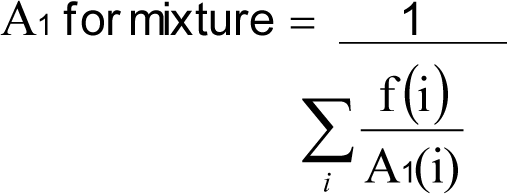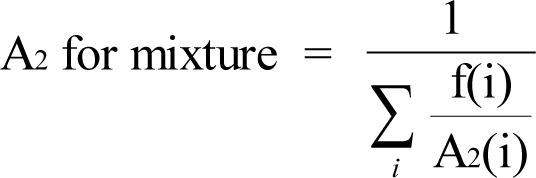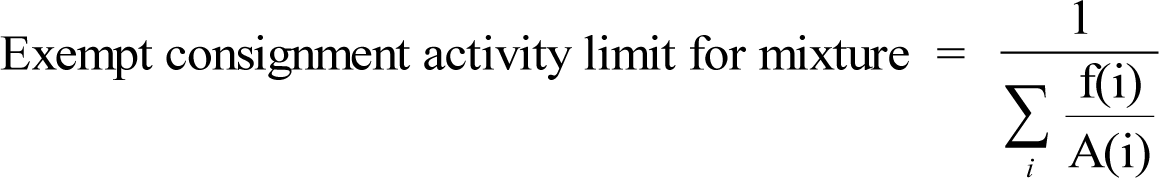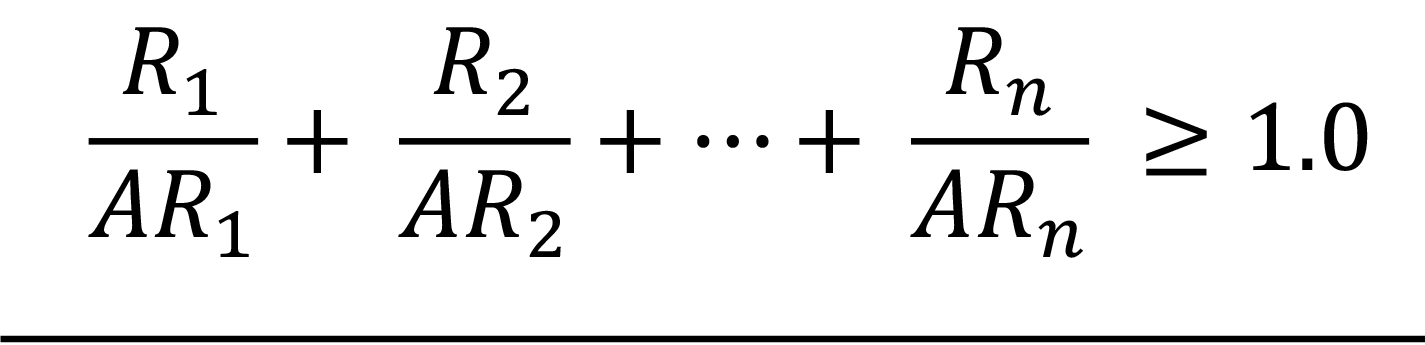WSR 23-15-095
PROPOSED RULES
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH
[Filed July 18, 2023, 1:01 p.m.]
Original Notice.
Title of Rule and Other Identifying Information: As required by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), the department of health (department) is proposing rule amendments to ensure that the following chapters are consistent with NRC rules: Chapter 246-221 WAC, Radiation protection standards; chapter 246-231 WAC, Packaging and transportation of radioactive material; chapter 246-237 WAC, Radiation protection—Physical protection of category 1 and category 2 quantities of radioactive material; and chapter 246-240 WAC, Radiation protection. Amendments are necessary to ensure that these chapters are consistent with NRC rules. The department is also proposing other editorial and nonsubstantive changes.
Hearing Location(s): On August 30, 2023, at 11:30 a.m. The department is holding a virtual-only hearing. Register in advance for this webinar https://us02web.zoom.us/webinar/register/WN_MwQ0imC1SKWy3mkm0WD_2A. After registering, you will receive a confirmation email containing information about joining the webinar.
Date of Intended Adoption: September 6, 2023.
Submit Written Comments to: Department of Health, C/O Nina Helpling, P.O. Box 47820, Olympia, WA 98504-7820, email radruleupdates@doh.wa.gov, https://fortress.wa.gov/doh/policyreview/, by August 30, 2023.
Assistance for Persons with Disabilities: Contact Nina Helpling, phone 360-236-3065, TTY 711, email nina.helpling@doh.wa.gov, by August 23, 2023.
Purpose of the Proposal and Its Anticipated Effects, Including Any Changes in Existing Rules: This proposed rule making amends four chapters of rules to adopt federally required rule changes without material change related to licensing radioactive materials. This rule making adopts the following NRC rule changes that are identified by NRC Regulation Amendments Tracking System (RATS) numbers as follows:
(1) 2020-2 Social Security Fraud Prevention - 85 F.R. 33527 and 85 F.R. 44685: Amends chapter 246-240 WAC to make miscellaneous corrections that are nonsubstantive changes to clarify rule language.
(2) 2020-3 Miscellaneous Corrections - 85 F.R. 65656: Amends chapters 246-221, 246-231, and 246-240 WAC to make nonsubstantive changes such as updating titles, removing outdated requirements, and updating outdated calculations.
(3) 2021-1 Miscellaneous Corrections - 86 F.R. 43397 and 86 F.R. 47209: Amends chapters 246-221, 246-232, 246-237, and 246-240 WAC to remove outdated requirements, update organization names, and update license titles.
(4) 2021-2 Miscellaneous Corrections - 86 F.R. 67839: Amends chapter 246-357 WAC to correct a calculation.
The proposed rule also makes other editorial and nonsubstantive changes.
Reasons Supporting Proposal: The rule making is required to comply with RCW
70A.388.040 State radiation control agency, and
70A.388.110 Federal-state agreements. Under the formal state agreement between the governor and NRC, the department is required to remain compatible with NRC rules. This is done through rule amendments to make our state rules consistent with, and at-least-as-stringent-as, the NRC's rules. Additional nonsubstantive formatting changes are being proposed to make the rule easier to read.
Rule is necessary because of federal law, 85 F.R. 33527, 44685 and 65656; and 86 F.R. 43397, 47209, and 67839.
Name of Proponent: Department of health, governmental.
Name of Agency Personnel Responsible for Drafting, Implementation, and Enforcement: Earl Fordham, 309 Bradley Boulevard, Suite 201, Richland, WA 99352, 509-628-7628.
A school district fiscal impact statement is not required under RCW
28A.305.135.
A cost-benefit analysis is not required under RCW
34.05.328. RCW
34.05.328 (5)(b)(iii) exempts rules that adopt or incorporate by reference without material change federal statutes or regulations, Washington state law, the rules of other Washington state agencies, or national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards. RCW
34.05.328 (5)(b)(iv) exempts rules that only correct typographical errors, make address or name changes, or clarify the language of a rule without changing its effect.
This rule proposal, or portions of the proposal, is exempt from requirements of the Regulatory Fairness Act because the proposal:
Is exempt under RCW
19.85.061 because this rule making is being adopted solely to conform and/or comply with federal statute or regulations. Citation of the specific federal statute or regulation and description of the consequences to the state if the rule is not adopted: 85 F.R. 33527, 44685 and 65656; and 86 F.R. 43397, 47209, and 67839 identify updates to C.F.R., Title 10 - Energy, Chapter I. NRC. Per RCW
70A.388.040 State radiation control agency, and
70A.388.110 Federal-state agreements. Under the formal state agreement between the governor and NRC, the department is required to remain compatible with NRC rules. If the department did not adopt these proposed changes the department would be out of compliance with state compatibility requirements of the NRC, and RCW
70A.388.110 Federal-state agreements.
Is exempt under RCW
19.85.025(3) as the rules are adopting or incorporating by reference without material change federal statutes or regulations, Washington state statutes, rules of other Washington state agencies, shoreline master programs other than those programs governing shorelines of statewide significance, or, as referenced by Washington state law, national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards, if the material adopted or incorporated regulates the same subject matter and conduct as the adopting or incorporating rule; and rules only correct typographical errors, make address or name changes, or clarify language of a rule without changing its effect.
Explanation of exemptions: The agency is exempt from requirements of the Regulatory Fairness Act because the proposed rule only incorporates by reference the federally required standards necessary for the department to maintain full delegation as required by NRC.
Scope of exemption for rule proposal:
Is fully exempt.
July 18, 2023
Kristen Peterson, JD
Chief of Policy
for Umair A. Shah, MD, MPH
Secretary
OTS-4711.2
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 01-05-110, filed 2/21/01, effective 3/24/01)
WAC 246-221-005Radiation protection programs.
(1) Each specific licensee shall develop, document, and implement a radiation protection program sufficient to ensure compliance with the provisions of this chapter.
(2) The licensee shall use, to the extent practical, procedures and engineering controls based upon sound radiation protection principles to achieve occupational doses and doses to members of the public that are as low as is reasonably achievable (ALARA).
(3) The licensee shall review the radiation protection program content and implementation at ((the frequency specified in the license))least annually.
(4) To implement the ALARA requirements of subsection (2) of this section, and notwithstanding the requirements of WAC 246-221-060, a constraint on air emission of radioactive material to the environment, excluding radon-220, radon-222 and their daughters, shall be established by licensees such that the individual member of the public likely to receive the highest dose will not be expected to receive a total effective dose equivalent in excess of 0.1 mSv (10 mrem) per year from these emissions. This dose constraint does not apply to sealed sources or to accelerators less than 200MeV. If a licensee subject to this requirement exceeds this dose constraint, the licensee shall report the exceedance as provided in WAC 246-221-260 and promptly take appropriate corrective action to ensure against recurrence.
(5) Each licensee shall maintain records of the radiation protection program, including:
(a) The provisions of the program; and
(b) Audits, where required, and other reviews of program content and implementation.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 18-21-020, filed 10/4/18, effective 11/4/18)
WAC 246-221-010Occupational dose limits for adults.
(1) The licensee or registrant shall control the occupational dose to individual adults, except for planned special exposures pursuant to WAC 246-221-030, to the following dose limits:
(a) An annual limit, which is the more limiting of:
(i) The total effective dose equivalent being equal to 0.05 Sv (((5))five rem); or
(ii) The sum of the deep dose equivalent and the committed dose equivalent to any individual organ or tissue other than the lens of the eye being equal to 0.50 Sv (50 rem).
(b) The annual limits to the lens of the eye, to the skin of the whole body, and to the skin of the extremities which are:
(i) A lens dose equivalent of 0.15 Sv (15 rem); and
(ii) A shallow dose equivalent of 0.50 Sv (50 rem) to the skin of the whole body or to the skin of any extremity.
(2) Doses received in excess of the annual limits, including doses received during accidents, emergencies, and planned special exposures, must be subtracted from the limits specified in WAC 246-221-030 for planned special exposures that the individual may receive during the current year and during the individual's lifetime.
(3) When the external exposure is determined by measurement with an external personal monitoring device, the deep-dose equivalent must be used in place of the effective dose equivalent, unless the effective dose equivalent is determined by a dosimetry method approved by the NRC or the department. The assigned deep-dose equivalent must be for the part of the body receiving the highest exposure. The assigned shallow dose equivalent shall be the dose averaged over the contiguous ((ten))10 square centimeters of skin receiving the highest exposure. The deep dose equivalent, lens dose equivalent, and shallow dose equivalent may be assessed from surveys or other radiation measurements for the purpose of demonstrating compliance with the occupational dose limits, if the individual monitoring device was not in the region of highest potential exposure, or the results of the individual monitoring are unavailable.
(4) Derived air concentration (DAC) and annual limit on intake (ALI) values are specified in WAC 246-221-290 and may be used to determine the individual's dose and to demonstrate compliance with the occupational dose limits.
(5) Notwithstanding the annual dose limits, the licensee shall limit the soluble uranium intake by an individual to 10 milligrams in a week in consideration of chemical toxicity.
(6) The licensee or registrant shall reduce the dose that an individual may be allowed to receive in the current year by the amount of occupational dose received while employed by any other person during the current year as determined in accordance with WAC 246-221-020.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 01-05-110, filed 2/21/01, effective 3/24/01)
WAC 246-221-015Compliance with requirements for summation of external and internal doses.
(1) If the licensee is required to monitor under both WAC 246-221-090 and 246-221-100, the licensee shall demonstrate compliance with the dose limits by summing external and internal doses. If the licensee is required to monitor only under WAC 246-221-090 or only under WAC 246-221-100, then summation is not required to demonstrate compliance with the dose limits. The licensee may demonstrate compliance with the requirements for summation of external and internal doses under subsections (2), (3), and (4) of this section. The dose equivalents for the lens of the eye, the skin, and the extremities are not included in the summation, but are subject to separate limits.
(2) Intake by inhalation. If the only intake of radionuclides is by inhalation, the total effective dose equivalent limit is not exceeded if the sum of the deep dose equivalent divided by the total effective dose equivalent limit, and one of the following, does not exceed unity:
(a) The sum of the fractions of the inhalation ALI for each radionuclide; or
(b) The total number of derived air concentration-hours (DAC-hours) for all radionuclides divided by ((two thousand))2,000; or
(c) The sum of the calculated committed effective dose equivalents to all significantly irradiated organs or tissues (T) calculated from bioassay data using appropriate biological models and expressed as a fraction of the annual limit. For purposes of this requirement, an organ or tissue is deemed to be significantly irradiated if, for that organ or tissue, the product of the weighting factors, wT, and the committed dose equivalent, HT,50, per unit intake is greater than ((ten))10 percent of the maximum weighted value of H50, that is, wTHT,50, per unit intake for any organ or tissue.
(3) Intake by oral ingestion. If the occupationally exposed individual also receives an intake of radionuclides by oral ingestion greater than ((ten))10 percent of the applicable oral ALI, the licensee shall account for this intake and include it in demonstrating compliance with the limits.
(4) Intake through wounds or absorption through skin. The licensee shall evaluate and, to the extent practical, account for intakes through wounds or skin absorption. The intake through intact skin has been included in the calculation of DAC for hydrogen-3 and does not need to be evaluated or accounted for pursuant to this section.
(5) External dose from airborne radioactive material. Licensees shall, when determining the dose from airborne radioactive material, include the contribution to the deep dose equivalent, lens dose equivalent, and shallow dose equivalent from external exposure to the radioactive cloud. Airborne radioactivity measurements and DAC values shall not be used as the primary means to assess the deep dose equivalent when the airborne radioactive material includes radionuclides other than noble gases or if the cloud of airborne radioactive material is not relatively uniform. The determination of the deep dose equivalent to an individual shall be based upon measurements using instruments or individual monitoring devices.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 01-05-110, filed 2/21/01, effective 3/24/01)
WAC 246-221-030Requirements for planned special exposures.
A licensee or registrant may authorize an adult worker to receive doses in addition to and accounted for separately from the doses received under the limits specified in WAC 246-221-010 provided that each of the following conditions is satisfied:
(1) The licensee or registrant authorizes a planned special exposure only in an exceptional situation when alternatives that might avoid the dose estimated to result from the planned special exposure are unavailable or impractical.
(2) The licensee or registrant, and employer if the employer is not the licensee or registrant, specifically authorizes the planned special exposure, in writing, before the exposure occurs.
(3) Before a planned special exposure, the licensee or registrant ensures that each individual involved is:
(a) Informed of the purpose of the planned operation; and
(b) Informed of the estimated doses and associated potential risks and specific radiation levels or other conditions that might be involved in performing the task; and
(c) Instructed in the measures to be taken to keep the dose ALARA considering other risks that may be present.
(4) Prior to permitting an individual to participate in a planned special exposure, the licensee or registrant ascertains prior doses as required by WAC 246-221-020(2) during the lifetime of the individual for each individual involved.
(5) Subject to WAC 246-221-010(2), the licensee or registrant shall not authorize a planned special exposure that would cause an individual to receive a dose from all planned special exposures and all doses in excess of the limits to exceed:
(a) The numerical values of any of the dose limits in WAC 246-221-010(1) in any year; and
(b) Five times the annual dose limits in WAC 246-221-010(1) during the individual's lifetime.
(6) The licensee or registrant maintains records that describe:
(a) The exceptional circumstances requiring the use of a planned special exposure;
(b) The name of the management official who authorized the planned special exposure and a copy of the signed authorization;
(c) What actions were necessary;
(d) Why the actions were necessary;
(e) What precautions were taken to assure that doses were maintained ALARA; and
(f) What individual and collective doses were expected to result.
(7) The licensee or registrant records the best estimate of the dose resulting from the planned special exposure in the individual's record and informs the individual, in writing, of the dose within ((thirty))30 days from the date of the planned special exposure. The dose from planned special exposures shall not be considered in controlling future occupational dose of the individual under WAC 246-221-010(1) but shall be included in evaluations required by subsections (4) and (5) of this section.
(8) The licensee or registrant submits a written report in accordance with WAC 246-221-265.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 14-01-077, filed 12/16/13, effective 1/16/14)
WAC 246-221-040Determination of internal exposure of individuals to concentrations of radioactive materials in restricted areas.
(1) For purposes of assessing dose used to determine compliance with occupational dose equivalent limits, the licensee shall, when required under WAC 246-221-100, take suitable and timely measurements of:
(a) Concentrations of radioactive materials in air in work areas; or
(b) Quantities of radionuclides in the body; or
(c) Quantities of radionuclides excreted from the body; or
(d) Combinations of these measurements.
(2) Unless respiratory protective equipment is used, as provided in WAC 246-221-117, or the assessment of intake is based on bioassays, the licensee shall assume that an individual inhales radioactive material at the airborne concentration in which the individual is present.
(3) When specific information on the physical and biochemical properties of the radionuclides taken into the body or the behavior or the material in an individual is known, the licensee may:
(a) Use that information to calculate the committed effective dose equivalent, and, if used, the licensee shall document that information in the individual's record; and
(b) Upon prior approval of the department, adjust the DAC or ALI values to reflect the actual physical and chemical characteristics of airborne radioactive material, for example, aerosol size distribution or density; and
(c) Separately assess the contribution of fractional intakes of Class D, W, or Y compounds of a given radionuclide to the committed effective dose equivalent. See WAC 246-221-290.
(4) If the licensee chooses to assess intakes of Class Y material using the measurements given in subsection (1)(b) or (c) of this section, the licensee may delay the recording and reporting of the assessments for periods up to seven months, unless otherwise required by WAC 246-221-250 or 246-221-260. This delay permits the licensee to make additional measurements basic to the assessments.
(5) If the identity and concentration of each radionuclide in a mixture are known, the fraction of the DAC applicable to the mixture for use in calculating DAC-hours shall be either:
(a) The sum of the ratios of the concentration to the appropriate DAC value, that is, D, W, or Y, from WAC 246-221-290 for each radionuclide in the mixture; or
(b) The ratio of the total concentration for all radionuclides in the mixture to the most restrictive DAC value for any radionuclide in the mixture.
(6) If the identity of each radionuclide in a mixture is known, but the concentration of one or more of the radionuclides in the mixture is not known, the DAC for the mixture shall be the most restrictive DAC of any radionuclide in the mixture.
(7) When a mixture of radionuclides in air exists, a licensee may disregard certain radionuclides in the mixture if:
(a) The licensee uses the total activity of the mixture in demonstrating compliance with the dose limits in WAC 246-221-010 and in complying with the monitoring requirements in WAC 246-221-100; and
(b) The concentration of any radionuclide disregarded is less than ((ten))10 percent of its DAC; and
(c) The sum of these percentages for all of the radionuclides disregarded in the mixture does not exceed ((thirty))30 percent.
(8) When determining the committed effective dose equivalent, the following information may be considered:
(a) In order to calculate the committed effective dose equivalent, the licensee may assume that the inhalation of one ALI, or an exposure of 2,000 DAC-hours, results in a committed effective dose equivalent of 0.05 Sv (((5))five rem) for radionuclides that have their ALIs or DACs based on the committed effective dose equivalent.
(b) For an ALI and the associated DAC determined by the nonstochastic organ dose limit of 0.50 Sv (50 rem), the intake of radionuclides that would result in a committed effective dose equivalent of 0.05 Sv (((5))five rem), that is, the stochastic ALI, is listed in parentheses in Table I of WAC 246-221-290. The licensee may, as a simplifying assumption, use the stochastic ALIs to determine committed effective dose equivalent. However, if the licensee uses the stochastic ALIs, the licensee shall also demonstrate that the limit in WAC 246-221-010 (1)(a)(ii) is met.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-046, filed 6/1/17, effective 7/2/17)
WAC 246-221-055Dose equivalent to an embryo/fetus.
(1) The licensee or registrant shall ensure that the dose equivalent to an embryo/fetus during the entire pregnancy, due to occupational exposure of a declared pregnant woman, does not exceed ((5))five mSv (0.5 rem).
(2) Once pregnancy has been declared, the licensee or registrant shall make every effort to avoid substantial variation above a uniform monthly exposure rate to a declared pregnant woman in order to satisfy the limit in subsection (1) of this section.
(3) If by the time the woman declares pregnancy to the licensee or registrant, the dose equivalent to the embryo/fetus has exceeded ((5))five mSv (0.5 rem), or is within 0.50 mSv (0.05 rem) of this dose, the licensee or registrant shall be deemed to be in compliance with subsection (1) of this section if the additional dose equivalent to the embryo/fetus does not exceed 0.50 mSv (0.05 rem) during the remainder of the pregnancy.
(4) The dose equivalent to an embryo/fetus shall be taken as the sum of:
(a) The deep dose equivalent to the declared pregnant woman; and
(b) The dose equivalent to the embryo/fetus from radionuclides in the embryo/fetus and radionuclides in the declared pregnant woman.
(5) The licensee or registrant shall maintain the records of dose equivalent to an embryo/fetus with the records of dose equivalent to the declared pregnant woman. The declaration of pregnancy, including the estimated date of conception, shall also be kept on file, but may be maintained separately from the dose records.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 14-01-077, filed 12/16/13, effective 1/16/14)
WAC 246-221-060Dose limits for individual members of the public.
(1) Each licensee or registrant shall conduct operations so that:
(a) The total effective dose equivalent to individual members of the public from the licensed or registered operation does not exceed ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem) in a year, exclusive of the dose contributions from background radiation, from any medical administration the individual has received, from exposure to individuals administered radioactive material and released under chapter 246-240 WAC, from voluntary participation in medical research programs, and from the licensee's or registrant's disposal of radioactive material into sanitary sewerage in accordance with WAC 246-221-190; and
(b) The dose in any unrestricted area from external sources, exclusive of the dose contributions from patients administered radioactive material and released under chapter 246-240 WAC, does not exceed 0.02 mSv (0.002 rem) in any one hour.
(2) If the licensee or registrant permits members of the public to have access to restricted areas, they shall be escorted and the limits for members of the public continue to apply to those individuals.
(3) Notwithstanding subsection (1) of this section, a licensee or registrant may continue to operate a facility constructed and put into operation prior to January 1, 1994, where the annual dose limit for an individual member of the public is more than ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem) and less than ((5))five mSv (0.5 rem) total effective dose equivalent, if:
(a) The facility's approved operating conditions for each radiation source remain the same. Any increase in the following operating conditions shall require reevaluation by the department and modification of the facility shielding applicable to the source of radiation to meet the ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem) total effective dose equivalent limit for individual members of the public: Size of the radiation source, workload, or occupancy factors associated with the source of radiation; and
(b) Any change in the permanent shielding of the facility due to remodeling, repair or replacement requires the facility to meet the ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem) total effective dose equivalent limit for individual members of the public for areas affected by that portion of the shielding.
(4) Each licensee or registrant shall maintain records sufficient to demonstrate compliance with the dose limit for individual members of the public.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 14-01-077, filed 12/16/13, effective 1/16/14)
WAC 246-221-080Leak tests.
(1) Each sealed radioactive source possessed under the provisions of a specific license, other than hydrogen-3 (tritium), with a half-life greater than ((thirty))30 days and in any form other than gas, shall be tested and results obtained for leakage or contamination prior to initial use and at six-month intervals or as specified by the license, except that each source designed for the purpose of emitting alpha particles shall be tested at intervals not to exceed three months. If at any other time there is reason to suspect that a sealed source might have been damaged, it shall be tested for leakage and results obtained before further use. In the absence of a certificate from a transferor indicating that a test for leakage has been made within six months prior to the transfer (three months for a source designed to emit alpha particles), the sealed source shall not be put into use until tested and the results received.
(2) Leak tests shall be capable of detecting the presence of 185 Bq (0.005 microcurie) of removable contamination. The results of leak tests made pursuant to subsection (1) of this section shall be recorded in units of becquerel or microcuries and shall be maintained for inspection by the department. Any test conducted pursuant to subsection (1) of this section which reveals the presence of 185 Bq (0.005 microcurie) or more of removable contamination shall be considered evidence that the sealed source is leaking. The licensee shall immediately withdraw the source from use shall take action to prevent the spread of contamination and shall cause it to be decontaminated and repaired or to be disposed in accordance with WAC 246-232-080. If a sealed source shows evidence of leaking, a report shall be filed with the department within five days of the test, describing the equipment involved, the test results, and the corrective action taken.
(3) Test samples shall be taken from the sealed source or from the internal surfaces or the opening of the container in which the sealed source is stored or from surfaces of devices or equipment in which the sealed source is permanently mounted. Tests for contamination and leakage may be made by wiping appropriate accessible surfaces on which one might expect contamination to accumulate and measuring these wipes for transferred contamination. Test samples shall also be taken from the interior surfaces of the container in which a sealed source of radium is stored.
(4) Leak tests are required for sealed radioactive sources that are greater than 3.7 MBq (100 microcuries) for beta and gamma emitting sources and greater than 370 KBq (10 microcuries) for sources designed to emit alpha particles.
(5) Tests for leakage or contamination shall be performed by persons specifically authorized by the department, an agreement state, or the NRC to perform such services.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 01-05-110, filed 2/21/01, effective 3/24/01)
WAC 246-221-090Personnel monitoring for external dose.
Each licensee or registrant shall monitor occupational exposure from sources of radiation at levels sufficient to demonstrate compliance with the occupational dose limits of WAC 246-221-010, 246-221-030, 246-221-050 and 246-221-055.
(1) Each licensee or registrant shall monitor occupational exposure to radiation from licensed (or registered) and unlicensed (or unregistered) radiation sources under the control of the licensee or registrant and shall supply and shall require the use of individual monitoring devices by:
(a) Each adult likely to receive, in one year from sources external to the body, a dose in excess of ((ten))10 percent of the applicable limits specified in WAC 246-221-010(1).
(b) Each minor likely to receive, in one year from sources external to the body, a deep dose equivalent in excess of ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem), a lens dose equivalent in excess of 1.5 mSv (0.15 rem), or a shallow dose equivalent to the skin or to the extremities in excess of ((5))five mSv (0.5 rem).
(c) Each declared pregnant woman likely to receive during the entire pregnancy, from radiation sources external to the body, a deep dose equivalent in excess of ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem). All of the occupational dose limits specified in WAC 246-221-010 continue to be applicable to the declared pregnant worker as long as the embryo/fetus dose limit is not exceeded.
(d) Each individual who enters a high or very high radiation area.
(2) Personnel monitoring devices assigned to an individual:
(a) Shall not intentionally be exposed to give a false or erroneous reading;
(b) Shall be assigned to one individual per exposure interval (i.e., weekly, monthly) and used to determine exposure for that individual only;
(c) Shall not be worn by any individual other than that individual originally assigned to the device;
(d) Personnel monitoring devices that are exposed while not being worn by the assigned individual shall be processed and recorded as soon as possible. A replacement monitoring device shall be assigned to the individual immediately. A record of the circumstances of the exposure shall be retained.
(3) All personnel dosimeters, except for direct and indirect reading pocket ionization chambers and those dosimeters used to measure the dose to any extremities, that require processing to determine the radiation dose and that are utilized by licensees or registrants to comply with subsection (1) of this section, with other applicable provisions of chapters 246-220 through 246-255 WAC, or with conditions specified in a licensee's license must be processed and evaluated by a dosimetry processor:
(a) Holding current personnel dosimetry accreditation from either the National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP) of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (formerly known as the National Bureau of Standards) or the United States Department of Energy Laboratory Accreditation Program for Personnel Dosimetry Systems (DOELAP); and
(b) Approved in this accreditation process for the type of radiation or radiations included in the NVLAP or DOELAP program that most closely approximate the type of radiation or radiations for which the individual wearing the dosimeter is monitored.
(4) For the purposes of this section "dosimetry processor" means an individual or an organization that processes and evaluates personnel monitoring devices in order to determine the radiation dose delivered to the device.
(5) Each licensee or registrant shall maintain records of doses received by all individuals for whom monitoring was required under subsection (1) of this section, and records of doses received during planned special exposures, accidents, and emergency conditions. Assessments of dose equivalent and records made using units in effect before January 1, 1994, need not be changed. These records shall include, when applicable:
(a) The deep dose equivalent to the whole body, lens dose equivalent, shallow dose equivalent to the skin, and shallow dose equivalent to the extremities; and
(b) The total effective dose equivalent when required by WAC 246-221-015; and
(c) The total of the deep dose equivalent and the committed dose to the organ receiving the highest total dose (total organ dose equivalent).
(6) The licensee or registrant shall maintain the records specified in subsection (5) of this section on department Form RHF-5A, in accordance with the instructions provided on the form, or in clear and legible records containing all the information required by Form RHF-5A; and shall update the information at least annually.
(7) Each licensee or registrant shall ensure that individuals, for whom they are required to monitor occupational doses in accordance with subsection (1) of this section, wear individual monitoring devices as follows:
(a) An individual monitoring device used for monitoring the dose to the whole body shall be worn at the unshielded or least shielded location of the whole body likely to receive the highest exposure. When a protective apron is worn, the location of the individual monitoring device is typically at the neck (collar).
(b) Any additional individual monitoring device used for monitoring the dose to an embryo/fetus of a declared pregnant woman, pursuant to WAC 246-221-055(1), shall be located at the waist under any protective apron being worn by the woman.
(c) An individual monitoring device used for monitoring the lens dose equivalent, to demonstrate compliance with WAC 246-221-010 (1)(b)(i), shall be located at the neck (collar), outside any protective apron being worn by the monitored individual, or at an unshielded location closer to the eye.
(d) An individual monitoring device used for monitoring the dose to the extremities, to demonstrate compliance with WAC 246-221-010 (1)(b)(ii), shall be worn on the extremity likely to receive the highest exposure. Each individual monitoring device shall be oriented to measure the highest dose to the extremity being monitored.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 01-05-110, filed 2/21/01, effective 3/24/01)
WAC 246-221-100Personnel monitoring for internal dose.
(1) Each licensee shall monitor, to determine compliance with WAC 246-221-040, the occupational intake of radioactive material by and assess the committed effective dose equivalent to:
(a) Adults likely to receive, in ((1))one year, an intake in excess of ((ten))10 percent of the applicable ALI in Table I, Columns 1 and 2, of WAC 246-221-290;
(b) Minors likely to receive, in one year, a committed effective dose equivalent in excess of ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem); and
(c) Declared pregnant women likely to receive, during the entire pregnancy, a committed effective dose equivalent in excess of ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem).
(2) Where necessary or desirable in order to aid in determining the extent of an individual's exposure to concentrations of radioactive material, the department may incorporate license provisions or issue an order requiring a licensee or registrant to make available to the individual appropriate bioassay services and to furnish a copy of the reports of such services to the department.
(3) Each licensee shall maintain records of doses received by all individuals for whom monitoring was required pursuant to subsections (1) and (2) of this section, and records of doses received during planned special exposures, accidents, and emergency conditions. Assessments of dose equivalent and records made using units in effect before January 1, 1994, need not be changed. These records shall include, when applicable:
(a) The estimated intake or body burden of radionuclides;
(b) The committed effective dose equivalent assigned to the intake or body burden of radionuclides;
(c) The specific information used to calculate the committed effective dose equivalent pursuant to WAC 246-221-040;
(d) The total effective dose equivalent when required by WAC 246-221-015; and
(e) The total of the deep dose equivalent and the committed dose to the organ receiving the highest total dose (total organ dose equivalent).
(4) The licensee or registrant shall maintain the records specified in subsection (3) of this section on department Form RHF-5A, in accordance with the instructions provided on the form, or in clear and legible records containing all the information required by Form RHF-5A; and shall update the information at least annually.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 94-01-073, filed 12/9/93, effective 1/9/94)
WAC 246-221-102Control of access to high radiation areas.
(1) The licensee or registrant shall ensure that each entrance or access point to a high radiation area has one or more of the following features:
(a) A control device that, upon entry into the area, causes the level of radiation to be reduced below that level at which an individual might receive a deep dose equivalent of ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem) in one hour at ((thirty))30 centimeters from the source of radiation or from any surface that the radiation penetrates; or
(b) A control device that energizes a conspicuous visible or audible alarm signal so that the individual entering the high radiation area and the supervisor of the activity are made aware of the entry; or
(c) Entryways that are locked, except during periods when access to the areas is required, with positive control over each individual entry.
(2) In place of the controls required by subsection (1) of this section for a high radiation area, the licensee or registrant may substitute continuous direct or electronic surveillance that is capable of preventing unauthorized entry.
(3) The licensee or registrant may apply to the department for approval of alternative methods for controlling access to high radiation areas.
(4) The licensee or registrant shall establish the controls required by subsections (1) and (3) of this section in a way that does not prevent individuals from leaving a high radiation area.
(5) The licensee is not required to control each entrance or access point to a room or other area that is a high radiation area solely because of the presence of radioactive materials prepared for transport and packaged and labeled in accordance with the regulations of the United States Department of Transportation provided that:
(a) The packages do not remain in the area longer than three days; and
(b) The dose rate at one meter from the external surface of any package does not exceed 0.1 mSv (0.01 rem) per hour.
(6) The licensee is not required to control entrance or access to rooms or other areas in hospitals solely because of the presence of patients containing radioactive material, provided that there are personnel in attendance who are taking the necessary precautions to prevent the exposure of individuals to radiation or radioactive material in excess of the established limits and to operate within the ALARA provisions of the licensee's radiation protection program.
(7) The licensee or registrant is not required to control entrance or access to rooms or other areas as described in this section if the licensee or registrant has met all the specific requirements for access and control specified in other applicable chapters of these regulations, such as, chapter 246-243 WAC for industrial radiography, chapter 246-225 WAC for X-rays in the healing arts, and chapter 246-229 WAC for particle accelerators.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 14-01-077, filed 12/16/13, effective 1/16/14)
WAC 246-221-110Surveys.
(1) Each licensee or registrant shall make or cause to be made such surveys, as defined in WAC 246-220-010, as may be necessary for the licensee or registrant to establish compliance with these regulations and are reasonable under the circumstances to evaluate the magnitude and extent of radiation levels, concentrations or quantities of radioactive material, and potential radiation hazards. Records of such surveys shall be preserved as specified in WAC 246-221-230. Information on performing surveys may be found in the NRC's Regulatory Guide 8.23 "Radiation Safety Surveys at Medical Institutions."
(2) The licensee shall ensure that instruments and equipment used for quantitative radiation measurements, for example, dose rate and effluent monitoring, are calibrated annually at intervals not to exceed ((thirteen))13 months for the radiation measured.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 01-05-110, filed 2/21/01, effective 3/24/01)
WAC 246-221-117Use of individual respiratory protection equipment.
If the licensee assigns or permits the use of respiratory protection equipment to limit the intake of radioactive material:
(1) The licensee shall use only respiratory protection equipment that is:
(a) Tested and certified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH); or
(b) Approved by the department on the basis of the licensee's submittal of an application for authorized use of other respiratory protection equipment, including a demonstration by testing, or a demonstration on the basis of reliable test information, that the material and performance characteristics of the equipment are capable of providing the proposed degree of protection under anticipated conditions of use.
(2) The licensee shall implement and maintain a respiratory protection program that includes:
(a) Air sampling sufficient to identify the potential hazard, permit proper equipment selection, and estimate exposures;
(b) Surveys and bioassays, as appropriate, to evaluate actual intakes;
(c) Testing of respirators for operability (user seal check for face sealing devices and functional check for others) immediately prior to each use;
(d) Written procedures regarding:
(i) Monitoring, including air sampling and bioassays;
(ii) Supervision and training of respirator users;
(iii) Fit testing;
(iv) Respirator selection;
(v) Breathing air quality;
(vi) Inventory and control;
(vii) Storage, issuance, maintenance, repair, testing, and quality assurance of respiratory protection equipment;
(viii) Recordkeeping; and
(ix) Limitations on periods of respirator use and relief from respirator use;
(e) Determination by a physician that the individual user is medically fit to use respiratory protection equipment:
(i) Before the initial fitting of a face sealing respirator;
(ii) Before the first field use of nonface sealing respirators; and
(iii) Either every ((twelve))12 months thereafter, or periodically at a frequency determined by a physician; and
(f) Fit testing, with a fit factor greater than or equal to ((ten))10 times the APF for negative pressure devices, and a fit factor greater than or equal to ((five hundred))500 for any positive pressure, continuous flow, and pressure-demand devices, before the first field use of tight fitting, face sealing respirators, and periodically thereafter at a frequency not to exceed one year. Fit testing must be performed with the facepiece operating in the negative pressure mode.
(3) The licensee shall advise each respirator user that the user may leave the area at any time for relief from respirator use in the event of equipment malfunction, physical or psychological distress, procedural or communication failure, significant deterioration of operating conditions, or any other conditions that might require relief.
(4) The licensee shall also consider limitations appropriate to the type and mode of use. When selecting respiratory devices the licensee shall provide for vision correction, adequate communication, low temperature work environments, and the concurrent use of other safety or radiological protection equipment. The licensee shall use equipment in such a way as not to interfere with the proper operation of the respirator.
(5) Standby rescue persons are required whenever one-piece atmosphere-supplying suits, or any combination of supplied air respiratory protection device and personnel protective equipment are used from which an unaided individual would have difficulty extricating himself or herself. The standby persons must be equipped with respiratory protection devices or other apparatus appropriate for the potential hazards. The standby rescue persons shall observe or otherwise maintain continuous communication with the workers (visual, voice, signal line, telephone, radio, or other suitable means), and be immediately available to assist them in case of a failure of the air supply or for any other reason that requires relief from distress. A sufficient number of standby rescue persons must be immediately available to assist all users of this type of equipment and to provide effective emergency rescue if needed.
(6) Atmosphere-supplying respirators must be supplied with respirable air of grade D quality or better as defined by the Compressed Gas Association in publication G-7.1, "Commodity Specification for Air," 1997 and included in the regulations of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (29 C.F.R. 1910.134 (i)(1)(ii)(A) through (E)). Grade D quality air criteria include:
(a) Oxygen content (v/v) of 19.5-23.5%;
(b) Hydrocarbon (condensed) content of ((5))five milligrams per cubic meter of air or less;
(c) Carbon monoxide (CO) content of 10 ppm or less;
(d) Carbon dioxide content of 1,000 ppm or less; and
(e) Lack of noticeable odor.
(7) The licensee shall ensure that no objects, materials or substances, such as facial hair, or any conditions that interfere with the face-to-facepiece seal or valve function, and that are under the control of the respirator wearer, are present between the skin of the wearer's face and the sealing surface of a tight-fitting respirator facepiece.
(8) In estimating the dose to individuals from intake of airborne radioactive materials, the concentration of radioactive material in the air that is inhaled when respirators are worn is initially assumed to be the ambient concentration in air without respiratory protection, divided by the assigned protection factor. If the dose is later found to be greater than the estimated dose, the corrected value must be used. If the dose is later found to be less than the estimated dose, the corrected value may be used.
(9) The department may impose restrictions in addition to the provisions of this section, WAC 246-221-113 and 246-221-285, in order to:
(a) Ensure that the respiratory protection program of the licensee is adequate to limit doses to individuals from intakes of airborne radioactive materials consistent with maintaining total effective dose equivalent ALARA; and
(b) Limit the extent to which a licensee may use respiratory protection equipment instead of process or other engineering controls.
