WSR 23-24-084
PROPOSED RULES
DEPARTMENT OF
LABOR AND INDUSTRIES
[Filed December 5, 2023, 11:56 a.m.]
Original Notice.
Preproposal statement of inquiry was filed as WSR 23-08-066.
Title of Rule and Other Identifying Information: Electrical rules—Code adoption. Chapter 296-46B WAC, Electrical safety standards, administration, and installation, excluding WAC 296-46B-945 Qualifying for master, journey level, specialty electrician examinations.
Hearing Location(s): On January 9, 2024, at 9:00 a.m., at the Department of Labor and Industries (L&I), 7273 Linderson Way S.W., Tumwater, WA 98501; or join electronically https://lni-wa-gov.zoom.us/j/81522232436?pwd=dStmUVdoU0o4WGtsbUsvT2I5RDk2UT09, Passcode xZ+m4AFj; or join by phone (audio only) 253-215-8782, Meeting ID 815 2223 2436, Passcode 50041258. The in-person and virtual/telephonic hearing starts at 9:00 a.m. and will continue until all oral comments are received.
Date of Intended Adoption: February 20, 2024.
Submit Written Comments to: Meagan Edwards, L&I, Field Services and Public Safety Division, P.O. Box 44400, Olympia, WA 98504-4400, email Meagan.Edwards@Lni.wa.gov, fax 360-902-6134, by 5 p.m. on January 9, 2024.
Assistance for Persons with Disabilities: Contact Meagan Edwards, phone 360-522-0125, fax 360-902-6134, email Meagan.Edwards@Lni.wa.gov, by December 20, 2023.
Purpose of the Proposal and Its Anticipated Effects, Including Any Changes in Existing Rules: This rule making proposes amendments to adopt the 2023 edition of the National Fire Protection Agency (NFPA) 70, the National Electrical Code (NEC), and other related codes for electrical. The 2023 NEC (NFPA 70-2023) would replace the current 2020 NEC (NFPA 70-2020) adopted standards.
The electrical program reviewed the existing rules and 2023 NEC (NFPA 70-2023) to update rules for consistency with the latest national safety standards and industry practice. The 2023 edition of the code presents the latest comprehensive regulations for electrical wiring, overcurrent protection, grounding and installation of equipment.
Washington's electrical stakeholders and other interested parties were invited to participate in the review process, submit proposals and provide recommendations to L&I for possible rule amendments. A technical advisory committee of industry experts and the electrical board reviewed the proposals and provided recommendations on adoption of the rules. This rule making is necessary to adopt the latest safety codes, and other amendments to the rules identified during the formal review process and recommended by stakeholders to improve public safety.
Proposed rules to this chapter are as follows:
New Sections:
WAC 296-46B-235 Branch circuits, feeders, and services over 1,000 volts ac, 1,500 volts dc nominal.
| |
| • | Creates a new section for an exception to not restrict wiring methods when proper overcurrent protection is provided. |
WAC 296-46B-692 Fuel cell systems.
| |
| • | Creates a new section requiring installers to provide a system design review defined under WAC 296-46B-100 that will likely improve conformance to code requirements intended to protect life and property. |
WAC 296-46B-710 Standalone systems.
| |
| • | Creates a new section to implement a design review requirement for standalone systems. |
Amended Sections:
WAC 296-46B-010 General.
| |
| • | Amends references to adopt the 2023 NEC (NFPA 70-2023), which is the latest version of the code published in September 2022. |
| • | Amends language to automatically adopt the latest published versions of the American National Standards Institute and Telecommunications Industry Association (ANSI/TIA) codes and National Electrical Safety Codes (NESC). |
| • | Removes references to the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA), as this organization no longer exists. |
| • | Amends language for general housekeeping, such as updating references, clarifying language, removing obsolete language, renumbering subsections, etc. |
WAC 296-46B-100 General definitions.
| |
| • | Adds a new definition to define the meaning of "equivalent apprenticeship program," due to the passage of SSB 6126, chapter 249, Laws of 2018. |
| • | Amends the definitions of "WAC" and "RCW" to clarify that only electronic copies of the electrical laws and rules are available from L&I and the office of the code reviser. |
WAC 296-46B-110 General—Requirements for electrical installations.
| |
| • | Amends language for general housekeeping, such as punctuation and updating the section title. |
WAC 296-46B-210 Wiring and protection—Branch circuits.
| |
| • | Adds language that does not require future provisions for receptacle outlets installed on islands or peninsular countertops or work surfaces. |
| • | Adds language that clarifies "accessible" locations for equipment that requires servicing outdoors, as the code is unclear. |
| • | Amends the section title for consistency with the 2023 NEC and to narrow content. |
WAC 296-46B-215 Wiring and protection—Feeders.
| |
| • | Amends the section title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-220 Wiring and protection—Branch circuit, feeder, and service calculations.
| |
| • | Amends the section title, header and references for consistency with the 2023 NEC. |
WAC 296-46B-225 Wiring and protection—Outside branch circuits and feeders.
| |
| • | Amends references related to feeder disconnecting means for uniformity with the 2023 NEC. |
| |
| • | Amends language for general housekeeping, such as updating the section title and headers, clarifying language, and relocating and restructuring existing language. |
WAC 296-46B-230 Wiring and protection—Services.
| |
| • | Adds exceptions to wiring methods for service conductors within a building or structure when protected by customer owned supply side overcurrent protection. |
| • | Adds language that clarifies when an emergency disconnecting means must be installed if replacing existing equipment. |
| • | Amends language for general housekeeping, such as the section title, renumbering subsections, relocating language, and removing obsolete language. |
WAC 296-46B-240 Overcurrent protection.
| |
| • | Includes roofs in the requirement that overcurrent protection equipment enclosures be installed 24 inches above the surface. |
| • | Creates new subsections requiring documentation to assure [ensure] that testing required by the NEC 240.67 and NEC 240.87 is performed. |
WAC 296-46B-250 Wiring and protection—Grounding and bonding.
| |
| • | Adds new language to clarify when concrete electrode requirements apply where additions are made to existing foundations. |
| • | Amends the section title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-300 Wiring methods and materials—Wiring methods.
| |
| • | Amends language for general housekeeping, such as updating section title and header and reference. |
WAC 296-46B-314 Wiring methods and materials—Outlet, device, pull, and junction boxes.
| |
| • | Adds a new subsection to clarify the locations acceptable for installing ceiling-suspended (paddle) fans for consistency with L&I's existing practice. |
| |
| • | Adds clarifying language to include device accessibility for consistency with the 2023 NEC. |
| |
| • | Amends the section title and header for consistency with the 2023 NEC and to narrow content. |
WAC 296-46B-334 Wiring methods and materials—Nonmetallic-sheathed cable.
| |
| • | Adds new language that clarifies wet or damp locations and conditions for installing non-metallic sheath (NM) cables for consistency with L&I's existing practice. |
| • | Amends the title for consistency with the 2023 NEC. |
WAC 296-46B-358 Wiring methods and materials—Electrical metallic tubing.
| |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-394 Wiring methods and materials—Concealed knob-and-tube wiring.
| |
| • | Updates table references for consistency with the 2023 NEC table. |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-408 Equipment for general use—Switchboards, switchgear, and panelboards.
| |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-410 Equipment for general use—Luminaires.
| |
| • | Amends language for general housekeeping, such as updating section title and header, and term for use in the 2023 NEC. |
WAC 296-46B-422 Equipment for general use—Appliances.
| |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
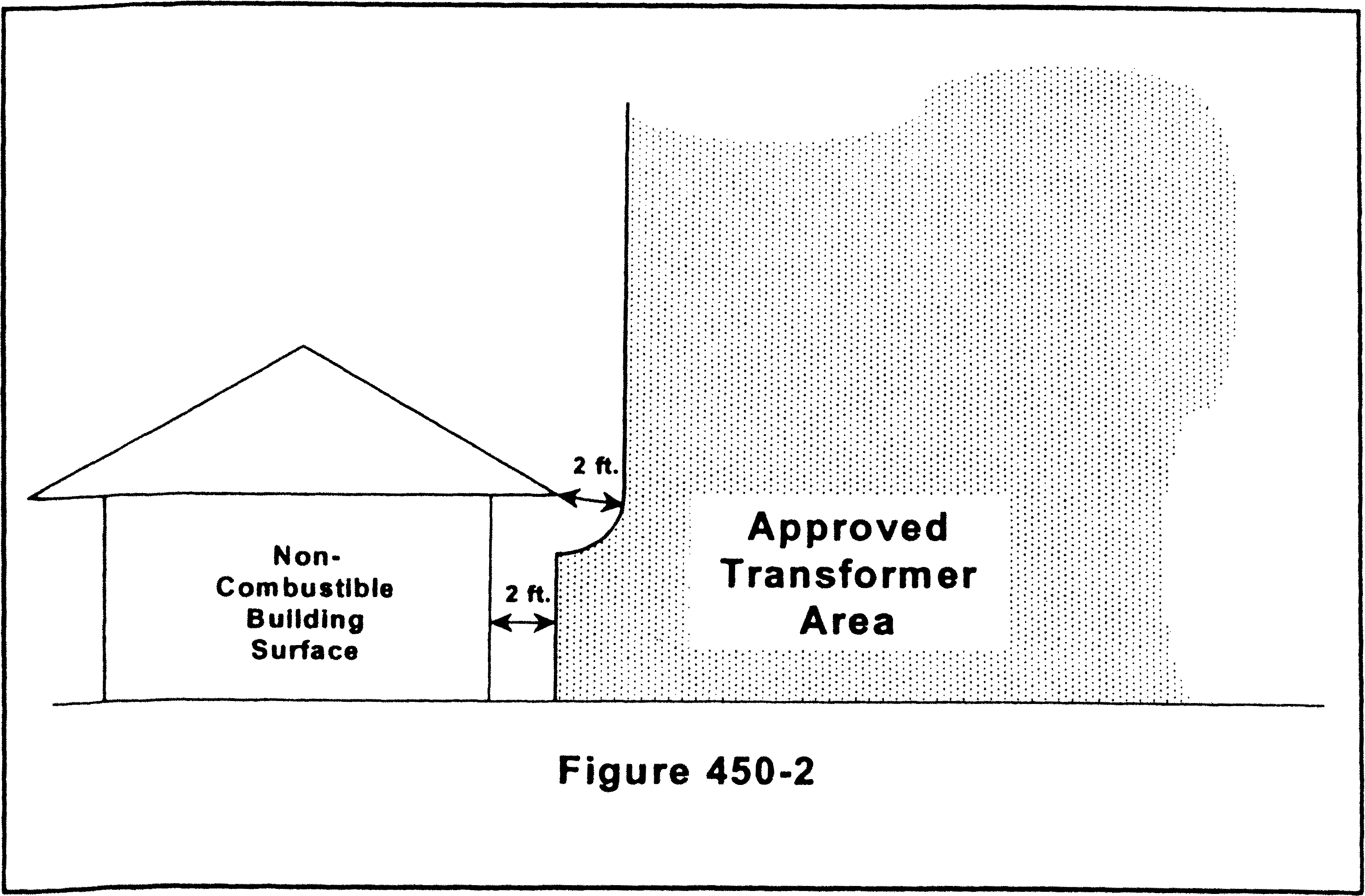
WAC 296-46B-450 Equipment for general use—Transformers and transformer vaults.
| |
| • | Amends the title and header for consistency with the 2023 NEC and to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-501 Special occupancies NEC Class I locations.
| |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-505 Class I, Zone 0, 1, and 2 locations.
| |
| • | Amends the title for consistency with the 2023 NEC. |
WAC 296-46B-513 Special occupancies—Aircraft hangars.
| |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-514 Special occupancies—Motor fuel dispensing facilities.
| |
| • | Updated reference to align with the 2023 NEC. |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-517 Special occupancies—Health care facilities.
| |
| • | Amends the title and header for consistency with the [2023] NEC and to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-547 Special occupancies—Agricultural buildings.
| |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-550 Special occupancies—Mobile homes, manufactured homes and mobile home parks.
| |
| • | Adds new language to allow for mounting of service equipment on mobile/manufactured homes if approved by the manufacturer. |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-555 Special occupancies—Marinas, boatyards, floating buildings, and commercial and noncommercial docking facilities.
| |
| • | Amends language to clarify the meaning of corrosion resistant and provide information for what is acceptable. |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-590 Special occupancies—Temporary installations.
| |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-600 Special equipment—Electric signs and outline lighting.
| |
| • | Amends the title to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-620 Special equipment—Elevators.
| |
| • | Amends the title for consistency with the 2023 NEC and to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-680 Special equipment—Swimming pools, fountains, and similar installations.
| |
| • | Amends language for general housekeeping, such as updating the title, removing a header, and renumbering subsections. |
WAC 296-46B-690 Solar photovoltaic systems.
| |
| • | Adds new language to clarify availability of the design review defined under WAC 296-46B-100. |
WAC 296-46B-694 Wind electric systems.
| |
| • | Adds new language that clarifies the availability of the design review defined under WAC 296-46B-100. |
WAC 296-46B-700 Emergency systems.
| |
| • | Adds new requirements for selective coordination when overcurrent devices are replaced for consistency with the 2023 NEC. |
| • | Amends header for consistency with the 2023 NEC. |
WAC 296-46B-701 Legally required standby systems.
| |
| • | Adds new requirements for selective coordination when overcurrent devices are replaced for consistency with the 2023 NEC. |
| • | Amends header for consistency with the 2023 NEC. |
WAC 296-46B-702 Optional standby systems.
| |
| • | Amends the requirements pertaining to placing signs for consistency with the 2023 NEC. |
WAC 296-46B-705 Interconnected electric power production sources.
| |
| • | Adds new subsection requiring installers to provide a system design review for interconnected electric power production sources. |
WAC 296-46B-800 Communications systems—Communications circuits.
| |
| • | Amends the title and header for consistency with the 2023 NEC and to narrow focus of content. |
WAC 296-46B-908 Class B permits. Class B electrical work permit—Use.
| |
| • | Amends language to extend the validity of Class B permits to 120 days to allow more time for installations. |
WAC 296-46B-920 Electrical/telecommunications license/certificate types and scope of work.
| |
| • | Updates the (06A) scope of work to allow these electricians to perform certain work when it is directly related to the mini-split HVAC refrigeration systems, install lower rated overcurrent devices that are compatible with replacement gas or oil furnaces, and install devices to protect sensitive electronics in HVAC/refrigeration equipment. |
| • | Amends language for general housekeeping, such as relocating and restructuring requirements for the (06A) and (06B) scopes of work, clarifying language, updating references, renumbering subsections, etc. |
WAC 296-46B-925 Electrical/telecommunications contractor's license. General.
| |
| • | Amends subsection numbers for consistency with SB 6170, chapter 153, Laws of 2020. |
WAC 296-46B-942 Training certificate required. General.
| |
| • | Amends language to clarify the submittal requirements for affidavits to streamline the process. |
| • | Removes obsolete language. |
WAC 296-46B-960 Administrator and electrician certificate of competency examinations. General.
| |
| • | Amends language that allows special accommodations for candidates with language barriers when taking the electrician certificate of competency examination. This also includes: |
| |
| o | Removing the requirement for a notarized release to discuss matters, written opinion from a physician or other appropriate specialist is adequate. |
| o | Amending the order of actions necessary for approval of a special accommodations request. |
| o | Streamlines requirements an applicant with limit English proficiency to request an accommodation. |
Repealed Section:
WAC 296-46B-406R Equipment for general use—Receptacles.
| |
| • | Repeals the rule as these requirements are obsolete and now addressed in 2023 NEC 406.12. |
WAC 296-46B-440 Air conditioning and refrigerating equipment.
| |
| • | Repeals the rule to align with NEC 440.8 that may consider split systems a "single machine" under certain conditions. |
Reasons Supporting Proposal: NEC sets the standard for safe electrical design, installation and inspection in homes, businesses, industry, and institutions to protect people and property from electrical hazards. These rules are necessary to ensure the new safety codes that affect electrical work align with existing rules and Washington state is consistent with other states that regulate the industry.
Statutory Authority for Adoption: Chapter
19.28 RCW, Electricians and electrical installations, including RCW
19.28.031 and
19.28.251.
Statute Being Implemented: Chapter
19.28 RCW, Electricians and electrical installations, including RCW
19.28.031 and
19.28.251.
Rule is not necessitated by federal law, federal or state court decision.
Name of Proponent: L&I, governmental.
Name of Agency Personnel Responsible for Drafting: Wayne Molesworth, Program Manager, Tumwater, Washington, 360-902-6234; Implementation and Enforcement: Steve Reinmuth, Assistant Director, Tumwater, Washington, 360-902-6348.
A school district fiscal impact statement is not required under RCW
28A.305.135.
A cost-benefit analysis is required under RCW
34.05.328. A preliminary cost-benefit analysis may be obtained by contacting Meagan Edwards, L&I, Field Services and Public Safety, P.O. Box 44400, Olympia, WA 98504-4400, phone 360-522-0125, fax 360-902-6134, email
Meagan.Edwards@Lni.wa.gov.
This rule proposal, or portions of the proposal, is exempt from requirements of the Regulatory Fairness Act because the proposal:
Is exempt under RCW
19.85.025(3) as the rules are adopting or incorporating by reference without material change federal statutes or regulations, Washington state statutes, rules of other Washington state agencies, shoreline master programs other than those programs governing shorelines of statewide significance, or, as referenced by Washington state law, national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards, if the material adopted or incorporated regulates the same subject matter and conduct as the adopting or incorporating rule; and rules only correct typographical errors, make address or name changes, or clarify language of a rule without changing its effect.
Scope of exemption for rule proposal:
Is partially exempt:
Explanation of partial exemptions:
| Proposed WAC Sections and Title | This proposed rule section is not exempt - Analysis is required | This proposed rule section is exempt. Provide RCW to support this exemption. |
1. | WAC 296-46B-010 General. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) and 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards and changes that only clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
2. | WAC 296-46B-100 General definitions. | X | |
3. | WAC 296-46B-110 General—Requirements for electrical installations. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
4. | WAC 296-46B-210 Wiring and protection—Branch circuits. | X | |
5. | WAC 296-46B-215 Wiring and protection—Feeders. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
6. | WAC 296-46B-220 Wiring and protection—Branch circuit, feeder, and service calculations. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) and 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards and changes that only clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
7. | WAC 296-46B-225 Wiring and protection—Outside branch circuits and feeders. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) and 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards and changes that only clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
8. | WAC 296-46B-230 Wiring and protection—Services. | X | |
9. | WAC 296-46B-235 Branch circuits, feeders, and services over 1,000 volts act [ac], 1,500 volts dc nominal. | X | |
10. | WAC 296-46B-240 Overcurrent protection. | X | |
11. | WAC 296-46B-250 Wiring and protection—Grounding and bonding. | X | |
12. | WAC 296-46B-300 Wiring methods and materials—Wiring methods. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
13. | WAC 296-46B-314 Wiring methods and materials—Outlet, device, pull, and junction boxes. | X | |
14. | WAC 296-46B-334 Wiring methods and materials—Nonmetallic-sheathed cable. | X | |
15. | WAC 296-46B-358 Wiring methods and materials—Electrical metallic tubing. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
16. | WAC 296-46B-394 Wiring methods and materials—Concealed knob-and-tube wiring. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) and 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards and changes that only clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
17. | WAC 296-46B-406R Equipment for general use—Receptacles. | □ | As this is being repealed. |
18. | WAC 296-46B-408 Equipment for general use—Switchboards, switchgear, and panelboards. | X | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
19. | WAC 296-46B-410 Equipment for general use—Luminaires. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
20. | WAC 296-46B-422 Equipment for general use—Appliances. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
21. | WAC 296-46B-440 Air conditioning and refrigerating equipment. | □ | As this is being repealed. |
22. | WAC 296-46B-450 Equipment for general use—Transformers and transformer vaults. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
23. | WAC 296-46B-501 Special occupancies NEC Class I locations. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
24. | WAC 296-46B-505 Class I, Zone 0, 1, and 2 locations. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
25. | WAC 296-46B-513 Special occupancies—Aircraft hangars. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
26. | WAC 296-46B-514 Special occupancies—Motor fuel dispensing facilities. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) and 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards and changes that only clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
27. | WAC 296-46B-517 Special occupancies—Health care facilities. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
28. | WAC 296-46B-547 Special occupancies—Agricultural buildings. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
29. | WAC 296-46B-550 Special occupancies—Mobile homes, manufactured homes and mobile home parks. | X | |
30. | WAC 296-46B-555 Special occupancies—Marinas, boatyards, floating buildings, and commercial and noncommercial docking facilities. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) and 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards and changes that only clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
31. | WAC 296-46B-590 Special occupancies—Temporary installations. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
32. | WAC 296-46B-600 Special equipment—Electric signs and outline lighting. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
33. | WAC 296-46B-620 Special equipment—Elevators. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
34. | WAC 296-46B-680 Special equipment—Swimming pools, fountains, and similar installations. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) and 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards and changes that only clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
35. | WAC 296-46B-690 Solar photovoltaic systems. | X | |
36. | WAC 296-46B-692 Fuel cell systems. | X | |
37. | WAC 296-46B-694 Wind electric systems. | X | |
38. | WAC 296-46B-700 Emergency systems. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) and 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards and changes that only clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
39. | WAC 296-46B-701 Legally required standby systems. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) and 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards and changes that only clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
40. | WAC 296-46B-702 Optional standby systems. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(c) because it adopts national consensus codes that generally establish industry standards. |
41. | WAC 296-46B-705 Interconnected electric power production sources. | X | |
42. | WAC 296-46B-710 Standalone systems. | X | |
43. | WAC 296-46B-800 Communications systems—Communications circuits. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
44. | WAC 296-46B-908 Class B permits. Class B electrical work permit—Use. | X | |
45. | WAC 296-46B-920 Electrical/telecommunications license/certificate types and scope of work. | X | |
46. | WAC 296-46B-925 Electrical/telecommunications contractor's license. General. | □ | This section is exempt under RCW 34.05.310 (4)(d) because it adopts changes that clarify language of a rule without changing the substance or effect of requirements. |
47. | WAC 296-46B-942 Training certificate required. General. | X | |
48. | WAC 296-46B-960 Administrator and electrician certificate of competency examinations. General. | X | |
The proposed rule does not impose more-than-minor costs on businesses. Following is a summary of the agency's analysis showing how costs were calculated. As documented in the cost-benefit analysis, the changes that are not exempt under the Regulatory Fairness Act under RCW
19.85.030 do not have any new compliance costs for businesses. Most changes increase flexibility by adding options for compliance. Other changes include expanding the scope [of] work for 06A electricians may choose to perform and changes to ensure that existing required documentation be available to inspectors.
December 5, 2023
Joel Sacks
Director
OTS-4900.10
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-010General.
Adopted standards.
(1) The ((2020))2023 edition of the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70 - ((2020))2023) published ((August, 2019))September, 2023 including Annex A, B, C, and subsequent Errata and Tentative Interim Amendments issued by the National Fire Protection Association; the latest published versions of Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard (((ANSI/TIA-568-C series, February 2009)))(ANSI/TIA-568); Commercial Building Standard for Telecommunications Pathway and Spaces (((TIA-569-B, October 2004)))(ANSI/TIA-569); Commercial Building Grounding and Bonding Requirements for Telecommunications (((ANSI-TIA-607-B, August 2011)))(ANSI/TIA-607); Residential Telecommunications Cable Standard (((ANSI/TIA/EIA 570-B-2004)))(ANSI/TIA-570); and the latest published version of the National Electrical Safety Code (NESC ((C2-2017)) excluding Appendixes A and B) are hereby adopted by reference as part of this chapter.
This chapter will be followed where there is any conflict between this chapter and the above adopted standards.
The National Electrical Code will be followed where there is any conflict between the National Electrical Code and, ((ANSI/TIA/EIA 568-C, ANSI/TIA/EIA 569-B, ANSI/TIA/EIA 607-B, ANSI/TIA/EIA 570-B))ANSI/TIA 568, ANSI/TIA 569, ANSI/TIA 607, ANSI/TIA/570, or the NESC ((C2)).
