) 1. Moustache, stubble, sideburns, bangs, hairline, and other types of facial hair in areas where the respirator facepiece seals or that interfere with valve function. | |
((•)) 2. Temple bars of corrective eyewear or headgear that extend through the face seal area. |
(7) Follow the appropriate fit test exercises in Table 19 as indicated.
Table 11
Procedure for Choosing a Respirator for Fit Testing |
|||
1. Inform the employee: |
|||
((•)) a. To choose the most comfortable respirator that provides an adequate fit |
|||
((•)) b. That each respirator sample represents a different size and, if more than one model is supplied, a different shape |
|||
((•)) c. That if fitted and used properly, the respirator chosen will provide adequate protection |
|||
2. Provide a mirror and show the employee how to: |
|||
((•)) a. Put on the respirator |
|||
((•)) b. Position the respirator on the face |
|||
((•)) c. Set strap tension. |
|||
Note: This instruction does NOT take the place of the employee's formal training since it is only a review. |
|||
3. Review with the employee how to check for a comfortable fit around the nose, cheeks and other areas on the face. |
|||
((•)) Tell the employee the respirator should be comfortable while talking or wearing eye protection. |
|||
4. Have the employee hold each facepiece against the face, taking enough time to compare the fit of each. The employee can then either: |
|||
((•)) a. Reject any facepiece that clearly does not feel comfortable or fit adequately; or |
|||
((OR |
|||
•)) b. Choose which facepiece is most acceptable and which are less acceptable, if any. |
|||
Note: ((•)) a. Supply as many respirator models and sizes as needed to make sure the employee finds a respirator that is acceptable and fits correctly ((•)) b. To save time later, during this step note the more acceptable facepieces in case the one chosen fails the fit test or proves unacceptable later. |
|||
5. Have the employee wear the most acceptable respirator for AT LEAST 5 minutes to evaluate comfort and fit. Do ALL of the following during this time: |
|||
((•)) a. Ask the employee to observe and comment about the comfort and fit: |
|||
((–)) i. Around the nose, cheeks, and other areas on the face |
|||
((–)) ii. When talking or wearing eye protection |
|||
((•)) b. Have the employee put on the respirator and adjust the straps until they show proficiency |
|||
((•)) c. Evaluate the respirator's general fit by checking: |
|||
((–)) i. Proper chin placement |
|||
((–)) ii. Properly tightened straps (do NOT over tighten) |
|||
((–)) iii. Acceptable fit across the nose bridge |
|||
((–)) iv. Respirator size; it must span the distance from nose to chin |
|||
((–)) v. To see if the respirator stays in position |
|||
((•)) d. Have the employee complete a successful seal check as specified in WAC 296-842-22020 of this chapter |
|||
((–)) Prior to the seal check they must settle the respirator on their face by taking a few slow deep breaths WHILE SLOWLY: |
|||
((■)) i. Moving their head from side-to-side; and |
|||
((AND |
|||
■)) ii. Up and down. |
|||
6. If the employee finds the respirator unacceptable, allow the employee to select another one and return to Step 5. Otherwise, proceed to Step 7. |
|||
7. Before starting the fit test, you must: |
|||
((•)) a. Describe the fit test including screening procedures, employee responsibilities, and test exercises; and |
|||
((AND |
|||
•)) b. Make sure the employee wears the respirator AT LEAST five minutes. |
|||
Table 12
Isoamyl Acetate (Banana Oil) Vapor Test Procedure |
|||
Important: |
|||
((•)) 1. This is a qualitative fit-test (QLFT) procedure |
|||
((•)) 2. The success of this test depends on preserving the employee's odor sensitivity to isoamyl acetate (IAA) vapor |
|||
((–)) a. Vapor accumulations in ambient air can decrease odor sensitivity. To prevent this: |
|||
((■)) i. Prepare ALL solutions in a location separate from screening and test areas |
|||
((■)) ii. Conduct screening and tests in separate well-ventilated rooms. For example, use an exhaust fan or laboratory hood to prevent IAA vapor from accumulating in the room air |
|||
((–)) b. Always use odor-free water, for example, distilled or spring water that is 25°C (77°F). |
|||
((•)) 3. Isoamyl acetate is also known as isopentyl acetate. |
|||
Screening Preparations |
|||
Important: |
|||
Odor threshold screening determines if the employee can detect weak concentrations of IAA vapor. |
|||
1. Choose an appropriate location to conduct screening. |
|||
((•)) Conduct screening and tests in separate well-ventilated rooms. |
|||
2. Prepare a stock solution AT LEAST weekly as follows: |
|||
((•)) a. Add one milliliter (ml) of pure IAA to 800 ml of odor-free water in a one-liter glass jar with a metal lid using a measuring dropper or pipette |
|||
((•)) b. Seal the jar with the lid and shake it for 30 seconds |
|||
((•)) c. Clean the dropper or pipette. |
|||
3. Prepare the odor test solution daily as follows: |
|||
((•)) a. Add 0.4 ml from the stock solution to 500 ml of water in a one liter glass jar with a metal lid using a clean pipette or dropper |
|||
((•)) b. Seal the jar with the lid and shake it for 30 seconds |
|||
((•)) c. Let this solution stand for 2-3 minutes so the IAA concentration above the liquid reaches equilibrium |
|||
((•)) d. Label this jar so you know the contents but the employee cannot know its contents, for example, "1." |
|||
Note: To maintain the integrity of the test, use labels that peel off easily AND periodically switch the labels. |
|||
4. Prepare a "test blank" solution as follows: |
|||
((•)) a. Add 500 ml of odor-free water to a one liter glass jar with a metal lid |
|||
((•)) b. Seal the jar |
|||
((•)) c. Label the jar so you know the contents but the employee cannot know its contents. |
|||
5. Type or neatly print the following instructions on a card and place it on the table in front of the two test jars: |
|||
"The purpose of this test is to find out if you can smell banana oil at a low concentration. While both jars contain water, one ALSO contains a small amount of banana oil. |
|||
Make sure the lid is secure then pick up a jar and shake it for two seconds. Open the jar and sniff at the opening. Repeat this for the second jar. |
|||
Tell the individual conducting the fit test which jar contains banana oil." |
|||
Test Preparations |
|||
6. Choose an appropriate location to conduct fit testing. |
|||
((•)) Conduct screening and tests in separate well-ventilated rooms. |
|||
7. Assemble the fit test enclosure in the room. |
|||
((•)) a. Invert a clear 55-gallon drum liner over a circular 2-foot diameter frame made of plywood or other lightweight rigid material OR construct a similar enclosure using plastic sheeting |
|||
((•)) b. Hang the frame with the plastic covering so the top of the enclosure is about six inches above the employee's head |
|||
((•)) c. Attach a small hook inside top center of the enclosure |
|||
((•)) d. Tape a copy of the test exercises (see Table 19) to the inside of the test enclosure where the employee can read it. |
|||
8. Have organic vapor cartridges or equivalent on hand for each employee's chosen respirator. |
|||
9. Have ready a 6 x 5-inch piece of paper towel or other porous absorbent single-ply material AND 0.75 ml of pure IAA. Do NOT apply IAA yet. |
|||
Note: As an alternative to using the paper towel, you may use an IAA test swab OR ampoule if it has been demonstrated to generate an equivalent test concentration. |
|||
Screening |
|||
10. Have the employee, while NOT wearing a respirator, follow the instructions on the card provided. |
|||
((•)) a. If the employee correctly identifies the jar containing IAA, proceed to conduct testing (Step 11) |
|||
((•)) b. If the employee is NOT able to correctly identify the jar containing IAA, you must STOP and use a different fit test protocol. |
|||
Testing |
|||
11. BEFORE entering the fit test room, have the employee attach cartridges, put on, properly adjust, and seal check the respirator. Have the employee enter the test enclosure. |
|||
12. Wet the paper towel with 0.75 ml of pure IAA AND fold it in half. |
|||
13. Pass the paper towel to the employee inside the enclosure AND instruct the employee to hang it on the hook at the top of the enclosure. |
|||
14. Wait two minutes for the IAA vapor to fill the enclosure. |
|||
((•)) a. While waiting, explain the fit test, including the purpose of the test exercises, the importance of cooperation, and that you must be informed if a banana-like odor is detected during the test |
|||
((•)) b. You may also demonstrate the test exercises. |
|||
15. Have the employee perform the appropriate fit-test exercises in Table 19. |
|||
((•)) a. If the employee does NOT detect IAA while performing test exercises, the fit test has been PASSED. Proceed as follows: |
|||
((–)) i. BEFORE leaving the enclosure, have the employee break the respirator seal and inhale. If they detect IAA, the test is valid |
|||
((–)) ii. When exiting the employee must remove the paper towel and give it to the individual conducting the fit test. This prevents IAA vapor from building up in the enclosure during subsequent tests |
|||
((–)) iii. The individual conducting the fit test must keep used paper towels in a self-sealing plastic bag to prevent area contamination |
|||
((•)) b. If the employee detects IAA during any test exercise, the fit test has FAILED. STOP and have the employee do the following: |
|||
((–)) i. Quickly return to the selection room to remove the respirator. This avoids decreasing the employee's odor sensitivity |
|||
((–)) ii. Select another respirator |
|||
((–)) iii. Repeat screening and testing |
|||
((■)) At this stage, if the employee fails the screening part of this procedure, the employee can repeat it AFTER waiting at least five minutes for odor sensitivity to return. |
|||
Table 13
Saccharin Aerosol Test Procedure |
|||
Screening Preparations |
|||
Important: |
|||
((•)) This is a qualitative fit-test (QLFT) procedure |
|||
((•)) Taste threshold screening determines whether the employee being tested can detect the taste of saccharin |
|||
((–)) The employee must NOT eat, smoke, chew gum or drink anything but plain water for at least fifteen minutes BEFORE the fit test. Sweet foods or drink consumed before the test may make the employee unable to detect saccharin during screening |
|||
((–)) Nebulizers must be thoroughly rinsed in water and shaken dry: |
|||
((■)) Each morning and afternoon |
|||
OR |
|||
((■)) At least every four hours. |
|||
((•)) You may use commercially prepared solutions if they meet the requirements in this procedure. |
|||
1. Obtain a test enclosure (hood) that meets the following specifications: |
|||
((•)) a. Twelve inches in diameter by fourteen inches tall |
|||
((•)) b. A clear front portion |
|||
((•)) c. Enough space inside to allow free movement of the head when a respirator is worn |
|||
((•)) d. A 3/4 inch (or 1.9 centimeter) hole to accommodate the nebulizer nozzle. The hole must line up in front of the wearer's nose and mouth. |
|||
Note: ((•)) An enclosure similar to the 3M hood assembly, parts #FT 14 and #FT 15 combined, meets these specifications ((•)) This enclosure can also be used for testing. |
|||
2. Obtain and assemble two clean DeVilbiss Model 40 Inhalation Medication Nebulizers OR equivalent. |
|||
3. Prepare the screening solution as follows: |
|||
((•)) a. Dissolve 830.0 milligrams of sodium saccharin USP in 100 ml of warm distilled water; or |
|||
((OR |
|||
•)) b. IF you have already prepared the fit-test solution, you can make the screening solution by adding 1 ml of this solution to 100 ml of distilled water. |
|||
4. Add about 1 ml of the screening solution to one of the nebulizers. |
|||
((•)) Mark this nebulizer to distinguish it from the one to be used for fit testing. |
|||
Test Preparations |
|||
5. Prepare the fit-test solution as follows: |
|||
((•)) Add 83.0 grams of sodium saccharin to 100 ml of warm water. |
|||
6. Add about 1 ml of the test solution to the second nebulizer. |
|||
((•)) Mark this nebulizer to distinguish it from the one to be used for screening. |
|||
7. Have particulate filters ready for the employee's chosen respirator or have filtering-facepiece respirators ready. |
|||
Screening |
|||
8. Have the employee, while NOT wearing a respirator, put on the test enclosure. |
|||
9. Instruct the employee to: |
|||
((• Breath)) a. Breathe through a slightly open mouth with tongue extended during screening AND testing |
|||
((•)) b. Immediately report when a sweet taste is detected. |
|||
10. Insert the nebulizer into the front hole of the test enclosure AND administer saccharin as follows: |
|||
((•)) a. Direct the nozzle away from the employee's nose and mouth |
|||
((•)) b. Complete 10 squeezes in rapid succession |
|||
((•)) c. Each time firmly squeeze the bulb so it collapses completely, then release and allow it to fully expand. |
|||
11. Ask the employee if a sweet taste is detected. |
|||
((•)) a. If YES, screening is completed. Proceed to conduct testing, Step 14, AFTER you: |
|||
((–)) i. Ask the employee to remember the taste for reference during the fit test |
|||
((–)) ii. Note the employee's taste threshold as "10" regardless of the number of squeezes actually completed |
|||
((•)) b. If NO, screening must continue. Proceed to Step 12. |
|||
12. Repeat with 10 more squeezes. Then follow Step 11 again; EXCEPT this time note the employee's taste threshold as "20" IF a sweet taste is reported. |
|||
((•)) If a sweet taste is still NOT detected, repeat with 10 more squeezes and follow Step 11 one last time; EXCEPT this time note "30" for the taste threshold IF a sweet taste is reported. |
|||
13. If NO sweet taste is reported after 30 squeezes, you must STOP and choose a different fit-test protocol for the employee. |
|||
Test |
|||
Important! |
|||
((•)) Periodically check nebulizers to make sure they do not clog during use. A test is NOT valid if the nebulizer is clogged at the end of the test. |
|||
14. Have the employee attach particulate filters, put on, properly adjust, and seal check the respirator. Have the employee put on the test enclosure (hood). |
|||
15. Instruct the employee to immediately report if a sweet taste is detected. |
|||
16. Insert the nebulizer into the front hole of the test enclosure AND administer the same number of squeezes, either 10, 20, or 30, as noted during screening. |
|||
17. Have the employee perform the appropriate fit-test exercises as described in Table 19. During this step: |
|||
((•)) a. Replenish the aerosol in the hood EVERY 30 seconds using 1/2 the number of squeezes used in Step 16, either 5, 10, or 15 |
|||
((•)) b. The employee must report if a sweet taste is detected: |
|||
((–)) If NO saccharin is tasted, the test has been PASSED |
|||
((■)) i. If saccharin is tasted the test has FAILED, have the employee select another respirator; and |
|||
((AND |
|||
■)) ii. Repeat screening and testing. |
|||
Table 14
Bitrex™ Aerosol Test Procedure |
|||
Important! |
|||
((•)) This is a qualitative fit-test (QLFT) procedure |
|||
((•)) Bitrex™ (denatonium benzoate) is routinely used as a taste aversion agent in household liquids that children should not drink and is endorsed by the American Medical Association, the National Safety Council, and the American Association of Poison Control Centers |
|||
((•)) The employee must NOT eat, smoke, chew gum or drink anything but plain water for at least fifteen minutes BEFORE the fit test. |
|||
Screening Preparations |
|||
Important! |
|||
((•)) Taste threshold screening determines whether the employee being tested can detect the taste of Bitrex™ |
|||
((•)) Nebulizers must be thoroughly rinsed in water and shaken dry: |
|||
((–)) Each morning and afternoon |
|||
OR |
|||
((–)) At least every four hours. |
|||
((•)) You may use commercially prepared solutions if they meet the requirements in this procedure. |
|||
1. Obtain a test enclosure that meets the following specifications: |
|||
((•)) a. Twelve inches in diameter by fourteen inches tall |
|||
((•)) b. A clear front portion |
|||
((•)) c. Enough space inside the front to allow free movement of the head when a respirator is worn |
|||
((•)) d. 3/4 inch (or 1.9 centimeter) hole to accommodate the nebulizer nozzle. The hole must line up in front of the wearer's nose and mouth. |
|||
Note: ((•)) An enclosure similar to the 3M hood assembly, parts #FT 14 and #FT 15 combined, meets these specifications ((•)) This enclosure can also be used for testing. |
|||
2. Obtain and assemble two clean DeVilbiss Model 40 Inhalation Medication Nebulizers OR equivalent: |
|||
3. Prepare the screening solution as follows: |
|||
((•)) a. Make up a 5% salt solution by dissolving 5.0 grams of salt (sodium chloride) into 100 ml of distilled water |
|||
((•)) b. Dissolve 13.5 milligrams of Bitrex™ in the salt solution. |
|||
4. Add about 1 ml of the screening solution to one of the nebulizers. |
|||
((•)) Mark this nebulizer to distinguish it from the one to be used for fit testing. |
|||
Test Preparations |
|||
5. Prepare the fit test solution. |
|||
((•)) a. Dissolve 10.0 grams of salt (sodium chloride) into 200 ml of distilled water |
|||
((•)) b. Add 337.5 milligrams of Bitrex™ to the warmed salt solution. |
|||
6. Add about 1 ml of the test solution to the second nebulizer. |
|||
((•)) Mark this nebulizer to distinguish it from the one used for screening. |
|||
7. Have particulate filters ready for the employee's chosen respirator or have filtering-facepiece respirators ready. |
|||
Screening |
|||
Important: The employee must NOT eat, smoke, chew gum or drink anything but plain water for at least fifteen minutes BEFORE the screening and test |
|||
8. Have the employee, while NOT wearing a respirator, put on the test enclosure. |
|||
9. Instruct the employee to: |
|||
((• Breath)) a. Breathe through a slightly opened mouth with tongue extended during screening AND testing |
|||
((•)) b. Immediately report when a bitter taste is detected. |
|||
10. Insert the nebulizer into the front hole of the test enclosure AND administer Bitrex™ as follows: |