(10) The licensee shall obtain authorization from the department before using assigned protection factors in excess of those specified in WAC 246-221-285. The department may authorize a licensee to use higher assigned protection factors on receipt of an application that:
(a) Describes the situation for which a need exists for higher protection factors; and
(b) Demonstrates that the respiratory protection equipment provides these higher protection factors under the proposed conditions of use.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-054, filed 6/10/16, effective 7/11/16)
WAC 246-221-160Procedures for picking up, receiving, and opening packages.
(1) Each licensee who expects to receive a package containing quantities of radioactive material in excess of the Type A1 or A2 quantities specified in WAC 246-231-200 shall make arrangements to receive:
(a) The package when it is offered for delivery by the carrier; or
(b) Immediate notification from the carrier of the arrival of the package at the carrier's terminal.
(2) Each licensee who picks up a package of radioactive material from a carrier's terminal shall pick up the package expeditiously upon receipt of notification from the carrier of its arrival.
(3) Each licensee shall:
(a) Monitor for radioactive contamination the external surfaces of any package labeled with a Radioactive White I, Yellow II or Yellow III label unless the package contains only radioactive material in the form of gas or in special form as defined in WAC 246-231-010; and
(b) Monitor the radiation levels of the external surfaces of any package labeled with a Radioactive White I, Yellow II or Yellow III label unless the package contains quantities of radioactive material that are less than or equal to the Type A quantity, as defined in WAC 246-231-200; and
(c) Monitor all packages known to contain radioactive material for radioactive contamination and radiation levels if the package has evidence of potential contamination, such as packages that are crushed, wet, or damaged.
(4) Monitoring shall be performed:
(a) Immediately upon receipt if there is evidence of package degradation or any other evidence of potential contamination or excessive radiation levels; or
(b) As soon as practicable after receipt, but no later than three hours after the package is received at the licensee's facility if received during the licensee's normal working hours, or no later than three hours from the beginning of the next working day if received after normal working hours.
(5) The licensee shall immediately notify the final delivery carrier and, by telephone, facsimile, or email, ((or letter,)) the department when:
(a) For normal shipments, removable radioactive surface contamination exceeds either 22 dpm/cm2 for beta-gamma emitting radionuclides, all radionuclides with half-lives less than ((ten))10 days, natural uranium, natural thorium, uranium-235, uranium-238, thorium-232, and thorium-228 and thorium 230 when contained in ores or concentrates; or 2.2 dpm/cm2 for all other alpha emitting radionuclides; or
(b) For exclusive use shipments, removable radioactive surface contamination exceeds either 220 dpm/cm2 for beta-gamma emitting radionuclides, all radionuclides with half-lives less than ((ten))10 days, natural uranium, natural thorium, uranium-235, uranium-238, thorium-232, and thorium-228 and thorium 230 when contained in ores or concentrates; or 22 dpm/cm2 for all other alpha emitting radionuclides; or
(c) For normal or exclusive use shipments, external radiation levels exceed two mSv/hour (200 millirem per hour) at any point on the external surface of the package; or
(d) For exclusive use shipments where the shipment is made in a closed transport vehicle, packages are secured in a fixed position, and no loading or unloading occurs between the beginning and end of transportation, external radiation levels exceed ((ten))10 mSv/hour (1000 millirem per hour) at any point on the external surface of the package.
(6) Each licensee shall establish and maintain procedures for safely opening packages in which radioactive material is received, and shall assure that such procedures are followed and that due consideration is given to instructions for the type of package being opened and the monitoring of potentially contaminated packaging material (including packages containing radioactive material in gaseous form) to assure that only background levels of radiation are present prior to disposal of such material as nonradioactive waste.
(7) Licensees transferring special form sources to and from a work site in vehicles owned or operated by the licensee are exempt from the contamination monitoring requirements of subsection (3)(a) of this section but are not exempt from the monitoring requirement in subsection (3)(b) of this section for measuring radiation levels to ensure that the source is still properly lodged in its shield.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 94-01-073, filed 12/9/93, effective 1/9/94)
WAC 246-221-190Disposal by release into sanitary sewerage systems.
(1) No licensee shall discharge radioactive material into a sanitary sewerage system unless:
(a) It is readily soluble or it is biological material which is readily dispersible in water;
(b) The quantity of any radioactive material released in any one month, if diluted by the average monthly quantity of water released by the licensee, will not result in an average concentration exceeding the limits specified in WAC 246-221-290, Table III; and
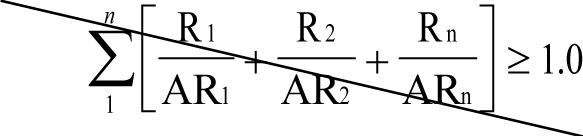
(c) The sum of the fractions for each radionuclide, if more than one radionuclide is released, will not exceed unity; where the fraction for each radionuclide is determined by dividing the actual monthly average concentration of each radionuclide released by the licensee into the sewer by the concentration of that radionuclide listed in Table III of WAC 246-221-290; and
(d) The total quantity of licensed and other radioactive material that the licensee releases into the sanitary sewerage system in a year does not exceed 185 GBq (((5))five Ci) of hydrogen-3, 37 GBq (((1))one Ci) of carbon-14, and 37 GBq (((1))one Ci) of all other radioactive materials combined.
(2) Excreta from individuals undergoing medical diagnosis or therapy with radioactive material shall be exempt from any limitations contained in this section.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 01-05-110, filed 2/21/01, effective 3/24/01)
WAC 246-221-230Records important to radiation safety.
(1) Each licensee or registrant shall make and retain records of activities, program reviews, measurements, and calculations which may be necessary to determine the extent of occupational and public exposure from sources of radiation under the control of the licensee or registrant.
(2) Each record required by this section shall be legible throughout the specified retention period.
(3) Each licensee or registrant shall use the SI units: Becquerel, gray, sievert and coulomb per kilogram, or the special units: Curie, rad, rem, and roentgen, including multiples and subdivisions, and shall clearly indicate the units of all quantities on records required by these regulations.
(4) The licensee or registrant shall make a clear distinction among the quantities entered on the records required by these regulations such as, total effective dose equivalent, total organ dose equivalent, shallow dose equivalent, lens dose equivalent, deep dose equivalent, or committed effective dose equivalent.
(5) Records which must be maintained under this part shall be the original or a reproduced copy or microform if such reproduced copy or microform is duly authenticated by authorized personnel and the microform is capable of producing a clear and legible copy after storage for the period specified by department regulations. The record may also be stored in electronic media with the capability for producing legible, accurate, and complete records during the required retention period. Electronic media data storage systems shall incorporate standard or universally recognized security measures. Records, such as letters, drawings, and specifications, shall include all pertinent information, such as stamps, initials, and signatures.
(6) The licensee shall maintain adequate safeguards against tampering with and loss of records.
(7) The licensee or registrant shall retain the following required records until the department terminates each pertinent license or registration requiring the record, and upon termination of the license or registration, the licensee or registrant shall store for at least ((thirty))30 years:
(a) Records of prior occupational dose and exposure history as recorded on department Form RHF-4 or RHF-4A, or equivalent;
(b) Records on department Form RHF-5 or RHF-5A, or equivalent, of doses received by all individuals for whom monitoring was required pursuant to WAC 246-221-090 and 246-221-100;
(c) Records of doses received during planned special exposures, accidents, and emergency conditions;
(d) The specific information used to calculate the committed effective dose equivalent pursuant to WAC 246-221-040(3);
(e) Records of the results of surveys to determine the dose from external sources of radiation used, in the absence of or in combination with individual monitoring data, in the assessment of individual dose equivalents;
(f) Records of the results of measurements and calculations used to determine individual intakes of radioactive material and used in the assessment of internal dose;
(g) Records showing the results of air sampling, surveys, and bioassays required pursuant to WAC 246-221-117 (1)(b)(i) and (ii);
(h) Records of the results of measurements and calculations used to evaluate the release of radioactive effluents to the environment.
(8) The licensee or registrant shall retain the following records until the department terminates the pertinent license or registration requiring the record:
(a) Records of waste disposal made under the provisions of WAC 246-221-180, 246-221-190, 246-221-210 and 246-221-220, chapter 246-249 WAC, and any burials in soil as previously authorized;
(b) Records of dose to individual members of the public as required by WAC 246-221-060(4);
(c) Records of the provisions of the radiation protection program as required by WAC 246-221-005.
(9) The licensee or registrant shall retain the following records for three years after the record is made:
(a) Records of testing entry control devices for very high radiation areas as required by WAC 246-221-106(3);
(b) Records used in preparing department Form RHF-4 or RHF-4A;
(c) Records showing the results of general surveys required by WAC 246-221-110 and package surveys required by WAC 246-221-160;
(d) Records of calibrations required by WAC 246-221-110;
(e) Records of program audits and other reviews of the content and implementation of the radiation protection program required by WAC 246-221-005;
(f) Records of waste disposal by decay in storage.
(10) If there is a conflict between the department's regulations in this part, license condition, or other written department approval or authorization pertaining to the retention period for the same type of record, the retention period specified in the regulations in this part for such records shall apply unless the department, under WAC 246-220-050, has granted a specific exemption from the record retention requirements specified in the regulations in this part.
(11) The discontinuance or curtailment of activities does not relieve the licensee or registrant of responsibility for retaining all records required by this section.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 09-06-003, filed 2/18/09, effective 3/21/09)
WAC 246-221-235Reports of transactions involving nationally tracked sources.
Each licensee who manufactures, transfers, receives, disassembles, or disposes of a nationally tracked source shall complete and submit a National Source Tracking Transaction Report as specified in subsections (1) through (5) of this section for each type of transaction.
(1) Each licensee who manufactures a nationally tracked source shall complete and submit a National Source Tracking Transaction Report. The report must include the following information:
(a) The name, address, and license number of the reporting licensee;
(b) The name of the individual preparing the report;
(c) The manufacturer, model, and serial number of the source;
(d) The radioactive material in the source;
(e) The initial source strength in becquerels (curies) at the time of manufacture; and
(f) The manufacture date of the source.
(2) Each licensee that transfers a nationally tracked source to another person shall complete and submit a National Source Tracking Transaction Report. The report must include the following information:
(a) The name, address, and license number of the reporting licensee;
(b) The name of the individual preparing the report;
(c) The name and license number of the recipient facility and the shipping address;
(d) The manufacturer, model, and serial number of the source or, if not available, other information to uniquely identify the source;
(e) The radioactive material in the source;
(f) The initial or current source strength in becquerels (curies);
(g) The date for which the source strength is reported;
(h) The shipping date;
(i) The estimated arrival date; and
(j) For nationally tracked sources transferred as waste under a Uniform Low-Level Radioactive Waste Manifest, the waste manifest number and the container identification of the container with the nationally tracked source.
(3) Each licensee that receives a nationally tracked source shall complete and submit a National Source Tracking Transaction Report. The report must include the following information:
(a) The name, address, and license number of the reporting licensee;
(b) The name of the individual preparing the report;
(c) The name, address, and license number of the person that provided the source;
(d) The manufacturer, model, and serial number of the source or, if not available, other information to uniquely identify the source;
(e) The radioactive material in the source;
(f) The initial or current source strength in becquerels (curies);
(g) The date for which the source strength is reported;
(h) The date of receipt; and
(i) For material received under a Uniform Low-Level Radioactive Waste Manifest, the waste manifest number and the container identification with the nationally tracked source.
(4) Each licensee that disassembles a nationally tracked source shall complete and submit a National Source Tracking Transaction Report. The report must include the following information:
(a) The name, address, and license number of the reporting licensee;
(b) The name of the individual preparing the report;
(c) The manufacturer, model, and serial number of the source or, if not available, other information to uniquely identify the source;
(d) The radioactive material in the source;
(e) The initial or current source strength in becquerels (curies);
(f) The date for which the source strength is reported;
(g) The disassemble date of the source.
(5) Each licensee who disposes of a nationally tracked source shall complete and submit a National Source Tracking Transaction Report. The report must include the following information:
(a) The name, address, and license number of the reporting licensee;
(b) The name of the individual preparing the report;
(c) The waste manifest number;
(d) The container identification with the nationally tracked source;
(e) The date of disposal; and
(f) The method of disposal.
(6) The reports discussed in subsections (1) through (5) of this section must be submitted by the close of the next business day after the transaction. A single report may be submitted for multiple sources and transactions. The reports must be submitted to the National Source Tracking System by using:
(a) The online National Source Tracking System;
(b) Electronically using a computer-readable format;
(c) By facsimile;
(d) By mail to the address on the National Source Tracking Transaction Report Form (NRC Form 748); or
(e) By telephone with follow-up by facsimile or mail.
(7) Each licensee shall correct any error in previously filed reports or file a new report for any missed transaction within five business days of the discovery of the error or missed transaction. Such errors may be detected by a variety of methods such as administrative reviews or by physical inventories required by regulation. In addition, each licensee shall reconcile the inventory of nationally tracked sources possessed by the licensee against that licensee's data in the National Source Tracking System. The reconciliation must be conducted during the month of January in each year. The reconciliation process must include resolving any discrepancies between the National Source Tracking System and the actual inventory by filing the reports identified by subsections (1) through (5) of this section. By January 31, of each year, each licensee must submit to the National Source Tracking System confirmation that the data in the National Source Tracking System is correct.
(((8) Each licensee that possesses Category 1 or 2 nationally tracked sources shall report its initial inventory of Category 1 or 2 nationally tracked sources to the National Source Tracking System by January 31, 2009. The information may be submitted by using any of the methods identified in subsection (6)(a) through (d) of this section. The initial inventory report shall include the following information:
(a) The name, address, and license number of the reporting licensee;
(b) The name of the individual preparing the report;
(c) The manufacturer, model, and serial number of each nationally tracked source or, if not available, other information to uniquely identify the source;
(d) The radioactive material in the sealed source;
(e) The initial or current source strength in becquerels (curies); and
(f) The date for which the source strength is reported.))
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-054, filed 6/10/16, effective 7/11/16)
WAC 246-221-240Reports of stolen, lost or missing radiation sources.
(1) Each licensee and registrant shall report by telephone (206-682-5327) and confirm promptly by letter, facsimile, or email to the State Department of Health, Office of Radiation Protection, P.O. Box 47827, Olympia, Washington 98504-7827.
(a) Immediately after its occurrence becomes known to the licensee, stolen, lost, or missing radioactive material in an aggregate quantity equal to or greater than ((one thousand))1,000 times the quantity specified in WAC 246-221-300, Appendix B; or
(b) Within ((thirty))30 days after its occurrence becomes known to the licensee, lost, stolen, or missing radioactive material in an aggregate quantity greater than ((ten))10 times the quantity specified in WAC 246-221-300, Appendix B that is still missing or any item not exempted in chapter 246-232 WAC; or
(c) Immediately after its occurrence becomes known to the registrant, a stolen, lost, or missing radiation machine.
(2) Each licensee or registrant required to make a report pursuant to subsection (1) of this section shall, within ((thirty))30 days after making the telephone report, make a written report to the department setting forth the following information:
(a) A description of the licensed or registered source of radiation involved, including, for radioactive material, the kind, quantity, and chemical and physical form; and, for radiation machines, the manufacturer, model and serial number, type and maximum energy of radiation emitted; and
(b) A description of the circumstances under which the loss or theft occurred; and
(c) A statement of disposition, or probable disposition, of the licensed or registered source of radiation involved; and
(d) Exposures of individuals to radiation, circumstances under which the exposures occurred, and the possible total effective dose equivalent to persons in unrestricted areas; and
(e) Actions that have been taken, or will be taken, to recover the source of radiation; and
(f) Procedures or measures that have been, or will be, adopted to ensure against a recurrence of the loss or theft of licensed or registered sources of radiation.
(3) Subsequent to filing the written report, the licensee or registrant shall also report additional substantive information on the loss or theft within ((thirty))30 days after the licensee or registrant learns of such information.
(4) The licensee or registrant shall prepare any report filed with the department pursuant to this section so that names of individuals who may have received exposure to radiation are stated in a separate and detachable portion of the report.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-054, filed 6/10/16, effective 7/11/16)
WAC 246-221-250Notification of incidents.
(1) Immediate notification. Notwithstanding other requirements for notification, each licensee and registrant shall immediately (as soon as possible but no later than four hours after discovery of an incident) notify the State Department of Health, Office of Radiation Protection, P.O. Box 47827, Olympia, Washington 98504-7827, by telephone (206-682-5327) and confirming letter, facsimile, or email with a follow-up written report within ((thirty))30 days of any incident involving any radiation source which may have caused or threatens to cause:
(a) An individual to receive:
(i) A total effective dose equivalent of 0.25 Sv (25 rem) or more;
(ii) A lens dose equivalent of 0.75 Sv (75 rem) or more; or
(iii) A shallow dose equivalent to the skin or extremities or a total organ dose equivalent of 2.5 Sv (250 rem) or more;
(b) The release of radioactive material, inside or outside of a restricted area, so that, had an individual been present for ((twenty-four))24 hours, the individual could have received an intake five times the occupational ALI. This provision does not apply to locations where personnel are not normally stationed during routine operations, such as hot-cells or process enclosures; or
(c) The loss of ability to take immediate protective actions necessary to avoid exposure to sources of radiation or releases of radioactive material that could exceed regulatory limits. Events which could cause such a loss of ability include fires, explosions, toxic gas releases, etc.
(2) Twenty-four hour notification. Each licensee and registrant shall within ((twenty-four))24 hours of discovery of the event, notify the State Department of Health, Office of Radiation Protection, P.O. Box 47827, Olympia, Washington 98504-7827, by telephone (206-682-5327) and confirming letter, facsimile, or email with a follow-up written report within ((thirty))30 days of any incident involving any radiation source possessed which may have caused or threatens to cause:
(a) An individual to receive, in a period of ((twenty-four))24 hours:
(i) A total effective dose equivalent exceeding 0.05 Sv (((5))five rem);
(ii) A lens dose equivalent exceeding 0.15 Sv (15 rem); or
(iii) A shallow dose equivalent to the skin or extremities or a total organ dose equivalent exceeding 0.5 Sv (50 rem);
(b) The release of radioactive material, inside or outside of a restricted area, so that, had an individual been present for ((twenty-four))24 hours, the individual could have received an intake in excess of one occupational ALI. This provision does not apply to locations where personnel are not normally stationed during routine operations, such as hot-cells or process enclosures;
(c) An unplanned contamination incident that:
(i) Requires access to the contaminated area, by workers or the general public, to be restricted for more than ((twenty-four))24 hours by imposing additional radiological controls or by prohibiting entry into the area;
(ii) Involves a quantity of material greater than five times the lowest annual limit on intake specified in WAC 246-221-290; and
(iii) Has access to the area restricted for a reason other than to allow radionuclides with a half-life of less than ((twenty-four))24 hours to decay prior to decontamination;
(d) Equipment failure or inability to function as designed when:
(i) The equipment is required by regulation or license condition to prevent releases exceeding regulatory limits, to prevent exposures to radiation and radioactive material exceeding regulatory limits or to mitigate the consequences of an accident;
(ii) The equipment is required to be available and operable at the time it becomes disabled or fails to function; and
(iii) No redundant equipment is available and operable to perform the required safety functions;
(e) An unplanned medical treatment at a medical facility of an individual with removable radioactive contamination on the individual's clothing or body; or
(f) An unplanned fire or explosion damaging any radioactive material or any device, container or equipment containing radioactive material when:
(i) The quantity of radioactive material involved is greater than five times the lowest annual limit on intake specified in WAC 246-221-290; and
(ii) The damage affects the integrity of the radioactive material or its container.
(3) For each occurrence requiring notification pursuant to this section, a prompt investigation of the situation shall be initiated by the licensee/registrant. A written report of the findings of the investigation shall be sent to the department within ((thirty))30 days.
(4) The licensee or registrant shall prepare each report filed with the department under this section so that names of individuals who have received exposure to sources of radiation are stated in a separate and detachable portion of the report.
Any report filed with the department under this section shall contain the information described in WAC 246-221-260 (2) and (3).
(5) The provisions of this section do not apply to doses that result from planned special exposures, provided such doses are within the limits for planned special exposures and are reported pursuant to WAC 246-221-265.
(6) Telephone notifications that do not involve immediate or ((twenty-four))24 hour notification should be made to the Tumwater office (360-236-3300).
(7) Telephone notification required under this section shall include, to the extent that the information is available at the time of notification:
(a) The caller's name and call-back telephone number;
(b) A description of the incident including date and time;
(c) The exact location of the incident;
(d) The radionuclides, quantities, and chemical and physical forms of the radioactive materials involved; and
(e) Any personnel radiation exposure data available.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 99-15-105, filed 7/21/99, effective 8/21/99)
WAC 246-221-260Reports of overexposures and excessive levels and concentrations.
(1) In addition to any notification required by WAC 246-221-250, each licensee or registrant shall submit a written report to the department within ((thirty))30 days after learning of any of the following occurrences:
(a) Incidents for which notification is required by WAC 246-221-250; or
(b) Doses in excess of any of the following:
(i) The occupational dose limits for adults in WAC 246-221-010; or
(ii) The occupational dose limits for a minor in WAC 246-221-050; or
(iii) The limits for an embryo/fetus of a declared pregnant woman in WAC 246-221-055; or
(iv) The limits for an individual member of the public in WAC 246-221-060; or
(v) Any applicable limit in the license; or
(vi) The ALARA constraints for air emissions established under WAC 246-221-005; or
(c) Levels of radiation or concentrations of radioactive material in:
(i) A restricted area in excess of applicable limits in the license; or
(ii) An unrestricted area in excess of ((ten))10 times the applicable limit set forth in this chapter or in the license or registration, whether or not involving exposure of any individual in excess of the limits in WAC 246-221-060; or
(d) For source materials milling licensees and nuclear power plants subject to the provisions of United States Environmental Protection Agency's generally applicable environmental radiation standards in 40 C.F.R. 190, levels of radiation or releases of radioactive material in excess of those standards, or of license conditions related to those standards.
(2) Each report required by subsection (1) of this section shall describe:
(a) The incident and its exact location, time and date;
(b) The extent of exposure of individuals to radiation or to radioactive material, including estimates of each individual's dose as required by subsection (3) of this section;
(c) Levels of radiation and concentrations of radioactive material involved, including the radionuclides, quantities, and chemical and physical form;
(d) The cause or probable cause of the exposure, levels of radiation or concentrations;
(e) The manufacturer and model number (if applicable) of any equipment that failed or malfunctioned;
(f) The results of any evaluations or assessments; and
(g) Corrective steps taken or planned to assure against a recurrence, including the schedule for achieving conformance with applicable limits, ALARA constraints, generally applicable environmental standards, and associated license conditions.
(3) Each report filed with the department pursuant to this section shall include for each individual exposed the name, Social Security number, and date of birth, and an estimate of the individual's dose. With respect to the limit for the embryo/fetus in WAC 246-221-055, the identifiers should be those of the declared pregnant woman. The report shall be prepared so that this information is stated in a separate and detachable part of the report.
(4) Individuals shall be notified of reports in accordance with the requirements of WAC 246-222-040.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 99-05-013, filed 2/5/99, effective 3/8/99)
WAC 246-221-265Special reports to the department—Planned special exposures and leaking sources.
(1) The licensee or registrant shall submit a written report to the department within ((thirty))30 days following any planned special exposure conducted in accordance with WAC 246-221-030. The written report shall:
(a) Inform the department that a planned special exposure was conducted;
(b) Indicate the date the planned special exposure occurred; and
(c) Provide the information required by WAC 246-221-030.
(2) The licensee shall file a written report with the department within five days after learning that a sealed source is leaking or contaminated. The report shall describe:
(a) The source;
(b) The source holder;
(c) The equipment in which the source is installed;
(d) The test results; and
(e) The corrective action taken.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 00-07-085, filed 3/15/00, effective 4/15/00)
WAC 246-221-270Vacating premises and release of equipment.
(1) Each specific licensee shall notify the department in writing of intent to vacate, at least ((thirty))30 days before vacating or relinquishing possession or control of premises which may have been contaminated with radioactive material as a result of licensed activities.
(2) Each licensee shall permanently decontaminate the premise, before vacating any premise or transferring the premise, in accordance with the standards specified in chapter 246-246 WAC. A survey by the licensee shall be made after the decontamination and the department and the landlord or subsequent tenant or transferee shall be provided with a copy of the survey no later than the date of vacating or relinquishing possession or control of the premise.
(3) No machinery, instruments, laboratory equipment or any other property used in contact with, or close proximity to radioactive material at a licensed premise shall be assigned, sold, leased, or transferred to an unlicensed person unless the property has been decontaminated and meets the standards specified in WAC 246-232-140. A survey shall be made after the decontamination and the department and subsequent owner or transferee shall be provided with a copy of the survey report.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 01-05-110, filed 2/21/01, effective 3/24/01)
WAC 246-221-285Assigned protection factors for respiratorsa.
| | Operating mode | Assigned Protection Factors |
I. | Air-Purifying Respirators (Particulate b only) c: | | |
| Filtering facepiece disposable d | Negative Pressure . . . . | (d) |
| Facepiece, half e. . . . | Negative Pressure . . . . | 10 |
| Facepiece, full . . . . | Negative Pressure . . . . | 100 |
| Facepiece, half . . . . | Powered air-purifying respirators . . . . | 50 |
| Facepiece, full . . . . | Powered air-purifying respirators . . . . | 1000 |
| Helmet/hood . . . . | Powered air-purifying respirators . . . . | 1000 |
| Facepiece, loose-fitting . . . . | Powered air-purifying respirators . . . . | 25 |
II. | Atmosphere-Supplying Respirators (Particulate, gases and vaporsf): | | |
| 1. Air-line respirator: | | |
| Facepiece, half . . . . | Demand . . . . | 10 |
| Facepiece, half . . . . | Continuous Flow . . . . | 50 |
| Facepiece, half . . . . | Pressure Demand . . . . | 50 |
| Facepiece, full . . . . | Demand . . . . | 100 |
| Facepiece, full . . . . | Continuous Flow . . . . | 1000 |
| Facepiece, full . . . . | Pressure Demand . . . . | 1000 |
| Helmet/hood . . . . | Continuous Flow . . . . | 1000 |
| Facepiece, loose-fitting . . . . | Continuous Flow . . . . | 25 |
| Suit . . . . | Continuous Flow . . . . | (g) |
| 2. Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA): | | |
| Facepiece, full . . . . | Demand . . . . | h100 |
| Facepiece, full . . . . | Pressure Demand . . . . | i10,000 |
| Facepiece, full . . . . | Demand, Recirculating . . . . | h100 |
| Facepiece, full . . . . | Positive Pressure Recirculating . . . . | i10,000 |
III. | Combination Respirators: | | |
| Any combination of air-purifying and atmosphere-supplying respirators. | Assigned protection factor for type and mode of operation as listed above. | |
a | These assigned protection factors apply only in a respiratory protection program that meets the requirements of this chapter. They are applicable only to airborne radiological hazards and may not be appropriate to circumstances when chemical or other respiratory hazards exist instead of, or in addition to, radioactive hazards. Selection and use of respirators for these circumstances must also comply with Department of Labor regulations. |
| Radioactive contaminants for which the concentration values in Table 1, Column 3 of WAC 246-221-290, Appendix A, are based on internal dose due to inhalation may, in addition, present external exposure hazards at higher concentrations. Under these circumstances, limitations on occupancy may have to be governed by external dose limits. |
b | Air-purifying respirators with APF <100 must be equipped with particulate filters that are at least 95 percent efficient. Air-purifying respirators with APF = 100 must be equipped with particulate filters that are at least 99 percent efficient. Air-purifying respirators with APFs ˃100 must be equipped with particulate filters that are at least 99.97 percent efficient. |
c | The licensee may apply to the department for the use of an APF greater than ((1))one for sorbent cartridges as protection against airborne radioactive gases and vapors (e.g., radioiodine). |
d | Licensees may permit individuals to use this type of respirator who have not been medically screened or fit tested on the device provided that no credit be taken for their use in estimating intake or dose. It is also recognized that it is difficult to perform an effective positive or negative pressure preuse user seal check on this type of device. All other respiratory protection program requirements listed in WAC 246-221-117 apply. An assigned protection factor has not been assigned for these devices. However, an APF equal to 10 may be used if the licensee can demonstrate a fit factor of at least 100 by use of a validated or evaluated, qualitative or quantitative fit test. |
e | Under-chin type only. No distinction is made in this section between elastomeric half-masks with replaceable cartridges and those designed with the filter medium as an integral part of the facepiece (e.g., disposable or reusable disposable). Both types are acceptable so long as the seal area of the latter contains some substantial type of seal-enhancing material such as rubber or plastic, the two or more suspension straps are adjustable, the filter medium is at least 95 percent efficient and all other requirements of this part are met. |
f | The assigned protection factors for gases and vapors are not applicable to radioactive contaminants that present an absorption or submersion hazard. For tritium oxide vapor, approximately ((one-third))1/3 of the intake occurs by absorption through the skin so that an overall protection factor of ((3))three is appropriate when atmosphere-supplying respirators are used to protect against tritium oxide. Exposure to radioactive noble gases is not considered a significant respiratory hazard, and protective actions for these contaminants should be based on external (submersion) dose considerations. |
g | No NIOSH approval schedule is currently available for atmosphere-supplying suits. This equipment may be used in an acceptable respiratory protection program as long as all the other minimum program requirements, with the exception of fit testing, are met (i.e., WAC 246-221-117). |
h | The licensee should implement institutional controls to assure that these devices are not used in areas immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH). |
i | This type of respirator may be used as an emergency device in unknown concentrations for protection against inhalation hazards. External radiation hazards and other limitations to permitted exposure such as skin absorption shall be taken into account in these circumstances. This device may not be used by any individual who experiences perceptible outward leakage of breathing gas while wearing the device. |
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 11-03-068, filed 1/18/11, effective 2/18/11)
WAC 246-221-290Appendix A—Annual limits on intake (ALI) and derived air concentrations (DAC) of radionuclides for occupational exposure; effluent concentrations; concentrations for release to sanitary sewerage.
For each radionuclide, Table I indicates the chemical form which is to be used for selecting the appropriate ALI or DAC value. The ALIs and DACs for inhalation are given for an aerosol with an activity median aerodynamic diameter (AMAD) of ((1))one µm (micron) and for three classes (D,W,Y) of radioactive material, which refer to their retention (approximately days, weeks or years) in the pulmonary region of the lung. This classification applies to a range of clearance half-times for D if less than ((ten))10 days, for W from ((ten to one hundred))10 to 100 days, and for Y greater than ((one hundred))100 days. Table II provides concentration limits for airborne and liquid effluents released to the general environment. Table III provides concentration limits for discharges to sanitary sewerage.
Note: | The values in Tables I, II, and III are presented in the computer "E" notation. In this notation a value of 6E-02 represents a value of 6 x 10-2 or 0.06, 6E+2 represents 6 x 102 or 600, and 6E+0 represents 6 x 100 or 6. |
Table I "Occupational Values"
Note that the columns in Table I of this appendix captioned "Oral Ingestion ALI," "Inhalation ALI," and "DAC," are applicable to occupational exposure to radioactive material.
The ALIs in this appendix are the annual intakes of given radionuclide by "Reference Man" which would result in either: A committed effective dose equivalent of 0.05 Sv (((5))five rem), stochastic ALI; or a committed dose equivalent of 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to an organ or tissue, nonstochastic ALI. The stochastic ALIs were derived to result in a risk, due to irradiation of organs and tissues, comparable to the risk associated with deep dose equivalent to the whole body of 0.05 Sv (((5))five rem). The derivation includes multiplying the committed dose equivalent to an organ or tissue by a weighting factor, wT. This weighting factor is the proportion of the risk of stochastic effects resulting from irradiation of the organ or tissue, T, to the total risk of stochastic effects when the whole body is irradiated uniformly. The values of wT are listed under the definition of weighting factor in WAC 246-221-005. The nonstochastic ALIs were derived to avoid nonstochastic effects, such as prompt damage to tissue or reduction in organ function.
A value of wT = 0.06 is applicable to each of the five organs or tissues in the "remainder" category receiving the highest dose equivalents, and the dose equivalents of all other remaining tissues may be disregarded. The following portions of the GI tract — stomach, small intestine, upper large intestine, and lower large intestine — are to be treated as four separate organs.
Note that the dose equivalents for an extremity, elbows, arms below the elbows, feet and lower legs, knees, and legs below the knees, skin, and lens of the eye are not considered in computing the committed effective dose equivalent, but are subject to limits that must be met separately.
When an ALI is defined by the stochastic dose limit, this value alone is given. When an ALI is determined by the non-stochastic dose limit to an organ, the organ or tissue to which the limit applies is shown, and the ALI for the stochastic limit is shown in parentheses. Abbreviated organ or tissue designations are used:
LLI wall | = | lower large intestine wall; |
St. wall | = | stomach wall; |
Blad wall | = | bladder wall; and |
Bone surf | = | bone surface. |
The use of the ALIs listed first, the more limiting of the stochastic and nonstochastic ALIs, will ensure that nonstochastic effects are avoided and that the risk of stochastic effects is limited to an acceptably low value. If, in a particular situation involving a radionuclide for which the nonstochastic ALI is limiting, use of that nonstochastic ALI is considered unduly conservative, the licensee may use the stochastic ALI to determine the committed effective dose equivalent. However, the licensee shall also ensure that the 0.5 Sv (50 rem) dose equivalent limit for any organ or tissue is not exceeded by the sum of the external deep dose equivalent plus the internal committed dose equivalent to that organ, not the effective dose. For the case where there is no external dose contribution, this would be demonstrated if the sum of the fractions of the nonstochastic ALIs (ALIns) that contribute to the committed dose equivalent to the organ receiving the highest dose does not exceed unity, that is, ∑ (intake (in µCi) of each radionuclide/ALIns) ≤ 1.0. If there is an external deep dose equivalent contribution of Hd, then this sum must be less than ((1))one - (Hd/50), instead of ≤ 1.0.
The derived air concentration (DAC) values are derived limits intended to control chronic occupational exposures. The relationship between the DAC and the ALI is given by:
DAC = ALI (in µCi)/(2000 hours per working year x 60 minutes/hour x 2 x 104 ml per minute) = [ALI/2.4 x 109] µCi/ml, |
where 2 x 104 ml per minute is the volume of air breathed per minute at work by Reference Man under working conditions of light work. |
The DAC values relate to one of two modes of exposure: Either external submersion or the internal committed dose equivalents resulting from inhalation of radioactive materials. DACs based upon submersion are for immersion in a semi-infinite cloud of uniform concentration and apply to each radionuclide separately.
The ALI and DAC values include contributions to exposure by the single radionuclide named and any in-growth of daughter radionuclides produced in the body by decay of the parent. However, intakes that include both the parent and daughter radionuclides should be treated by the general method appropriate for mixtures.
The values of ALI and DAC do not apply directly when the individual both ingests and inhales a radionuclide, when the individual is exposed to a mixture of radionuclides by either inhalation or ingestion or both, or when the individual is exposed to both internal and external irradiation. See WAC 246-221-015. When an individual is exposed to radioactive materials which fall under several of the translocation classifications of the same radionuclide, such as, Class D, Class W, or Class Y, the exposure may be evaluated as if it were a mixture of different radionuclides.
It should be noted that the classification of a compound as Class D, W, or Y is based on the chemical form of the compound and does not take into account the radiological half-life of different radionuclides. For this reason, values are given for Class D, W, and Y compounds, even for very short-lived radionuclides.
Table II "Effluent Concentrations"
The columns in Table II of this appendix captioned "Effluents," "Air" and "Water" are applicable to the assessment and control of dose to the public, particularly in the implementation of the provisions of WAC 246-221-070. The concentration values given in Columns 1 and 2 of Table II are equivalent to the radionuclide concentrations which, if inhaled or ingested continuously over the course of a year, would produce a total effective dose equivalent of 0.50 mSv (0.05 rem).
Consideration of nonstochastic limits has not been included in deriving the air and water effluent concentration limits because nonstochastic effects are presumed not to occur at or below the dose levels established for individual members of the public. For radionuclides, where the nonstochastic limit was governing in deriving the occupational DAC, the stochastic ALI was used in deriving the corresponding airborne effluent limit in Table II. For this reason, the DAC and airborne effluent limits are not always proportional as was the case in the previous Appendix A of this chapter.
The air concentration values listed in Table II, Column 1 were derived by one of two methods. For those radionuclides for which the stochastic limit is governing, the occupational stochastic inhalation ALI was divided by 2.4 x 109, relating the inhalation ALI to the DAC, as explained above, and then divided by a factor of ((three hundred))300. The factor of ((three hundred))300 includes the following components: A factor of ((fifty))50 to relate the 0.05 Sv (((5))five rem) annual occupational dose limit to the ((1))one mSv (0.1 rem) limit for members of the public, a factor of three to adjust for the difference in exposure time and the inhalation rate for a worker and that for members of the public; and a factor of two to adjust the occupational values, derived for adults, so that they are applicable to other age groups.
For those radionuclides for which submersion, that is external dose, is limiting, the occupational DAC in Table I, Column 3 was divided by ((two hundred nineteen))219. The factor of ((two hundred nineteen))219 is composed of a factor of ((fifty))50, as described above, and a factor of 4.38 relating occupational exposure for ((two thousand))2,000 hours per year to full-time exposure (((eight thousand seven hundred sixty))8,760 hours per year). Note that an additional factor of two for age considerations is not warranted in the submersion case.
The water concentrations were derived by taking the most restrictive occupational stochastic oral ingestion ALI and dividing by 7.3 x 107. The factor of 7.3 x 107 (ml) includes the following components: The factors of ((fifty))50 and two described above and a factor of 7.3 x 105 (ml) which is the annual water intake of Reference Man.
Note 2 of this appendix provides groupings of radionuclides which are applicable to unknown mixtures of radionuclides. These groupings, including occupational inhalation ALIs and DACs, air and water effluent concentrations and releases to sewer, require demonstrating that the most limiting radionuclides in successive classes are absent. The limit for the unknown mixture is defined when the presence of one of the listed radionuclides cannot be definitely excluded as being present either from knowledge of the radionuclide composition of the source or from actual measurements.