Adopted standards apply to installations when issue dates of electrical permits are on and after adoption dates of standards except for:
(a) New one- and two-family dwellings, or multifamily dwellings where the issue date of building permits for the premises is before the adoption date of standards; or
(b) New installations where plan review is required by WAC 296-46B-900 when plans are received and accepted for review before the adoption date of standards.
Inspections - General.
(2) Electrical inspectors will give information as to the interpretation or application of the standards in this chapter, but will not lay out work or act as consultants for contractors, owners, or users.
(3) A variance from the electrical installation requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW or this chapter may be granted by the department or the city that has electrical inspection jurisdiction when it is assured that equivalent objectives can be achieved by establishing and maintaining effective safety.
(a) Any electrical permit holder may request a variance.
(b) The permit holder must make the request in writing, using a form provided by the department, to the chief electrical inspector or to the city that has electrical inspection jurisdiction. The request must include:
(i) A description of the installation as installed or proposed;
(ii) A detailed list of the applicable code violations;
(iii) A detailed list of safety violations;
(iv) A description of the proposal for meeting equivalent objectives for code and/or safety violations; and
(v) Appropriate variance application fee as listed in chapter 296-46B WAC, Part C.
(4) Electrical wiring or equipment subject to this chapter must be sufficiently accessible, at the time of inspection, to allow the inspector to visually inspect the installation to verify conformance with the NEC and any other electrical requirements of this chapter with the exception of not more than ((8))eight feet of electrical conduit in a foundation of a one- or two-family dwelling or residential outbuilding for use as service entrance raceway.
(5) All required equipment grounding conductors installed in concealed cable or flexible conduit systems must be completely installed and made up at the time of the rough-in cover inspection.
(6) The installation of all structural elements and mechanical systems (e.g., framing, plumbing, ducting, etc.) must be complete in the area(s) where electrical inspection is requested. Prior to completion of an exterior wall cover inspection, either:
(a) The exterior shear panel/sheathing nail inspection must be completed by the building code inspector and, where siding nails or fasteners which penetrate into the wall cavity are to be used, all siding must be installed; or
(b) All wiring and device boxes must be a minimum of 2 1/2 inches from the exterior surface of the framing member; or
(c) All wiring and device boxes must be protected by a steel plate a minimum of 1/16 inch thick and of appropriate width and height installed to cover the area of the wiring or box.
(7) In order to meet the minimum electrical safety standards for installations, all materials, devices, appliances, and equipment, not exempted in chapter
19.28 RCW, must conform to applicable electrical product standards recognized by the department, be listed, or field evaluated. For any equipment that requires an amusement operating permit under chapter
67.42 RCW, the operating permit is prima facie evidence of an appropriate standard. Other than as authorized by the chief electrical inspector or a city authorized to do electrical inspection, equipment must not be energized until such standards are met.
(8) The state department of transportation is recognized as the inspection authority for telecommunications systems installations within the rights of way of state highways provided the department of transportation maintains and enforces an equal, higher or better standard of construction, and of materials, devices, appliances, and equipment than is required for telecommunications systems installations by chapter
19.28 RCW and this chapter.
Inspection move on buildings and structures.
(9) All buildings or structures relocated into or within the state:
(a) Other than residential, wired inside the United States (U.S.) must be inspected to ensure compliance with current requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW and the rules developed by the department.
(b) Wired outside the U.S. or Canada must be inspected to ensure compliance with all current requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW and the rules developed by the department.
(10) Residential buildings or structures wired in the U.S., to NEC requirements, and moved into or within a county, city, or town must be inspected to ensure compliance with the NEC requirements in effect at the time and place the original wiring was made. The building or structure must be inspected to ensure compliance with all current requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW and the rules developed by the department if:
(a) The original occupancy classification of the building or structure is changed as a result of the move; or
(b) The building or structure has been substantially remodeled or rehabilitated as a result of the move.
(11) Residential buildings or structures wired in Canada to Canadian Electrical Code (CEC) standards and moved into or within a county, city, or town, must be inspected to ensure compliance with the following minimum safety requirements:
(a) Service, service grounding, and service bonding must comply with the current chapter
19.28 RCW and rules adopted by the department.
(b) Canadian Standards Association (CSA) listed Type NMD cable is allowed with the following qualifications:
(i) CSA listed Type NMD cable, American Wire Gauge #10 and smaller installed after 1964 utilizing an equipment grounding conductor smaller than the phase conductors, must be:
(A) Replaced with a cable utilizing a full-size equipment grounding conductor; or
(B) Protected by a ground fault circuit interrupter protection device.
(ii) CSA listed Type NMD cable, #8 AWG and larger, must:
(A) Utilize an equipment grounding conductor sized according to the requirements of the NEC in effect at the time of the installation;
(B) Be protected by a ground fault circuit interrupter protection device; or
(C) Be replaced.
(c) Other types of wiring and cable must be:
(i) Replaced with wiring listed or field evaluated in accordance with U.S. standards by a laboratory approved by the department; or
(ii) Protected by a ground fault circuit interrupter protection device and arc fault circuit protection device.
(d) Equipment, other than wiring or panelboards, manufactured and installed prior to 1997 must be listed and identified by laboratory labels approved by the department or CSA labels.
(e) All panelboards must be listed and identified by testing laboratory labels approved by the department with the following qualifications:
(i) CSA listed panelboards labeled "suitable for use as service equipment" will be considered to be approved as "suitable for use only as service equipment."
(ii) CSA listed panelboards used as panelboards as described in the NEC, must meet all current requirements of the NEC and this chapter.
(f) Any wiring or panelboards replaced or changed as a result of the move must meet current requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW and this chapter.
(g) The location, type, and ground fault circuit interrupter protection of receptacles and equipment in a bathroom, kitchen, basement, garage, or outdoor area must meet the Washington requirements in effect at the time the wiring was installed.
(h) 4, 15-ampere, kitchen small appliance circuits will be accepted in lieu of ((2))two, 20-ampere, kitchen small appliance circuits. Receptacles will not be required to be added on kitchen peninsular or island counters.
(i) Spacing requirements for all other receptacles must meet the Washington requirements in effect at the time the wiring was installed.
(j) Receptacles installed above baseboard or fixed wall space heaters must be removed and the outlet box covered with a blank cover. The receptacle is required to be relocated as closely as possible to the existing location.
(k) Lighting outlet and switch locations must meet the Washington requirements in effect at the time the wiring was installed.
(l) Dedicated 20-ampere small appliance circuits are not required in dining rooms.
(m) Electric water heater branch circuits must be adequate for the load.
(n) The location, type, and circuit protection of feeders must meet the Washington requirements in effect at the time the wiring was installed.
Wiring methods for designated building occupancies.
(12) Wiring methods in educational or institutional facilities as defined in this chapter must be metallic or nonmetallic raceways, MI, MC, or AC cable. Places of assembly located within these facilities must comply with NEC 518.4(A) and (B).
(13) Assisted living facility generator systems may be wired and installed per NEC 517.
(14) Lawfully installed existing electrical installations that do not comply with the provisions of this chapter and remain in compliance with the code at the time of the installation, will be permitted to be continued without change (i.e., without circuitry or occupancy change). Additions, alterations, modifications, or repairs to the electrical system must conform to the current requirements of this chapter.
(((15) See WAC 296-46B-406R for tamper-resistant receptacle requirements in psychiatric patient care facilities.))
Traffic management systems.
(((16)))(15) The department or city authorized to do electrical inspections will perform the electrical inspection and acceptance of traffic management systems within its jurisdiction. A traffic management system includes:
(a) Traffic illumination systems;
(b) Traffic signal systems;
(c) Traffic monitoring systems;
(d) The electrical service cabinet and all related components and equipment installed on the load side of the service cabinet supplying electrical power to the traffic management system; and
(e) Signalization system(s) necessary for the operation of a light rail system.
A traffic management system can provide signalization for controlling vehicular traffic, pedestrian traffic, or rolling stock.
((
(17)))
(16) The department or city authorized to do electrical inspections recognizes that traffic signal conductors, pole and bracket cables, signal displays, traffic signal controllers/cabinets and associated components used in traffic management systems are acceptable for the purpose of meeting the requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW provided they conform with the following standards or are listed on the Washington state department of transportation (WSDOT) qualified products list.
(a) WSDOT/APWA standard specifications and plans;
(b) WSDOT Design Manual;
(c) International Municipal Signal Association (IMSA);
(d) National Electrical Manufacturer's Association (NEMA);
(e) Federal Standards 170/Controller Cabinets;
(f) Manual for Uniform Road, Bridge, and Municipal Construction;
(g) Institute of Transportation Engineers (ITE); or
(h) Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD).
(((18)))(17) Associated induction detection loop or similar circuits will be accepted by the department or city authorized to do electrical inspections without inspection.
((
(19)))
(18) For the licensing requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW, jurisdictions will be considered owners of traffic management systems when doing electrical work for another jurisdiction(s) under a valid interlocal agreement, as permitted by chapter
39.34 RCW. Interlocal agreements for traffic management systems must be filed with the department or city authorized to do electrical inspections prior to work being performed for this provision to apply.
((
(20)))
(19) Jurisdictions, with an established electrical inspection authority, and WSDOT may perform electrical inspection on their rights of way for each other by interlocal agreement. They may not perform electrical inspection on other rights of way except as allowed in chapter
19.28 or
39.34 RCW.
(((21)))(20) Underground installations.
(a) In other than open trenching, raceways will be considered "fished" according to the NEC and do not require visual inspection.
(b) The department or city authorized to do electrical inspections will conduct inspections in open trenching within its jurisdiction. The electrical work permit purchaser must coordinate the electrical inspection. A written request (e.g., letter, email, fax, etc.) for inspection, made to the department or city authorized to do electrical inspections office having the responsibility to perform the inspection, must be made a minimum of two working days prior to the day inspection is needed (e.g., two working days 10:00 a.m. Tuesday request for a 10:00 a.m. Thursday inspection, excluding holidays and weekends).
If, after proper written request, the department or city authorized to do electrical inspections fails to make an electrical inspection at the time requested, underground conduit may be covered after inspection by the local government jurisdiction's project inspector/designee. Written documentation of a local government jurisdiction inspection must be provided to the department or city authorized to do electrical inspections when requested. Written documentation will include:
(i) Date and time of inspection;
(ii) Location;
(iii) Installing firm;
(iv) Owner;
(v) Type of conduit;
(vi) Size of conduit;
(vii) Depth of conduit; and
(viii) Project inspector/designee name and contact information.
(((22)))(21) Identification of traffic management system components. Local government jurisdictions or WSDOT may act as the certifying authority for the safety evaluation of all components.
(a) An electrical service cabinet must contain only listed components. The electrical service cabinet enclosure is not required to be listed but will conform to the standards in subsection (((17)))(16) of this section.
(b) The local government jurisdiction must identify, as acceptable, the controller cabinet or system component(s) with an identification plate. The identification plate must be located inside the cabinet and may be attached with adhesive.
(((23)))(22) Conductors of different circuits in same cable, enclosure, or raceway. All traffic management system circuits will be permitted to occupy the same cable, enclosure, or raceway without regard to voltage characteristics, provided all conductors are insulated for the maximum voltage of any conductor in the cable, enclosure, or raceway.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-100General definitions.
All definitions listed in the National Electrical Code and chapter
19.28 RCW are recognized in this chapter unless other specific definitions are given in this chapter and chapter
19.28 RCW. The definitions in this section apply to all parts of this chapter. Some sections may have definitions specific to that section.
"Accreditation" is a determination by the department that a laboratory meets the requirements of this chapter and is therefore authorized to evaluate electrical products that are for sale in the state of Washington.
"Administrative law judge" means an administrative law judge (ALJ) appointed pursuant to chapter
34.12 RCW and serving in board proceedings pursuant to chapter
19.28 RCW and this chapter.
"ANSI" means American National Standards Institute. Copies of ANSI standards are available from the National Conference of States on Building Codes and Standards, Inc.
"Appeal" is a request for review of a department action by the board as authorized by chapter
19.28 RCW.
"Appellant" means any person, firm, partnership, corporation, or other entity that has filed an appeal or request for board review.
"Appliance" means household appliance.
"ASTM" means the American Society for Testing and Materials. Copies of ASTM documents are available from ASTM International.
"AWG" means American Wire Gauge.
"Basement" means that portion of a building that is partly or completely below grade plane. A basement will be considered as a story above grade plane and not a basement where the finished surface of the floor above the basement is:
(a) More than ((6))six feet above grade plane;
(b) More than ((6))six feet above the finished ground level for more than 50((%))percent of the total building perimeter; or
(c) More than 12 feet above the finished ground level at any point. Also see "mezzanine" and "story."
"Board" means the electrical board established and authorized under chapter
19.28 RCW.
"Category list" is a list of manufacturing safety standards or product types determined by the department.
A "certified electrical product" is an electrical product to which a laboratory, accredited by the state of Washington, has the laboratory's certification mark attached.
A "certification mark" is a specified laboratory label, symbol, or other identifying mark that indicates the manufacturer produced the product in compliance with appropriate standards or that the product has been tested for specific end uses.
"Certificate of competency" includes the certificates of competency for master journey level electrician, master specialty electrician, journey level, and specialty electrician.
A laboratory "certification program" is a specified set of testing, inspection, and quality assurance procedures, including appropriate implementing authority, regulating the evaluation of electrical products for certification marking by an electrical products certification laboratory.
A "complete application" includes the submission of all appropriate fees, documentation, and forms.
"Chapter" means chapter 296-46B WAC unless expressly used for separate reference.
"Construction," for the purposes of chapter
19.28 RCW, means electrical construction.
"Coordination (selective)" as defined in NEC 100 must be determined and documented by a professional engineer registered under chapter
18.43 RCW.
"Department" means the department of labor and industries of the state of Washington.
"Director" means the director of the department, or the director's designee.
"Egress - Unobstructed (as applied to NEC 110.26 (C)(2)(a))" means an egress path that allows a worker to travel to the exit from any other area in the room containing the equipment described in NEC 110.26 (C)(2) without having to pass through that equipment's required working space.
"Electrical equipment" includes electrical conductors, conduit, raceway, apparatus, materials, components, and other electrical equipment not exempted by RCW
19.28.006(9). Any conduit/raceway of a type listed for electrical use is considered to be electrical equipment even if no wiring is installed in the conduit/raceway at the time of the conduit/raceway installation.
An "electrical products certification laboratory" is a laboratory or firm accredited by the state of Washington to perform certification of electrical products.
An "electrical products evaluation laboratory" is a laboratory or firm accredited by the state of Washington to perform on-site field evaluation of electrical products for safety.
An "equivalent apprenticeship program" for the purposes of RCW 19.28.161 (2)(a)(i), means one that is party to a reciprocal agreement recognized by the Washington state apprenticeship and training council (WSATC) under WAC 296-05-011(3). "Field evaluated" means an electrical product to which a field evaluation mark is attached. Field evaluation must include job site inspection unless waived by the department, and may include component sampling and/or laboratory testing.
"Field evaluation mark" is a specified laboratory label, symbol, or other identifying mark indicating the manufacturer produced the product in essential compliance with appropriate standards or that the product has been evaluated for specific end uses.
A "field evaluation program" is a specified set of testing, inspection, and quality assurance procedures, including appropriate implementing authority regulating the testing and evaluation of electrical products for field evaluation marking.
The "filing" is the date the document is actually received in the office of the chief electrical inspector.
"Final judgment" means any money that is owed to the department under this chapter, including fees and penalties, or any money that is owed to the department as a result of an individual's or contractor's unsuccessful appeal of a citation.
"Fished wiring" is when cable or conduit is installed within the finished surfaces of an existing building or building structure (e.g., wall, floor or ceiling cavity).
"Household appliance" means utilization equipment installed in a dwelling unit that is built in standardized sizes or types and is installed or connected as a unit to perform one or more household functions such as food preparation, cooking, and cleaning. Includes appliances typically installed in a dwelling unit kitchen, clothes washing, drying, and water heating appliances, portable room air conditioning units and portable heaters, etc. Fixed electric space-heating equipment covered in NEC 424 (furnaces, baseboard and wall heaters, electric heat cable, etc.) and fixed air-conditioning/heat pump equipment (NEC 440) are not household appliances. Household appliance does not mean any utilization equipment that:
(a) Supplies electrical power, other than Class 2, to other utilization equipment; or
(b) Receives electrical power, other than Class 2, through other utilization equipment.
HVAC/refrigeration specific definitions:
(a) "HVAC/refrigeration" means heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration.
(b) "HVAC/refrigeration component" means electrical power and limited energy components within the "HVAC/refrigeration system," including, but not limited to: Pumps, compressors, motors, heating coils, controls, switches, thermostats, humidistats, low-voltage damper controls, outdoor sensing controls, outside air dampers, stand-alone duct smoke detectors, air monitoring devices, zone control valves and equipment for monitoring of HVAC/refrigeration control panels and low-voltage connections. This definition excludes equipment and components of non-"HVAC/refrigeration control systems."
(c) "HVAC/refrigeration control panel" means an enclosed, manufactured assembly of electrical components designed specifically for the control of a HVAC/refrigeration system. Line voltage equipment that has low voltage, NEC Class 2 control or monitoring components incidental to the designed purpose of the equipment is not an HVAC/refrigeration control panel (e.g., combination starters).
(d) "HVAC/refrigeration control system" means a network system regulating and/or monitoring a HVAC/refrigeration system. Equipment of a HVAC/refrigeration control system includes, but is not limited to: Control panels, data centers, relays, contactors, sensors, and cables related to the monitoring and control of a HVAC/refrigeration system(s).
(e) "HVAC/refrigeration equipment" means the central unit primary to the function of the "HVAC/refrigeration system." HVAC/refrigeration includes, but is not limited to: Heat pumps, swamp coolers, furnaces, compressor packages, and boilers.
(f) "HVAC/refrigeration system" means a system of HVAC/refrigeration: Wiring, equipment, and components integrated to generate, deliver, or control heated, cooled, filtered, refrigerated, or conditioned air. This definition excludes non-HVAC/refrigeration control systems (e.g., fire alarm systems, intercom systems, building energy management systems, and similar non-HVAC/refrigeration systems).
"IBC" means the International Building Code. Copies of the IBC are available from the International Code Council.
An "individual" or "party" or "person" means an individual, firm, partnership, corporation, association, government subdivision or unit thereof, or other entity.
An "installation" includes the act of installing, connecting, repairing, modifying, or otherwise performing work on an electrical system, component, equipment, or wire except as exempted by WAC 296-46B-925. An installation is not the passive testing or operational programming of an electrical system, component, equipment, or wire. See "passive testing."
An "identification plate" is suitable for the environment and is a printed or etched adhesive label approved by the department or a phenolic or metallic plate or other similar material engraved in block letters at least 1/4 inch high unless specifically required to be larger by this chapter, suitable for the environment and application. The letters and the background must be in contrasting colors. Screws, rivets, permanent adhesive, or methods specifically described in this chapter must be used to affix an identification plate to the equipment or enclosure.
"Job site" means a specific worksite having a single address or specific physical location (e.g., a single-family residence, a building, a structure, a marina, an individual apartment building with a specific address, etc.).
"Journey level electrician" means a person who has been issued a journey level electrician certificate of competency by the department. The terms "journey level" and "journeyperson" in chapter
19.28 RCW are synonymous.
"Labeled" means an electrical product that bears a certification mark issued by a laboratory accredited by the state of Washington.
A "laboratory" may be either an electrical product(s) certification laboratory or an electrical product(s) evaluation laboratory.
A "laboratory operations control manual" is a document to establish laboratory operation procedures and may include a laboratory quality control manual.
"License" means a license required under chapter
19.28 RCW.
"Like-in-kind" means having the same overcurrent protection requirements and similar characteristics such as voltage requirement, current draw, short circuit characteristics, and function within the system and being in the same location. Like-in-kind also includes any equipment component authorized by the manufacturer as a suitable component replacement part.
For the purpose of WAC 296-46B-940, a "lineworker" is a person employed by a serving electrical utility or employed by a licensed general electrical contractor who carries, on their person, evidence that they:
(a) Have graduated from a department-approved lineworker's apprenticeship course; or
(b) Are currently registered in a department-approved lineworker's apprenticeship course and are working under the direct ((one hundred))100 percent supervision of a journey level electrician or a graduate of a lineworker's apprenticeship course approved by the department. The training received in the lineworker's apprenticeship program must include training in applicable articles of the currently adopted National Electrical Code.
"Listed" means equipment has been listed and identified by a laboratory approved by the state of Washington for the appropriate equipment standard per this chapter.
"Low voltage" means:
(a) NEC, Class 1 power limited circuits at 30 volts maximum.
(b) NEC, Class 2 circuits powered by a Class 2 power supply as defined in NEC 725.121(A).
(c) NEC, Class 3 circuits powered by a Class 3 power supply as defined in NEC 725.121(A).
(d) Circuits of telecommunications systems as defined in chapter
19.28 RCW.
"Member of the firm" means the member(s) on file with the department of licensing for sole proprietorships/partnerships or with the secretary of state for corporations.
"Mezzanine" is the intermediate level or levels between the floor and ceiling of any story with an aggregate floor area of not more than one-third of the area of the room or space in which the level or levels are located. Also see "basement" and "story."
"NEC" means National Electrical Code. Copies of the NEC are available from the National Fire Protection Association.
"NEMA" means National Electrical Manufacturer's Association. Copies of NEMA standards are available from the National Electrical Manufacturer's Association.
"NESC" means National Electrical Safety Code. Copies of the NESC are available from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
"NETA" means International Electrical Testing Association, Inc. Copies of the NETA standards and information are available from the International Electrical Testing Association, Inc.
"NFPA" means the National Fire Protection Association. Copies of NFPA documents are available from the National Fire Protection Association.
"NRTL" means Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory accredited by the federal Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) after meeting the requirements of 29 C.F.R. 1910.7.
A "new building" for the purposes of RCW
19.28.261 includes the setting of a manufactured, mobile, or modular building.
"Passive testing" (e.g., pressing of test buttons, use of testing equipment like voltage testers, clamp-on meters, removal of a device head where the wiring is terminated on a separate base plate, etc.) means testing that does not require any:
(a) Physical modification to the electrical system wiring; or
(b) Wiring to be disconnected or terminated, except as necessary for an approved electrical testing laboratory or approved engineer performing an equipment evaluation.
"Point of contact" or "point of connection" means the service point.
"Proceeding" means any matter regarding an appeal before the board including hearings before an administrative law judge.
"Public area or square" is an area where the public has general, clear, and unrestricted access.
A "quality control manual" is a document to maintain the quality control of the laboratory's method of operation. It consists of specified procedures and information for each test method responding to the requirements of the product standard. Specific information must be provided for portions of individual test methods when needed to comply with the standard's criteria or otherwise support the laboratory's operation.
"RCW" means the Revised Code of Washington. Electronic copies of electrical RCW are available from the department and the office of the code reviser (https://leg.wa.gov/codereviser).
"Readily accessible" means the definition as defined in NEC 100. In addition, it means that, except for keys, no tools or other devices are necessary to gain access (e.g., covers secured with screws, etc.).
"Service" or "served" means that as defined in RCW
34.05.010(19) when used in relation to department actions or proceedings.
A "sign," when required by the NEC, for use as an identification method (e.g., legibly marked, legible warning notice, marked, field marked, permanent plaque/directory, etc.) means "identification plate."
A "stand-alone amplified sound or public address system" is a system that has distinct wiring and equipment for audio signal generation, recording, processing, amplification, and reproduction. This definition does not apply to telecommunications installations.
"Story" is that portion of a building included between the upper surface of a floor and the upper surface of the floor or roof next above. Next above means vertically and not necessarily directly above. Also see "basement" and "mezzanine."
"Structure," for the purposes of this chapter and in addition to the definition in the NEC, means something constructed either in the field or factory that is used or intended for supporting or sheltering any use or occupancy as defined by the IBC.
"Supervision" for the purpose of supervising electrical trainees, means that the appropriately certified supervising electrician is on the same job site as the trainee being supervised. The trainee is not considered to be on the same job site if the supervising electrician and the trainee are working:
(a) In separate buildings at a single address (e.g., a campus, multibuilding industrial complex, multibuilding apartment complex, etc.) except for a single-family residence; or
(b) On an outdoor project (e.g., irrigation system, farm, street lighting, traffic signalization, etc.) where the trainee is more than 1,000 feet from the supervising electrician or where the trainee is more than 200 feet from the supervising electrician and out of sight.