|||
((•)) a. Direct the nozzle away from the employee's nose and mouth |
|||
((•)) b. Complete 10 squeezes in rapid succession |
|||
((•)) c. Each time firmly squeeze the bulb so it collapses completely, then release and allow it to fully expand. |
|||
11. Ask the employee whether a bitter taste is detected. |
|||
((•)) a. If YES, screening is completed. Proceed to conduct testing, Step 14, AFTER you: |
|||
((–)) i. Ask the employee to remember the taste for reference during the fit test |
|||
((–)) ii. Note the employee's taste threshold as "10," regardless of the number of squeezes actually completed |
|||
((•)) b. If NO, screening must continue. Proceed to Step 12. |
|||
12. Repeat with 10 more squeezes. Then follow Step 11 again; EXCEPT this time note the employee's taste threshold as "20" IF a bitter taste is reported. |
|||
((•)) If a bitter taste is still NOT detected repeat with 10 more squeezes and follow Step 11 one last time; EXCEPT this time note "30" for the taste threshold IF a bitter taste is reported. |
|||
13. If NO bitter taste is reported after 30 squeezes, you must STOP and choose a different fit-test protocol for the employee. |
|||
Test |
|||
14. Have the employee attach particulate filters, put on, properly adjust, and seal check the respirator. Have the employee put on the test enclosure. |
|||
15. Instruct the employee to: |
|||
((•)) a. Breathe through a slightly opened mouth with tongue extended during screening AND testing |
|||
((•)) b. Immediately report when a bitter taste is detected. |
|||
16. Insert the nebulizer into the front hole of the test enclosure AND administer the same number of squeezes, either 10, 20, or 30, as noted during screening. |
|||
17. Have the employee perform the appropriate fit-test exercises as described in Table 19. During this step: |
|||
((•)) a. Replenish the aerosol in the hood EVERY 30 seconds using 1/2 the number of squeezes used in Step 16, either 5, 10, or 15 |
|||
((•)) b. The employee must report if a bitter taste is detected: |
|||
((–)) i. If NO Bitrex™ is tasted, the test has been PASSED |
|||
((–)) ii. If Bitrex™ is tasted the test has FAILED. Have the employee: |
|||
((■)) A. Select another respirator; and |
|||
((AND |
|||
■)) B. Repeat all screening and testing steps. |
|||
Table 15
Irritant Smoke (Stannic Chloride) Test Procedure |
||
Important: |
||
((•)) DO NOT USE A TEST ENCLOSURE OR HOOD FOR THIS FIT TEST! |
||
((•)) This is a qualitative fit-test (QLFT) procedure |
||
((•)) During this test an employee is exposed to irritating smoke containing hydrochloric acid produced by a stannic chloride ventilation smoke tube to detect leakage. The smoke will irritate eyes, lungs, and nasal passages |
||
((•)) Employee sensitivity varies, and certain employees may respond more intensely than others exposed to irritant smoke. The individual conducting the fit test must take precautions to minimize the employees' exposure to irritant smoke |
||
((•)) Conduct fit testing in an area with adequate ventilation to prevent exposure of the individual conducting the fit test and build-up of irritant smoke in the ambient air. |
||
Screening AND Test Preparations |
||
Important: |
||
Sensitivity screening is necessary to determine whether the employee can detect a weak concentration of irritant smoke AND whether any gross facepiece leakage is detected. |
||
1. Obtain only stannic chloride (ventilation) smoke tubes, AND an aspirator squeeze bulb OR use a low-flow air pump set to deliver 200 milliliters of air flow per minute. |
||
2. Equip the employee's chosen respirator with P100 series filters if a negative pressure air-purifying respirator will be tested. If a powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) will be tested equip the respirator with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters. |
||
Screening |
||
Important! |
||
When performing sensitivity screening checks use only the MINIMUM amount of smoke necessary to elicit a response from the employee. |
||
3. Advise the employee that the smoke can be irritating to eyes, lungs, and nasal passages AND instruct the employee to keep eyes closed while exposed. |
||
4. Break both ends of the ventilation smoke tube AND fit a short piece of plastic tubing, for example, two-to-six inches of tygon tubing, over one end to prevent exposure to the sharp end of the tube. Connect the other end to an aspirator bulb or a low-flow air pump set to deliver a flow of 200 ml per minute. |
||
5. While the employee is NOT wearing a respirator, have the employee smell a weak concentration of irritant smoke to become familiar with its irritating properties. |
||
((•)) Carefully direct a small amount of irritant smoke toward the employee. |
||
Test |
||
Test 6. Have the employee attach respirator filters, put on, adjust, and seal check the respirator without assistance. The employee must be proficient at these tasks. |
||
7. Remind the employee to keep eyes closed during testing. |
||
8. Direct a stream of irritant smoke toward the respirator's face seal area as follows: |
||
((•)) a. Begin at least 12 inches from the facepiece AND move the smoke around the whole perimeter of the mask |
||
((•)) b. Gradually make two more passes around the perimeter of the facepiece, moving to within 6 inches of the respirator |
||
((•)) c. STOP at any time the employee detects smoke in the facepiece. If this occurs a different respirator will need to be chosen and tested, beginning with sensitivity screening. |
||
9. Have the employee perform appropriate fit-test exercises in Table 19 IF the employee has NOT had an involuntary response such as evidence of coughing, flinching, or other response, OR detected smoke in the facepiece. |
||
((•)) Continue to direct smoke from a distance of 6 inches around the facepiece perimeter |
||
((–)) If smoke is detected at any time the test has FAILED. A different respirator must be chosen and tested, starting with sensitivity screening |
||
((–)) If NO smoke is detected proceed to Step 10. |
||
10. Have the employee remove the respirator AND perform another sensitivity screening check as follows: |
||
((•)) a. Continue to use the smoke tube used for fit testing |
||
((•)) b. Carefully direct a SMALL amount of irritant smoke toward the employee |
||
((–)) i. The test has been PASSED IF the employee responds to the smoke |
||
((–)) ii. The fit test is VOIDED IF the employee does NOT respond to the smoke. |
||
Table 16
Ambient Aerosol Condensation Nuclei Counter (Portacount™) Test Procedure |
|||
Important: |
|||
((•)) This is a quantitative (QNFT) fit-test procedure |
|||
((•)) This method uses a particle counting instrument that measures and compares the particle concentration both inside and outside the respirator facepiece while the employee performs a series of test exercises |
|||
((•)) Particles in the ambient air are used as the test aerosol. |
|||
Test Preparations |
|||
1. Obtain a test instrument such as a Portacount™. |
|||
2. Have probed respirators available for each respirator model and size the employer uses, OR have a sampling adapter available if the employee's actual or chosen respirator will be tested. |
|||
Note: ((•)) A probed respirator has a special fitting installed on the facepiece designed to connect with the end of the test instrument's plastic sampling tube so that air samples can be taken inside the facepiece. Probed respirators can be obtained from the respirator manufacturer, or distributor, AND can only be used for fit-testing purposes ((•)) Contact TSI Inc., OR the respirator's manufacturer to obtain probed respirators or facepiece sampling adapters. |
|||
3. Follow the test instrument manufacturer's instructions for test preparation, including particle, zero, and system checks. Make sure the instrument's pass OR fail criterion is programmed to the following MINIMUM performance levels: |
|||
((•)) a. For half-facepiece respirators, an overall minimum fit factor of 100 as a passing level |
|||
((•)) b. For full-facepiece respirators, an overall minimum fit factor of 500 as a passing level |
|||
4. Have high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, OR other respirator filters available that are capable of preventing significant penetration by particles generated by the test instrument such as, P100 or N95 series filters. |
|||
((•)) If you will use a sampling adapter instead of probed respirators be sure to have the correct type for the respirators chosen. |
|||
Test |
|||
5. Properly attach the sampling line to the facepiece probe or sampling adapter. |
|||
6. Have the employee attach respirator filters, put on, properly adjust, and wear the respirator five minutes BEFORE the fit test. During this time you and the employee must evaluate the respirator's general fit by checking: |
|||
((•)) a. Proper chin placement |
|||
((•)) b. Properly tightened straps (do NOT over tighten) |
|||
((•)) c. Acceptable fit across the nose bridge |
|||
((•)) d. Respirator size. It must span the distance from nose to chin |
|||
((•)) e. To see if the respirator stays in position. |
|||
Note: Wearing the respirator for five minutes permits the employee to make certain the respirator is comfortable AND allows for purging of ambient particles trapped inside the facepiece. |
|||
7. Have the employee perform a seal check. Make sure the sampling line is crimped to avoid leakage during the seal check. If NO leakage is detected, proceed to Step 8. If leakage is detected: |
|||
((•)) a. Determine the cause; and |
|||
((AND |
|||
•)) b. If leakage is due to a poorly fitting facepiece, have the employee: |
|||
((–)) i. Choose another respirator size or model; and |
|||
((AND |
|||
–)) ii. Start again at Step 6. |
|||
8. Start the fit test cycle. |
|||
((•)) a. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for operating the test instrument |
|||
((•)) b. Have the employee perform the appropriate fit-test exercises in Table 19 |
|||
((–)) The test instrument will automatically stop and calculate the overall fit factor. Use this result to determine whether or not the test is passed |
|||
((■)) The test has been PASSED if the overall fit factor is at least 100 for a half facepiece, OR 500 for a full facepiece |
|||
((■)) The test has FAILED if the overall fit factor is below 100 for a half facepiece or 500 for a full facepiece. |
|||
Note: If the test has failed, have the employee select another respirator model or size following Table 11 AND repeat this procedure. |
|||
Table 17
Controlled Negative Pressure (CNP) Test Procedure |
|||||||
Important! |
|||||||
((•)) This is a quantitative fit-test (QNFT) procedure |
|||||||
((•)) This method determines respirator fit by measuring how much the facepiece leaks when it is subject to a slight negative pressure AFTER various premeasurement activities |
|||||||
((•)) Instruments used must have a nonadjustable test pressure of 15.0 mm water pressure |
|||||||
((•)) Measurements occur while employees remain still AND hold their breath for 10 seconds |
|||||||
((•)) No test aerosols are used. Respirator cartridges are not needed for this test. Sampling manifolds that replace the filter cartridges are available from the instrument manufacturer, and allow fit testing of an employee's own respirator. |
|||||||
Test Preparations |
|||||||
1. Make sure the individual conducting the fit test is thoroughly trained to perform this test. |
|||||||
2. Obtain a CNP test instrument such as a FitTester 3000™. Make sure: |
|||||||
((•)) a. Defaults are set at: |
|||||||
((–)) i. -15mm (-0.58 inches) of water test pressure; and |
|||||||
((AND |
|||||||
–)) ii. A modeled inspiratory flow rate of 53.8 liters per minute |
|||||||
((•)) b. It has an effective audio warning device or visual screen tracing that signals when employees fail to hold their breath. |
|||||||
Note: ((•)) You are not required to obtain test recording and printing equipment such as computers OR printers. Hand recording results is acceptable ((•)) To see default settings, check the instrument's "REDON protocol." |
|||||||
3. Obtain facepiece adapters appropriate for each test respirator. |
|||||||
Note: ((•)) Adapters are either a one-piece (for SCBA facepieces), OR two-piece (for dual cartridge facepieces) device providing a manifold and breathing valve system. For positive pressure respirators, you will need to obtain an additional fitting, available from the respirator manufacturer, to convert the facepiece to negative pressure ((•)) To obtain adapters, contact the CNP instrument's distributor, Occupational Health Dynamics, OR the respirator manufacturer. |
|||||||
Test |
|||||||
Important! |
|||||||
((•)) The respirator must not be adjusted once the fit-test exercises begin. Any adjustment voids the test and the test must be repeated. |
|||||||
4. Explain the test procedure to the employee. |
|||||||
5. Train the employee on how to hold a breath for at least 10 seconds. |
|||||||
6. Prepare the respirator for the fit test as follows: |
|||||||
((•)) a. Remove or prop open the inhalation valves. If a breathing tube is present, disconnect it |
|||||||
((•)) b. Replace cartridges, if present, with the manifold and breathing valve adapter |
|||||||
((–)) For positive pressure facepieces, mount the manufacturer's additional fitting followed by the manifold-breathing valve adapter |
|||||||
((•)) c. Connect the respirator to the CNP device according to the CNP instrument manufacturer's directions. |
|||||||
7. Have the employee put on, adjust, and seal check the respirator without assistance. |
|||||||
8. Turn on the instrument AND have the employee stand and perform the fit-test exercises in Table 19. Once exercises begin, any adjustments will void the test and you must begin again. |
|||||||
9. Once test exercises are completed, ask the employee about facepiece comfort. If the employee states the respirator is unacceptable, repeat the fit test using another size or model. |
|||||||
10. Determine the overall fit factor for each employee by calculating the harmonic mean of the fit-testing exercises as follows: |
|||||||
Overall fit factor = |
n |
||||||
1/ffE1 + 1/ffE2 + 1/ffE3 . . . + 1/ffEn |
|||||||
Where: |
|||||||
n = The number of exercises; |
|||||||
ffE1 = The fit factor for the first exercise; |
|||||||
ffE2 = The fit factor for the second exercise; |
|||||||
ffE3 = The fit factor for the third exercise; and |
|||||||
ffEn = The fit factor for the nth exercise. |
|||||||
((•)) The test is PASSED IF the overall fit factor obtained is at least 100 for a half facepiece, or at least 500 for a full facepiece |
|||||||
((•)) The test has FAILED IF the fit factor is less than 100 for a half facepiece; 500 for a full facepiece |
|||||||
((–)) If the test has FAILED you must have the employee select another respirator model or size following the steps in Table 11 AND repeat this procedure, starting at Step 6. |
|||||||
Table 18
Generated Aerosol Test Procedure |
||||||||
Important: |
||||||||
• This is a quantitative (QNFT) fit-test procedure |
||||||||
• In this method, a test aerosol is used to challenge the facepiece seal while aerosol concentrations inside and outside the facepiece are measured during test exercises |
||||||||
• Special equipment is needed to generate, disperse, detect, and measure test aerosols. |
||||||||
Test Preparations |
||||||||
1. Test aerosol. |
||||||||
((•)) Use a particulate, for example, corn oil, polyethylene glycol 400, di-2-ethyl hexyl sebacate, or sodium chloride. |
||||||||
2. Instrumentation. |
||||||||
((•)) Do ALL the following: |
||||||||
((–)) a. Obtain and use aerosol generation, dilution, and measurement systems appropriate for particulates |
||||||||
((–)) b. Use an aerosol-generating instrument that will maintain test concentrations within a 10% variation |
||||||||
((–)) c. Select a sampling instrument that allows for a computer record or strip chart record to be created |
||||||||
((■)) The record must show the rise and fall of test agent concentration during each inhalation and exhalation at fit factors of at least 2000. |
||||||||
Note: |
Integrators, or computers that integrate the amount of test agent penetration leakage into the respirator for each exercise, may be used if a record of the readings is made. |
|||||||
((–)) d. Minimize the time interval between the activity and the recording of the activity so you can clearly connect what you see to what is being recorded. For example, use a small diameter and length of sampling line. |
||||||||
3. Test enclosure. |
||||||||
((•)) Do ALL the following: |
||||||||
((–)) a. Make sure the enclosure is equipped and constructed to effectively: |
||||||||
((■)) i. Maintain a uniform concentration of the test agent inside the enclosure. For example, the enclosure must be large enough to allow ALL employees freedom of movement during testing WITHOUT disturbing the test concentration or measurement instrument |
||||||||
((■)) ii. Keep the test agent from contaminating the air outside the enclosure. For example, use a HEPA filter to purify exhausted air |
||||||||
((■)) iii. Allow the individual conducting the fit test to view the employee during the test |
||||||||
((–)) b. Make sure the tubing used to collect samples from the enclosure AND respirator is the same material, diameter, AND length. This makes the effect of aerosol loss caused by deposition in each sample line equal |
||||||||
((–)) c. If sodium chloride is used, relative humidity inside the enclosure must be kept below 50%. |
||||||||
4. Prepare test respirators. |
||||||||
((•)) Do ALL the following: |
||||||||
((–)) a. Inspect test respirators regularly for missing parts AND damage |
||||||||
((–)) b. Keep test respirators in proper working order |
||||||||
((–)) c. Make sure in-mask sampling probes are: |
||||||||
((■)) i. Designed and installed so the air sample will be drawn from the employee's breathing zone; midway between the nose and mouth; and |
||||||||
((AND |
||||||||
■)) ii. The probe extends inside the facepiece at least 1/4 inch |
||||||||
((–)) d. Make sure sampling ports such as probes, or adapters on respirators are constructed and installed so they do NOT: |