Table III "Releases to Sewers"
The monthly average concentrations for release to sanitary sewerage are applicable to the provisions in WAC 246-221-190. The concentration values were derived by taking the most restrictive occupational stochastic oral ingestion ALI and dividing by 7.3 x 106 (ml). The factor of 7.3 x 106 (ml) is composed of a factor of 7.3 x 105 (ml), the annual water intake by Reference Man, and a factor of ((ten))10, such that the concentrations, if the sewage released by the licensee were the only source of water ingested by a Reference Man during a year, would result in a committed effective dose equivalent of ((5))five mSv (0.5 rem).
list of elements |
Name | Symbol | Atomic Number | Name | Symbol | Atomic Number |
Actinium | Ac | 89 | Molybdenum | Mo | 42 |
Aluminum | Al | 13 | Neodymium | Nd | 60 |
Americium | Am | 95 | Neptunium | Np | 93 |
Antimony | Sb | 51 | Nickel | Ni | 28 |
Argon | Ar | 18 | Nitrogen | N | 7 |
Arsenic | As | 33 | Niobium | Nb | 41 |
Astatine | At | 85 | Osmium | Os | 76 |
Barium | Ba | 56 | Oxygen | O | 8 |
Berkelium | Bk | 97 | Palladium | Pd | 46 |
Beryllium | Be | 4 | Phosphorus | P | 15 |
Bismuth | Bi | 83 | Platinum | Pt | 78 |
Bromine | Br | 35 | Plutonium | Pu | 94 |
Cadmium | Cd | 48 | Polonium | Po | 84 |
Calcium | Ca | 20 | Potassium | K | 19 |
Californium | Cf | 98 | Praseodymium | Pr | 59 |
Carbon | C | 6 | Promethium | Pm | 61 |
Cerium | Ce | 58 | Protactinium | Pa | 91 |
Cesium | Cs | 55 | Radium | Ra | 88 |
Chlorine | Cl | 17 | Radon | Rn | 86 |
Chromium | Cr | 24 | Rhenium | Re | 75 |
Cobalt | Co | 27 | Rhodium | Rh | 45 |
Copper | Cu | 29 | Rubidium | Rb | 37 |
Curium | Cm | 96 | Ruthenium | Ru | 44 |
Dysprosium | Dy | 66 | Samarium | Sm | 62 |
Einsteinium | Es | 99 | Scandium | Sc | 21 |
Erbium | Er | 68 | Selenium | Se | 34 |
Europium | Eu | 63 | Silicon | Si | 14 |
Fermium | Fm | 100 | Silver | Ag | 47 |
Fluorine | F | 9 | Sodium | Na | 11 |
Francium | Fr | 87 | Strontium | Sr | 38 |
Gadolinium | Gd | 64 | Sulfur | S | 16 |
Gallium | Ga | 31 | Tantalum | Ta | 73 |
Germanium | Ge | 32 | Technetium | Tc | 43 |
Gold | Au | 79 | Tellurium | Te | 52 |
Hafnium | Hf | 72 | Terbium | Tb | 65 |
Holmium | Ho | 67 | Thallium | Tl | 81 |
Hydrogen | H | 1 | Thorium | Th | 90 |
Indium | In | 49 | Thulium | Tm | 69 |
Iodine | I | 53 | Tin | Sn | 50 |
Iridium | Ir | 77 | Titanium | Ti | 22 |
Iron | Fe | 26 | Tungsten | W | 74 |
Krypton | Kr | 36 | Uranium | U | 92 |
Lanthanum | La | 57 | Vanadium | V | 23 |
Lead | Pb | 82 | Xenon | Xe | 54 |
Lutetium | Lu | 71 | Ytterbium | Yb | 70 |
Magnesium | Mg | 12 | Yttrium | Y | 39 |
Manganese | Mn | 25 | Zinc | Zn | 30 |
Mendelevium | Md | 101 | Zirconium | Zr | 40 |
Mercury | Hg | 80 | | | |
| | | Table 1 Occupational Values | Table II Effluent Concentration | Table III Releases to Sewers |
| | | Col. 1 | Col. 2 | Col. 3 | Col. 1 | Col. 2 | Monthly Average Concen- tration |
| | | Oral Ingestion | Inhalation | | |
Atomic No. | Radionuclide | Class | ALI µCi | ALI µCi | DAC µCi/ml | Air µCi/ml | Water µCi/ml | µCi/ml |
1 | Hydrogen-3 | Water, DAC includes skin absorption | 8E+4 | 8E+4 | 2E-5 | 1E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| Gas (HT or T2) Submersion1: Use above values as HT and T2 oxidize in air and in the body to HTO. | | |
4 | Beryllium-7 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 4E+4 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | Y, oxides, halides, and nitrates | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
4 | Beryllium-10 | W, see 7Be | 1E+3 | 2E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 7Be | - | 1E+1 | 6E-9 | 2E-11 | - | - |
6 | Carbon-112 | Monoxide | - | 1E+6 | 5E-4 | 2E-6 | - | - |
| | Dioxide | - | 6E+5 | 3E-4 | 9E-7 | - | - |
| | Compounds | 4E+5 | 4E+5 | 2E-4 | 6E-7 | 6E-3 | 6E-2 |
6 | Carbon-14 | Monoxide | - | 2E+6 | 7E-4 | 2E-6 | - | - |
| | Dioxide | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | Compounds | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
7 | Nitrogen-132 | Submersion1 | - | - | 4E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
8 | Oxygen-152 | Submersion1 | - | - | 4E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
9 | Fluorine-182 | D, fluorides of H, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr | 5E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (5E+4) | - | - | - | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | W, fluorides of Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra, Al, Ga, In, Tl, As, Sb, Bi, Fe, Ru, Os, Co, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, V, Nb, Ta, Mn, Tc, and Re Y, lanthanum fluoride | - - | 9E+4 8E+4 | 4E-5 3E-5 | 1E-7 1E-7 | - - | - - |
11 | Sodium-22 | D, all compounds | 4E+2 | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
11 | Sodium-24 | D, all compounds | 4E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
12 | Magnesium-28 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 7E+2 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, halides, and nitrates | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
13 | Aluminum-26 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 4E+2 | 6E+1 | 3E-8 | 9E-11 | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, halides, and nitrates | - | 9E+1 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
14 | Silicon-31 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 9E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, and nitrates Y, aluminosilicate glass | - - | 3E+4 3E+4 | 1E-5 1E-5 | 5E-8 4E-8 | - - | - - |
14 | Silicon-32 | D, see 31Si | 2E+3 | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | 3E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+3) | - | - | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 31Si | - | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 31Si | - | 5E+0 | 2E-9 | 7E-12 | - | - |
15 | Phosphorus-32 | D, all compounds except phosphates given for W | 6E+2 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, phosphates of Zn2+, S3+, Mg2+, Fe3+, Bi3+, and lanthanides | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 5E-10 | - | - |
15 | Phosphorus-33 | D, see 32P | 6E+3 | 8E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
| | W, see 32P | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
16 | Sulfur-35 | Vapor | - | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | D, sulfides and sulfates except those given for W | 1E+4 | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (8E+3) | - | - | - | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, elemental sulfur, sulfides of Sr, Ba, Ge, Sn, Pb, As, Sb, Bi, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, W, and Mo. Sulfates of Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra, As, Sb, and Bi | 6E+3 - | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
17 | Chlorine-36 | D, chlorides of H, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, chlorides of lantha-nides, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Ge, Sn, Pb, As, Sb, Bi, Fe, Ru, Os, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Tc, and Re | - | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | 3E-10 | - | - |
17 | Chlorine-382 | D, see 36Cl | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 36Cl | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
17 | Chlorine-392 | D, see 36Cl | 2E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 36Cl | - | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
18 | Argon-37 | Submersion1 | - | - | 1E+0 | 6E-3 | - | - |
18 | Argon-39 | Submersion1 | - | - | 2E-4 | 8E-7 | - | - |
18 | Argon-41 | Submersion1 | - | - | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
19 | Potassium-40 | D, all compounds | 3E+2 | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | 4E-6 | 4E-5 |
19 | Potassium-42 | D, all compounds | 5E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
19 | Potassium-43 | D, all compounds | 6E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 9E-5 | 9E-4 |
19 | Potassium-442 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
19 | Potassium-452 | D, all compounds | 3E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (5E+4) | - | - | - | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
20 | Calcium-41 | W, all compounds | 3E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E+3) | Bone surf (4E+3) | - | 5E-9 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
20 | Calcium-45 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 8E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
20 | Calcium-47 | W, all compounds | 8E+2 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
21 | Scandium-43 | Y, all compounds | 7E+3 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
21 | Scandium-44m | Y, all compounds | 5E+2 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
21 | Scandium-44 | Y, all compounds | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
21 | Scandium-46 | Y, all compounds | 9E+2 | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | 3E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
21 | Scandium-47 | Y, all compounds | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+3) | - | - | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
21 | Scandium-48 | Y, all compounds | 8E+2 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
21 | Scandium-492 | Y, all compounds | 2E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
22 | Titanium-44 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 3E+2 | 1E+1 | 5E-9 | 2E-11 | 4E-6 | 4E-5 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, halides, and nitrates | - | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | 4E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, SrTi0 | - | 6E+0 | 2E-9 | 8E-12 | - | - |
22 | Titanium-45 | D, see 44Ti | 9E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 44Ti | - | 4E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 44Ti | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
23 | Vanadium-472 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 3E+4 | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, and halides | - | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
23 | Vanadium-48 | D, see 47V | 6E+2 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, see 47V | - | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
23 | Vanadium-49 | D, see 47V | 7E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (9E+4) | Bone surf (3E+4) | - | 5E-8 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 47V | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
24 | Chromium-48 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 6E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
| | W, halides and nitrates | - | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
24 | Chromium-492 | D, see 48Cr | 3E+4 | 8E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 48Cr | - | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 48Cr | - | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
24 | Chromium-51 | D, see 48Cr | 4E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 48Cr | - | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 48Cr | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
25 | Manganese-512 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 2E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, halides, and nitrates | - | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
25 | Manganese-52m2 | D, see 51Mn | 3E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 51Mn | - | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
25 | Manganese-52 | D, see 51Mn | 7E+2 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 51Mn | - | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
25 | Manganese-53 | D, see 51Mn | 5E+4 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | - | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E+4) | - | 3E-8 | - | - |
| | W, see 51Mn | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
25 | Manganese-54 | D, see 51Mn | 2E+3 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 51Mn | - | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
25 | Manganese-56 | D, see 51Mn | 5E+3 | 2E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 51Mn | - | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
26 | Iron-52 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 9E+2 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, and halides | - | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
26 | Iron-55 | D, see 52Fe | 9E+3 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 52Fe | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
26 | Iron-59 | D, see 52Fe | 8E+2 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 5E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 52Fe | - | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 7E-10 | - | - |
26 | Iron-60 | D, see 52Fe | 3E+1 | 6E+0 | 3E-9 | 9E-12 | 4E-7 | 4E-6 |
| | W, see 52Fe | - | 2E+1 | 8E-9 | 3E-11 | - | - |
27 | Cobalt-55 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, oxides, hydroxides, halides, and nitrates | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
27 | Cobalt-56 | W, see 55Co | 5E+2 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
| | Y, see 55Co | 4E+2 | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | 3E-10 | - | - |
27 | Cobalt-57 | W, see 55Co | 8E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | Y, see 55Co | 4E+3 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
27 | Cobalt-58m | W, see 55Co | 6E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
| | Y, see 55Co | - | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
27 | Cobalt-58 | W, see 55Co | 2E+3 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 55Co | 1E+3 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
27 | Cobalt-60m2 | W, see 55Co | 1E+6 | 4E+6 | 2E-3 | 6E-6 | - | - |
| | | St wall (1E+6) | - | - | - | 2E-2 | 2E-1 |
| | Y, see 55Co | - | 3E+6 | 1E-3 | 4E-6 | - | - |
27 | Cobalt-60 | W, see 55Co | 5E+2 | 2E+2 | 7E-8 | 2E-10 | 3E-6 | 3E-5 |
| | Y, see 55Co | 2E+2 | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | 5E-11 | - | - |
27 | Cobalt-612 | W, see 55Co | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | Y, see 55Co | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
27 | Cobalt-62m2 | W, see 55Co | 4E+4 | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (5E+4) | - | - | - | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | Y, see 55Co | - | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
28 | Nickel-56 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, and carbides | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | Vapor | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
28 | Nickel-57 | D, see 56Ni | 2E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 56Ni | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | Vapor | - | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
28 | Nickel-59 | D, see 56Ni | 2E+4 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 56Ni | - | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | Vapor | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
28 | Nickel-63 | D, see 56Ni | 9E+3 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 56Ni | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | Vapor | - | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
28 | Nickel-65 | D, see 56Ni | 8E+3 | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 56Ni | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
| | Vapor | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
28 | Nickel-66 | D, see 56Ni | 4E+2 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+2) | - | - | - | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
| | W, see 56Ni | - | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
| | Vapor | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
29 | Copper-602 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 3E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, sulfides, halides, and nitrates | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
29 | Copper-61 | D, see 60Cu | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 60Cu | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 60Cu | - | 4E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
29 | Copper-64 | D, see 60Cu | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 60Cu | - | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 60Cu | - | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
29 | Copper-67 | D, see 60Cu | 5E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | W, see 60Cu | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 60Cu | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
30 | Zinc-62 | Y, all compounds | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
30 | Zinc-632 | Y, all compounds | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
30 | Zinc-65 | Y, all compounds | 4E+2 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | 5E-6 | 5E-5 |
30 | Zinc-69m | Y, all compounds | 4E+3 | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
30 | Zinc-692 | Y, all compounds | 6E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
30 | Zinc-71m | Y, all compounds | 6E+3 | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
30 | Zinc-72 | Y, all compounds | 1E+3 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
31 | Gallium-652 | D, all compounds ((excep [except]))except those given for W | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, halides, and nitrates | - | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
31 | Gallium-66 | D, see 65Ga | 1E+3 | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 65Ga | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
31 | Gallium-67 | D, see 65Ga | 7E+3 | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 65Ga | - | 1E+4 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
31 | Gallium-682 | D, see 65Ga | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 65Ga | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
31 | Gallium-702 | D, see 65Ga | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (7E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 65Ga | - | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
31 | Gallium-72 | D, see 65Ga | 1E+3 | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 65Ga | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
31 | Gallium-73 | D, see 65Ga | 5E+3 | 2E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 65Ga | - | 2E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
32 | Germanium-66 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 2E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, oxides, sulfides, and halides | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
32 | Germanium-672 | D, see 66Ge | 3E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | W, see 66Ge | - | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
32 | Germanium-68 | D, see 66Ge | 5E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | W, see 66Ge | - | 1E+2 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
32 | Germanium-69 | D, see 66Ge | 1E+4 | 2E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 66Ge | - | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
32 | Germanium-71 | D, see 66Ge | 5E+5 | 4E+5 | 2E-4 | 6E-7 | 7E-3 | 7E-2 |
| | W, see 66Ge | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
32 | Germanium-752 | D, see 66Ge | 4E+4 | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (7E+4) | - | - | - | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
| | W, see 66Ge | - | 8E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
32 | Germanium-77 | D, see 66Ge | 9E+3 | 1E+4 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 66Ge | - | 6E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | - | - |
32 | Germanium-782 | D, see 66Ge | 2E+4 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (2E+4) | - | - | - | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 66Ge | - | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
33 | Arsenic-692 | W, all compounds | 3E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
33 | Arsenic-702 | W, all compounds | 1E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
33 | Arsenic-71 | W, all compounds | 4E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
33 | Arsenic-72 | W, all compounds | 9E+2 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
33 | Arsenic-73 | W, all compounds | 8E+3 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
33 | Arsenic-74 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
33 | Arsenic-76 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
33 | Arsenic-77 | W, all compounds | 4E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+3) | - | - | - | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
33 | Arsenic-782 | W, all compounds | 8E+3 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
34 | Selenium-702 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, and elemental Se | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
34 | Selenium-73m2 | D, see 70Se | 6E+4 | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 70Se | 3E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
34 | Selenium-73 | D, see 70Se | 3E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 70Se | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
34 | Selenium-75 | D, see 70Se | 5E+2 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
| | W, see 70Se | - | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
34 | Selenium-79 | D, see 70Se | 6E+2 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
| | W, see 70Se | - | 6E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
34 | Selenium-81m2 | D, see 70Se | 4E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 70Se | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
34 | Selenium-812 | D, see 70Se | 6E+4 | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (8E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 70Se | - | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | - | - |
34 | Selenium-832 | D, see 70Se | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 70Se | 3E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-74m2 | D, bromides of H, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (2E+4) | - | - | - | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, bromides of lantha-nides, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Ge, Sn, Pb, As, Sb, Bi, Fe, Ru, Os, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Mn, Tc, and Re | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-742 | D, see 74mBr | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 5E-45E-3 | - |
| | W, see 74mBr | - | 8E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-752 | D, see 74mBr | 3E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 74mBr | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-76 | D, see 74mBr | 4E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | W, see 74mBr | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-77 | D, see 74mBr | 2E+4 | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 74mBr | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-80m | D, see 74mBr | 2E+4 | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 74mBr | - | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-802 | D, see 74mBr | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (9E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 74mBr | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-82 | D, see 74mBr | 3E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 74mBr | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-83 | D, see 74mBr | 5E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (7E+4) | - | - | - | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
| | W, see 74mBr | - | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
35 | Bromine-842 | D, see 74mBr | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 74mBr | - | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-742 | Submersion1 | - | - | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-76 | Submersion1 | - | - | 9E-6 | 4E-8 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-772 | Submersion1 | - | - | 4E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-79 | Submersion1 | - | - | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-81 | Submersion1 | - | - | 7E-4 | 3E-6 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-83m2 | Submersion1 | - | - | 1E-2 | 5E-5 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-85m | Submersion1 | - | - | 2E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-85 | Submersion1 | - | - | 1E-4 | 7E-7 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-872 | Submersion1 | - | - | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
36 | Krypton-88 | Submersion1 | - | - | 2E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
37 | Rubidium-792 | D, all compounds | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
37 | Rubidium-81m2 | D, all compounds | 2E+5 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 5E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+5) | - | - | - | 4E-3 | 4E-2 |
37 | Rubidium-81 | D, all compounds | 4E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
37 | Rubidium-82m | D, all compounds | 1E+4 | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
37 | Rubidium-83 | D, all compounds | 6E+2 | 1E+3 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
37 | Rubidium-84 | D, all compounds | 5E+2 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
37 | Rubidium-86 | D, all compounds | 5E+2 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
37 | Rubidium-87 | D, all compounds | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
37 | Rubidium-882 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
37 | Rubidium-892 | D, all compounds | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
38 | Strontium-802 | D, all soluble compound except SrTiO | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | Y, all insoluble compounds and SrTi0 | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-812 | D, see 80Sr | 3E+4 | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | 2E+4 | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-82 | D, see 80Sr | 3E+2 | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+2) | - | - | - | 3E-6 | 3E-5 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | 2E+2 | 9E+1 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-83 | D, see 80Sr | 3E+3 | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | 2E+3 | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-85m2 | D, see 80Sr | 2E+5 | 6E+5 | 3E-4 | 9E-7 | 3E-3 | 3E-2 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | - | 8E+5 | 4E-4 | 1E-6 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-85 | D, see 80Sr | 3E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | - | 2E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-87m | D, see 80Sr | 5E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | 4E+4 | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-89 | D, see 80Sr | 6E+2 | 8E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (6E+2) | - | - | - | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | 5E+2 | 1E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-90 | D, see 80Sr | 3E+1 | 2E+1 | 8E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E+1) | Bone surf (2E+1) | - | 3E-11 | 5E-7 | 5E-6 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | - | 4E+0 | 2E-9 | 6E-12 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-91 | D, see 80Sr | 2E+3 | 6E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | - | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
38 | Strontium-92 | D, see 80Sr | 3E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | Y, see 80Sr | - | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-86m2 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-86 | W, see 86mY | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-87 | W, see 86mY | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-88 | W, see 86mY | 1E+3 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 3E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | 3E-10 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-90m | W, see 86mY | 8E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-90 | W, see 86mY | 4E+2 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+2) | - | - | - | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-91m2 | W, see 86mY | 1E+5 | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-91 | W, see 86mY | 5E+2 | 2E+2 | 7E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (6E+2) | - | - | - | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-92 | W, see 86mY | 3E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-93 | W, see 86mY | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-942 | W, see 86mY | 2E+4 | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
39 | Yttrium-952 | W, see 86mY | 4E+4 | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (5E+4) | - | - | - | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | Y, see 86mY | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
40 | Zirconium-86 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 1E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, halides, and nitrates | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, carbide | - | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
40 | Zirconium-88 | D, see 86Zr | 4E+3 | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | 3E-10 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | W, see 86Zr | - | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 7E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 86Zr | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
40 | Zirconium-89 | D, see 86Zr | 2E+3 | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 86Zr | - | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 86Zr | - | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
40 | Zirconium-93 | D, see 86Zr | 1E+3 | 6E+0 | 3E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (3E+3) | Bone surf (2E+1) | - | 2E-11 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 86Zr | - | 2E+1 | 1E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (6E+1) | - | 9E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, see 86Zr | - | 6E+1 | 2E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (7E+1) | - | 9E-11 | - | - |
40 | Zirconium-95 | D, see 86Zr | 1E+3 | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (3E+2) | - | 4E-10 | - | - |
| | W, see 86Zr | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 5E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 86Zr | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
40 | Zirconium-97 | D, see 86Zr | 6E+2 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, see 86Zr | - | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 86Zr | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-882 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (7E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-892 (66 min) | W, see 88Nb | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-89 (122 min) | W, see 88Nb | 5E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 2E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-90 | W, see 88Nb | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-93m | W, see 88Nb | 9E+3 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+4) | - | - | - | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 2E+2 | 7E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-94 | W, see 88Nb | 9E+2 | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | 3E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 2E+1 | 6E-9 | 2E-11 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-95m | W, see 88Nb | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-95 | W, see 88Nb | 2E+3 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-96 | W, see 88Nb | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-972 | W, see 88Nb | 2E+4 | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
41 | Niobium-982 | W, see 88Nb | 1E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | Y, see 88Nb | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
42 | Molybdenum-90 | D, all compounds except those given for Y | 4E+3 | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, oxides, hydroxides, and MoS | 2E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
42 | Molybdenum-93m | D, see 90Mo | 9E+3 | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | Y, see 90Mo | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
42 | Molybdenum-93 | D, see 90Mo | 4E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | Y, see 90Mo | 2E+4 | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
42 | Molybdenum-99 | D, see 90Mo | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 90Mo | 1E+3 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
42 | Molybdenum-1012 | D, see 90Mo | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (5E+4) | - | - | - | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | Y, see 90Mo | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-93m2 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 7E+4 | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, halides, and nitrates | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-93 | D, see 93mTc | 3E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-94m2 | D, see 93mTc | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-94 | D, see 93mTc | 9E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-95m | D, see 93mTc | 4E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-95 | D, see 93mTc | 1E+4 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-96m2 | D, see 93mTc | 2E+5 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-96 | D, see 93mTc | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-97m | D, see 93mTc | 5E+3 | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | - | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | | - | St wall (7E+3) | - | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-97 | D, see 93mTc | 4E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 6E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-98 | D, see 93mTc | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-99m | D, see 93mTc | 8E+4 | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-99 | D, see 93mTc | 4E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | - | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | | - | St wall (6E+3) | - | 8E-9 | - | - |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-1012 | D, see 93mTc | 9E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 5E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (1E+5) | - | - | - | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 4E+5 | 2E-4 | 5E-7 | - | - |
43 | Technetium-1042 | D, see 93mTc | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 93mTc | - | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
44 | Ruthenium-942 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, halides | - | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
44 | Ruthenium-97 | D, see 94Ru | 8E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 94Ru | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 94Ru | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
44 | Ruthenium-103 | D, see 94Ru | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 94Ru | - | 1E+3 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 94Ru | - | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
44 | Ruthenium-105 | D, see 94Ru | 5E+3 | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 94Ru | - | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 94Ru | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
44 | Ruthenium-106 | D, see 94Ru | 2E+2 | 9E+1 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+2) | - | - | - | 3E-6 | 3E-5 |
| | W, see 94Ru | - | 5E+1 | 2E-8 | 8E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, see 94Ru | - | 1E+1 | 5E-9 | 2E-11 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-99m | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, halides | - | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-99 | D, see 99mRh | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-100 | D, see 99mRh | 2E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-101m | D, see 99mRh | 6E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 8E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-101 | D, see 99mRh | 2E+3 | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 7E-10 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 2E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-102m | D, see 99mRh | 1E+3 | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 7E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 5E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-102 | D, see 99mRh | 6E+2 | 9E+1 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 2E+2 | 7E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 6E+1 | 2E-8 | 8E-11 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-103m2 | D, see 99mRh | 4E+5 | 1E+6 | 5E-4 | 2E-6 | 6E-3 | 6E-2 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 1E+6 | 5E-4 | 2E-6 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 1E+6 | 5E-4 | 2E-6 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-105 | D, see 99mRh | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (4E+3) | - | - | - | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 6E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-106m | D, see 99mRh | 8E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 4E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
45 | Rhodium-1072 | D, see 99mRh | 7E+4 | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (9E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 99mRh | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 99mRh | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | - | - |
46 | Palladium-100 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 1E+3 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, nitrates | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
46 | Palladium-101 | D, see 100Pd | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 100Pd | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 100Pd | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
46 | Palladium-103 | D, see 100Pd | 6E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (7E+3) | - | - | - | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 100Pd | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 100Pd | - | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
46 | Palladium-107 | D, see 100Pd | 3E+4 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (4E+4) | Kidneys (2E+4) | - | 3E-8 | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 100Pd | - | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 100Pd | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | - | - |
46 | Palladium-109 | D, see 100Pd | 2E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 100Pd | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 100Pd | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
47 | Silver-1022 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
| | W, nitrates and sulfides | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
47 | Silver-1032 | D, see 102Ag | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
47 | Silver-104m2 | D, see 102Ag | 3E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
47 | Silver-1042 | D, see 102Ag | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
47 | Silver-105 | D, see 102Ag | 3E+3 | 1E+3 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
47 | Silver-106m | D, see 102Ag | 8E+2 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
47 | Silver-1062 | D, see 102Ag | 6E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St. wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
47 | Silver-108m | D, see 102Ag | 6E+2 | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | 3E-10 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 2E+1 | 1E-8 | 3E-11 | - | - |
47 | Silver-110m | D, see 102Ag | 5E+2 | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | 3E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 9E+1 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
47 | Silver-111 | D, see 102Ag | 9E+2 | 2E+3 | 6E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | Liver (2E+3) | - | 2E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
47 | Silver-112 | D, see 102Ag | 3E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 1E+4 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
47 | Silver-1152 | D, see 102Ag | 3E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 102Ag | - | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 102Ag | - | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
48 | Cadmium-1042 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, sulfides, halides, and nitrates | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
48 | Cadmium-107 | D, see 104Cd | 2E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 104Cd | - | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 104Cd | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
48 | Cadmium-109 | D, see 104Cd | 3E+2 | 4E+1 | 1E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | Kidneys (4E+2) | Kidneys (5E+1) | - | 7E-11 | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
| | W, see 104Cd | - | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Kidneys (1E+2) | - | 2E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 104Cd | - | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
48 | Cadmium-113m | D, see 104Cd | 2E+1 | 2E+0 | 1E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | Kidneys (4E+1) | Kidneys (4E+0) | - | 5E-12 | 5E-7 | 5E-6 |
| | W, see 104Cd | - | 8E+0 | 4E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Kidneys (1E+1) | - | 2E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, see 104Cd | - | 1E+1 | 5E-9 | 2E-11 | - | - |
48 | Cadmium-113 | D, see 104Cd | 2E+1 | 2E+0 | 9E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Kidneys (3E+1) | Kidneys (3E+0) | - | 5E-12 | 4E-7 | 4E-6 |
| | W, see 104Cd | - | 8E+0 | 3E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Kidneys (1E+1) | - | 2E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, see 104Cd | - | 1E+1 | 6E-9 | 2E-11 | - | - |
48 | Cadmium-115m | D, see 104Cd | 3E+2 | 5E+1 | 2E-8 | - | 4E-6 | 4E-5 |
| | | - | Kidneys (8E+1) | - | 1E-10 | - | - |
| | W, see 104Cd | - | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 104Cd | - | 1E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
48 | Cadmium-115 | D, see 104Cd | 9E+2 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 104Cd | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 104Cd | - | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
48 | Cadmium-117m | D, see 104Cd | 5E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | W, see 104Cd | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 104Cd | - | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
48 | Cadmium-117 | D, see 104Cd | 5E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | W, see 104Cd | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 104Cd | - | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
49 | Indium-109 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, halides, and nitrates | - | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
49 | Indium-1102 | D, see 109In | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| (69.1 min) | W, see 109In | - | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
49 | Indium-110 | D, see 109In | 5E+3 | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| (4.9 h) | W, see 109In | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
49 | Indium-111 | D, see 109In | 4E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
49 | Indium-1122 | D, see 109In | 2E+5 | 6E+5 | 3E-4 | 9E-7 | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 7E+5 | 3E-4 | 1E-6 | - | - |
49 | Indium-113m2 | D, see 109In | 5E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
49 | Indium-114m | D, see 109In | 3E+2 | 6E+1 | 3E-8 | 9E-11 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (4E+2) | - | - | - | 5E-6 | 5E-5 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 1E+2 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
49 | Indium-115m | D, see 109In | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
49 | Indium-115 | D, see 109In | 4E+1 | 1E+0 | 6E-10 | 2E-12 | 5E-7 | 5E-6 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 5E+0 | 2E-9 | 8E-12 | - | - |
49 | Indium-116m2 | D, see 109In | 2E+4 | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
49 | Indium-117m2 | D, see 109In | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
49 | Indium-1172 | D, see 109In | 6E+4 | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
49 | Indium-119m2 | D, see 109In | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (5E+4) | - | - | - | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | W, see 109In | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
50 | Tin-110 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | W, sulfides, oxides, hydroxides, halides, nitrates, and stannic phosphate | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
50 | Tin-1112 | D, see 110Sn | 7E+4 | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
50 | Tin-113 | D, see 110Sn | 2E+3 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
50 | Tin-117m | D, see 110Sn | 2E+3 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | Bone surf (2E+3) | - | 3E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
50 | Tin-119m | D, see 110Sn | 3E+3 | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (4E+3) | - | - | - | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 1E+3 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
50 | Tin-121m | D, see 110Sn | 3E+3 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (4E+3) | - | - | - | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
50 | Tin-121 | D, see 110Sn | 6E+3 | 2E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (6E+3) | - | - | - | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
50 | Tin-123m2 | D, see 110Sn | 5E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
50 | Tin-123 | D, see 110Sn | 5E+2 | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (6E+2) | - | - | - | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 2E+2 | 7E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
50 | Tin-125 | D, see 110Sn | 4E+2 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+2) | - | - | - | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 4E+2 | 1E-7 | 5E-10 | - | - |
50 | Tin-126 | D, see 110Sn | 3E+2 | 6E+1 | 2E-8 | 8E-11 | 4E-6 | 4E-5 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 7E+1 | 3E-8 | 9E-11 | - | - |
50 | Tin-127 | D, see 110Sn | 7E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 9E-5 | 9E-4 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
50 | Tin-1282 | D, see 110Sn | 9E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 110Sn | - | 4E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-1152 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 8E+4 | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, halides, sulfides, sulfates, and nitrates | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-116m2 | D, see 115Sb | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-1162 | D, see 115Sb | 7E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (9E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 5E-7 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-117 | D, see 115Sb | 7E+4 | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-118m | D, see 115Sb | 6E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 115Sb | 5E+3 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-119 | D, see 115Sb | 2E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 115Sb | 2E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-1202 | D, see 115Sb | 1E+5 | 4E+5 | 2E-4 | 6E-7 | - | - |
| (16 min) | | St wall (2E+5) | - | - | - | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 5E+5 | 2E-4 | 7E-7 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-120 (5.76 d) | D, see 115Sb | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 115Sb | 9E+2 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-122 | D, see 115Sb | 8E+2 | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (8E+2) | - | - | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 115Sb | 7E+2 | 1E+3 | 4E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-124m2 | D, see 115Sb | 3E+5 | 8E+5 | 4E-4 | 1E-6 | 3E-3 | 3E-2 |
| | W, see 115Sb | 2E+5 | 6E+5 | 2E-4 | 8E-7 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-124 | D, see 115Sb | 6E+2 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
| | W, see 115Sb | 5E+2 | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | 3E-10 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-125 | D, see 115Sb | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 7E-10 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-126m2 | D, see 115Sb | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (7E+4) | - | - | - | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-126 | D, see 115Sb | 6E+2 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
| | W, see 115Sb | 5E+2 | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 7E-10 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-127 | D, see 115Sb | 8E+2 | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (8E+2) | - | - | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 115Sb | 7E+2 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-1282 | D, see 115Sb | 8E+4 | 4E+5 | 2E-4 | 5E-7 | - | - |
| (10.4 min) | | St wall (1E+5) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 4E+5 | 2E-4 | 6E-7 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-128 | D, see 115Sb | 1E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| (9.01 h) | W, see 115Sb | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-129 | D, see 115Sb | 3E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-1302 | D, see 115Sb | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
51 | Antimony-1312 | D, see 115Sb | 1E+4 | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (2E+4) | Thyroid (4E+4) | - | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 115Sb | - | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | | - | - |
| | | - | Thyroid (4E+4) | - | 6E-8 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-116 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 8E+3 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, and nitrates | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-121m | D, see 116Te | 5E+2 | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (7E+2) | Bone surf (4E+2) | - | 5E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-121 | D, see 116Te | 3E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-123m | D, see 116Te | 6E+2 | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+3) | Bone surf (5E+2) | - | 8E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-123 | D, see 116Te | 5E+2 | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+3) | Bone surf (5E+2) | - | 7E-10 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E+3) | - | 2E-9 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-125m | D, see 116Te | 1E+3 | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+3) | Bone surf (1E+3) | - | 1E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-127m | D, see 116Te | 6E+2 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | - | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | | - | Bone surf (4E+2) | - | 6E-10 | - | - |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-127 | D, see 116Te | 7E+3 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-129m | D, see 116Te | 5E+2 | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | 3E-10 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-1292 | D, see 116Te | 3E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-131m | D, see 116Te | 3E+2 | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (6E+2) | Thyroid (1E+3) | - | 2E-9 | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Thyroid (9E+2) | - | 1E-9 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-1312 | D, see 116Te | 3E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (6E+3) | Thyroid (1E+4) | - | 2E-8 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Thyroid (1E+4) | - | 2E-8 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-132 | D, see 116Te | 2E+2 | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (7E+2) | Thyroid (8E+2) | - | 1E-9 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Thyroid (6E+2) | - | 9E-10 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-133m2 | D, see 116Te | 3E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (6E+3) | Thyroid (1E+4) | - | 2E-8 | 9E-5 | 9E-4 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Thyroid (1E+4) | - | 2E-8 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-1332 | D, see 116Te | 1E+4 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (3E+4) | Thyroid (6E+4) | - | 8E-8 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Thyroid (6E+4) | - | 8E-8 | - | - |
52 | Tellurium-1342 | D, see 116Te | 2E+4 | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (2E+4) | Thyroid (5E+4) | - | 7E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 116Te | - | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | - | - | - |
| | | | Thyroid | | | | |
| | | - | (5E+4) | - | 7E-8 | - | - |
53 | Iodine-120m2 | D, all compounds | 1E+4 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (1E+4) | - | - | - | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