"System design review" means a set of design documents that include the manufacturer's installation information, a legible one-line diagram of the system design, and calculations used to determine voltage and current within the system. The one-line diagram must show the system equipment, devices, overcurrent protection, conductor sizing, grounding, ground fault protection if required, and any system interconnection points. The review must be available to the inspector during all inspections.
A "telecommunications local service provider" is a regulated or unregulated (e.g., by the Federal Communications Commission or the utilities and transportation commission as a telephone or telecommunications provider) firm providing telecommunications service ahead of the telecommunications network demarcation point to an end-user's facilities.
"TIA/EIA" means the Telecommunications Industries Association/Electronic Industries Association which publishes the TIA/EIA Telecommunications Building Wiring Standards. Standards and publications are adopted by TIA/EIA in accordance with the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) patent policy.
A "training school" is a Washington public community or technical college or not-for-profit nationally accredited technical or trade school licensed by the work force training and education coordinating board under chapter
28C.10 RCW.
"Under the control of a utility" for the purposes of RCW
19.28.091 and
19.28.101 is when electrical equipment is not owned by a utility and:
(a) Is located in a vault, room, closet, or similar enclosure that is secured by a lock or seal so that access is restricted to the utility's personnel; or
(b) The utility is obligated by contract to maintain the equipment and the contract provides that access to the equipment is restricted to the utility's personnel or other qualified personnel.
"UL" means Underwriters Laboratory.
"Utility" means an electrical utility.
"Utility system" means electrical equipment owned by or under the control of a serving utility that is used for the transmission or distribution of electricity from the source of supply to the point of contact and is defined in section 90.2 (b)(5) of the National Electrical Code, 1981 edition (see RCW
19.28.010(1)).
"Utilization voltage" means the voltage level employed by the utility's customer for connection to lighting fixtures, motors, heaters, or other electrically operated equipment other than power transformers.
"Variance" is a modification of the electrical requirements as adopted in chapter
19.28 RCW or any other requirements of this chapter that may be approved by the chief electrical inspector if assured that equivalent objectives can be achieved by establishing and maintaining effective safety.
"WAC" means the Washington Administrative Code. Electronic copies of this chapter of the WAC are available from the department and the office of the code reviser (https://leg.wa.gov/codereviser).
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-110General((—))requirements for electrical installations.
003 Examination, identification, installation, ((and)) use, and listing (product certification) of equipment.
(1) Listed electrical conduit can only be installed and used in accordance with its listing (i.e., as an electrical raceway for electrical conductors). If used as a sleeve for electrical conductors or other listed electrical conduits, the installation of a listed electrical conduit will be assumed to be for use as an electrical raceway and must be installed as allowed by chapter
19.28 RCW and this chapter (e.g., owner exemption, electrical contractor, etc.).
EXCEPTION: | Electrical nonmetallic elbow fittings may be connected to piping other than electrical conduit for the purposes of enclosing mechanical piping systems provided the elbows are distinctively marked to indicate their use as nonelectrical fittings prior to installation. For underground installations outside of buildings, elbows used for purposes other than electrical must be substantially painted to match the color of piping to which they are connected. |
011 Deteriorating agents.
(2) Electrical equipment and wiring that has been submerged or exposed to water must comply with the following:
(a) All breakers, fuses, controllers, receptacles, lighting switches/dimmers, electric heaters, and any sealed device/equipment (e.g., relays, contactors, etc.) must be replaced.
(b) All other electrical equipment (e.g., wiring, breaker panelboards, disconnect switches, switchgear, motor control centers, boiler controls, HVAC/R equipment, electric motors, transformers, appliances, water heaters, and similar appliances) must be replaced or reconditioned by the original manufacturer or by its approved representative.
022 Identification of disconnecting means.
(3) For the purposes of legibly marking a disconnecting means, as required in NEC 110.22, an identification plate is required unless the disconnect is a circuit breaker/fused switch installed within a panelboard and the circuit breaker/fused switch is identified by a panelboard schedule. In other than dwelling units, the identification plate must include the identification designation of the circuit source panelboard that supplies the disconnecting means.
030 Over 1,000 volts - General.
(4) Each cable operating at over 1,000 volts and installed on customer-owned systems must be legibly marked in a permanent manner at each termination point and at each point the cable is accessible. The required marking must use phase designation, operating voltage, and circuit number if applicable.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-210((Wiring and protection—))Branch circuits not over 1,000 volts ac, 1,500 volts dc nominal.
008(A) Dwelling units GFCI requirements.
(1) In a garage or unfinished basement, a red receptacle, with a red cover plate, supplying a fire alarm system is not required to have ground-fault circuit-interrupter protection. The receptacle must be identified for use only with the fire alarm system by an identification plate or engraved cover with letters at least 1/4 inch high.
(2) All fixed electrical equipment with exposed grounded metal parts within an enclosed shower area or within ((5))five feet of the top inside edge of a bathtub must have ground fault circuit interrupter protection.
008(B) Other than dwelling units - GFCI requirements.
(3) GFCI requirements. GFCI protection for personnel will not be required for:
(a) Three-phase receptacles unless specifically required elsewhere in the NEC; or
(b) Receptacles other than 125-volt, single phase, 15- or 20-ampere used for: Recreational vehicle supply equipment or for attachment of a mobile home supply cord.
For the purposes of NEC 210.8(B), kitchen means any area where utensils, dishes, etc., are cleaned or where food or beverages are prepared or cooked.
011 Branch circuits.
(4) A raceway system or one dedicated 15-ampere minimum, 120 volt circuit must be taken to all unfinished space areas adaptable to future dwelling unit living areas that are not readily accessible to the service or branch circuit panelboard. One circuit or raceway is required for each 480 square feet or less of unfinished space area. If the total adjacent unfinished space area is less than 480 square feet, the circuit can be an extension of an existing circuit. The circuits must terminate in a suitable box(es). The box must contain an identification of the intended purpose of the circuit(s). The branch circuit panelboard must have adequate space and capacity for the intended load(s).
013 Ground fault protection of equipment.
(5) Equipment ground fault protection systems required by the NEC must be tested prior to being placed into service to verify proper installation and operation of the system as determined by the manufacturer's published instructions. A firm having qualified personnel and proper equipment must perform the tests required. A copy of the manufacturer's performance testing instructions and a written performance acceptance test record signed by the person performing the test must be available at the time of inspection. The performance acceptance test record must include test details including, but not limited to, all trip settings and measurements taken during the test.
025 Common area branch circuits.
(6) For the purpose of NEC 210.25, loads for septic or water well systems that are shared by no more than two dwelling units may be supplied from either of the two dwelling units if approved by the local building official and local health department.
052 (A)(2) Dwelling unit receptacle outlets.
(7) For the purpose of NEC 210.52 (A)(2)(1), "similar openings" include the following configurations that are a permanent part of the dwelling configuration or finish:
(a) Window seating; and
(b) Bookcases or cabinets that extend from the floor to a level at least ((5))five feet ((6))six inches above the floor.
Any outlets eliminated by such window seating, bookcases, or cabinets must be installed elsewhere within the room.
052 (C)(2) Island and peninsular countertop and work surfaces.
(8) If receptacle outlets are not installed to serve an island or peninsular countertop or work surface, no future provisions to do so are required.
063 Equipment requiring servicing.
(9) For the purposes of NEC 210.63, when equipment requiring servicing is located outdoors, accessible locations for receptacle outlets do not include locations accessed through doors or windows.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-215((Wiring and protection—))Feeders.
002 Minimum rating and size.
(1) For other than one- or two-family dwelling feeders rated up to 400 amperes, if the feeder conductors have a lesser ampacity than the equipment rating that they terminate in or on, an identification plate showing conductor ampacity stating: "Feeder conductor ampacity: _____ " must be installed on the equipment at the load end of the feeder conductors.
005 Diagrams of feeders.
(2) Other than plan review projects, the installer must provide a one-line diagram showing the service and feeder details for the project before the initial inspection can be approved for all nondwelling services or feeders:
(a) Larger than 400 amperes; or
(b) Over 600 volts.
The diagram must be signed and dated by the project owner if the owner is doing the work, the assigned administrator or master electrician if an electrical contractor is doing the work, or stamped with an engineer's mark and signature who is registered under chapter
18.43 RCW. The diagram must show:
(c) All services including: Wire size(s), wire type(s), service size(s) (e.g., voltage, phase, ampacity), overcurrent protection, available symmetrical fault current at the service point, equipment short-circuit rating, total load before and after demand factors have been applied including any demand factors used, and a panel schedule where multiple disconnecting devices are present; and
(d) All feeders including: Wire size(s), wire type(s), feeder size(s) (e.g., voltage, phase, ampacity), overcurrent protection, total calculated load before and after demand factors have been applied including any demand factors used, and a panel schedule(s) where multiple disconnecting devices are present.
If the installer deviates, in any way, from the service/feeder design shown on the diagram, a supplemental diagram must be supplied to the inspector showing the most recent design before inspection can proceed. Load reductions and moving branch circuit locations within a panelboard do not require a supplemental diagram. Written documentation must also be provided to the inspector that the supplemental diagram was provided to the project owner at the time of submission to the inspector.
The diagram must be available on the job site during the inspection process.
010 Ground fault protection testing.
(3) Equipment ground fault protection systems required by the NEC must be tested prior to being placed into service to verify proper installation and operation of the system as determined by the manufacturer's published instructions. This test or a subsequent test must include all system feeders unless the installer can demonstrate, in a manner acceptable to the inspector, that there are no grounded conductor connections to the feeder(s). A firm having qualified personnel and proper equipment must perform the tests required. A copy of the manufacturer's performance testing instructions and a written performance acceptance test record signed by the person performing the test must be available at the time of inspection. The performance acceptance test record must include test details including, but not limited to, all trip settings and measurements taken during the test.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-220((Wiring and protection—))Branch circuit, feeder, and service calculations.
((012))042 Lighting load calculations.
In determining feeder and service entrance conductor sizes and equipment ratings, a building that is designed and constructed to comply with the currently adopted Washington state energy code unit lighting power allowance table and footnotes may be used in lieu of NEC ((220.12))220.42. The requirements of NEC ((220.12(B)))220.42(B), items 1, 2, and 3 do not apply.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-225((Wiring and protection—))Outside branch circuits and feeders.
019 Clearances from buildings for conductors of not over 1,000 volts, nominal.
(1) Add the following exception to NEC 225.19(A): Where the voltage between conductors does not exceed 300 and the roof area is guarded or isolated, a reduction in clearance to ((3))three feet shall be permitted.
((032))031(B) Location of outside feeder disconnecting means.
(2) The disconnecting means required by NEC ((225.32))225.31(B) must be provided to disconnect all ungrounded conductors that supply or pass through a building/structure in accordance with the requirements of NEC ((225.32))225.31(B) with the following exceptions.
(a) Outside location: A feeder disconnecting means, including that required by NEC 700, 701, or 702 for a generator, is considered in the building if installed on the outside of the building/structure or within sight and within ((fifteen))15 feet of the building/structure. The building disconnecting means may supply only one building/structure unless the secondary building(s)/structure(s) has a separate building disconnecting means meeting the requirements of the NEC and this subsection. The disconnecting means must have an identification plate with at least one-half-inch high letters identifying:
(i) The building/structure served; and
(ii) Its function as the building/structure main disconnect(s).
(b) Inside location: The feeder disconnecting means ((may be installed anywhere inside a building or structure when there is a feeder disconnecting means, located elsewhere on the premises, with overcurrent protection sized for the feeder conductors))must comply with NEC 225.31(B).
036 Suitable for use as service equipment.
(3) A generator disconnecting means installed per subsection (2)(a) ((or (b))) of this section, is not required to be suitable for use as service equipment.
(4) A generator disconnecting means installed per subsection (2)(b) of this section, is not required to be suitable for use as service equipment when there is a feeder disconnecting means, located elsewhere on the premises, with overcurrent protection sized for feeder conductors.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-230((Wiring and protection—))Services.
001 General service requirements.
(1) The owner, the owner's agent, or the electrical contractor making the installation must consult the serving utility regarding the utility's service entrance requirements for equipment location and meter equipment requirements before installing the service and equipment. Provisions for a meter and related equipment, an attachment of a service drop, or an underground service lateral must be made at a location acceptable to the serving utility. The point of contact for a service drop must permit the clearances required by the NEC.
(2) A firewall must have a minimum two-hour rating as defined by the local building official to be considered a building separation in accordance with Article 100 NEC.
(3) The height of the center of the service meter must be as required by the serving utility. Secondary instrument transformer metering conductor(s) are not permitted in the service raceway.
028 Service or other masts.
(4) Conduit extended through the roof to provide means of attaching:
(a) All overhead drops for service, feeder, or branch circuits exceeding #1 AWG aluminum or #3 AWG copper must be rigid steel galvanized conduit no smaller than ((2))two inches.
(b) All overhead drops for service, feeder or branch circuits not exceeding #1 AWG aluminum or #3 AWG copper must be rigid steel galvanized conduit no smaller than 1 1/4 inches. The installation must comply with drawings E-101 and/or E-102, or must provide equivalent strength by other approved means. Masts for altered or relocated installations will be permitted to comply with drawing E-103.
Notes to drawings E-101, E-102, and E-103
| |
| (1) | An approved roof flashing must be installed on each mast where it passes through a roof. Plastic, nonhardening mastic must be placed between lead-type flashings and the conduit. Neoprene type flashings will also be permitted to be used. |
| (2) | Masts must be braced, secured, and supported in such a manner that no pressure from the attached conductors will be exerted on a roof flashing, meter base, or other enclosures. |
| (3) | Utilization of couplings for a mast is permitted only below the point the mast is braced, secured, or supported. There must be a minimum of two means of support above any couplings used. A properly installed cable or stiff leg type support qualifies as one of the two required means of support. |
| (4) | Except as otherwise required by the serving utility, service mast support guys must be installed if the service drop attaches to the mast more than 24 inches above the roof line or if the service drop is greater than 100 feet in length from the pole or support. Masts for support of other than service drops must comply with this requirement as well. |
| (5) | Intermediate support masts must be installed in an approved manner with methods identical or equal to those required for service masts. |
| (6) | For altered services, where it is impractical to install U bolt mast supports due to interior walls remaining closed, it will be permissible to use other alternate mast support methods such as heavy gauge, galvanized, electrical channel material that is secured to two or more wooden studs with 5/16 inch diameter or larger galvanized lag bolts. |
| (7) | Conductors must extend at least 18 inches from all mastheads to permit connection to the connecting overhead wiring. |
040 Service conductors - Two-family and multiple-occupancy buildings.
(5) Two-family and multiple-occupancy buildings. A second or additional service drop or lateral to a building having more than one occupancy will be permitted to be installed at a location separate from other service drops or laterals to the building provided that all the following conditions are complied with:
(a) Each service drop or lateral must be sized in accordance with the NEC for the calculated load to be served by the conductors;
(b) Each service drop or lateral must terminate in listed metering/service equipment;
(c) Each occupant must have access to the occupant's service disconnecting means;
(d) No more than six service disconnects may be supplied from a single transformer;
(e) All service drops or laterals supplying a building must originate at the same transformer or power supply;
(f) A permanent identification plate must be placed at each service disconnect location that identifies all other service disconnect locations in or on the building, the area or units served by each, the total number of service disconnecting means on the building/structure and the area or units served. If a structure consists of multiple buildings (i.e., by virtue of fire separation), all service disconnects in or on the entire structure must be labeled to identify all service disconnects in or on the structure; and
(g) A permanent identification plate must be placed at each feeder disconnecting means identifying the area or units served if the feeder disconnecting means is remote from the area or unit served.
042 Service conductor - Size and rating.
(6) For other than one- or two-family dwelling services rated up to 400 amperes, if the service conductors have a lesser ampacity than the overcurrent protection, permitted by NEC 230.90 or NEC 310.15, or the equipment rating that they terminate in or on, an identification plate showing the ampacity of the conductors stating: "Service conductor ampacity: _____" must be installed on the service equipment.
043 Wiring methods for 1,000 volts, nominal or less.
(7) The installation of service conductors not exceeding 1,000 volts, nominal, within a building or structure is limited to the following methods: Galvanized or aluminum rigid metal conduit; galvanized intermediate metal conduit; wireways; busways; auxiliary gutters; minimum schedule 40 rigid polyvinyl chloride conduit; cablebus; or mineral-insulated, metal-sheathed cable (type MI). Exception: Wiring methods per NEC 230.43 shall be permitted for service conductors within a building or structure when those conductors are protected by customer owned supply side overcurrent protection sized per NEC 240.4.
(8) ((Electrical metallic tubing must not be installed as the wiring method for service entrance conductors inside a building.)) Existing electrical metallic tubing, installed prior to October 1984, which is properly grounded and used for service entrance conductors may be permitted to remain if the conduit is installed in a nonaccessible location and is the proper size for the installed conductors.
(9) In addition to methods allowed in the NEC, the grounded service conductor is permitted to be identified with a yellow jacket or with one or more yellow stripes.
070 Service equipment - Disconnecting means.
(10) The service disconnecting means must be installed at a readily accessible location in accordance with (a) or (b) of this subsection.
(a) Outside location: Service disconnecting means will be permitted on the building or structure or within sight and within ((fifteen))15 feet of the building or structure served. The building disconnecting means may supply only one building/structure. The service disconnecting means must have an identification plate with one-half-inch high letters identifying:
(i) The building/structure served; and
(ii) Its function as the building/structure main service disconnect(s).
(b) Inside location: When the service disconnecting means is installed inside the building or structure, it must be located so that the service raceway extends no more than ((fifteen))15 feet inside the building/structure. Exception: There is no limit to the length of service raceway when conductors are protected by customer owned supply side overcurrent protection sized per NEC 240.4.
085(C) Replacements.
(11) This subsection replaces NEC 230.85(C). When service equipment suppling one- and two-family dwellings is replaced, an emergency disconnecting means must be installed whenever the service ampacity is increased or decreased, or when any of the following are relocated: Service disconnects, meter bases, overhead service masts, or underground service risers.
095 Ground-fault protection of equipment.
(((11)))(12) Equipment ground-fault protection systems required by the NEC must be tested prior to being placed into service to verify proper installation and operation of the system as determined by the manufacturer's published instructions. This test or a subsequent test must include all service voltage feeders unless the installer can demonstrate, in a manner acceptable to the department, that there are no grounded conductor connections to the feeder(s). A firm having qualified personnel and proper equipment must perform the tests required. A copy of the manufacturer's performance testing instructions and a written performance acceptance test record signed by the person performing the test must be available for the inspector at the time of inspection. The performance acceptance test record must include test details including, but not limited to, all trip settings and measurements taken during the test.
((200 Wiring methods exceeding 1000 volts.
(12) The installation of service conductors exceeding 1000 volts, nominal, within a building or structure must be limited to the following methods: Galvanized rigid metal conduit, galvanized intermediate metal conduit, schedule 80 polyvinyl chloride conduit, metal-clad cable that is exposed for its entire length, cablebus, or busways.
(13) In addition to methods allowed in the NEC, the grounded service conductor is permitted to be identified with a yellow jacket or with one or more yellow stripes.))
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-46B-235Branch circuits, feeders, and services over 1,000 volts ac, 1,500 volts dc nominal.
402(B) Wiring methods.
The installation of service entrance conductors exceeding 1,000 volts ac, 1,500 volts dc, nominal, within a building or structure must be limited to the following methods: Galvanized rigid metal conduit, galvanized intermediate metal conduit, schedule 80 polyvinyl chloride conduit, metal-clad cable that is exposed for its entire length, cablebus, or busways. Exception: Wiring methods per NEC 235.402(B) shall be permitted for service conductors within a building or structure when customer owned overcurrent protection in accordance with NEC requirements is provided outside the building.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-021, filed 5/30/17, effective 7/1/17)
WAC 296-46B-240Overcurrent protection.
024(C) Not exposed to physical damage.
(1) Where the NEC or manufacturer's instructions do not specify minimum height requirements for equipment enclosures, enclosures installed outdoors containing an overcurrent device(s) shall be installed so the bottom of the enclosure containing the overcurrent device(s) is not less than 24 inches above finished grade unless:
(a) The equipment enclosure or listed equipment on which the enclosure is mounted is approved for pad-, floor-, ground-, dock-, or pier-mounting; or
(b) The equipment enclosure is located over((:
(i)))concrete or asphalt paving that extends ((3))three or more feet horizontally from the surface of the enclosure((; or
(ii) Roofs)).
024(F) Not located over steps.
(2) If the overcurrent device is a part of a panelboard that is being repaired or replaced in an existing location, the installation is allowed to be made above the steps.
067(C) Performance testing.
(3) Where fuses rated 1,200 amperes and higher are installed, the following shall be available to the inspector at the installation site at the time of inspection prior to placing the equipment into service:
(a) Documentation of all calculations used to determine available arcing current at each set of fuses rated 1,200 amperes and higher and documentation proving a clearing time of 0.07 seconds or less at the available arcing current;
(b) A copy of the written performance test report for the arc energy reduction protection system detailing results for tests for each set of fuses suppling known loads. The report shall include all of the following:
(i) The date when tests were performed.
(ii) Address of the property where tests were performed.
(iii) The business name and contact information for the employer of persons performing tests.
(iv) Names and dated signatures of all persons performing the tests.
(v) Documentation of all calculations used to determine available arcing current at each set of fuses rated 1,200 amperes and higher.
(vi) Documentation required by 240.67(A) and documentation of all equipment settings made or verified during testing.
(vii) A copy of the equipment manufacturer's instructions used to perform the test.
(viii) Documentation of all testing equipment including dates of calibration.
087(C) Performance testing.
(4) Where the highest continuous current trip setting for the actual overcurrent device installed in a circuit breaker is rated or can be adjusted is 1,200 amperes or higher, a copy of the written performance test report for the arc energy reduction protection system detailing results for tests for each device with a known load. The report shall be available to the inspector at the installation site at the time of inspection prior to placing the equipment into service. The report shall include all of the following:
(a) The date when tests were performed.
(b) Address of the property where tests were performed.
(c) The business name and contact information for the employer of persons performing tests.
(d) Names and dated signatures of all persons performing the tests.
(e) Documentation of all calculations used to determine available arcing current at each circuit breaker described in subsection (4) of this section.
(f) Documentation required by 240.87(A) and documentation of all equipment settings made or verified during testing.
(g) A copy of the equipment manufacturer's instructions used to perform the test.
(h) Documentation of all testing equipment including dates of calibration.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-250((Wiring and protection—))Grounding and bonding.
028 (D)(3) Separately derived system with more than one enclosure.
(1) NEC 250.28 (D)(3) is amended to read: Where a separately derived system supplies more than a single enclosure, the system bonding jumper for each enclosure shall be sized in accordance with 250.28 (D)(1) based on the largest ungrounded feeder/tap conductor serving that enclosure, or a single system bonding jumper shall be installed at the source and sized in accordance with 250.28 (D)(1) based on the equivalent size of the largest supply conductor determined by the largest sum of the areas of the corresponding conductors of each set.
052 Grounding electrodes.
(2) Except for mobile/manufactured homes, a concrete encased grounding electrode must be installed and used at each new building or structure that is built upon a permanent concrete foundation. The electrode must comply, with NEC 250.52 (A)(3). Inspection of the electrode may be accomplished by the following methods:
(a) At the time of inspection of other work on the project, providing the concrete encased electrode is accessible for a visual inspection;
(b) At the time of the service inspection providing the installer has provided a method so the inspector can verify the continuity of the electrode conductor along its entire length, with a minimum 20 foot linear span between testing points (e.g., attaching a length of copper wire to one end of the electrode that reaches the location of the grounding electrode conductor that will enable the inspector to measure the resistance with a standard resistance tester). The concrete encased electrode does not have to be accessible for a visual inspection; or
(c) Other method when prior approval, on a job site basis, is given by the inspector.
If a special inspection trip is required to inspect a grounding electrode conductor, a trip fee will be charged for that inspection in addition to the normal permit fee.