||||||||
((■)) i. Block air flow into the sampling line |
||||||||
((■)) ii. Leak |
||||||||
((■)) iii. Interfere with the respirator's fit or performance |
||||||||
((•)) Have high efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters OR P100 series filter available |
||||||||
((–)) Replace filters when increased breathing resistance is detected OR when the test agent has altered the filter material's integrity. |
||||||||
Test |
||||||||
Important! |
||||||||
((•)) Throughout the test, maintain the employee's exposure to any test agent below the established exposure limit. Exposures allowed must be based on exposure time and exposure limit duration |
||||||||
((•)) If a single peak penetration exceeds 5% for half facepieces OR 1% for full facepieces: |
||||||||
((–)) STOP the test; and |
||||||||
((AND |
||||||||
–)) Have the employee select another respirator for testing. |
||||||||
5. Have the employee attach filters, put on, adjust, and seal check the respirator. |
||||||||
((•)) a. Be sure to crimp the sampling line to avoid pressure leaks during the seal check; and |
||||||||
((AND |
||||||||
•)) b. Have the employee adjust the respirator straps, without assistance, so the fit is comfortable. Do NOT over tighten. |
||||||||
6. OPTIONAL Step. To save time conduct a screening test to quickly identify poorly fitting respirators. |
||||||||
Note: You may use a qualitative screening test OR an ambient aerosol condensation nuclei counter instrument in the count mode. |
||||||||
7. Make sure test aerosol concentration is reasonably stable. |
||||||||
((•)) If a canopy or shower curtain enclosure is used, determine stability of the test aerosol concentration AFTER the employee enters the enclosure. |
||||||||
8. Have the employee enter the test enclosure and connect the respirator to the sample lines. |
||||||||
9. Immediately after entering the enclosure measure test aerosol concentration inside the respirator. |
||||||||
((•)) Make sure the peak penetration does NOT exceed 5% for half facepieces, OR 1% for full facepieces. |
||||||||
10. Have employee perform the appropriate fit-test exercises in Table 19. |
||||||||
((•)) Do NOT adjust the respirator once exercises begin. |
||||||||
11. Calculate the overall fit factor as specified in Steps 12-13. The fit test is: |
||||||||
((•)) a. PASSED IF the minimum fit factor of 100 for half facepieces OR 500 for full facepieces is obtained; or |
||||||||
((OR |
||||||||
•)) b. IF a passing fit factor is NOT obtained, the test has FAILED and you must have the employee select and test another respirator. |
||||||||
Calculations |
||||||||
Important! |
||||||||
((•)) Do NOT count the grimace exercise measurements during these calculations |
||||||||
((•)) Take into account the limitations of instrument detection when determining fit factors. |
||||||||
12. Calculate individual fit factors for EACH exercise by applying the following: |
||||||||
Exercise fit factor (ffE) = Average test enclosure concentration |
||||||||
Test aerosol concentration inside the respirator |
||||||||
((•)) a. To determine the average test enclosure concentration use one of the following methods: |
||||||||
((–)) i. Arithmetic average of the concentration before and after each test (an average of two values per entire test) |
||||||||
((–)) ii. Arithmetic average of concentration before and after each exercise (an average of two values per exercise) |
||||||||
((–)) iii. True average measured continuously during the respirator sample |
||||||||
((•)) b. Determine the test aerosol concentration inside the respirator in one of the following ways: |
||||||||
((–)) Average peak penetration values. Determine aerosol penetration for each exercise by: |
||||||||
((■)) i. Using integrators or computers that calculate the actual test agent penetration; or |
||||||||
((OR |
||||||||
■)) ii. Average the peak heights shown on the strip chart recording, graph, or by computer integration |
||||||||
((–)) c. Maximum peak penetration. Use strip chart recordings to determine the highest peak penetration for each exercise and use this value |
||||||||
((–)) d. Area under the peaks. Use computerized integration or other appropriate calculations to integrate the area under individual peaks for each exercise. |
||||||||
13. Using individual exercise fit factors (ffE) calculate the overall fit factor by doing ALL of the following: |
||||||||
((•)) a. Convert each exercise fit factor to a penetration value; |
||||||||
((•)) b. Determine the average penetration value; |
||||||||
((•)) c. Convert the average penetration value back to a fit factor; or |
||||||||
((OR)) |
||||||||
Use this equation to calculate the overall fit factor: |
||||||||
Overall fit factor = |
n |
|||||||
1/ffE1 + 1/ffE2 + 1/ffE3 . . . + 1/ffEn |
||||||||
Where: |
||||||||
n = The number of exercises; |
||||||||
ffE1 = The fit factor for the first exercise; |
||||||||
ffE2 = The fit factor for the second exercise; |
||||||||
ffE3 = The fit factor for the third exercise; and |
||||||||
ffEn = The fit factor for the nth exercise. |
||||||||
Table 19
Fit-Test Exercises |
|||||
Important: |
|||||
((•)) This list applies when you use any fit test |
|||||
((•)) Employees tested must perform ALL exercises marked with an "X" as described for the fit-test procedure used |
|||||
((–)) Once exercises begin, any adjustments made void the test AND you must begin again |
|||||
((–)) After test exercises are completed, you must ask the employee about the comfort of the respirator. If it has become unacceptable, have the employee choose another one for testing |
|||||
((•)) When the controlled negative pressure procedure is used, STOP and repeat the test if the employee adjusts the respirator OR takes a breath and fails to hold it for 10 seconds |
|||||
((•)) Controlled negative pressure tests conducted according to the method published in 29 C.F.R. 1910.134, Appendix A are an acceptable alternative to the method outlined below. |
|||||
Description of Required Fit-Test Exercises |
Fit-Test Procedures |
||||
Qualitative Procedures |
Quantitative Procedures; EXCEPT the CNPP |
Controlled Negative Pressure Procedure (CNPP) |
|||
((•)) Normal breathing |
|||||
((–)) Breathe normally, while standing for one minute |
X |
X |
|||
((•)) Deep breathing |
|||||
((–)) Breathe slowly and deeply while standing for one minute |
X |
X |
|||
((–)) Take caution to avoid hyperventilating |
|||||
((•)) Head side to side |
|||||
((–)) Slowly turn head from side to side while standing for one minute, pausing at each extreme position to inhale |
X |
X |
|||
((–)) Be careful to NOT bump the respirator |
|||||
((•)) Head up and down |
|||||
((–)) Slowly move head up and down while standing for one minute, inhaling in the up position |
X |
X |
|||
((–)) Be careful to NOT bump the respirator |
|||||
((•)) Talking |
|||||
((–)) Talk slowly and loud enough to be heard clearly by the individual conducting fit testing for one minute. Choose ONE of the following: |
|||||
((■)) Read from a prepared text such as the Rainbow Passage1 |
X |
X |
|||
((■)) Count backward from 100 |
|||||
((■)) Recite a memorized poem or song. |
|||||
((•)) Grimace |
|||||
((–)) Smile or frown for fifteen seconds. |
X |
||||
((•)) Bending over |
|||||
((–)) Bend over to touch toes while standing. Repeat at a comfortable pace for one minute |
|||||
OR |
X |
X |
|||
((–)) Jog in place for one minute if the test enclosure, such as a hood, does not permit bending over |
|||||
((•)) Normal breathing |
|||||
((–)) Breathe normally while standing for one minute |
X |
X |
|||
((•)) Face forward |
|||||
((–)) Premeasurement activity: Stand and breath normally, without talking, for 30 seconds |
X |
||||
((–)) Measurement position: Face forward while holding breath for 10 seconds |
|||||
((•)) Bending over |
|||||
((–)) Premeasurement activity: While standing, bend at the waist, as if to touch toes |
X |
||||
((–)) Measurement position: Hold the bending position with face parallel to the floor while holding breath for 10 seconds |
|||||
((•)) Head shaking |
|||||
((–)) Premeasurement activity: Vigorously shake head from side to side for about 3 seconds while shouting |
X |
||||
((–)) Measurement position: Face forward, while holding breath for 10 seconds |
|||||
((•)) Redon-1 |
|||||
((–)) Premeasurement activity: Loosen all facepiece straps and remove the respirator completely, then put it back on |
X |
||||
((–)) Measurement position: Face forward while holding breath for 10 seconds |
|||||
((•)) Redon-2 |
|||||
((–)) Repeat the premeasurement activity and measurement position described in Redon-1 |
X |
||||
1The Rainbow Passage: | |
"When the sunlight strikes raindrops in the air, they act like a prism and form a rainbow. The rainbow is a division of white light into many beautiful colors. These take the shape of a long round arch, with its path high above, and its two ends apparently beyond the horizon. There is, according to legend, a boiling pot of gold at one end. People look, but no one ever finds it. When a man looks for something beyond reach, his friends say he is looking for the pot of gold at the end of the rainbow." | |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-05-072, filed 2/20/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-842-22015 Follow procedures established for cleaning and disinfecting respirators.
Follow the procedure in Table 20 for cleaning and disinfecting respirators.
Table 20
Respirator Cleaning Procedure
Step |
Task |
|||
1. |
Remove filters, cartridges, canisters, speaking diaphragms, demand and pressure valve assemblies, hoses, or any components recommended by the manufacturer. |
|||
• Discard or repair any defective parts. |
||||
2. |
Wash components in warm (43°C (110°F) maximum) water with a mild detergent or with a cleaner recommended by the manufacturer |
|||
((•)) a. A stiff bristle (not wire) brush may be used to help remove the dirt |
||||
((•)) b. If the detergent or cleaner does not contain a disinfecting agent, respirator components should be immersed for two minutes in one of the following: |
||||
((–)) i. A bleach solution (concentration of 50 parts per million of chlorine). Make this by adding approximately one milliliter of laundry bleach to one liter of water at 43°C (110°F) |
||||
((–)) ii. A solution of iodine (50 parts per million iodine). Make this in two steps: |
||||
((■)) A. First, make a tincture of iodine by adding 6-8 grams of solid ammonium iodide and/or potassium iodide to 100 cc of 45% alcohol approximately |
||||
((■)) B. Second, add 0.8 milliliters of the tincture to one liter of water at 43°C (110°F) to get the final solution |
||||
((–)) c. Other commercially available cleansers of equivalent disinfectant quality when used as directed, if their use is recommended or approved by the respirator manufacturer. |
||||
3. |
Rinse components thoroughly in clean, warm (43°C (110°F) maximum), preferably, running water. |
|||
Note: The importance of thorough rinsing cannot be overemphasized. Detergents or disinfectants that dry on facepieces could cause dermatitis. In addition, some disinfectants may cause deterioration of rubber or corrosion of metal parts, if not completely removed. |
||||
4. |
Drain components. |
|||
5. |
Air-dry components or hand dry components with a clean, lint-free cloth. |
|||
6. |
Reassemble the facepiece components. |
|||
((•)) Replace filters, cartridges, and canisters, if necessary (for testing). |
||||
7. |
Test the respirator to make sure all components work properly. |
|||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 09-19-119, filed 9/22/09, effective 12/1/09)
WAC 296-842-22020 Follow procedures established for seal checking respirators.
Make sure employees perform a user seal check as outlined in Table 21 each time the respirator is worn, to make sure the seal is adequate.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) 1. User seal checks are NOT a substitute for fit tests. See WAC 296-842-22010 for fit test procedures.
((•)) 2. You may use a seal check procedure recommended by the respirator manufacturer INSTEAD of the procedure outlined in Table 21 if you can demonstrate the procedure is based on a scientific study that, for example, demonstrates the procedure effectively identifies respirators that fit poorly when put on or adjusted.
Table 21
User Seal Check Procedure |
||
Important information for employees: |
||
((•)) You need to conduct a seal check each time you put your respirator on BEFORE you enter the respirator use area. The purpose of a seal check is to make sure your respirator (which has been previously fit tested by your employer) is properly positioned on your face to prevent leakage during use and to detect functional problems |
||
((•)) The procedure below has two parts; a positive pressure check and a negative pressure check. You must complete both parts each time. It should only take a few seconds to perform, once you learn it |
||
((♦)) If you cannot pass both parts, your respirator is NOT functioning properly, see your supervisor for further instruction. |
||
Positive pressure check: |
||
1. Remove exhalation valve cover, if removable. |
||
2. Cover the exhalation valve completely with the palm of your hand WHILE exhaling gently to inflate the facepiece slightly. |
||
3. The respirator facepiece should remain inflated (indicating a build-up of positive pressure and NO outward leakage). |
||
((•)) a. If you detect NO leakage, replace the exhalation valve cover (if removed), and proceed to conduct the negative pressure check |
||
((•)) b. If you detect evidence of leakage, reposition the respirator (after removing and inspecting it), and try the positive pressure check again. |
||
Negative pressure check: |
||
4. Completely cover the inhalation opening(s) on the cartridges or canister with the palm(s) of your hands WHILE inhaling gently to collapse the facepiece slightly. |
||
((•)) If you cannot use the palm(s) of your hands to effectively cover the inhalation openings on cartridges or canisters, you may use: |
||
((–)) Filter seal(s) (if available) |
||
OR |
||
((–)) Thin rubber gloves. |
||
5. Once the facepiece is collapsed, hold your breath for 10 seconds WHILE keeping the inhalation openings covered. |
||
6. The facepiece should remain slightly collapsed (indicating negative pressure and NO inward leakage). |
||
((•)) a. If you detect NO evidence of leakage, the tightness of the facepiece is considered adequate, the procedure is completed, and you may now use the respirator |
||
((•)) b. If you detect leakage, reposition the respirator (after removing and inspecting it) and repeat BOTH the positive and negative fit checks. |
||
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-863-099 Definitions.
ANSI. The American National Standards Institute.
Authorized person (maintenance). A person who has been designated to perform maintenance on a PIT.
Authorized person (training). A person approved or assigned by the employer to perform training for powered industrial truck operators.
Approved. Listed or approved by a nationally recognized testing laboratory or a federal agency that issues approvals for equipment such as the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA); the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH); Department of Transportation; or U.S. Coast Guard, which issue approvals for such equipment.
Bridge plate (dock-board). A device used to span the distance between rail cars or highway vehicles and loading platforms.
Classified location or hazardous location. Areas that could be hazardous because of explosive or flammable atmospheres. These locations are broken down into the following categories:
(a) Class I locations are areas where flammable gases or vapors are or may be present in the air in quantities sufficient to produce explosive or ignitable mixtures.
(b) Class II locations are areas where the presence of combustible dust could be sufficient to produce explosions.
(c) Class III locations are areas where the presence of easily ignitable fibers are suspended in the air but are not in large enough quantities to produce ignitable mixtures.
Counterweight. A weight used to counteract or the load being carried by the truck, or to increase the load carrying capacity of a truck.
Designations. A code used to show the different types of hazardous (classified) locations where PITs can be safely used:
(a) D refers to trucks that are diesel engine powered that have minimum safeguards against inherent fire hazards.
(b) DS refers to diesel powered trucks that, in addition to meeting all the requirements for type D trucks, are provided with additional safeguards to the exhaust, fuel and electrical systems.
(c) DY refers to diesel powered trucks that have all the safe-guards of the DS trucks and, in addition, any electrical equipment is completely enclosed. They are equipped with temperature limitation features.
(d) E refers to electrically powered trucks that have minimum acceptable safeguards against inherent fire hazards.
(e) ES refers to electrically powered trucks that, in addition to all of the requirements for the E trucks, have additional safeguards to the electrical system to prevent emission of hazardous sparks and to limit surface temperatures.
(f) EE refers to electrically powered trucks that have, in addition to all of the requirements for the E and ES type trucks, have their electric motors and all other electrical equipment completely enclosed.
(g) EX refers to electrically powered trucks that differ from E, ES, or EE type trucks in that the electrical fittings and equipment are designed, constructed and assembled to be used in atmospheres containing flammable vapors or dusts.
(h) G refers to gasoline powered trucks that have minimum acceptable safeguards against inherent fire hazards.
(i) GS refers to gasoline powered trucks that are provided with additional exhaust, fuel, and electrical systems safeguards.
(j) LP refers to liquefied petroleum gas-powered trucks that, in addition to meeting all the requirements for type G trucks, have minimum acceptable safeguards against inherent fire hazards.