53 | Iodine-1202 | D, all compounds | 4E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (8E+3) | Thyroid (1E+4) | - | 2E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
53 | Iodine-121 | D, all compounds | 1E+4 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (3E+4) | Thyroid (5E+4) | - | 7E-8 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
53 | Iodine-123 | D, all compounds | 3E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (1E+4) | Thyroid (2E+4) | - | 2E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
53 | Iodine-124 | D, all compounds | 5E+1 | 8E+1 | 3E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (2E+2) | Thyroid (3E+2) | - | 4E-10 | 2E-6 | 2E-5 |
53 | Iodine-125 | D, all compounds | 4E+1 | 6E+1 | 3E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (1E+2) | Thyroid (2E+2) | - | 3E-10 | 2E-6 | 2E-5 |
53 | Iodine-126 | D, all compounds | 2E+1 | 4E+1 | 1E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (7E+1) | Thyroid (1E+2) | - | 2E-10 | 1E-6 | 1E-5 |
53 | Iodine-1282 | D, all compounds | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
53 | Iodine-129 | D, all compounds | 5E+0 | 9E+0 | 4E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (2E+1) | Thyroid (3E+1) | - | 4E-11 | 2E-7 | 2E-6 |
53 | Iodine-130 | D, all compounds | 4E+2 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (1E+3) | Thyroid (2E+3) | - | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
53 | Iodine-131 | D, all compounds | 3E+1 | 5E+1 | 2E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (9E+1) | Thyroid (2E+2) | - | 2E-10 | 1E-6 | 1E-5 |
53 | Iodine-132m2 | D, all compounds | 4E+3 | 8E+3 | 4E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (1E+4) | Thyroid (2E+4) | - | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
53 | Iodine-132 | D, all compounds | 4E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (9E+3) | Thyroid (1E+4) | - | 2E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
53 | Iodine-133 | D, all compounds | 1E+2 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (5E+2) | Thyroid (9E+2) | - | 1E-9 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
53 | Iodine-1342 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
53 | Iodine-135 | D, all compounds | 8E+2 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | Thyroid (3E+3) | Thyroid (4E+3) | - | 6E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
54 | Xenon-1202 | Submersion1 | - | - | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-1212 | Submersion1 | - | - | 2E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-122 | Submersion1 | - | - | 7E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-123 | Submersion1 | - | - | 6E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-125 | Submersion1 | - | - | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-127 | Submersion1 | - | - | 1E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-129m | Submersion1 | - | - | 2E-4 | 9E-7 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-131m | Submersion1 | - | - | 4E-4 | 2E-6 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-133m | Submersion1 | - | - | 1E-4 | 6E-7 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-133 | Submersion1 | - | - | 1E-4 | 5E-7 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-135m2 | Submersion1 | - | - | 9E-6 | 4E-8 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-135 | Submersion1 | - | - | 1E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
54 | Xenon-1382 | Submersion1 | - | - | 4E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
55 | Cesium-1252 | D, all compounds | 5E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (9E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
55 | Cesium-127 | D, all compounds | 6E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
55 | Cesium-129 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
55 | Cesium-1302 | D, all compounds | 6E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (1E+5) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
55 | Cesium-131 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
55 | Cesium-132 | D, all compounds | 3E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
55 | Cesium-134m | D, all compounds | 1E+5 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (1E+5) | - | - | - | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
55 | Cesium-134 | D, all compounds | 7E+1 | 1E+2 | 4E-8 | 2E-10 | 9E-7 | 9E-6 |
55 | Cesium-135m2 | D, all compounds | 1E+5 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
55 | Cesium-135 | D, all compounds | 7E+2 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
55 | Cesium-136 | D, all compounds | 4E+2 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
55 | Cesium-137 | D, all compounds | 1E+2 | 2E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | 1E-6 | 1E-5 |
55 | Cesium-1382 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
56 | Barium-1262 | D, all compounds | 6E+3 | 2E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
56 | Barium-128 | D, all compounds | 5E+2 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
56 | Barium-131m2 | D, all compounds | 4E+5 | 1E+6 | 6E-4 | 2E-6 | - | - |
| | | St wall (5E+5) | - | - | - | 7E-3 | 7E-2 |
56 | Barium-131 | D, all compounds | 3E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
56 | Barium-133m | D, all compounds | 2E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+3) | - | - | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
56 | Barium-133 | D, all compounds | 2E+3 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
56 | Barium-135m | D, all compounds | 3E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
56 | Barium-1392 | D, all compounds | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
56 | Barium-140 | D, all compounds | 5E+2 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (6E+2) | - | - | - | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
56 | Barium-1412 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
56 | Barium-1422 | D, all compounds | 5E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
57 | Lanthanum-1312 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 5E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | W, oxides and hydroxides | - | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
57 | Lanthanum-132 | D, see 131La | 3E+3 | 1E+4 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 131La | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
57 | Lanthanum-135 | D, see 131La | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 131La | - | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
57 | Lanthanum-137 | D, see 131La | 1E+4 | 6E+1 | 3E-8 | - | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | | - | Liver (7E+1) | - | 1E-10 | - | - |
| | W, see 131La | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Liver (3E+2) | - | 4E-10 | - | - |
57 | Lanthanum-138 | D, see 131La | 9E+2 | 4E+0 | 1E-9 | 5E-12 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 131La | - | 1E+1 | 6E-9 | 2E-11 | - | - |
57 | Lanthanum-140 | D, see 131La | 6E+2 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, see 131La | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
57 | Lanthanum-141 | D, see 131La | 4E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | W, see 131La | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
57 | Lanthanum-1422 | D, see 131La | 8E+3 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 131La | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
57 | Lanthanum-1432 | D, see 131La | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 131La | - | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
58 | Cerium-134 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 5E+2 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (6E+2) | - | - | - | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
| | Y, oxides, hydroxides, and fluorides | - | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
58 | Cerium-135 | W, see 134Ce | 2E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 134Ce | - | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
58 | Cerium-137m | W, see 134Ce | 2E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 134Ce | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
58 | Cerium-137 | W, see 134Ce | 5E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | Y, see 134Ce | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
58 | Cerium-139 | W, see 134Ce | 5E+3 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | Y, see 134Ce | - | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
58 | Cerium-141 | W, see 134Ce | 2E+3 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 134Ce | - | 6E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
58 | Cerium-143 | W, see 134Ce | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 134Ce | - | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
58 | Cerium-144 | W, see 134Ce | 2E+2 | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | 4E-11 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+2) | - | - | - | 3E-6 | 3E-5 |
| | Y, see 134Ce | - | 1E+1 | 6E-9 | 2E-11 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-1362 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall | | | | | |
| | | (7E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | Y, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, and fluorides | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-1372 | W, see 136Pr | 4E+4 | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | Y, see 136Pr | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-138m | W, see 136Pr | 1E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | Y, see 136Pr | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-139 | W, see 136Pr | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | Y, see 136Pr | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-142m2 | W, see 136Pr | 8E+4 | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | Y, see 136Pr | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-142 | W, see 136Pr | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | Y, see 136Pr | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-143 | W, see 136Pr | 9E+2 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 136Pr | - | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-1442 | W, see 136Pr | 3E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | Y, see 136Pr | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-145 | W, see 136Pr | 3E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | Y, see 136Pr | - | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
59 | Praseodymium-1472 | W, see 136Pr | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (8E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | Y, see 136Pr | - | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
60 | Neodymium-1362 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 1E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | Y, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, and fluorides | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
60 | Neodymium-138 | W, see 136Nd | 2E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 136Nd | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | - | - |
60 | Neodymium-139m | W, see 136Nd | 5E+3 | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | Y, see 136Nd | - | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
60 | Neodymium-1392 | W, see 136Nd | 9E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 5E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | Y, see 136Nd | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
60 | Neodymium-141 | W, see 136Nd | 2E+5 | 7E+5 | 3E-4 | 1E-6 | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
| | Y, see 136Nd | - | 6E+5 | 3E-4 | 9E-7 | - | - |
60 | Neodymium-147 | W, see 136Nd | 1E+3 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 136Nd | - | 8E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
60 | Neodymium-1492 | W, see 136Nd | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | Y, see 136Nd | - | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | - | - |
60 | Neodymium-1512 | W, see 136Nd | 7E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
| | Y, see 136Nd | - | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-1412 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
| | Y, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, and fluorides | - | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-143 | W, see 141Pm | 5E+3 | 6E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-144 | W, see 141Pm | 1E+3 | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-145 | W, see 141Pm | 1E+4 | 2E+2 | 7E-8 | - | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E+2) | - | 3E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | 3E-10 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-146 | W, see 141Pm | 2E+3 | 5E+1 | 2E-8 | 7E-11 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 4E+1 | 2E-8 | 6E-11 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-147 | W, see 141Pm | 4E+3 | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+3) | Bone surf (2E+2) | - | 3E-10 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 1E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-148m | W, see 141Pm | 7E+2 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 5E-10 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-148 | W, see 141Pm | 4E+2 | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+2) | - | - | - | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 7E-10 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-149 | W, see 141Pm | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-150 | W, see 141Pm | 5E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
61 | Promethium-151 | W, see 141Pm | 2E+3 | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 141Pm | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
62 | Samarium-141m2 | W, all compounds | 3E+4 | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
62 | Samarium-1412 | W, all compounds | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
62 | Samarium-1422 | W, all compounds | 8E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
62 | Samarium-145 | W, all compounds | 6E+3 | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 7E-10 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
62 | Samarium-146 | W, all compounds | 1E+1 | 4E-2 | 1E-11 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (3E+1) | Bone surf (6E-2) | - | 9E-14 | 3E-7 | 3E-6 |
62 | Samarium-147 | W, all compounds | 2E+1 | 4E-2 | 2E-11 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (3E+1) | Bone surf (7E-2) | - | 1E-13 | 4E-7 | 4E-6 |
62 | Samarium-151 | W, all compounds | 1E+4 | 1E+2 | 4E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+4) | Bone surf (2E+2) | - | 2E-10 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
62 | Samarium-153 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
62 | Samarium-1552 | W, all compounds | 6E+4 | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (8E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
62 | Samarium-156 | W, all compounds | 5E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
63 | Europium-145 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
63 | Europium-146 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
63 | Europium-147 | W, all compounds | 3E+3 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
63 | Europium-148 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 4E+2 | 1E-7 | 5E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
63 | Europium-149 | W, all compounds | 1E+4 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
63 | Europium-150 (12.62h) | W, all compounds | 3E+3 | 8E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
63 | Europium-150 (34.2 y) | W, all compounds | 8E+2 | 2E+1 | 8E-9 | 3E-11 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
63 | Europium-152m | W, all compounds | 3E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
63 | Europium-152 | W, all compounds | 8E+2 | 2E+1 | 1E-8 | 3E-11 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
63 | Europium-154 | W, all compounds | 5E+2 | 2E+1 | 8E-9 | 3E-11 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
63 | Europium-155 | W, all compounds | 4E+3 | 9E+1 | 4E-8 | - | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E+2) | - | 2E-10 | - | - |
63 | Europium-156 | W, all compounds | 6E+2 | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
63 | Europium-157 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
63 | Europium-1582 | W, all compounds | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
64 | Gadolinium-1452 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall | | | | | |
| | | (5E+4) | - | - | - | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, and fluorides | - | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
64 | Gadolinium-146 | D, see 145Gd | 1E+3 | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 145Gd | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
64 | Gadolinium-147 | D, see 145Gd | 2E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 145Gd | - | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
64 | Gadolinium-148 | D, see 145Gd | 1E+1 | 8E+3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | Bone surf (2E+2) | - | 2E-14 | 3E-7 | 3E-6 |
| | W, see 145Gd | - | 3E-2 | 1E-11 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (6E-2) | - | 8E-14 | - | - |
64 | Gadolinium-149 | D, see 145Gd | 3E+3 | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 145Gd | - | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
64 | Gadolinium-151 | D, see 145Gd | 6E+3 | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | - | 9E-5 | 9E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (6E+2) | - | 9E-10 | - | - |
| | W, see 145Gd | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
64 | Gadolinium-152 | D, see 145Gd | 2E+1 | 1E-2 | 4E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (3E+1) | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 3E-14 | 4E-7 | 4E-6 |
| | W, see 145Gd | - | 4E-2 | 2E-11 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (8E-2) | - | 1E-13 | - | - |
64 | Gadolinium-153 | D, see 145Gd | 5E+3 | 1E+2 | 6E-8 | - | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E+2) | - | 3E-10 | - | - |
| | W, see 145Gd | - | 6E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
64 | Gadolinium-159 | D, see 145Gd | 3E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 145Gd | - | 6E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | - | - |
65 | Terbium-1472 | W, all compounds | 9E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
65 | Terbium-149 | W, all compounds | 5E+3 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
65 | Terbium-150 | W, all compounds | 5E+3 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
65 | Terbium-151 | W, all compounds | 4E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
65 | Terbium-153 | W, all compounds | 5E+3 | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
65 | Terbium-154 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
65 | Terbium-155 | W, all compounds | 6E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
65 | Terbium-156m (5.0 h) | W, all compounds | 2E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
65 | Terbium-156m (24.4 h) | W, all compounds | 7E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
65 | Terbium-156 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
65 | Terbium-157 | W, all compounds | 5E+4 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+4) | Bone surf (6E+2) | - | 8E-10 | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
65 | Terbium-158 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 2E+1 | 8E-9 | 3E-11 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
65 | Terbium-160 | W, all compounds | 8E+2 | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | 3E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
65 | Terbium-161 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
66 | Dysprosium-155 | W, all compounds | 9E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
66 | Dysprosium-157 | W, all compounds | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
66 | Dysprosium-159 | W, all compounds | 1E+4 | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
66 | Dysprosium-165 | W, all compounds | 1E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
66 | Dysprosium-166 | W, all compounds | 6E+2 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (8E+2) | - | - | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
67 | Holmium-1552 | W, all compounds | 4E+4 | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
67 | Holmium-1572 | W, all compounds | 3E+5 | 1E+6 | 6E-4 | 2E-6 | 4E-3 | 4E-2 |
67 | Holmium-1592 | W, all compounds | 2E+5 | 1E+6 | 4E-4 | 1E-6 | 3E-3 | 3E-2 |
67 | Holmium-161 | W, all compounds | 1E+5 | 4E+5 | 2E-4 | 6E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
67 | Holmium-162m2 | W, all compounds | 5E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
67 | Holmium-1622 | W, all compounds | 5E+5 | 2E+6 | 1E-3 | 3E-6 | - | - |
| | | St wall (8E+5) | - | - | - | 1E-2 | 1E-1 |
67 | Holmium-164m2 | W, all compounds | 1E+5 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
67 | Holmium-1642 | W, all compounds | 2E+5 | 6E+5 | 3E-4 | 9E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (2E+5) | - | - | - | 3E-3 | 3E-2 |
67 | Holmium-166m | W, all compounds | 6E+2 | 7E+0 | 3E-9 | 9E-12 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
67 | Holmium-166 | W, all compounds | 9E+2 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (9E+2) | - | - | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
67 | Holmium-167 | W, all compounds | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
68 | Erbium-161 | W, all compounds | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
68 | Erbium-165 | W, all compounds | 6E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
68 | Erbium-169 | W, all compounds | 3E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (4E+3) | - | - | - | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
68 | Erbium-171 | W, all compounds | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
68 | Erbium-172 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
69 | Thulium-1622 | W, all compounds | 7E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (7E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
69 | Thulium-166 | W, all compounds | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
69 | Thulium-167 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
69 | Thulium-170 | W, all compounds | 8E+2 | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | 3E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
69 | Thulium-171 | W, all compounds | 1E+4 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+4) | Bone surf (6E+2) | - | 8E-10 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
69 | Thulium-172 | W, all compounds | 7E+2 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (8E+2) | - | - | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
69 | Thulium-173 | W, all compounds | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
69 | Thulium-1752 | W, all compounds | 7E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (9E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
70 | Ytterbium-1622 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 7E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | Y, oxides, hydroxides, and fluorides | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
70 | Ytterbium-166 | W, see 162Yb | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 162Yb | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
70 | Ytterbium-1672 | W, see 162Yb | 3E+5 | 8E+5 | 3E-4 | 1E-6 | 4E-3 | 4E-2 |
| | Y, see 162Yb | - | 7E+5 | 3E-4 | 1E-6 | - | - |
70 | Ytterbium-169 | W, see 162Yb | 2E+3 | 8E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 162Yb | - | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
70 | Ytterbium-175 | W, see 162Yb | 3E+3 | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+3) | - | - | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | Y, see 162Yb | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
70 | Ytterbium-1772 | W, see 162Yb | 2E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | Y, see 162Yb | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
70 | Ytterbium-1782 | W, see 162Yb | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | Y, see 162Yb | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-169 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 3E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, oxides, hydroxides, and fluorides | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-170 | W, see 169Lu | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-171 | W, see 169Lu | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-172 | W, see 169Lu | 1E+3 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-173 | W, see 169Lu | 5E+3 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | - | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (5E+2) | - | 6E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-174m | W, see 169Lu | 2E+3 | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+3) | Bone surf (3E+2) | - | 5E-10 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | 3E-10 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-174 | W, see 169Lu | 5E+3 | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | - | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E+2) | - | 3E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 2E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-176m | W, see 169Lu | 8E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-176 | W, see 169Lu | 7E+2 | 5E+0 | 2E-9 | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E+1) | - | 2E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 8E+0 | 3E-9 | 1E-11 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-177m | W, see 169Lu | 7E+2 | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E+2) | - | 2E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 8E+1 | 3E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-177 | W, see 169Lu | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+3) | - | - | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-178m2 | W, see 169Lu | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St. wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-1782 | W, see 169Lu | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
71 | Lutetium-179 | W, see 169Lu | 6E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 9E-5 | 9E-4 |
| | Y, see 169Lu | - | 2E+4 | 6E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-170 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 3E+3 | 6E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, carbides, and nitrates | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-172 | D, see 170Hf | 1E+3 | 9E+0 | 4E-9 | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E+1) | - | 3E-11 | - | - |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 4E+1 | 2E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (6E+1) | - | 8E-11 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-173 | D, see 170Hf | 5E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-175 | D, see 170Hf | 3E+3 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E+3) | - | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-177m2 | D, see 170Hf | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-178m | D, see 170Hf | 3E+2 | 1E+0 | 5E-10 | - | 3E-6 | 3E-5 |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E+0) | - | 3E-12 | - | - |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 5E+0 | 2E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (9E+0) | - | 1E-11 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-179m | D, see 170Hf | 1E+3 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (6E+2) | - | 8E-10 | - | - |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-180m | D, see 170Hf | 7E+3 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-181 | D, see 170Hf | 1E+3 | 2E+2 | 7E-8 | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (4E+2) | - | 6E-10 | - | - |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-182m2 | D, see 170Hf | 4E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-182 | D, see 170Hf | 2E+2 | 8E-1 | 3E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E+2) | Bone surf (2E+0) | - | 2E-12 | 5E-6 | 5E-5 |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 3E+0 | 1E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (7E+0) | - | 1E-11 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-1832 | D, see 170Hf | 2E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
72 | Hafnium-184 | D, see 170Hf | 2E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 170Hf | - | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-1722 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | Y, elemental Ta, oxides, hydroxides, halides, carbides, nitrates, and nitrides | - | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-173 | W, see 172Ta | 7E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 9E-5 | 9E-4 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-1742 | W, see 172Ta | 3E+4 | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-175 | W, see 172Ta | 6E+3 | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-176 | W, see 172Ta | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-177 | W, see 172Ta | 1E+4 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-178 | W, see 172Ta | 2E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-179 | W, see 172Ta | 2E+4 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-180m | W, see 172Ta | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-180 | W, see 172Ta | 1E+3 | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 2E+1 | 1E-8 | 3E-11 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-182m2 | W, see 172Ta | 2E+5 | 5E+5 | 2E-4 | 8E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (2E+5) | - | - | - | 3E-3 | 3E-2 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 4E+5 | 2E-4 | 6E-7 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-182 | W, see 172Ta | 8E+2 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 5E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 1E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-183 | W, see 172Ta | 9E+2 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 1E+3 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-184 | W, see 172Ta | 2E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-1852 | W, see 172Ta | 3E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | - | - |
73 | Tantalum-1862 | W, see 172Ta | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (7E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | Y, see 172Ta | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
74 | Tungsten-176 | D, all compounds | 1E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
74 | Tungsten-177 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
74 | Tungsten-178 | D, all compounds | 5E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
74 | Tungsten-1792 | D, all compounds | 5E+5 | 2E+6 | 7E-4 | 2E-6 | 7E-3 | 7E-2 |
74 | Tungsten-181 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
74 | Tungsten-185 | D, all compounds | 2E+3 | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+3) | - | - | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
74 | Tungsten-187 | D, all compounds | 2E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
74 | Tungsten-188 | D, all compounds | 4E+2 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+2) | - | - | - | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
75 | Rhenium-1772 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 9E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (1E+5) | - | - | - | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, and nitrates | - | 4E+5 | 1E-4 | 5E-7 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-1782 | D, see 177Re | 7E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (1E+5) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-181 | D, see 177Re | 5E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-182 | D, see 177Re | 7E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 9E-5 | 9E-4 |
| (12.7 h) | W, see 177Re | - | 2E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-182 | D, see 177Re | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| (64.0 h) | W, see 177Re | - | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-184m | D, see 177Re | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-184 | D, see 177Re | 2E+3 | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-186m | D, see 177Re | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | St wall (2E+3) | St wall (2E+3) | - | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 2E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-186 | D, see 177Re | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-187 | D, see 177Re | 6E+5 | 8E+5 | 4E-4 | - | 8E-3 | 8E-2 |
| | | - | St wall (9E+5) | - | 1E-6 | - | - |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-188m2 | D, see 177Re | 8E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-188 | D, see 177Re | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
75 | Rhenium-189 | D, see 177Re | 3E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 177Re | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
76 | Osmium-1802 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 1E+5 | 4E+5 | 2E-4 | 5E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, halides and nitrates | - | 5E+5 | 2E-4 | 7E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 5E+5 | 2E-4 | 6E-7 | - | - |
76 | Osmium-1812 | D, see 180Os | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 180Os | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 180Os | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
76 | Osmium-182 | D, see 180Os | 2E+3 | 6E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 180Os | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 180Os | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
76 | Osmium-185 | D, see 180Os | 2E+3 | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 7E-10 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 180Os | - | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 180Os | - | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
76 | Osmium-189m | D, see 180Os | 8E+4 | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 180Os | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 180Os | - | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
76 | Osmium-191m | D, see 180Os | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 180Os | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 180Os | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
76 | Osmium-191 | D, see 180Os | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 180Os | - | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 180Os | - | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
76 | Osmium-193 | D, see 180Os | 2E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 180Os | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 180Os | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
76 | Osmium-194 | D, see 180Os | 4E+2 | 4E+1 | 2E-8 | 6E-11 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (6E+2) | - | - | - | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
| | W, see 180Os | - | 6E+1 | 2E-8 | 8E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, see 180Os | - | 8E+0 | 3E-9 | 1E-11 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-1822 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 4E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (4E+4) | - | - | - | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | W, halides, nitrates, and metallic iridium | - | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-184 | D, see 182Ir | 8E+3 | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-185 | D, see 182Ir | 5E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 1E+4 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-186 | D, see 182Ir | 2E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 6E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-187 | D, see 182Ir | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-188 | D, see 182Ir | 2E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-189 | D, see 182Ir | 5E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+3) | - | - | - | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-190m2 | D, see 182Ir | 2E+5 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-190 | D, see 182Ir | 1E+3 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 1E+3 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-192m | D, see 182Ir | 3E+3 | 9E+1 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | 3E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 2E+1 | 6E-9 | 2E-11 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-192 | D, see 182Ir | 9E+2 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | 3E-10 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-194m | D, see 182Ir | 6E+2 | 9E+1 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 2E+2 | 7E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 1E+2 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-194 | D, see 182Ir | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-195m | D, see 182Ir | 8E+3 | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
77 | Iridium-195 | D, see 182Ir | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 182Ir | - | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 7E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, see 182Ir | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
78 | Platinum-186 | D, all compounds | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
78 | Platinum-188 | D, all compounds | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
78 | Platinum-189 | D, all compounds | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
78 | Platinum-191 | D, all compounds | 4E+3 | 8E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
78 | Platinum-193m | D, all compounds | 3E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 8E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
78 | Platinum-193 | D, all compounds | 4E+4 | 2E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+4) | - | - | - | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
78 | Platinum-195m | D, all compounds | 2E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
78 | Platinum-197m2 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
78 | Platinum-197 | D, all compounds | 3E+3 | 1E+4 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
78 | Platinum-1992 | D, all compounds | 5E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
78 | Platinum-200 | D, all compounds | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
79 | Gold-193 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 9E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, halides and nitrates | - | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | - | - |
79 | Gold-194 | D, see 193Au | 3E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 193Au | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 193Au | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | - | - |
79 | Gold-195 | D, see 193Au | 5E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 193Au | - | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 193Au | - | 4E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | - | - |
79 | Gold-198m | D, see 193Au | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 193Au | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 193Au | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
79 | Gold-198 | D, see 193Au | 1E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 193Au | - | 2E+3 | 8E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 193Au | - | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
79 | Gold-199 | D, see 193Au | 3E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+3) | - | - | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 193Au | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 193Au | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
79 | Gold-200m | D, see 193Au | 1E+3 | 4E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 193Au | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 193Au | - | 2E+4 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
79 | Gold-2002 | D, see 193Au | 3E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, see 193Au | - | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 193Au | - | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
79 | Gold-2012 | D, see 193Au | 7E+4 | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (9E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | W, see 193Au | - | 2E+5 | 1E-4 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 193Au | - | 2E+5 | 9E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
80 | Mercury-193m | Vapor | - | 8E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | Organic D | 4E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | D, sulfates | 3E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, halides, nitrates, and sulfides | - | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
80 | Mercury-193 | Vapor | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
| | Organic D | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | D, see 193mHg | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 193mHg | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | - | - |
80 | Mercury-194 | Vapor | - | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | 4E-11 | - | - |
| | Organic D | 2E+1 | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | 4E-11 | 2E-7 | 2E-6 |
| | D, see 193mHg | 8E+2 | 4E+1 | 2E-8 | 6E-11 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 193mHg | - | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
80 | Mercury-195m | Vapor | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
| | Organic D | 3E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 8E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | D, see 193mHg | 2E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 193mHg | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | - | - |
80 | Mercury-195 | Vapor | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
| | Organic D | 2E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | D, see 193mHg | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 193mHg | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
80 | Mercury-197m | Vapor | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | - | - |
| | Organic D | 4E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | D, see 193mHg | 3E+3 | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | W, see 193mHg | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | - | - |
80 | Mercury-197 | Vapor | - | 8E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | Organic D | 7E+3 | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | 2E-8 | 9E-5 | 9E-4 |
| | D, see 193mHg | 6E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
| | W, see 193mHg | - | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
80 | Mercury-199m2 | Vapor | - | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
| | Organic D | 6E+4 | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (1E+5) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
| | D, see 193mHg | 6E+4 | 1E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
| | W, see 193mHg | - | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
80 | Mercury-203 | Vapor | - | 8E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | Organic D | 5E+2 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
| | D, see 193mHg | 2E+3 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 193mHg | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
81 | Thallium-194m2 | D, all compounds | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (7E+4) | - | - | - | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
81 | Thallium-1942 | D, all compounds | 3E+5 | 6E+5 | 2E-4 | 8E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+5) | - | - | - | 4E-3 | 4E-2 |
81 | Thallium-1952 | D, all compounds | 6E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
81 | Thallium-197 | D, all compounds | 7E+4 | 1E+5 | 5E-5 | 2E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
81 | Thallium-198m2 | D, all compounds | 3E+4 | 5E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
81 | Thallium-198 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 5E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
81 | Thallium-199 | D, all compounds | 6E+4 | 8E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
81 | Thallium-200 | D, all compounds | 8E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
81 | Thallium-201 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 2E+4 | 9E-6 | 3E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
81 | Thallium-202 | D, all compounds | 4E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 7E-9 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
81 | Thallium-204 | D, all compounds | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
82 | Lead-195m2 | D, all compounds | 6E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
82 | Lead-198 | D, all compounds | 3E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
82 | Lead-1992 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
82 | Lead-200 | D, all compounds | 3E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
82 | Lead-201 | D, all compounds | 7E+3 | 2E+4 | 8E-6 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
82 | Lead-202m | D, all compounds | 9E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
82 | Lead-202 | D, all compounds | 1E+2 | 5E+1 | 2E-8 | 7E-11 | 2E-6 | 2E-5 |
82 | Lead-203 | D, all compounds | 5E+3 | 9E+3 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
82 | Lead-205 | D, all compounds | 4E+3 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
82 | Lead-209 | D, all compounds | 2E+4 | 6E+4 | 2E-5 | 8E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
82 | Lead-210 | D, all compounds | 6E-1 | 2E-1 | 1E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (4E-1) | - | 6E-13 | 1E-8 | 1E-7 |
82 | Lead-2112 | D, all compounds | 1E+4 | 6E+2 | 3E-7 | 9E-10 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
82 | Lead-212 | D, all compounds | 8E+1 | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | 5E-11 | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+2) | - | - | - | 2E-6 | 2E-5 |
82 | Lead-2142 | D, all compounds | 9E+3 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
83 | Bismuth-2002 | D, nitrates | 3E+4 | 8E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | W, all other compounds | - | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-2012 | D, see 200Bi | 1E+4 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-2022 | D, see 200Bi | 1E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 6E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-203 | D, see 200Bi | 2E+3 | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-205 | D, see 200Bi | 1E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-206 | D, see 200Bi | 6E+2 | 1E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | 9E-6 | 9E-5 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-207 | D, see 200Bi | 1E+3 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 4E+2 | 1E-7 | 5E-10 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-210m | D, see 200Bi | 4E+1 | 5E+0 | 2E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | Kidneys (6E+1) | Kidneys (6E+0) | - | 9E-12 | 8E-7 | 8E-6 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 7E-1 | 3E-10 | 9E-13 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-210 | D, see 200Bi | 8E+2 | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | | - - | Kidneys (4E+2) | - | 5E-10 | - | - |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | 4E-11 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-2122 | D, see 200Bi | 5E+3 | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | 3E-10 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-2132 | D, see 200Bi | 7E+3 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 4E+2 | 1E-7 | 5E-10 | - | - |
83 | Bismuth-2142 | D, see 200Bi | 2E+4 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | St wall (2E+4) | - | - | - | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 200Bi | - | 9E-2 | 4E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
84 | Polonium-2032 | D, all compounds except those given for W | 3E+4 | 6E+4 | 3E-5 | 9E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, oxides, hydroxides, and nitrates | - | 9E+4 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
84 | Polonium-2052 | D, see 203Po | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
| | W, see 203Po | - | 7E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | - | - |
84 | Polonium-207 | D, see 203Po | 8E+3 | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 3E-8 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | W, see 203Po | - | 3E+4 | 1E-5 | 4E-8 | - | - |
84 | Polonium-210 | D, see 203Po | 3E+0 | 6E-1 | 3E-10 | 9E-13 | 4E-8 | 4E-7 |
| | W, see 203Po | - | 6E-1 | 3E-10 | 9E-13 | - | - |
85 | Astatine-2072 | D, halides | 6E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 8E-5 | 8E-4 |
| | W | - | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
85 | Astatine-211 | D, halides | 1E+2 | 8E+1 | 3E-8 | 1E-10 | 2E-6 | 2E-5 |
| | W | - | 5E+1 | 2E-8 | 8E-11 | - | - |
86 | Radon-220 | With daughters removed | - | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | 2E-8 | - | - |
| | With daughters present | - | 2E+1 | 9E-9 | 3E-11 | - | - |
| | | | (or 12 working level months) | | (or 1.0 working level) | | |
86 | Radon-222 | With daughters removed | - | 1E+4 | 4E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | With daughters present | - | 1E+2 | 3E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
| | | | (or 4 working level months) | | (or 0.33 working level) | | |
87 | Francium-2222 | D, all compounds | 2E+3 | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | 6E-10 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
87 | Francium-2232 | D, all compounds | 6E+2 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | 8E-6 | 8E-5 |
88 | Radium-223 | W, all compounds | 5E+0 | 7E-1 | 3E-10 | 9E-13 | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (9E+0) | - | - | - | 1E-7 | 1E-6 |
88 | Radium-224 | W, all compounds | 8E+0 | 2E+0 | 7E-10 | 2E-12 | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | - | - | - | 2E-7 | 2E-6 |
88 | Radium-225 | W, all compounds | 8E+0 | 7E-1 | 3E-10 | 9E-13 | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | - | - | - | 2E-7 | 2E-6 |
88 | Radium-226 | W, all compounds | 2E+0 | 6E-1 | 3E-10 | 9E-13 | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (5E+0) | - | - | - | 6E-8 | 6E-7 |
88 | Radium-2272 | W, all compounds | 2E+4 | 1E+4 | 6E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+4) | Bone surf (2E+4) | - | 3E-8 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
88 | Radium-228 | W, all compounds | 2E+0 | 1E+0 | 5E-10 | 2E-12 | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E+0) | - | - | - | 6E-8 | 6E-7 |
89 | Actinium-224 | D, all compounds except those given for W and Y | 2E+3 | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | Bone surf (4E+1) | - | 5E-11 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, halides and nitrates | - | 5E+1 | 2E-8 | 7E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 5E+1 | 2E-8 | 6E-11 | - | - |
89 | Actinium-225 | D, see 224Ac | 5E+1 | 3E-1 | 1E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (5E+1) | Bone surf (5E-1) | - | 7E-13 | 7E-7 | 7E-6 |
| | W, see 224Ac | - | 6E-1 | 3E-10 | 9E-13 | - | - |
| | Y, see 224Ac | - | 6E-1 | 3E-10 | 9E-13 | - | - |
89 | Actinium-226 | D, see 224Ac | 1E+2 | 3E+0 | 1E-9 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (1E+2) | Bone surf (4E+0) | - | 5E-12 | 2E-6 | 2E-5 |
| | W, see 224Ac | - | 5E+0 | 2E-9 | 7E-12 | - | - |
| | Y, see 224Ac | - | 5E+0 | 2E-9 | 6E-12 | - | - |
89 | Actinium-227 | D, see 224Ac | 2E-1 | 4E-4 | 2E-13 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E-1) | Bone surf (8E-4) | - | 1E-15 | 5E-9 | 5E-8 |
| | W, see 224Ac | - | 2E-3 | 7E-13 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (3E-3) | - | 4E-15 | - | - |
| | Y, see 224Ac | - | 4E-3 | 2E-12 | 6E-15 | - | - |
89 | Actinium-228 | D, see 224Ac | 2E+3 | 9E+0 | 4E-9 | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E+1) | - | 2E-11 | - | - |
| | W, see 224Ac | - | 4E+1 | 2E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | | Bone surf | | | | |
| | | - | (6E+1) | - | 8E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, see 224Ac | - | 4E+1 | 2E-8 | 6E-11 | - | - |
90 | Thorium-2262 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 5E+3 | 2E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
| | | St wall | | | | | |
| | | (5E+3) | - | - | - | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 1E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
90 | Thorium-227 | W, see 226Th | 1E+2 | 3E-1 | 1E-10 | 5E-13 | 2E-6 | 2E-5 |
| | Y, see 226Th | - | 3E-1 | 1E-10 | 5E-13 | - | - |
90 | Thorium-228 | W, see 226Th | 6E+0 | 1E-2 | 4E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+1) | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 3E-14 | 2E-7 | 2E-6 |
| | Y, see 226Th | - | 2E-2 | 7E-12 | 2E-14 | - | - |