Exceptions: | (1) If the concrete encased grounding electrode is not available for connection, a ground ring must be installed per NEC 250 or other grounding electrode installed per NEC 250 verified to measure 25 ohms or less to ground. Resistance verification testing must be performed by an independent firm having qualified personnel and proper equipment. A copy of the testing procedures used and a written resistance test record signed by the person performing the test must be available at the time of inspection. The resistance test record must include test details including, but not limited to, the type of test equipment used, the last calibration date of the test equipment, and all measurements taken during the test. |
|
(2) Where a concrete encased electrode is not part of the grounding electrode system of an existing building or structure, a concrete encased electrode that may be available as a result of a new addition to the foundation is not required to be connected to service equipment that existed before the addition.
|
053 (A)(2) Resistance of rod, pipe, and plate electrodes.
(3) For rod, pipe, and plate electrodes other than those installed in accordance with the exception in subsection (2) of this section, if a ground resistance test is not performed to ensure a resistance to ground of 25 ohms or less, two or more electrodes as specified in NEC 250.52 must be installed a minimum of ((6))six feet apart. A temporary construction service is not required to have more than one made electrode.
(4) For services only, when multiple buildings or structures are located adjacent, but structurally separate from each other, any installed rod, pipe, or plate electrodes used for those services must be installed so that each building's or structure's electrodes are not less than ((6))six feet apart from the adjacent building's or structure's electrodes.
064 Grounding electrode conductor installation – Physical protection.
(5) Grounding electrode conductors will be considered to be not exposed to physical damage when the conductor(s) are:
(a) Buried more than 12 inches deep in the earth outside the building's footprint;
(b) Encased or covered by ((2))two inches of concrete or asphalt;
(c) Located inside the building footprint and protected by the building's structural elements or when inside and determined, by the inspector, to not be subject to physical damage; or
(d) Enclosed by a metal or nonmetallic raceway or enclosure. The raceway or enclosure must be approved to protect from severe physical damage if it is not protected by appropriate physical barriers from contact with vehicles, lawn mowers, and other equipment that might damage the conductor or enclosure.
068 Accessibility.
(6) The termination point of a grounding electrode conductor tap to the grounding electrode conductor must be accessible unless the connection is made using an exothermic or irreversible compression connection.
090 Bonding.
(7) Metallic stubs or valves used in nonmetallic plumbing systems are not required to be bonded to the electrical system unless required by an electrical equipment manufacturer's instructions.
(8) Hot and cold water plumbing lines are not required to be bonded together if, at the time of inspection, the inspector can determine the lines are mechanically and electrically joined by one or more metallic mixing valves.
104(B) Bonding - Other metal piping.
(9) For flexible metal gas piping, installed new or extended from an existing rigid metal piping system, either:
(a) Provide a copy of the manufacturer's bonding instructions to the inspector at the time of inspection and follow those instructions; or
(b) The bonding conductor for the gas system must:
(i) Be a minimum 6 AWG copper; and
(ii) Terminate at:
(A) An accessible location at the gas meter end of the gas piping system on either a solid iron gas pipe or a cast flexible gas piping fitting using a listed grounding connector; and
(B) Either the service equipment enclosure, service grounding electrode conductor or electrode, or neutral conductor bus in the service enclosure.
184 Solidly grounded neutral systems over 1,000 volts.
(10) In addition to the requirements of NEC 250.184(A), the following applies for:
(a) Existing installations.
(i) The use of a concentric shield will be allowed for use as a neutral conductor for extension, replacement, or repair, if all of the following are complied with:
(A) The existing system uses the concentric shield as a neutral conductor;
(B) Each individual conductor contains a separate concentric shield sized to no less than ((thirty-three and one-half))33 1/2 percent of the ampacity of the phase conductor for three-phase systems or ((one hundred))100 percent of the ampacity of the phase conductor for single-phase systems;
(C) The new or replacement cable's concentric shield is enclosed inside an outer insulating jacket; and
(D) Existing cable (i.e., existing cable installed directly in the circuit between the work and the circuit's overcurrent device) successfully passes the following tests:
• A cable maintenance high potential dielectric test. The test must be performed in accordance with the cable manufacturer's instruction or the 2019 ANSI/NETA maintenance test specifications; and
• A resistance test of the cable shield. Resistance must be based on the type, size, and length of the conductor used as the cable shield using the conductor properties described in NEC Table 8 Conductor Properties.
An electrical engineer must provide a specific certification to the electrical plan review supervisor in writing that the test results of the maintenance high potential dielectric test and the resistance test have been reviewed by the electrical engineer and that the cable shield is appropriate for the installation. The electrical engineer must stamp the certification document with the engineer's stamp and signature. The document may be in the form of a letter or electrical plans.
Testing results are valid for a period of seven years from the date of testing. Cable will not be required to be tested at a shorter interval.
(ii) A concentric shield used as a neutral conductor in a multigrounded system fulfills the requirements of an equipment grounding conductor.
(b) New installations.
(i) New installations do not include extensions of existing circuits.
(ii) The use of the concentric shield will not be allowed for use as a neutral conductor for new installations. A listed separate neutral conductor meeting the requirements of NEC 250.184(A) must be installed.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-021, filed 5/30/17, effective 7/1/17)
WAC 296-46B-300General requirements for wiring methods and materials((—Wiring methods)).
(1) Cables and raceways for power limited, NEC Class 2 and Class 3 conductors must be installed in compliance with Chapter 3 NEC unless other methods are specifically required elsewhere in the NEC, chapter
19.28 RCW, or this chapter.
005 Underground installations.
(2) Induction loops.
See WAC 296-46B-010(((18)))(17) for induction detection loops that are made in a public roadway and regulated by a governmental agency.
Other induction loops must comply with the following requirements:
(a) General:
(i) A preformed direct burial induction loop is designed to be installed within the road surface base (e.g., concrete or asphalt) or below the road surface of a road with an unpaved surface (e.g., gravel or brick pavers);
(ii) A saw-cut induction detection loop is designed to be installed into a groove saw-cut into an existing paved road surface (e.g., concrete or asphalt);
(iii) The loop system includes the loop and the lead-in conductor;
(iv) The loop system must be:
(A) Tested to assure that at 500 volts DC, the resistance between the conductor and ground equals or exceeds 50 megohms; and
(B) Without splice; or
(C) If spliced, the splice must be soldered and appropriately insulated;
(v) The lead-in conductor must comply with the following:
(A) Must be stranded and have a lay (i.e., twist) of two turns per foot; and
(B) If installed in an electrical raceway;
• Are not required to be listed or suitable for wet locations; and
• Must have a burial cover of at least ((6))six inches; or
(C) If direct buried;
• Must be listed for the use; and
• Must have a burial cover of at least 18 inches.
(b) Preformed direct burial induction detection loops must conform with the following:
(i) The loop conductor must be rated for direct burial and be a minimum of No. 16 AWG;
(ii) The loop design must not allow movement of the loop conductor within the outer jacket. The outer jacket containing the loop conductor is not required to be listed;
(iii) The loop yoke casing (i.e., the location where the lead-in conductor is connected to the loop):
(A) Includes any device used to house the "loop to lead-in splice" or to otherwise couple the loop with the lead-in electrical raceway;
(B) Is not required to be listed; and
(C) Must have a coupler that will create a waterproof bond with the electrical raceway, containing the lead-in conductor, or a direct buried lead-in conductor.
(c) Saw-cut induction detection loops:
(i) The loop conductor must be cross-linked polyethylene or EPR Type USE insulation and be a minimum of No. 18 AWG stranded;
(ii) The saw-cut groove must not cut into rebar installed within the roadway.
011 Support of raceways, cables, or boxes in suspended ceilings.
(3) NEC power limited, Class 2, and Class 3 cables must be secured in compliance with NEC 334.30 and must be secured to boxes in compliance with NEC 314.17.
(4) Telecommunications cables must be secured in a manner that will not cause damage to the cables and at intervals not exceeding five feet. Cables are considered adequately supported when run through holes in building structural elements or other supporting elements. Telecommunications cables may be fished into inaccessible hollow spaces of finished buildings. Clamps or fittings are not required where telecommunications cables enter boxes.
(5) Optical fiber cables must be secured in a manner that will not cause damage to the cables and at intervals not exceeding five feet. Cables are considered adequately supported when run through holes in building structural elements or other supporting elements. Optical fiber cables may be fished into inaccessible hollow spaces of finished buildings. Supports must allow a bending radius that will not cause damage to the cables.
(6) Where not restricted by the building code official or Article 300 NEC, the wires required in NEC 300.11(B) may support raceways, cables, or boxes under the following conditions:
(a) Raceways and/or cables are not larger than three-quarter-inch trade size;
(b) No more than two raceways or cables are supported by a support wire. The two-cable limitation does not apply to telecommunications cables, Class 2 cables, or Class 3 cables on support wires installed exclusively for such cables. The support wire must be adequate to carry the cable(s) weight and all attached cables must be secured with approved fittings; or
(c) Raceways and cables are secured to the support wires by fittings designed and manufactured for the purpose.
In addition to (a), (b), and (c) of this subsection, the following conditions must be complied with:
(d) The support wires are minimum #12 AWG and are securely fastened to the structural ceiling and to the ceiling grid system; and
(e) The raceways or cables serve equipment that is located within the ceiling cavity or is mounted on or supported by the ceiling grid system. Telecommunications cables, Class 2 cables, or Class 3 cables supported as required by this section, may pass through ceiling cavities without serving equipment mounted on or supported by the ceiling grid system.
017 Conductors in raceway.
(7) Cables will be permitted in all raceway systems if:
(a) The cable is appropriate for the environment; and
(b) The percentage fill does not exceed that allowed in NEC Chapter 9, Table 1.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-021, filed 5/30/17, effective 7/1/17)
WAC 296-46B-314((Wiring methods and materials—))Outlet, device, pull, and junction boxes; conduit bodies; fittings; and handhole enclosures.
((001 Boxes and fittings.))029(A) Accessibility of conduit bodies and boxes.
(1) Conduit bodies, junction, pull, and outlet boxes must be installed so that the wiring and devices contained in them is accessible without removing any part of the building structure, including insulation material.
023(H) Flexible cord connection of pendant boxes.
(2) The flexible cord and cord connection must comply with NEC 314.23(H) and the following:
(a) A suspended pendant box must not contain conduit "knockouts" and connection to a suspended box must utilize an integral threaded hub;
(b) The maximum length of the cord for a suspended pendant drop from a permanently installed junction box to a suitable tension take-up device above the pendant box must not exceed ((6))six feet;
(c) The flexible cord must be supported at each end with an approved cord grip or strain relief connector fitting/device that will eliminate all stress on the conductor connections;
(d) The flexible cord must be a minimum #14 AWG copper;
(e) The flexible cord ampacity must be determined using NEC Table 400.5(A) column A; and
(f) The flexible cord must be hard or extra hard usage.
027(C) Boxes at ceiling-suspended (paddle) fan outlets.
(3) For the purposes of NEC 314.27(C), locations acceptable for the installation of ceiling-suspended (paddle) fans include all ceiling areas of habitable rooms of dwelling occupancies except: Areas within four feet of walls, soffits, or fixed cabinetry; or areas directly above permanently installed island or peninsular countertop surfaces.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-334((Wiring methods and materials—))Nonmetallic-sheathed cable.
010 Nonmetallic-sheathed cable.
(1) The building classification, for subsections (2), (3), and (4) of this section, will be as determined by the building official. For the purposes of this section, Type III, IV-HT and V may be as defined in the International Building Code adopted in the state of Washington. The installer must provide the inspector documentation substantiating the type of building construction and finish material rating(s) prior to any electrical inspection.
(2) This section replaces NEC 334.10(2). In multifamily dwellings, Type NM, Type NMC, and Type NMS cable(s) may be used in structures of Types III, IV-HT, and V construction except as prohibited in NEC 334.12.
(3) This section replaces NEC 334.10(3). In all other structures, Type NM, Type NMC, and Type NMS cable(s) may be used in structures of Types III, IV-HT, and V construction except as prohibited in NEC 334.12. All cable(s) must be concealed within walls, floors, or ceilings that provide a thermal barrier of material that has at least a 15-minute finish rating as identified in listings of fire-rated assemblies.
(4) This section replaces NEC 334.10(4). Cable trays in structures of Types III, IV-HT, and V construction, where the cable(s) is identified for the use, except as prohibited in NEC 334.12.
015 Exposed work.
(5) Where Type NMC cable is installed in shallow chases in plaster, masonry, concrete, adobe or similar material, the cable must be protected against nails or screws by:
(a) A steel plate at least 1/16 inch thick and covered with plaster, adobe, or similar finish; or
(b) Being recessed in a chase at least 2 3/4 inches deep, as measured from the finished surface, and covered with plaster, adobe, or similar finish. The cable(s) must be at least 2 1/2 inches from the finished surface.
(6) The requirements for nonmetallic sheathed cable protection in NEC 334.15(C) do not apply in crawl spaces.
(7) Wet or damp locations prohibited in NEC 334.12 (B)(4) do not include the interior of conduits installed outdoors used for physical protection of NM cables under the following conditions:
(a) Cables emerging from a building interior, attic, or crawlspace remain unbroken until terminated; and
(b) Flexible metal conduits are not used; and
(c) No conduit systems are longer than 10 feet or below grade; and
(d) Conduits are sealed to prevent air movement and are arranged to naturally drain.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 08-24-048, filed 11/25/08, effective 12/31/08)
WAC 296-46B-358((Wiring methods and materials—))Electrical metallic tubing.
012 Electrical metallic tubing.
(1) In addition to complying with the provisions of Article 358 NEC, electrical metallic tubing may not be installed in direct contact with the earth or in concrete on or below grade. Also see NEC 300.6 for resistance to corrosion.
(2) Where electrical metallic tubing is installed in wet locations, an equipment grounding conductor must be provided within the raceway and sized per NEC 250.122.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-021, filed 5/30/17, effective 7/1/17)
WAC 296-46B-394((Wiring methods and materials—))Concealed knob-and-tube wiring.
001 Knob-and-tube wiring.
Article 394 NEC does not prohibit the installation of loose or rolled thermal insulating material in spaces containing existing knob-and-tube wiring provided that all the following conditions are met:
(1) The wiring must be surveyed by an appropriately licensed electrical contractor who must certify in writing to the department that the wiring is in good condition with no evidence of improper overcurrent protection, conductor insulation failure or deterioration, and with no improper connections or splices. The electrical inspector must inspect all repairs, alterations, or extensions to the electrical system.
(2) The insulation must meet Class I specifications as identified in the Uniform Building Code, with a flame spread factor of ((twenty-five))25 or less as tested using ASTM E84-81a. Foam insulation may not be used with knob-and-tube wiring.
(3) All knob-and-tube circuits must have overcurrent protection in compliance with NEC Table ((310.15 (B)(16)))310.16, 60 degree centigrade((, Column C))column. Overcurrent protection must be either circuit breakers or Type S fuses.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-408((Equipment for general use—))Switchboards, switchgear, and panelboards.
In addition to the requirements of NEC 230.70(A), service equipment, subpanels, and similar electrical equipment must be installed so that they are readily accessible and may not be installed in clothes closets, toilet rooms, or shower rooms.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-410((Equipment for general use—))Luminaires, lampholders, and lamps.
010 Luminaires in specific locations.
(1) All luminaires within an enclosed shower area or within five feet of the waterline of a bathtub must be enclosed, unless specifically listed for such use; these luminaires, with exposed metal parts that are grounded, must be ground fault circuit interrupter protected.
042 ((Exposed luminaire (fixture) parts))Luminaires with exposed conductive surfaces.
(2) Replacement luminaires that are directly wired or attached to boxes supplied by wiring methods that do not provide a ready means for grounding and that have exposed conductive ((parts))surfaces will be permitted only where the luminaires are provided with ground-fault circuit-interrupter protection and marked "no equipment ground."
056 Protection of conductors and insulation.
(3) Requirements for stranded conductors in NEC 410.56(E) do not apply to branch-circuit conductors.
062 Flexible cord connection of electric discharge luminaires.
(4) A ground-type attachment plug cap and receptacle connection at the source junction box is not required when the flexible cord complies with NEC 410.62 and the following:
(a) Connection to a source junction box must utilize an approved cable connector or clamp;
(b) The maximum length of the cord for a suspended pendant drop from a permanently installed junction box to a suitable tension take-up device above the pendant luminaire must not exceed ((6))six feet;
(c) The flexible cord must be supported at each end with an approved cord grip or strain relief connector fitting/device that will eliminate all stress on the conductor connections;
(d) The flexible cord must be a minimum #14 AWG copper;
(e) The flexible cord ampacity must be determined in NEC Table 400.5(A) column A;
(f) The flexible cord must be hard or extra hard usage; and
(g) A vertical flexible cord supplying electric discharge luminaires must be secured to the luminaire support as per NEC 334.30(A).
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 03-09-111, filed 4/22/03, effective 5/23/03)
WAC 296-46B-422((Equipment for general use—))Appliances.
010 Water heater circuit.
Water heaters with a rated circuit load in excess of 3,500 watts at 208 or 240 volts must be provided with branch circuit conductors not smaller than #10 AWG copper or equal. Overcurrent protection must comply with NEC 422.11(E).
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-021, filed 5/30/17, effective 7/1/17)
WAC 296-46B-450((Equipment for general use—))Transformers and transformer vaults (including secondary ties).
027 Flammable-liquid or oil-filled transformers installed outdoors.
(1) Flammable-liquid or oil-filled transformers installed outdoors must meet the following requirements:
(a) A transformer installed adjacent to a building/structure with any combustible surface may be located only in the shaded "Approved Transformer Area" shown in Figure 450-1;
"Approved Transformer Area" shown in Figure 450-1;
(b) A transformer installed adjacent to a building/structure with no combustible surface(s) may be located only in the shaded "Approved Transformer Area" shown in Figure 450-2;
(c) In an area in which a transformer is to be installed next to a nonhabitable structure, the transformer may be no closer than ((2))two feet to the building/structure and must be outside a line extended vertically from the ends of the eaves or rooflines;
(d) A building/structure may have no doors, windows, stairways, or other openings closer than ((8))eight feet to the transformer;
(e) The finished grade at the location of the transformer must be such that any oil leaking from the transformer will flow away from the building/structure and will not pool; and
(f) If transformers are installed in areas subject to traffic other than pedestrian traffic, they must be provided with adequate guarding.
(2) Enclosures for total underground flammable-liquid or oil-filled transformers must not be located within ((8))eight feet of a doorway, operable window, stairways or fire escape. Adequate space must be maintained above the enclosure so that a boom may be used to lift the transformer from the enclosure.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-501((Special occupancies NEC)) Class I locations.
001 Sewage disposal systems.
(1) Pumping chambers for sewage, effluent, or grinder pumps in on-site and septic tank effluent pump (S.T.E.P.) disposal systems will be considered unclassified when not more than five residential units are connected to the system, residential units are connected to a utility sewage system, or when nonresidential systems have residential loading characteristics and all of the following general installations requirements are complied with:
(a) The pumping chamber must be adequately vented. Venting may be accomplished through the building or structure plumbing vents where the system venting has been approved by the local jurisdiction authority or by a direct two-inch minimum vent to the atmosphere;
(b) Equipment that in normal operation may cause an arc or spark must not be installed in any pumping chamber;
(c) Float switches installed in a pumping chamber must be hermetically sealed to prevent the entrance of gases or vapors;
(d) Junction boxes, conduits and fittings installed in the septic atmosphere must be of a noncorrosive type, installed to prevent the entrance of gases or vapors;
(e) Where a conduit system is installed between the pumping chamber and the control panel, motor disconnect, or power source, an approved sealing method must be installed to prevent the migration of gases or vapors from the pumping chamber, and must remain accessible; and
(f) Wire splices in junction boxes installed in pumping chambers must be suitable for wet locations.
(2) Residential wastewater loading characteristics in a nonresidential installation:
(a) For systems that process less than ((three thousand five hundred))3,500 gallons of wastewater per day may be certified by:
(i) An on-site wastewater designer licensed under chapter
18.210 RCW; or
(ii) A professional engineer, engaged in the business of on-site wastewater system design, licensed under chapter
18.43 RCW.
(b) For systems that process ((
three thousand five hundred))
3,500 gallons or more of wastewater per day may be certified by a professional engineer, engaged in the business of on-site wastewater system design, licensed under chapter
18.43 RCW.
Written documentation must be signed and stamped by the designer or engineer and provided to the electrical inspector prior to inspection.
(3) Any residential or nonresidential system that has building or structure floor drains being discharged into the system is classified as Class I Division 1. Drains from any commercially made tub, shower, basin, sink, or toilet are not considered floor drains.
(4) Pumping chamber access covers can be covered by gravel, light aggregate, or noncohesive granulated soil, and must be accessible for excavation. Access covers that are buried must have their exact location identified at the electrical panel or other prominent location by an identification plate. The authority having jurisdiction for performing electrical inspections must approve the identification plate location.
(5) Indoor grinder pumps installed in chambers with less than ((fifty))50 gallons capacity are not required to meet the requirements of this section, except for the venting requirements in subsection (1)(a) of this section. Indoor grinder pumps installed in chambers with less than ((fifty))50 gallons capacity are not classified systems as described in Article 500 NEC.
(6) Secondary treatment effluent pumping chambers such as sand filters are unclassified, and require no special wiring methods.
(7) Inspection approval is required prior to covering or concealing any portion of the septic electrical system, including the pump. New septic and effluent tanks containing electrical wires and equipment must be inspected and approved prior to being loaded with sewage.
(8) On-site sewage disposal systems using pumps must have audible and visual alarms designed to alert the resident of a malfunction. The alarm must be placed on a circuit independent of the pump circuit.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 08-24-048, filed 11/25/08, effective 12/31/08)
WAC 296-46B-505((Class I,)) Zone 0, 1, and 2 locations.
007 Implementation of zone classification.
For the purposes of NEC 505.7, qualified person means a professional engineer registered in Washington.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 13-03-128, filed 1/22/13, effective 3/1/13)
WAC 296-46B-513((Special occupancies—))Aircraft hangars.
001 Scope.
The scope for NEC 513 applies only when the property containing the building is classified or zoned as an aircraft hangar by the authority having jurisdiction.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-514((Special occupancies—))Motor fuel dispensing facilities.
001 General.
(1) In addition to the scope included in NEC 514.1, Article 514 NEC must be complied with for all liquefied flammable gas storage or transfer facilities.
003 Classifications of locations.
(2) For the purposes of NEC 514.3 (D)(2), delete Exception No. 1 and No. 2 and replace with:
Dock, pier, or wharf sections that do not support fuel dispensers and may abut a section(s) that supports a fuel dispenser(s) are permitted to be unclassified where documented air space between the sections is provided and where flammable liquids or vapors cannot travel to these sections. See NEC 500.4(((A))) for documentation requirements.
011 Emergency disconnecting means - Dispensing and service stations.
(3) An emergency disconnecting means or operator must be provided to disconnect the pump or dispensing equipment serving gasoline, volatile flammable liquids, or liquefied flammable gases. The emergency disconnecting means or operator must disconnect all conductors of the circuit supplying all station dispensers and/or pumps (including the grounded conductor) simultaneously from the source(s) of supply.
(4) For installations with only one dispensing device, the emergency disconnecting means/operator may be used to satisfy subsection (3) of this section.
(5) For multicircuit installations, an electrically held normally open contactor operated by a push-button may serve as the disconnecting means to satisfy subsection (3) of this section. If a disconnecting pushbutton is used, the pushbutton may not function as the resetting mechanism for the electrically held contactor. The resetting means must be:
(a) Located at least 15 feet or out of sight from the disconnecting pushbutton;
(b) Installed behind a cover or guard; and
(c) Identified with an identification plate that is substantially black in color.
(6) The disconnecting means satisfying subsection (3) of this section must be labeled with an identification plate, with letters at least ((1))one inch high, as the emergency disconnecting means. The disconnecting means or operator must be substantially red in color.
013 Maintenance and service of dispensing equipment.
(7) The means to remove all external voltage sources for maintenance and service of dispensing equipment required by NEC 514.13 must be capable of isolating each dispenser individually from all external voltage sources including the grounded conductor, while all other dispensers remain operational.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-021, filed 5/30/17, effective 7/1/17)
WAC 296-46B-517((Special occupancies—))Health care facilities.