(k) LPS refers to liquefied petroleum gas powered trucks that in addition to meeting the requirements for LP type trucks, have additional exhaust, fuel, and electrical systems safeguards.
Electrolyte. A chemical, usually acid, that is mixed with water to produce electricity.
Flammable liquid. Any liquid having a flashpoint at or below 199.4°F (93°C). Flammable liquids are divided into four categories as follows:
(a) Category 1 includes liquids having flashpoints below 73.4°F (23°C) and having a boiling point at or below 95°F (35°C).
(b) Category 2 includes liquids having flashpoints below 73.4°F (23°C) and having a boiling point above 95°F (35°C).
(c) Category 3 includes liquids having flashpoints at or above 73.4°F (23°C) and at or below 140°F (60°C). When a Category 3 liquid with a flashpoint at or above 100°F (37.8°C) is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it must be handled in accordance with the requirements for a Category 3 liquid with a flashpoint below 100°F (37.8°C).
(d) Category 4 includes liquids having flashpoints above 140°F (60°C) and at or below 199.4°F (93°C). When a Category 4 flammable liquid is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it must be handled in accordance with the requirements for a Category 3 liquid with a flashpoint at or above 100°F (37.8°C).
(e) When liquid with a flashpoint greater than 199.4°F (93°C) is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it must be handled in accordance with the requirements for a Category 4 flammable liquid.
Flashpoint. The minimum temperature at which a liquid gives off vapor within a test vessel in sufficient concentration to form an ignitable mixture with air near the surface of the liquid, and shall be determined as follows:
(a) For a liquid which has a viscosity of less than 45 SUS at 100°F (37.8°C), does not contain suspended solids, and does not have a tendency to form a surface film while under test, the procedure specified in the Standard Method of Test for Flashpoint by Tag Closed Tester (ASTM D-56-70), WAC 296-901-14024 Appendix B—Physical hazard criteria shall be used.
(b) For a liquid which has a viscosity of 45 SUS or more at 100°F (37.8°C), or contains suspended solids, or has a tendency to form a surface film while under test, the Standard Method of Test for Flashpoint by Pensky-Martens Closed Tester (ASTM D-93-71) or an equivalent method as defined by WAC 296-91-14024 Appendix B—Physical hazard criteria, shall be used, except that the methods specified in Note 1 to section 1.1 of ASTM D-93-71 may be used for the respective materials specified in the note.
(c) For a liquid that is a mixture of compounds that have different volatilities and flashpoints, its flashpoint shall be determined by using the procedure specified in (a) or (b) of this subsection on the liquid in the form it is shipped.
(d) Organic peroxides, which undergo auto-accelerating thermal decomposition, are excluded from any of the flashpoint determination methods specified in this section.
Front-end attachment. A device that is attached to the forks or lifting device of the truck.
Lanyard. A flexible line of webbing, rope, or cable used to secure a harness to an anchor point.
Liquefied petroleum gas. Any gas that is composed predominantly of the following hydrocarbons, or mixtures of them; propane, propylene, butanes (normal butane or iso-butane), and butylenes.
Listed by report. A report listing the field assembly, installation procedures, or both, for a UL listed product that does not have generally recognized installation requirements.
Load engaging. A device attached to a powered industrial truck and used to manipulate or carry a load.
Motorized hand truck. A powered truck with wheeled forks designed to go under or between pallets and is controlled by a walking or riding operator.
Nationally recognized testing laboratory. An organization recognized by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration that conducts safety tests on equipment and materials.
Order picker. A truck controlled by an operator who is stationed on a platform that moves with the load engaging means.
Powered industrial truck (PIT). A mobile, power-driven vehicle used to carry, push, pull, lift, stack, or tier material.
Rough terrain forklift truck. A truck intended to be used on unimproved natural terrain and at construction sites.
Safety harness (full body harness). A configuration of connected straps to distribute a fall arresting force over at least the thighs, shoulders and pelvis, with provisions for attaching a lanyard, lifeline, or deceleration devices.
Tie-off point (anchorage). A secure point to attach a lanyard that meets the requirements of WAC 296-24-88050, Appendix—C Personal fall arrest systems.
Vertical load backrest extension. A device that extends vertically from the fork carriage frame.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-863-100 Scope.
This chapter applies to powered industrial trucks that use electric motors or internal combustion engines. This includes, but is not limited to:
((•)) (1) Fork trucks.
((•)) (2) Forklifts.
((•)) (3) Tractors.
((•)) (4) Platform lift trucks.
((•)) (5) Motorized hand trucks.
((•)) (6) Other specialized industrial trucks.
((Definition:
A powered industrial truck (PIT) is a mobile, power-driven vehicle used to carry, push, pull, lift, stack, or tier material.))
Exemption: | This chapter does not apply to: |
((•)) 1. Compressed air-powered industrial trucks. | |
((•)) 2. Nonflammable compressed gas-operated industrial trucks. | |
((•)) 3. Vehicles covered by chapter 296-307 WAC, Safety standards for agriculture. | |
((•)) 4. Vehicles intended primarily for earth moving or over-the-road hauling. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-200 Design, construction, and equipment.
Summary:
Your responsibility:
To make sure PITs are properly designed, constructed, and equipped.
((You must:
Design and construction
Make sure PITs meet design and construction requirements
WAC 296-863-20005.
Meet these requirements when modifying or altering PITs
WAC 296-863-20010.
Labeling
Make sure PITs are properly labeled
WAC 296-863-20015.
Equipment
Protect operators from falling objects
WAC 296-863-20020.
Provide fall protection on order pickers
WAC 296-863-20025.
Provide directional lights when required
WAC 296-863-20030.
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) PITs
Make sure liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs meet these requirements
WAC 296-863-20035.
Meet these requirements when converting gasoline fuel PITs to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fuel
WAC 296-863-20040.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Design and Construction |
|
Make sure PITs meet design and construction requirements |
WAC 296-863-20005 |
Meet these requirements when modifying or altering PITs |
WAC 296-863-20010 |
Labeling |
|
Make sure PITs are properly labeled |
WAC 296-863-20015 |
Equipment |
|
Protect operators from falling objects |
WAC 296-863-20020 |
Provide fall protection on order pickers |
WAC 296-863-20025 |
Provide directional lights on PITs when required |
WAC 296-863-20030 |
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) PITs |
|
Make sure liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs meet these requirements |
WAC 296-863-20035 |
Meet these requirements when converting gasoline fuel PITs to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fuel |
WAC 296-863-20040 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-20005 Make sure PITs meet design and construction requirements.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure PITs meet American National Standards Institute (ANSI) design and construction requirements.
((•)) (2) You must make sure PITs manufactured before March 1, 2000, meet the requirements of ANSI B56.1-1969, Safety Standards for Powered Industrial Trucks.
((•)) (3) You must make sure PITs manufactured on or after March 1, 2000, meet the requirements of ANSI B56.1-1993, Safety Standards for Powered Industrial Trucks.
((•)) (4) You must make sure rough terrain forklift trucks manufactured on or after January 1, 2005, meet the design and construction requirements of ANSI B56.6-1992, Safety Standard for Rough Terrain Forklift Trucks.
Note: | There may be a nameplate on the PIT or a statement in the instruction manual indicating that the PIT meets the requirement of the appropriate ANSI standard. If in doubt, check with the manufacturer. |
ANSI B56.1-1993 and B56.6-1992 are available by:
((–)) (a) Purchasing copies by writing:
American National Standards Institute
11 West 42nd Street
New York, NY 10036
OR
((–)) (b) Contacting the ANSI web site at www.ansi.org.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-20010 Meet these requirements when modifying or altering PITs.
((You must:)) (1) You must have written approval from the PIT manufacturer before making any modifications to the PIT that:
((–)) (a) Change the relative position of the various parts of the PIT from what they were when originally received from the manufacturer((.));
((–)) (b) Add extra parts not provided by the PIT manufacturer((.));
((–)) (c) Eliminate any parts((.));
((–)) (d) Affect capacity or safe operation.
Exemption: | This does not apply to converting PITs from gasoline to LPG fuel. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must make sure any modifications or additions to the PIT are shown on the plates, tags, or decals to reflect any changes in the PITs:
((–)) (a) Capacity((.));
((–)) (b) Operation((.));
((–)) (c) Maintenance instructions.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-20015 Make sure PITs are properly labeled.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure all PIT nameplates as well as any stickers, stencils or marks that relate to the stability and safety of the PIT are:
((–)) (a) In place((.));
((–)) (b) Legible.
Note: | PITs should have a nameplate installed by the manufacturer that contains at least the following information: |
((–)) 1. Model and serial number. | |
((–)) 2. Approximate weight of the PIT. | |
((–)) 3. Certification that the manufacturer has met the mandatory requirements of ANSI B56.1 Safety Standards for Powered Industrial Trucks. | |
((–)) 4. Type designation to show the PIT meets the applicable requirements of a nationally recognized testing laboratory. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must make sure PITs approved for hazardous (classified) locations have a label or some other identifying mark indicating acceptance by a nationally recognized testing laboratory.
((•)) (3) You must make sure PITs with front-end attachments, including fork extensions, are marked to:
((–)) (a) Identify the attachment((.));
((–)) (b) Show the approximate combined weight of the PIT and attachment((.));
((–)) (c) Show the maximum capacity of the PIT with attachments at their highest elevation and the load laterally centered.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-20020 Protect operators from falling objects.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must use an overhead guard to protect operators from falling objects such as small packages, boxes, and bagged material.
Exception: | A high lift rider truck may be operated without the guard, providing all of the following conditions are met: ((•)) 1. Vertical movement of the lifting mechanism is restricted to seventy-two inches (1800 mm) or less from the ground. ((•)) 2. The high lift rider truck will operate only in an area where: ((–)) a. The top of a tiered load will not be more than one hundred twenty inches (3000 mm) high. ((–)) b. The bottom of a tiered load will not be more than seventy-two inches (1800 mm) high. ((–)) c. Only stable loads are handled. ((–)) d. The operator is protected from objects falling from high stack areas. |
Note: | The overhead guard is not intended to withstand the impact of a maximum capacity load of the PIT. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must equip all high lift rider trucks with overhead guards that meet the design and construction requirements of American National Standards Institute (ANSI) B56.1-1993, Safety Standards for Powered Industrial Trucks.
((•)) (3) You must use a vertical load backrest extension to keep all or any part of the load from falling backwards towards the operator if the load presents a hazard.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-863-20025 Provide fall protection on order pickers.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure order pickers have either:
((–)) (a) Standard guardrails on all open sides; or
((OR
–)) (b) A safety harness and lanyard that are connected to a tie off point that has been approved by the PIT manufacturer.
((•)) (2) You must make sure personal fall arrest equipment meets the requirements of WAC 296-24-88050, Appendix C—Personal fall arrest systems.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-20030 Provide directional lights on PITs when required.
((You must:
•)) You must provide PITs with directional lighting if the general lighting is less than two lumens per square foot.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Lighting levels can be measured with a light meter. |
((•)) 2. Conversion information: One foot-candle = one lumen incident per square foot = 10.76 lux. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-20035 Make sure liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs meet these requirements.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must use fuel containers that meet either of the following minimum requirements:
((–)) (a) A U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT) approved container authorized for LP-gas service that has a minimum service pressure of two hundred forty pounds per square inch gage (psig); or
((OR
–)) (b) A container Type 250 that has a design pressure of 312.5 psig.
((•)) (2) You must make sure fuel containers do not use variable liquid-level gages that require venting fuel to the atmosphere.
((•)) (3) You must make sure the fuel system of PITs used inside buildings:
((–)) (a) Has an approved automatic shutoff valve, located ahead of the inlet of the gas-air mixer, that will stop the flow of fuel to the mixer if the engine stops; and
((AND
–)) (b) Use not more than two LP-gas fuel containers.
((•)) (4) You must make sure the fuel system of PITs used outdoors has an approved automatic shutoff valve, located ahead of the inlet of the gas-air mixer, that will stop the flow of fuel to the mixer if both:
((–)) (a) The ignition is OFF((.));
((–)) (b) The engine is not running.
Note: | You may use an atmospheric type regulator (zero governor) as a shutoff valve if the PIT is used outdoors. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-20040 Meet these requirements when converting gasoline fuel PITs to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fuel.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure PITs originally approved to use gasoline for fuel that are then converted to LPG fuel:
((–)) (1) Meet the requirements for LP or LPS designated PITs; and
((AND
–)) (2) Are converted using only approved equipment.
Definitions:
((•)) LP. Refers to liquefied petroleum gas-powered trucks that, in addition to meeting all the requirements for type G trucks, have minimum acceptable safeguards against inherent fire hazards.
((•)) LPS. Refers to liquefied petroleum gas powered trucks that in addition to meeting the requirements for LP type trucks, have additional exhaust, fuel, and electrical systems safeguards.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Tables 1, 2, and 3 list the types of PITs and the locations where they can be used safely. |
((•)) 2. The description of the component parts of the conversion system and the recommended method of installation on specific PITs are contained in the "Listed by Report" provided by the testing laboratory. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-300 Inspection, repair, maintenance, and servicing.
Summary:
Your responsibility:
To make sure PITs are kept in safe condition and properly serviced.
References: | ((•)) 1. Appropriate respiratory protection may need to be used when operating PITs. See chapter 296-841 WAC, Respiratory hazards, for more information. |
((•)) 2. Appropriate PPE may need to be worn. See WAC 296-800-160 in the Safety and Health Core Rules for more information. |
((You must:
Inspect, repair and maintain PITs
Make sure PITs are in safe working condition
WAC 296-863-30005.
Inspect your PITs
WAC 296-863-30010.
Meet these requirements when repairing PITs
WAC 296-863-30015.
Maintain your PITs properly
WAC 296-863-30020.
Service your PITs
Service gasoline fueled PITs safely
WAC 296-863-30025.
Service liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs safely
WAC 296-863-30030.
Make sure battery charging areas are safe
WAC 296-863-30035.
Service batteries for electric PITs safely
WAC 296-863-30040.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Inspect, Repair and Maintain PITs |
|
Make sure PITs are in safe working condition |
WAC 296-863-30005 |
Inspect your PITs |
WAC 296-863-30010 |
Meet these requirements when repairing PITs |
WAC 296-863-30015 |
Maintain your PITs properly |
WAC 296-863-30020 |
Service Your PITs |
|
Service gasoline fueled PITs safely |
WAC 296-863-30025 |
Service liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs safely |
WAC 296-863-30030 |
Make sure battery charging areas are safe |
WAC 296-863-30035 |
Service batteries for electric PITs safely |
WAC 296-863-30040 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-30005 Make sure PITs are in safe working condition.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must remove any PIT from service that is not in safe operating condition.
((•)) (2) You must immediately remove PITs from service that have any of the following problems, and do not return them to service until the cause of the problem has been eliminated:
((–)) (a) A leak in the fuel system((.));
((–)) (b) A clogged water muffler screen or other muffler part((.));
((–)) (c) An exhaust system that is emitting hazardous sparks or flames((.));
((–)) (d) A part that is hotter than its normal operating temperature thus creating a hazardous condition.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-30010 Inspect your PITs.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must inspect PITs according to the manufacturer's instructions.
((•)) (2) You must inspect PITs at these times:
((–)) (a) Daily before being put into service; and
((AND
–)) (b) After each shift, if the PIT is used on a continuous (twenty-four-hour) basis.
Note: | You can designate someone on the off-going shift, on-coming shift, or some other person to do the inspection. |
((You must:
•)) (3) You must report and correct any deficiencies noted during the inspection.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-30015 Meet these requirements when repairing PITs.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure repairs are made by authorized persons.
((•)) (2) You must make sure replacement parts are equivalent to the parts used in the original design.
((•)) (3) You must make sure repairs are not made in Class I, II, or III locations. See Tables 1, 2, and 3 for more information.
Definitions:
Class I locations ((are)). Areas where flammable gases or vapors are or may be present in the air in quantities sufficient to produce explosive or ((ignitible)) ignitable mixtures.
Class II locations ((are)). Areas where the presence of combustible dust could be sufficient to produce explosions.
Class III locations ((are)). Areas where the presence of easily ((ignitible)) ignitable fibers are suspended in the air but are not in large enough quantities to produce ((ignitible)) ignitable mixtures.
((You must:
•)) (4) You must make sure fuel and ignition system repairs that involve fire hazards are made only in locations designated for such repairs.
((•)) (5) You must disconnect the battery before starting repairs to a PIT electrical system.
((•)) (6) You must close the fuel container shutoff valve before repairing an LP-gas fueled PIT in a garage.
Exemption: | The container shutoff valve may be left open if it is necessary to run the engine. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-863-30020 Maintain your PITs properly.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must maintain PITs according to this chapter and the manufacturer's instructions.
((•)) (2) You must keep PITs:
((–)) (a) Clean((.));
((–)) (b) Free of excess lint, oil, and grease.