90 | Thorium-229 | W, see 226Th | 6E-1 | 9E-4 | 4E-13 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (2E-3) | - | 3E-15 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
| | Y, see 226Th | - | 2E-3 | 1E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (3E-3) | - | 4E-15 | - | - |
90 | Thorium-230 | W, see 226Th | 4E+0 | 6E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (9E+0) | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 1E-7 | 1E-6 |
| | Y, see 226Th | - | 2E-2 | 6E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 3E-14 | - | - |
90 | Thorium-231 | W, see 226Th | 4E+3 | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | Y, see 226Th | - | 6E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
90 | Thorium-232 | W, see 226Th | 7E-1 | 1E-3 | 5E-13 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+0) | Bone surf (3E-3) | - | 4E-15 | 3E-8 | 3E-7 |
| | Y, see 226Th | - | 3E-3 | 1E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (4E-3) | - | 6E-15 | - | - |
90 | Thorium-234 | W, see 226Th | 3E+2 | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | 3E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (4E+2) | - | - | - | 5E-6 | 5E-5 |
| | Y, see 226Th | - | 2E+2 | 6E-8 | 2E-10 | - | - |
91 | Protactinium-2272 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 4E+3 | 1E+2 | 5E-8 | 2E-10 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 1E+2 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | - | - |
91 | Protactinium-228 | W, see 227Pa | 1E+3 | 1E+1 | 5E-9 | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E+1) | - | 3E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, see 227Pa | - | 1E+1 | 5E-9 | 2E-11 | - | - |
91 | Protactinium-230 | W, see 227Pa | 6E+2 | 5E+0 | 2E-9 | 7E-12 | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (9E+2) | - | - | - | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
| | Y, see 227Pa | - | 4E+0 | 1E-9 | 5E-12 | - | - |
91 | Protactinium-231 | W, see 227Pa | 2E-1 | 2E-3 | 6E-13 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (5E-1) | Bone surf (4E-3) | - | 6E-15 | 6E-9 | 6E-8 |
| | Y, see 227Pa | - | 4E-3 | 2E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (6E-3) | - | 8E-15 | - | - |
91 | Protactinium-232 | W, see 227Pa | 1E+3 | 2E+1 | 9E-9 | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (6E+1) | - | 8E-11 | - | - |
| | Y, see 227Pa | - | 6E+1 | 2E-8 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (7E+1) | - | 1E-10 | - | - |
91 | Protactinium-233 | W, see 227Pa | 1E+3 | 7E+2 | 3E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | Y, see 227Pa | - | 6E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
91 | Protactinium-234 | W, see 227Pa | 2E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 227Pa | - | 7E+3 | 3E-6 | 9E-9 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-230 | D, UF6, UO2F2, UO2(NO3)2 | 4E+0 | 4E-1 | 2E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (6E+0) | Bone surf (6E-1) | - | 8E-13 | 8E-8 | 8E-7 |
| | W, UO3, UF4, UCl4 | - | 4E-1 | 1E-10 | 5E-13 | - | - |
| | Y, UO2, U3O8 | - | 3E-1 | 1E-10 | 4E-13 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-231 | D, see 230U | 5E+3 | 8E+3 | 3E-6 | 1E-8 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (4E+3) | - | - | - | 6E-5 | 6E-4 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 6E+3 | 2E-6 | 8E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-232 | D, see 230U | 2E+0 | 2E-1 | 9E-11 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E+0) | Bone surf (4E-1) | - | 6E-13 | 6E-8 | 6E-7 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 4E-1 | 2E-10 | 5E-13 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 8E-3 | 3E-12 | 1E-14 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-233 | D, see 230U | 1E+1 | 1E+0 | 5E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | Bone surf (2E+0) | - | 3E-12 | 3E-7 | 3E-6 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 7E-1 | 3E-10 | 1E-12 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 4E-2 | 2E-11 | 5E-14 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-2343 | D, see 230U | 1E+1 | 1E+0 | 5E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | Bone surf (2E+0) | - | 3E-12 | 3E-7 | 3E-6 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 7E-1 | 3E-10 | 1E-12 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 4E-2 | 2E-11 | 5E-14 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-2353 | D, see 230U | 1E+1 | 1E+0 | 6E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | Bone surf (2E+0) | - | 3E-12 | 3E-7 | 3E-6 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 8E-1 | 3E-10 | 1E-12 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 4E-2 | 2E-11 | 6E-14 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-236 | D, see 230U | 1E+1 | 1E+0 | 5E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | Bone surf (2E+0) | - | 3E-12 | 3E-7 | 3E-6 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 8E-1 | 3E-10 | 1E-12 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 4E-2 | 2E-11 | 6E-14 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-237 | D, see 230U | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 2E+3 | 6E-7 | 2E-9 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-2383 | D, see 230U | 1E+1 | 1E+0 | 6E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | Bone surf (2E+0) | - | 3E-12 | 3E-7 | 3E-6 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 8E-1 | 3E-10 | 1E-12 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 4E-2 | 2E-11 | 6E-14 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-2392 | D, see 230U | 7E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | 9E-4 | 9E-3 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 2E+5 | 7E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 2E+5 | 6E-5 | 2E-7 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-240 | D, see 230U | 1E+3 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 2E+3 | 1E-6 | 3E-9 | - | - |
92 | Uranium-natural3 | D, see 230U | 1E+1 | 1E+0 | 5E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | Bone surf (2E+0) | - | 3E-12 | 3E-7 | 3E-6 |
| | W, see 230U | - | 8E-1 | 3E-10 | 9E-13 | - | - |
| | Y, see 230U | - | 5E-2 | 2E-11 | 9E-14 | - | - |
93 | Neptunium-2322 | W, all compounds | 1E+5 | 2E+3 | 7E-7 | - | 2E-3 | 2E-2 |
| | | - | Bone surf (5E+2) | - | 6E-9 | - | - |
93 | Neptunium-2332 | W, all compounds | 8E+5 | 3E+6 | 1E-3 | 4E-6 | 1E-2 | 1E-1 |
93 | Neptunium-234 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
93 | Neptunium-235 | W, all compounds | 2E+4 | 8E+2 | 3E-7 | - | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+4) | Bone surf (1E+3) | - | 2E-9 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
93 | Neptunium-236 | W, all compounds | 3E+0 | 2E-2 | 9E-12 | - | - | - |
| (1.15E+5 y) | | Bone surf (6E+0) | Bone surf (5E-2) | - | 8E-14 | 9E-8 | 9E-7 |
93 | Neptunium-236 | W, all compounds | 3E+3 | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | - | - | - |
| (22.5 h) | | Bone surf (4E+3) | Bone surf (7E+1) | - | 1E-10 | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
93 | Neptunium-237 | W, all compounds | 5E-1 | 4E-3 | 2E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 1E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
93 | Neptunium-238 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 6E+1 | 3E-8 | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E+2) | - | 2E-10 | - | - |
93 | Neptunium-239 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 2E+3 | 9E-7 | 3E-9 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (2E+3) | - | - | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
93 | Neptunium-2402 | W, all compounds | 2E+4 | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 3E-4 | 3E-3 |
94 | Plutonium-234 | W, all compounds except PuO2 | 8E+3 | 2E+2 | 9E-8 | 3E-10 | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | Y, PuO2 | - | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | 3E-10 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-2352 | W, see 234Pu | 9E+5 | 3E+6 | 1E-3 | 4E-6 | 1E-2 | 1E-1 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 3E+6 | 1E-3 | 3E-6 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-236 | W, see 234Pu | 2E+0 | 2E-2 | 8E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E+0) | Bone surf (4E-2) | - | 5E-14 | 6E-8 | 6E-7 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 4E-2 | 2E-11 | 6E-14 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-237 | W, see 234Pu | 1E+4 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 5E-9 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-238 | W, see 234Pu | 9E-1 | 7E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 2E-2 | 8E-12 | 2E-14 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-239 | W, see 234Pu | 8E-1 | 6E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 2E-2 | 7E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 2E-14 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-240 | W, see 234Pu | 8E-1 | 6E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 2E-2 | 7E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 2E-14 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-241 | W, see 234Pu | 4E+1 | 3E-1 | 1E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (7E+1) | Bone surf (6E-1) | - | 8E-13 | 1E-6 | 1E-5 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 8E-1 | 3E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E+0) | - | 1E-12 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-242 | W, see 234Pu | 8E-1 | 7E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 2E-2 | 7E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 2E-14 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-243 | W, see 234Pu | 2E+4 | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 4E+4 | 2E-5 | 5E-8 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-244 | W, see 234Pu | 8E-1 | 7E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 2E-2 | 7E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 2E-14 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-245 | W, see 234Pu | 2E+3 | 5E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | 6E-9 | - | - |
94 | Plutonium-246 | W, see 234Pu | 4E+2 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (4E+2) | - | - | - | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
| | Y, see 234Pu | - | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | 4E-10 | - | - |
95 | Americium-2372 | W, all compounds | 8E+4 | 3E+5 | 1E-4 | 4E-7 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
95 | Americium-2382 | W, all compounds | 4E+4 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | - | 5E-4 | 5E-3 |
| | | - | Bone surf (6E+3) | - | 9E-9 | - | - |
95 | Americium-239 | W, all compounds | 5E+3 | 1E+4 | 5E-6 | 2E-8 | 7E-5 | 7E-4 |
95 | Americium-240 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
95 | Americium-241 | W, all compounds | 8E-1 | 6E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
95 | Americium-242m | W, all compounds | 8E-1 | 6E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
95 | Americium-242 | W, all compounds | 4E+3 | 8E+1 | 4E-8 | - | 5E-5 | 5E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (9E+1) | - | 1E-10 | - | - |
95 | Americium-243 | W, all compounds | 8E-1 | 6E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
95 | Americium-244m2 | W, all compounds | 6E+4 | 4E+3 | 2E-6 | - | - | - |
| | | St wall (8E+4) | Bone surf (7E+3) | - | 1E-8 | 1E-3 | 1E-2 |
95 | Americium-244 | W, all compounds | 3E+3 | 2E+2 | 8E-8 | - | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (3E+2) | - | 4E-10 | - | - |
95 | Americium-245 | W, all compounds | 3E+4 | 8E+4 | 3E-5 | 1E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
95 | Americium-246m2 | W, all compounds | 5E+4 | 2E+5 | 8E-5 | 3E-7 | - | - |
| | | St wall (6E+4) | - | - | - | 8E-4 | 8E-3 |
95 | Americium-2462 | W, all compounds | 3E+4 | 1E+5 | 4E-5 | 1E-7 | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
96 | Curium-238 | W, all compounds | 2E+4 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 2E-4 | 2E-3 |
96 | Curium-240 | W, all compounds | 6E+1 | 6E-1 | 2E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (8E+1) | Bone surf (6E-1) | - | 9E-13 | 1E-6 | 1E-5 |
96 | Curium-241 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 3E+1 | 1E-8 | - | 2E-5 | 2E-4 |
| | | - | Bone surf (4E+1) | - | 5E-11 | - | - |
96 | Curium-242 | W, all compounds | 3E+1 | 3E-1 | 1E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (5E+1) | Bone surf (3E-1) | - | 4E-13 | 7E-7 | 7E-6 |
96 | Curium-243 | W, all compounds | 1E+0 | 9E-3 | 4E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+0) | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 3E-8 | 3E-7 |
96 | Curium-244 | W, all compounds | 1E+0 | 1E-2 | 5E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (3E+0) | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 3E-14 | 3E-8 | 3E-7 |
96 | Curium-245 | W, all compounds | 7E-1 | 6E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
96 | Curium-246 | W, all compounds | 7E-1 | 6E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
96 | Curium-247 | W, all compounds | 8E-1 | 6E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
96 | Curium-248 | W, all compounds | 2E-1 | 2E-3 | 7E-13 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E-1) | Bone surf (3E-3) | - | 4E-15 | 5E-9 | 5E-8 |
96 | Curium-2492 | W, all compounds | 5E+4 | 2E+4 | 7E-6 | - | 7E-4 | 7E-3 |
| | | - | Bone surf (3E+4) | - | 4E-8 | - | - |
96 | Curium-250 | W, all compounds | 4E-2 | 3E-4 | 1E-13 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (6E-2) | Bone surf (5E-4) | - | 8E-16 | 9E-10 | 9E-9 |
97 | Berkelium-245 | W, all compounds | 2E+3 | 1E+3 | 5E-7 | 2E-9 | 3E-5 | 3E-4 |
97 | Berkelium-246 | W, all compounds | 3E+3 | 3E+3 | 1E-6 | 4E-9 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
97 | Berkelium-247 | W, all compounds | 5E-1 | 4E-3 | 2E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (9E-3) | - | 1E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
97 | Berkelium-249 | W, all compounds | 2E+2 | 2E+0 | 7E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (5E+2) | Bone surf (4E+0) | - | 5E-12 | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
97 | Berkelium-250 | W, all compounds | 9E+3 | 3E+2 | 1E-7 | - | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | | - | Bone surf (7E+2) | - | 1E-9 | - | - |
98 | Californium-2442 | W, all compounds except those given for Y | 3E+4 | 6E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
| | | St wall (3E+4) | - | - | - | 4E-4 | 4E-3 |
| | Y, oxides and hydroxides | - | 6E+2 | 2E-7 | 8E-10 | - | - |
98 | Californium-246 | W, see 244Cf | 4E+2 | 9E+0 | 4E-9 | 1E-11 | 5E-6 | 5E-5 |
| | Y, see 244Cf | - | 9E+0 | 4E-9 | 1E-11 | - | - |
98 | Californium-248 | W, see 244Cf | 8E+0 | 6E-2 | 3E-11 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | Bone surf (1E-1) | - | 2E-13 | 2E-7 | 2E-6 |
| | Y, see 244Cf | - | 1E-1 | 4E-11 | 1E-13 | - | - |
98 | Californium-249 | W, see 244Cf | 5E-1 | 4E-3 | 2E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (9E-3) | - | 1E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
| | Y, see 244Cf | - | 1E-2 | 4E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | - | - |
98 | Californium-250 | W, see 244Cf | 1E+0 | 9E-3 | 4E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+0) | Bone surf (2E-2) | - | 3E-14 | 3E-8 | 3E-7 |
| | Y, see 244Cf | - | 3E-2 | 1E-11 | 4E-14 | - | - |
98 | Californium-251 | W, see 244Cf | 5E-1 | 4E-3 | 2E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (1E+0) | Bone surf (9E-3) | - | 1E-14 | 2E-8 | 2E-7 |
| | Y, see 244Cf | - | 1E-2 | 4E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E-2) | - | 2E-14 | - | - |
98 | Californium-252 | W, see 244Cf | 2E+0 | 2E-2 | 8E-12 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (5E+0) | Bone surf (4E-2) | - | 5E-14 | 7E-8 | 7E-7 |
| | Y, see 244Cf | - | 3E-2 | 1E-11 | 5E-14 | - | - |
98 | Californium-253 | W, see 244Cf | 2E+2 | 2E+0 | 8E-10 | 3E-12 | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E+2) | - | - | - | 5E-6 | 5E-5 |
| | Y, see 244Cf | - | 2E+0 | 7E-10 | 2E-12 | - | - |
98 | Californium-254 | W, see 244Cf | 2E+0 | 2E-2 | 9E-12 | 3E-14 | 3E-8 | 3E-7 |
| | Y, see 244Cf | - | 2E-2 | 7E-12 | 2E-14 | - | - |
99 | Einsteinium-250 | W, all compounds | 4E+4 | 5E+2 | 2E-7 | - | 6E-4 | 6E-3 |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E+3) | - | 2E-9 | - | - |
99 | Einsteinium-251 | W, all compounds | 7E+3 | 9E+2 | 4E-7 | - | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | | - | Bone surf (1E+3) | - | 2E-9 | - | - |
99 | Einsteinium-253 | W, all compounds | 2E+2 | 1E+0 | 6E-10 | 2E-12 | 2E-6 | 2E-5 |
99 | Einsteinium-254m | W, all compounds | 3E+2 | 1E+1 | 4E-9 | 1E-11 | - | - |
| | | LLI wall (3E+2) | - | - | - | 4E-6 | 4E-5 |
99 | Einsteinium-254 | W, all compounds | 8E+0 | 7E-2 | 3E-11 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (2E+1) | Bone surf (1E-1) | - | 2E-13 | 2E-7 | 2E-6 |
100 | Fermium-252 | W, all compounds | 5E+2 | 1E+1 | 5E-9 | 2E-11 | 6E-6 | 6E-5 |
100 | Fermium-253 | W, all compounds | 1E+3 | 1E+1 | 4E-9 | 1E-11 | 1E-5 | 1E-4 |
100 | Fermium-254 | W, all compounds | 3E+3 | 9E+1 | 4E-8 | 1E-10 | 4E-5 | 4E-4 |
100 | Fermium-255 | W, all compounds | 5E+2 | 2E+1 | 9E-9 | 3E-11 | 7E-6 | 7E-5 |
100 | Fermium-257 | W, all compounds | 2E+1 | 2E-1 | 7E-11 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (4E+1) | Bone surf (2E-1) | - | 3E-13 | 5E-7 | 5E-6 |
101 | Mendelevium-257 | W, all compounds | 7E+3 | 8E+1 | 4E-8 | - | 1E-4 | 1E-3 |
| | | - | Bone surf (9E+1) | - | 1E-10 | - | - |
101 | Mendelevium-258 | W, all compounds | 3E+1 | 2E-1 | 1E-10 | - | - | - |
| | | Bone surf (5E+1) | Bone surf (3E-1) | - | 5E-13 | 6E-7 | 6E-6 |
- | Any single radionuclide not listed above with decay mode other than alpha emission or spontaneous fission and with radioactive half-life less than ((2))two hours | Submersion1 | - | 2E+2 | 1E-7 | 1E-9 | - | - |
- | Any single radionuclide not listed above with decay mode other than alpha emission or spontaneous fission and with radioactive half-life greater than ((2))two hours | . . . . | - | 2E-1 | 1E-10 | 1E-12 | 1E-8 | 1E-7 |
- | Any single radionuclide not listed above that decays by alpha emission or spontaneous fission, or any mixture for which either the identity or the concentration of any radionuclide in the mixture is not known | . . . . | - | 4E-4 | 2E-13 | 1E-15 | 2E-9 | 2E-8 |
FOOTNOTES: 1"Submersion" means that values given are for submersion in a hemispherical semi-infinite cloud of airborne material. 2These radionuclides have radiological half-lives of less than ((2))two hours. The total effective dose equivalent received during operations with these radionuclides might include a significant contribution from external exposure. The DAC values for all radionuclides, other than those designated Class "Submersion," are based upon the committed effective dose equivalent due to the intake of the radionuclide into the body and do NOT include potentially significant contributions to dose equivalent from external exposures. The licensee may substitute 1E-7 µCi/ml for the listed DAC to account for the submersion dose prospectively, but should use individual monitoring devices or other radiation measuring instruments that measure external exposure to demonstrate compliance with the limits. (See WAC 246-221-015(5).) 3For soluble mixtures of U-238, U-234, and U-235 in air, chemical toxicity may be the limiting factor (see WAC 246-221-010(5)). If the percent by weight (enrichment) of U-235 is not greater than ((5))five, the concentration value for a 40-hour workweek is 0.2 milligrams uranium per cubic meter of air average. For any enrichment, the product of the average concentration and time of exposure during a 40-hour workweek shall not exceed 8E-3 (SA) µCi-hr/ml, where SA is the specific activity of the uranium inhaled. The specific activity for natural uranium is 6.77E-7 curies per gram U. The specific activity for other mixtures of U-238, U-235, and U-234, if not known, shall be: SA = 3.6E-7 curies/gram U, U-depleted SA = [0.4 + 0.38 (enrichment) + 0.0034 (enrichment)2] E-6, enrichment ≥ 0.72 where enrichment is the percentage by weight of U-235, expressed as percent. NOTE: 1. If the identity of each radionuclide in a mixture is known but the concentration of one or more of the radionuclides in the mixture is not known, the DAC for the mixture shall be the most restrictive DAC of any radionuclide in the mixture. 2. If the identity of each radionuclide in the mixture is not known, but it is known that certain radionuclides specified in this appendix are not present in the mixture, the inhalation ALI, DAC, and effluent and sewage concentrations for the mixture are the lowest values specified in this appendix for any radionuclide that is not known to be absent from the mixture; or |
If it is known that Ac-227-D and Cm-250-W are not present | - | 7E-4 | 3E-13 | - | - | - |
If, in addition, it is known that Ac-227-W,Y, Th-229-W,Y, Th-230-W, Th-232-W,Y, Pa-231-W,Y, Np-237-W, Pu-239-W, Pu-240-W, Pu-242-W, Am-241-W, Am-242m-W, Am-243-W, Cm-245-W, Cm-246-W, Cm-247-W, Cm-248-W, Bk-247-W, Cf-249-W, and Cf-251-W are not present | - | 7E-3 | 3E-12 | - | - | - |
If, in addition, it is known that Sm-146-W, Sm-147-W, Gd-148-D,W, Gd-152-D,W, Th-228-W,Y, Th-230-Y, U-232-Y, U-233-Y, U-234-Y, U-235-Y, U-236-Y, U-238-Y, Np-236-W, Pu-236-W,Y, Pu-238-W,Y, Pu-239-Y, Pu-240-Y, Pu-242-Y, Pu-244-W,Y, Cm-243-W, Cm-244-W, Cf-248-W, Cf-249-Y, Cf-250-W,Y, Cf-251-Y, Cf-252-W,Y, and Cf-254-W,Y are not present | - | 7E-2 | 3E-11 | - | - | - |
If, in addition, it is known that Pb-210-D, Bi-210m-W, Po-210-D,W, Ra-223-W, Ra-225-W, Ra-226-W, Ac-225-D,W,Y, Th-227-W,Y, U-230-D,W,Y, U-232-D,W, Pu-241-W, Cm-240-W, Cm-242-W, Cf-248-Y, Es-254-W, Fm-257-W, and Md-258-W are not present | - | 7E-1 | 3E-10 | - | - | - |
If, in addition, it is known that Si-32-Y, Ti-44-Y, Fe-60-D, Sr-90-Y, Zr-93-D, Cd-113m-D, Cd-113-D, In-115-D,W, La-138-D, Lu-176-W, Hf-178m-D,W, Hf-182-D,W, Bi-210m-D, Ra-224-W, Ra-228-W, Ac-226-D,W,Y, Pa-230-W,Y, U-233-D,W, U-234-D,W, U-235-D,W, U-236-D,W, U-238-D,W, Pu-241-Y, Bk-249-W, Cf-253-W,Y, and Es-253-W are not present | - | 7E+0 | 3E-9 | - | - | - |
If it is known that Ac-227-D,W,Y, Th-229-W,Y, Th-232-W,Y, Pa-231-W,Y, Cm-248-W, and Cm-250-W are not present | - | - | - | 1E-14 | - | - |
If, in addition, it is known that Sm-146-W, Gd-148-D,W, Gd-152-D, Th-228-W,Y, Th-230-W,Y, U-232-Y, U-233-Y, U-234-Y, U-235-Y, U-236-Y, U-238-Y, U-Nat-Y, Np-236-W, Np-237-W, Pu-236-W,Y, Pu-238-W,Y, Pu-239-W,Y, Pu-240-W,Y, Pu-242-W,Y, Pu-244-W,Y, Am-241-W, Am-242m-W, Am-243-W, Cm-243-W, Cm-244-W, Cm-245-W, Cm-246-W, Cm-247-W, Bk-247-W, Cf-249-W,Y, Cf-250-W,Y, Cf-251-W,Y, Cf-252-W,Y, and Cf-254-W,Y are not present | - | - | - | 1E-13 | - | - |
If, in addition, it is known that Sm-147-W, Gd-152-W, Pb-210-D, Bi-210m-W, Po-210-D,W, Ra-223-W, Ra-225-W, Ra-226-W, Ac-225-D,W,Y, Th-227-W,Y, U-230-D,W,Y, U-232-D,W, U-Nat-W, Pu-241-W, Cm-240-W, Cm-242-W, Cf-248-W,Y, Es-254-W, Fm-257-W, and Md-258-W are not present | - | - | - | - | 1E-12 | - |
If, in addition, it is known that Fe-60, Sr-90, Cd-113m, Cd-113, In-115, I-129, Cs-134, Sm-145, Sm-147, Gd-148, Gd-152, Hg-194 (organic), Bi-210m, Ra-223, Ra-224, Ra-225, Ac-225, Th-228, Th-230, U-233, U-234, U-235, U-236, U-238, U-Nat, Cm-242, Cf-248, Es-254, Fm-257, and Md-258 are not present | - | - | - | - | 1E-6 | 1E-5 |
3. If a mixture of radionuclides consists of uranium and its daughters in ore dust (10 µm AMAD particle distribution assumed) prior to chemical separation of the uranium from the ore, the following values may be used for the DAC of the mixture: 6E-11 µCi of gross alpha activity from uranium-238, uranium-234, thorium-230, and radium-226 per milliliter of air; 3E-11 µCi of natural uranium per milliliter of air; or 45 micrograms of natural uranium per cubic meter of air. 4. If the identity and concentration of each radionuclide in a mixture are known, the limiting values should be derived as follows: Determine, for each radionuclide in the mixture, the ratio between the concentration present in the mixture and the concentration otherwise established in this section for the specific radionuclide when not in a mixture. The sum of such ratios for all of the radionuclides in the mixture may not exceed "1" (i.e., "unity"). Example: If radionuclides "A," "B," and "C" are present in concentrations CA, CB, and CC, and if the applicable DACs are DACA, DACB, and DACC, respectively, then the concentrations shall be limited so that the following relationship exists: |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040. OTS-4712.1
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-01-034, filed 12/12/16, effective 1/12/17)
WAC 246-231-010Definitions, abbreviations, and acronyms.
The definitions, abbreviations, and acronyms in this section and in WAC 246-220-010 apply throughout this chapter unless the context clearly indicates otherwise. To ensure compatibility with international transportation standards, all limits in this chapter are given in terms of dual units: The International System of Units (SI) followed or preceded by U.S. standard or customary units. The U.S. customary units are not exact equivalents, but are rounded to a convenient value, providing a functionally equivalent unit. For the purpose of this chapter, either unit may be used.
(1) "A1" means the maximum activity of special form radioactive material permitted in a Type A package. This value is either listed in WAC 246-231-200, Table A-1 or may be derived in accordance with the procedures prescribed in WAC 246-231-200.
(2) "A2" means the maximum activity of radioactive material, other than special form material, LSA and SCO material, permitted in a Type A package. This value is either listed in WAC 246-231-200, Table A-1, or may be derived in accordance with the procedure prescribed in WAC 246-231-200.
(3) "Carrier" means a person engaged in the transportation of passengers or property by land or water as a common, contract, or private carrier, or by civil aircraft.
(4) "Certificate holder" means a person who has been issued a certificate of compliance or other package approval by NRC.
(5) "Certificate of compliance" means the certificate issued by NRC under 10 C.F.R. 71 Subpart D which approves the design of a package for the transportation of radioactive material.
(6) "Close reflection by water" means immediate contact by water of sufficient thickness for maximum reflection of neutrons.
(7) "Consignment" means each shipment of a package or groups of packages or load of radioactive material offered by a shipper for transport.
(8) "Containment system" means the assembly of components of the packaging intended to retain the radioactive material during transport.
(9) "Contamination" means the presence of a radioactive substance on a surface in quantities in excess of 0.4 Bq/cm2(1x10-5 µCi/cm2) for beta and gamma emitters and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 0.04 Bq/cm2(1x10-6 µCi/cm2) for all other alpha emitters.
(a) Fixed contamination means contamination that cannot be removed from a surface during normal conditions of transport.
(b) Nonfixed contamination means contamination that can be removed from a surface during normal conditions of transport.
(10) "Conveyance" means:
(a) For transport by public highway or rail any transport vehicle or large freight container;
(b) For transport by water any vessel, or any hold, compartment, or defined deck area of a vessel including any transport vehicle on board the vessel; and
(c) For transport by any aircraft.
(11) "Criticality safety index (CSI)" means the dimensionless number (rounded up to the next tenth) assigned to and placed on the label of a fissile material package, to designate the degree of control of accumulation of packages, overpacks, or freight containers containing fissile material during transportation. Determination of the criticality safety index is described in WAC 246-231-094, 246-231-096, and 10 C.F.R. 71.22, 71.23, and 71.59. The criticality safety index for an overpack, freight container, consignment, or conveyance containing fissile material packages is the arithmetic sum of the criticality safety indices of all the fissile material packages contained within the overpack, freight container, consignment, or conveyance.
(12) "Deuterium" means, for the purposes of WAC 246-231-040 and 246-231-094, deuterium and any deuterium compounds, including heavy water, in which the ratio of deuterium atoms to hydrogen atoms exceeds 1:5000.
(13) "DOT" means the United States Department of Transportation. DOT regulations are found in Code of Federal Regulations Title 49 Transportation.
(14) "Exclusive use" means the sole use by a single consignor of a conveyance for which all initial, intermediate, and final loading and unloading are carried out in accordance with the direction of the consignor or consignee. The consignor and the carrier must ensure that any loading or unloading is performed by personnel having radiological training and resources appropriate for safe handling of the consignment. The consignor must issue specific instructions, in writing, for maintenance of exclusive use shipment controls, and include them with the shipping paper information provided to the carrier by the consignor.
(15) "Fissile material" means the radionuclides uranium-233, uranium-235, plutonium-239, and plutonium-241, or any combination of these radionuclides. Fissile material means the fissile nuclides themselves, not material containing fissile nuclides. Unirradiated natural uranium and depleted uranium, and natural uranium or depleted uranium that has been irradiated in thermal reactors only are not included in this definition. Certain exclusions from fissile material controls are provided in WAC 246-231-040.
(16) "Graphite" means graphite with a boron equivalent content less than ((5))five parts per million and density greater than 1.5 grams per cubic centimeter.
(17) "Indian Tribe" means an Indian or Alaskan native Tribe, band, nation, pueblo, village, or community that the Secretary of the Interior acknowledges to exist as an Indian Tribe pursuant to the Federally Recognized Indian Tribe List Act of 1994, 25 U.S.C. 479a. A current listing of officially recognized Indian Tribes may be found at: http://www.bia.gov/cs/groups/mywcsp/documents/text/idc-020733.pdf.
(18) "Low specific activity (LSA) material" means radioactive material with limited specific activity which is nonfissile or is excepted under WAC 246-231-040 or 10 C.F.R. 71.15 and which satisfies the descriptions and limits set forth below. Shielding materials surrounding the LSA material may not be considered in determining the estimated average specific activity of the package contents. LSA material must be in one of three groups:
(a) LSA-I.
(i) Uranium and thorium ores, concentrates of uranium and thorium ores, and other ores containing naturally occurring radioactive radionuclides which are intended to be processed for the use of these radionuclides;
(ii) Natural uranium, depleted uranium, natural thorium, or their compounds or mixtures, provided they are unirradiated and in solid or liquid form; or
(iii) Radioactive material other than fissile material for which the A2 value is unlimited; or
(iv) Other radioactive material in which the activity is distributed throughout and the estimated average specific activity does not exceed 30 times the value for exempt material activity concentration determined in accordance with Appendix A.
(b) LSA-II.
(i) Water with tritium concentration up to 0.8 TBq/liter (20.0 Ci/liter); or
(ii) Other radioactive material in which the activity is distributed throughout, and the estimated average specific activity does not exceed 1x10-4 A2/g for solids and gases, and 1x10-5 A2/g for liquids.
(c) LSA-III. Solids (e.g., consolidated wastes, activated materials), excluding powders, that satisfy the requirements of the 10 C.F.R. 71.77, in which:
(i) The radioactive material is distributed throughout a solid or a collection of solid objects, or is essentially uniformly distributed in a solid compact binding agent (such as concrete, bitumen, ceramic, etc.); and
(ii) The radioactive material is relatively insoluble, or it is intrinsically contained in a relatively insoluble material, so that, even under loss of packaging, the loss of radioactive material per package by leaching, when placed in water for seven days, would not exceed 0.1 A2; and
(iii) The estimated average specific activity of the solid, excluding any shielding material, does not exceed 2x10-3 A2/g.
(19) "Low toxicity alpha emitters" means natural uranium, depleted uranium, natural thorium; uranium-235, uranium-238, thorium-232, thorium-228 or thorium-230 when contained in ores or physical or chemical concentrates or tailings; or alpha emitters with a half-life of less than ((ten))10 days.
(20) "Maximum normal operating pressure" means the maximum gauge pressure that would develop in the containment system in a period of one year under the heat condition specified in NRC regulations 10 C.F.R. 71.71 (c)(1), in the absence of venting, external cooling by an ancillary system, or operational controls during transport.
(21) "Natural thorium" means thorium with the naturally occurring distribution of thorium isotopes (essentially 100 weight percent thorium-232).
(22) "Normal form radioactive material" means radioactive material that has not been demonstrated to qualify as "special form radioactive material."
(23) "Nuclear waste" as used in WAC 246-231-140 means any quantity of radioactive material (not including radiography sources being returned to the manufacturer) required to be in Type B packaging while transported to, through, or across state boundaries to a disposal site, or to a collection point for transport to a disposal site. Nuclear waste, as used in these regulations, is a special classification of radioactive waste.
(24) "Optimum interspersed hydrogenous moderation" means the presence of hydrogenous material between packages to such an extent that the maximum nuclear reactivity results.
(25) "Package" means the packaging together with its radioactive contents as presented for transport.
(a) "Fissile material package" or Type AF package, Type BF package, Type B(U)F package or Type B(M)F package means a fissile material packaging together with its fissile material contents.
(b) "Type A package" means a Type A packaging together with its radioactive contents. A Type A package is defined and must comply with the DOT regulations in 49 C.F.R. 173.
(c) "Type B package" means a Type B packaging together with its radioactive contents. Upon approval by NRC, a Type B package design is designated by NRC as B(U) unless the package has a maximum normal operating pressure of more than 700 kPa (100 lbs/in2) gauge or a pressure relief device that would allow the release of radioactive material to the environment under the tests specified in NRC regulations 10 C.F.R. 71.73 (hypothetical accident conditions), in which case it will receive a designation B(M). B(U) refers to the need for unilateral approval of international shipments; B(M) refers to the need for multilateral approval of international shipments. There is no distinction made in how packages with these designations may be used in domestic transportation. To determine their distinction for international transportation, see DOT regulations in 49 C.F.R. 173. A Type B package approved before September 6, 1983, was designated only as Type B. Limitations on its use are specified in 10 C.F.R. 71.19.
(26) "Packaging" means the assembly of components necessary to ensure compliance with the packaging requirements of this chapter. It may consist of one or more receptacles, absorbent materials, spacing structures, thermal insulation, radiation shielding, and devices for cooling or absorbing mechanical shocks. The vehicle, tie-down system, and auxiliary equipment may be designated as part of the packaging.
(27) "Special form radioactive material" means radioactive material that satisfies the following conditions:
(a) It is either a single solid piece or is contained in a sealed capsule that can be opened only by destroying the capsule;
(b) The piece or capsule has at least one dimension not less than ((5))five mm (0.2 in); and
(c) It satisfies the requirements of 10 C.F.R. 71.75. A special form encapsulation designed in accordance with the requirements of 10 C.F.R. 71.4 in effect on June 30, 1983, (see 10 C.F.R. 71, revised as of January 1, 1983), and constructed before July 1, 1985; a special form encapsulation designed in accordance with the requirements of 10 C.F.R. 71.4 in effect on March 31, 1996 (see 10 C.F.R. 71, revised as of January 1, 1996), and constructed before April 1, 1998; and special form material that was successfully tested before September 10, 2015, in accordance with the requirements of 10 C.F.R. 71.75(d) in effect before September 10, 2015, may continue to be used. Any other special form encapsulation must meet the specifications of this definition.
(28) "Specific activity of a radionuclide" means the radioactivity of the radionuclide per unit mass of that nuclide. The specific activity of a material in which the radionuclide is essentially uniformly distributed is the radioactivity per unit mass of the material.
(29) "Spent nuclear fuel" or "spent fuel" means fuel that has been withdrawn from a nuclear reactor following irradiation, has undergone at least one year's decay since being used as a source of energy in a power reactor, and has not been chemically separated into its constituent elements by reprocessing. Spent fuel includes the special nuclear material, by-product material, source material, and other radioactive materials associated with fuel assemblies.
(30) "State" means a state of the United States, the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands.
(31) "Surface contaminated object (SCO)" means a solid object that is not itself classed as radioactive material, but which has radioactive material distributed on any of its surfaces. SCO must be in one of two groups with surface activity not exceeding the following limits:
(a) SCO-I: A solid object on which:
(i) The nonfixed contamination on the accessible surface averaged over 300 cm2 (or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm2) does not exceed ((4))four Bq/cm2 (1x10-4 microcurie/cm2) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 0.4 Bq/cm2 (1x10-5 microcurie/cm2) for all other alpha emitters;
(ii) The fixed contamination on the accessible surface averaged over 300 cm2 (or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm2) does not exceed 4x104 Bq/cm2 (1.0 microcurie/cm2) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 4x103 Bq/cm2 (0.1 microcurie/cm2) for all other alpha emitters; and
(iii) The nonfixed contamination plus the fixed contamination on the inaccessible surface averaged over 300 cm2 (or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm2) does not exceed 4x104 Bq/cm2 (((1))one microcurie/cm2) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 4x103 Bq/cm2 (0.1 microcurie/cm2) for all other alpha emitters.
(b) SCO-II: A solid object on which the limits for SCO-I are exceeded and on which:
(i) The nonfixed contamination on the accessible surface averaged over 300 cm2 (or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm2) does not exceed 400 Bq/cm2 (1x10-2 microcurie/cm2) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters or 40 Bq/cm2 (1x10-3 microcurie/cm2) for all other alpha emitters;
(ii) The fixed contamination on the accessible surface averaged over 300 cm2 (or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm2) does not exceed 8x105 Bq/cm2 (20 microcuries/cm2) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 8x104 Bq/cm2 (((2))two microcuries/cm2) for all other alpha emitters; and
(iii) The nonfixed contamination plus the fixed contamination on the inaccessible surface averaged over 300 cm2 (or the area of the surface if less than 300 cm2) does not exceed 8x105 Bq/cm2 (20 microcuries/cm2) for beta and gamma and low toxicity alpha emitters, or 8x104 Bq/cm2 (((2))two microcuries/cm2) for all other alpha emitters.
(32) "Transport index (TI)" means the dimensionless number (rounded up to the next tenth) placed on the label of a package, to designate the degree of control to be exercised by the carrier during transportation. The transport index is the number determined by multiplying the maximum radiation level in millisievert (mSv) per hour at ((1))one meter (3.3 ft) from the external surface of the package by 100 (equivalent to the maximum radiation level in millirem per hour at ((1))one meter (3.3 ft)).
(33) "Tribal official" means the highest ranking individual who represents Tribal leadership, such as the chief, president, or Tribal council leadership.
(34) "Type A quantity" means a quantity of radioactive material, the aggregate radioactivity of which does not exceed A1 for special form radioactive material, or A2 for normal form radioactive material, where A1 and A2 are given in Table A-1 of WAC 246-231-200, or may be determined by procedures described in WAC 246-231-200.
(35) "Type B quantity" means a quantity of radioactive material greater than a Type A quantity.
(36) "Unirradiated uranium" means uranium containing not more than 2x103 Bq of plutonium per gram of uranium-235, not more than 9x106 Bq of fission products per gram of uranium-235, and not more than 5x10-3 g of uranium-236 per gram of uranium-235.
(37) Uranium-natural, depleted, enriched.
(a) "Natural uranium" means uranium (which may be chemically separated) with the naturally occurring distribution of uranium isotopes (approximately 0.711 weight percent uranium-235, and the remainder by weight essentially uranium-238).
(b) "Depleted uranium" means uranium containing less uranium-235 than the naturally occurring distribution of uranium isotopes.
(c) "Enriched uranium" means uranium containing more uranium-235 than the naturally occurring distribution of uranium isotopes.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-01-034, filed 12/12/16, effective 1/12/17)
WAC 246-231-040Exemptions.
(1) Common and contract carriers, freight forwarders, warehouse workers, and the U.S. Postal Service are exempt from this chapter and chapters 246-232, 246-233, 246-235, 246-237, 246-240, 246-243, and 246-244 WAC to the extent that they transport or store radioactive material in the regular course of their carriage for another or storage incident thereto.
(2) Any licensee who delivers radioactive material to a carrier for transport, where such transport is subject to the regulations of the United States Postal Service, is exempt from the provisions of WAC 246-231-005.
(3) Exemption of physicians. Any physician as defined in WAC 246-220-010 who is licensed by the department, NRC or an agreement state, to dispense drugs in the practice of medicine, is exempt from WAC 246-220-030 with respect to transport by the physician of licensed material for use in the practice of medicine. However, any physician operating under this exemption must be licensed under chapter 246-240 WAC, 10 C.F.R. 35, or the equivalent agreement state regulations.
(4) Exemption for low-level materials. A licensee is exempt from all requirements of this chapter with respect to shipment or carriage of the following low-level materials:
(a) Natural material and ores containing naturally occurring radionuclides that are either in their natural state, or have only been processed for purposes other than for the extraction of the radionuclides, and which are not intended to be processed for use of these radionuclides, provided the activity concentration of the material does not exceed ((ten))10 times the applicable radionuclide activity concentration values specified in WAC 246-231-200, Table A-2 or Table A-3.
(b) Materials for which the activity concentration is not greater than the activity concentration values specified in WAC 246-231-200, Table A-2 or Table A-3, or for which the consignment activity is not greater than the limit for an exempt consignment found in WAC 246-231-200, Table A-2 or Table A-3.
(c) Nonradioactive solid objects with radioactive substances present on any surfaces in quantities not in excess of the levels cited in the definition of contamination in WAC 246-231-010.
(5) A licensee is exempt from all the requirements of this chapter, other than 10 C.F.R. 71.5 and 71.88, with respect to shipment or carriage of the following packages, provided the packages do not contain any fissile material, or the material is exempt from classification as fissile material in this subsection;
(a) A package that contains no more than a Type A quantity of radioactive material;
(b) A package transported within the United States that contains no more than 0.74 TBq (20 Ci) of special form plutonium-244; or
(c) The package contains only LSA or SCO radioactive material, provided:
(i) That the LSA or SCO material has an external radiation dose of less than or equal to 10 mSv/h (((1))one rem/h), at a distance of three meters from the unshielded material; or
(ii) That the package contains only LSA-I or SCO-I material.
(6) Exemption from classification as fissile material. Fissile material meeting at least one of the requirements in (a) through (f) of this subsection is exempt from classification as fissile material and from the fissile material package standards of 10 C.F.R. 71.55 and 71.59, but are subject to all other requirements of this chapter, except as noted.
(a) Individual package containing ((2))two grams or less fissile material.
(b) Individual or bulk packaging containing 15 grams or less of fissile material provided the package has at least 200 grams of solid nonfissile material for every gram of fissile material. Lead, beryllium, graphite, and hydrogenous material enriched in deuterium may be present in the package but must not be included in determining the required mass for solid nonfissile material.
(c)(i) Low concentrations of solid fissile material commingled with solid nonfissile material, provided that:
(A) There are at least 2000 grams of solid nonfissile material for every gram of fissile material; and
(B) There are no more than 180 grams of fissile material distributed within 360 kg of contiguous nonfissile material.
(ii) Lead, beryllium, graphite, and hydrogenous material enriched in deuterium may be present in the package but must not be included in determining the required mass of solid nonfissile material.
(d) Uranium enriched in uranium-235 to a maximum of ((1))one percent by weight, and with total plutonium and uranium-233 content of up to ((1))one percent of the mass of uranium-235, provided that the mass of any beryllium, graphite, and hydrogenous material enriched in deuterium constitutes less than ((5))five percent of the uranium mass, and that the fissile material is distributed homogeneously and does not form a lattice arrangement within the package.
(e) Liquid solutions of uranyl nitrate enriched in uranium-235 to a maximum of ((2))two percent by mass, with a total plutonium and uranium-233 content not exceeding 0.002 percent of the mass of uranium, and with a minimum nitrogen to uranium atomic ratio (N/U) of ((2))two. The material must be contained in at least a DOT Type A package.
(f) Packages containing, individually, a total plutonium mass of not more than 1000 grams, of which not more than 20 percent by mass may consist of plutonium-239, plutonium-241, or any combination of these radionuclides.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 14-09-017, filed 4/7/14, effective 5/8/14)
WAC 246-231-094General license—Fissile material.
(1) A general license is issued to any licensee of the department, NRC, or an agreement state, to transport fissile material, or to deliver fissile material to a carrier for transport, if the material is shipped in accordance with this section. The fissile material need not be contained in a package which meets the standards of 10 C.F.R. 71 Subparts E and F; however, the material must be contained in a Type A package. The Type A package must also meet the DOT requirements of 49 C.F.R. 173.417(a).
(2) The general license applies only to a licensee who has a quality assurance program approved by NRC as satisfying the provisions of 10 C.F.R. 71 Subpart H.
(3) The general license applies only when a package's contents:
(a) Contain no more than a Type A quantity of radioactive material; and
(b) Contain less than 500 total grams of beryllium, graphite, or hydrogenous material enriched in deuterium.
(4) The general license applies only to packages containing fissile material that are labeled with a CSI which:
(a) Has been determined in accordance with subsection (5) of this section;
(b) Has a value less than or equal to 10; and
(c) For a shipment of multiple packages containing fissile material, the sum of the CSIs must be less than or equal to 50 (for shipment on a nonexclusive use conveyance) and less than or equal to 100 (for shipment on an exclusive use conveyance).
(5)(a) The value for the CSI must be greater than or equal to the number calculated by the following equation:
(b) The calculated CSI must be rounded up to the first decimal place;
(c) The values of X, Y, and Z used in the CSI equation must be taken from WAC 246-231-200 Table-1 or Table-2, as appropriate;
(d) If Table-2 is used to obtain the value of X, then the values for the terms in the equation for uranium-233 and plutonium must be assumed to be zero; and
(e) Values from Table-1 for X, Y, and Z must be used to determine the CSI if:
(i) Uranium-233 is present in the package;
(ii) The mass of plutonium exceeds ((1))one percent of the mass of uranium-235;
(iii) The uranium is of unknown uranium-235 enrichment or greater than 24 weight percent enrichment; or
(iv) Substances having a moderating effectiveness (i.e., an average hydrogen density greater than H2O) (e.g., certain hydrocarbon oils or plastics) are present in any form, except as polyethylene used for packing or wrapping.
Table-1.
Mass Limits for General License Packages Containing Mixed Quantities of Fissile Material or Uranium-235 of Unknown Enrichment per WAC 246-231-094(5)
Fissile material | Fissile material mass mixed with moderating substances having an average hydrogen density less than or equal to H2O (grams) | Fissile material mass mixed with moderating substances having an average hydrogen density greater than H2Oa (grams) |
235U (X) | 60 | 38 |
233U (Y) | 43 | 27 |
239Pu or 241Pu (Z) | 37 | 24 |
a | When mixtures of moderating substances are present, the lower mass limits shall be used if more than 15 percent of the moderating substance has an average hydrogen density greater than H2O. |
Table-2.
Mass Limits for General License Packages Containing Uranium-235 of Known Enrichment per WAC 246-231-094(5)
Uranium enrichment in weight percent of 235U not exceeding | Fissile material mass of 235U (X) (grams) |
| 24 | 60 | |
| 20 | 63 | |
| 15 | 67 | |
| 11 | 72 | |
| 10 | 76 | |
| 9.5 | 78 | |
| 9 | 81 | |
| 8.5 | 82 | |
| 8 | 85 | |
| 7.5 | 88 | |
| 7 | 90 | |
| 6.5 | 93 | |
| 6 | 97 | |
| 5.5 | 102 | |
| 5 | 108 | |
| 4.5 | 114 | |
| 4 | 120 | |
| 3.5 | 132 | |
| 3 | 150 | |
| 2.5 | 180 | |
| 2 | 246 | |
| 1.5 | 408 | |
| 1.35 | 480 | |
| 1 | 1,020 | |
| 0.92 | 1,800 | |
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 14-09-017, filed 4/7/14, effective 5/8/14)
WAC 246-231-098External radiation standards for all packages.
(1) Except as provided in subsection (2) of this section, each package of radioactive materials offered for transportation must be designed and prepared for shipment so that under conditions normally incident to transportation the radiation level does not exceed ((2))two mSv/hour (200 mrem/hour) at any point on the external surface of the package, and the transport index does not exceed 10.
(2) A package that exceeds the radiation level limits specified in subsection (1) of this section must be transported by exclusive use shipment only, and the radiation levels for such shipment must not exceed the following during transportation:
(a) ((2))Two mSv/hour (200 mrem/hour) on the external surface of the package, unless the following conditions are met, in which case the limit is 10 mSv/hour (1000 mrem/hour):
(i) The shipment is made in a closed transport vehicle;
(ii) The package is secured within the vehicle so that its position remains fixed during transportation; and
(iii) There are no loading or unloading operations between the beginning and end of the transportation;
(b) ((2))Two mSv/hour (200 mrem/hour) at any point on the outer surface of the vehicle, including the top and underside of the vehicle; or in the case of a flat-bed style vehicle, at any point on the vertical planes projected from the outer edges of the vehicle, on the upper surface of the load or enclosure, if used, and on the lower external surface of the vehicle; and
(c) 0.1 mSv/hour (10 mrem/hour) at any point ((2))two meters (80 in) from the outer lateral surfaces of the vehicle (excluding the top and underside of the vehicle); or in the case of a flat-bed style vehicle, at any point ((2))two meters (6.6 feet) from the vertical planes projected by the outer edges of the vehicle (excluding the top and underside of the vehicle); and
(d) 0.02 mSv/hour (((2))two mrem/hour) in any normally occupied space, except that this provision does not apply to private carriers, if exposed personnel under their control wear radiation dosimetry devices in conformance with WAC 246-221-090 and 246-221-100.
(3) For shipments made under the provisions of subsection (2) of this section, the shipper shall provide specific written instructions to the carrier for maintenance of the exclusive use shipment controls. The instructions must be included with the shipping paper information.