001 Health care facilities.
In health care facilities, the following methods must be used to determine adequate capacity and ratings of equipment providing electrical power for the essential electrical systems defined in Article 517 NEC:
(1) Systems in new facilities:
(a) Essential electrical system: The essential electrical system must consist of three branches known as:
(i) Life safety branch: The feeder conductors and equipment used to supply electrical power to the life safety branch must be determined by summation of the connected loads as determined by Article 220 NEC and may not be subjected to any reduction due to the diversity of the loads. Feeder and equipment will be subject to a ((one hundred twenty-five))125 percent multiplier for continuous loads in accordance with Article 220 NEC.
(ii) Critical branch: The feeder conductors and equipment must be calculated in accordance with Article 220 NEC, including a level of diversity as determined by such article.
(iii) Equipment branch: The feeder conductors and equipment used to supply electrical power to the equipment branch of the essential electrical system must be calculated in accordance with Article 220 NEC, including a level of diversity as determined by such article.
(b) Generator sizing: The rating of the generator(s) supplying electrical power to the essential system of a health care facility must meet or exceed the summation of the loads determined in (a) of this subsection with no additional demand factors applied. Momentary X-ray loads may be ignored if the generator is rated at least ((three hundred))300 percent of the largest momentary X-ray load connected.
(2) Existing essential systems in facilities to which additional load is to be added:
(a) Existing loads: The existing loads of the separate branches of the essential electrical system may be determined by WAC 296-46B-900 (3)(j).
(b) Added loads: Added loads to the separate branches of the essential electrical system must be determined by subsection (1) of this section.
(c) Generator sizing: The rating of the generator(s) supplying electrical power to the essential electrical system must meet or exceed the summation of the loads determined by (a) and (b) of this subsection with no additional demand factors applied.
013 Wiring methods.
(3) The last sentence of NEC 517.13(A) is modified to read: The metal raceway system, or metallic cable armor, or sheath assembly shall itself qualify as an equipment grounding conductor in accordance with 250.118 with the exception of 250.118 (10)(a).
017 Ground-fault protection of equipment.
(4) The applicability of NEC 700.31 ground-fault protection of equipment, specified by NEC 517.26 for the life safety branch, will also apply to the NEC 517 essential electrical system's critical branch(es) and equipment branch(es).
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 08-24-048, filed 11/25/08, effective 12/31/08)
WAC 296-46B-547((Special occupancies—))Agricultural buildings.
001 Scope.
NEC 547 requirements apply only when the agricultural building is greater than 1,000 square feet and is used as part of a business or commercial farming activity.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 13-03-128, filed 1/22/13, effective 3/1/13)
WAC 296-46B-550((Special occupancies—))Mobile homes, manufactured homes and mobile home parks.
001 Mobile/manufactured homes - Inspection.
(1) All alterations to the mobile/manufactured home electrical system must be permitted and inspected.
(a) Any circuit or feeder that is fed from the pedestal or panel from an outbuilding feeding the mobile/manufactured home requires a permit from the electrical section.
(b) Any circuit or feeder that originates from the mobile/manufactured home's (i.e., red factory assembled structures label) panel and feeds an addition or equipment that is attached (e.g., garage, heat pump, or air conditioning unit) requires an FAS alteration permit.
(c) Any circuit or feeder that originates in the mobile/manufactured home panel and feeds an unattached structure or equipment (e.g., detached garage, hot tub, pool, well, septic system, yard lighting, or generation equipment, etc.) requires two inspections. An FAS permit is required for the circuit or feeder from the panel and must terminate in a J-box located under the home's exterior wall near the rim joist. A second permit is required from the electrical section for electrical work from the J-box to the equipment or structure.
032 Mobile/manufactured homes - Service.
(2) If an electrical service is installed on the mobile/manufactured home:
(a) The manufacturer's instructions allowing mounting of service equipment on the mobile/manufactured home must be available to the inspector at the installation site at the time of the first inspection of the electrical service. The instructions must be specific regarding the type of service allowed: Overhead or underground; or
(b) It must be installed only by the manufacturer, at the manufacturing plant. The manufacturer must complete the service except for service connections, meter, and grounding electrode conductor; and
(((b)))(c) The owner or an electrical contractor must complete the service at the site.
033 Mobile/manufactured homes - Feeder.
(3) When the mobile or manufactured home is supplied with power using a permanent wiring method, the equipment grounding conductor will be permitted to be bare. Bare conductors used underground must be copper. For the purposes of this section, portable cord is not considered a permanent wiring method.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-555((Special occupancies—))Marinas, boatyards, floating buildings, and commercial and noncommercial docking facilities.
(1) For the purposes of NEC 555.7, transformer terminations must be located a minimum of 12 inches above the deck of a dock (datum plane requirements do not apply for this section).
(2) For the purposes of NEC 555.4, adjacent means within sight.
(3) For the purposes of NEC 555.30, all electrical connections must be installed a minimum of 12 inches above the deck of a pier unless the connections are within junction boxes identified for wet locations, utilizing sealed wire connector systems listed and identified for submersion (datum plane requirements do not apply for this section).
(4) For the purposes of NEC 555.31, all enclosures ((must be corrosion resistant))of a type referenced in NEC 110.28 must be marked with an enclosure type number referenced in NEC Table 110.28 that protects against corrosive agents. All gasketed enclosures must be arranged with a weep hole to discharge condensation.
(5) For the purposes of NEC 555.32, gasketed enclosures are only required for wet locations.
(6) For the purposes of NEC 555.34, the following wiring methods are allowed:
(a) All wiring installed in a damp or wet location must be suitable for wet locations.
(b) Extra-hard usage portable power cables rated not less than 75°C, 600 volts, listed for wet locations and sunlight resistance and having an outer jacket rated for the environment are permitted. Portable power cables are permitted as a permanent wiring method under or within docks and piers or where provided with physical protection. The requirements of NEC 555.34 (B)(3)(b) do not apply.
(c) Overhead wiring must be installed at the perimeter of areas where boats are moored, stored, moved, or serviced to avoid possible contact with masts and other parts of boats. NEC Article 398 open wiring on insulators is not an approved wiring method in or above any portion of a marina or docking facility.
(d) For the purposes of NEC 555.34 (B)(4), the wiring methods of Chapter 3 NEC will be permitted.
(7) For the purposes of NEC 555.33, receptacles must be mounted not less than 12 inches above the deck surface of the pier or dock (datum plane requirements do not apply for this section). Shore power receptacles that provide shore power for boats must be rated not less than 20 amperes and must be single outlet type and must be of the locking and grounding type or pin and sleeve type.
Floating buildings.
(8) Where shore power is provided, a disconnecting means must be located within sight of each floating building or similar facility. The disconnecting means must be installed adjacent to but not in or on the floating building or similar facility.
(9) NEC 555.53 is amended to read: The overcurrent protective device(s) that supply the floating building shall have ground-fault protection not exceeding 30 mA.
(10) Conductors operating in excess of 600 volts, nominal may not be installed on floating portions of a floating building or similar facility.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 08-24-048, filed 11/25/08, effective 12/31/08)
WAC 296-46B-590((Special occupancies—))Temporary installations.
001 Temporary installations.
(1) For the purposes of this section, any circuit used for construction purposes is considered to be temporary.
003 Temporary installations - Time constraints.
(2) Temporary construction service equipment may only be used for construction purposes and must be disconnected when the permanent service is connected unless the department grants an extension of time.
004 Temporary installations - Splices.
(3) A splice or junction box is required for all wiring splice or junction connections in a temporary installation.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-600((Special equipment—))Electric signs and outline lighting.
001 Electrical signs - General.
(1) All electrical signs and outline lighting, regardless of voltage, must be listed or field evaluated by a testing laboratory accredited by the department to the applicable ANSI UL Standard. Installations will be inspected for compliance with installation instructions and the NEC.
(2) Luminaires in outdoor awnings must be suitable for wet locations and be connected by a wiring method suitable for wet locations.
(3) Fluorescent luminaires must be located at least ((6))six inches from the awning fabric. Incandescent lamps or luminaires must be located at least 18 inches from the awning fabric. A disconnecting means must be installed per Article 600 NEC.
(4) Listed awning signs must be installed in compliance with the manufacturer's instructions and the NEC.
(5) Retrofitting signs. When listed signs or listed outline lighting are retrofitted to an LED light source, a licensed (01) general electrical contractor or (04) sign contractor using properly certified individuals or properly supervised trainees may make the retrofit in place so long as all the retrofit components and retrofit kit are listed and installation instructions applicable to the sign for making the retrofit are available for the inspector's use at the time of the inspection and physical access is provided to allow the inspector access to all components of the retrofit kit.
004 Markings.
(6) In addition to the markings required by the NEC, retrofit signs and outline lighting shall be marked with a label, made of a background color contrasting to the listed product, in a location visible during servicing near the listed retrofit subassembly that states, "This equipment contains a retrofit subassembly that may present a risk of electrical hazard. Replace parts only with same type and rating." The label's font must be Arial size 16 bold. This label may be an identification plate as described in WAC 296-46B-100 or an adhesive label approved by the electrical inspector. This label is in addition to any labeling required by the manufacturer's instructions or the UL Standard used to manufacture the retrofit kit.
007 Grounding and bonding.
(7) Remote metal parts of a section sign or outline lighting system only supplied by a remote Class 2 power supply that is listed or is a recognized component in a listed section sign or outline lighting is not required to be bonded to an equipment grounding conductor.
010 Portable or mobile outdoor electrical signs.
(8) A GFCI receptacle outlet that is weatherproof with the supply cord connected must be installed within ((6))six feet of each portable or mobile electrical sign.
(9) Extension cords are not permitted to supply portable outdoor signs.
(10) All portable outdoor electrical signs must be listed by a qualified electrical testing laboratory accredited by the department.
030 Neon tubing.
(11) NEC 600, Part II, Field-Installed Skeleton Tubing, will apply to the installation of all neon tubing and neon circuit conductors.
(12) Field-installed skeleton tubing is not required to be listed. Installations will be inspected for compliance with installation instructions and the NEC.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-620((Special equipment—))Elevators, dumbwaiters, escalators, moving walks, platform lifts, and stairway chairlifts.
051 Disconnecting means.
In accordance with WAC 296-96-02460, elevator section:
(1) The main line disconnect(s) must be located per NFPA 70, Article 620.51(C) and:
(a) Inside the machine room door on the strike side of the machine or control room door;
(b) Not more than ((twenty-four))24 inches from the door to the operating handle; and
(c) Be at a height not less than ((thirty-six))36 inches nor more than ((sixty-six))66 inches above the finish floor as measured centerline to the disconnect handle.
(2) For multicar machine rooms the switches shall be grouped together as close as possible to that location.
(3) For machine rooms with double swing doors, the doors must swing out and the switch(es) shall be located on the wall adjacent to the hinge side of the active door panel.
(4) Shunt-trip breakers, where provided shall be located in the elevator machine room or control room.
(5) Where shunt-trip breakers are also being used as a main line disconnect, they shall comply with subsections (1) through (3) of this section.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-021, filed 5/30/17, effective 7/1/17)
WAC 296-46B-680((Special equipment—))Swimming pools, fountains, and similar installations.
001 General.
(1) Package spa or hot tubs. Electrical heating, pumping, filtering, and/or control equipment installed within ((5))five feet of a spa or hot tub must be listed or field evaluated as a package with the spa or hot tub.
(2) A factory assembled skid pack of electrical heating, pumping, filtering, and/or control equipment must be installed more than ((5))five feet from a spa or hot tub and must be listed as a package unit.
(3) The maintenance disconnect and field installed, listed electrical equipment for a hot tub, spa, or swim spa must be located at least five feet from the hot tub, spa or swim spa. Field installed listed equipment must meet the following additional requirements:
(a) The heater is listed as a "spa heater or swimming pool heater";
(b) The pump is listed as a "spa pump" or "swimming pool/spa pump" (the pump may be combined with a filter assembly); and
(c) Other listed equipment such as panelboards, conduit, and wire are suitable for the environment and comply with the applicable codes.
(4) Field installed, listed electrical equipment for a swimming pool must be located at least ((5))five feet from the swimming pool. Field installed listed equipment must meet the following additional requirements:
(a) The heater must be listed as a "swimming pool heater or a spa heater";
(b) The pump must be listed as a "swimming pool pump" or "spa pump" or "swimming pool/spa pump"; and
(c) Other equipment such as panelboards, conduit, and wire must be suitable for the environment and comply with the applicable codes.
The ((5))five foot separation may be reduced by the installation of a permanent barrier, such as a solid wall, fixed glass windows or doors, etc. The ((5))five foot separation will be determined by the shortest path or route that a cord can travel from the spa, hot tub, swim spa, or swimming pool to an object.
(5) The field assembly or installation of "recognized components" will not be permitted.
(6) Hydromassage bathtubs must be listed as a unit and bear a listing mark which reads "hydromassage bathtub."
(7) Manufacturers' instructions must be followed as part of the listing requirements.
(8) Electrical components which have failed and require replacement must be replaced with identical products unless the replacement part is no longer available; in which case, a like-in-kind product may be substituted provided the mechanical and grounding integrity of the equipment is maintained.
(9) Cut-away-type display models may not be sold for other than display purposes and are not expected to bear a listing mark.
((040 Spas and hot tubs.
(10) NEC 680.42(C) will apply for interior and exterior wiring to outdoor installations of spas and hot tubs.))
070 Hydromassage bathtubs.
(((11)))(10) For hydromassage bathtubs, the ground fault circuit interrupter device must be identified as to use and not located in a building or tub cavity, crawlspace, or attic.
(((12)))(11) For hydromassage bathtubs, all electrical equipment installed to support the bathtub (e.g., disconnecting means, motor, etc.) must be accessible at the same grade level as the tub or from a landing on the exterior of the building without the use of a ladder or other access device.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-690Solar photovoltaic systems.
002 Definitions.
(1) Building integrated means: Photovoltaic cells, modules, panels, or arrays that are integrated into the outer surface or structure of a building and serve as the outer protective surface of that building, such as the roof, skylights, windows, or facades.
004 Installation.
(2) Support structure or foundation. For the purposes of this section, those portions of the structure support or foundation that are exclusively mechanical and are not part of a bonding or grounding path will not be considered part of the photovoltaic system as defined by this section. Such structural support or foundation may be done by the owner, registered general contractor, or licensed electrical contractor without electrical permit or inspection.
(3) A photovoltaic system design review defined in WAC 296-46B-100 must be available at the installation site at the time of the first inspection and until the inspection process is complete.
(4) The entity placing a building integrated cell, module, panel, or array is not subject to the requirements for electrical inspection, licensing, or certification so long as the work is limited to the placement and securing of the device and an electrical work permit has been previously obtained for the electrical work related to the equipment by an entity authorized to do that electrical work.
(5) All electrical work, including wiring installation, terminations, etc., necessary to complete the electrical installations must be completed by the entity authorized to do the electrical work (i.e., owner or appropriate electrical contractor).
007 Maximum voltage.
(6) The open-circuit voltage temperature coefficients supplied in the instructions of listed photovoltaic modules will be used to determine the maximum direct current photovoltaic system voltage. Otherwise the voltage will be calculated using Table 690.7 of the NEC. For the purposes of this calculation, a temperature correction factor of 1.25 will be used unless another factor can be justified and is approved by the authority having jurisdiction.
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-46B-692Fuel cell systems.
A fuel cell system design review defined in WAC 296-46B-100 must be available at the installation site at the time of the first inspection and until the inspection process is complete.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 14-11-075, filed 5/20/14, effective 7/1/14)
WAC 296-46B-694Wind electric systems.
A wind driven generator system design review defined in WAC 296-46B-100 must be available at the installation site at the time of the first inspection and until the inspection process is complete.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-700Emergency systems.
001 Emergency systems - General.
(1) In all health or personal care facilities defined in this chapter, educational facilities, institutional facilities, hotels, motels, and places of assembly for ((
one hundred))
100 or more persons, all exit and emergency lights must be installed in accordance with Article 700 NEC and located as required in standards adopted by the state building code council under chapter
19.27 RCW.
007 Signs.
(2) The sign(s) required in NEC 700.7 must be placed at the service disconnecting means and the meter base if the service disconnecting means and meter base are not located within sight and within ((5))five feet of each other.
010 Emergency systems - Equipment identification.
(3) All exit and emergency lights, whether or not required by the NEC, must be installed in accordance with Article 700 NEC.
(4) All boxes and enclosures, for Article 700 NEC systems, larger than ((6))six inches by ((6))six inches, including transfer switches, generators, and power panels for emergency systems and circuits must be permanently identified with an identification plate that is substantially orange in color, except in existing health care facilities the existing nameplate identification color scheme can be retained for transfer switches, generators, and power panels for existing emergency systems that are not being replaced or modified. All other device and junction boxes for emergency systems and circuits must be substantially orange in color, both inside and outside.
032 Selective coordination.
(5) The requirements for selective coordination described in NEC 700.32 are not required where the emergency system was installed prior to June 1, 2006, provided that no system modifications, additions, deletions, or overcurrent protective devices in that system were replaced on or after April 1, 2024. For new emergency systems that are supplied from an existing emergency system installed prior to June 1, 2006, the new portion of the emergency system must comply with NEC 700.32. The ground fault sensing function of overcurrent protective devices will only be required to selectively coordinate with the ground fault sensing functions of other overcurrent protective devices.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-021, filed 5/30/17, effective 7/1/17)
WAC 296-46B-701Legally required standby systems.
007 Signs.
(1) The sign(s) required in NEC 701.7 must be placed at the service disconnecting means and the meter base if the service disconnecting means and meter base are not located within sight and within ((5))five feet of each other.
((027))032 Selective coordination.
(2) The requirements for selective coordination described in NEC ((701.27))701.32 are not required where the legally required standby system was installed prior to June 1, 2006, provided that no system modifications, additions, deletions, or overcurrent protective devices in that system were replaced on or after April 1, 2024. For new legally required standby systems that are supplied from an existing legally required standby system installed prior to June 1, 2006, the new portion of the legally required standby system must comply with NEC 701.27. The ground fault sensing function of overcurrent protective devices will only be required to selectively coordinate with the ground fault sensing functions of other overcurrent protective devices.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 17-12-021, filed 5/30/17, effective 7/1/17)
WAC 296-46B-702Optional standby systems.
007 Signs.
The sign(s) required in NEC 702.7(A) must be placed ((at the service disconnecting means))where required and at the meter base if the ((service disconnecting means and)) meter base ((are))is not located within sight and within ((5))five feet of ((each other))where a sign is required by NEC 702.7(A). When a disconnecting means required by NEC 230.85 is not present, the sign(s) required in NEC 702.7(A) must be placed at the service disconnecting means and the meter base if the service disconnecting means and the meter base are not located within sight and within five feet of each other.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-705Interconnected electric power production sources.
(1) For utility interactive systems, any person making interconnections between a power production source and the utility distribution network must consult the serving utility and is required to meet all additional utility standards.
011 Supply side source connections.
(2) In addition to the requirements of NEC 705.11, electric power production source conductors connected to the supply side of the service disconnecting means must be installed using wiring methods specified for service conductors in WAC 296-46B-230(7). The disconnecting means providing overcurrent protection for the electric power production source conductors must comply with NEC 230.82(6). This disconnect is not required to be grouped with the service disconnecting means for the building or structure. Grounding and bonding must be in accordance with NEC 250.25.
(3) A system design review defined in WAC 296-46B-100 is required when any power sources regulated under NEC articles 230 (Services); 445 (Generators); 480 (Stationary Standby Batteries); 690 (Photovoltaic Systems); 692 (Fuel Cell Systems); 694 (Wind Electric Systems); 700 (Emergency Systems); 701 (Legally Required Systems); 702 (Optional Standby Systems); 706 (Energy Storage Systems), or other power sources are interconnected as part of a NEC 705 system. The system design review must be available at the installation site at the time of the first inspection and until the inspection process is complete.
NEW SECTION
WAC 296-46B-710Standalone systems.
A system design review defined in WAC 296-46B-100 is required when power sources regulated under NEC articles 445 (Generators); 480 (Stationary Standby Batteries); 690 (Photovoltaic Systems); 692 (Fuel Cell Systems); 694 (Wind Electric Systems); 700 (Emergency Systems); 701 (Legally Required Systems); 702 (Optional Standby Systems); 706 (Energy Storage Systems), or other power sources are interconnected as part of a NEC 710 system. The system design review must be available at the installation site at the time of the first inspection and until the inspection process is complete.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 13-03-128, filed 1/22/13, effective 3/1/13)
WAC 296-46B-800((Communications systems—Communications circuits.))General requirements for communications systems.
((General.))
Chapters 1 through 7, NEC, supplement and modify the requirements of chapter 8, NEC. If there are specific requirements or exceptions described in chapter 8, NEC, that are different from those in chapters 1 through 7, NEC, chapter 8 will prevail.
001 Installation.
(1) All telecommunications installations on an end-user's property, beyond the end-user's telecommunications network demarcation point, made by a telecommunications service provider, both inside and outside of a building or structure, must conform to all licensing, certification, installation, permitting, and inspection requirements described in chapter
19.28 RCW and this chapter.
(2) Telecommunications service providers including its subcontractors and agents must install and maintain points of demarcation in conformance with Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.), Title 47, Chapter 1, Part 68, Subpart B, Sec. 68.105 and may not place a point of demarcation further than ((twelve))12 inches within an end-user's occupied space.
(3) The telecommunications service provider must identify the telecommunications network demarcation point(s) with an identification plate or label having:
(a) The provider's name;
(b) Customer/end-user's name; and
(c) If a CWSTP is used, the option type used.
(4) The C.F.R. prescribes that telecommunications service providers must choose either a MPOE (minimum point of entry) or CWSTP (cable wire service termination policy) which regulates where demarcations are placed within a multitenant environment.
(5) A telecommunications service provider, including its subcontractors and agents provisioning service for a second provider who is not the end-user of the service, must place the point of demarcation no further than ((twelve))12 inches from the nearest POP (point of presence), of the serving provider, to the eventual end-user.
(6) Telecommunications service providers must designate each building that they provide services to with labeling at the terminating point(s) of their facilities indicating:
(a) Whether the building is under a MPOE policy; or
(b) Which option of a CWSTP is in effect.
(7) The CWSTP options for demarcation placement are as follows:
(a) All telecommunications service provider facilities will terminate at one location, mutually agreed upon by the provider and the building owner or designee, upon entry into the building, normally at the lowest common serving point. All demarcations will be placed no more than ((twelve))12 inches from this point. The building owner and/or tenants will provide, manage and maintain building wire and cable placed beyond this demarcation point location.
(b) The telecommunications service provider's facilities will terminate at common locations, mutually agreed upon by the provider and the building owner or designee, throughout the building (terminal rooms, utility closets, etc.). The telecommunications service provider will provide, manage and maintain the building cable and registration jacks that denote the demarcation points. The demarcation points will be placed at these locations and will be accessible to end-users at these locations. This (b) is not an option for single tenant buildings.
(c) The telecommunications service provider will terminate facilities and place demarcations at locations, mutually agreed upon by the provider and the building owner or designee, within the individually occupied units, within ((twelve))12 inches or a similarly reasonable distance of cable/wire entry. The provider will provide, manage and maintain the building cable, network terminating wire and registration jacks that denote the demarcation point. This (c) is not an option for single tenant buildings.
(d) All telecommunications service provider facilities and demarcations will terminate at one location on the property, mutually agreed upon by the provider and the building owner or designee. The building owner and/or tenants will provide, manage and maintain building wire and cable placed beyond the demarcation point location.
(8) The telecommunications installer must confer with the telecommunications provider when determining the point of demarcation.
002 Definitions.
(9) "CWSTP (cable, wire and service termination policy)" is the policy of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the Washington utilities and transportation commission (WUTC) prescribed by tariff that governs negotiations between building owners and telecommunications service providers regarding the configuration of POP(s) and demarcation point(s) in multitenant buildings when a MPOE policy is not elected by the telecommunications service provider.