((•)) (3) You must take appropriate precautions to protect employees from the hazards associated with the cleaning agents or solvents used.
((–)) Precautions could include methods such as ventilation.
((•)) (4) You must make sure solvents used for cleaning PITs have a flash point of 100° Fahrenheit or more.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-30025 Service gasoline fueled PITs safely.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must handle and store liquid fuels, such as gasoline and diesel fuel, according to the National Fire Protection Association Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code (NFPA No. 30-1996).
Note: | National Fire Protection Association codes are available by: |
Purchasing copies by writing: | |
National Fire Protection Association | |
1 Batterymarch Park | |
Quincy, MA 02169-7471 | |
OR | |
Contacting the NFPA web site at www.nfpa.org. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must stop the engine before filling a fuel tank.
((•)) (3) You must avoid spilling fuel during servicing.
((•)) (4) You must make sure you do not use open flames to check the gasoline level in fuel tanks.
((•)) (5) You must do the following before restarting the engine after fueling:
((–)) (a) Put on the fuel tank cap((.));
((–)) (b) Make sure spilled oil or fuel is completely washed away or evaporated.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-30030 Service liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs safely.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must handle and store liquefied petroleum gas fuel according to the National Fire Protection Association Storage and Handling of Liquefied Petroleum Gases (NFPA No. 58-1998).
((•)) (2) You must shut down the engine while fueling.
((•)) (3) You must fuel PITs equipped with permanently mounted fuel containers outdoors.
((•)) (4) You must make sure filling fuel containers from industrial bulk storage containers is done at least:
((–)) (a) Ten feet from the nearest masonry-walled building((.));
((–)) (b) Twenty-five feet from the nearest building or other construction((.));
((–)) (c) Twenty-five feet from any building opening.
((•)) (5) You must make sure PITs are stored or serviced inside garages only when:
((–)) (a) There are no leaks in the fuel system; and
((AND
–)) (b) The fuel tanks are not filled beyond the maximum filling density specified in WAC 296-24-47505 (12)(a), Storage and handling of liquefied petroleum gases.
Reference: | See chapter 296-24 WAC, Part F-1, for LPG charging equipment requirements and maximum filling density and LPG service stations. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-30035 Make sure battery charging areas are safe.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure battery charging areas are designated and provided with all of the following:
((–)) (a) Means to flush and neutralize spilled electrolyte((.));
((–)) (b) Fire protection((.));
((–)) (c) Ventilation that is adequate to disperse fumes from gassing batteries.
((•)) (2) You must prohibit smoking in battery charging areas.
((•)) (3) You must take precautions to prevent open flames, sparks, or electric arcs in battery charging areas.
((•)) (4) You must protect battery charging equipment from being damaged by PITs.
((•)) (5) You must provide at least one of the following to handle batteries:
((–)) (a) Conveyor((.));
((–)) (b) Overhead hoist((.));
((–)) (c) Other equivalent material handling equipment.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-30040 Service batteries for electric PITs safely.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure PITs are properly positioned with the brake on before charging or changing batteries.
((•)) (2) You must make sure you do not use open flames to check the electrolyte level in storage batteries.
((•)) (3) You must do the following when charging batteries:
((–)) (a) Make sure vent caps are functioning((.));
((–)) (b) Open the battery or compartment covers to dissipate heat((.));
((–)) (c) Pour acid into water, never pour water into acid.
((•)) (4) You must provide a carboy tilter or siphon to handle electrolyte.
((•)) (5) You must keep tools and other metallic objects away from the top of uncovered batteries.
((•)) (6) You must make sure reinstalled batteries are properly positioned and secured.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-400 Operations.
Summary:
Your responsibility:
To operate your PITs safely.
((You must:
General operations
Protect employees around PITs
WAC 296-863-40005.
Operate PITs safely
WAC 296-863-40010.
Make sure PIT loads are carried safely
WAC 296-863-40015.
Meet these requirements when the operator leaves the normal operating position
WAC 296-863-40020.
Meet these requirements when operating near railroad tracks
WAC 296-863-40025.
Special operations
Meet this requirement when using motorized hand trucks
WAC 296-863-40030.
Meet these requirements when using elevators
WAC 296-863-40035.
Meet these requirements when using dockboards (bridge plates)
WAC 296-863-40040.
Meet these requirements when loading or unloading railroad cars with a PIT
WAC 296-863-40045.
Meet these requirements when loading or unloading highway trucks with PITs
WAC 296-863-40050.
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs
Meet these additional requirements when operating liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs
WAC 296-863-40055.
Personnel lifting
Make sure work platforms and PITs used to lift people meet these requirements
WAC 296-863-40060.
Operate PITs using elevated work platforms safely
WAC 296-863-40065.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
General Operations |
|
Protect employees around PITs |
WAC 296-863-40005 |
Operate PITs safely |
WAC 296-863-40010 |
Make sure PIT loads are carried safely |
WAC 296-863-40015 |
Meet these requirements when the operator leaves the normal operating position |
WAC 296-863-40020 |
Meet these requirements when operating near railroad tracks |
WAC 296-863-40025 |
Special Operations |
|
Meet this requirement when using motorized hand trucks |
WAC 296-863-40030 |
Meet these requirements when using elevators |
WAC 296-863-40035 |
Meet these requirements when using dock-boards (bridge plates) |
WAC 296-863-40040 |
Meet these requirements when loading or unloading railroad cars with a PIT |
WAC 296-863-40045 |
Meet these requirements when loading or unloading highway trucks with PITs |
WAC 296-863-40050 |
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) Fueled PITs |
|
Meet these additional requirements when operating liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs |
WAC 296-863-40055 |
Personnel Lifting |
|
Make sure work platforms and PITs used to lift people meet these requirements |
WAC 296-863-40060 |
Operate PITs using elevated work platforms safely |
WAC 296-863-40065 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40005 Protect employees around PITs.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure operators use restraint devices, such as seatbelts or lap-bars, when they are provided on the PIT.
((•)) (2) You must make sure you do not allow people:
((–)) (a) Under the elevated part of any PIT, whether it is loaded or empty;
((–)) (b) To put any part of their body between the uprights of the mast; or
((OR
–)) (c) Outside the running lines of the PIT.
((•)) (3) You must make sure you do not allow unauthorized people to ride on PITS.
((•)) (4) You must make sure people riding on PITs have a safe place to ride.
((•)) (5) You must make sure you do not allow stunt driving or horseplay.
((•)) (6) You must make sure PITs are not driven up to anyone in front of a bench or other fixed object.
((•)) (7) You must make sure access to fire aisles, stairways, and fire equipment is kept clear.
((•)) (8) You must make sure there is sufficient headroom under overhead installations such as lights, pipes, and sprinkler systems to safely operate PITs.
Reference: | PIT operations may cause the airborne concentration levels of carbon monoxide gas to increase. You have to keep the concentration levels below the levels specified in chapter 296-841 WAC, Respiratory hazards. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40010 Operate PITs safely.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must operate PITs according to the manufacturer's instructions.
((•)) (2) You must make sure PIT operators do all of the following:
((–)) (a) Obey all traffic regulations, including authorized workplace speed limits((.));
((–)) (b) Yield the right of way to ambulances, fire trucks, and other vehicles in emergency situations((.));
((–)) (c) Keep a safe distance of approximately three truck lengths from the PIT ahead((.));
((–)) (d) Look in the direction they are going and keep a clear view of their path of travel((.));
((–)) (e) Slow down and sound the horn at cross aisles and other locations where vision is obstructed((.));
((–)) (f) Do not pass other PITs traveling in the same direction at intersections, blind spots, or other dangerous locations((.));
((–)) (g) Keep a safe distance from the edge of ramps or platforms while on any of the following:
((■)) (i) Elevated docks((.));
((■)) (ii) Elevated platforms((.));
((■)) (iii) Freight cars.
((•)) (3) You must make sure operators keep PITs under control at all times, including doing all of the following:
((–)) (a) Drive at a speed that allows the PIT to be stopped safely((.));
((–)) (b) Drive more slowly on wet or slippery floors((.));
((–)) (c) Reduce speed to a safe level while turning((.));
((–)) (d) Avoid driving over loose objects.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40015 Make sure PIT loads are carried safely.
((You must:))
(1) You must make sure loads are stable, safe and within the rated load capacity of the PIT.
(2) You must do both of the following when picking up a load:
((•)) (a) Place the load engaging means under the load as far as possible((.));
((•)) (b) Tilt the mast carefully backwards to stabilize the load.
(3) You must make sure not to tilt the load engaging means forward when it is elevated unless:
((•)) (a) Picking up a load; or
((OR
•)) (b) Depositing a load on a rack or stack.
(4) You must do both of the following when traveling with a load:
((•)) (a) Keep the load trailing if it obstructs the operator's forward view((.));
((•)) (b) Travel with the load upslope when climbing or descending slopes of more than ten percent.
(5) You must do both of the following when climbing a slope:
((•)) (a) Tilt the load and load engagement means backwards if necessary to stabilize the load; and
((AND
•)) (b) Raise the load and load engagement means only as far as necessary to clear the surface.
(6) You must make sure PITS with attachments are operated as partially loaded trucks, even if they are not carrying a load.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40020 Meet these requirements when the operator leaves the normal operating position.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure operators do the following when getting off the PIT:
((–)) (a) Fully lower the load engaging means((.));
((–)) (b) Neutralize the controls((.));
((–)) (c) Set the brakes.
((•)) (2) Make sure operators do the following when leaving a PIT unattended:
((–)) (a) Fully lower the load engaging means((.));
((–)) (b) Neutralize the controls((.));
((–)) (c) Shut off power((.));
((–)) (d) Set the brakes((.));
((–)) (e) Block the wheels, if parked on an incline.
Note: | A PIT is unattended when the operator: |
((•)) 1. Is more than twenty-five feet away; or | |
((OR | |
• Can not)) 2. Cannot see the PIT. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40025 Meet these requirements when operating near railroad tracks.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure PITs are driven diagonally across railroad tracks, whenever possible.
((•)) (2) You must make sure PITs are parked eight feet six inches or more from the center of any railroad tracks.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40030 Meet this requirement when using motorized hand trucks.
((You must:
•)) You must make sure motorized hand trucks enter elevators and other confining areas with the load end forward.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40035 Meet these requirements when using elevators.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must do both of the following when driving PITs onto an elevator:
((–)) (a) Approach slowly((.));
((–)) (b) Enter the elevator squarely after the elevator car is leveled.
((•)) (2) You must do all the following after the PIT is positioned on the elevator:
((–)) (a) Neutralize the controls((.));
((–)) (b) Shut off the power((.));
((–)) (c) Set the brakes.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40040 Meet these requirements when using ((dockboards)) dock-boards (bridge plates).
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure ((dockboards)) dock-boards are not overloaded:
((–)) (a) Make sure they are strong enough to carry the load imposed on them.
((–)) (b) Make sure loads do not exceed the ((dockboard's)) dock-board's rated capacity.
((•)) (2) You must do the following when using ((dockboards)) dock-boards:
((–)) (a) Drive slowly and carefully over ((dockboards.)) dock-boards;
((–)) (b) Properly secure ((dockboards)) dock-boards before driving on them.
((•)) (3) You must make sure powered ((dockboards)) dock-boards meet the design and construction requirements of U.S. Department of Commerce Commercial Standard CS 202-56 (1961) "Industrial Lifts and Hinged Loading Ramps."
((•)) (4) You must do the following when using portable ((dockboards)) dock-boards:
((–)) (a) Use anchors or other devices that will prevent slipping((.));
((–)) (b) Make sure they have handholds or other effective means for safe handling.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40045 Meet these requirements when loading or unloading railroad cars with a PIT.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must check the railroad car flooring for breaks or weakness before driving on it.
((•)) (2) You must set the brakes and use wheel stops or other recognized positive protection to keep railcars from moving:
((–)) (a) During loading or unloading operations; or
((OR
–)) (b) While ((dockboards)) dock-boards (bridge plates) are in position.
((•)) (3) You must meet these requirements when using PITs to open or close freight car doors:
((–)) (a) The PIT has to have an approved device specifically designed to open and close doors((.));
((–)) (b) The device has to be designed so that force will be applied to the door parallel to door travel((.));
((–)) (c) The PIT operator has to be trained to use the device and have full view of the operation((.));
((–)) (d) People must be kept clear while the door is being moved.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40050 Meet these requirements when loading or unloading highway trucks with PITs.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must check the truck or trailer flooring for breaks or weakness before driving on it.
((•)) (2) You must prevent movement of trucks or trailers during loading or unloading by:
((–)) (a) Setting the brakes; and
((AND
–)) (b) Chocking or blocking the wheels.
Exemptions: | ((•)) 1. You can use mechanical means instead of wheel chocks or blocks to secure the trailer to the loading dock. |
((•)) 2. Wheel chocks or blocks are not required when: | |
((–)) a. The mechanical means prevents the trailer from moving away from the dock. | |
((–)) b. The mechanical equipment is used and maintained as recommended by the manufacturer. | |
((–)) c. Damaged mechanical equipment is immediately removed from service. |
Note: | You may need to use fixed jacks to keep a semi-trailer that is not coupled to a tractor from up ending during loading or unloading. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40055 Meet these additional requirements when operating liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fueled PITs.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure you do not park PITs near:
((–)) (a) Sources of heat, open flames, or similar ignition sources; or
((OR
–)) (b) Open pits, such as service pits, that do not have adequate ventilation.
((•)) (2) You must make sure PITs stored inside a garage do not have:
((–)) (a) A leak in the fuel system((.));
((–)) (b) Fuel containers filled beyond the maximum filling capacity.
Reference: | See WAC 296-24-47505(12), Storage and handling of liquefied petroleum gases, for maximum filling capacities. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40060 Make sure work platforms and PITs used to lift people meet these requirements.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure work platforms:
((–)) (a) Are securely fastened to the lifting carriage or forks((.));
((–)) (b) Have standard guardrails and toeboards on all sides.
((•)) (2) You must guard the area between the platform and the PIT mast to prevent employee contact with chains or other shear points.
((•)) (3) You must make sure PITs used to elevate a work platform have a lift mechanism that ((can not)) cannot drop faster than one hundred thirty five feet per minute in the event of a system failure.
((•)) (4) You must make sure the lifting carriage or forks are prevented from tilting.
Note: | Examples of how this may be accomplished are the use of: |
((•)) 1. A control lever that prevents the inadvertent movement; or | |
((•)) 2. Use of a strap or other device to hold the control lever in position. |
((You must:
•)) (5) You must make sure PITs with controls (vertical only or horizontal and vertical) that can be elevated with the lifting carriage or forks, have a way for people on the platform to shut off power to the PIT.
Note: | You can find the minimum requirements for standard railings of various types of construction in WAC 296-24-75011, Railings, toeboards and cover specifications. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-40065 Operate PITs using elevated work platforms safely.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure the PIT operator:
((–)) (a) Is attending the lift equipment when workers are on the platform((.));
((–)) (b) Is in the normal operating position while raising or lowering the platform.
Note: | A PIT is unattended when the operator: |
((•)) 1. Is more than twenty-five feet away; or | |
((OR | |
•)) 2. Cannot see the PIT. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must make sure the operator does not move the PIT from one point to another while workers are on the platform.
((–)) The operator may inch or maneuver the PIT at very low speed with workers on the platform.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-500 Hazardous (classified) locations.
Summary:
Your responsibility:
To use PITs safely in hazardous (classified) locations.
((You must:
Use the appropriate approved PITs in hazardous (classified) locations
WAC 296-863-50005.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Use the appropriate approved PITs in hazardous (classified) locations |
WAC 296-863-50005 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-863-50005 Use the appropriate PITs in hazardous (classified) locations.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure PITS are used in hazardous (classified) locations as follows:
((–)) (a) PITS authorized to be used in Class 1 locations are shown in Table 1, Approved PIT Use in Class 1 Locations((.));
((–)) (b) PITS authorized to be used in Class 2 locations are shown in Table 2, Approved PIT Use in Class 2 Locations((.));
((–)) (c) PITS authorized to be used in Class 3 locations are shown in Table 3, Approved PIT Use in Class 3 Locations.
((•)) (2) You must ensure PITS authorized to be used in unclassified locations are:
((–)) (a) Approved PITS designated as Type D, E, G, or LP; and
((AND
-)) (b) PITs that meet the requirements of a Type D, E, G, or LP PIT.
Definitions:
((• An)) Unclassified location ((is)). An area that is not designated as a Class 1, 2, or 3 location.
((•)) Designations ((means)). A a code used to show the different types of hazardous (classified) locations where PITs can be safely used:
((–)) D. Refers to trucks that are diesel engine powered that have minimum safeguards against inherent fire hazards.