(4) The written instructions required for exclusive use shipments must be sufficient so that, when followed, they will cause the carrier to avoid actions that will unnecessarily delay delivery or unnecessarily result in increased radiation levels or radiation exposures to transport workers or members of the general public.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-01-034, filed 12/12/16, effective 1/12/17)
WAC 246-231-106Preliminary determinations.
Before the first use of any packaging for the shipment of licensed material:
(1) The licensee shall ascertain that there are no cracks, pinholes, uncontrolled voids, or other defects that could significantly reduce the effectiveness of the packaging;
(2) Where the maximum normal operating pressure will exceed 35 kPa (((5))five lbs/in2) gauge, the licensee shall test the containment system at an internal pressure at least ((fifty))50 percent higher than the maximum normal operating pressure, to verify the capability of that system to maintain its structural integrity at that pressure;
(3) The licensee shall conspicuously and durably mark the packaging with its model number, serial number, gross weight, and a package identification number assigned by NRC. Before applying the model number, the licensee shall determine that the packaging has been fabricated in accordance with the design approved by NRC; and
(4) The licensee shall ascertain that the determinations in subsections (1) through (3) of this section have been made.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-11-063, filed 5/16/22, effective 6/16/22)
WAC 246-231-140Advance notification of shipment of irradiated reactor fuel and nuclear waste.
(1)(a) As specified in subsections (2), (3), and (4) of this section, each licensee shall provide advance notification to the governor of a state, or the governor's designee, of the shipment of licensed material, within or across the boundary of the state, before the transport, or delivery to a carrier, for transport, of licensed material outside the confines of the licensee's plant or other place of use or storage.
(b) As specified in subsections (2), (3), and (4) of this section, after June 11, 2013, each licensee shall provide advance notification to the Tribal official of participating tribes referenced in subsection (3)(c)(iii) of this section, or the official's designee, of the shipment of licensed material within or across the boundary of the Tribe's reservation before the transport, or delivery to a carrier for transport, of licensed material outside the confines of the licensee's plant or other place of use or storage.
(2) Advance notification is required under this section for shipments of irradiated reactor fuel in quantities less than that subject to advance notification requirements of NRC regulations 10 C.F.R. 73.37(f). Advance notification is also required under this section for shipment of licensed material, other than irradiated fuel, meeting the following three conditions:
(a) The licensed material is required by this section to be in Type B packaging for transportation;
(b) The licensed material is being transported to or across a state boundary ((en route))enroute to a disposal facility or to a collection point for transport to a disposal facility; and
(c) The quantity of licensed material in a single package exceeds the least of the following:
(i) Three thousand times the A1 value of the radionuclides as specified in WAC 246-231-200, Table A-1 for special form radioactive material;
(ii) Three thousand times the A2 value of the radionuclides as specified in WAC 246-231-200, Table A-1 for normal form radioactive material; or
(iii) One thousand TBq (27,000 Ci).
(3) Procedures for submitting advance notification.
(a) The notification must be made in writing to the office of each appropriate governor or governor's designee, to the office of each appropriate Tribal official or Tribal official's designee, and to the Director, Office of Nuclear Security and Incident Response.
(b) A notification delivered by mail must be postmarked at least seven days before the beginning of the seven-day period during which departure of the shipment is estimated to occur.
(c) A notification delivered by any other means than mail must reach the office of the governor or the governor's designee, or of the Tribal official or the Tribal official's designee, at least four days before the beginning of the seven-day period during which departure of the shipment is estimated to occur.
(i) ((A list of the names and mailing addresses of the governors' designees receiving advance notification of transportation of nuclear waste was published in the Federal Register on June 30, 1995, (60 FR 34306).))Reserved.
(ii) Contact information for each state, including telephone and mailing addresses of governors and governors' designees, and participating Tribes, including telephone and mailing addresses of Tribal officials and Tribal official's designees, is available on the NRC website at https://scp.nrc.gov/special/designee.pdf.
(iii) A list of the names and mailing addresses of the governors' designees and Tribal officials' designees of participating Tribes is available on request from the Director, Division of Materials Safety, Security, State, and Tribal Programs, Office of Nuclear Material Safety and Safeguards, U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Washington, D.C. 20555-0001.
(d) The licensee shall retain a copy of the notification as a record for three years.
(4) Information to be furnished in advance notification of shipment. Each advance notification of shipment of irradiated reactor fuel or nuclear waste must contain the following information:
(a) The name, address, and telephone number of the shipper, carrier, and receiver of the irradiated reactor fuel or nuclear waste shipment;
(b) A description of the irradiated reactor fuel or nuclear waste contained in the shipment, as specified in the regulations of DOT in 49 C.F.R. 172.202 and 172.203(d);
(c) The point of origin of the shipment and the seven-day period during which departure of the shipment is estimated to occur;
(d) The seven-day period during which arrival of the shipment at state boundaries or Tribal reservation boundaries is estimated to occur;
(e) The destination of the shipment, and the seven-day period during which arrival of the shipment is estimated to occur; and
(f) A point of contact, with a telephone number, for current shipment information.
(5) Revision notice. A licensee who finds that schedule information previously furnished to a governor or governor's designee, or a Tribal official or Tribal official's designee, in accordance with this section, will not be met, shall telephone a responsible individual in the office of the governor of the state or of the governor's designee or the Tribal official or the Tribal official's designee, and inform that individual of the extent of the delay beyond the schedule originally reported. The licensee shall maintain a record of the name of the individual contacted for three years.
(6) Cancellation notice.
(a) Each licensee who cancels an irradiated reactor fuel or nuclear waste shipment for which advance notification has been sent shall send a cancellation notice to the governor of each state or to the governor's designee previously notified, to each Tribal official or to the Tribal official's designee previously notified, and to the Director, Office of Nuclear Security and Incident Response.
(b) The licensee shall state in the notice that it is a cancellation and identify the advance notification that is being canceled. The licensee shall retain a copy of the notice as a record for three years.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-01-034, filed 12/12/16, effective 1/12/17)
WAC 246-231-174Changes to quality assurance program.
(1) Each quality assurance program approval holder shall submit, in accordance with 10 C.F.R. 71.1(a), a description of a proposed change to its NRC-approved quality assurance program that will reduce commitments in the program description as approved by the NRC. The quality assurance program approval holder shall not implement the change before receiving NRC approval.
(a) The description of a proposed change to the NRC-approved quality assurance program must identify the change, the reason for the change, the basis for concluding that the revised program incorporating the change continues to satisfy the applicable requirements of 10 C.F.R. Subpart H.
(b) (Reserved.)
(2) Each quality assurance program approval holder may change a previously approved quality assurance program without prior NRC approval, if the change does not reduce the commitments in the quality assurance program previously approved by the NRC. Changes to the quality assurance program that do not reduce the commitments shall be submitted to the NRC every ((twenty-four))24 months, in accordance with 10 C.F.R. 71.1(a). In addition to quality assurance program changes involving administrative improvements and clarifications, spelling corrections, and nonsubstantive changes to punctuation or editorial items, the following changes are not considered reductions in commitment:
(a) The use of a quality assurance standard approved by the NRC that is more recent than the quality assurance standard in the certificate holder's or applicant's current quality assurance program at the time of the change;
(b) The use of generic organizational position titles that clearly denote the position function, supplemented as necessary by descriptive text, rather than specific titles, provided that there is no substantive change to either the functions of the position or reporting responsibilities;
(c) The use of generic organization charts to indicate functional relationships, authorities, and responsibilities, or alternatively, the use of descriptive text, provided that there is no substantive change to the functional relationships, authorities, or responsibilities;
(d) The elimination of quality assurance program information that duplicates language in quality assurance regulatory guides and quality assurance standards to which the quality assurance program approval holder has committed to on record; and
(e) Organizational revisions that ensure that persons and organizations performing quality assurance functions continue to have the requisite authority and organizational freedom, including sufficient independence from cost and schedule when opposed to safety considerations.
(3) Each quality assurance program approval holder shall maintain records of quality assurance program changes.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-01-034, filed 12/12/16, effective 1/12/17)
WAC 246-231-200Appendix A—Determination of A1 and A2.
(1) Values of A1 and A2 for individual radionuclides, which are the basis for many activity limits elsewhere in these regulations, are given in this section, Table A-1. The curie (Ci) values specified are obtained by converting from the Terabecquerel (TBq) value. The Terabecquerel values are the regulatory standard. The curie values are for information only and are not intended to be the regulatory standard. Where values of A1 or A2 are unlimited, it is for radiation control purposes only. For nuclear criticality safety, some materials are subject to controls placed on fissile material.
(2)(a) For individual radionuclides whose identities are known, but which are not listed in this section, Table A-1, the A1 and A2 values contained in this section, Table A-3 may be used. Otherwise, the licensee shall obtain prior NRC approval of the A1 and A2 values for radionuclides not listed in this section, Table A-1, before shipping the material.
(b) For individual radionuclides whose identities are known, but which are not listed in this section, Table A-2, the exempt material activity concentration and exempt consignment activity values contained in this section, Table A-3 may be used. Otherwise, the licensee shall obtain prior NRC approval of the exempt material activity concentration and exempt consignment activity values for radionuclides not listed in this section, Table A-2, before shipping the material.
(c) The licensee shall submit requests for prior approval, described under (a) and (b) of this subsection, to NRC in accordance with 10 C.F.R. 71.1.
(3) In the calculations of A1 and A2 for a radionuclide not in this section, Table A-1, a single radioactive decay chain, in which radionuclides are present in their naturally occurring proportions, and in which no daughter radionuclide has a half-life either longer than ((ten))10 days, or longer than that of the parent radionuclide, shall be considered as a single radionuclide, and the activity to be taken into account, and the A1 or A2 value to be applied shall be those corresponding to the parent radionuclide of that chain. In the case of radioactive decay chains in which any daughter radionuclide has a half-life either longer than ((ten))10 days, or greater than that of the parent radionuclide, the parent and those daughter radionuclides shall be considered as mixtures of different radionuclides.
(4) For mixtures of radionuclides whose identities and respective activities are known, the following conditions apply:
(a) For special form radioactive material, the maximum quantity transported in a Type A package is as follows:
Where B(i) is the activity of radionuclide i in special form, and A1(i) is the A1 value for radionuclide i.
(b) For normal form radioactive material, the maximum quantity transported in a Type A package:
Where B(i) is the activity of radionuclide i in normal form, and A2(i) is the A2 value for radionuclide i.
(c) If the package contains both special and normal form radioactive material, the activity that may be transported in a Type A package is as follows:
Where B(i) is the activity of radionuclide i as special form radioactive material, A1(i) is the A1 value for radionuclide i, C(j) is the activity of radionuclide j as normal form radioactive material, and A2(j) is the A2 value for radionuclide j.
(d) Alternatively, the A1 value for mixtures of special form material may be determined as follows:
Where f(i) is the fraction of activity for radionuclide i in the mixture and A1(i) is the appropriate A1 value for radionuclide i.
(e) Alternatively, the A2 value for mixtures of normal form material may be determined as follows:
Where f(i) is the fraction of activity for radionuclide i in the mixture and A2(i) is the appropriate A2 value for radionuclide i.
(f) The exempt activity concentration for mixtures of nuclides may be determined as follows:
Where f(i) is the fraction of activity concentration of radionuclide i in the mixture, and [A](i) is the activity concentration for exempt material containing radionuclide i.
(g) The activity limit for an exempt consignment for mixtures of radionuclides may be determined as follows:
Where f(i) is the fraction of activity of radionuclide i in the mixture and A(i) is the activity limit for exempt consignments for radionuclide i.
(5)(a) When the identity of each radionuclide is known, but the individual activities of some of the radionuclides are not known, the radionuclides may be grouped and the lowest A1 or A2 value, as appropriate, for the radionuclides in each group may be used in applying the formulas in subsection (4) of this section. Groups may be based on the total alpha activity and the total beta/gamma activity when these are known, using the lowest A1 or A2 values for the alpha emitters and beta/gamma emitters.
(b) When the identity of each radionuclide is known but the individual activities of some of the radionuclides are not known, the radionuclides may be grouped and the lowest [A] (activity concentration for exempt material) or A (activity limit for exempt consignment) value, as appropriate, for the radionuclides in each group may be used in applying the formulas in paragraph IV of this appendix. Groups may be based on the total alpha activity and the total beta/gamma activity when these are known, using the lowest [A] or A values for the alpha emitters and beta/gamma emitters, respectively.
Table A-1.—A1 and A2 Values for Radionuclides
Symbol of radionuclide | Element and atomic number | A1 (TBq) | A1 (Ci)b | A2 (TBq) | A2 (Ci)b | Specific activity |
(TBq/g) | (Ci/g) |
Ac-225 (a) | Actinium (89) | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 6.0X10-3 | 1.6X10-1 | 2.1X103 | 5.8X104 |
Ac-227 (a) | | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 9.0X10-5 | 2.4X10-3 | 2.7 | 7.2X101 |
Ac-228 | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 8.4X104 | 2.2X106 |
Ag-105 | Silver (47) | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0X104 |
Ag-108m (a) | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 9.7X10-1 | 2.6X101 |
Ag-110m (a) | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.8X102 | 4.7X103 |
Ag-111 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 5.8X103 | 1.6X105 |
Al-26 | Aluminum (13) | 1.0X10-1 | 2.7 | 1.0X10-1 | 2.7 | 7.0X10-4 | 1.9X10-2 |
Am-241 | Americium (95) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 1.3X10-1 | 3.4 |
Am-242m (a) | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 3.6X10-1 | 1.0X101 |
Am-243 (a) | | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 7.4X10-3 | 2.0X10-1 |
Ar-37 | Argon (18) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.7X103 | 9.9X104 |
Ar-39 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 1.3 | 3.4X101 |
Ar-41 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 1.5X106 | 4.2X107 |
As-72 | Arsenic (33) | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 6.2X104 | 1.7X106 |
As-73 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 8.2X102 | 2.2X104 |
As-74 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 3.7X103 | 9.9X104 |
As-76 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 5.8X104 | 1.6X106 |
As-77 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 3.9X104 | 1.0X106 |
At-211 (a) | Astatine (85) | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 7.6X104 | 2.1X106 |
Au-193 | Gold (79) | 7.0 | 1.9X102 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 3.4X104 | 9.2X105 |
Au-194 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.5X104 | 4.1X105 |
Au-195 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 6.0 | 1.6X102 | 1.4X102 | 3.7X103 |
Au-198 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 9.0X103 | 2.4X105 |
Au-199 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 7.7X103 | 2.1X105 |
Ba-131 (a) | Barium (56) | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 3.1X103 | 8.4X104 |
Ba-133 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 9.4 | 2.6X102 |
Ba-133m | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.2X104 | 6.1X105 |
Ba-140 (a) | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 2.7X103 | 7.3X104 |
Be-7 | Beryllium (4) | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 1.3X104 | 3.5X105 |
Be-10 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 8.3X10-4 | 2.2X10-2 |
Bi-205 | Bismuth (83) | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 1.5X103 | 4.2X104 |
Bi-206 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.8X103 | 1.0X105 |
Bi-207 | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 1.9 | 5.2X101 |
Bi-210 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 4.6X103 | 1.2X105 |
Bi-210m (a) | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 2.1X10-5 | 5.7X10-4 |
Bi-212 (a) | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 5.4X105 | 1.5X107 |
Bk-247 | Berkelium (97) | 8.0 | 2.2X102 | 8.0X10-4 | 2.2X10-2 | 3.8X10-2 | 1.0 |
Bk-249 (a) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 6.1X101 | 1.6X103 |
Br-76 | Bromine (35) | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 9.4X104 | 2.5X106 |
Br-77 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 2.6X104 | 7.1X105 |
Br-82 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X104 | 1.1X106 |
C-11 | Carbon (6) | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.1X107 | 8.4X108 |
C-14 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 1.6X10-1 | 4.5 |
Ca-41 | Calcium (20) | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 3.1X10-3 | 8.5X10-2 |
Ca-45 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.6X102 | 1.8X104 |
Ca-47 (a) | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 2.3X104 | 6.1X105 |
Cd-109 | Cadmium (48) | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 9.6X101 | 2.6X103 |
Cd-113m | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 8.3 | 2.2X102 |
Cd-115 (a) | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.9X104 | 5.1X105 |
Cd-115m | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 9.4X102 | 2.5X104 |
Ce-139 | Cerium (58) | 7.0 | 1.9X102 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.5X102 | 6.8X103 |
Ce-141 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.8X104 |
Ce-143 | | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.5X104 | 6.6X105 |
Ce-144 (a) | | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 1.2X102 | 3.2X103 |
Cf-248 | Californium (98) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 6.0X10-3 | 1.6X10-1 | 5.8X101 | 1.6X103 |
Cf-249 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 8.0X10-4 | 2.2X10-2 | 1.5X10-1 | 4.1 |
Cf-250 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.0X10-3 | 5.4X10-2 | 4.0 | 1.1X102 |
Cf-251 | | 7.0 | 1.9X102 | 7.0X10-4 | 1.9X10-2 | 5.9X10-2 | 1.6 |
Cf-252 | | 1.0X10-1 | 2.7 | 3.0X10-3 | 8.1X10-2 | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 |
Cf-253 (a) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X10-2 | 1.1 | 1.1X103 | 2.9X104 |
Cf-254 | | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 3.1X102 | 8.5X103 |
Cl-36 | Chlorine (17) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.2X10-3 | 3.3X10-2 |
Cl-38 | | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 4.9X106 | 1.3X108 |
Cm-240 | Curium (96) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 7.5X102 | 2.0X104 |
Cm-241 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.1X102 | 1.7X104 |
Cm-242 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.0X10-2 | 2.7X10-1 | 1.2X102 | 3.3X103 |
Cm-243 | | 9.0 | 2.4X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 1.9X10-3 | 5.2X101 |
Cm-244 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.0X10-3 | 5.4X10-2 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 |
Cm-245 | | 9.0 | 2.4X102 | 9.0X10-4 | 2.4X10-2 | 6.4X10-3 | 1.7X10-1 |
Cm-246 | | 9.0 | 2.4X102 | 9.0X10-4 | 2.4X10-2 | 1.1X10-2 | 3.1X10-1 |
Cm-247 (a) | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 3.4X10-6 | 9.3X10-5 |
Cm-248 | | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 3.0X10-4 | 8.1X10-3 | 1.6X10-4 | 4.2X10-3 |
Co-55 | Cobalt (27) | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 1.1X105 | 3.1X106 |
Co-56 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 1.1X103 | 3.0X104 |
Co-57 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 3.1X102 | 8.4X103 |
Co-58 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.2X103 | 3.2X104 |
Co-58m | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.2X105 | 5.9X106 |
Co-60 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.2X101 | 1.1X103 |
Cr-51 | Chromium (24) | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 3.4X103 | 9.2X104 |
Cs-129 | Cesium (55) | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 2.8X104 | 7.6X105 |
Cs-131 | | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 3.8X103 | 1.0X105 |
Cs-132 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 5.7X103 | 1.5X105 |
Cs-134 | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 4.8X101 | 1.3X103 |
Cs-134m | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.0X105 | 8.0X106 |
Cs-135 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 4.3X10-5 | 1.2X10-3 |
Cs-136 | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 2.7X103 | 7.3X104 |
Cs-137 (a) | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.2 | 8.7X101 |
Cu-64 | Copper (29) | 6.0 | 1.6X102 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.4X105 | 3.9X106 |
Cu-67 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 2.8X104 | 7.6X105 |
Dy-159 | Dysprosium (66) | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.1X102 | 5.7X103 |
Dy-165 | | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.0X105 | 8.2X106 |
Dy-166 (a) | | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 8.6X103 | 2.3X105 |
Er-169 | Erbium (68) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 3.1X103 | 8.3X104 |
Er-171 | | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 9.0X104 | 2.4X106 |
Eu-147 | Europium (63) | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 1.4X103 | 3.7X104 |
Eu-148 | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 6.0X102 | 1.6X104 |
Eu-149 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 3.5X102 | 9.4X103 |
Eu-150 (short lived) | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 6.1X104 | 1.6X106 |
Eu-150 (long lived) | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 6.1X104 | 1.6X106 |
Eu-152 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.5 | 1.8X102 |
Eu-152m | | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 8.2X104 | 2.2X106 |
Eu-154 | | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 9.8 | 2.6X102 |
Eu-155 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 1.8X101 | 4.9X102 |
Eu-156 | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 2.0X103 | 5.5X104 |
F-18 | Fluorine (9) | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.5X106 | 9.5X107 |
Fe-52 (a) | Iron (26) | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 2.7X105 | 7.3X106 |
Fe-55 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 8.8X101 | 2.4X103 |
Fe-59 | | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 1.8X103 | 5.0X104 |
Fe-60 (a) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 7.4X10-4 | 2.0X10-2 |
Ga-67 | Gallium (31) | 7.0 | 1.9X102 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 2.2X104 | 6.0X105 |
Ga-68 | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 1.5X106 | 4.1X107 |
Ga-72 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.1X105 | 3.1X106 |
Gd-146 (a) | Gadolinium (64) | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 6.9X102 | 1.9X104 |
Gd-148 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.0X10-3 | 5.4X10-2 | 1.2 | 3.2X101 |
Gd-153 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 9.0 | 2.4X102 | 1.3X102 | 3.5X103 |
Gd-159 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.9X104 | 1.1X106 |
Ge-68 (a) | Germanium (32) | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 2.6X102 | 7.1X103 |
Ge-71 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 5.8X103 | 1.6X105 |
Ge-77 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 1.3X105 | 3.6X106 |
Hf-172 (a) | Hafnium (72) | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 4.1X101 | 1.1X103 |
Hf-175 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.9X102 | 1.1X104 |
Hf-181 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 6.3X102 | 1.7X104 |
Hf-182 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 8.1X10-6 | 2.2X10-4 |
Hg-194 (a) | Mercury (80) | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.3X10-1 | 3.5 |
Hg-195m (a) | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 1.5X104 | 4.0X105 |
Hg-197 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 9.2X103 | 2.5X105 |
Hg-197m | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 2.5X104 | 6.7X105 |
Hg-203 | | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 5.1X102 | 1.4X104 |
Ho-166 | Holmium (67) | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 2.6X104 | 7.0X105 |
Ho-166m | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 6.6X10-2 | 1.8 |
I-123 | Iodine (53) | 6.0 | 1.6X102 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 7.1X104 | 1.9X106 |
I-124 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 9.3X103 | 2.5X105 |
I-125 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 6.4X102 | 1.7X104 |
I-126 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 2.9X103 | 8.0X104 |
I-129 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 6.5X10-6 | 1.8X10-4 |
I-131 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 4.6X103 | 1.2X105 |
I-132 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 3.8X105 | 1.0X107 |
I-133 | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 4.2X104 | 1.1X106 |
I-134 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 9.9X105 | 2.7X107 |
I-135 (a) | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.3X105 | 3.5X106 |
In-111 | Indium (49) | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 1.5X104 | 4.2X105 |
In-113m | | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 6.2X105 | 1.7X107 |
In-114m (a) | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 8.6X102 | 2.3X104 |
In-115m | | 7.0 | 1.9X102 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 2.2X105 | 6.1X106 |
Ir-189 (a) | Iridium (77) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.9X103 | 5.2X104 |
Ir-190 | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 2.3X103 | 6.2X104 |
Ir-192 | | c1.0 | c2.7X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.4X102 | 9.2X103 |
Ir-194 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.1X104 | 8.4X105 |
K-40 | Potassium (19) | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 2.4X10-7 | 6.4X10-6 |
K-42 | | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.2X105 | 6.0X106 |
K-43 | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.2X105 | 3.3X106 |
Kr-79 | Krypton (36) | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 4.2X104 | 1.1X106 |
Kr-81 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 7.8X10-4 | 2.1X10-2 |
Kr-85 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.5X101 | 3.9X102 |
Kr-85m | | 8.0 | 2.2X102 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0X105 | 8.2X106 |
Kr-87 | | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 1.0X106 | 2.8X107 |
La-137 | Lanthanum (57) | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 6.0 | 1.6X102 | 1.6X10-3 | 4.4X10-2 |
La-140 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 2.1X104 | 5.6X105 |
Lu-172 | Lutetium (71) | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 4.2X103 | 1.1X105 |
Lu-173 | | 8.0 | 2.2X102 | 8.0 | 2.2X102 | 5.6X101 | 1.5X103 |
Lu-174 | | 9.0 | 2.4X102 | 9.0 | 2.4X102 | 2.3X101 | 6.2X102 |
Lu-174m | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 2.0X102 | 5.3X103 |
Lu-177 | | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 4.1X103 | 1.1X105 |
Mg-28 (a) | Magnesium (12) | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 2.0X105 | 5.4X106 |
Mn-52 | Manganese (25) | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 1.6X104 | 4.4X105 |
Mn-53 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 6.8X10-5 | 1.8X10-3 |
Mn-54 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 2.9X102 | 7.7X103 |
Mn-56 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 8.0X105 | 2.2X107 |
Mo-93 | Molybdenum (42) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 4.1X10-2 | 1.1 |
Mo-99 (a) (h) | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.8X104 | 4.8X105 |
N-13 | Nitrogen (7) | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 5.4X107 | 1.5X109 |
Na-22 | Sodium (11) | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 2.3X102 | 6.3X103 |
Na-24 | | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 3.2X105 | 8.7X106 |
Nb-93m | Niobium (41) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 8.8 | 2.4X102 |
Nb-94 | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 6.9X10-3 | 1.9X10-1 |
Nb-95 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.5X103 | 3.9X104 |
Nb-97 | | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 9.9X105 | 2.7X107 |
Nd-147 | Neodymium (60) | 6.0 | 1.6X102 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.0X103 | 8.1X104 |
Nd-149 | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 4.5X105 | 1.2X107 |
Ni-59 | Nickel (28) | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 3.0X10-3 | 8.0X10-2 |
Ni-63 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 2.1 | 5.7X101 |
Ni-65 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 7.1X105 | 1.9X107 |
Np-235 | Neptunium (93) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 5.2X101 | 1.4X103 |
Np-236 (short-lived) | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 4.7X10-4 | 1.3X10-2 |
Np-236 (long-lived) | | 9.0 | 2.4X102 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 4.7X10-4 | 1.3X10-2 |
Np-237 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.0X10-3 | 5.4X10-2 | 2.6X10-5 | 7.1X10-4 |
Np-239 | | 7.0 | 1.9X102 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 8.6X103 | 2.3X105 |
Os-185 | Osmium (76) | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 2.8X102 | 7.5X103 |
Os-191 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 1.6X103 | 4.4X104 |
Os-191m | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 4.6X104 | 1.3X106 |
Os-193 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | b2.0X104 | 5.3X105 |
Os-194 (a) | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 1.1X101 | 3.1X102 |
P-32 | Phosphorus (15) | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 1.1X104 | 2.9X105 |
P-33 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 5.8X103 | 1.6X105 |
Pa-230 (a) | Protactinium (91) | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 7.0X10-2 | 1.9 | 1.2X103 | 3.3X104 |
Pa-231 | | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 4.0X10-4 | 1.1X10-2 | 1.7X10-3 | 4.7X10-2 |
Pa-233 | | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.7X102 | 2.1X104 |
Pb-201 | Lead (82) | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.2X104 | 1.7X106 |
Pb-202 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 1.2X10-4 | 3.4X10-3 |
Pb-203 | | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 1.1X104 | 3.0X105 |
Pb-205 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 4.5X10-6 | 1.2X10-4 |
Pb-210 (a) | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 5.0X10-2 | 1.4 | 2.8 | 7.6X101 |
Pb-212 (a) | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 5.1X104 | 1.4X106 |
Pd-103 (a) | Palladium (46) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.8X103 | 7.5X104 |
Pd-107 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 1.9X10-5 | 5.1X10-4 |
Pd-109 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 7.9X104 | 2.1X106 |
Pm-143 | Promethium (61) | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 1.3X102 | 3.4X103 |
Pm-144 | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 9.2X101 | 2.5X103 |
Pm-145 | | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 5.2 | 1.4X102 |
Pm-147 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 3.4X101 | 9.3X102 |
Pm-148m (a) | | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 7.9X102 | 2.1X104 |
Pm-149 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.5X104 | 4.0X105 |
Pm-151 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.7X104 | 7.3X105 |
Po-210 | Polonium (84) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 1.7X102 | 4.5X103 |
Pr-142 | Praseodymium (59) | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.3X104 | 1.2X106 |
Pr-143 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.5X103 | 6.7X104 |
Pt-188 (a) | Platinum (78) | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 2.5X103 | 6.8X104 |
Pt-191 | | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 8.7X103 | 2.4X105 |
Pt-193 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.4 | 3.7X101 |
Pt-193m | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.8X103 | 1.6X105 |
Pt-195m | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 6.2X103 | 1.7X105 |
Pt-197 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.2X104 | 8.7X105 |
Pt-197m | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.7X105 | 1.0X107 |
Pu-236 | Plutonium (94) | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 3.0X10-3 | 8.1X10-2 | 2.0X101 | 5.3X102 |
Pu-237 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 4.5X102 | 1.2X104 |
Pu-238 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 6.3X10-1 | 1.7X101 |
Pu-239 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 2.3X10-3 | 6.2X10-2 |
Pu-240 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 8.4X10-3 | 2.3X10-1 |
Pu-241 (a) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 6.0X10-2 | 1.6 | 3.8 | 1.0X102 |
Pu-242 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 1.5X10-4 | 3.9X10-3 |
Pu-244 (a) | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 6.7X10-7 | 1.8X10-5 |
Ra-223 (a) | Radium (88) | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 7.0X10-3 | 1.9X10-1 | 1.9X103 | 5.1X104 |
Ra-224 (a) | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 5.9X103 | 1.6X105 |
Ra-225 (a) | | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 4.0X10-3 | 1.1X10-1 | 1.5X103 | 3.9X104 |
Ra-226 (a) | | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 3.0X10-3 | 8.1X10-2 | 3.7X10-2 | 1.0 |
Ra-228 (a) | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 |
Rb-81 | Rubidium (37) | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 3.1X105 | 8.4X106 |
Rb-83 (a) | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 6.8X102 | 1.8X104 |
Rb-84 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.8X103 | 4.7X104 |
Rb-86 | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 3.0X103 | 8.1X104 |
Rb-87 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 3.2X10-9 | 8.6X10-8 |
Rb (nat) | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 6.7X106 | 1.8X108 |
Re-184 | Rhenium (75) | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.9X102 | 1.9X104 |
Re-184m | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.6X102 | 4.3X103 |
Re-186 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 6.9X103 | 1.9X105 |
Re-187 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 1.4X10-9 | 3.8X10-8 |
Re-188 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 3.6X104 | 9.8X105 |
Re-189 (a) | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.5X104 | 6.8X105 |
Re (nat) | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 0.0 | 2.4X10-8 |
Rh-99 | Rhodium (45) | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 3.0X103 | 8.2X104 |
Rh-101 | | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 4.1X101 | 1.1X103 |
Rh-102 | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 4.5X101 | 1.2X103 |
Rh-102m | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.3X102 | 6.2X103 |
Rh-103m | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.2X106 | 3.3X107 |
Rh-105 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 3.1X104 | 8.4X105 |
Rn-222 (a) | Radon (86) | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 4.0X10-3 | 1.1X10-1 | 5.7X103 | 1.5X105 |
Ru-97 | Ruthenium (44) | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 1.7X104 | 4.6X105 |
Ru-103 (a) | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 1.2X103 | 3.2X104 |
Ru-105 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.5X105 | 6.7X106 |
Ru-106 (a) | | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 1.2X102 | 3.3X103 |
S-35 | Sulphur (16) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 1.6X103 | 4.3X104 |
Sb-122 | Antimony (51) | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.5X104 | 4.0X105 |
Sb-124 | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 6.5X102 | 1.7X104 |
Sb-125 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 3.9X101 | 1.0X103 |
Sb-126 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 3.1X103 | 8.4X104 |
Sc-44 | Scandium (21) | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 6.7X105 | 1.8X107 |
Sc-46 | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 1.3X103 | 3.4X104 |
Sc-47 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 3.1X104 | 8.3X105 |
Sc-48 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 5.5X104 | 1.5X106 |
Se-75 | Selenium (34) | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 5.4X102 | 1.5X104 |
Se-79 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.6X10-3 | 7.0X10-2 |
Si-31 | Silicon (14) | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.4X106 | 3.9X107 |
Si-32 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 3.9 | 1.1X102 |
Sm-145 | Samarium (62) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 9.8X101 | 2.6X103 |
Sm-147 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | ((8.5X10-1))8.5X10-10 | 2.3X10-8 |
Sm-151 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 9.7X10-1 | 2.6X101 |
Sm-153 | | 9.0 | 2.4X102 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.6X104 | 4.4X105 |
Sn-113 (a) | Tin (50) | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 3.7X102 | 1.0X104 |
Sn-117m | | 7.0 | 1.9X102 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 3.0X103 | 8.2X104 |
Sn-119m | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 1.4X102 | 3.7X103 |
Sn-121m (a) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 |
Sn-123 | | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 3.0X102 | 8.2X103 |
Sn-125 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X103 | 1.1X105 |
Sn-126 (a) | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.8X10-2 |
Sr-82 (a) | Strontium (38) | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.3X103 | 6.2X104 |
Sr-85 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 8.8X102 | 2.4X104 |
Sr-85m | | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 1.2X106 | 3.3X107 |
Sr-87m | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 4.8X105 | 1.3X107 |
Sr-89 | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.9X104 |
Sr-90 (a) | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 5.1 | 1.4X102 |
Sr-91 (a) | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 1.3X105 | 3.6X106 |
Sr-92 (a) | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 4.7X105 | 1.3X107 |
T(H-3) | Tritium (1) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.6X102 | 9.7X103 |
Ta-178 (long-lived) | Tantalum (73) | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 4.2X106 | 1.1X108 |
Ta-179 | | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 4.1X101 | 1.1X103 |
Ta-182 | | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 2.3X102 | 6.2X103 |
Tb-157 | Terbium (65) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 5.6X10-1 | 1.5X101 |
Tb-158 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 5.6X10-1 | 1.5X101 |
Tb-160 | | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 4.2X102 | 1.1X104 |
Tc-95m (a) | Technetium (43) | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 8.3X102 | 2.2X104 |
Tc-96 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.2X104 | 3.2X105 |
Tc-96m (a) | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.4X106 | 3.8X107 |
Tc-97 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 5.2X10-5 | 1.4X10-3 |
Tc-97m | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 5.6X102 | 1.5X104 |
Tc-98 | | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 3.2X10-5 | 8.7X10-4 |
Tc-99 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 6.3X10-4 | 1.7X10-2 |
Tc-99m | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 1.9X105 | 5.3X106 |
Te-121 | Tellurium (52) | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.4X103 | 6.4X104 |
Te-121m | | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 2.6X102 | 7.0X103 |
Te-123m | | 8.0 | 2.2X102 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 3.3X102 | 8.9X103 |
Te-125m | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 6.7X102 | 1.8X104 |
Te-127 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 9.8X104 | 2.6X106 |
Te-127m (a) | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 3.5X102 | 9.4X103 |
Te-129 | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 7.7X105 | 2.1X107 |
Te-129m (a) | | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0X104 |
Te-131m (a) | | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 3.0X104 | 8.0X105 |
Te-132 (a) | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 1.1X104 | 3.0X105 |
Th-227 | Thorium (90) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 5.0X10-3 | 1.4X10-1 | 1.1X103 | 3.1X104 |
Th-228 (a) | | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 3.0X101 | 8.2X102 |
Th-229 | | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 5.0X10-4 | 1.4X10-2 | 7.9X10-3 | 2.1X10-1 |
Th-230 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 7.6X10-4 | 2.1X10-2 |
Th-231 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 2.0X104 | 5.3X105 |
Th-232 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 4.0X10-9 | 1.1X10-7 |
Th-234 (a) | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 8.6X102 | 2.3X104 |
Th(nat) | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 8.1X10-9 | 2.2X10-7 |
Ti-44 (a) | Titanium (22) | 5.0X10-1 | 1.4X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 6.4 | 1.7X102 |
Tl-200 | Thallium (81) | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 2.2X104 | 6.0X105 |
Tl-201 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 7.9X103 | 2.1X105 |
Tl-202 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0X103 | 5.3X104 |
Tl-204 | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 1.7X101 | 4.6X102 |
Tm-167 | Thulium (69) | 7.0 | 1.9X102 | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 3.1X103 | 8.5X104 |
Tm-170 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.2X102 | 6.0X103 |
Tm-171 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 |
U-230 (fast lung absorption) (a)(d) | Uranium (92) | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.0X10-1 | 2.7 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X104 |
U-230 (medium lung absorption) (a)(e) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X10-3 | 1.1X10-1 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X104 |
U-230 (slow lung absorption) (a)(f) | | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 3.0X10-3 | 8.1X10-2 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X104 |
U-232 (fast lung absorption) (d) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 1.0X10-2 | 2.7X10-1 | 8.3X10-1 | 2.2X101 |
U-232 (medium lung absorption) (e) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 7.0X10-3 | 1.9X10-1 | 8.3X10-1 | 2.2X101 |
U-232 (slow lung absorption) (f) | | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 1.0X10-3 | 2.7X10-2 | 8.3X10-1 | 2.2X101 |
U-233 (fast lung absorption) (d) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 9.0X10-2 | 2.4 | 3.6X10-4 | 9.7X10-3 |
U-233 (medium lung absorption) (e) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 3.6X10-4 | 9.7X10-3 |
U-233 (slow lung absorption) (f) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 6.0X10-3 | 1.6X10-1 | 3.6X10-4 | 9.7X10-3 |
U-234 (fast lung absorption) (d) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 9.0X10-2 | 2.4 | 2.3X10-4 | 6.2X10-3 |
U-234 (medium lung absorption) (e) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 2.3X10-4 | 6.2X10-3 |
U-234 (slow lung absorption) (f) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 6.0X10-3 | 1.6X10-1 | 2.3X10-4 | 6.2X10-3 |
U-235 (all lung absorption types) (a), (d), (e), (f) | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 8.0X10-8 | 2.2X10-6 |
U-236 (fast lung absorption) (d) | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 2.4X10-6 | 6.5X10-5 |
U-236 (medium lung absorption) (e) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 2.0X10-2 | 5.4X10-1 | 2.4X10-6 | 6.5X10-5 |
U-236 (slow lung absorption) (f) | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 6.0X10-3 | 1.6X10-1 | 2.4X10-6 | 6.5X10-5 |
U-238 (all lung absorption types) (d), (e), (f) | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 1.2X10-8 | 3.4X10-7 |
U (nat) | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 2.6X10-8 | 7.1X10-7 |
U (enriched to 20% or less) (g) | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | See Table A-4 | See Table A-4 |
U (dep) | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | See Table A-4 | See Table A-3 |
V-48 | Vanadium (23) | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 6.3X103 | 1.7X105 |
V-49 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.0X102 | 8.1X103 |
W-178 (a) | Tungsten (74) | 9.0 | 2.4X102 | 5.0 | 1.4X102 | 1.3X103 | 3.4X104 |
W-181 | | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 2.2X102 | 6.0X103 |
W-185 | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 3.5X102 | 9.4X103 |
W-187 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 2.6X104 | 7.0X105 |
W-188 (a) | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.7X102 | 1.0X104 |
Xe-122 (a) | Xenon (54) | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.8X104 | 1.3X106 |
Xe-123 | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 7.0X10-1 | 1.9X101 | 4.4X105 | 1.2X107 |
Xe-127 | | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 1.0X103 | 2.8X104 |
Xe-131m | | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 4.0X101 | 1.1X103 | 3.1X103 | 8.4X104 |
Xe-133 | | 2.0X101 | 5.4X102 | 1.0X101 | 2.7X102 | 6.9X103 | 1.9X105 |
Xe-135 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 9.5X104 | 2.6X106 |
Y-87 (a) | Yttrium (39) | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 1.7X104 | 4.5X105 |
Y-88 | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 5.2X102 | 1.4X104 |
Y-90 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 2.0X104 | 5.4X105 |
Y-91 | | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 9.1X102 | 2.5X104 |
Y-91m | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 1.5X106 | 4.2X107 |
Y-92 | | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 2.0X10-1 | 5.4 | 3.6X105 | 9.6X106 |
Y-93 | | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 3.0X10-1 | 8.1 | 1.2X105 | 3.3X106 |
Yb-169 | Ytterbium (70) | 4.0 | 1.1X102 | 1.0 | 2.7X101 | 8.9X102 | 2.4X104 |
Yb-175 | | 3.0X101 | 8.1X102 | 9.0X10-1 | 2.4X101 | 6.6X103 | 1.8X105 |
Zn-65 | Zinc (30) | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 3.0X102 | 8.2X103 |
Zn-69 | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.8X106 | 4.9X107 |
Zn-69m (a) | | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 6.0X10-1 | 1.6X101 | 1.2X105 | 3.3X106 |
Zr-88 | Zirconium (40) | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 3.0 | 8.1X101 | 6.6X102 | 1.8X104 |
Zr-93 | | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 9.3X10-5 | 2.5X10-3 |
Zr-95 (a) | | 2.0 | 5.4X101 | 8.0X10-1 | 2.2X101 | 7.9X102 | 2.1X104 |
Zr-97 (a) | | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 4.0X10-1 | 1.1X101 | 7.1X104 | 1.9X106 |
(a) | A1or A2values include contributions from daughter nuclides with half-lives less than ten days, as listed in the following: |
| Mg-28 | Al-28 |
| Ca-47 | Sc-47 |
| Ti-44 | Sc-44 |
| Fe-52 | Mn-52m |
| Fe-60 | Co-60m |
| Zn-69m | Zn-69 |
| Ge-68 | Ga-68 |
| Rb-83 | Kr-83m |
| Sr-82 | Rb-82 |
| Sr-90 | Y-90 |
| Sr-91 | Y-91m |
| Sr-92 | Y-92 |
| Y-87 | Sr-87m |
| Zr-95 | Nb-95m |
| Zr-97 | Nb-97m, Nb-97 |
| Mo-99 | Tc-99m |
| Tc-95m | Tc-95 |
| Tc-96m | Tc-96 |
| Ru-103 | Rh-103m |
| Ru-106 | Rh-106 |
| Pd-103 | Rh-103m |
| Ag-108m | Ag-108 |
| Ag-110m | Ag-110 |
| Cd-115 | In-115m |
| In-114m | In-114 |
| Sn-113 | In-113m |
| Sn-121m | Sn-121 |
| Sn-126 | Sb-126m |
| Te-127m | Te-127 |
| Te-129m | Te-129 |
| Te-131m | Te-131 |
| Te-132 | I-132 |
| I-135 | Xe-135m |
| Xe-122 | I-122 |
| Cs-137 | Ba-137m |
| Ba-131 | Cs-131 |
| Ba-140 | La-140 |
| Ce-144 | Pr-144m, Pr-144 |
| Pm-148m | Pm-148 |
| Gd-146 | Eu-146 |
| Dy-166 | Ho-166 |
| Hf-172 | Lu-172 |
| W-178 | Ta-178 |
| W-188 | Re-188 |
| Re-189 | Os-189m |
| Os-194 | Ir-194 |
| Ir-189 | Os-189m |
| Pt-188 | Ir-188 |
| Hg-194 | Au-194 |
| Hg-195m | Hg-195 |
| Pb-210 | Bi-210 |
| Pb-212 | Bi-212, Tl-208, Po-212 |
| Bi-210m | Tl-206 |
| Bi-212 | Tl-208, Po-212 |
| At-211 | Po-211 |
| Rn-222 | Po-218, Pb-214, At-218, Bi-214, Po-214 |
| Ra-223 | Rn-219, Po-215, Pb-211, Bi-211, Po-211, Tl-207 |
| Ra-224 | Rn-220, Po-216, Pb-212, Bi-212, Tl-208, Po-212 |
| Ra-225 | Ac-225, Fr-221, At-217, Bi-213, Tl-209, Po-213, Pb-209 |
| Ra-226 | Rn-222, Po-218, Pb-214, At-218, Bi-214, Po-214 |
| Ra-228 | Ac-228 |
| Ac-225 | Fr-221, At-217, Bi-213, Tl-209, Po-213, Pb-209 |
| Ac-227 | Fr-223 |
| Th-228 | Ra-224, Rn-220, Po-216, Pb-212, Bi-212, Tl-208, Po-212 |
| Th-234 | Pa-234m, Pa-234 |
| Pa-230 | Ac-226, Th-226, Fr-222, Ra-222, Rn-218, Po-214 |
| U-230 | Th-226, Ra-222, Rn-218, Po-214 |
| U-235 | Th-231 |
| Pu-241 | U-237 |
| Pu-244 | U-240, Np-240m |
| Am-242m | Am-242, Np-238 |
| Am-243 | Np-239 |
| Cm-247 | Pu-243 |
| Bk-249 | Am-245 |
| Cf-253 | Cm-249 |
| Am-243 | Np-239 |
| Cm-247 | Pu-243 |
| Bk-249 | Am-245 |
| Cf-253 | Cm-249 |
(b) | The values of A1 and A2 in Curies (Ci) are approximate and for information only the regulatory standard units are terabecquerels (TBq). |
(c) | The activity of IR-192 in special form may be determined from a measurement of the rate of decay or a measurement of the radiation level at a prescribed distance from the source. |
(d) | These values apply only to compounds of uranium that take the chemical form of UF6, UO2F2 and UO2(NO3)2 in both normal and accident conditions of transport. |
(e) | These values apply only to compounds of uranium that take the chemical form of UO3, UF4, UCI4 and hexavalent compounds in both normal and accident conditions of transport. |
(f) | These values apply to all compounds of uranium other than those specified in notes (d) and (e) of this table. |
(g) | These values apply to unirradiated uranium only. |
(h) | A2 = 0.74 TBq (20 Ci) for Mo-99 for domestic use. |
Table A-2.—Exempt Material Activity Concentrations and Exempt Consignment Activity Limits for Radionuclides
Symbol of radionuclide | Element and atomic number | Activity concentration for exempt material (Bq/g) | Activity concentration for exempt material (Ci/g) | Activity limit for exempt consignment (Bq) | Activity limit for exempt consignment (Ci) |
Ac-225 | Actinium (89) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Ac-227 | - | 1.0X10-1 | 2.7X10-12 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Ac-228 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ag-105 | Silver (47) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ag-108m (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ag-110m | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ag-111 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Al-26 | Aluminum (13) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Am-241 | Americium (95) | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Am-242m (b) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Am-243 (b) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Ar-37 | Argon (18) | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Ar-39 | - | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Ar-41 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X109 | 2.7X10-2 |