(10) "MPOE (minimum point of entry)" is a building wiring policy of the FCC and WUTC for multitenant environment locations that can be elected by telecommunications service providers. It prescribes that the telecommunications service provider will provide a single POP for access to its network and is located either at the closest practicable point to where a telecommunications service provider's facilities (fiber, coax, or copper) cross a property line or at the closest practicable point to where the wiring enters a multiunit building or buildings. All demarcations provided for customers and end-users by the provider will be placed within ((twelve))12 inches of that POP.
(11) "POP (point-of-presence)," also called a "POT (point-of-termination)," is a designated point at or near a customer premise at which a telecommunications service provider's facilities for the provision of access service ends. This can be a fiber, coax, or copper connection point. Depending on the telecommunications service provider's CWSTP with the individual building owner, demarcations may be established at the POP or at other designated locations. When the customer of a telecommunications service provider is another carrier, the demarcation will be at the closest POP to the end-user. A telecommunications service provider may have multiple POPs within a multiple tenant environment.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-908Class B permits.
Class B electrical work permit - Use.
(1) The Class B basic electrical random inspection process (Class B process) may only be used by:
(a) Licensed electrical/telecommunication contractors; or
(b) Health care, commercial, or industrial facilities using an employee(s) who is an appropriately certified electrician(s) after requesting, in writing, and receiving permission from the chief electrical inspector.
Each entity doing work must use a separate label.
(2) The Class B random inspection process is only available if the label is validated and the label or label number is posted before beginning the work.
(a) For Class B labels obtained after February 28, 2013:
(i) Prior to, or immediately upon posting the Class B label/number, the purchaser must use the department's online Class B system to enter the job site information for an unused Class B label obtained by the purchaser. If the posting occurs on a weekend or a federal/state holiday, the purchaser must use the online system to enter the information no later than the first business day after posting the label/number;
(ii) The person identified as the installer on the Class B label must post the Class B label or label number, in a conspicuous permanent manner, at the:
(A) Main service/feeder location supplying the structure or system; or
(B) Purchaser's equipment, or on the equipment conductors if the equipment is not in place.
(iii) The Class B label is valid immediately upon the purchaser completing the job site information in the department's online Class B system, and posting of the Class B label or label number per (a)(ii) of this subsection.
(b) For Class B labels obtained before March 1, 2013:
(i) The purchaser must fully enter the job site information on the job site and contractor portions of the Class B label.
(ii) The person identified as the installer on the Class B label must post the completed job site copy, in a conspicuous permanent manner, at the:
(A) Main service/feeder location supplying the structure or system;
(B) Purchaser's equipment, or on the conductors if the equipment is not available.
(iii) The purchaser must return the contractor copy to the Department of Labor and Industries, Electrical Section, Chief Electrical Inspector, P.O. Box 44460, Olympia, WA 98504-4460 within ((fifteen))15 working days after the job site portion of the Class B installation label is affixed.
(iv) The Class B label is valid immediately upon posting on the job site.
(3) Class B labels will be sold in blocks and are nonrefundable and nontransferable.
(4) Class B label installations will be inspected on a random basis as determined by the department.
(5) A progress inspection fee is required for any inspection required when a correction(s) is issued as a result of the inspection of a Class B label.
(6) Any entity using the Class B process may be audited for compliance with the provisions for purchasing, inspection, reporting of installations, and any other requirement of usage.
(7) A separate label is required for each line item listed below in subsection (10) of this section. For example, if the work includes an item under subsection (10)(a) and (b)(i) of this section, two labels are required.
(8) An entity using a Class B basic inspection label is restricted to using no more than two labels per week per job site.
(9) All Class B work must be completed within ((fifteen))15 days after the label is validated. If the work is not completed, another Class B may be posted.
Except that, in a one- or two-family residential structure, a label is valid for ((ninety))120 days after the label is validated, so long as all work described on the label is performed by the purchaser.
(10) Class B work includes the following:
(a) Extension of not more than one branch electrical circuit limited to 120 volts and 20 amps each where:
(i) No cover inspection is necessary. For the purposes of this section, cover inspection does not include work covered by any surface that may be removed for inspection without damaging the surface; and
(ii) The extension does not supply more than two outlets as defined by the NEC.
(b) Single like-in-kind replacement of:
(i) A motor larger than 10 horsepower; or
(ii) The internal wiring of a furnace, air conditioner, refrigeration unit or household appliance; or
(iii) An electric/gas/oil furnace not exceeding 240 volts and 100 amps and associated Class 2 low voltage wiring (i.e., altered and/or new low-voltage control wiring from the furnace to an existing and/or new thermostat, heat pump, air conditioner, condenser, etc.), when the furnace is connected to an existing branch circuit. For the purposes of this section, a boiler is not a furnace; or
(iv) An individually controlled electric room heater (e.g., baseboard, wall, fan forced air, etc.), air conditioning unit, heat pump unit, or refrigeration unit not exceeding 240 volts, 40 minimum circuit amps and associated Class 2 low voltage wiring when the unit is connected to an existing branch circuit; or
(v) Circuit modification required to install not more than five residential load control devices in a residence where installed as part of an energy conservation program sponsored by an electrical utility and where the circuit does not exceed 240 volts and 40 amps; or
(vi) A single, line-voltage flexible supply whip associated with (b)(i), (iii), or (iv) of this subsection, not over ((6))six feet in length, provided there are no modifications to the branch circuit/feeder load being supplied by the whip. May be done on the same Class B label with the replacement unit if done at the same time.
(c) The following low voltage systems:
(i) Repair and replacement of devices not exceeding 100 volt-amperes in Class 2, Class 3, or power limited low voltage systems in one- and two-family dwellings; or
(ii) Repair and replacement of devices not exceeding 100 volt-amperes in Class 2, Class 3, or power limited low voltage systems in other buildings, provided the equipment is not for fire alarm or nurse call systems and is not located in an area classified as hazardous by the NEC; or
(iii) The installation of Class 2 or 3 device(s) or wiring for thermostat, audio, security, burglar alarm, intercom, amplified sound, public address, or access control systems where the installation does not exceed ((twenty))20 devices or ((five thousand))5,000 square feet. This does not include fire alarm, nurse call, lighting control, industrial automation/control or energy management systems; or
(iv) Telecommunications cabling and equipment requiring inspection in RCW
19.28.470 where the installation does not exceed ((
twenty))
20 devices or ((
five thousand))
5,000 square feet;
(d) The replacement of not more than ((ten))10 standard receptacles with GFCI, AFCI, or dual function AFCI/GFCI receptacles;
(e) The conversion of not more than ((ten))10 snap switches to dimmers or occupancy sensors for the use of controlling a luminaire(s) conversion;
(f) The like-in-kind replacement of a maximum of ((twenty))20: Paddle fans, luminaires not exceeding 277 volts and 20 amperes; snap switches, dimmers, receptacle outlets, line voltage thermostats, heating elements, luminaire ballasts, or drivers/power supplies for single LED luminaires;
(g) The replacement of not more than two luminaires with paddle fans if a listed fan box has been previously installed to support the luminaires;
(h) The replacement of not more than four batteries rated not larger than 150 amp hours each that supply power to a single unit of equipment (e.g., uninterruptable power supply, photovoltaic storage system, control panel, etc.);
(i) The installation or repair of equipment powered by a stand-alone solar photovoltaic source where the:
(i) Electrical equipment requires no field assembly except for the attachment and electrical connection of the solar photovoltaic source to the equipment, the installation and attachment to a grounding electrode, and the placement of the equipment on a pad, pole, or other structure;
(ii) Solar photovoltaic source and the equipment operates at less than 15 volts DC;
(iii) Solar photovoltaic source is the only source of external power; and
(iv) Equipment and the solar photovoltaic source are appropriately labeled as a single unit. The label must be by an approved electrical testing laboratory or for equipment used for traffic control labeled according to WAC 296-46B-010(((21)))(20).
(j) The installation or replacement of a single electric sign on an existing single 120-volt, 20-amp maximum branch circuit;
(k) The like-in-kind replacement of output cables consisting of a length of flexible EV cable and an electric vehicle connector when connected to fixed in place electric vehicle supply equipment.
(11) Class B basic electrical work does not include any work in:
(a) Areas classified as Class I, Class II, Class III, or Zone locations per NEC 500; or
(b) Areas regulated by NEC 517 or 680; or
(c) Any work where electrical plan review is required; or
(d) Fire alarm, nurse call, lighting control, industrial automation/control or energy management systems.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-920Electrical/telecommunications license/certificate types and scope of work.
(1)
General electrical (01): A general electrical license and/or certificate encompasses all phases and all types of electrical and telecommunications installations and minor plumbing under RCW
18.106.150. For the purposes of RCW
18.106.150, the like-in-kind replacement includes the appliance or any component part of the appliance (e.g., such as, but not limited to, the thermostat in a water heater).
Specialties.
(2) All specialties listed in this subsection may perform the electrical work described within their specific specialty as allowed by the occupancy and location described within the specialty's scope of work. Except for residential (02), the scope of work for these specialties does not include plumbing work regulated under chapter
18.106 RCW. See RCW
18.106.150 for plumbing exceptions for the residential (02) specialty. For the purposes of RCW
18.106.150, the like-in-kind replacement includes the appliance or any component part of the appliance (e.g., such as, but not limited to, the thermostat in a water heater).
Specialty (limited) electrical licenses and/or certificates are as follows:
(a) Residential (02): Limited to the telecommunications, low voltage, and line voltage wiring of one- and two-family dwellings, or multifamily dwellings of types III, IV or V construction when there are not more than six stories of multifamily dwellings of types III, IV or V construction above grade or above types I or II construction. All line voltage wiring for receptacle outlets and lighting outlets required by the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) adopted under WAC 296-46B-010 is limited to nonmetallic sheathed cable, except for ((services and/or feeders, exposed installations where physical protection is required, and for wiring buried below grade)): Wiring subject to physical damage, wiring embedded in masonry or concrete, wiring buried below grade or located in a wet location, wiring to unfinished space areas adaptable to future dwelling unit living areas, or wiring where nonmetallic sheathed cable is not allowed by installation standards adopted under this chapter.
(i) This specialty also includes the wiring for ancillary structures located on the same property and under the same ownership as the dwelling structure(s) such as, but not limited to: Appliances, equipment, swimming pools, septic pumping systems, domestic water systems, limited energy systems (e.g., doorbells, intercoms, fire alarm, burglar alarm, energy control, HVAC/refrigeration, etc.), multifamily complex offices/garages, site lighting when supplied from the residence or ancillary structure, and other structures directly associated with the functionality of the residential units.
(ii) This specialty does not include wiring of:
(A) Any portion of any occupancy of types I or II construction; or
(B) Occupancies defined in WAC 296-46B-900(1), or commercial occupancies such as: Motels, hotels, offices, assisted living facilities, or stores; or
(C) Services, generators, HVAC/refrigeration equipment, fire pumps or other equipment that serve other than one- and two-family dwellings, or multifamily dwellings of types III, IV, or V construction or ancillary structures, or facilities or equipment used primarily for commercial purposes except those directly associated with the functionality of multifamily complex residential units; or
(D) Interconnected electric power production sources not connected to equipment that supplies one- and two-family dwellings, or multifamily dwellings of types III, IV or V construction, or ancillary structures; or
(E) Any portion of wiring for conveyances regulated under chapter
70.87 RCW serving more than one residential dwelling unit.
(iii) For the purposes of this section, classification of types of construction are as determined by the local building official.
(iv) See RCW
18.106.150 for plumbing exceptions for the residential (02) specialty.
(b) Pump and irrigation (03): Limited to the electrical connection of circuits, feeders, controls, low voltage, related telecommunications, and services to supply: Domestic water systems and public water systems include but are not limited to pumps, pressurization, filtration, treatment, or other equipment and controls, and irrigation water pumps, circular irrigating system's pumps and pump houses.
This specialty may also perform the work defined in (c) of this subsection.
(c) Domestic pump (03A): Limited to the extension of a branch circuit, which is supplied and installed by others, to signaling circuits, motor control circuits, motor control devices, and pumps which do not exceed 7 1/2 horsepower at 250 volts AC single phase input power, regardless of motor controller output or motor voltage/phase, used in residential potable water or residential sewage disposal systems. Domestic water systems and public water systems include but are not limited to pumps, pressurization, filtration, treatment, or other equipment and controls.
(d) Signs (04): Limited to placement and connection of signs and outline lighting, the electrical supply, related telecommunications, controls and associated circuit extensions thereto; and the installation of a maximum 60 ampere, 120/240 volt single phase service to supply power to a remote sign only. This specialty may service, maintain, repair, or install retrofit kits within housings of existing exterior luminaires that are mounted on a pole or other structure with like-in-kind or retrofit kit components.
(i) Electrical licensing/certification is not required to:
(A) Clean the nonelectrical parts of an electric sign;
(B) Form or pour a concrete pole base used to support a sign;
(C) Operate machinery used to assist an electrician in mounting an electric sign or sign supporting pole; or
(D) Assemble the structural parts of a billboard.
(ii) Electrical licensing/certification is required to: Install, modify, or maintain a sign, sign supporting pole, sign face, sign ballast, lamp socket, lamp holder, disconnect switch, or any other part of a listed electric sign.
(e) Limited energy system (06): Limited to the installation, repair, replacement, and maintenance of signaling and power limited circuits and related equipment. This specialty is restricted to low-voltage circuits. This specialty includes ((the installation of)) telecommunications, HVAC/refrigeration low-voltage wiring, fire protection signaling systems, intrusion alarms, energy management and control systems, industrial and automation control systems, lighting control systems, commercial and residential amplified sound, public address systems, and such similar low-energy circuits and equipment in all occupancies and locations.
(i) For the purposes of this section, when a line voltage connection is removed and reconnected to a replacement component located inside the control cabinet, the replacement must be like-in-kind or replaced using the equipment manufacturer's authorized replacement component. The line voltage circuit is limited to 120 volts 20 amps maximum and must have a means of disconnect.
(ii) The limited energy systems (06) specialty may repair or replace line voltage connections terminated inside the cabinet to power supplies internal to the low voltage equipment provided there are no modifications to the characteristics of the branch circuit/feeder load being supplied by the circuit.
(iii) The limited energy systems (06) specialty may not replace or modify the line voltage circuit or cabling or alter the means of connection of the line voltage circuit to the power supply or to the control cabinet.
Limited energy electrical contractors may perform all telecommunications work under their specialty (06) electrical license and administrator's certificate.
(f) HVAC/refrigeration system((s))specialties:
(i) See WAC 296-46B-100 for specific HVAC/refrigeration definitions.
(ii) For the purposes of this section when a component is replaced, the replacement must be like-in-kind or made using the equipment manufacturer's authorized replacement component.
(iii) ((The)) HVAC/refrigeration ((specialties described in (f)(v) and (vi) of this subsection))(06A):
(A) The (06A) specialty is not limited by voltage, phase, or amperage except as limited by (f)(iii)(A)(IX) and (X) of this subsection. No unsupervised electrical trainee can install, repair, replace, or maintain any part of a HVAC/refrigeration system that contains any circuit rated over 600 volts whether the circuit is energized or deenergized. This specialty may:
(((A)))(I) Install, repair, replace, and maintain HVAC/refrigeration: Telecommunications, Class 2 low-voltage control circuit wiring/components in all residential occupancies;
(((B)))(II) Install, repair, replace, and maintain line voltage components within HVAC/refrigeration equipment. Such line voltage components include product illumination luminaires installed within and powered from the HVAC/refrigeration system (e.g., reach-in beverage coolers, frozen food cases, produce cases, etc.) and new or replaced factory authorized accessories such as internally mounted outlets;
(((C)))(III) Repair, replace, or maintain the internal components of the HVAC/refrigeration equipment disconnecting means or controller so long as the disconnecting means or controller is not located within a motor control center or panelboard;
(((D)))(IV) Install, repair, replace, and maintain short sections of raceway to provide physical protection for low-voltage cables. For the purposes of this section a short section cannot mechanically interconnect two devices, junction boxes, or other equipment or components; and
(((E)))(V) Repair, replace, or maintain line voltage flexible supply whips not over six feet in length, provided there are no modifications to the characteristics of the branch circuit/feeder load being supplied by the whip other than a reduction in the HVAC unit's rated maximum overcurrent protection size. There is no limitation on the whip raceway method (e.g., metallic replaced by nonmetallic).
(((iv)))(VI) Install, repair, replace, and maintain HVAC/refrigeration: Telecommunications, Class 2 low-voltage control circuit wiring/components in other than residential occupancies:
That have no more than three stories on/above grade; or
Regardless of the number of stories above grade if the installation:
• Is made in a previously occupied and wired space; and
• Is restricted to the HVAC/refrigeration system;
(VII) Repair, replace, and maintain HVAC/refrigeration: Telecommunications, Class 2 low-voltage control circuit wiring/components in all occupancies regardless of the number of stories on/above grade.
(VIII) Install a bonding conductor for metal gas piping to an existing accessible grounding electrode conductor or grounding electrode only when terminations can be made external to electrical panelboards, switchboards, or other distribution equipment.
(IX) For mini-split HVAC/refrigeration systems installed for one- and two-family dwellings, or multifamily dwellings of types III, IV, or V construction when there are not more than six stories of multifamily dwellings of types III, IV, or V construction above grade or above types I or II construction or installed for other than residential occupancies that have no more than three stories on/above grade, install, repair, replace, and maintain: Single-phase branch circuits not exceeding 250 volts or 20 amps when those circuits are supplied from outdoor compressor/condensers units and distribution controllers of mini-split HVAC/refrigeration systems; wiring for condensate pumps connected to single-phase branch circuits allowed under this subsection when wiring is connected in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions for the mini-split HVAC/refrigeration system; disconnect switches and device, pull, and junction boxes, conduit bodies, and fittings when used for single-phase branch circuits allowed under this subsection; and raceway/conduit systems for single-phase branch circuits allowed under this section when the raceway/conduit system is installed outside of a building or when the raceway/conduit system is no more than six feet in length when connected to equipment located indoors provided that all the following conditions are met: HVAC/refrigeration equipment installed is certified for use as a system by an electrical product testing laboratory accredited by the department; manufacturer's instructions are provided for the system that include specifications for type and size of wiring between outdoor compressor/condenser units, distribution controllers, and indoor evaporators.
(X) Install, repair, replace, and maintain a single overcurrent device and branch circuit conductors connected to the load terminals of that device when used to supply replacement gas or oil fired HVAC/refrigeration equipment provided that all the following conditions are met: The replacement gas or oil fired HVAC/refrigeration equipment is installed in the same location as the gas or oil fired HVAC/refrigeration equipment it replaced; the overcurrent protection for the existing gas or oil fired HVAC/refrigeration equipment circuit exceeds the maximum overcurrent protection allowed for the replacement gas or oil fired HVAC/refrigeration equipment; the branch circuit supplying the HVAC/refrigeration equipment does not exceed 125 volts; the rating of the device does not exceed 20 amperes; the device is installed within sight of and within six feet of the gas or oil fired HVAC/refrigeration equipment it supplies; raceways/conduits used to connect the device to the gas or oil fired HVAC/refrigeration equipment do not exceed six feet in length; the device is not installed within a panelboard or switchboard;
(XI) Install, repair, replace, and maintain devices that provide HVAC/refrigeration equipment one or more of the following: Surge protection, undervoltage protection, overvoltage protection provided that all of the following conditions are met: The device(s) is installed on or within the HVAC/refrigeration equipment, or at the disconnecting means nearest the HVAC/refrigeration equipment it serves; raceways/conduits used to connect the device(s) to HVAC/refrigeration equipment do not exceed six feet in length; the point of connection for the device(s) is not within a panelboard, switchboard, or motor control center external to the HVAC/refrigeration equipment.
(B) The (06A) HVAC/refrigeration ((specialties described in (f)(v) and (vi) of this subsection))specialty may not:
(((A)))(I) Install line voltage controllers or disconnect switches external to HVAC/refrigeration equipment except disconnect switches allowed by (f)(iii)(A)(IX) of this subsection;
Exception: | If HVAC/R equipment is being replaced, this specialty may remove and replace a disconnecting means enclosure mounted on the surface of the HVAC/R equipment with a like-in-kind disconnecting means enclosure rated not more than 20 amperes and 120 volts using the existing wiring method. When performing this work, this specialty may install up to ten feet of raceway to provide physical protection for nonmetallic cables, but the raceway may not terminate in a panelboard. |
(((B)))(II) Install, repair, replace, or maintain:
• Integrated building control systems, other than HVAC/refrigeration systems;
• Single stand-alone line voltage equipment or components (e.g., heat cable, wall heaters, radiant panel heaters, baseboard heaters, contactors, motor starters, and similar equipment) unless the equipment or component:
Is exclusively controlled by the HVAC/refrigeration system and requires the additional external connection to a mechanical system(s) (e.g., connection to water piping, gas piping, refrigerant system, ducting for the HVAC/refrigeration system, gas fireplace flume, ventilating systems, etc. (i.e., as in the ducting connection to a bathroom fan)). The external connection of the equipment/component to the mechanical system must be required as an integral component allowing the operation of the HVAC/refrigeration system; or
Contains a HVAC/refrigeration mechanical system(s) (e.g., water piping, gas piping, refrigerant system, etc.) within the equipment (e.g., "through-the-wall" air conditioning units, self-contained refrigeration equipment, etc.);
• Luminaires that serve as a building or structure lighting source, even if mechanically connected to a HVAC/refrigeration system (e.g., troffer luminaire used as a return air device, lighting within a walk-in cooler/freezer used for personnel illumination);
• Raceway/conduit systems, except as allowed for the (06A) specialty by (f)(iii)(A)(IX), (X), and (XI) of this subsection;
• Line voltage: Service, feeder, or branch circuit conductors, except as allowed for the (06A) specialty by (f)(iii)(A)(IX) and (X) of this subsection. However, if a structure's feeder/branch circuit supplies HVAC/refrigeration equipment containing a supplementary overcurrent protection device(s), this specialty may install the conductors from the supplementary overcurrent device(s) to the supplemental HVAC/refrigeration equipment if the supplementary overcurrent device and the HVAC/refrigeration equipment being supplied are located within sight of each other; or
• Panelboards, switchboards, or motor control centers external to HVAC/refrigeration system.
(((v) HVAC/refrigeration (06A):
(A) This specialty is not limited by voltage, phase, or amperage.
(B) No unsupervised electrical trainee can install, repair, replace, or maintain any part of a HVAC/refrigeration system that contains any circuit rated over 600 volts whether the circuit is energized or deenergized.
(C) This specialty may:
• Install HVAC/refrigeration: Telecommunications, Class 2 low-voltage control circuit wiring/components in other than residential occupancies:
That have no more than three stories on/above grade; or
Regardless of the number of stories above grade if the installation:
• Is made in a previously occupied and wired space; and
• Is restricted to the HVAC/refrigeration system;
• Repair, replace, and maintain HVAC/refrigeration: Telecommunications, Class 2 low-voltage control circuit wiring/components in all occupancies regardless of the number of stories on/above grade.
• Install a bonding conductor for metal gas piping to an existing accessible grounding electrode conductor or grounding electrode only when terminations can be made external to electrical panelboards, switchboards, or other distribution equipment.
(D) This specialty may not))(III) Install, repair, replace, or maintain: Any electrical wiring governed under article(s) 500, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505, 510, 511, 513, 514, 515, or 516 NEC (i.e., classified locations) located outside the HVAC/refrigeration equipment.
(((vi)))(iv) HVAC/refrigeration - Restricted (06B):
(((A) This specialty may not perform any electrical work where the primary electrical power connection to the HVAC/refrigeration system exceeds: 250 volts, single phase, or 120 amps.
(B) This specialty may install, repair, replace, or maintain HVAC/refrigeration: Telecommunications, Class 2 low-voltage control circuit wiring/components in other than residential occupancies that have no more than three stories on/above grade.