((–)) DS. Refers to diesel powered trucks that, in addition to meeting all the requirements for type D trucks, are provided with additional safeguards to the exhaust, fuel and electrical systems.
((–)) DY. Refers to diesel powered trucks that have all the safeguards of the DS trucks and, in addition, any electrical equipment is completely enclosed. They are equipped with temperature limitation features.
((–)) E. Refers to electrically powered trucks that have minimum acceptable safeguards against inherent fire hazards.
((–)) ES. Refers to electrically powered trucks that, in addition to all of the requirements for the E trucks, have additional safeguards to the electrical system to prevent emission of hazardous sparks and to limit surface temperatures.
((–)) EE. Refers to electrically powered trucks that have, in addition to all of the requirements for the E and ES type trucks, have their electric motors and all other electrical equipment completely enclosed.
((–)) EX. Refers to electrically powered trucks that differ from E, ES, or EE type trucks in that the electrical fittings and equipment are designed, constructed and assembled to be used in atmospheres containing flammable vapors or dusts.
((–)) G. Refers to gasoline powered trucks that have minimum acceptable safeguards against inherent fire hazards.
((–)) GS. Refers to gasoline powered trucks that are provided with additional exhaust, fuel, and electrical systems safeguards.
((–)) LP. Refers to liquefied petroleum gas-powered trucks that, in addition to meeting all the requirements for type G trucks, have minimum acceptable safeguards against inherent fire hazards.
((–)) LPS. Refers to liquefied petroleum gas-powered trucks that in addition to meeting the requirements for LP type trucks, have additional exhaust, fuel, and electrical systems safeguards.
Note: | ((•)) 1. Tables 1, 2, and 3 show the type of approved PITs that can be used in the appropriate divisions and groups. |
((•)) 2. PITS cannot be used in divisions and groups that do not have a PIT designation listed. | |
((•)) 3. Approved PITs will be marked or labeled with the designation of the PIT. See WAC 296-863-20010, Make sure PITs are properly labeled. |
Table 1
Approved PIT Use in Class 1 Locations
Class 1 Locations in which flammable gases or vapors are, or may be, present in the air in quantities sufficient to produce explosive or ignitable mixtures. |
|||||||
Division 1 Conditions exist continuously, intermittently, or periodically under normal operating conditions. |
Division 2 Conditions may occur accidentally, for example, due to a puncture of a storage drum. |
||||||
Group A |
Group B |
Group C |
Group D |
Group A |
Group B |
Group C |
Group D |
Acetylene |
Hydrogen |
Ethyl ether |
Acetone Alcohols Benzene Gasoline Lacquer solvent |
Acetylene |
Hydrogen |
Ethyl ether |
Acetone Alcohols Benzene Gasoline Lacquer solvent |
No PIT type can be used |
No PIT type can be used |
No PIT type can be used |
Use this PIT type: EX |
No PIT type can be used |
No PIT type can be used |
No PIT type can be used |
Use this PIT type: DS DY ES EE EX GS LPS |
Table 2
Approved PIT Use in Class 2 Locations
Class 2 Locations which are hazardous because of the presence of combustible dust. |
|||||
Division 1 Explosive mixture may be present under normal operating conditions, or where failure of equipment may cause the condition to exist simultaneously with arcing or sparking of electrical equipment, or where dusts of an electrically conducting nature may be present. |
Division 2 Explosive mixture not normally present, but where deposits of dust may cause heat rise in electrical equipment, or where such deposits may be ignited by arcs or sparks from electrical equipment. |
||||
Group E |
Group F |
Group G |
Group E |
Group F |
Group G |
Metal dust |
Carbon black Coal dust Coke dust |
Grain dust Flour dust Starch dust Organic dust |
Metal dust |
Carbon black Coal dust Coke dust |
Grain dust Flour dust Starch dust Organic dust |
No PIT type can be used |
Use this PIT type: EX |
Use this PIT type: EX |
No PIT type can be used |
Use this PIT type: EX DY EE |
Use this PIT type: DS DY ES EE EX GS LPS |
Table 3
Approved PIT Use in Class 3 Locations
Class 3 Locations where easily ignitable fibers or flyings are present but not likely to be in suspension in quantities sufficient to produce ignitable mixtures. |
|
Division 1 |
Division 2 |
Locations in which easily ignitable fibers or materials producing combustible flyings are handled, manufactured, or used. |
Locations in which easily ignitable fibers are stored or handled (except in the process of manufacture). |
Use this PIT type: DY EE EX |
Use this PIT type: DS DY E ES EE EX GS LPS |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-600 Training.
Summary:
Your responsibility:
To make sure PIT operators are competent.
((You must:
Operator training
Make sure PIT operators are trained
WAC 296-863-60005.
Retrain PIT operators as required
WAC 296-863-60010.
Evaluate PIT operators performance
WAC 296-863-60015.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Operator Training |
|
Make sure PIT operators are trained |
WAC 296-863-60005 |
Retrain PIT operators as required |
WAC 296-863-60010 |
Evaluate PIT operators performance |
WAC 296-863-60015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-60005 Make sure PIT operators are trained.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must make sure employees successfully complete an operator training program before operating PITs. The only time a trainee can operate a PIT is:
((–)) (a) Under the direct supervision of a person who has the knowledge, training, and experience to train and evaluate operators; and
((AND
–)) (b) When operating the PIT does not endanger the trainee or other employees.
((•)) (2) You must make sure training is done by you or someone you designate that has the knowledge, training, and experience to:
((–)) (a) Conduct the training; and
((AND
–)) (b) Evaluate trainee competence.
((•)) (3) You must make sure your operator training program consists of:
((–)) (a) Formal instruction((.
■)) such as lecture and discussion, interactive computer learning, video tapes, and written material((.));
((–)) (b) Practical training((.
■)) such as demonstrations done by the trainer and practical exercises performed by trainees((.));
((–)) (c) Evaluation of trainee performance.
((•)) (4) You must make sure the initial operator training program covers the subjects in Table 4, Required Training Topics.
Note: | If an operator has previously received training specified in Table 4, Required Training Topics, additional training in that topic is not required if: |
((•)) 1. The training was appropriate to the PIT and working conditions in your workplace; and | |
((AND | |
•)) 2. The employee has passed a PIT performance evaluation within the last three years. |
Table 4
Required Training Topics
Topics related to powered industrial truck |
Topics related to your workplace |
((•)) Operating instructions((,)) |
((•)) Surface conditions where the PIT will be operated |
((•)) Warnings and precautions for the types of PIT the operator will be authorized to operate |
((•)) Composition of loads to be carried and load stability |
((•)) Differences between the PIT and the automobile |
((•)) Load manipulation, stacking, and unstacking |
((•)) PIT controls and instrumentation: Where they are located, what they do, and how they work |
((•)) Pedestrian traffic in areas where the PIT will be operated |
((•)) Engine or motor operation |
((•)) Narrow aisles and other restricted places where the PIT will be operated |
((•)) Steering and maneuvering |
((•)) Use of door opening and closing devices |
((•)) Visibility (including restrictions due to loading) |
((•)) Hazardous (classified) locations where the PIT will be operated |
((•)) Fork and attachment adaptation, operation, and use limitations |
((•)) Ramps and other sloped surfaces that could affect the PITs stability |
((•)) PIT capacity |
((•)) Closed environments and other areas where insufficient ventilation or poor PIT maintenance could cause a buildup of carbon monoxide or diesel exhaust |
((•)) PIT stability |
((•)) Other unique or potentially hazardous environmental conditions in the workplace that could affect safe operation |
((•)) Any PIT inspection and maintenance that the operator will be required to perform |
|
((•)) Refueling |
|
((•)) Charging and recharging of batteries |
|
((•)) Operating limitations |
|
((•)) Any other operating instructions, warnings, or precautions listed in the operator's manual for the types of PIT that the employee is being trained to operate |
((You must:
•)) (5) You must keep written records of operator training and evaluations that include the following information:
((–)) (a) Name of the operator((.));
((–)) (b) Date of the training((.));
((–)) (c) Date of the evaluation((.));
((–)) (d) Name of the person giving the training or evaluation.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-60010 Retrain PIT operators as required.
((You must:
•)) You must provide PIT operators refresher training if any of the following occur:
((–)) (1) The operator is involved in an accident or near-miss incident.
((–)) (2) The operator is seen operating the PIT in an unsafe manner.
((–)) (3) An evaluation shows the operator is not operating the PIT safely.
((–)) (4) The operator is assigned to drive a different type or modified PIT.
((–)) (5) Conditions in the workplace change that could affect safe operation of the PIT.
Note: | Refresher training is required only in those topics where the operator has been found deficient. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 04-19-051, filed 9/14/04, effective 2/1/05)
WAC 296-863-60015 Evaluate PIT operators performance.
((You must:
•)) You must evaluate PIT operators performance at each of these times:
((–)) (1) As part of their initial training program.
((–)) (2) After refresher training to determine the effectiveness of the training.
((–)) (3) At least once every three years.
REPEALER
The following section of the Washington Administrative Code is repealed:
WAC 296-863-700 |
Definitions. |
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-900-099 Definitions.
Affected employees. Employees who could be one of the following:
(a) Exposed to unsafe conditions or practices.
(b) Affected by a request for, or change in, a variance from WISHA requirements.
Applicant. The entity submitting an application and formal proposal for a safety and health investment projects award.
Assistant director. The assistant director for the division of occupational safety and health (DOSH) at the department of labor and industries or his/her designated representative.
Base penalty. The penalty amount calculated for a violation by considering either specific statutory penalty amounts or the gravity of the violation.
Board. The board of industrial insurance appeals.
Certification. An employer's written statement describing when and how a citation violation was corrected.
Citation. See citation and notice.
Citation and notice. Issued to an employer for any violation of WISHA safety and health requirements. Also known as a citation and notice of assessment, or simply citation.
Correction action plans. Your written plans for correcting a WISHA violation.
Correction date. The date by which you must meet the WISHA requirements listed on either a:
(a) Citation and notice (C&N); or
(b) A corrective notice of redetermination (CNR).
Corrective notice of redetermination (CNR). Issued by WISHA after WISHA has reassumed jurisdiction over an appealed citation and notice.
Department. The department of labor and industries.
Designated representative. Any of the following:
(a) Any individual or organization to which an employee gives written authorization.
(b) A recognized or certified collective bargaining agent without regard to written employee authorization.
(c) The legal representative of a deceased or legally incapacitated employee.
Division or DOSH. The division of occupational safety and health, Washington state department of labor and industries.
Documentation. Material that an employer submits to prove that a correction is completed. Documentation includes, but is not limited to, photographs, receipts for materials and labor.
Failure to abate (FTA). A violation that was cited previously which the employer has not fixed.
Final order. Any of the following (unless an employer or other party files a timely appeal):
(a) Citation and notice.
(b) Corrective notice of redetermination.
(c) Decision and order from the board of industrial insurance appeals.
(d) Denial of petition for review from the board of industrial insurance appeals.
(e) Decision from a Washington state superior court, court of appeals, or the state supreme court.
Final order date. The date a final order is issued.
Funding cycle. How frequently safety and health investment project awards are given.
Gravity. For purposes of calculating a penalty means the amount calculated by multiplying a violation's severity rate by its probability rate.
Hazard. Any condition, potential or inherent, which can cause injury, death, or occupational disease.
Imminent danger violation. Any violation resulting from conditions or practices in any place of employment, which are such that a danger exists which could reasonably be expected to cause death or serious physical harm, immediately or before such danger can be eliminated through the enforcement procedures otherwise provided by the Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act.
Inpatient hospitalization. Formal admission to the inpatient service of a hospital or an equivalent medical facility on an emergent basis for a work-related injury, or illness.
Interim order. An order allowing an employer to vary from WISHA requirements until a permanent or temporary variance is granted.
Medical aid fund. Industrial insurance funds established in chapter 51.44 RCW.
Milestones. Critical points of achievement for the safety and health investment projects, showing progress toward project completion. Milestones are interim accomplishments that define project progress.
Monetary penalties. Fines assessed against an employer for violations of safety and health requirements.
Movable equipment. A hand-held or nonhand-held machine or device that:
(a) Is powered or nonpowered.
(b) Can be moved within or between worksites.
Must. Means mandatory.
Permanent variance. Allows an employer to vary from WISHA requirements when an alternate means, that provides equal protection to workers, is used.
Probability. A number that describes the likelihood of an injury, illness, or disease occurring, ranging from 1 (lowest) to 3 (highest).
Product. Any of the following that are developed as the result of a safety and health investment project: Written materials; manufactured materials; designs; equipment; programs; services; workplace changes; or other results of any kind, tangible or intangible.
Reassume jurisdiction. WISHA has decided to provide the employer with an informal conference to discuss their appeal.
Recipient. An agency, firm, organization, individual or other legal entity receiving project award funds from the safety and health investment projects.
Repeat violation. A violation where the employer has been cited one or more times previously for a substantially similar hazard, and the prior violation has become a final order no more than three years prior to the employer committing the violation being cited.
Serious violation. When there is a substantial probability that death or serious physical harm could result from one of the following in the workplace:
(a) A condition that exists.
(b) One or more practices, means, methods, operations, or processes that have been adopted or are in use.
Severity. For purposes of calculating a penalty means the most serious injury, illness, or disease that could be reasonably expected to occur, ranging from 1 (lowest) to 3 (highest), because of a hazardous condition.
Temporary variance. Allows an employer to vary from WISHA requirements under certain circumstances.
Variance. Provides an approved alternative to WISHA requirements to protect employees from a workplace hazard. Variances can be permanent or temporary.
WAC. An acronym for Washington Administrative Code, which are rules developed to address state law.
WISHA. This is an acronym for the Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act.
You. An employer.
Sample Tag for Cited Moveable Equipment
WARNING: EQUIPMENT HAZARD Cited by the Department of Labor and Industries |
Equipment cited: |
|||
Hazard cited: |
||||
For detailed information, see L&I citation posted at: |
||||
WARNING: EQUIPMENT HAZARD See reverse side |
This tag or similar tag or a copy of the citation must remain attached to this equipment until the criteria for removal in WAC 296-900-15035 are met. The tag/citation copy must not be altered, defaced, or covered by other material. |
|||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 08-03-025, filed 1/8/08, effective 2/8/08)
WAC 296-900-100 Scope.
This chapter applies to the following requirements and information regarding administration of the Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act (WISHA), chapter 49.17 RCW:
((•)) (1) Employer requests for using an alternative to WISHA requirements.
((•)) (2) Workplace inspections conducted by WISHA.
((•)) (3) Citations and penalties for violations of WISHA safety and health requirements.
((•)) (4) How to respond to actions that WISHA may take when requirements have been violated.
((•)) (5) Employer correction of cited violations, and notification to WISHA when the corrections are made.
((•)) (6) Employer obligations to inform employees.
((•)) (7) Reporting alleged safety and health hazards.
((•)) (8) Appeal and hearing processes for employers and employees.
((•)) (9) Safety and health investment projects (SHIP).
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-110 Variances.
Summary:
Employer responsibility((:
To follow requirements on granted variances:
Applying for a variance
WAC 296-900-11005.
Interim orders
WAC 296-900-11010.
Renewing a temporary variance
WAC 296-900-11015.
Changing a variance
WAC 296-900-11020.
Variance hearings
WAC 296-900-11025)).
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Applying for a variance |
WAC 296-900-11005 |
Interim orders |
WAC 296-900-11010 |
Renewing a temporary variance |
WAC 296-900-11015 |
Changing a variance |
WAC 296-900-11020 |
Variance hearings |
WAC 296-900-11025 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-11005 Applying for a variance.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) 1. A variance provides an approved alternative to WISHA requirements to protect employees from a workplace hazard. Variances can be permanent or temporary.
((•)) 2. Variances will not be retroactive. Employers are obligated to follow WISHA requirements until the variance is granted.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must follow steps 1-5 to apply for a variance when you wish to use an alternative to WISHA requirements as a means to protect your employees.
Step 1: | Decide what type of variance is needed by reviewing the types of variances in Table 1, Requesting a Variance. |
Step 2: | Complete a written application for the variance, following the requirements in Table 1, Requesting a Variance. |
Note: | ((•)) A form, Variance Application (F414-021-000), is available for requesting variances: |
((–)) 1. From any L&I office. | |
((–)) 2. On our web site under Safety Forms, Variance Application http://www.lni.wa.gov/FormPublications/TablesForms/Safety/SafetyHealth.asp. |
Reference: | ((•)) For a list of the local L&I offices, see the resources section of the Safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC. |
Step 3: | Notify employees before submitting any type of variance request by doing all of the following: |
• Posting a copy of the request on your safety bulletin board. | |
• Using other appropriate means for notifying employees who may not be expected to receive notices posted on the safety bulletin board. For example, provide a copy to a designated representative or the safety committee. | |
Step 4: | Submit the written request, using one of the following means: |
• Mail to: | |
Assistant Director | |
WISHA Services | |
P.O. Box 44650 | |
Olympia, WA 98504-4650 | |
• Fax to: 360-902-5438 | |
• Take to any L&I office. | |
Step 5: | After receiving a written decision from WISHA about your request, immediately notify affected employees of the decision by using the methods in Step 3. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must follow the specific requirements of the variance that WISHA has granted.