As-72 | Arsenic (33) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
As-73 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
As-74 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
As-76 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
As-77 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
At-211 | Astatine (85) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Au-193 | Gold (79) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Au-194 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Au-195 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Au-198 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Au-199 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ba-131 | Barium (56) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ba-133 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ba-133m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ba-140 (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Be-7 | Beryllium (4) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Be-10 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Bi-205 | Bismuth (83) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Bi-206 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Bi-207 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Bi-210 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Bi-210m | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Bi-212 (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Bk-247 | Berkelium (97) | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Bk-249 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Br-76 | Bromine (35) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Br-77 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Br-82 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
C-11 | Carbon (6) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
C-14 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Ca-41 | Calcium (20) | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Ca-45 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Ca-47 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Cd-109 | Cadmium (48) | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Cd-113m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Cd-115 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Cd-115m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ce-139 | Cerium (58) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ce-141 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Ce-143 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ce-144 (b) | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cf-248 | Californium (98) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Cf-249 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Cf-250 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Cf-251 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Cf-252 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Cf-253 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cf-254 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Cl-36 | Chlorine (17) | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Cl-38 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cm-240 | Curium (96) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cm-241 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Cm-242 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cm-243 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Cm-244 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Cm-245 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Cm-246 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Cm-247 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Cm-248 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Co-55 | Cobalt (27) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Co-56 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Co-57 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Co-58 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Co-58m | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Co-60 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cr-51 | Chromium (24) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Cs-129 | Cesium (55) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cs-131 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Cs-132 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cs-134 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Cs-134m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cs-135 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Cs-136 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Cs-137 (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Cu-64 | Copper (29) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Cu-67 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Dy-159 | Dysprosium (66) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Dy-165 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Dy-166 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Er-169 | Erbium (68) | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Er-171 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Eu-147 | Europium (63) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Eu-148 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Eu-149 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Eu-150 (short lived) | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Eu-150 (long lived) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Eu-152 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Eu-152m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Eu-154 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Eu-155 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Eu-156 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
F-18 | Fluorine (9) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Fe-52 | Iron (26) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Fe-55 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Fe-59 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Fe-60 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Ga-67 | Gallium (31) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ga-68 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Ga-72 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Gd-146 | Gadolinium (64) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Gd-148 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Gd-153 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Gd-159 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ge-68 | Germanium (32) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Ge-71 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Ge-77 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Hf-172 | Hafnium (72) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Hf-175 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Hf-181 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Hf-182 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Hg-194 | Mercury (80) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Hg-195m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Hg-197 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Hg-197m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Hg-203 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Ho-166 | Holmium (67) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Ho-166m | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
I-123 | Iodine (53) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
I-124 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
I-125 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
I-126 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
I-129 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
I-131 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
I-132 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
I-133 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
I-134 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
I-135 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
In-111 | Indium (49) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
In-113m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
In-114m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
In-115m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ir-189 | Iridium (77) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Ir-190 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ir-192 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Ir-194 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
K-40 | Potassium (19) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
K-42 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
K-43 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Kr-79 | Krypton (36) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Kr-81 | | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Kr-85 | - | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Kr-85m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X1010 | 2.7X10-1 |
Kr-87 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X109 | 2.7X10-2 |
La-137 | Lanthanum (57) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
La-140 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Lu-172 | Lutetium (71) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Lu-173 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Lu-174 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Lu-174m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Lu-177 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Mg-28 | Magnesium (12) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Mn-52 | Manganese (25) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Mn-53 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X109 | 2.7X10-2 |
Mn-54 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Mn-56 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Mo-93 | Molybdenum (42) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Mo-99 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
N-13 | Nitrogen (7) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X109 | 2.7X10-2 |
Na-22 | Sodium (11) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Na-24 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Nb-93m | Niobium (41) | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Nb-94 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Nb-95 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Nb-97 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Nd-147 | Neodymium (60) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Nd-149 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ni-59 | Nickel (28) | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Ni-63 | - | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Ni-65 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Np-235 | Neptunium (93) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Np-236 (short-lived) | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Np-236 (long-lived) | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Np-237 (b) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Np-239 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Os-185 | Osmium (76) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Os-191 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Os-191m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Os-193 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Os-194 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
P-32 | Phosphorus (15) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
P-33 | - | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Pa-230 | Protactinium (91) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pa-231 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Pa-233 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Pb-201 | Lead (82) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pb-202 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pb-203 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pb-205 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Pb-210 (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Pb-212 (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Pd-103 | Palladium (46) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Pd-107 | - | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Pd-109 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pm-143 | Promethium (61) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pm-144 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pm-145 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Pm-147 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Pm-148m | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pm-149 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pm-151 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Po-210 | Polonium (84) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Pr-142 | Praseodymium (59) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Pr-143 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pt-188 | Platinum (78) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pt-191 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pt-193 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Pt-193m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Pt-195m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pt-197 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pt-197m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Pu-236 | Plutonium (94) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Pu-237 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Pu-238 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Pu-239 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Pu-240 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Pu-241 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Pu-242 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Pu-244 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Ra-223 (b) | Radium (88) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Ra-224 (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Ra-225 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Ra-226 (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Ra-228 (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Rb-81 | Rubidium (37) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Rb-83 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Rb-84 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Rb-86 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Rb-87 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Rb (nat) | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Re-184 | Rhenium (75) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Re-184m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Re-186 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Re-187 | - | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 | 1.0X109 | 2.7X10-2 |
Re-188 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Re-189 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Re (nat) | - | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 | 1.0X109 | 2.7X10-2 |
Rh-99 | Rhodium (45) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Rh-101 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Rh-102 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Rh-102m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Rh-103m | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Rh-105 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Rn-222 (b) | Radon (86) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Ru-97 | Ruthenium (44) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Ru-103 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ru-105 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ru-106 (b) | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
S-35 | Sulphur (16) | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Sb-122 | Antimony (51) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Sb-124 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sb-125 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sb-126 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Sc-44 | Scandium (21) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Sc-46 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sc-47 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sc-48 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Se-75 | Selenium (34) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Se-79 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Si-31 | Silicon (14) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Si-32 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sm-145 | Samarium (62) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Sm-147 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Sm-151 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Sm-153 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sn-113 | Tin (50) | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Sn-117m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sn-119m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Sn-121m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Sn-123 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sn-125 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Sn-126 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Sr-82 | Strontium (38) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Sr-85 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sr-85m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Sr-87m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sr-89 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Sr-90 (b) | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Sr-91 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Sr-92 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
T(H-3) | Tritium (1) | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 | 1.0X109 | 2.7X10-2 |
Ta-178 (long-lived) | Tantalum (73) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Ta-179 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Ta-182 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Tb-157 | Terbium (65) | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Tb-158 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tb-160 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tc-95m | Technetium (43) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tc-96 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tc-96m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Tc-97 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
Tc-97m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Tc-98 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tc-99 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Tc-99m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Te-121 | Tellurium (52) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Te-121m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Te-123m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Te-125m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Te-127 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Te-127m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Te-129 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Te-129m | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Te-131m | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Te-132 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Th-227 | Thorium (90) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Th-228 (b) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Th-229 (b) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Th-230 | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Th-231 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Th-232 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Th-234 (b) | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Th (nat) (b) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
Ti-44 | Titanium (22) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Tl-200 | Thallium (81) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tl-201 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tl-202 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tl-204 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Tm-167 | Thulium (69) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tm-170 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Tm-171 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X108 | 2.7X10-3 |
U-230 (fast lung absorption) (b), (d) | Uranium (92) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
U-230 (medium lung absorption) (e) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U-230 (slow lung absorption) (f) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U-232 (fast lung absorption) (b), (d) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
U-232 (medium lung absorption) (e) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U-232 (slow lung absorption) (f) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U-233 (fast lung absorption) (d) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U-233 (medium lung absorption) (e) | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
U-233 (slow lung absorption) (f) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
U-234 (fast lung absorption) (d) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U-234 (medium lung absorption) (e) | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
U-234 (slow lung absorption) (f) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
U-235 (all lung absorption types) (b), (d), (e), (f) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U-236 (fast lung absorption) (d) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U-236 (medium lung absorption) (e) | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
U-236 (slow lung absorption) (f) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U-238 (all lung absorption types) (b), (d), (e), (f) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
U (nat) (b) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
U (enriched to 20% or less) (g) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
U (dep) | - | 1.0 | 2.7X10-11 | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 |
V-48 | Vanadium (23) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
V-49 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
W-178 | Tungsten (74) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
W-181 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
W-185 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
W-187 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
W-188 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Xe-122 | Xenon (54) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X109 | 2.7X10-2 |
Xe-123 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X109 | 2.7X10-2 |
Xe-127 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Xe-131m | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Xe-133 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 |
Xe-135 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X1010 | 2.7X10-1 |
Y-87 | Yttrium (39) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Y-88 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Y-90 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Y-91 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Y-91m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Y-92 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Y-93 | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
Yb-169 | Ytterbium (70) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Yb-175 | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Zn-65 | Zinc (30) | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Zn-69 | - | 1.0X104 | 2.7X10-7 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Zn-69m | - | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Zr-88 | Zirconium (40) | 1.0X102 | 2.7X10-9 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Zr-93 (b) | - | 1.0X103 | 2.7X10-8 | 1.0X107 | 2.7X10-4 |
Zr-95 | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X106 | 2.7X10-5 |
Zr-97 (b) | - | 1.0X101 | 2.7X10-10 | 1.0X105 | 2.7X10-6 |
(a) | (Reserved) |
(b) | Parent nuclides and their progeny included in secular equilibrium are listed as follows: |
| Sr-90 | Y-90 |
| Zr-93 | Nb-93m |
| Zr-97 | Nb-97 |
| Ru-106 | Rh-106 |
| Ag-108m | Ag-108 |
| Cs-137 | Ba-137m |
| Ce-144 | Pr-144 |
| Ba-140 | La-140 |
| Bi-212 | Tl-208 (0.36), Po-212 (0.64) |
| Pb-210 | Bi-210, Po-210 |
| Pb-212 | Bi-212, Tl-208 (0.36), Po-212 (0.64) |
| Rn-222 | Po-218, Pb-214, Bi-214, Po-214 |
| Ra-223 | Rn-219, Po-215, Pb-211, Bi-211, Tl-207 |
| Ra-224 | Rn-220, Po-216, Pb-212, Bi-212, Tl-208 (0.36), Po-212 (0.64) |
| Ra-226 | Rn-222, Po-218, Pb-214, Bi-214, Po-214, Pb-210, Bi-210, Po-210 |
| Ra-228 | Ac-228 |
| Th-228 | Ra-224, Rn-220, Po-216, Pb-212, Bi-212, Tl-208 (0.36), Po-212 (0.64) |
| Th-229 | Ra-225, Ac-225, Fr-221, At-217, Bi-213, Po-213, Pb-209 |
| Th-nat | Ra-228, Ac-228, Th-228, Ra-224, Rn-220, Po-216, Pb-212, Bi-212, Tl-208 (0.36), Po-212 (0.64) |
| Th-234 | Pa-234m |
| U-230 | Th-226, Ra-222, Rn-218, Po-214 |
| U-232 | Th-228, Ra-224, Rn-220, Po-216, Pb-212, Bi-212, Tl-208 (0.36), Po-212 (0.64) |
| U-235 | Th-231 |
| U-238 | Th-234, Pa-234m |
| U-nat | Th-234, Pa-234m, U-234, Th-230, Ra-226, Rn-222, Po-218, Pb-214, Bi-214, Po-214, Pb-210, Bi-210, Po-210 |
| Np-237 | Pa-233 |
| Am-242m | Am-242 |
| Am-243 | Np-239 |
(c) | (Reserved) |
(d) | These values apply only to compounds of uranium that take the chemical form of UF6, UO2F2 and UO2(NO3)2 in both normal and accident conditions of transport. |
(e) | These values apply only to compounds of uranium that take the chemical form of UO3, UF4, UCl4 and hexavalent compounds in both normal and accident conditions of transport. |
(f) | These values apply to all compounds of uranium other than those specified in notes (d) and (e) of this table. |
(g) | These values apply to unirradiated uranium only. |
Table A-3. General Values for A1 and A2
| A1 | A2 | Activity concentration for exempt material (Bq/g) | Activity concentration for exempt material (Ci/g) | Activity limits for exempt consignments (Bq) | Activity limits for exempt consignments (Ci) |
Contents | (TBq) | (Ci) | (TBq) | (Ci) |
Only beta or gamma emitting radionuclides are known to be present | 1 x 10-1 | 2.7 x 100 | 2 x 10-2 | 5.4 x 10-1 | 1 x 101 | 2.7 x 10-10 | 1 x 104 | 2.7 x 10-7 |
Alpha emitting nuclides, but no neutron emitters, are known to be present (a) | 2 x 10-1 | 5.4 x 100 | 9 x 10-5 | 2.4 x 10-3 | 1 x 10-1 | 2.7 x 10-12 | 1 x 103 | 2.7 x 10-8 |
Neutron emitting nuclides are known to be present or no relevant data are available | 1 x 10-3 | 2.7 x 10-2 | 9 x 10-5 | 2.4 x 10-3 | 1 x 10-1 | 2.7 x 10-12 | 1 x 103 | 2.7 x 10-8 |
(a) | If beta or gamma emitting nuclides are known to be present, the A1 value of 0.1 TBq (2.7 Ci) should be used. |
Table A-4.
Activity-Mass Relationships for Uranium
Uranium Enrichment1 wt % U-235 present | Specific Activity |
TBq/g | Ci/g |
0.45 | 1.8 x 10-8 | 5.0 x 10-7 |
0.72 | 2.6 x 10-8 | 7.1 x 10-7 |
1 | 2.8 x 10-8 | 7.6 x 10-7 |
1.5 | 3.7 x 10-8 | 1.0 x 10-6 |
5 | 1.0 x 10-7 | 2.7 x 10-6 |
10 | 1.8 x 10-7 | 4.8 x 10-6 |
20 | 3.7 x 10-7 | 1.0 x 10-5 |
35 | 7.4 x 10-7 | 2.0 x 10-5 |
50 | 9.3 x 10-7 | 2.5 x 10-5 |
90 | 2.2 x 10-6 | 5.8 x 10-5 |
93 | 2.6 x 10-6 | 7.0 x 10-5 |
95 | 3.4 x 10-6 | 9.1 x 10-5 |
1 | The figures for uranium include representative values for the activity of the uranium-234 that is concentrated during the enrichment process. |
Reviser's note: The brackets and enclosed material in the text of the above section occurred in the copy filed by the agency and appear in the Register pursuant to the requirements of RCW 34.08.040. OTS-4713.1
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-11-063, filed 5/16/22, effective 6/16/22)
WAC 246-237-010Definitions, abbreviations, and acronyms.
The definitions, abbreviations, and acronyms in this section and in WAC 246-220-010 apply throughout this chapter unless the context clearly indicates otherwise:
(1) "Access control" means a system for allowing only approved individuals to have unescorted access to the security zone and for ensuring that all other individuals are subject to escorted access.
(2) "Act" means the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, including any amendments thereto.
(3) "Aggregated" means accessible by the breach of a single physical barrier that would allow access to radioactive material in any form, including any devices that contain the radioactive material, when the total activity equals or exceeds a Category 2 quantity of radioactive material.
(4) "Agreement state" means any state with which the Atomic Energy Commission or the NRC has entered into an effective agreement under subsection 274b of the act. Nonagreement state means any other state.
(5) "Approved individual" means an individual whom the licensee has determined to be trustworthy and reliable for unescorted access in accordance with WAC 246-237-021 through 246-237-033 and who has completed the training required by WAC 246-237-043(3).
(6) "Background investigation" means the investigation conducted by a licensee or applicant to support the determination of trustworthiness and reliability.
(7) "Becquerel (Bq)" means the SI unit of activity. One becquerel is equal to ((1))one disintegration or transformation per second (s-1).
(8) "By-product material" means:
(a) Any radioactive material (except special nuclear material) yielded in, or made radioactive by, exposure to the radiation incident to the process of producing or using special nuclear material;
(b) The tailings or wastes produced by the extraction or concentration of uranium or thorium from ore processed primarily for its source material content, including discrete surface wastes resulting from uranium solution extraction processes. Underground ore bodies depleted by these solution extraction operations do not constitute "by-product material" within this definition;
(c)(i) Any discrete source of radium-226 that is produced, extracted, or converted after extraction, before, on, or after August 8, 2005, for use for a commercial, medical, or research activity; or
(ii) Any material that:
(A) Has been made radioactive by use of a particle accelerator; and
(B) Is produced, extracted, or converted after extraction, before, on, or after August 8, 2005, for use for a commercial, medical, or research activity; and
(d) Any discrete source of naturally occurring radioactive material, other than source material, that:
(i) The NRC, in consultation with the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency, the Secretary of Energy, the Secretary of Homeland Security, and the head of any other appropriate federal agency, determines would pose a threat similar to the threat posed by a discrete source of radium-226 to the public health and safety or the common defense and security; and
(ii) Before, on, or after August 8, 2005, is extracted or converted after extraction for use in a commercial, medical, or research activity.
(9) "Carrier" means a person engaged in the transportation of passengers or property by land or water as a common, contract, or private carrier, or by civil aircraft.
(10) "Category 1 quantity of radioactive material" means a quantity of radioactive material meeting or exceeding the Category 1 threshold in Table 1 of WAC 246-237-900 Appendix A: Table 1—Category 1 and Category 2. This is determined by calculating the ratio of the total activity of each radionuclide to the Category 1 threshold for that radionuclide and adding the ratios together. If the sum equals or exceeds ((1))one, the quantity would be considered a Category 1 quantity. Category 1 quantities of radioactive material do not include the radioactive material contained in any fuel assembly, subassembly, fuel rod, or fuel pellet.
(11) "Category 2 quantity of radioactive material" means a quantity of radioactive material meeting or exceeding the Category 2 threshold but less than the Category 1 threshold in Table 1 of WAC 246-237-900 Appendix A: Table 1—Category 1 and Category 2. This is determined by calculating the ratio of the total activity of each radionuclide to the Category 2 threshold for that radionuclide and adding the ratios together. If the sum equals or exceeds one, the quantity would be considered a Category 2 quantity. Category 2 quantities of radioactive material do not include the radioactive material contained in any fuel assembly, subassembly, fuel rod, or fuel pellet.
(12) "Curie" means a unit of quantity of radioactivity. One curie (Ci) is that quantity of radioactive material which decays at the rate of 3.7 x 1010 transformations per second (tps).
(13) "Diversion" means the unauthorized movement of radioactive material subject to this chapter to a location different from the material's authorized destination inside or outside of the site at which the material is used or stored.
(14) "Escorted access" means accompaniment while in a security zone by an approved individual who maintains continuous direct visual surveillance at all times over an individual who is not approved for unescorted access.
(15) "FBI" means the federal bureau of investigation.
(16) "Fingerprint orders" means the orders issued by the NRC or the legally binding requirements issued by agreement states that require fingerprints and criminal history records checks for individuals with unescorted access to Category 1 and Category 2 quantities of radioactive material or safeguards information-modified handling.
(17) "Government agency" means any executive department, commission, independent establishment, corporation, wholly or partly owned by the United States of America which is an instrumentality of the United States, or any board, bureau, division, service, office, officer, authority, administration, or other establishment in the executive branch of the government.
(18) "License" means, except where otherwise specified, a license for radioactive material issued pursuant to the regulations in chapters 246-232, 246-233, 246-235, 246-240, 246-243, or 246-244 WAC.
(19) "License issuing authority" means the licensing agency (the department, NRC, or an agreement state) that issued the license.
(20) "LLEA (local law enforcement agency)" means a public or private organization that has been approved by a federal, state, or local government to carry firearms and make arrests, and is authorized and has the capability to provide an armed response in the jurisdiction where the licensed Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material is used, stored, or transported.
(21) "Lost or missing licensed material" means licensed material whose location is unknown. It includes material that has been shipped but has not reached its destination and whose location cannot be readily traced in the transportation system.
(22) "Mobile device" means a piece of equipment containing licensed radioactive material that is either mounted on wheels or casters, or otherwise equipped for moving without a need for disassembly or dismounting; or designed to be hand carried. Mobile devices do not include stationary equipment installed in a fixed location.
(23) "Movement control center" means an operations center that is remote from transport activity and that maintains position information on the movement of radioactive material, receives reports of attempted attacks or thefts, provides a means for reporting these and other problems to appropriate agencies, and can request and coordinate appropriate aid.
(24) "No-later-than arrival time" means the date and time that the shipping licensee and receiving licensee have established as the time at which an investigation will be initiated if the shipment has not arrived at the receiving facility. The no-later-than arrival time may not be more than six hours after the estimated arrival time for shipments of Category 2 quantities of radioactive material.
(25) "NRC" or "commission" means the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
(26) "Person" means any individual, corporation, partnership, firm, association, trust, estate, public or private institution, group, government agency other than NRC or the Department of Energy, any state or any political subdivision of, or any political entity within, a state, any foreign government or nation, or any political subdivision of any such government or nation, or other entity, and any legal successor, representative, agent or agency of the foregoing.
(27) "Reviewing official" means the individual who makes the trustworthiness and reliability determination of an individual to determine whether the individual may have, or continue to have, unescorted access to the Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive materials that are possessed by the licensee.
(28) "Sabotage" means deliberate damage, with malevolent intent, to a Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material, a device that contains a Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material, or the components of the security system.
(29) "Safe haven" means a readily recognizable and readily accessible site at which security is present or from which, in the event of an emergency, the transport crew can notify and wait for the local law enforcement authorities.
(30) "Security zone" means any temporary or permanent area determined and established by the licensee for the physical protection of Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material.
(31) "State" means a state of the United States, the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands.
(32) "Telemetric position monitoring system" means a data transfer system that captures information by instrumentation or measuring devices about the location and status of a transport vehicle or package between the departure and destination locations.
(33) "Trustworthiness and reliability" are characteristics of an individual considered dependable in judgment, character, and performance, such that unescorted access to Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material by that individual does not constitute an unreasonable risk to the public health and safety or security. A determination of trustworthiness and reliability for this purpose is based upon the results from a background investigation.
(34) "Unescorted access" means solitary access to an aggregated Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material or the devices that contain the material.
(35) "United States" means when used in a geographical sense includes Puerto Rico and all territories and possessions of the United States.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-079, filed 6/14/16, effective 7/15/16)
WAC 246-237-011Specific exemptions.
(1) The department may, upon application of any interested person or upon its own initiative, grant such exemptions from the requirements of the rules in this chapter as it determines are authorized by law and will not endanger life or property or the common defense and security, and are otherwise in the public interest.
(2) Any licensee's activities are exempt from the requirements of WAC 246-237-021 through 246-237-057 to the extent that its activities are included in a security plan required by 10 C.F.R. Part 73.
(3) A licensee who possesses radioactive waste that contains Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material is exempt from the requirements of WAC 246-237-021 through 246-237-081, except that any radioactive waste that contains discrete sources, ion-exchange resins, or activated material that weighs less than ((two thousand))2,000 kg (((four thousand four hundred nine))4,409 pounds) is not exempt from the requirements of this chapter. The licensee shall implement the following requirements to secure the radioactive waste:
(a) Use continuous physical barriers which allow access to the radioactive waste only through established access control points;
(b) Use a locked door or gate with monitored alarm at the access control point;
(c) Assess and respond to each actual or attempted unauthorized access to determine whether an actual or attempted theft, sabotage, or diversion occurred; and
(d) Immediately notify the LLEA and request an armed response from the LLEA upon determination that there was an actual or attempted theft, sabotage, or diversion of the radioactive waste that contains Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-01-034, filed 12/12/16, effective 1/12/17)
WAC 246-237-025Background investigations.
(1) Initial investigation. Before allowing an individual unescorted access to Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material or to the devices that contain the material, licensees shall complete a background investigation of the individual seeking unescorted access authorization. The scope of the investigation must encompass at least the seven years preceding the date of the background investigation or since the individual's ((eighteenth))18th birthday, whichever is shorter. The background investigation must include at a minimum:
(a) Fingerprinting and an FBI identification and criminal history records check in accordance with WAC 246-237-027;
(b) Verification of true identity. Licensees shall verify the true identity of the individual who is applying for unescorted access authorization to ensure that the applicant is who they claim to be. A licensee shall review official identification documents (driver's license; passport; government identification; certificate of birth issued by the state, province, or country of birth) and compare the documents to personal information data provided by the individual to identify any discrepancy in the information. Licensees shall document the type, expiration, and identification number of the identification document, or maintain a photocopy of identifying documents on file in accordance with WAC 246-237-031. Licensees shall certify in writing that the identification was properly reviewed, and shall maintain the certification and all related documents for review upon inspection;
(c) Employment history verification. Licensees shall complete an employment history verification, including military history. Licensees shall verify the individual's employment with each previous employer for the most recent seven years before the date of application;
(d) Verification of education. Licensees shall verify that the individual participated in the education process during the claimed period;
(e) Character and reputation determination. Licensees shall complete reference checks to determine the character and reputation of the individual who has applied for unescorted access authorization. Unless other references are not available, reference checks may not be conducted with any person who is known to be a close member of the individual's family including, but not limited to, the individual's spouse, parents, siblings, or children, or any individual who resides in the individual's permanent household. Reference checks under this chapter must be limited to whether the individual has been and continues to be trustworthy and reliable;
(f) The licensee shall also, to the extent possible, obtain independent information to corroborate that provided by the individual (for example, seek references not supplied by the individual); and
(g) If a previous employer, educational institution, or any other entity with which the individual claims to have been engaged fails to provide information or indicates an inability or unwillingness to provide information within a time frame deemed appropriate by the licensee but at least after ((ten))10 business days of the request or if the licensee is unable to reach the entity, the licensee shall document the refusal, unwillingness, or inability in the record of investigation; and attempt to obtain the information from an alternate source.
(2) Grandfathering.
(a) Individuals who have been determined to be trustworthy and reliable for unescorted access to Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material under the fingerprint orders may continue to have unescorted access to Category 1 and Category 2 quantities of radioactive material without further investigation. These individuals shall be subject to the reinvestigation requirement.
(b) Individuals who have been determined to be trustworthy and reliable under the provisions of 10 C.F.R. Part 73 or the security orders for access to safeguards information, safeguards information-modified handling, or risk-significant material may have unescorted access to Category 1 and Category 2 quantities of radioactive material without further investigation. The licensee shall document that the individual was determined to be trustworthy and reliable under the provisions of 10 C.F.R. Part 73 or a security order. Security order, in this context, refers to any order that was issued by the NRC that required fingerprints and an FBI criminal history records check for access to safeguards information, safeguards information-modified handling, or risk-significant material such as special nuclear material or large quantities of uranium hexafluoride. These individuals shall be subject to the reinvestigation requirement.
(3) Reinvestigations. Licensees shall conduct a reinvestigation every ((ten))10 years for any individual with unescorted access to Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material. The reinvestigation shall consist of fingerprinting and an FBI identification and criminal history records check in accordance with WAC 246-237-027. The reinvestigations must be completed within ((ten))10 years of the date on which these elements were last completed.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-079, filed 6/14/16, effective 7/15/16)
WAC 246-237-041Security program.
(1) Applicability.
(a) Each licensee who possesses an aggregated Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material shall establish, implement, and maintain a security program in accordance with the requirements of this chapter.
(b) An applicant for a new license, and each licensee who would become newly subject to the requirements of this chapter, upon application for modification of its license, shall implement the requirements of this chapter, as appropriate, before taking possession of an aggregated Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material.
(c) Any licensee who has not previously implemented the security orders or been subject to the provisions of WAC 246-237-041 through 246-237-057 shall provide written notification to the department at least ((ninety))90 days before aggregating radioactive material to a quantity that equals or exceeds the Category 2 threshold.
(2) General performance objective. Each licensee shall establish, implement, and maintain a security program designed to monitor and, without delay, detect, assess, and respond to an actual or attempted unauthorized access to Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material.
(3) Program features. Each licensee's security program must include the program features, as appropriate, described in WAC 246-237-043 through 246-237-055.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-079, filed 6/14/16, effective 7/15/16)
WAC 246-237-045LLEA coordination.
(1) A licensee subject to this chapter shall coordinate, to the extent practicable, with a LLEA for responding to threats to the licensee's facility, including any necessary armed response. The information provided to the LLEA must include:
(a) A description of the facilities and the Category 1 and Category 2 quantities of radioactive materials along with a description of the licensee's security measures which have been implemented to comply with this chapter; and
(b) A notification that the licensee will request a timely armed response by the LLEA to any actual or attempted theft, sabotage, or diversion of Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of material.
(2) The licensee shall notify the department within three business days if:
(a) The LLEA has not responded to the request for coordination within ((sixty))60 days of the coordination request; or
(b) The LLEA notifies the licensee that the LLEA does not plan to participate in coordination activities.
(3) The licensee shall document its efforts to coordinate with the LLEA. The documentation must be kept for three years.
(4) The licensee shall coordinate with the LLEA at least every ((twelve))12 months, or when changes to the facility design or operation adversely affect the potential vulnerability of the licensee's material to theft, sabotage, or diversion.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-079, filed 6/14/16, effective 7/15/16)
WAC 246-237-051Maintenance and testing.
(1) Each licensee subject to this chapter shall implement a maintenance and testing program to ensure that intrusion alarms, associated communication systems, and other physical components of the systems used to secure or detect unauthorized access to radioactive material are maintained in operable condition and are capable of performing their intended function when needed. The equipment relied on to meet the security requirements of this part must be inspected and tested for operability and performance at the manufacturer's suggested frequency. If there is no suggested manufacturer's suggested frequency, the testing must be performed at least annually, not to exceed ((twelve))12 months.
(2) The licensee shall maintain records of the maintenance and testing activities for three years.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-079, filed 6/14/16, effective 7/15/16)
WAC 246-237-057Reporting of events.
(1) The licensee shall immediately notify the LLEA after determining that an unauthorized entry resulted in an actual or attempted theft, sabotage, or diversion of a Category 1 or Category 2 quantity of radioactive material. As soon as possible after initiating a response, but not at the expense of causing delay or interfering with the LLEA response to the event, the licensee shall notify the department. In no case shall the notification to the department be later than four hours after the discovery of any attempted or actual theft, sabotage, or diversion.
(2) The licensee shall assess any suspicious activity related to possible theft, sabotage, or diversion of Category 1 or Category 2 quantities of radioactive material and notify the LLEA as appropriate. As soon as possible but not later than four hours after notifying the LLEA, the licensee shall notify the department.
(3) The initial telephonic notification required by subsection (1) of this section must be followed within a period of ((thirty))30 days by a written report submitted to the department. The report must include sufficient information for department analysis and evaluation, including identification of any necessary corrective actions to prevent future instances.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-079, filed 6/14/16, effective 7/15/16)
WAC 246-237-079Requirements for physical protection of Category 1 and Category 2 quantities of radioactive material during shipment.
(1) Shipments by road.
(a) Each licensee who transports, or delivers to a carrier for transport, in a single shipment, a Category 1 quantity of radioactive material shall:
(i) Ensure that movement control centers are established that maintain position information from a remote location. These control centers must monitor shipments ((twenty-four))24 hours a day, seven days a week, and have the ability to communicate immediately, in an emergency, with the appropriate law enforcement agencies.
(ii) Ensure that redundant communications are established that allow the transport to contact the escort vehicle (when used) and movement control center at all times. Redundant communications may not be subject to the same interference factors as the primary communication.
(iii) Ensure that shipments are continuously and actively monitored by a telemetric position monitoring system or an alternative tracking system reporting to a movement control center. A movement control center must provide positive confirmation of the location, status, and control over the shipment. The movement control center must be prepared to promptly implement preplanned procedures in response to deviations from the authorized route or a notification of actual, attempted, or suspicious activities related to the theft, loss, or diversion of a shipment. These procedures will include, but not be limited to, the identification of and contact information for the appropriate LLEA along the shipment route.
(iv) Provide an individual to accompany the driver for those highway shipments with a driving time period greater than the maximum number of allowable hours of service in a ((twenty-four))24 hour duty day as established by the Department of Transportation Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration. The accompanying individual may be another driver.
(v) Develop written normal and contingency procedures to address:
(A) Notifications to the communication center and law enforcement agencies;
(B) Communication protocols. Communication protocols must include a strategy for the use of authentication codes and duress codes and provisions for refueling or other stops, detours, and locations where communication is expected to be temporarily lost;
(C) Loss of communications; and
(D) Responses to an actual or attempted theft or diversion of a shipment.
(vi) Each licensee who makes arrangements for the shipment of Category 1 quantities of radioactive material shall ensure that drivers, accompanying personnel, and movement control center personnel have access to the normal and contingency procedures.
(b) Each licensee who transports Category 2 quantities of radioactive material shall maintain constant control or surveillance during transit and have the capability for immediate communication to summon appropriate response or assistance.
(c) Each licensee who delivers to a carrier for transport, in a single shipment, a Category 2 quantity of radioactive material shall:
(i) Use carriers who have established package tracking systems. An established package tracking system is a documented, proven, and reliable system routinely used to transport objects of value. In order for a package tracking system to maintain constant control or surveillance, the package tracking system must allow the shipper or transporter to identify when and where the package was last and when it should arrive at the next point of control.
(ii) Use carriers who maintain constant control or surveillance during transit and have the capability for immediate communication to summon appropriate response or assistance; and
(iii) Use carriers who have established tracking systems that require an authorized signature prior to releasing the package for delivery or return.