(C) This specialty may not))(A) The (06B) HVAC/refrigeration specialty may not perform any electrical work where the primary electrical power connection to the HVAC/refrigeration system exceeds: 250 volts, single phase, or 120 amps or electrical work outlined in (f)(iv)(B) of this subsection. The (06B) HVAC/refrigeration specialty may:
(I) Install, repair, replace, and maintain HVAC/refrigeration: Telecommunications, Class 2 low-voltage control circuit wiring/components in all residential occupancies;
(II) Install, repair, replace, or maintain HVAC/refrigeration: Telecommunications, Class 2 low-voltage control circuit wiring/components in other than residential occupancies that have no more than three stories on/above grade;
(III) Install, repair, replace, and maintain line voltage components within HVAC/refrigeration equipment. Such line voltage components include product illumination luminaires installed within and powered from the HVAC/refrigeration system (e.g., reach-in beverage coolers, frozen food cases, produce cases, etc.) and new or replaced factory authorized accessories such as internally mounted outlets;
(IV) Repair, replace, or maintain the internal components of the HVAC/refrigeration equipment disconnecting means or controller so long as the disconnecting means or controller is not located within a motor control center or panelboard;
(V) Install, repair, replace, and maintain short sections of raceway to provide physical protection for low-voltage cables. For the purposes of this section a short section cannot mechanically interconnect two devices, junction boxes, or other equipment or components; and
(IV) Repair, replace, or maintain line voltage flexible supply whips not over six feet in length, provided there are no modifications to the characteristics of the branch circuit/feeder load being supplied by the whip other than a reduction in the HVAC unit's rated maximum overcurrent protection size. There is no limitation on the whip raceway method (e.g., metallic replaced by nonmetallic).
(B) The (06B) HVAC/refrigeration specialty may not:
(I) Install line voltage controllers or disconnect switches external to HVAC/refrigeration equipment;
Exception: | If HVAC/R equipment is being replaced, this specialty may remove and replace a disconnecting means enclosure mounted on the surface of the HVAC/R equipment with a like-in-kind disconnecting means enclosure rated not more than 20 amperes and 120 volts using the existing wiring method. When performing this work, this specialty may install up to ten feet of raceway to provide physical protection for nonmetallic cables, but the raceway may not terminate in a panelboard. |
(II) Install, repair, replace, or maintain:
• Integrated building control systems, other than HVAC/refrigeration systems;
• Single stand-alone line voltage equipment or components (e.g., heat cable, wall heaters, radiant panel heaters, baseboard heaters, contactors, motor starters, and similar equipment) unless the equipment or component:
Is exclusively controlled by the HVAC/refrigeration system and requires the additional external connection to a mechanical system(s) (e.g., connection to water piping, gas piping, refrigerant system, ducting for the HVAC/refrigeration system, gas fireplace flume, ventilating systems, etc. (i.e., as in the ducting connection to a bathroom fan)). The external connection of the equipment/component to the mechanical system must be required as an integral component allowing the operation of the HVAC/refrigeration system; or
Contains a HVAC/refrigeration mechanical system(s) (e.g., water piping, gas piping, refrigerant system, etc.) within the equipment (e.g., "through-the-wall" air conditioning units, self-contained refrigeration equipment, etc.);
• Luminaires that serve as a building or structure lighting source, even if mechanically connected to a HVAC/refrigeration system (e.g., troffer luminaire used as a return air device, lighting within a walk-in cooler/freezer used for personnel illumination);
• Raceway/conduit systems;
• Line voltage: Service, feeder, or branch circuit conductors. However, if a structure's feeder/branch circuit supplies HVAC/refrigeration equipment containing a supplementary overcurrent protection device(s), this specialty may install the conductors from the supplementary overcurrent device(s) to the supplemental HVAC/refrigeration equipment if the supplementary overcurrent device and the HVAC/refrigeration equipment being supplied are located within sight of each other; or
• Panelboards, switchboards, or motor control centers external to HVAC/refrigeration system.
(III) Install, repair, replace, or maintain:
• The allowed telecommunications/low-voltage HVAC/refrigeration wiring in a conduit/raceway system; or
• Any electrical work governed under article(s) 500, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505, 510, 511, 513, 514, 515, or 516 NEC (i.e., classified locations).
(g) Nonresidential maintenance (07): Limited to maintenance, repair and replacement of like-in-kind existing electrical equipment and conductors. This specialty does not include maintenance activities in residential dwellings defined in (a) of this subsection for the purposes of accumulating training experience toward qualification for the residential (02) specialty electrician examination.
(i) This specialty includes the installation and connections of temporary conductors and equipment for the purpose of load testing, not to exceed 600 volts.
(ii) For the purposes of replacement of electrical equipment, where the new equipment has a lower ampere rating than the equipment being replaced and there are no modifications to the ampacity rating of the existing conductors, this specialty may replace a device(s) that provides overcurrent or overload protection for the new equipment with a device(s) having a lower ampere rating in accordance with the nameplate rating of the new equipment.
(iii) This specialty may perform the work defined in (h), (i), (j), (k), and (l) of this subsection.
(h) Nonresidential lighting maintenance and lighting retrofit (07A): Limited to working within the housing of existing nonresidential luminaires for work related to repair, service, maintenance of luminaires and installation of energy efficiency lighting retrofit upgrades. This specialty includes replacement of ballasts, sockets, and the installation of listed lighting retrofit reflectors and kits. All work is limited to the luminaire body, except remote located ballasts may be replaced or retrofitted with approved products. This specialty does not include installing new luminaires or branch circuits; moving or relocating existing luminaires; or altering existing branch circuits.
(i) Residential maintenance (07B): This specialty is limited to residential dwellings as defined in WAC 296-46B-920 (2)(a), multistory dwelling structures with no commercial facilities, and the interior of dwelling units in multistory structures with commercial facilities. This specialty may maintain, repair, or replace (like-in-kind) existing electrical utilization equipment, and all permit exempted work as defined in WAC 296-46B-901.
This specialty is limited to equipment and circuits to a maximum of 250 volts, 60 amperes, and single phase maximum.
This specialty may disconnect and reconnect low-voltage control and line voltage supply whips not over six feet in length provided there are no modifications to the characteristics of the branch circuit or whip.
For the purpose of this specialty, "electrical equipment" does not include electrical conductors, raceway or conduit systems external to the equipment or whip. This specialty cannot perform any plumbing work regulated under chapter
18.106 RCW.
(j) Restricted nonresidential maintenance (07C): This specialty may maintain, repair, or replace (like-in-kind) existing electrical utilization equipment, and all permit exempted work as defined in WAC 296-46B-901 except for the replacement or repair of circuit breakers.
This specialty is limited to equipment and circuits to a maximum of 277 volts and 20 amperes for lighting branch circuits only and/or maximum 250 volts and 60 amperes for other circuits.
The replacement of luminaires is limited to in-place replacement required by failure of the luminaire to operate. Luminaires installed in suspended lay-in tile ceilings may be relocated providing: The original field installed luminaire supply whip is not extended or relocated to a new supply point; or if a manufactured wiring assembly supplies luminaire power, a luminaire may be relocated no more than eight feet providing the manufactured wiring assembly circuiting is not changed.
This specialty may disconnect and reconnect low-voltage control and line voltage supply whips not over six feet in length provided there are no modifications to the characteristics of the branch circuit. For the purpose of this specialty, "electrical equipment" does not include electrical conductors, raceway or conduit systems external to the equipment or whip.
This specialty may perform the work defined in (h) and (i) of this subsection.
This specialty cannot perform any work governed under Article(s) 500, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505, 510, 511, 513, 514, 515, or 516 NEC (i.e., classified locations). This specialty cannot perform any plumbing work regulated under chapter
18.106 RCW.
(k) Appliance repair (07D): Servicing, maintaining, repairing, or replacing household appliances, small commercial/industrial appliances, and other small electrical utilization equipment.
(i) For the purposes of this subsection:
(A) The appliance or electrical utilization equipment must be self-contained and built to standardized sizes or types. The appliance/equipment must be connected as a single unit to a single source of electrical power limited to a maximum of 250 volts, 60 amperes, single phase.
(B) Appliances and electrical utilization equipment include, but are not limited to: Ovens, office equipment, vehicle repair equipment, commercial kitchen equipment, self-contained hot tubs and spas, grinders, and scales.
(C) Appliances and utilization equipment do not include systems and equipment such as: Alarm/energy management/similar systems, luminaires, furnaces/heaters/air conditioners/heat pumps, sewage disposal equipment, door/gate/similar equipment, or individual components installed so as to create a system (e.g., pumps, switches, controllers, etc.).
(ii) This specialty includes:
(A) The in-place like-in-kind replacement of the appliance or equipment if the same unmodified electrical circuit is used to supply the equipment being replaced. This specialty also includes the like-in-kind replacement of electrical components within the appliance or equipment;
(B) The disconnection and reconnection of low-voltage control and line voltage supply whips not over six feet in length provided there are no modifications to the characteristics of the branch circuit; and
(C) The installation of an outlet box and outlet at an existing appliance or equipment location when converting the appliance from a permanent electrical connection to a plug and cord connection. Other than the installation of the outlet box and outlet, there can be no modification to the existing branch circuit supplying the appliance or equipment.
(iii) This specialty does not include:
(A) The installation, repair, or modification of branch circuits conductors, services, feeders, panelboards, disconnect switches, or raceway/conductor systems interconnecting multiple appliances, equipment, or other electrical components.
(B) Any work governed under Article(s) 500, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505, 510, 511, 513, 514, 515, or 516 NEC (i.e., classified locations).
(C) Any plumbing work regulated under chapter
18.106 RCW.
(l) Equipment repair (07E): Servicing, maintaining, repairing, or replacing utilization equipment.
See RCW
19.28.095 for the equipment repair scope of work and definitions. This specialty cannot perform any plumbing work regulated under chapter
18.106 RCW.
(m) Telecommunications (09): Limited to the installation, maintenance, and testing of telecommunications systems, equipment, and associated hardware, pathway systems, and cable management systems.
(i) This specialty includes:
(A) Installation of open wiring systems of telecommunications cables.
(B) Surface nonmetallic raceways designated and used exclusively for telecommunications.
(C) Optical fiber innerduct raceway.
(D) Underground raceways designated and used exclusively for telecommunications and installed for additions or extensions to existing telecommunications systems not to exceed ((fifty))50 feet inside the building.
(E) Incidental short sections of circular or surface metal raceway, not to exceed ((ten))10 feet, for access or protection of telecommunications cabling and installation of cable trays and ladder racks in telecommunications service entrance rooms, spaces, or closets.
(F) Audio or paging systems where the amplification is integrated into the telephone system equipment.
(G) Audio or paging systems where the amplification is provided by equipment listed as an accessory to the telephone system equipment and requires the telephone system for the audio or paging system to function.
(H) Closed circuit video monitoring systems if there is no integration of line or low-voltage controls for cameras and equipment. Remote controlled cameras and equipment are considered (intrusion) security systems and must be installed by appropriately licensed electrical contractors and certified electricians.
(I) Customer satellite and conventional antenna systems receiving a telecommunications service provider's signal. All receiving equipment is on the customer side of the telecommunications network demarcation point.
(ii) This specialty does not include horizontal cabling used for fire protection signaling systems, intrusion alarms, access control systems, patient monitoring systems, energy management control systems, industrial and automation control systems, HVAC/refrigeration control systems, lighting control systems, and stand-alone amplified sound or public address systems. Telecommunications systems may interface with other building signal systems including security, alarms, and energy management at cross-connection junctions within telecommunications closets or at extended points of demarcation. Telecommunications systems do not include the installation or termination of premises line voltage service, feeder, or branch circuit conductors or equipment. Horizontal cabling for a telecommunications outlet, necessary to interface with any of these systems outside of a telecommunications closet, is the work of the telecommunications contractor.
(n) Door, gate, and similar systems (10): This specialty may install, service, maintain, repair, or replace door/gate/similar systems electrical operator wiring and equipment.
(i) For the purposes of this subsection, door/gate/similar systems electrical operator systems include electric gates, doors, windows, awnings, movable partitions, curtains and similar systems. These systems include, but are not limited to: Electric gate/door/similar systems operators, control push buttons, key switches, key pads, pull cords, air and electric treadle, air and electric sensing edges, coil cords, take-up reels, clocks, photo electric cells, loop detectors, motion detectors, remote radio and receivers, antenna, timers, lock-out switches, stand-alone release device with smoke detection, strobe light, annunciator, control panels, wiring and termination of conductors.
(ii) This specialty includes:
(A) Low-voltage, NEC Class 2, door/gate/similar systems electrical operator systems where the door/gate/similar systems electrical operator system is not connected to other systems.
(B) Branch circuits originating in a listed door/gate/similar systems electric operator control panel that supplies only door/gate/similar systems system components providing: The branch circuit does not exceed 600 volts, 20 amperes and the component is within sight of the listed door/gate/similar systems electric operator control panel.
(C) Reconnection of line voltage power to a listed door/gate/similar systems electric operator control panel is permitted provided:
• There are no modifications to the characteristics of the branch circuit/feeder;
• The circuit/feeder does not exceed 600 volts, 20 amperes; and
• The conductor or conduit extending from the branch circuit/feeder disconnecting means or junction box does not exceed six feet in length.
(iii) This specialty does not include any work governed under Article(s) 500, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505, 510, 511, 513, 514, 515, or 516 NEC (i.e., classified locations). This specialty may not install, repair, or replace branch circuit (line voltage) conductors, services, feeders, panelboards, or disconnect switches supplying the door/gate/similar systems electric operator control panel.
(3) A specialty electrical contractor, other than the (06) limited energy specialty electrical contractor, may only perform telecommunications work within the equipment or occupancy limitations of their specialty electrical contractor's license. Any other telecommunications work requires a telecommunications contractor's license.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 20-11-053 and 20-14-083, filed 5/19/20 and 6/30/20, effective 10/29/20)
WAC 296-46B-925Electrical/telecommunications contractor's license.
General.
(1) The department will issue an electrical/telecommunications contractor's license that will expire ((
twenty-four))
24 months following the date of issue to a person, firm, partnership, corporation or other entity that complies with requirements for such license in chapter
19.28 RCW. An electrical/telecommunications contractor's license will not be issued to or renewed for a person, firm, or partnership unless the Social Security number, date of birth, and legal address of each member(s) (see WAC 296-46B-100 definition for member), are submitted with the application. The department may issue an electrical/telecommunications contractor's license for a period greater or less than ((
twenty-four))
24 months for the purpose of equalizing the number of electrical contractor's licenses that expire each month. The department may prorate the electrical/telecommunications contractor's license fee according to the license period.
The applicant, upon application and renewal, must provide the department with the Social Security number, date of birth, and legal address of each member(s).
(2) Combination specialty contractor's license. The department may issue a combination specialty contractor's license to a firm that qualifies for more than one specialty electrical contractor's license. The assigned administrator must be certified in all specialties applicable to the combination specialty contractor's license. The license will plainly indicate the specialty licenses' codes included in the combination license. An administrator assigned to a telecommunications contractor must be certified as a telecommunications administrator. A combination license will not be issued for telecommunications (09).
(3) See RCW
19.28.041(7) for a contractor doing domestic pumping work as defined in RCW
18.106.010 ((
(10)))
(14)(c).
(4) The department may deny application, renewal, change of assignment of administrator/master electrician, reinstatement, or issuance of an electrical/telecommunications contractor's license if a firm, an owner, partner, member, or corporate officer owes money as a result of an outstanding final judgment(s) under chapter
19.28 RCW.
Electrical/telecommunications contractor bond, cash or securities deposit.
(5) Bond, cash, or securities deposit.
(a) The electrical/telecommunications contractor may furnish the department with a cash or security deposit to meet the bond requirements in lieu of posting a bond. A cash or security deposit assigned to the department for bond requirements will be held in place for one year after the contractor's license is expired, revoked, or the owner notifies the department in writing that the company is no longer doing business in the state of Washington as an electrical/telecommunications contractor. Upon written request, the cash or security deposit will then be released by the department providing there is no pending legal action against the contractor under chapter
19.28 RCW of which the department has been notified.
(b) See RCW
19.28.041(7) for a contractor doing domestic pumping work as defined in RCW
18.106.010 ((
(10)))
(14)(c).
Telecommunications contractor insurance.
(6) To obtain a telecommunications contractor's license, the applicant must provide the department with an original certificate of insurance naming the department of labor and industries, electrical section as the certificate holder. Insurance coverage must be no less than ((twenty thousand dollars))$20,000 for injury or damages to property, ((fifty thousand dollars))$50,000 for injury or damage including death to any one person, and ((one hundred thousand dollars))$100,000 for injury or damage including death to more than one person. The insurance will be considered a continuing obligation unless canceled by the insurance company. The insurance company must notify the department in writing ((ten))10 days prior to the effective date of said cancellation or failure to renew.
(7) The telecommunications contractor may furnish the department with an assigned account to meet the insurance requirements in lieu of a certificate of insurance. An account assigned to the department for insurance requirements will be held in place for three years after the contractor's license is expired, revoked, or the owner notifies the department in writing that the company is no longer doing business in the state of Washington as a telecommunications contractor. Upon written request, the account then will be released by the department providing there is no pending legal action against the contractor under chapter
19.28 RCW of which the department has been notified.
Electrical/telecommunications contractor exemptions.
(8) The following types of systems and circuits are considered exempt from the requirements for licensing and permitting described in chapter
19.28 RCW. The electrical failure of these systems does not inherently or functionally compromise safety to life or property.
Low-voltage thermocouple derived circuits and low-voltage circuits for:
(a) Residential: Garage doors and built-in vacuum systems; and
(b) Underground: Landscape sprinkler systems, landscape lighting, and antennas for wireless animal containment fences.
For these types of systems and circuits to be considered exempt, the following conditions must be met:
(c) The power supplying the installation must be derived from a listed Class 2 power supply;
(d) The installation and termination of line voltage equipment and conductors supplying these systems is performed by appropriately licensed and certified electrical contractors and electricians;
(e) The conductors of these systems do not pass through fire-rated walls, fire-rated ceilings or fire-rated floors in other than residential units; and
(f) Conductors or luminaires are not installed in installations covered by the scope of Article 680 NEC (swimming pools, fountains, and similar installations).
(9) Firms who clean and/or replace lamps in luminaires are not included in the requirements for licensing in chapter
19.28 RCW. This exemption does not apply to electric signs as defined in the NEC.
(10) Firms who install listed plug and cord connected utilization equipment are not included in the requirements for licensing in chapter
19.28 RCW. The plug and cord must be a single listed unit consisting of a molded plug and cord and not exceeding 250 volt 60 ampere single phase. The plug and cord can be field installed per the manufacturer's instructions and the product listing requirements. The utilization equipment must be a single manufactured unit, including the plug and cord, that does not require any electrical field assembly except for the installation of the plug and cord and is allowed to be plug and cord connected by the NEC. Firms who perform field electrical servicing, maintaining, or repairing of plug and cord connected utilization equipment other than household appliances are not included in this exemption.
(11) Firms regulated by the Federal Communications Commission or the utilities and transportation commission, supplying telecommunications service to an end-user's property, are not required to be licensed as a telecommunications contractor under chapter
19.28 RCW for telecommunications installations made ahead of the telecommunications network demarcation point.
(12) Unregulated firms, supplying telecommunications service to an end-user's property, are not required to be licensed as a telecommunications contractor under chapter
19.28 RCW for telecommunications installations made ahead of the telecommunications network demarcation point.
(13) Leaseholders. For electrical installations, maintenance, or alterations to existing buildings only, any person, firm, partnership, corporation, or other entity holding a valid, signed lease from the property owner authorizing the leaseholder to perform electrical work, on the property the leaseholder occupies, will be allowed to purchase an electrical permit(s) and do electrical work on or within the property described in the lease. The lessee and/or his or her regularly employed employees must perform the electrical installation, maintenance and alteration.
The lessee who performs the electrical maintenance or installation work must be the sole occupant of the property or space. Property owners or leaseholders cannot perform electrical work on new buildings for rent, sale, or lease, without the proper electrical licensing and certification. For the purposes of this section, electrical work associated with setting a manufactured, mobile, or modular building is considered electrical work on a new building. Refer to RCW
19.28.261 for exemptions from licensing and certification.
(14) Assisting a householder. A friend, neighbor, relative, or other person (including a certified electrician) may assist a householder, at his/her residence in the performance of electrical work on the condition that the householder is present when the work is performed and the person assisting the householder does not accept money or other forms of compensation for the volunteer work. For the purposes of this subsection, a residence is a single-family residence.
(15) Volunteering to do electrical work. There are no exceptions from the electrical contractor's license or electrician certification requirements to allow persons to perform volunteer electrical work for anyone other than a householder or a nonprofit organization as allowed by RCW
19.28.091(7). For the purpose of this section, volunteer means that there is no remuneration or receiving of goods or services in return for electrical installations performed.
(16) Farms or place of business. See RCW
19.28.261 for licensing/certification exemptions allowed for the owner(s) of a farm or other place of business and for the employees of the owner.
(17) The licensing and certification requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW do not apply to persons or firms who remove electrical wiring and/or equipment for the purpose of disposal when all conductors, raceways, and equipment to be disposed of have been physically separated from the source of power by a properly certified electrician employed by a licensed electrical contractor, or person(s) meeting the exemptions listed in RCW
19.28.261. Removal of a component or only a portion of an equipment unit is considered electrical maintenance and does not qualify for this exemption.
Exemptions - Electrical utility and electrical utility's contractor.
(18) Electrical utility exemptions.
(i) Neither a serving electrical utility nor a contractor or subcontractor employed by the serving electrical utility is required to have an electrical contractor's license for work on the "utility system" or on service connections or on meters or other apparatus used to measure the consumption of electricity.
(ii) Exemption from inspection. The work of a serving electrical utility and its contractor(s) on the work exempted by NEC 90.2 (b)(5), 1981 edition, is not subject to inspection.
(b) Street/area lighting exemption - RCW
19.28.091 (2)(a).
(i) On:
(A) Publicly owned streets, parks, athletic/play fields, beaches, and similar areas where the public has general, clear, and unrestricted access; or
(B) Outside area lighting installed on a utility owned pole(s) that is used to support the utility's electric distribution wiring or equipment that supplies a private property owner's property, the serving electrical utility is considered to be an owner and is not required to have an electrical contractor's license or electrical permit to install or work on wiring or equipment, owned by the utility and used in the lighting of those streets/areas.
(ii) On other privately or publicly owned property (e.g., private streets, parking lots, businesses, schools, etc.), the serving utility is not required to have an electrical contractor's license or electrical permit to install or work on outside street/area lighting where the light(s) is supplied directly from the utility system and installed according to the NESC or NEC.
This work is considered to be utility type work.
An electric utility is not allowed to install or work on street/area lighting:
(A) When the area is privately or publicly owned and the public does not have general, clear, and otherwise unrestricted access such as: Industrial property, residential property, or other property where the public's access is restricted in any manner.
(B) Where the lighting is supplied from a source of power derived from a customer-owned electrical system.
(C) Where the lighting or wiring is attached to a building or other customer-owned structure.
(D) If the utility does not directly perform the installation or work, it may only contract the work to an appropriately licensed electrical contractor(s). See RCW
19.28.091(3).
(c) Customer-owned equipment exemption - RCW
19.28.091 (2)(b). A serving electrical utility is not required to have an electrical contractor's license to work on electrical equipment owned by a commercial, industrial, or public institution customer if:
(i) The utility has not solicited such work; and
(ii) Such equipment:
(A) Is located outside a building or structure; and
(B) The work performed is ahead of the secondary side of the customer's transformer(s) which supplies power at the customer's utilization voltage.
If the utility does not directly perform the installation or work, it may only contract the work to an appropriately licensed electrical contractor(s). See RCW
19.28.091(3).
This work is considered to be utility type work.
The owner will provide the electrical work permit and be responsible for requesting inspections and for ensuring the work is installed per chapter
19.28 RCW and this chapter.
Exemptions - Electrical utility telecommunications transition equipment installations, maintenance and repair.