Note: | ((•)) 1. If employers fail to follow Steps 1-5 above, the variance cannot be granted. |
((•)) 2. Citations may be issued for failing to follow a variance. | |
((•)) 3. Employers can always follow the original WISHA requirements instead of the variance requirements. | |
((•)) 4. If your variance is no longer necessary and you decide to follow the WISHA requirements instead, please advise WISHA in writing. |
Table 1
Requesting a Variance
For this type of variance: |
Include the following on your written application: |
||
Permanent variance |
|||
– |
Request a permanent variance if you can show that you will be providing alternate methods of protecting employees from hazards that are as effective as those provided by the requirements from which you are requesting relief. |
• |
Employer name and address |
• |
Employer or employer representative signature |
||
• |
Work locations and situations that apply to the variance |
||
• |
Which specific requirements you want to vary from, with WAC numbers |
||
• |
Description of proposed alternative methods of protection, and how they will protect employees. |
||
Note: |
• |
How employees will be notified: |
|
• |
A permanent variance remains in effect unless WISHA modifies or revokes it. Examples of reasons a variance might be revoked include: |
– |
About the variance request, as required in Step 2 |
– |
That they may request a hearing |
||
– |
An employer requests the variance be revoked |
• |
The following notice on the first page of your posted application, written in large and clear enough print to be easily read: |
– |
Requirements that existed when the variance was approved are modified |
"Attention Employees: Your employer is applying to WISHA for a variance from safety and health requirements. You have a right to ask WISHA for a hearing on the variance request, but you must ask for the hearing in writing by (date*). If no hearing is requested, WISHA will act on the variance request without a hearing." |
|
– |
The work location is changed |
*This date must be 21 calendar days after the variance request is mailed or delivered. |
|
Temporary variance |
|||
Request a temporary variance if both of the following apply: |
• |
Provide all the information required above for permanent variances |
|
• |
New WISHA requirements ((can't)) cannot be met for any of the following reasons: |
• |
Also provide all of the following: |
– |
Professional or technical people are not available |
– |
An explanation of why WISHA requirements ((can't)) cannot be met, including documentation that supports this belief |
– |
Materials or equipment are not available |
– |
Steps that will be taken to protect employees until WISHA requirements can be met |
– |
Construction or alteration of facilities cannot be completed by the effective date of the requirements |
– |
When WISHA requirements will be met |
• |
You have an effective plan for meeting WISHA requirements as soon as possible. |
– |
A statement that this request is from a qualified person who has first hand knowledge of the facts represented |
Note: |
|||
• |
Temporary variances remain in effect: |
||
– |
Until current WISHA requirements are met |
||
– |
No longer than one year, unless extended |
||
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (3) A review of all variance requests.
((–)) If more information is needed to make a decision, WISHA may:
((■)) (a) Contact you or others who may have the needed information.
((■)) (b) Visit your workplace after contacting you to make arrangements.
((■)) (c) Deny your request if you ((don't)) do not provide information needed to make a decision on it.
((•)) (4) A decision at least twenty-one calendar days from when the request was posted for employees.
((–)) The twenty-one-day period allows employees time to request a hearing on your variance application. See Variance hearings, WAC 296-900-11025.
((•)) (5) A written decision either granting or denying the variance.
((–)) (a) If granted, the written decision will include all of the following:
((■)) (i) The requirement for which the variance applies.
((■)) (ii) The locations where the variance applies.
((■)) (iii) What you must do as an alternative means of protecting employees.
((■)) (iv) The effective date of the variance.
((■)) (v) An expiration date for the variance, if applicable.
((■)) (vi) The requirement to post the decision.
((–)) (b) If denied, the written decision will include:
((■)) (i) A brief statement with reasons for the denial.
((■)) (ii) The requirement to post the decision.
((•)) (6) WISHA will review permanent variances periodically after they have been in effect for six months, to decide whether they are still needed or need to be changed.
Note: | If ((there's)) there is an appealed WISHA citation and notice that relates to the variance request, the decision on the variance may be delayed until the appeal is resolved. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-11010 Interim orders.
Definition:
An interim order allows an employer to vary from WISHA requirements until a permanent or temporary variance is granted.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must request an interim order if alternate methods of protecting employees are needed while waiting for a permanent or temporary variance.
Note: | An interim order may be requested at the same time a permanent or temporary variance is requested, or anytime after that. |
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (2) A review of the request for an interim order.
((–)) If more information is needed to make a decision, WISHA may:
((■)) (a) Contact the employer or others who may have the needed information.
((■)) (b) Visit the workplace after contacting the employer to make arrangements.
((■)) (c) Deny the request if the employer ((doesn't)) does not provide information needed to make a decision.
((•)) (3) A decision at least twenty-one calendar days from when the request was posted for employees.
((–)) The twenty-one-day period allows employees time to request a hearing on your temporary variance renewal. See Variance hearings, WAC 296-900-11025.
((•)) (4) A written decision either granting or denying the interim order request.
((–)) (a) If granted, the decision will include all of the following:
((■)) (i) The requirement for which the interim order applies.
((■)) (ii) The locations where the interim order applies.
((■)) (iii) What you must do as an alternative means of protecting employees.
((■)) (iv) The effective date of the interim order.
((■)) (v) An expiration date for the interim order.
((■)) (vi) The requirement to post the decision.
((–)) (b) If denied, the decision will include:
((■)) (i) A brief statement with reasons for the denial.
((■)) (ii) The requirement to post the decision.
Note: | ((•)) 1. WISHA's decision to grant or deny an interim order request will not affect the decision on a permanent or temporary variance request. |
((•)) 2. WISHA may choose to issue an interim order in response to a variance request, even when the interim order ((wasn't)) was not specifically requested. | |
((•)) 3. Interim orders are effective until they are revoked, or until the variance request is granted or denied. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-11015 Renewing a temporary variance.
IMPORTANT:
Temporary variances can be renewed up to two times, for up to one hundred eighty days each time.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must apply for a temporary variance renewal at least ninety days before the temporary variance expires.
((•)) (2) You must send a letter, explaining why more time is needed to fulfill the current requirements.
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (3) A review of the temporary variance renewal request.
((–)) If more information is needed to make a decision, WISHA may:
((■)) (a) Contact you or others who may have the needed information.
((■)) (b) Visit your workplace after contacting you to make arrangements.
((■)) (c) Deny your request if you ((don't)) do not provide information needed to make a decision.
((•)) (4) A decision at least twenty-one calendar days from when the request was posted for employees.
((–)) The twenty-one-day period allows employees time to request a hearing on your temporary variance renewal. See Variance hearings, WAC 296-900-11025.
((•)) (5) A written decision either granting or denying the temporary variance renewal request.
((–)) (a) If granted, the written decision will include all of the following:
((■)) (i) The requirements for which the temporary variance applies.
((■)) (ii) The locations where the temporary variance applies.
((■)) (iii) What you must do as an alternative means of protecting employees.
((■)) (iv) The effective date of the temporary variance.
((■)) (v) An expiration date for the temporary variance.
((■)) (vi) The requirement to post the decision.
((–)) (b) If denied, the written decision will include:
((■)) (i) A brief statement with reasons for the denial.
((■)) (ii) The requirement to post the decision.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-11020 Changing a variance.
((You, your employees, or their representatives may:
•)) (1) You, your employees, or their representatives may request changes to variances in writing as follows:
((–)) (a) For a permanent variance only after ((it's)) it has been in effect for at least six months.
((–)) (b) For a temporary variance, only when renewing it.
Note: | ((■)) 1. After six months, WISHA may initiate changes to a variance if they appear to be warranted. |
((■)) 2. Employers can decide at any time to follow the original requirement, instead of the requested variance. |
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (2) A review of your request to change a variance.
((–)) If more information is needed to make a decision, WISHA may:
((■)) (a) Contact you or others who may have the needed information.
((■)) (b) Visit your workplace after contacting you to make arrangements.
((■)) (c) Deny your request for a change if you ((don't)) do not provide information needed to make a decision.
((•)) (3) A decision at least twenty-one calendar days from when the request was posted for employees.
((–)) The twenty-one-day period allows employees time to request a hearing on your request to change a variance. See Variance hearings, WAC 296-900-11025.
((•)) (4) A written decision either granting or denying the change in variance.
((–)) (a) If granted, the written decision will include all of the following:
((■)) (i) The requirements for which the variance applies.
((■)) (ii) The locations for which the variance applies.
((■)) (iii) What you must do as an alternative means of protecting employees.
((■)) (iv) The effective date of the change in variance.
((■)) (v) An expiration date of the variance, if applicable.
((■)) (vi) The requirement to post the decision.
((–)) (b) If denied, the written decision will include:
((■)) (i) A brief statement with reasons for the denial.
((■)) (ii) The requirement to post the decision.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-11025 Variance hearings.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) Employers, affected employees, or employee representatives may request a hearing on any of the following:
((–)) 1. Permanent or temporary variance requests.
((–)) 2. Changes to existing variances.
((You and your affected employees must:
•)) (1) You and your affected employees must do all of the following if requesting a variance hearing:
((–)) (a) Put the request in writing and sign it.
((–)) (b) Make sure the request is posted or delivered to the department within twenty-one calendar days from the variance application date, or renewal request date.
((–)) (c) Send the written request to WISHA, using one of the following means:
((•)) Mail to:
Assistant Director
WISHA Services
P.O. Box 44650
Olympia, WA 98504-4650
((•)) Fax to: 360-902-5438
((•)) Take to any L&I office.
((You must:
•)) (2) You must immediately do all of the following when you receive a notice of the hearing from WISHA:
((–)) (a) Post a copy of the notice on the safety bulletin board.
((–)) (b) Give a copy of the notice to affected employees and employee representatives.
((–)) (c) Use any other appropriate means for notifying employees who may not receive notices posted on the safety bulletin board. For example, provide a copy to a designated representative or the safety committee.
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (3) WISHA will do both of the following after receiving a request for a hearing on a variance, change of variance, or temporary variance renewal:
((–)) (a) Within ten days, issue a notice advising all interested parties listed on the application that they have the option to participate in the hearing.
((–)) (b) Provide you with a notice of the hearing at least twenty calendar days before the hearing date.
((•)) (4) A hearing for the variance or variance change will be conducted as follows:
((–)) (a) A WISHA representative will explain WISHA's view of the request for a variance or any proposed change to a variance.
((–)) (b) Employers, employees, or employee representatives will then have an opportunity to explain their views and provide any relevant documents or information.
((•)) (5) Information gathered at the hearing will be used to make a decision about whether to grant or deny the request for a variance or change in variance.
Note: | ((•)) 1. WISHA may record a variance hearing. |
((•)) 2. Employers, employees, or employee representatives may request copies of recordings or transcripts of variance hearings at cost. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-120 Inspections.
Summary((:
WISHA inspections
WAC 296-900-12005.
Inspection techniques
WAC 296-900-12010.
Complaints
WAC 296-900-12015)).
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
WISHA inspections |
WAC 296-900-12005 |
Inspection techniques |
WAC 296-900-12010 |
Complaints |
WAC 296-900-12015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-12005 WISHA inspections.
((•)) (1) WISHA conducts the following types of programmed inspections:
((–)) (a) Hazardous workplaces.
WISHA identifies hazardous workplaces using objective criteria and inspection-scheduling systems that may include any of the following factors:
((■)) (i) Type of industry.
((■)) (ii) Injury and illness data that identifies hazards.
((■)) (iii) Employer's industrial insurance experience.
((■)) (iv) Number, type, and toxicity of contaminants in the workplace.
((■)) (v) Degree of exposure to hazards.
((■)) (vi) Number of employees exposed.
((■)) (vii) Other factors, such as history of employee complaints.
Note: | WISHA periodically reviews the scheduling systems and may adjust the type or significance of each criteria. |
((–)) (b) High hazard industries that include the following:
((■)) (i) Agriculture.
((■)) (ii) Asbestos renovation and demolition.
((■)) (iii) Construction.
((■)) (iv) Electrical utilities and communications.
((■)) (v) Logging.
((■)) (vi) Maritime.
((•)) (2) WISHA conducts the following types of unprogrammed inspections of workplaces that may be in violation of WISHA safety or health requirements or chapter 49.17 RCW, ((the)) Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act. These inspections may focus only on certain areas or processes in a workplace or, depending on initial findings, may be expanded to include the entire workplace. Unprogrammed inspections may occur because of:
((–)) (a) Complaints from current employees or employee representatives who believe they have been exposed to a hazard because of a violation.
((–)) (b) Referrals from anyone, including former employees, who reasonably believes that workers under WISHA jurisdiction are being, or have been, exposed to a hazard because of a violation.
((–)) (c) Workplace deaths, catastrophic events, or serious injury or illness.
((–)) (d) A reason to believe that employees may be in imminent danger of serious injury or death.
((–)) (e) Follow-up inspections to verify that hazards identified in a previous inspection have been corrected.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-12010 Inspection techniques.
((•)) During an inspection, WISHA staff may:
((–)) (1) Take samples, photographs, videotapes, or audiotapes.
((–)) (2) Conduct tests or interviews.
((–)) (3) Ask employees to wear sampling devices.
((–)) (4) Privately question, on or off the worksite, any:
((■)) (a) Employer.
((■)) (b) Employer representative.
((■)) (c) Owner.
((■)) (d) Operator.
((■)) (e) Employee.
((■)) (f) Employee representative.
((–)) (5) Employ any other reasonable investigative techniques.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-12015 Complaints.
((Employees or employee representatives may:
•)) (1) Employees or employee representatives may file a written complaint if they believe they have been exposed to a hazard that is a violation of WISHA safety and health requirements.
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (2) After receiving a written complaint from an employee or employee representative, WISHA reviews the allegations and responds according to Table 2, WISHA Responses to Employee Complaints.
Table 2
WISHA Responses to Employee Complaints
For this determination: |
WISHA will take the following actions: |
|
The complaint is within WISHA jurisdiction and an inspection ((doesn't)) does not appear to be needed at this time |
• • |
Call the employer to discuss the complaint Set a deadline for the employer to respond in writing |
• |
Fax or mail a complaint notification letter to the employer. Before the complaint is faxed or mailed, the following names will be removed unless specific permission is given to include them: |
|
– |
The name of the person submitting the complaint |
|
– |
The names of any employees identified in the complaint |
|
• |
Evaluate the employer's response, and do one of the following: |
|
– |
Close the complaint because the issues have been addressed, and send a copy of the employer's response to the person filing the complaint |
|
– |
Inspect the workplace |
|
Note: |
||
• |
If the complaint is closed and additional information is received from the person filing the complaint disputing the employer's written response, WISHA may schedule an inspection |
|
• |
If the person who filed the original complaint requests in writing that WISHA review a decision not to conduct an inspection, WISHA will review the decision and notify the person in writing of the results |
|
• |
If the person requesting the review is not satisfied with the results of the review, they may request a second review by the assistant director or designee |
|
The complaint is within WISHA jurisdiction and an inspection needs to be conducted |
• • |
Conduct an inspection Issue a citation and notice that shows one of the following: |
– |
Violations found |
|
– |
No violations were found |
|
• |
Send a letter to the person filing the complaint with inspection results |
|
Reference: For citation and notice information, turn to citation and notice, WAC 296-900-130 |
||
The complaint is not within WISHA jurisdiction |
• |
Send a written response to the person filing the complaint explaining the matter is not within WISHA jurisdiction |
Note: WISHA may make a referral to the proper authority |
||
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-900-130 Citation and notice.
Summary:
Employer responsibility:
To notify employees when a citation and notice is received((:
Citation and notice
WAC 296-900-13005.
Copies of future citations and notices
WAC 296-900-13010.
Posting citation and notices
WAC 296-900-13015)).
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Citation and notice |
WAC 296-900-13005 |
Copies of future citations and notices |
WAC 296-900-13010 |
Posting citation and notices |
WAC 296-900-13015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-13005 Citation and notice.
Definition:
(1) A citation and notice is a document issued to an employer notifying them of:
((•)) (a) Inspection results.
((•)) (b) Any specific violations of WISHA safety and health requirements.
((•)) (c) Any monetary penalties assessed.
((•)) (d) Employer certification of correction requirements.
((•)) (e) WISHA will mail a citation and notice to you as soon as possible but not later than six months following any inspection or investigation.
((–)) (2) If violations are found, the citation and notice will include:
((■)) (a) A description of violations found.
((■)) (b) The amount and type of assessed penalties.