(2) Shipments by rail.
(a) Each licensee who transports, or delivers to a carrier for transport, in a single shipment, a Category 1 quantity of radioactive material shall:
(i) Ensure that rail shipments are monitored by a telemetric position monitoring system or an alternative tracking system reporting to the licensee, third-party, or railroad communications center. The communications center shall provide positive confirmation of the location of the shipment and its status. The communications center shall implement preplanned procedures in response to deviations from the authorized route or to a notification of actual, attempted, or suspicious activities related to the theft or diversion of a shipment. These procedures will include, but not be limited to, the identification of and contact information for the appropriate LLEA along the shipment route.
(ii) Ensure that periodic reports to the communications center are made at preset intervals.
(b) Each licensee who transports, or delivers to a carrier for transport, in a single shipment, a Category 2 quantity of radioactive material shall:
(i) Use carriers who have established package tracking systems. An established package tracking system is a documented, proven, and reliable system routinely used to transport objects of value. In order for a package tracking system to maintain constant control or surveillance, the package tracking system must allow the shipper or transporter to identify when and where the package was last and when it should arrive at the next point of control.
(ii) Use carriers who maintain constant control or surveillance during transit and have the capability for immediate communication to summon appropriate response or assistance; and
(iii) Use carriers who have established tracking systems that require an authorized signature prior to releasing the package for delivery or return.
(3) Investigations. Each licensee who makes arrangements for the shipment of Category 1 quantities of radioactive material shall immediately conduct an investigation upon discovery that a Category 1 shipment is lost or missing. Each licensee who makes arrangements for the shipment of Category 2 quantities of radioactive material shall immediately conduct an investigation, in coordination with the receiving licensee, of any shipment that has not arrived by the designated no-later-than arrival time.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-079, filed 6/14/16, effective 7/15/16)
WAC 246-237-081Reporting requirements.
(1) The shipping licensee shall notify the appropriate LLEA and the department within one hour of its determination that a shipment of Category 1 quantities of radioactive material is lost or missing. The appropriate LLEA would be the law enforcement agency in the area of the shipment's last confirmed location. During the investigation required by WAC 246-237-079(3), the shipping licensee will provide agreed upon updates to the department on the status of the investigation.
(2) The shipping licensee shall notify the department within four hours of its determination that a shipment of Category 2 quantities of radioactive material is lost or missing. If, after ((twenty-four))24 hours of the determination that the shipment is lost or missing, the radioactive material has not been located and secured, the licensee shall immediately notify the department.
(3) The shipping licensee shall notify the designated LLEA along the shipment route as soon as possible upon discovery of any actual or attempted theft or diversion of a shipment or suspicious activities related to the theft or diversion of a shipment of a Category 1 quantity of radioactive material. As soon as possible after notifying the LLEA, the licensee shall notify the department upon discovery of any actual or attempted theft or diversion of a shipment, or any suspicious activity related to the shipment of Category 1 radioactive material.
(4) The shipping licensee shall notify the department as soon as possible upon discovery of any actual or attempted theft or diversion of a shipment, or any suspicious activity related to the shipment, of a Category 2 quantity of radioactive material.
(5) The shipping licensee shall notify the department and the LLEA as soon as possible upon recovery of any lost or missing Category 1 quantities of radioactive material.
(6) The shipping licensee shall notify the department as soon as possible upon recovery of any lost or missing Category 2 quantities of radioactive material.
(7) The initial telephonic notification required by subsections (1) through (4) of this section must be followed within a period of ((thirty))30 days by a written report submitted to the department by an appropriate method. A written report is not required for notifications of suspicious activities required by subsections (3) and (4) of this section. In addition, the licensee shall provide a copy of the written report to the department. The report must set forth the following information:
(a) A description of the licensed material involved, including kind, quantity, chemical and physical form;
(b) A description of the circumstances under which the loss or theft occurred;
(c) A statement of disposition, or probable disposition, of the licensed material involved;
(d) Actions that have been taken, or will be taken, to recover the material; and
(e) Procedures or measures that have been, or will be, adopted to ensure against a recurrence of the loss or theft of licensed material.
(8) Subsequent to filing the written report, the licensee shall also report any additional substantive information about the loss or theft to the department within ((thirty))30 days after the licensee learns of such information.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 16-13-079, filed 6/14/16, effective 7/15/16)
WAC 246-237-900Appendix A: Table 1—Category 1 and Category 2 thresholds.
Terabecquerel (TBq) values are the regulatory standard. The curie (Ci) values specified are obtained by converting from the TBq value. The curie values provided for practical usefulness only.
Radioactive material | Category 1 (TBq) | Category 1 (Ci) | Category 2 (TBq) | Category 2 (Ci) |
Americium-241 | | 60 | | 1,620 | | 0.6 | | 16.2 |
Americium-241/Be | | 60 | | 1,620 | | 0.6 | | 16.2 |
Californium-252 | | 20 | | 540 | | 0.2 | | 5.40 |
Cobalt-60 | | 30 | | 810 | | 0.3 | | 8.10 |
Curium-244 | | 50 | | 1,350 | | 0.5 | | 13.5 |
Cesium-137 | | 100 | | 2,700 | | 1 | | 27.0 |
Gadolinium-153 | | 1,000 | | 27,000 | | 10 | | 270 |
Iridium-192 | | 80 | | 2,160 | | 0.8 | | 21.6 |
Plutonium-238 | | 60 | | 1,620 | | 0.6 | | 16.2 |
Plutonium-239/Be | | 60 | | 1,620 | | 0.6 | | 16.2 |
Promethium-147 | | 40,000 | | 1,080,000 | | 400 | | 10,800 |
Radium-226 | | 40 | | 1,080 | | 0.4 | | 10.8 |
Selenium-75 | | 200 | | 5,400 | | 2 | | 54.0 |
Strontium-90 | | 1,000 | | 27,000 | | 10 | | 270 |
Thulium-170 | | 20,000 | | 540,000 | | 200 | | 5,400 |
Ytterbium-169 | | 300 | | 8,100 | | 3 | | 81.0 |
Note: Calculations Concerning Multiple Sources or Multiple Radionuclides
The "sum of fractions" methodology for evaluating combinations of multiple sources or multiple radionuclides is to be used in determining whether a location meets or exceeds the threshold and is thus subject to the requirements of this chapter.
I. If multiple sources of the same radionuclide or multiple radionuclides are aggregated at a location, the sum of the ratios of the total activity of each of the radionuclides must be determined to verify whether the activity at the location is less than the Category 1 or Category 2 thresholds of Table 1, as appropriate. If the calculated sum of the ratios, using the equation below, is greater than or equal to 1.0, then the applicable requirements of this chapter apply.
II. First determine the total activity for each radionuclide from Table 1. This is done by adding the activity of each individual source, material in any device, and any loose or bulk material that contains the radionuclide. Then use the equation below to calculate the sum of the ratios by inserting the total activity of the applicable radionuclides from Table 1 in the numerator of the equation and the corresponding threshold activity from Table 1 in the denominator of the equation. Calculations must be performed in metric values (TBq) and the numerator and denominator values must be in the same units.
R1= total activity for radionuclide 1
R2= total activity for radionuclide 2
RN= total activity for radionuclide n
AR1= activity threshold for radionuclide 1
AR2= activity threshold for radionuclide 2
ARN= activity threshold for radionuclide n
OTS-4714.1
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-19-084, filed 9/20/22, effective 10/21/22)
WAC 246-240-010Definitions, abbreviations, and acronyms.
The definitions, abbreviations, and acronyms in this section and in WAC 246-220-010 apply throughout this chapter unless the context clearly indicates otherwise.
(1) "Address of use" means the building or buildings that are identified on the license and where radioactive material may be received, prepared, used, or stored.
(2) "Area of use" means a portion of an address of use that has been set aside for the purpose of receiving, preparing, using, or storing radioactive material.
(3) "Associate radiation safety officer" means an individual who:
(a) Meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-069 and 246-240-081; and
(b) Is currently identified as an associate radiation safety officer for the types of use of radioactive material for which the individual has been assigned duties and tasks by the radiation safety officer on:
(i) A specific medical use license issued by the department, NRC, or an agreement state; or
(ii) A medical use permit issued by an NRC master material licensee.
(4) "Attestation" means written certification under oath.
(5) "Authorized medical physicist" means an individual who:
(a) Meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-072 and 246-240-081; or
(b) Is identified as an authorized medical physicist or teletherapy physicist on:
(i) A specific medical use license issued by the department, NRC, or an agreement state;
(ii) A medical use permit issued by an NRC master material licensee;
(iii) A permit issued by an NRC or agreement state broad scope medical use licensee; or
(iv) A permit issued by an NRC master material license broad scope medical use permittee.
(6) "Authorized nuclear pharmacist" means a pharmacist who:
(a) Meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-075 and 246-240-081; or
(b) Is identified as an authorized nuclear pharmacist on:
(i) A specific license issued by the department, NRC, or an agreement state, that authorizes medical use or the practice of nuclear pharmacy;
(ii) A permit issued by an NRC master material licensee that authorizes medical use or the practice of nuclear pharmacy;
(iii) A permit issued by an NRC or agreement state broad scope medical use licensee that authorizes medical use or the practice of nuclear pharmacy; or
(iv) A permit issued by an NRC master material license broad scope medical use permittee that authorizes medical use or the practice of nuclear pharmacy; or
(c) Is identified as an authorized nuclear pharmacist by a commercial nuclear pharmacy that has been authorized to identify authorized nuclear pharmacists; or
(d) Is designated as an authorized nuclear pharmacist in accordance with WAC 246-235-100(2).
(7) "Authorized user" means a physician, dentist, or podiatrist who:
(a) Meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-081 and 246-240-154, 246-240-163, 246-240-210, 246-240-213, 246-240-216, 246-240-278, 246-240-301, or 246-240-399; or
(b) Is identified as an authorized user on:
(i) A department, NRC, or agreement state license that authorizes the medical use of radioactive material; or
(ii) A permit issued by an NRC master material licensee that is authorized to permit the medical use of radioactive material; or
(iii) A permit issued by a department, NRC, or agreement state specific licensee of broad scope that is authorized to permit the medical use of radioactive material; or
(iv) A permit issued by an NRC master material license broad scope permittee that is authorized to permit the medical use of radioactive material.
(8) "Brachytherapy" means a method of radiation therapy in which sources are used to deliver a radiation dose at a distance of up to a few centimeters by surface, intracavitary, intraluminal, or interstitial application.
(9) "Brachytherapy source" means a radioactive source or a manufacturer-assembled source train or a combination of these sources that is designed to deliver a therapeutic dose within a distance of a few centimeters.
(10) "Client's address" means the area of use or a temporary job site for the purpose of providing mobile medical service in accordance with WAC 246-240-125.
(11) "Cyclotron" means a particle accelerator in which the charged particles travel in an outward spiral or circular path. A cyclotron accelerates charged particles at energies usually in excess of 10 mega-electron volts and is commonly used for production of short half-life radionuclides for medical use.
(12) "Dedicated check source" means a radioactive source that is used to assure the constant operation of a radiation detection or measurement device over several months or years.
(13) "Dentist" means an individual licensed by a state or territory of the United States, the District of Columbia, or the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico to practice dentistry.
(14) "FDA" means the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
(15) "High dose-rate remote afterloader" means a brachytherapy device that remotely delivers a dose rate in excess of 12 gray (1200 rads) per hour at the point or surface where the dose is prescribed.
(16) "Low dose-rate remote afterloader" means a brachytherapy device that remotely delivers a dose rate of less than or equal to two gray (200 rads) per hour at the point or surface where the dose is prescribed.
(17) "Management" means the chief executive officer or other individual having the authority to manage, direct, or administer the licensee's activities, or that person's delegate or delegates.
(18) "Manual brachytherapy" means a type of brachytherapy in which the brachytherapy sources (e.g., seeds, ribbons) are manually placed topically on or inserted either into the body cavities that are in close proximity to a treatment site or directly into the tissue volume.
(19) "Medical event" means an event that meets the criteria in WAC 246-240-651.
(20) "Medical institution" means an organization in which more than one medical discipline is practiced.
(21) "Medical use" means the intentional internal or external administration of radioactive material or the radiation from radioactive material to patients or human research subjects under the supervision of an authorized user.
(22) "Medium dose-rate remote afterloader" means a brachytherapy device that remotely delivers a dose rate of greater than two gray (200 rads), but less than or equal to 12 grays (1200 rads) per hour at the point or surface where the dose is prescribed.
(23) "Mobile medical service" means the transportation of radioactive material to and its medical use at the client's address.
(24) "Ophthalmic physicist" means an individual who:
(a) Meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-272 (1)(b) and 246-240-081; and
(b) Is identified as an ophthalmic physicist on a:
(i) Specific medical use license issued by the NRC or an agreement state;
(ii) Permit issued by an NRC or agreement state broad scope medical use licensee;
(iii) Medical use permit issued by an NRC master material licensee; or
(iv) Permit issued by an NRC master material licensee broad scope medical use permittee.
(25) "Output" means the exposure rate, dose rate, or a quantity related in a known manner to these rates from a brachytherapy source or a teletherapy, remote afterloader, or gamma stereotactic radiosurgery unit for a specified set of exposure conditions.
(26) "Patient intervention" means actions by the patient or human research subject, whether intentional or unintentional, such as dislodging or removing treatment devices or prematurely terminating the administration.
(27) "Podiatrist" means an individual licensed by a state or territory of the United States, the District of Columbia, or the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico to practice podiatry.
(28) "Positron emission tomography (PET) radionuclide production facility" means a facility operating an accelerator for the purpose of producing positron emission tomography radionuclides.
(29) "Preceptor" means an individual who provides, directs, or verifies training and experience required for an individual to become an authorized user, an authorized medical physicist, an authorized nuclear pharmacist, an authorized radiation safety officer, or an associate radiation safety officer.
(30) "Prescribed dosage" means the specified activity or range of activity of unsealed radioactive material as documented:
(a) In a written directive; or
(b) In accordance with the directions of the authorized user for procedures performed under WAC 246-240-151 and 246-240-157.
(31) "Prescribed dose" means:
(a) For gamma stereotactic radiosurgery, the total dose as documented in the written directive;
(b) For teletherapy, the total dose and dose per fraction as documented in the written directive;
(c) For manual brachytherapy, either the total source strength and exposure time or the total dose, as documented in the written directive; or
(d) For remote brachytherapy afterloaders, the total dose and dose per fraction as documented in the written directive.
(32) "Pulsed dose-rate remote afterloader" means a special type of remote afterloading brachytherapy device that uses a single source capable of delivering dose rates in the "high dose-rate" range, but:
(a) Is approximately ((one-tenth))1/10th of the activity of typical high dose-rate remote afterloader sources; and
(b) Is used to simulate the radiobiology of a low dose-rate treatment by inserting the source for a given fraction of each hour.
(33) "Sealed source and device registry" means the national registry that contains all the registration certificates, generated by NRC and the agreement states, that summarize the radiation safety information for the sealed sources and devices and describe the licensing and use conditions approved for the product.
(34) "Stereotactic radiosurgery" means the use of external radiation in conjunction with a stereotactic guidance device to very precisely deliver a therapeutic dose to a tissue volume.
(35) "Structured educational program" means an educational program designed to impart particular knowledge and practical education through interrelated studies and supervised training.
(36) "Teletherapy" means a method of radiation therapy in which collimated gamma rays are delivered at a distance from the patient or human research subject.
(37) "Temporary job site" means a location where mobile medical services are conducted at other than those fixed locations of use authorized by the license.
(38) "Therapeutic dosage" means a dosage of unsealed radioactive material that is intended to deliver a radiation dose to a patient or human research subject for palliative or curative treatment.
(39) "Therapeutic dose" means a radiation dose delivered from a source containing radioactive material to a patient or human research subject for palliative or curative treatment.
(40) "Treatment site" means the anatomical description of the tissue intended to receive a radiation dose, as described in a written directive.
(41) "Type of use" means use of radioactive material under WAC 246-240-151, 246-240-157, 246-240-201, 246-240-251, 246-240-301, 246-240-351, or 246-240-501.
(42) "Unit dosage" means a dosage prepared for medical use for administration as a single dosage to a patient or human research subject without any further manipulation of the dosage after it is initially prepared.
(43) "Written directive" means an authorized user's written order for the administration of radioactive material or radiation from radioactive material to a specific patient or human research subject, as specified in WAC 246-240-060.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-19-084, filed 9/20/22, effective 10/21/22)
WAC 246-240-075Training for an authorized nuclear pharmacist.
Except as provided in WAC 246-240-078, the licensee shall require the authorized nuclear pharmacist to be a pharmacist who:
(1) Is certified by a specialty board whose certification process has been recognized by the department, NRC, or an agreement state. The names of board certifications that have been recognized by the department, NRC, or an agreement state are posted on the NRC's medical uses licensee toolkit web page. To have its certification process recognized, a specialty board shall require all candidates for certification to:
(a) Have graduated from a pharmacy program accredited by the ((American))Accreditation Council ((on Pharmaceutical))for Pharmacy Education (ACPE) or have passed the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Examination Committee (FPGEC) examination;
(b) Hold a current, active license to practice pharmacy;
(c) Provide evidence of having acquired at least 4,000 hours of training/experience in nuclear pharmacy practice. Academic training may be substituted for no more than 2,000 hours of the required training and experience; and
(d) Pass an examination in nuclear pharmacy administered by diplomates of the specialty board, which assesses knowledge and competency in procurement, compounding, quality assurance, dispensing, distribution, health and safety, radiation safety, provision of information and consultation, monitoring patient outcomes, research and development; or
(2)(a) Has completed 700 hours in a structured educational program consisting of both:
(i) Two hundred hours of classroom and laboratory training in the following areas:
(A) Radiation physics and instrumentation;
(B) Radiation protection;
(C) Mathematics pertaining to the use and measurement of radioactivity;
(D) Chemistry of radioactive material for medical use; and
(E) Radiation biology; and
(ii) Supervised practical experience in a nuclear pharmacy involving:
(A) Shipping, receiving, and performing related radiation surveys;
(B) Using and performing checks for proper operation of instruments used to determine the activity of dosages, survey meters, and, if appropriate, instruments used to measure alpha-or beta-emitting radionuclides;
(C) Calculating, assaying, and safely preparing dosages for patients or human research subjects;
(D) Using administrative controls to avoid medical events in the administration of radioactive material; and
(E) Using procedures to prevent or minimize radioactive contamination and using proper decontamination procedures; and
(b) Has obtained written attestation, signed by a preceptor authorized nuclear pharmacist, that the individual has satisfactorily completed the requirements in (a) of this subsection and is able to independently fulfill the radiation safety-related duties as an authorized nuclear pharmacist.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-19-084, filed 9/20/22, effective 10/21/22)
WAC 246-240-078Training for experienced radiation safety officer, teletherapy or medical physicist, authorized medical physicist, authorized user, nuclear pharmacist, and authorized nuclear pharmacist.
(1)(a) An individual identified on a department, NRC, or an agreement state license; or a permit issued by a department, NRC, or an agreement state broad scope licensee or master material license permit; or by a master material license permittee of broad scope as a radiation safety officer, a teletherapy or medical physicist, an authorized medical physicist, a nuclear pharmacist or authorized nuclear pharmacist on or before January 14, 2019, need not comply with the training requirements of WAC 246-240-069, 246-240-072, or 246-240-075, respectively except the radiation safety officers and authorized medical physicists identified in this subsection must meet the training requirements in WAC 246-240-069(4) or 246-240-072(3), as appropriate, for any material or uses for which they were not authorized prior to this date.
(b) Any individual certified by the American Board of Health Physics in Comprehensive Health Physics; American Board of Radiology; American Board of Nuclear Medicine; American Board of Science in Nuclear Medicine; Board of Pharmaceutical Specialties in Nuclear Pharmacy; American Board of Medical Physics in radiation oncology physics; Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada in nuclear medicine; American Osteopathic Board of Radiology; or American Osteopathic Board of Nuclear Medicine on or before October 24, 2005, need not comply with the training requirements of WAC 246-240-069 to be identified as a radiation safety officer or as an associate radiation safety officer on a department, NRC, or an agreement state license or NRC master material license permit for those materials and uses that these individuals performed on or before October 24, 2005.
(c) Any individual certified by the American Board of Radiology in therapeutic radiological physics, Roentgen ray and gamma ray physics, X-ray and radium physics, or radiological physics, or certified by the American Board of Medical Physics in radiation oncology physics, on or before October 24, 2005, need not comply with the training requirements for an authorized medical physicist described in WAC 246-240-072, for those materials and uses that these individuals performed on or before October 24, 2005.
(d) A radiation safety officer, a medical physicist, or a nuclear pharmacist, who used only accelerator-produced radioactive materials, discrete sources of radium-226, or both, for medical uses or in the practice of nuclear pharmacy at a government agency or federally recognized Indian tribe before November 30, 2007, or at all other locations of use before August 8, 2009, or an earlier date as noticed by the NRC, need not comply with the training requirements of WAC 246-240-069, 246-240-072 or 246-240-075, respectively, when performing the same uses. A nuclear pharmacist, who prepared only radioactive drugs containing accelerator-produced radioactive materials, or a medical physicist, who used only accelerator-produced radioactive materials, at the locations and during the time period identified in this subsection, qualifies as an authorized nuclear pharmacist or an authorized medical physicist, respectively, for those materials and uses performed before these dates, for the purposes of this chapter.
(2)(a) Physicians, dentists, or podiatrists identified as authorized users for the medical use of radioactive material on a license issued by the department, NRC, or an agreement state, a permit issued by an NRC master material license, a permit issued by a department, NRC, or an agreement state broad scope licensee, or permit issued by an NRC master material license broad scope permittee on or before January 14, 2019, who perform only those medical uses for which they were authorized on or before that date need not comply with the training requirements of WAC 246-240-151 through 246-240-399.
(b) Physicians, dentists, or podiatrists not identified as authorized users for the medical use of radioactive material on a license issued by the department, NRC, or an agreement state, a permit issued by an NRC master material licensee, a permit issued by the department, NRC, or an agreement state broad scope licensee, or a permit issued in accordance with ((an NRC))a commission master material broad scope license on or before October 24, 2005, need not comply with the training requirements of WAC 246-240-151 through 246-240-399 for those materials and uses that these individuals performed on or before October 24, 2005, as follows:
(i) For uses authorized under WAC 246-240-151 or 246-240-157, or oral administration of sodium iodide I–131 requiring a written directive for imaging and localization purposes, a physician who was certified on or before October 24, 2005, in nuclear medicine by the American Board of Nuclear Medicine; diagnostic radiology by the American Board of Radiology; diagnostic radiology or radiology by the American Osteopathic Board of Radiology; nuclear medicine by the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada; or American Osteopathic Board of Nuclear Medicine in nuclear medicine;
(ii) For uses authorized under WAC 246-240-201, a physician who was certified on or before October 24, 2005, by the American Board of Nuclear Medicine; the American Board of Radiology in radiology, therapeutic radiology, or radiation oncology; nuclear medicine by the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada; or the American Osteopathic Board of Radiology after 1984;
(iii) For uses authorized under WAC 246-240-251 or 246-240-351, a physician who was certified on or before October 24, 2005, in radiology, therapeutic radiology or radiation oncology by the American Board of Radiology; radiation oncology by the American Osteopathic Board of Radiology; radiology, with specialization in radiotherapy, as a British "Fellow of the Faculty of Radiology" or "Fellow of the Royal College of Radiology"; or therapeutic radiology by the Canadian Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons; and
(iv) For uses authorized under WAC 246-240-301, a physician who was certified on or before October 24, 2005, in radiology, diagnostic radiology, therapeutic radiology, or radiation oncology by the American Board of Radiology; nuclear medicine by the American Board of Nuclear Medicine; diagnostic radiology or radiology by the American Osteopathic Board of Radiology; or nuclear medicine by the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.
(c) Physicians, dentists, or podiatrists who used only accelerator-produced radioactive materials, discrete sources of radium-226, or both, for medical uses performed at a government agency or federally recognized Indian tribe before November 30, 2007, or at all other locations of use before August 8, 2009, or an earlier date as noticed by the NRC, need not comply with the training requirements of WAC 246-240-151 through 246-240-399 of this chapter when performing the same medical uses. A physician, dentist, or podiatrist, who used only accelerator-produced radioactive materials, discrete sources of radium-226, or both, for medical uses at the locations and time period identified in this subsection, qualifies as an authorized user for those materials and uses performed before these dates, for the purposes of this chapter.
(3) Individuals who need not comply with training requirements as described in this section may serve as preceptors for, and supervisors of, applicants seeking authorization on state of Washington radioactive materials licenses for the same uses for which these individuals are authorized.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-19-084, filed 9/20/22, effective 10/21/22)
WAC 246-240-210Training for use of unsealed radioactive material for which a written directive is required.
Except as provided in WAC 246-240-078, the licensee shall require an authorized user of unsealed radioactive material for the uses authorized under WAC 246-240-201 to be a physician who:
(1) Is certified by a medical specialty board whose certification process has been recognized by the department, NRC, or an agreement state and who meets the requirements in subsection (2)(a)(ii)(G) of this section. The names of board certifications that have been recognized by the department, NRC, or an agreement state are posted on the NRC's medical uses licensee toolkit web page. To have its certification process recognized, a specialty board shall require all candidates for certification to:
(a) Successfully complete a residency training in a radiation therapy or nuclear medicine training program or a program in a related medical specialty that includes 700 hours of training and experience as described in subsection (2)(a)(i) through (ii)(E) of this section. Eligible training programs must be approved by the Residency Review Committee of the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education or Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada or the ((Committee on Postgraduate))Council on Postdoctoral Training of the American Osteopathic Association; and
(b) Pass an examination, administered by diplomates of the specialty board, which tests knowledge and competence in radiation safety, radionuclide handling, quality assurance, and clinical use of unsealed radioactive material for which a written directive is required; or
(2)(a) Has completed 700 hours of training and experience, including a minimum of 200 hours of classroom and laboratory training, in basic radionuclide handling techniques applicable to the medical use of unsealed radioactive material requiring a written directive. The training and experience must include:
(i) Classroom and laboratory training in the following areas:
(A) Radiation physics and instrumentation;
(B) Radiation protection;
(C) Mathematics pertaining to the use and measurement of radioactivity;
(D) Chemistry of radioactive material for medical use; and
(E) Radiation biology; and
(ii) Work experience, under the supervision of an authorized user who meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-078, or this section, or equivalent NRC or agreement state requirements. A supervising authorized user, who meets the requirements in this subsection, must also have experience in administering dosages in the same dosage category or categories (as in (a)(ii)(G) of this subsection) as the individual requesting authorized user status. The work experience must involve:
(A) Ordering, receiving, and unpacking radioactive materials safely and performing the related radiation surveys;
(B) Performing quality control procedures on instruments used to determine the activity of dosages and performing checks for proper operation of survey meters;
(C) Calculating, measuring, and safely preparing patient or human research subject dosages;
(D) Using administrative controls to prevent a medical event involving the use of unsealed radioactive material;
(E) Using procedures to contain spilled radioactive material safely and using proper decontamination procedures;
(F) (Reserved);
(G) Administering dosages of radioactive drugs to patients or human research subjects from the three categories in this subsection. Radioactive drugs containing radionuclides in categories not included in this subsection are regulated under WAC 246-240-501. This work experience must involve a minimum of three cases in each of the following categories for which the individual is requesting authorized user status:
(I) Oral administration of less than or equal to 1.22 gigabecquerels (33 millicuries) of sodium iodide I-131 for which a written directive is required;
(II) Oral administration of greater than 1.22 gigabecquerels (33 millicuries) of sodium iodide I-131. Experience with at least three cases in this also satisfies the requirement in (a)(ii)(G)(I) of this subsection;
(III) Parenteral administration of any radioactive drug that contains a radionuclide that is primarily used for its electron emission, beta radiation characteristics, alpha radiation characteristics, or photon energy less than 150 keV for which a written directive is required; and
(b) Has obtained written attestation that the individual has satisfactorily completed the requirements in (a) of this subsection, and is able to independently fulfill at radiation safety-related duties as an authorized user for the medical uses authorized under WAC 246-240-201 for which the individual is requesting authorized user status. The written attestation must be obtained from either:
(i) A preceptor authorized user who meets the requirements in this section, WAC 246-240-078, 246-240-210, or equivalent NRC or agreement state requirements, and has experience in administering dosages in the same dosage category or categories (as in (a)(ii)(G) of this subsection) as the individual requesting authorized user status; or
(ii) A residency program director who affirms in writing that the attestation represents the consensus of the residency program faculty where at least one faculty member is an authorized user who meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-078, 246-240-210, or equivalent NRC or agreement state requirements, has experience in administering dosages in the same dosage category or categories as the individual requesting authorized user status, and concurs with the attestation provided by the residency program director. The residency training program must be approved by the Residency Review Committee of the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education or the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada or the Council on Postdoctoral Training of the American Osteopathic Association and must include training and experience specified in (a) of this subsection.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-19-084, filed 9/20/22, effective 10/21/22)
WAC 246-240-278Training for use of manual brachytherapy sources.
Except as provided in WAC 246-240-078, the licensee shall require an authorized user of a manual brachytherapy source for the uses authorized under WAC 246-240-251 to be a physician who:
(1) Is certified by a medical specialty board whose certification process has been recognized by the department, NRC, or an agreement state. The names of board certifications that have been recognized by the department, NRC, or an agreement state are posted on the NRC's medical uses licensee toolkit web page. To have its certification process recognized, a specialty board shall require all candidates for certification to:
(a) Successfully complete a minimum of three years of residency training in a radiation oncology program approved by the Residency Review Committee of the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education or Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada or the ((Committee on Postgraduate))Council on Postdoctoral Training of the American Osteopathic Association; and
(b) Pass an examination, administered by diplomates of the specialty board, which tests knowledge and competence in radiation safety, radionuclide handling, treatment planning, quality assurance, and clinical use of manual brachytherapy; or
(2)(a) Has completed a structured educational program in basic radionuclide handling techniques applicable to the use of manual brachytherapy sources that includes:
(i) Two hundred hours of classroom and laboratory training in the following areas:
(A) Radiation physics and instrumentation;
(B) Radiation protection;
(C) Mathematics pertaining to the use and measurement of radioactivity; and
(D) Radiation biology; and
(ii) Five hundred hours of work experience, under the supervision of an authorized user who meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-078, 246-240-278 or equivalent agreement state or NRC requirements at a medical institution authorized to use radioactive materials under WAC 246-240-251, involving:
(A) Ordering, receiving, and unpacking radioactive materials safely and performing the related radiation surveys;
(B) Checking survey meters for proper operation;
(C) Preparing, implanting, and removing brachytherapy sources;
(D) Maintaining running inventories of material on hand;
(E) Using administrative controls to prevent a medical event involving the use of radioactive material;
(F) Using emergency procedures to control radioactive material; and
(b) Has completed three years of supervised clinical experience in radiation oncology, under an authorized user who meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-078, 246-240-278, or equivalent NRC or agreement state requirements, as part of a formal training program approved by the Residency Review Committee for Radiation Oncology of the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education or the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada or the ((Committee))Council on Postdoctoral Training of the American Osteopathic Association. This experience may be obtained concurrently with the supervised work experience required by (a)(ii) of this subsection; and
(c) Has obtained written attestation that the individual has satisfactorily completed the requirements in (a) and (b) of this subsection and is able to independently fulfill the radiation safety-related duties as an authorized user of manual brachytherapy sources for the medical uses authorized under WAC 246-240-251. The attestation must be obtained from either:
(i) A preceptor authorized user who meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-078, 246-240-278, or equivalent agreement state or NRC requirements; or
(ii) A residency program director who affirms in writing that the attestation represents the consensus of the residency program faculty where at least one faculty member is an authorized user who meets the requirements in WAC 246-240-078, 246-240-278, or equivalent NRC or agreement state requirements, and concurs with the attestation provided by the residency program director. The residency training program must be approved by the Residency Review Committee of the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education or the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada or the Council on Postdoctoral Training of the American Osteopathic Association and must include training and experience specified in (a) and (b) of this subsection.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-19-084, filed 9/20/22, effective 10/21/22)
WAC 246-240-651Report and notification of a medical event.
(1) A licensee shall report any event as a medical event, except for an event that results from patient intervention, in which:
(a) The administration of radioactive material or radiation from radioactive material, except permanent implant brachytherapy, results in:
(i) A dose that differs from the prescribed dose or dose that would have resulted from the prescribed dosage by more than 0.05 Sv (five rem) effective dose equivalent, 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to an organ or tissue, or 0.5 Sv (50 rem) shallow dose equivalent to the skin; and
(A) The total dose delivered differs from the prescribed dose by 20 percent or more;
(B) The total dosage delivered differs from the prescribed dosage by 20 percent or more or falls outside the prescribed dosage range; or
(C) The fractionated dose delivered differs from the prescribed dose, for a single fraction, by 50 percent or more.
(ii) A dose that exceeds 0.05 Sv (five rem) effective dose equivalent, 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to an organ or tissue, or 0.5 Sv (50 rem) shallow dose equivalent to the skin from any of the following:
(A) An administration of a wrong radioactive drug containing radioactive material or the wrong radionuclide for a brachytherapy procedure;
(B) An administration of a radioactive drug containing radioactive material by the wrong route of administration;
(C) An administration of a dose or dosage to the wrong individual or human research subject;
(D) An administration of a dose or dosage delivered by the wrong mode of treatment; or
(E) A leaking sealed source.
(iii) A dose to the skin or an organ or tissue other than the treatment site that exceeds by:
(A) 0.5 Sv (50 rem) or more the expected dose to that site from the procedure if the administration had been given in accordance with the written directive prepared or revised before administration; and
(B) Fifty percent or more the expected dose to that site from the procedure if the administration had been given in accordance with the written directive prepared or revised before administration.
(b) For permanent implant brachytherapy, the administration of radioactive material or radiation from radioactive material (excluding sources that were implanted in the correct site but migrated outside the treatment site) that results in:
(i) The total source strength administered differing by 20 percent or more from the total source strength documented in the post-implantation portion of the written directive;
(ii) The total source strength administered outside of the treatment site exceeding 20 percent of the total source strength documented in the post-implantation portion of the written directive; or
(iii) An administration that includes any of the following:
(A) The wrong radionuclide;
(B) The wrong individual or human research subject;
(C) Sealed sources implanted directly into a location discontiguous from the treatment site, as documented in the post-implantation portion of the written directive; or
(D) A leaking sealed source resulting in a dose that exceeds 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to an organ or tissue.
(2) A licensee shall report any event resulting from intervention of a patient or human research subject in which the administration of radioactive material or radiation from radioactive material results or will result in unintended permanent functional damage to an organ or a physiological system, as determined by a physician.
(3) The licensee shall notify by telephone (360-236-3300) the department no later than the next calendar day after discovery of the medical event.
(4) By an appropriate method listed in WAC 246-221-250, the licensee shall submit a written report to the department at P.O. Box 47827, Olympia WA 98504-7827 within 15 days after discovery of the medical event.
(a) The written report must include:
(i) The licensee's name;
(ii) The name of the prescribing physician;
(iii) A brief description of the event;
(iv) Why the event occurred;
(v) The effect, if any, on the individuals who received the administration;
(vi) What actions, if any, have been taken or are planned to prevent recurrence; and
(vii) Certification that the licensee notified the individual (or the individual's responsible relative or guardian), and if not, why not.
(b) The report may not contain the individual's name or any other information that could lead to identification of the individual.
(5) The licensee shall provide notification of the event to the referring physician and also notify the individual who is the subject of the medical event no later than 24 hours after its discovery, unless the referring physician personally informs the licensee either that they will inform the individual or that, based on medical judgment, telling the individual would be harmful. The licensee is not required to notify the individual without first consulting the referring physician. If the referring physician or the affected individual cannot be reached within 24 hours, the licensee shall notify the individual as soon as possible thereafter. The licensee may not delay any appropriate medical care for the individual, including any necessary remedial care as a result of the medical event, because of any delay in notification. To meet the requirements of this subsection, the notification of the individual who is the subject of the medical event may be made instead to that individual's responsible relative or guardian. If a verbal notification is made, the licensee shall inform the individual, or appropriate responsible relative or guardian, that a written description of the event can be obtained from the licensee upon request. The licensee shall provide a written description if requested.
(6) Aside from the notification requirement, nothing in this section affects any rights or duties of licensees and physicians in relation to each other, to individuals affected by the medical event, or to that individual's responsible relatives or guardians.
(7) A licensee shall:
(a) Annotate a copy of the report provided to the department with the:
(i) Name of the individual who is the subject of the event; and
(ii) Identification number or if no other identification number is available, the Social Security number ((or other identification number, if one has been assigned,)) of the individual who is the subject of the event; and
(b) Provide a copy of the annotated report to the referring physician, if other than the licensee, no later than 15 days after the discovery of the event.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 22-19-084, filed 9/20/22, effective 10/21/22)
WAC 246-240-654Report and notification of a dose to an embryo/fetus or a nursing child.
(1) A licensee shall report to the department at P.O. Box 47827, Olympia WA 98504-7827, (phone 360-236-3300), any dose to an embryo/fetus that is greater than 50 mSv (five rem) dose equivalent that is a result of an administration of radioactive material or radiation from radioactive material to a pregnant individual unless the dose to the embryo/fetus was specifically approved, in advance, by the authorized user.
(2) A licensee shall report any dose to a nursing child that is a result of an administration of radioactive material to a breast-feeding individual that:
(a) Is greater than 50 mSv (five rem) total effective dose equivalent; or
(b) Has resulted in unintended permanent functional damage to an organ or a physiological system of the child, as determined by a physician.
(3) The licensee shall notify by telephone the department no later than the next calendar day after discovery of a dose to the embryo/fetus or nursing child that requires a report in subsection (1) or (2) of this section.
(4) By an appropriate method listed in WAC 246-221-250, the licensee shall submit a written report to the department within 15 days after discovery of a dose to the embryo/fetus or nursing child that requires a report in subsection (1) or (2) of this section.
(a) The written report must include:
(i) The licensee's name;
(ii) The name of the prescribing physician;
(iii) A brief description of the event;
(iv) Why the event occurred;
(v) The effect, if any, on the embryo/fetus or the nursing child;
(vi) What actions, if any, have been taken or are planned to prevent recurrence; and
(vii) Certification that the licensee notified the pregnant individual or mother (or the mother's or child's responsible relative or guardian), and if not, why not.
(b) The report must not contain the individual's or child's name or any other information that could lead to identification of the individual or child.
(5) The licensee shall provide notification of the event to the referring physician and also notify the pregnant individual or mother, both hereafter referred to as the mother, no later than 24 hours after discovery of an event that would require reporting under subsection (1) or (2) of this section, unless the referring physician personally informs the licensee either that they will inform the mother or that, based on medical judgment, telling the mother would be harmful. The licensee is not required to notify the mother without first consulting with the referring physician. If the referring physician or mother cannot be reached within 24 hours, the licensee shall make the appropriate notifications as soon as possible thereafter. The licensee may not delay any appropriate medical care for the embryo/fetus or for the nursing child, including any necessary remedial care as a result of the event, because of any delay in notification. To meet the requirements of this subsection, the notification may be made to the mother's or child's responsible relative or guardian instead of the mother. If a verbal notification is made, the licensee shall inform the mother, or the mother's or child's responsible relative or guardian, that a written description of the event can be obtained from the licensee upon request. The licensee shall provide a written description if requested.
(6) A licensee shall:
(a) Annotate a copy of the report provided to the department with the:
(i) Name of the pregnant individual or the nursing child who is the subject of the event; and
(ii) Identification number or if no other identification number is available, the Social Security number ((or other identification number, if one has been assigned, of the pregnant individual or the nursing child))of the individual who is the subject of the event; and
(b) Provide a copy of the annotated report to the referring physician, if other than the licensee, no later than 15 days after the discovery of the event.