(19) No license, inspection or other permit will be required by the department of any electric utility or, of any person, firm, partnership or corporation or other entity employed or retained by an electric utility or its contractor, because of work in connection with the installation, maintenance, or repair of telecommunications transition equipment located ahead of the utility's telecommunications network demarcation point on the outside of a building or other structure when the work is performed by a qualified person consistent with the requirements of the National Electric Code (NEC) except as provided in (a) and (b) of this subsection:
(a) The following exceptions to the NEC will be permitted:
(i) An additional service disconnect supplying power to the transition equipment can be connected on the supply side of the main service disconnect supplying general power to the building;
(ii) Service entrance disconnects may be separated when clearly labeled;
(iii) The service disconnect used for supplying power to the transition equipment must be connected to the grounding electrode system using:
(A) #8 AWG copper or larger grounding electrode conductor if protected from physical damage; or
(B) #6 AWG copper or larger grounding electrode conductor if not protected from physical damage;
(iv) Use of equipment or materials that have been listed/field evaluated by a recognized independent testing laboratory or the department;
(v) Low-voltage circuits do not require a separate disconnecting means and may be grounded to the transition equipment grounding system;
(vi) Any other variance to the NEC must be approved by the department.
(b) A variance recommended by a joint utility standards group composed of representatives of both public and private utilities or certified by a professional engineer will be approved by the department unless the recommendation is inconsistent with meeting equivalent objectives for public safety.
(c) For the purposes of this section, a qualified worker is employed by a utility or its contractor and is familiar with the construction or operation of such lines and/or equipment that concerns his/her position and who is proficient with respect to the safety hazards connected therewith, or, one who has passed a journey status examination for the particular branch of the electrical trades with which he/she may be connected or is in a recognized training or apprenticeship course and is supervised by a journey level person.
(d) Although the utility is responsible for inspection and approval of the installation, including the selection of material and equipment, the department reserves the right to audit worker qualifications and inspect such installations semiannually for conformance with the requirements of (a), (b) and (c) of this subsection but will not collect a permit fee for such inspection or audit.
(e) If a utility fails to meet the requirements of this section, the department may require the utility to develop and submit a remedial action plan and schedule to attain compliance with this section which may be enforced by the department.
(f) This exemption will be in addition to any other exemption provided in chapter
19.28 RCW, this chapter or other applicable law.
Exemptions - Independent electrical power production equipment exemption.
(20) An independent electrical power production entity is not required to have an electrical contractor's license to work on electrical equipment used to produce or transmit electrical power if:
(a) The entity is:
(i) The owner or operator of the generating facility is regulated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC);
(ii) A municipal utility, or other form of governmental electric utility, or by an electrical cooperative or mutual corporation; or
(iii) The owner or operator of the generating facility is an independent electrical power producer and the facility generates electrical power only for sale to one or more:
(A) Electrical utilities regulated by FERC, municipal utility, or other form of governmental utility, or to an electric cooperative or mutual corporation; and
(B) The electrical power generated by the facility is not used for self-generation or any other on- or off-site function other than sale to one or more utilities regulated by FERC or by one or more state public utilities commissions, or to a PUD, municipal utility, or other form of governmental electric utility, or to an electric cooperative or mutual corporation.
(b) The entity must supply the chief electrical inspector a valid master business license issued by the department of licensing, state of Washington so that the entity's status as a revenue generating business can be confirmed.
(c) The entity has entered into an agreement to sell electricity to a utility or to a third party; and
(d) The electrical equipment is used to transmit electricity from the terminals of an electrical generating unit located on premises to the point of interconnection with a utility system.
(e) The electrical power production facility's generation capacity exceeds 100 KVA.
(f) Notwithstanding that a generating facility may be granted an exemption pursuant to this section, the facility will be subject to all the requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW if the facility at any time in the future ceases to comply with the requirements for exemption. All site facilities not exclusively and directly required to generate and/or distribute the electrical power generated on the site are subject to all the licensing and inspection requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW. All facility services, feeders, and circuits not exclusively and directly required to generate and/or distribute the electrical power (e.g., lights, outlets, etc.) must comply with all requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW for licensing and inspection. Facility circuits supplied to equipment required for the function of generation equipment (e.g., block heaters, power supplies, wind generator tower circuits, etc.) must comply with all requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW for licensing and inspection up to and including the equipment termination point.
(g) The generation equipment must not be mounted on or in any building or structure not required for generation of power (e.g., schools, offices, residences, apartment buildings, hospitals, etc.).
Exemptions - Telegraph and telephone utility and telegraph and telephone utility's contractor.
(21) Telegraph and telephone utility exempted equipment and installations. No person, firm, partnership, corporation, or other entity is required to have an electrical contractor's license for work on electrical equipment and installations thereof that are exempted by RCW
19.28.151. For the purposes of this exemption, "building or buildings used exclusively for that purpose" may mean any separate building or space of a building where the space is separated from the remainder of the building by a two-hour fire wall. The telecommunications or telegraph equipment within such a space must supply telephone or telegraph service to other customer's buildings (i.e., telecommunications or telegraph equipment cannot solely supply the building containing the telephone/telegraph space).
Exemptions - Manufacturers of electrical/telecommunications products.
(22) Manufacturers of electrical/telecommunications systems products will be allowed to utilize a manufacturer's authorized factory-trained technician to perform initial calibration, testing, adjustment, modification incidental to the startup and checkout of the equipment, or replacement of components within the confines of the specific product, without permit or required licensing:
(a) Provided the product:
(i) Has not been previously energized;
(ii) Has been recalled by the Consumer Product Safety Commission;
(iii) Is within the manufacturer's written warranty period, a period not to exceed one year from date of original installation of the new product; or
(iv) The manufacturer is working under the written request and supervision of an appropriately licensed electrical contractor.
(b) Except for the replacement of individual components, as allowed above, this exemption does not include the on-site assembly, installation, removal, or replacement of the electrical product. Modifications to the equipment, as designated above, must not include any changes to the original intended configuration nor changes or contact with external or field-connected components or wiring.
(c) The manufacturer will be responsible for obtaining any required reapproval/recertification from the original listing or field evaluation laboratory.
(d) The manufacturer must notify the department if any modifications have been made or reapproval/recertification is required.
Premanufactured electric power generation equipment assemblies and control gear.
(23) Premanufactured electric power generation equipment assemblies and control gear.
(a) Manufacturers of premanufactured electric power generation equipment assemblies and control gear will be allowed to utilize a manufacturer's authorized factory-trained technician to perform initial calibration, testing, adjustment, modification incidental to the startup and checkout of the equipment, or replacement of components within the confines of the specific product, without permit or required licensing, provided:
(i) For transfer equipment, the product has not been previously energized or is within the manufacturer's written warranty period;
(ii) Modifications to the equipment, as designated above, must not include any changes to the original intended configuration nor changes or contact with external or field-connected components or wiring;
(iii) The manufacturer will be responsible for obtaining any required reapproval/recertification from the original listing or field evaluation laboratory; or
(iv) The manufacturer must notify the department if any modifications have been made or reapproval/recertification is required.
(b) Premanufactured electric power generation equipment assemblies are made up of reciprocating internal combustion engines and the associated control gear equipment. Control gear equipment includes control logic, metering, and annunciation for the operation and the quality of power being generated by the reciprocating internal combustion engine and does not have the function of distribution of power.
(c) Modifications of a transfer switch must not include changes to the original intended configuration or changes or contact with externally field-connected components.
(d) For the purposes of this subsection, the following work on premanufactured electric power generation equipment assemblies is not exempt from the requirements of chapter
19.28 RCW:
(i) Installation or connection of conduit or wiring between the power generation unit, transfer switch, control gear;
(ii) Installation of the transfer switch;
(iii) Connections between the power generation unit, transfer switch, control gear, and utility's transmission or distribution systems;
(iv) Connections between the power generation unit, transfer switch, control gear, and any building or structure; or
(v) Test connections with any part of:
(A) The utility's transmission or distribution system; or
(B) The building or structure.
(24) The installation, maintenance, or repair of a medical device deemed in compliance with chapter
19.28 RCW is exempt from licensing requirements under RCW
19.28.091, certification requirements under RCW
19.28.161, and inspection and permitting requirements under RCW
19.28.101. This exemption does not include work providing electrical feeds into the power distribution unit or installation of conduits and raceways. This exemption covers only those factory engineers or third-party service companies with equivalent training who are qualified to perform such service.
(25) Coincidental electrical/plumbing work. See RCW
19.28.091(8) for the plumber exemption. For the purposes of RCW
19.28.091(8), the like-in-kind replacement includes the appliance or any component part of the appliance such as, but not limited to, the thermostat in a water heater.
(26) Nothing in this section will alter or amend any other exemptions from or requirement for licensure or inspection, chapter
19.28 RCW or this chapter.
Photovoltaic equipment.
(27) See WAC 296-46B-690 for specific exemptions related to photovoltaic installations.
Submersible well pump installers.
(28) Firms that install submersible pumps and associated wiring in well casings, (excluding connection of pump wiring at the top of the wellhead) are not included in the requirements for licensing in chapter
19.28 RCW.
EXCEPTION: | For testing purposes of a new submersible pump, well drillers and submersible pump installers registered under chapter 18.27 RCW may temporarily connect a submersible well pump to a portable generator with cord and plug output. All temporary wiring and equipment must be removed immediately upon completion of testing. |
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-942Training certificate required.
General.
(1) To work in the electrical construction trade as an electrical trainee, an individual must possess, wear, and visibly display a current valid electrical training certificate, learning the trade in the proper ratio, per RCW
19.28.161, under the supervision of a certified master journey level electrician, journey level electrician, master specialty electrician working in their specialty, or specialty electrician working in their specialty.
The trainee must meet all the requirements of WAC 296-46B-940 related to visibly displaying a current certificate and having a valid photo identification on his/her person.
((Beginning July 1, 2023,))Unless working in a specialty, apprentices and individuals learning the electrical construction trade must have in their possession proof of apprenticeship or journey level training program registration. They must show their apprenticeship or training program registration documents to an authorized representative of the department at the representative's request.
(2) An active training certificate is required for all individuals throughout the individual's enrollment and matriculation in an approved construction electrician training school program described in RCW
19.28.191. A training certificate is required to work in the electrical construction trade if an individual does not:
(a) Possess a current journey level certificate of competency issued by the department;
(b) Possess a current specialty electrician certificate of competency issued by the department while working in that specialty's scope of work; or
(c) Is not working in exempt status as allowed by chapter
19.28 RCW.
(3) Trainees who have had their training certificates revoked or suspended (during the duration of the revocation or suspension) will not be issued a training certificate.
Original training certificates.
(4) The department will issue an original training certificate when the trainee applicant submits a complete training certificate application including:
(a) Date of birth, mailing address, Social Security number; and
(b) All appropriate fees as listed in WAC 296-46B-909.
All applicants for an electrical training certificate must be at least ((sixteen))16 years of age. The original training certificate will be valid for two years. If an individual has previously held an electrical training certificate, then that individual is not eligible for a subsequent original training certificate.
Specialty specific - Zero percent and ((seventy-five))75 percent supervision modified training certificates.
(5) For specialties as allowed in Table 945-1 (i.e., specialties with ((seven hundred twenty))720 minimum hours of work experience required to be eligible for examination):
(a) The department will approve the trainee to take the appropriate specialty competency examination necessary to qualify for a zero percent supervision modified training certificate. To qualify, the trainee applicant must submit a complete zero percent supervision modified training certificate application including:
(i) Date of birth, mailing address, Social Security number;
(ii) Affidavit of experience fulfilling the minimum work experience hours required to qualify for the specialty examination described in Table 945-1; and
(iii) All appropriate fees as listed in WAC 296-46B-909.
Upon successful completion of the appropriate examination, the trainee will be issued a nonrenewable zero percent supervision modified training certificate for the appropriate specialty. The zero percent supervision modified training certificate will be restricted in duration to the time allowed in Table 945-1, note 2.
(b) Prior to the expiration of the zero percent supervision modified training certificate, the individual must submit a complete application for a ((seventy-five))75 percent supervision modified training certificate for the appropriate specialty including:
(i) Seventy-five percent supervision training certificate application including: Date of birth, mailing address, Social Security number; and
(ii) All appropriate fees as listed in WAC 296-46B-909.
(c) A trainee may possess multiple (i.e., in different specialties) modified supervision training certificates for specialties where reduced supervision is allowed in Table 945-1. Combination training certificates will not be issued.
Renewal of training certificates.
(6) An individual must apply for renewal of their training certificate on or before the expiration date of the certificate. The individual may not apply for renewal more than ((ninety))90 days prior to the expiration date. Renewed certificates are valid for two years.
(7) An individual may renew their training certificate after the expiration date if the individual pays the late renewal fee listed in WAC 296-46B-909.
(8) All applicants for training certificate renewal must:
(a) Submit a complete renewal application;
(b) Pay all appropriate fees; and
(c) Complete the approved basic trainee classes required by WAC 296-46B-970. Basic trainee classes are only valid when all the requirements of WAC 296-46B-970 are completed.
(d) Within ((one hundred eighty))180 days after the expiration date of an electrical training certificate, the individual, if not enrolled in a department approved apprenticeship program, must submit a completed, signed, and notarized affidavit(s) of experience for all hours of experience gained since the individual's last training certificate was effective. Affidavits must be received by the department within 180 days after the expiration date of an electrical training certificate.
Employers are required to provide the necessary documentation and signed affidavit of experience to the trainee within ((twenty))20 days after the trainee requests the affidavit. See WAC 296-46B-942(12). See WAC 296-46B-985(4) for the penalty for providing a false or inaccurate affidavit of experience. If the individual is enrolled in a department approved apprenticeship program, the program may submit the required affidavit(s) of experience upon the individual's completion of the required experience hours without cost to the individual. The affidavit of experience must accurately attest to:
(i) The electrical installation work performed for each employer the individual worked for in the electrical trade during the previous period;
(ii) The correct electrical category the individual worked in; and
(iii) The actual number of hours worked in each category under the proper supervision of a Washington certified, master journey level electrician, journey level electrician or appropriate master specialty electrician or specialty electrician under that specific training certificate. If a trainee possesses multiple training certificates, an affidavit must be submitted for each training certificate for the hours worked under that specific training certificate.
If the individual is enrolled in a department approved apprenticeship program, the program may submit the required affidavit(s) of experience upon the individual's completion of the required experience hours without cost to the individual.
(9) ((Until July 1, 2020, an individual who has not completed the required hours of basic trainee class education can renew a training certificate if the individual applies for renewal before the training certificate expires and pays the appropriate renewal fee. However, the training certificate will be placed in an inactive status. The inactive training certificate will be returned to current status upon validation, by the department, of the required basic trainee class education. Effective July 1, 2020,))An individual may not renew a training certificate until the required hours of basic classroom education have been completed.
(10) An individual may renew a suspended training certificate by submitting a complete renewal application including obtaining and submitting the basic trainee class education required for renewal. However, the certificate will remain in a suspended status for the duration of the suspension period.
(11) An individual will not be issued a renewed or reinstated training certificate if the individual owes the department money as a result of an outstanding final judgment under chapter
19.28 RCW.
(12) The individual should ask each employer and/or apprenticeship training director for an accurately completed, signed, and notarized affidavit of experience for the previous certification period. The employer(s) or apprenticeship training director(s) must provide the previous period's affidavit of experience to the individual within ((
twenty))
20 days of the request. If an individual is enrolled in an approved electrical construction trade apprenticeship program under chapter
49.04 RCW ((
when the individual renews an electrical training certificate)), the individual and their apprenticeship training director and/or each employer must give the department an accurately completed, signed, and notarized affidavit of experience accurately attesting to:
(a) The electrical installation work the individual performed in the electrical trade during the previous certification period;
(b) The correct electrical category the individual worked in; and
(c) The actual number of hours worked in each category under the proper supervision of a Washington certified master journey level electrician, journey level electrician or appropriate master specialty or specialty electrician for each employer. For apprentices enrolled in a registered apprenticeship program, ((the applicant and)) the training director or their designated authorized signer are the only authorized signatures the department will accept on affidavits of experience.
(13) The ((individual and their)) employer(s) and/or apprenticeship training director(s) or their designated authorized signer must sign and have notarized the affidavit of experience attesting to the accuracy of all information contained in the affidavit.
(14) The trainee, supervising electrician, contractor, and assigned administrator or master electrician are responsible for ensuring compliance with subsection (13) of this section. See WAC 296-46B-985 and 296-46B-990 (3)(c) and (f) for information about failing to submit or submitting false/fraudulent documents. Falsifying documents may be considered perjury and might result in criminal prosecution, civil penalty, or certificate revocation or suspension.
Trainees without supervision present on the job site.
(15) When the supervising electrician is found to not be present on the job site, the trainee may be given a form by the inspector that must be fully completed and returned or postmarked within ((twenty-four))24 hours to the inspector. The supervising electrician must sign the statement for the trainee if appropriate supervision was provided. If the supervising electrician fails or refuses to assist the trainee in completing the form, the trainee must return the form with a signed and dated statement stating the supervising electrician's name and saying that the supervising electrician refused to assist.
Trainees seeking a journey level electrician certificate - Working with no supervision.
(16) Trainee seeking a general (01) journey level electrician certificate of competency. After review by the department, a trainee may be issued a six-month, nonrenewable unsupervised electrical training certificate that will allow the individual to work without supervision if the trainee:
(a) Has submitted a complete application for an unsupervised electrical training certificate;
(b) Has worked over ((seven thousand))7,000 hours properly supervised not to include more than ((four thousand))4,000 of specialty experience;
(c) Has successfully completed or is currently enrolled in an approved apprenticeship program or an electrical construction trade program in a school approved by the board of community and technical colleges;
(d) Has paid all appropriate training certificate fees listed in WAC 296-46B-909;
(e) Is currently working for and continues to work for a licensed electrical contractor that employs at least one certified journey level or specialty electrician in the appropriate specialty; and
(f) Has not previously failed a journey level electrician certificate of competency examination (see WAC 296-46B-960(11)).
Trainees seeking certain specialty electrician certificates - Working with reduced or no supervision.
(17) After review by the department, a trainee may be issued a nonrenewable zero percent supervision training certificate that will allow the individual to work without supervision if the trainee meets the requirements in subsection (5) of this section.
(18) Electrical trainees may work unsupervised when installing HVAC/R thermostat cable when the HVAC/R system consists of a single thermostat in one- and two-family dwelling units where line voltage power has not been connected to the dwelling's electrical system.
AMENDATORY SECTION(Amending WSR 19-15-117, filed 7/23/19, effective 8/23/19)
WAC 296-46B-960Administrator and electrician certificate of competency examinations.
General.
(1) The minimum passing score on any examination or examination section is ((seventy))70 percent. If examination is requested to be administered by the department, an application is required and the examination must be successfully completed within one year of application or the individual must submit a new application for exam including all appropriate fees.
(2) All examinations are open book.
(a) Candidates may use:
(i) Any original copyrighted material;
(ii) A silent, nonprinting, nonprogrammable calculator that is not designed for preprogrammed electrical calculations;
(iii) Copies of chapter
19.28 RCW and this chapter; or
(iv) A foreign language dictionary that does not contain definitions.
(b) Candidates may not use:
(i) Copies of copyrighted material;
(ii) Copies of internet publications, except for RCWs or WACs;
(iii) Personal notes; or
(iv) A personal computing device of any type other than the calculator in (a)(ii) of this subsection.
(3) Administrator, master electrician, and electrician examinations may consist of multiple sections. For all administrator examinations, all sections must be successfully completed within a one-year examination period after beginning the examination. For all master electrician and electrician examinations, all sections must be successfully completed within a one-year examination period beginning with the date of the examination approval. Within the one-year examination period, the candidate does not have to retake any sections successfully completed within the examination period. If all sections are not successfully completed within the one-year period, the candidate must begin a new examination period and retake all sections.
Special accommodations for examination.
(4) An applicant for an examination who, due to a specific physical, mental, ((or)) sensory impairment, requires special accommodation in examination procedures, may submit a written request to the chief electrical inspector for the specific accommodation needed.
(a) ((The applicant must also submit to the department a signed and notarized release, authorizing the specifically identified physician or other specialist to discuss the matter with the department representative.)) The applicant must ((also)) submit an individualized written opinion from a physician or other appropriate specialist:
(i) Verifying the existence of a specific physical, mental, ((or)) sensory impairment;
(ii) Stating whether special accommodation is needed for a specific examination;
(iii) Stating what special accommodation is necessary; and
(iv) Stating if extra time for an examination is necessary and if so, how much time is required. The maximum allowance for extra time is double the normal time allowed.
(b) The written request for special accommodation and individualized written opinion ((must))should be submitted to the department ((at least six weeks in advance of the examination date and must be accompanied by a completed application and fees as described in WAC 296-46B-909.
(c) Only readers and interpreters provided from the administrative office of the courts and/or approved by the department may be used for reading or interpreting the examination. The applicant will be required to bear all costs associated with providing any reading or interpretive services used for an examination.
(d) Applicants who pass the examination with the assistance of a reader or interpreter will be issued a certificate with the following printed restriction: "Requires reading supervision for product usage." A competent reader or interpreter must be present on any job site where a person with this restriction is performing electrical work as described in chapter 19.28 RCW. Applicants who pass the examination with the assistance of a mechanical device (e.g., magnifier, etc.) will be issued a certificate with the following printed restriction: "Requires mechanical reading assistance for product usage." Appropriate mechanical reading assistance must be present on any job site where a person with this restriction is performing electrical work as described in chapter 19.28 RCW. If a candidate successfully retakes the examination without the assistance of a reader or translator, a new certificate will be issued without the restriction.
(5) Applicants who wish to use a foreign language dictionary during an examination must obtain approval at the examination site prior to the examination. Only dictionaries without definitions will be approved for use.))only after the applicant has made application and received an examination approval from the department.
(5) An applicant for an examination who, due to limited English proficiency, requires special accommodation in examination procedures, including requesting extra time for examination, may submit a written request to the chief electrical inspector. The maximum allowance for extra time is double the normal time allowed. The written request should be submitted to the department after the applicant has made application and received an examination approval from the department.
Failed examination appeal procedures.
(6) Any candidate who takes an examination and does not pass the examination may request a review of the examination.
(a) The department will not modify examination results unless the candidate presents clear and convincing evidence of error in the grading of the examination.
(b) The department will not consider any challenge to examination grading unless the total of the potentially revised score would result in a passing score.
(7) The procedure for requesting an informal review of examination results is as follows:
(a) The request must be made in writing to the chief electrical inspector and must be received within ((twenty))20 days of the date of the examination and must request a rescore of the examination. The written request must include the appropriate fees for examination review described in WAC 296-46B-909.
(b) The following procedures apply to a review of the results of the examination:
(i) The candidate will be allowed one hour to review their examination.
(ii) The candidate must identify the challenged questions of the examination and must state the specific reason(s) why the results should be modified with multiple published reference material supporting the candidate's position.
(iii) Within ((fifteen))15 days of the candidate's review, the department will review the examination and candidate's justification and notify the candidate in writing of the department's decision.
Failing an administrator certificate exam or electrician certificate of competency examination.
(8) Anyone failing an administrator or electrician competency examination may retake the examination by making arrangements with the testing agency and paying the retesting fee.
(9) If the individual makes a failing score, the individual must wait two weeks before being eligible to retest.
(10) If the individual fails a part of an electrician, administrator, or master electrician examination three times within a one-year period, the individual must wait three months to retake the failed portion of the examination.
(11) Anyone failing an electrician competency examination may continue to work in the electrical trade if they have a valid electrical training certificate and work under the direct supervision of a certified journey level or specialty electrician in the proper ratio, per RCW
19.28.161.
Cheating on an examination.
(12) Anyone found cheating on an examination, attempting to bribe a proctor or other agent involved in administering an examination, or using inappropriate materials/equipment during an examination will be required to wait at least ((
eleven))
11 months before being allowed to reexamine. All such reexaminations will be administered by the department in Tumwater, Washington and the candidate will be required to apply and schedule for the examination with the chief electrical inspector. The department may also file a civil penalty action under chapter
19.28 RCW.
Examination confidentiality.
(13) All examination questions are confidential. Examination candidates and persons who have taken an examination are not allowed to copy or otherwise make note of or share examination content, in any manner, outside the individual's examination environment. Examination candidates must agree, prior to beginning an examination, to keep all examination content confidential. The department may also file a civil penalty action under chapter
19.28 RCW.
REPEALER
The following sections of the Washington Administrative Code are repealed:
WAC 296-46B-406R | Equipment for general use—Receptacles. |
WAC 296-46B-440 | Air conditioning and refrigerating equipment. |