((■)) (c) The length of time given to correct the violations not already corrected during the inspection.
((–)) (3) If no violations are found, a notice of inspection results will be sent stating that no violations were found or penalties assessed.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-13010 Copies of future citation and notices.
Employees or their representatives wishing to receive copies of citation and notices during the next twelve months must:
((•)) (1) Submit a request for copy of citation and notice form to the following:
Department of Labor and Industries
Standards and Information
P.O. Box 44638
Olympia, WA 98504-4638
Note: | ((•)) A request for copy of citation and notice form can be obtained by: |
((–)) 1. Calling 360-902-5553. | |
((–)) 2. Contacting the local L&I office. |
Reference: | ((■)) For a list of the local L&I offices, see the resources section of the Safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC. |
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (2) WISHA may decide who will receive copies of the citation and notices if more than one employee or employee representative requests a copy.
((•)) (3) WISHA may deny a request for copies of citation and notices if the person filing the request is not an employee or employee representative.
((•)) (4) If WISHA grants the request for copies of citation and notices, the employee or employee representative will:
((–)) (a) Receive an approval document from WISHA.
((–)) (b) Receive all citation and notices issued to that employer for the next twelve months.
((–)) (c) Continue receiving citation and notices for an additional twelve months if a one-year extension is requested and approved.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-13015 Posting citation and notices.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must immediately notify employees of a citation and notice by posting it and any correspondence related to an employee complaint on the safety bulletin board for three working days or until all violations are corrected, whichever time period is longer.
((•)) (2) You must use any other appropriate means to notify employees who may receive notices posted on the safety bulletin board.
((–)) Examples of other appropriate means include sending a copy by mail or electronically to any of the following:
((■)) (a) A designated employee representative.
((■)) (b) Safety representatives.
((■)) (c) The safety committee.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 07-03-163, filed 1/24/07, effective 4/1/07)
WAC 296-900-150 Certifying violation corrections.
Summary:
Employer responsibility:
((•)) (1) To certify that violations to safety and health requirements have been corrected.
((•)) (2) To submit, if required:
((–)) (a) Additional information.
((–)) (b) Correction action plans.
((–)) (c) Progress reports.
((•)) (3) To comply with correction due dates.
((•)) (4) To tag cited moveable equipment to warn employees of a hazard.
((•)) (5) To inform affected employees that each violation was corrected.
((Certifying violation correction
WAC 296-900-15005.
Violation correction action plans
WAC 296-900-15010.
Progress reports
WAC 296-900-15015.
Timeliness of violation correction documents
WAC 296-900-15020.
Inform employees about violation correction
WAC 296-900-15025.
Tag moveable equipment
WAC 296-900-15030.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Certifying violation correction |
WAC 296-900-15005 |
Violation correction action plans |
WAC 296-900-15010 |
Progress reports |
WAC 296-900-15015 |
Timeliness of violation correction documents |
WAC 296-900-15020 |
Inform employees about violation correction |
WAC 296-900-15025 |
Tag moveable equipment |
WAC 296-900-15030 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-15005 Certifying violation correction.
Definition:
A correction date is the date by which you must meet the WISHA requirements listed on either a: ((•)) Citation and notice (C&N)((;
OR
•)) or a corrective notice of redetermination (CNR).
((You must:
•)) (1) You must certify in writing within ten calendar days following the correction date shown on the C&N that each violation has been corrected. Include the following:
((–)) (a) Employer name and address.
((–)) (b) The inspection number involved.
((–)) (c) The citation and item numbers which have been corrected.
((–)) (d) The date each violation was corrected and the method used to correct them.
((–)) (e) A statement that both:
((■)) (i) Affected employees and their representatives were informed that each violation was corrected; and
((AND
■)) (ii) The information submitted is accurate.
((–)) (f) Employer's signature or the signature of employer's designated representative.
Note: | Certification is not required if the WISHA compliance officer indicates in the C&N, or a reassumption hearings officer indicates in a CNR, that they have already been corrected. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must submit additional documentation for willful or repeated violations, demonstrating that they were corrected. This documentation may include, but is not limited to:
((–)) (a) Evidence of the purchase or repair of equipment.
((–)) (b) Photographic or video evidence of corrections.
((–)) (c) Other written records.
((•)) (3) You must submit additional documentation for serious violations when required in the C&N or CNR.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-15010 Violation correction action plans.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must submit a written violation correction action plan within twenty-five calendar days from the final order date when the citation and notice or corrective notice of redetermination requires it. Include all of the following in the violation correction action plan:
((–)) (a) Identification of the violation.
((–)) (b) The steps that will be taken to correct the violation.
((–)) (c) A schedule to complete the steps.
((–)) (d) A description of how employees will be protected until the corrections are completed.
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (2) WISHA will notify you in writing only if your plan is not adequate, and describe necessary changes.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-15015 Progress reports.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must submit written progress reports on corrections when required in the citation and notice (C&N) or corrective notice of redetermination (CNR), and briefly explain the:
((–)) (a) Status of each violation.
((–)) (b) Action taken to correct each violation.
((–)) (c) Date each action has or will be taken.
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (2) WISHA will state in the C&N or CNR if progress reports are required, including:
((–)) (a) Items that require progress reports.
((–)) (b) Date when an initial progress report must be submitted. The initial progress report is due no sooner than thirty calendar days after you submit a correction action plan.
((–)) (c) Whether additional progress reports are required, and the dates by which they must be submitted.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-15020 Timeliness of violation correction documents.
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) WISHA will determine the timeliness of violation correction documents by reviewing the following:
((–)) (1) The postmark date for documents sent by mail.
((–)) (2) The date received by other means, such as personal delivery or fax.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-15025 Inform employees about violation correction.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must inform employees about violation corrections by doing the following:
((–)) (a) Post a copy of each violation correction document submitted to WISHA, or a summary, near the place where the violations occurred, if practical.
((■)) If posting near the place where the violation occurred is not practical, such as with a mobile work operation, post in a place readily accessible to affected employees or take other steps to fully communicate actions taken to affected employees or their representatives.
((–)) (b) Keep violation correction information posted for at least three working days after submitting the correction documents to WISHA.
((–)) (c) Give notice to employees and their representatives on or before the date you submit correction information to WISHA.
((–)) (d) Make sure that all posted correction documents are not altered, defaced, or covered by other materials.
((•)) (2) You must inform employees and their representatives of their right to examine and copy all correction documents submitted to WISHA.
((–)) If they ask to examine or copy documents within three working days of receiving notice that the documents were submitted to WISHA, provide access or copies no later than five days after receiving their request.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-15030 Tag moveable equipment.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must tag moveable equipment that has been cited to warn employees if a hazard has not been corrected, as follows:
((–)) (a) Attach a warning tag or a copy of the citation to the equipment's operating controls or to the cited component.
((■)) (b) For hand-held equipment, tag it immediately after you receive a citation.
((■)) (c) For other equipment, tag it before moving it within the worksite or between worksites.
Note: | The tag should warn employees about the nature of the violation and tell them where the citation is posted. |
Reference: | For a sample tag that meets this requirement, go to helpful tools, sample tag for cited moveable equipment, in the resources section of this chapter. |
((You must:
•)) (2) You must make sure that the tag or copy of the citation attached to movable equipment is not altered, defaced, or covered by other materials.
((•)) (3) You must keep the tag or copy of the citation attached to movable equipment until one of the following occurs:
((–)) (a) Violations have been corrected and all certification documents have been submitted to WISHA.
((–)) (b) Cited equipment is permanently removed from service.
((–)) (c) The final order from an appeal vacates (voids) the violation.
Note: | Safety standards for construction work, chapter 296-155 WAC, has information on warning tags. You can use warning tags that meet those requirements instead of the warning tags required by this rule. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-160 More time to comply.
Summary:
Your responsibility:
To submit timely requests when more time is needed to correct violations. To post requests for more time for employees.
((Requesting more time to comply
WAC 296-900-16005.
Post WISHA's response to requests for more time
WAC 296-900-16010.
Correction date hearing requests
WAC 296-900-16015.
Post WISHA's violation correction hearing notice
WAC 296-900-16020.
Violation correction hearing procedures
WAC 296-900-16025.
Post the violation correction hearing decision
WAC 296-900-16030.))
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Requesting more time to comply |
WAC 296-900-16005 |
Post WISHA's response to requests for more time |
WAC 296-900-16010 |
Correction date hearing requests |
WAC 296-900-16015 |
Post WISHA's violation correction hearing notice |
WAC 296-900-16020 |
Violation correction hearing procedures |
WAC 296-900-16025 |
Post the violation correction hearing decision |
WAC 296-900-16030 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-16005 Requesting more time to comply.
IMPORTANT:
((• Employers)) You can request more time to correct violations if they:
((–)) 1. Have made a good faith effort to correct the violation.
((–)) 2. Have not corrected the violation because of factors beyond their control.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must submit any requests for more time to correct violations in writing. Requests must be received or postmarked before midnight of the correction date shown on the citation and notice (C&N) or corrective notice of redetermination (CNR), and include:
((–)) (a) The business name.
((–)) (b) The address of the workplaces.
((–)) (c) The citation and the correction dates to be extended.
((–)) (d) The new correction date and length of correction period being requested.
((–)) (e) A description of the actions that have been, and are being, taken to meet the correction dates in the C&N or CNR.
((–)) (f) Factors preventing correction of violations by the date required.
((–)) (g) The means that will be used to protect employees while the violation is being corrected.
((–)) (h) Certification that the request for correction date extension has been posted, and if appropriate, certification that a copy was delivered to affected employees or their representatives.
((–)) (i) Employer's signature or the signature of the employer's representative.
((–)) (j) Date.
((•)) (2) You must submit requests by one of the following methods:
((–)) (a) First class mail, postage prepaid to any L&I office.
((–)) (b) Take to any L&I office.
((–)) (c) Fax to the number shown in the C&N.
Reference: | For a list of the local offices, see the resources section of the Safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC. |
What to expect from WISHA:
((• WISHA may:
–)) (3) WISHA may accept late requests if they are both:
((■)) (a) Received within five days following the related correction date; and
((AND
■)) (b) Accompanied by your written statement explaining the exceptional circumstances that caused the delay.
Note: | WISHA ((doesn't)) does not accept late requests when compliance activity has already started. |
((• WISHA may:
–)) (4) WISHA may respond to telephone requests or personal conversations asking for more time to comply if timely, and followed up in writing within twenty-four hours.
((–)) (5) WISHA may conduct an investigation before making a decision whether to grant a request for more time.
((• WISHA will:
–)) (6) WISHA will make a decision whether or not to grant the employer more time. Once made, the decision remains in effect unless an employee or employee representative requests a hearing.
((–)) (7) WISHA will keep the original correction date in effect unless a notice granting more time is sent.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-16010 Post WISHA's response to requests for more time.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must post notices from WISHA approving additional time to correct citations, with the related citation, immediately upon receipt.
((•)) (2) You must keep the notices posted until one of the following occur:
((–)) (a) The correction date has passed.
((–)) (b) A hearing notice is requested and posted.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-16015 Correction date hearing requests.
IMPORTANT:
((•)) 1. Affected employees or their designated representatives may request a hearing if they disagree with WISHA's decision to grant an employer more time to correct a violation.
((•)) 2. Employers may request a hearing if WISHA denies their request for more time to correct a violation.
((You, your employees, or their representatives must:
•)) You, your employees, or their representatives must send requests for hearings, if desired, in writing no later than ten calendar days after the issue date of the notice granting more time to correct a violation to:
((–)) Mail to:
Assistant Director for WISHA Services
Attn: WISHA Appeals
P.O. Box 44604
Olympia, WA 98504-4604
((–)) Fax to: 360-902-5581
((–)) Take to any department service location.
Reference: | For a list of the local offices, see the resources section of the Safety and health core rules, chapter 296-800 WAC. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-16020 Post WISHA's violation correction hearing notice.
((You must:
•)) You must post WISHA's hearing notice or a complete copy until the hearing is held, along with the:
((–)) (1) Citation containing the correction date for which more time was requested.
((–)) (2) Department notices issued in response to the employer's request for more time.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-16025 Violation correction hearing procedures.
What to expect from WISHA:
((•)) (1) After receiving a hearing request, the assistant director for WISHA services will appoint someone from WISHA to act as a hearings officer.
((•)) (2) The hearings officer:
((–)) (a) Will send a hearing notice to the employer and employee at least twenty days before the hearing date that includes all of the following:
((■)) (i) A statement that all interested parties can participate in the hearing.
((■)) (ii) The time, date, and place of the hearing.
((■)) (iii) A short and clear explanation why a hearing was requested.
((■)) (iv) The nature of the proceeding, including the specific sections of the statute or rule involved.
((■)) (v) The legal authority and jurisdiction under which the hearing will be held.
((–)) (b) May discuss the material to be presented to determine how the hearing will proceed.
((•)) (3) An assistant attorney general may be present at the hearing to give legal advice to the hearings officer.
((•)) (4) The hearing will be conducted by either:
((–)) (a) The hearings officer; or
((OR
–)) (b) The assistant attorney general, if requested by the hearings officer.
((•)) (5) After the hearing, WISHA will issue an order that either affirms or modifies the correction date that caused the hearing.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 06-06-020, filed 2/21/06, effective 6/1/06)
WAC 296-900-16030 Post the violation correction hearing decision.
((You must:
•)) You must post a complete, unedited copy of the order affirming or modifying the correction date as soon as it is received, along with the applicable citation.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-02-055, filed 1/3/12, effective 7/1/12)
WAC 296-900-170 Appeals.
Summary:
Employer responsibility:
To post information regarding appeals in a conspicuous area where notices to employees are normally posted((:
Appealing a citation and notice (C&N)
WAC 296-900-17005.
Stay of abatement date request
WAC 296-900-17006.
Appealing a corrective notice of redetermination (CNR)
WAC 296-900-17010.
Posting appeals
WAC 296-900-17015)).
You must meet the requirements… |
in this section: |
Appealing a citation and notice (C&N) |
WAC 296-900-17005 |
Stay of abatement date request |
WAC 296-900-17006 |
Appealing a corrective notice of redetermination (CNR) |
WAC 296-900-17010 |
Posting appeals |
WAC 296-900-17015 |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-02-055, filed 1/3/12, effective 7/1/12)
WAC 296-900-17010 Appealing a corrective notice of redetermination (CNR).
IMPORTANT:
((•)) 1. Employers may appeal CNRs.
((•)) 2. Employees who could be affected by a CNR, or their designated representatives, may appeal abatement dates.
((•)) 3. Employers must renew requests to stay abatement dates if a stay request is denied when they appeal CNRs.
((You must:
•)) (1) You must appeal a CNR, if desired, in writing within fifteen working days after it was received to the:
Board of Industrial Insurance Appeals
2430 Chandler Court S.W.
P.O. Box 42401
Olympia, WA 98504-2401
((•)) (2) You must send a copy of the appeal to the CNR to the:
Assistant Director for DOSH Services
Attn: DOSH Appeals
P.O. Box 44604
Olympia, WA 98504-4604
((–)) Fax to: 360-902-5581
((–)) Take to any department service location.
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-02-055, filed 1/3/12, effective 7/1/12)
WAC 296-900-17015 Posting appeals.
((You must:
•)) You must immediately post notices and information related to any appeal or stay of abatement date request in the same place where DOSH citation and notices (C&Ns) are posted. These notices and information include:
((–)) (1) The notice of appeal, until the appeal is resolved.
((–)) (2) Notices about DOSH reassuming jurisdiction, and any extension of the review period until the end of review period.
((–)) (3) A notice of an informal conference until after the conference is held.
((–)) (4) A corrective notice of redetermination for as long as C&Ns are to be posted.
Reference: | For C&N posting requirements, see Posting citation and notices, WAC 296-900-13015. |
AMENDATORY SECTION (Amending WSR 12-03-090, filed 1/17/12, effective 3/1/12)
WAC 296-900-17505 Scope and purpose.
(1) The program for safety and health investment projects (SHIP) was established during the 2011 legislative session to provide funding for safety and health projects for workplaces insured for workers' compensation through the department's state fund. The purpose of these projects shall be to: Prevent workplace injuries, illnesses, and fatalities; create early return to work programs; and reduce long-term disability through the cooperation of employers and employees or their representatives.
(2) Funds for awards shall be distributed as follows:
((•)) (a) At least twenty-five percent for projects designed to develop and implement innovative and effective return-to-work programs for injured workers;
((•)) (b) At least twenty-five percent for projects that specifically address the needs of small businesses; and
((•)) (c) At least fifty percent for projects that foster workplace injury and illness prevention by addressing priorities identified by the department in cooperation with the Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act advisory committee and the workers' compensation advisory committee.
REPEALER
The following sections of the Washington Administrative Code are repealed:
WAC 296-900-17510 |
Definitions. |
WAC 296-900-180 |
Definitions. |